Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Mathematics Trigonemetry
Загружено:
Kimbo NugyenАвторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Mathematics Trigonemetry
Загружено:
Kimbo NugyenАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
HSC MATHEMATICS GENERAL 2
MEASUREMENT
MM5: APPLICATIONS OF TRIGONOMETRY
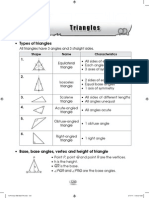
Right-angled triangles
Example
Find the length of the unknown side x in the triangle shown. Answer correct
to two decimal places.
Example
A vertical tent pole is supported by a rope tied to the top of
the pole and to a peg on the ground. The rope is 3m in
length and makes an angle of 29 to the horizontal. What is
the height of the tent pole? Answer correct to two decimal
places.
Page | 1 | CLASSWORK
HSC MATHEMATICS GENERAL 2
MEASUREMENT
MM5: APPLICATIONS OF TRIGONOMETRY
Question 1
Find the length of the unknown side x in each triangle, correct to two decimal places
Question 2
Find the unknown angle in each triangle. Answer correct to the nearest minute
Page | 2 | CLASSWORK
HSC MATHEMATICS GENERAL 2
MEASUREMENT
MM5: APPLICATIONS OF TRIGONOMETRY
Question 3
Find the length of the unknown side x in each triangle, correct to two decimal places
Question 4
Find the unknown angle in each triangle. Answer correct to the nearest degree
Question 5
Jack measures the angle of elevation to the top of a tree from a point on
level ground as 35. What is the height of the tree if Jack is 50m from the
base of the tree? Answer to the nearest metre.
Question 6
A 3m ladder has its foot 1.5m out from the base of the wall. What angle does
the ladder make with the ground? Answer correct to the nearest degree.
Bearings
Page | 3 | CLASSWORK
HSC MATHEMATICS GENERAL 2
MEASUREMENT
MM5: APPLICATIONS OF TRIGONOMETRY
There are two types of bearings:
1) Compass bearings
2) True bearings
Compass Bearings
Example
A boat leaves Sydney and travels 420 km on a bearing of N37E. How far
did the boat travel due north, to the nearest kilometre?
True Bearings
Example
Joel walks north for 3.2 km and then west for 4.4 km. What is his true bearing from his starting point,
to the degree?
Question 1
Page | 4 | CLASSWORK
HSC MATHEMATICS GENERAL 2
MEASUREMENT
MM5: APPLICATIONS OF TRIGONOMETRY
Aaron runs a distance of 7.2 km in the SE direction. How far east has Aaron
run? Answer correct to one decimal place.
Question 2
A plane is travelling on a bearing of 030 from A to B.
a) What is the compass bearing of A to B?
b) What is the true bearing of B to A?
c) What is the compass bearing of B to A?
Question 3
The diagram shows the position of P, Q and R relative to S. In the diagram, R
is NE of S, Q is NW of S and PSR is 155.
a) What is the true bearing of R from S?
b) What is the true bearing of Q from S?
c) What is the true bearing of P from S?
Question 4
The bearing of E from D is N38E, F is east of D and DEF is 87
a) Find the values of x and y
b) What is the compass bearing of E from F?
c) What is the true bearing of E from F?
Question 5
Mia cycled for 15 km west and then 24 km south
a) What is the value of to the nearest degree?
b) What is Mias true bearing from her starting point?
c) What is Mias compass bearing from her starting point?
Question 6
A boat sails 137 k from Port Stephens on a bearing on 065T
a) How far east has the boat sailed? Answer correct to one decimal place
b) How far north has the boat sailed? Answer correct to one decimal place
Question 7
A ship sails 5 kilometres west, then 5 kilometres south
Page | 5 | CLASSWORK
HSC MATHEMATICS GENERAL 2
MEASUREMENT
MM5: APPLICATIONS OF TRIGONOMETRY
a) What is the compass bearing of the ship from its original position?
b) What is the true bearing of the ship from its original position?
Question 8
Harry travelled for 8.5 km on a bearing of S30W from his home
a) How far west is Harry from home? Answer correct to two decimal places
b) How far south if Harry from home? Answer correct to two decimal places
c) What is the compass bearing of his home from his current position?
Question 9
A plane left from O and travelled 350 km in the direction
225T to reach P. It then changed direction and travelled due
north for 500 km to reach point N
a) What was the distance from P to M? (Answer
correct to two decimal places)
b) What was the distance from M to O? (Answer
correct to two decimal places)
c) What was the distance from M to N? (Answer
correct to two decimal places)
d) What is the angle , correct to the nearest degree?
e) What is the true bearing of N from O?
[Trigonometry with obtuse angles]
The Sine Rule
Page | 6 | CLASSWORK
HSC MATHEMATICS GENERAL 2
MEASUREMENT
MM5: APPLICATIONS OF TRIGONOMETRY
Example
Find the value of x correct to one decimal place
Example
Hannah is standing 4.5m from the base of a 3m sloping wall.
The angle of elevation to the top of the wall is 36. Find the
angle at the top of the wall, to the nearest minute.
Question 1
Find the length of the unknown side x in each triangle, correct to two decimal places
Page | 7 | CLASSWORK
HSC MATHEMATICS GENERAL 2
MEASUREMENT
MM5: APPLICATIONS OF TRIGONOMETRY
Question 2
Find the length of the unknown side x in each triangle, correct to two decimal places
Question 3
Benjamin is planning to build a triangular garden for his daughter. The vertices of the triangle are
named PQR. He measured PQ as 2.7m, OR as 3.1 m and PRQ as 57. Use the sine rule to
find the size of RPQ, correct to the nearest degree.
Question 4
Triangle ABC has ABC = 71, BCA = 69 and CAB = 40. The length of AB is 10
a) What is the value of a, correct to one decimal place?
b) What is the value of b, correct to one decimal place?
Question 5
Refer to the picture on the right. Use the sine rule to:
Page | 8 | CLASSWORK
HSC MATHEMATICS GENERAL 2
MEASUREMENT
MM5: APPLICATIONS OF TRIGONOMETRY
a) Find the size of angle XYZ. Give your answer to the
nearest degree
b) Find the size of y. Give your answer to the nearest
centimetre
Question 6
Sienna was located at X and saw a fire in the direction
N15E. Seven kilometres to the east of X at Z, Dylan
saw the fire in the direction N50W
a) How far is X from the fire? Answer in
kilometres correct to one decimal place
b) How far is Z from the fire? Answer in
kilometres correct to one decimal place
Question 7
Chelsea is travelling due east from A to B. Unfortunately,
the road is blocked and she makes a detour by traveling
from A to C a distance of 30 km, on a bearing of 040.
Chelsea then turns and travels south-east until she
reaches B.
a) What are the sizes of CAB and CBA?
b) How far did Chelsea travel from C to B?
Answer correct to the nearest
kilometre
c) What was the extra distance travelled
on the detour? Answer correct to the nearest kilometre
Area of a triangle
Page | 9 | CLASSWORK
HSC MATHEMATICS GENERAL 2
MEASUREMENT
MM5: APPLICATIONS OF TRIGONOMETRY
Example
Find the area of the triangle to the nearest square centimetre
Question 1
In triangle ABC, side a is 36 cm, side b is 48cm and angle C is 68. Find the area of the triangle.
Answer correct to two decimal places
Question 2
In the triangle XYZ, side x is 4m, side y is 7m and angle Z is 34. Find the area of the triangle.
Answer correct to two decimal places
Question 3
A parallelogram has sides of length 7cm and 5.2 cm, and the included angle of 130. Calculate its
area, correct to one decimal place.
Question 4
A kite has adjacent sides of length 4cm and 7cm. The longer diagonal makes angles of 45 and 23.8
with the sides of the kite. Find the area if the kite.
Question 5
Find the area of each triangle, correct to one decimal place
Page | 10 | CLASSWORK
HSC MATHEMATICS GENERAL 2
MEASUREMENT
MM5: APPLICATIONS OF TRIGONOMETRY
Question 6
In triangle DEF, the length of DF is 21cm, EF is 28cm, FDE is 64
and DEF is 43. Find the area of triangle DEF to the
nearest square centimetre
Question 7
A parallelogram PQRS has PS = 4cm, SR = 5cm and
PSR = 40
a) What is the area of triangle PRS? Answer correct to one
decimal place
b) What is the area of the parallelogram? Answer correct to one
decimal place
Question 8
A drawing of a farmers property is shown below
a) What is the area of triangle WXZ?
b) What is the area of triangle XYZ?
c) Find the total area of the property in square kilometres.
The Cosine Rule
Page | 11 | CLASSWORK
HSC MATHEMATICS GENERAL 2
MEASUREMENT
MM5: APPLICATIONS OF TRIGONOMETRY
Example
Find the value of x correct to two decimal places
Example
Find the value of the angle . Answer in degrees, correct to one decimal place
Question 1
DEF is a triangle for which DF = 37cm, EF = 46cm and DFE = 44. Use the cosine rule to
find the length of DE, to the nearest millimetre.
Page | 12 | CLASSWORK
HSC MATHEMATICS GENERAL 2
MEASUREMENT
MM5: APPLICATIONS OF TRIGONOMETRY
Question 2
A triangle RST has RST = 51, STR = 63, RT = 40 and
RS = 48
a) What is the size of TRS?
b) Find the length of x using the cosine rule. Answer
correct to three significant figures
Question 3
Ruby drives a four-wheel drive along a track from point A due west to a
point B, a distance of 14 km. She then turns and travels 19 km to point C.
Use the cosine rule to calculate the distance Ruby is from her starting
point. Answer correct to one decimal place.
Question 4
Passengers in a car travelling east, along a road that runs west-east, see a castle 10km away in the
direction N65E. When they have travelled a further 4 km east along the road, what will be the
distance to the castle? Answer correct to two decimal places?
Question 5
A stepladder has legs of length 120cm and the angle between them is 15. Calculate the distance (to
the nearest centimetre) between the legs on the ground.
Question 6
A triangle has sides measuring 4m, 5m and 7m.
a) What is the size of the smallest angle in this triangle?
b) What is the size of the largest angle in this triangle?
Question 7
A running circuit is in the shape of a triangle with lengths of 6 km, 6.5 km and 7 km. What are the
sizes of the angles (in minutes) between each of the sides?
Page | 13 | CLASSWORK
HSC MATHEMATICS GENERAL 2
MEASUREMENT
MM5: APPLICATIONS OF TRIGONOMETRY
Question 8
The lengths of the sides of triangle ABC are in the ratio 7: 8: 9. Find the size of each angle, correct to
the nearest minute.
Mixed questions
Question 1
The dimensions of a block of land are shown opposite
a) What is the length of x, correct to the nearest metre?
b) What is the length of y, correct to the nearest metre?
Question 2
Madison measures the angle of elevation to the top of a wall as
32. She walks 10m horizontally towards the wall and measures
the angle of elevation as 51. Find the height of the wall.
Question 3
The bearing of Y from X is 240 and the distance of Y from X is 20km.
a) What is the value of a?
b) If Z is 18km due north of X, calculate the distance of Y from Z,
correct to the nearest kilometre
c) What is the value of b to the nearest degree?
Question 4
Andrew plans to build a triangular flower bed in the lower part of a circular
garden. The length is TS is 24m, TSR is 45 and RTS is 40.
a) What is the size ofSRT?
b) Use the sine rule to find the length of TR. Answer correct to the
nearest metre.
Question 5
Page | 14 | CLASSWORK
HSC MATHEMATICS GENERAL 2
MEASUREMENT
MM5: APPLICATIONS OF TRIGONOMETRY
The diagram shoes information about the locations of towns P, Q and
R. Amber takes 2 hours and 30 minutes to walk directly from Town P
to Town Q
a) What is Ambers walking speed, correct to the nearest km/h.
b) What is the distance from P to R? Answer correct to the
nearest kilometre
c) How long would it take Amber to walk from P to R? Answer
to nearest minute
Question 6
M is 50km north of O. The bearing of N from M is 108 and from O it is
061. Answer the following questions to the nearest kilometre
a) What is the distance between M and N?
b) What is the distance between N and O?
Question 7
The diagram shows five roads: DE, DG, EF, GE and GF. The bearing of FG is 304. ED is 292 and
DG is 040. The distance from E to F is 8lm and E is due west of F.
a) Find the size of GFE
b) What is the distance GE? Answer correct to one decimal
place
c) What is the size of DGE, GED and GDE? (Answer
to the nearest degree.)
d) What is the distance DE? Answer correct to one decimal
place
e) What is the distance DG? Answer correct to one decimal
place
Question 8
A survey of a park is shown in the diagram. A path is proposed from B to D
and a fence is required from B to C to D.
a) What is the length of the path? Answer correct to the nearest metre
b) Calculate the required length of fencing. Answer correct to the
nearest metre
c) What is the area of the park? Answer correct to the nearest square
metre.
Surveying
-
Offset survey
Page | 15 | CLASSWORK
HSC MATHEMATICS GENERAL 2
MEASUREMENT
MM5: APPLICATIONS OF TRIGONOMETRY
Example
The field book entry and field diagram from an offset survey are shown opposite. Find the area of the
quadrilateral ABCD. Measurements are in metres. Answer correct to nearest metre.
Radial Survey
Page | 16 | CLASSWORK
HSC MATHEMATICS GENERAL 2
MEASUREMENT
MM5: APPLICATIONS OF TRIGONOMETRY
Example
A plane-table radial survey is shown opposite. What is the
area of ABC? Answer correct to one decimal place.
Example
A compass radial survey for a field is shown opposite
Page | 17 | CLASSWORK
HSC MATHEMATICS GENERAL 2
MEASUREMENT
MM5: APPLICATIONS OF TRIGONOMETRY
a) What is the size of POQ?
b) What is the size of POR?
c) Calculate the length of PQ correct to two decimal
places
d) Calculate the length of PR correct to two decimal
places
e) What is the perimeter of the field? Answer correct
to three significant figures.
Question 1
Find the area of the following fields. Units are metres
Page | 18 | CLASSWORK
HSC MATHEMATICS GENERAL 2
MEASUREMENT
MM5: APPLICATIONS OF TRIGONOMETRY
Question 2
The diagram on the right shows a block of land that has been surveyed. All
measurements are in metres
a) Find the area of the quadrilateral ABCD. Answer correct to the
nearest square metre
b) What is the length of AB? Answer correct to the nearest metre
c) What is the length of AC? Answer correct to the nearest metre
Question 3
The field book entry on the right shoes a block of land that has been surveyed.
All measurements are in metres
a) Find the area of the block ABCDE. Answer correct to one decimal
place
b) What is the length of AC? Answer correct to the nearest metre
c) What is the length of CE? Answer correct to the nearest metre
Question 4
Page | 19 | CLASSWORK
HSC MATHEMATICS GENERAL 2
MEASUREMENT
MM5: APPLICATIONS OF TRIGONOMETRY
A radial survey of land DEFG is shown opposite
a) What is the size of FOG?
b) Find the area of the triangle FOG to the nearest
square metre
c) What is the length of FG correct to the nearest
metre?
Question 5
The diagram opposite is a compass radial survey of field
VWXYZ. All distances are in metres. Answer the
following questions correct to one decimal place
a)
b)
c)
d)
e)
f)
What is the length of XY?
What is the length of ZY?
What is the length of VZ?
What is the length of VW?
What is the length of XW?
Calculate the perimeter of the field
Question 6
A radial survey of land ABCD is shown
a) What is the size of AOB?
b) What is the area of AOB? Answer correct to the nearest
square metre
c) What is the area of the land? Answer correct to the nearest
square metre
Question 7
Alex, Blake and Connor are standing in a field. Connor is 15 metres away from Blake (B) on a
bearing of 032. Alex (A) is 20 metres away from Blake on a bearing of 315.
a) Draw a diagram to represent the positions A, B and C. Mark the information from the
question on the diagram
b) What is the size of ABC to the nearest degree?
c) What is the area of ABC? Answer correct to the nearest square metre
d) How far is Alex from Connor? Answer correct to the nearest metre.
Page | 20 | CLASSWORK
Вам также может понравиться
- Worksheet For HomeworkДокумент10 страницWorksheet For HomeworkDivaОценок пока нет
- The Six Trigonometric RatiosДокумент20 страницThe Six Trigonometric Ratioseustoque2668Оценок пока нет
- Problem SetДокумент8 страницProblem SetbaterbeeОценок пока нет
- Varsity Math QuestionsДокумент19 страницVarsity Math QuestionsSlasher124Оценок пока нет
- ch-12 Herons FormulaДокумент2 страницыch-12 Herons Formulaapi-286106888Оценок пока нет
- Math Reviewer Exam SampleДокумент2 страницыMath Reviewer Exam SampleEugene CardamaОценок пока нет
- Prelim Reviewer - Ce LawДокумент14 страницPrelim Reviewer - Ce Lawm.hamsyyОценок пока нет
- Prelim Reviewer - Ce LawДокумент14 страницPrelim Reviewer - Ce Lawm.hamsyyОценок пока нет
- Good Morning Grade 8 Learners!: Mathematics 8 Ma'Am Angelica Joy V. DumalayДокумент25 страницGood Morning Grade 8 Learners!: Mathematics 8 Ma'Am Angelica Joy V. DumalayAngelica Joy Villanueva DumalayОценок пока нет
- Trigo Bridging 1 and 2Документ19 страницTrigo Bridging 1 and 2blackmasque100% (1)
- TrigonometryДокумент4 страницыTrigonometrydayatОценок пока нет
- Trigo Bridging 3Документ7 страницTrigo Bridging 3Jacob SantosОценок пока нет
- TrigonometryДокумент43 страницыTrigonometryAnwar Hossain75% (8)
- Answer: The Measure of The Central Angles of An Equilateral TriangleДокумент4 страницыAnswer: The Measure of The Central Angles of An Equilateral Trianglesunil_ibmОценок пока нет
- The Pythagorean Theorem Demo JVLДокумент14 страницThe Pythagorean Theorem Demo JVLNeperare LeonesОценок пока нет
- Year 10 Trigonometry 2Документ4 страницыYear 10 Trigonometry 2Jack LagerОценок пока нет
- Ch11-Review1Документ20 страницCh11-Review1Dana Al-WakilОценок пока нет
- AUTOMATHICДокумент11 страницAUTOMATHICSherwin ConcepcionОценок пока нет
- Triangle Inequalities: Modified by Lisa PalenДокумент12 страницTriangle Inequalities: Modified by Lisa PalenRalph Rexor Macarayan BantuganОценок пока нет
- RCE2018 math and geometry problems solutions under 40 charactersДокумент1 страницаRCE2018 math and geometry problems solutions under 40 charactersArwin VillegasОценок пока нет
- HW Chapter 6Документ12 страницHW Chapter 6crampingpaul100% (1)
- Grade 8 Math Word Problems: Find Unknown Numbers, Angles, Dimensions and MoreTITLEGrade 9 Math Word Problems: Calculate Speed, Volume, Area, Averages and MoreДокумент5 страницGrade 8 Math Word Problems: Find Unknown Numbers, Angles, Dimensions and MoreTITLEGrade 9 Math Word Problems: Calculate Speed, Volume, Area, Averages and MoreApipa Lumabao Pendinatar100% (1)
- Wajo 2012 QaДокумент13 страницWajo 2012 QaSmpnsatubontang KaltimОценок пока нет
- Topic 4 - TrianglesДокумент6 страницTopic 4 - TrianglesTheresa NelОценок пока нет
- WS - Pythagorean Theorem-Blizzard Bag1Документ2 страницыWS - Pythagorean Theorem-Blizzard Bag1Cynthia VelvetОценок пока нет
- Pythagoras Theorem Ps 1Документ4 страницыPythagoras Theorem Ps 1api-250809257Оценок пока нет
- Finding An Unknown SideДокумент4 страницыFinding An Unknown SideGeoffОценок пока нет
- Geometry: College Admission Test ReviewДокумент9 страницGeometry: College Admission Test ReviewdonlynОценок пока нет
- Similarity and Trigonometry - DocДокумент19 страницSimilarity and Trigonometry - DocJuan Moya Moreno100% (1)
- ArMath1 - Presentation3Документ31 страницаArMath1 - Presentation3Jayson RamirezОценок пока нет
- Math8 Q4 SLM WK2Документ7 страницMath8 Q4 SLM WK2Juvelyn Teves MunalemОценок пока нет
- 2016 Regional Geometry Exam Final PDFДокумент15 страниц2016 Regional Geometry Exam Final PDFPartha SarathiОценок пока нет
- Speed Math Trig Applications: 10 Problem CardsДокумент10 страницSpeed Math Trig Applications: 10 Problem CardsJonathan Rothman100% (1)
- Bka 4Документ43 страницыBka 4Aimee HernandezОценок пока нет
- NamaДокумент19 страницNamaRizki Zunianto 2005111038Оценок пока нет
- POLYGONSДокумент45 страницPOLYGONSBlessa Mae100% (1)
- 7 Asm Unit-4 PDFДокумент6 страниц7 Asm Unit-4 PDFAahana MuhaneОценок пока нет
- Geometry Exam QuestionДокумент3 страницыGeometry Exam QuestionAnwar Hosen OntorОценок пока нет
- 13 Pri WB Math P5 PDFДокумент11 страниц13 Pri WB Math P5 PDFteerapong onogk0% (1)
- Name: Pythagorean Theorem - WorksheetДокумент2 страницыName: Pythagorean Theorem - Worksheet29mah120.studentОценок пока нет
- Section A 1 Mark EachДокумент1 страницаSection A 1 Mark EachAnanthakrishnan Tinneveli VОценок пока нет
- Remedial Test (Just The Answers)Документ13 страницRemedial Test (Just The Answers)lornehessОценок пока нет
- GR 7 Wks Perimeter and Area 2023 - 24Документ4 страницыGR 7 Wks Perimeter and Area 2023 - 24vanessaforever72013Оценок пока нет
- Trigonometry Ratios and Word ProblemsДокумент8 страницTrigonometry Ratios and Word ProblemsKikiez PathanasriwongОценок пока нет
- Fundamental of Engineering Mathematics Midterm ExamДокумент2 страницыFundamental of Engineering Mathematics Midterm ExamrowelОценок пока нет
- Yr 10 Revision SheetДокумент4 страницыYr 10 Revision Sheetsaishaalva777Оценок пока нет
- Area TrianglesДокумент6 страницArea TrianglesFatos ShuliОценок пока нет
- UNIT 1 Lesson 3 TrianglesДокумент9 страницUNIT 1 Lesson 3 TrianglesAaron BrennОценок пока нет
- Pythagorean Relationship Practice Test AnswersДокумент3 страницыPythagorean Relationship Practice Test Answerssikatlearning1Оценок пока нет
- Pythagoras and The Pythagorean Theorem: Grade 8-9 Lesson by Lindsay KallishДокумент14 страницPythagoras and The Pythagorean Theorem: Grade 8-9 Lesson by Lindsay KallishgraalhackerОценок пока нет
- A2 - (Sub 5,6,8) - Intan Sri Maharani - E1b120010Документ7 страницA2 - (Sub 5,6,8) - Intan Sri Maharani - E1b120010Intan MaharaniОценок пока нет
- Math 9Документ5 страницMath 9Mary May Blancia - GarciaОценок пока нет
- Solve Quadrilaterals Problems: Areas, Perimeters, DiagonalsДокумент1 страницаSolve Quadrilaterals Problems: Areas, Perimeters, DiagonalsJoshua AquinoОценок пока нет
- Ch7_Review3Документ17 страницCh7_Review3Dana Al-WakilОценок пока нет
- RevisionДокумент27 страницRevisionEylul RusoОценок пока нет
- SK 2015 Q PDFДокумент4 страницыSK 2015 Q PDFAtlas ErnhardtОценок пока нет
- Chap19 - 295-315Документ21 страницаChap19 - 295-315jfarrell_ie5767Оценок пока нет
- Patterns and Algebra Homework AnswersДокумент12 страницPatterns and Algebra Homework AnswersKimbo NugyenОценок пока нет
- Scientific NotationsДокумент23 страницыScientific NotationsKimbo NugyenОценок пока нет
- Trigonometric Functions: All Rights ReservedДокумент8 страницTrigonometric Functions: All Rights ReservedKimbo NugyenОценок пока нет
- Patterns and Algebra TEACHERДокумент10 страницPatterns and Algebra TEACHERKimbo NugyenОценок пока нет
- Geo Worksheet - Isosceles Triangles (Section 4-6)Документ5 страницGeo Worksheet - Isosceles Triangles (Section 4-6)Kimbo Nugyen50% (2)
- Angles Parallel Line RevisionДокумент4 страницыAngles Parallel Line RevisionKimbo NugyenОценок пока нет
- Indices Revision Extra WorkДокумент4 страницыIndices Revision Extra WorkKimbo NugyenОценок пока нет
- Indices HomeworkДокумент13 страницIndices HomeworkKimbo NugyenОценок пока нет
- Orders of Operation (BODMAS) : Indices Year 7Документ10 страницOrders of Operation (BODMAS) : Indices Year 7Kimbo NugyenОценок пока нет
- Understanding Acting Out in ChildrenДокумент2 страницыUnderstanding Acting Out in ChildrenKimbo NugyenОценок пока нет
- Indices HomeworkДокумент13 страницIndices HomeworkKimbo Nugyen100% (1)
- Mathematics Test 2Документ15 страницMathematics Test 2annabellehoohОценок пока нет
- Indices Revision Extra WorkДокумент4 страницыIndices Revision Extra WorkKimbo NugyenОценок пока нет
- Index Laws RevisionДокумент4 страницыIndex Laws RevisionMaria Rajendran M100% (1)
- Week 6 SolutionsДокумент10 страницWeek 6 SolutionsKimbo NugyenОценок пока нет
- MATH203 Lecture Notes 2015Документ60 страницMATH203 Lecture Notes 2015Kimbo NugyenОценок пока нет
- Angles: Syllabus OutcomesДокумент42 страницыAngles: Syllabus OutcomesKimbo Nugyen100% (1)
- Angles: Syllabus OutcomesДокумент42 страницыAngles: Syllabus OutcomesKimbo Nugyen100% (1)
- Fractions: Addition and Subtraction: Syllabus OutcomesДокумент24 страницыFractions: Addition and Subtraction: Syllabus OutcomesKimbo NugyenОценок пока нет
- Fractions: Addition and Subtraction: Syllabus OutcomesДокумент24 страницыFractions: Addition and Subtraction: Syllabus OutcomesKimbo NugyenОценок пока нет
- Angle Sum of Triangles and Quadrilaterals PDFДокумент4 страницыAngle Sum of Triangles and Quadrilaterals PDFKimbo NugyenОценок пока нет
- 7 CH 10Документ38 страниц7 CH 10Kimbo NugyenОценок пока нет
- Bluestone Alley With Key NamesДокумент2 страницыBluestone Alley With Key NamesKimbo Nugyen100% (1)
- 93 Recurring Decimals Into FractionsДокумент8 страниц93 Recurring Decimals Into FractionsJoel GrayОценок пока нет
- Linear Non Ch9Документ38 страницLinear Non Ch9Kimbo NugyenОценок пока нет
- Angle Sum of Triangles and Quadrilaterals PDFДокумент4 страницыAngle Sum of Triangles and Quadrilaterals PDFKimbo NugyenОценок пока нет
- Physics SyllabusДокумент78 страницPhysics SyllabusdalarmclockОценок пока нет
- Pyrotechnic Seatbelt PretensionersДокумент1 страницаPyrotechnic Seatbelt PretensionersKimbo NugyenОценок пока нет
- HomeworkДокумент2 страницыHomeworkKimbo NugyenОценок пока нет
- Operators Manual For Sea Tel Dac-2302 Antenna Control UnitДокумент34 страницыOperators Manual For Sea Tel Dac-2302 Antenna Control UnitDmitryОценок пока нет
- Kami Export - 3145 - 01 - 6RP - AFP - tcm143-665876 PDFДокумент20 страницKami Export - 3145 - 01 - 6RP - AFP - tcm143-665876 PDFMa'an Al Sabri100% (1)
- Technology Attribute Sector 01 Sector 02: Site ID: Site NameДокумент15 страницTechnology Attribute Sector 01 Sector 02: Site ID: Site NameMoses MussОценок пока нет
- Leica 307 ManualДокумент4 страницыLeica 307 ManualRaluca Sandu100% (2)
- Magnetostatics Part1Документ11 страницMagnetostatics Part1SureshОценок пока нет
- Survey Pocket PDFДокумент11 страницSurvey Pocket PDFniteshОценок пока нет
- SR4 Class A Compass - v2Документ2 страницыSR4 Class A Compass - v2Paul VoytОценок пока нет
- Operator's Manual: Double Gyro Compass Change Over UnitДокумент69 страницOperator's Manual: Double Gyro Compass Change Over UnitSerhiiОценок пока нет
- Hp-33a User Manual v1.2 NDMДокумент98 страницHp-33a User Manual v1.2 NDMCharles ThompsonОценок пока нет
- Mufon Ufo Journal - May 1985Документ20 страницMufon Ufo Journal - May 1985Carlos RodriguezОценок пока нет
- Igcse 61 Magnetism&ElectromagnetismДокумент32 страницыIgcse 61 Magnetism&ElectromagnetismHany ElGezawy100% (4)
- Navigation LogДокумент23 страницыNavigation LogMio cursoОценок пока нет
- Standart 20-22 Instalation ManualДокумент247 страницStandart 20-22 Instalation ManualСергей Бородин100% (1)
- 1 Vastu PrinciplesДокумент100 страниц1 Vastu PrinciplesSrinikumar Giduthuri100% (5)
- V103 - V113 Manual Del UsuarioДокумент60 страницV103 - V113 Manual Del UsuarioAntenor GordilloОценок пока нет
- Borysenko - Your Souls CompassДокумент5 страницBorysenko - Your Souls Compassharry BennetОценок пока нет
- Catalogue Content (New)Документ108 страницCatalogue Content (New)Atongo George AtiahОценок пока нет
- Surveying ManualДокумент55 страницSurveying ManualafrdhkОценок пока нет
- Earth As A SphereДокумент8 страницEarth As A SphereNur HafizhaОценок пока нет
- Capt. Dela CuestaДокумент43 страницыCapt. Dela CuestaJerick Christian P Dagdagan100% (2)
- Compass ReadingДокумент6 страницCompass Readingmorfeo_1977100% (1)
- Unit 9 Geography, Map Skills & OrienteeringДокумент182 страницыUnit 9 Geography, Map Skills & OrienteeringRavi BhollahОценок пока нет
- Inspire 1: Quick Start GuideДокумент10 страницInspire 1: Quick Start GuidesenzualeОценок пока нет
- Survey Record Full Merged 1 &2Документ125 страницSurvey Record Full Merged 1 &2oxygen oxygenОценок пока нет
- Calculating True North and Grid NorthДокумент16 страницCalculating True North and Grid NorthFreddy QuinteroОценок пока нет
- Chart Work Pages 125Документ21 страницаChart Work Pages 125arafeeu100% (8)
- Magnetism and Electromagnetism School Lab Manual by Junior ScientistДокумент12 страницMagnetism and Electromagnetism School Lab Manual by Junior ScientistGopi Chand100% (1)
- mdc721 eДокумент2 страницыmdc721 eSaltojitoОценок пока нет
- Length NMDCДокумент8 страницLength NMDCAlish SBОценок пока нет
- Army - stp21 1 - Soldier's Manual of Common Tasks - Warrior Skills Level 1Документ748 страницArmy - stp21 1 - Soldier's Manual of Common Tasks - Warrior Skills Level 1Meowmix96% (26)