Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
American History - Chapters 2-4 Test Review
Загружено:
TomasАвторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
American History - Chapters 2-4 Test Review
Загружено:
TomasАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
AMERICAN HISTORY
CHAPTERS 2-4 REVIEW
Joint stock company: a form of business organization devised around
1600 by European nationals to finance business ventures; pooled the
funds of many investors by selling shares in the company.
Christopher Columbus: Italian explorer who, on October 12th, 1492,
discovered the American continent while searching for a profitable new
western trade route to Asia for Spain. He also discovered the West
Indies.
13 Colonies: Massachusetts, New Hampshire, Connecticut, Rhode
Island (New England Colonies); New York, Delaware, New Jersey,
Pennsylvania (Middle Colonies); Virginia, Maryland, North Carolina,
South Carolina, Georgia (Southern Colonies).
Subsistence farming: a level of farming at which farmers produce
just enough to feed their families.
Black robes: Spanish missionaries who arrived in the New World to
convert the Natives to Christianity.
Molasses Act: an act passed in 1733 by Great Britain which imposed
a stiff tax on all molasses or rum imported from the foreign West
Indies.
Conquistadores: professional Spanish soldiers who explored and
conquered lands in the New World.
Separatists: dissenters who believed that the Church of England was
so impure that true believers should separate from it completely.
Pilgrims: separatists who sailed aboard the Mayflower and landed on
the coast of North America that was outside the authority of the
London Company; they drafted the Mayflower Compact and set up the
Plymouth colony in Massachusetts.
Jamestown: the first permanent English settlement in American,
founded by the London Company in 1607 in Virginia; horrific conditions
caused the deaths of many of the settlers; John Smith led the
settlement.
Mayflower Compact: an agreement by the first Pilgrims to make
decisions by majority rule.
London Company: a group of merchants who sponsored the
Jamestown settlement.
Presidio: a Spanish settlement in the New World built for military
activities.
Navigation Acts: acts passed in 1660 and 1663 by British Parliament
to ensure the colonists traded only with England to ensure the British
of valuable revenues and to maintain their world power; involved three
components: colonial merchants could only ship goods on colonial or
English-owned vessels with three quarters being colonial or English
sailors, a list of colonial products (enumerated commodities) could only
be shipped to England sugar, cotton, indigo, ginger, tobacco, and
woods used for dye had to pass through England before being sent
elsewhere (rice, furs, and naval supplies were added later on), and
colonies were prohibited from importing most products from other
European nations unless those products passed through England first
(the only exceptions were slaves, wines, horses, and salt).
Mercantilism: an economic system prevalent in Europe after the
Middle Ages in which each nation attempted to sell more than it
bought in order to increase its supply of gold.
Encomienda: the right granted to conquistadores to demand a tax
from Native Americans living on a given piece of land.
Magellan: discovered the Pacific Ocean and the Philippine Islands; his
crew was the first to circumnavigate the globe.
Cortes: defeated the Aztec empire and discovered Mexico.
John Cabot: explorer employed by England to search for a waterway
to the east; sailed along the North American coast; gathered valuable
geographic information but ultimately found no passage to the Pacific.
William Pitt: British secretary of state (1756) whose confidence led
the British to reverse their string of defeats during the French-Indian
War; launched three-pronged attack on the French that helped bring
about victory.
John Smith: experienced soldier who led the Jamestown settlement
with efficiency and order; demand for food at his price cooled Indian
relations; chiefs young daughter Pocahontas saved Smith when he
was held hostage, which helped bring about friendly relations between
English and Natives once again.
Conditions in Jamestown
Marshy swamp provided a breeding ground for malaria-carrying
mosquitoes.
Drinking water was salty, and the unusually damp air sped the decay
of the wooden buildings.
It was past crop season, so the land could not be cultivated.
Residents were beset by disease.
Most colonists were not accustomed to hard physical labour because
they were soldiers and aristocrats. Others could make glass, do
brickwork, or make iron tools, but virtually no one had the basic
farming skills needed to survive.
Little important work was accomplished because the London Company
insisted the colonists to search for gold in hopes of rivalling the
Spaniards mines.
Within a year, nearly half of the original 104 settlers had died.
In 1609, leader John Smith departed the colony for England; the
following winter, food became so scarce that the colonists were
reduced to eating rats, horses, frogs, roots, insects... even each other
(cannibalism). In the years that followed, the unhealthy conditions
persisted and colonists died in large numbers.
By 1617, only 400 of more than 2000 people who had come to
Jamestown had survived.
Вам также может понравиться
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (121)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (400)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (266)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2259)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (345)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (895)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- Permanently End Premature EjaculationДокумент198 страницPermanently End Premature EjaculationZachary Leow100% (5)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- Reply Speeches What Are They?Документ2 страницыReply Speeches What Are They?Yan Hao Nam89% (9)
- Ezra Pound - PersonaeДокумент34 страницыEzra Pound - PersonaedanielrdzambranoОценок пока нет
- FICCI-BCG Report On Railway Station RedevelopmentДокумент47 страницFICCI-BCG Report On Railway Station RedevelopmentRahul MehrotraОценок пока нет
- TorqueArm PDFДокумент186 страницTorqueArm PDFanush_swaminathanОценок пока нет
- Lipoproteins in Diabetes Mellitus: Alicia J. Jenkins Peter P. Toth Timothy J. Lyons EditorsДокумент468 страницLipoproteins in Diabetes Mellitus: Alicia J. Jenkins Peter P. Toth Timothy J. Lyons EditorsFELELОценок пока нет
- Doanh Nghiep Viet Nam Quang CaoДокумент1 страницаDoanh Nghiep Viet Nam Quang Caodoanhnghiep100% (1)
- CS101 Solved File For Final Term MCQS 1 To 45 LecturesДокумент130 страницCS101 Solved File For Final Term MCQS 1 To 45 LecturesHisan Mehmood64% (28)
- Cb-3 Mech'l Plans 05.06.22Документ12 страницCb-3 Mech'l Plans 05.06.22Mark Vincent MoraОценок пока нет
- Control Work.: ..... Is A Typical ..... DishДокумент4 страницыControl Work.: ..... Is A Typical ..... DishАндрій ХомишакОценок пока нет
- Febryruthwahyuni Lds g1718 Bilphy MRДокумент11 страницFebryruthwahyuni Lds g1718 Bilphy MRfebry sihiteОценок пока нет
- JournalДокумент3 страницыJournalJuvz BezzОценок пока нет
- Problematic Customers and Turnover Intentions of CustomerДокумент10 страницProblematic Customers and Turnover Intentions of Customernaqash1111Оценок пока нет
- City Marketing: Pengelolaan Kota Dan WilayahДокумент21 страницаCity Marketing: Pengelolaan Kota Dan WilayahDwi RahmawatiОценок пока нет
- Students Name - Kendrick Joel Fernandes ROLL NO. 8250 Semester Vi Subject - Turnaround Management Topic-Industrial SicknessДокумент15 страницStudents Name - Kendrick Joel Fernandes ROLL NO. 8250 Semester Vi Subject - Turnaround Management Topic-Industrial SicknesskarenОценок пока нет
- IHE ITI Suppl XDS Metadata UpdateДокумент76 страницIHE ITI Suppl XDS Metadata UpdateamОценок пока нет
- Unit 5 Performance ManagementДокумент20 страницUnit 5 Performance Managementbhavisha_30kОценок пока нет
- BMW I3 Wheel Airbag RemovalДокумент6 страницBMW I3 Wheel Airbag RemovalAjmaster.ltОценок пока нет
- Aporte Al IPSS Del Empleador Por TrabajadorДокумент4 страницыAporte Al IPSS Del Empleador Por Trabajadorvagonet21Оценок пока нет
- List of Mines in IndiaДокумент4 страницыList of Mines in IndiaNAMISH MAHAKULОценок пока нет
- Math - Gr6 - Q2 - Week-08 - Comparing and Arranging Integers On The Number LineДокумент37 страницMath - Gr6 - Q2 - Week-08 - Comparing and Arranging Integers On The Number LineDiana TubigОценок пока нет
- Au 170Документ1 страницаAu 170Ida Bagus Gede PalgunaОценок пока нет
- Towards (De-) Financialisation: The Role of The State: Ewa KarwowskiДокумент27 страницTowards (De-) Financialisation: The Role of The State: Ewa KarwowskieconstudentОценок пока нет
- Business Management Business ManagementДокумент31 страницаBusiness Management Business ManagementDoyieОценок пока нет
- The SPIN Model CheckerДокумент45 страницThe SPIN Model CheckerchaitucvsОценок пока нет
- Monthly Film Bulletin: 1T1IcqДокумент12 страницMonthly Film Bulletin: 1T1IcqAlfred_HitzkopfОценок пока нет
- Chapter 1Документ25 страницChapter 1Aditya PardasaneyОценок пока нет
- The Fat Cat Called PatДокумент12 страницThe Fat Cat Called PatAlex ArroОценок пока нет
- Rhavif's ResumeДокумент1 страницаRhavif's ResumeRhavif BudiboyОценок пока нет
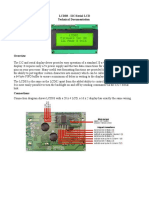
- Datasheet lcd03 20x4 B PDFДокумент8 страницDatasheet lcd03 20x4 B PDFFrancis100% (1)