Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Force Acceleration Newton's Second Law of Motion Gravity Archimedes
Загружено:
Jason HarrisonИсходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Force Acceleration Newton's Second Law of Motion Gravity Archimedes
Загружено:
Jason HarrisonАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
-, electrical, or other forms.
According to the law of conservation of energy, the total energy of a system remains
constant, though energy may transform into another form. The SI unit of energy is the joule (J) or newtonmeter (N * m).
The kinetic energy of an object is the energy which it possesses due to its motion.[1] It is defined
as the work needed to accelerate a body of a given mass from rest to its stated velocity.
pendulum is defined as a mass, or bob, connected to a rod or rope, that experiences simple
harmonic motion as it swings back and forth without friction. The equilibrium position of the
pendulum is the position when the mass is hanging directly downward.
Definition: Oscillation is a motion that repeats itself in a regular cycle, such as a sine wave or pendulum.
Also Known As: periodic motion
efinition: Mass is the quantity of inertia possessed by an object or the proportion between force and acceleration
referred to in Newton's Second Law of Motion.
This is not a very good operational definition of mass, of course. In most common instances, mass is determined
by weighing the object and using the force of gravity Answer: A material's density is defined as its mass per unit
volume. It is, essentially, a measuremement of how tightly matter is crammed together. The principle of density
was discovered by the Greek scientist Archimedes.
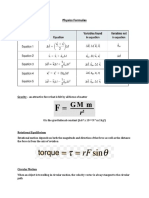
To calculate the density (usually represented by the Greek letter "rho") of an object, take the mass (m) and divide
by the volume (v): rho = m / v
to calculate the value automatically - which is why you can get on a scale and have read your mass. The SI unit of
mass is the kilogram (kg).
magnetic flux
(Physics / General Physics) a measure of the strength of a magnetic field over a given area perpendicular to it,
equal to the product of the area and the magnetic flux density through it. Symbol
The magnetic field B is defined from the Lorentz Force Law, and specifically from the magnetic force on a
moving charge:
Electric field is defined as the electric force per unit charge. The direction of the field is taken to be
the direction of the force it would exert on a positive test charge. The electric field is radially
outward from a positive charge and radially in toward a negative point charge.
Electric current is the rate of charge flow past a given point in an electric circuit, measured in
Coulombs/second which is named Amperes.
magnetic lines of force----Curved lines used to represent a magnetic field, drawn such that the number of lines is
related to the strength of the magnetic field at a given point and the tangent of any curve at a particular point is
along the direction of magnetic force at that point.
A 'unit' is exactly equivalent to one kilowatt hour, and is used in Britain as the unit of measurement
for purchasing electrical energy.
The horsepower (hp) is a unit in the foot-pound-second ( fps ) or English system, sometimes used to express the
rate at which mechanical energy is expended. It was originally defined as 550 foot-pounds per second (ft-lb/s).
A power level of 1 hp is approximately equivalent to 746 watt s (W) or 0.746 kilowatt s (kW).
Вам также может понравиться
- Mathematical Solution Unifying the Four Fundamental Forces in NatureОт EverandMathematical Solution Unifying the Four Fundamental Forces in NatureОценок пока нет
- Power, Momentum and Collisions - Physics for Kids - 5th Grade | Children's Physics BooksОт EverandPower, Momentum and Collisions - Physics for Kids - 5th Grade | Children's Physics BooksОценок пока нет
- Archimedes: Electric ForceДокумент1 страницаArchimedes: Electric ForceJason HarrisonОценок пока нет
- Archimedes: ChargeДокумент1 страницаArchimedes: ChargeJason HarrisonОценок пока нет
- Physics Position Velocity Acceleration Displacement Time: Kinematics Speed Vector Physical QuantityДокумент3 страницыPhysics Position Velocity Acceleration Displacement Time: Kinematics Speed Vector Physical QuantityJason HarrisonОценок пока нет
- CCC Yenching College CKNGДокумент12 страницCCC Yenching College CKNGEmily LukОценок пока нет
- Viva Questions PhysicsДокумент10 страницViva Questions PhysicsAbaan KoulОценок пока нет
- Engineering MechanicsДокумент3 страницыEngineering MechanicszacpopecornОценок пока нет
- AcousticsДокумент23 страницыAcousticsNadheen AnОценок пока нет
- Physics DefinitionДокумент9 страницPhysics Definitionaishah.wasim2004Оценок пока нет
- Physics Unit 4 Revision NotesДокумент12 страницPhysics Unit 4 Revision Notespraphul4u100% (1)
- A Level Physics Definitions (As)Документ4 страницыA Level Physics Definitions (As)Sabih SiddiqiОценок пока нет
- Module 3: Electromagnetism: Lecture - Magnetic FieldДокумент36 страницModule 3: Electromagnetism: Lecture - Magnetic FieldSayan Kumar KhanОценок пока нет
- Group 1Документ10 страницGroup 1feugueng john francis kingОценок пока нет
- All Definitions For O Level PhysicsДокумент3 страницыAll Definitions For O Level PhysicsMichelleОценок пока нет
- Class: BS Second SemesterДокумент8 страницClass: BS Second SemesterMUHAMMAD FURQAN ALI MALIKОценок пока нет
- 物理定义Документ4 страницы物理定义Ming ZengОценок пока нет
- 05 D FieldsДокумент80 страниц05 D FieldsKatia Reales PazОценок пока нет
- 1 Basic Electrical IdeasДокумент19 страниц1 Basic Electrical IdeasYeri KimОценок пока нет
- DefinitionsДокумент9 страницDefinitionsshirley wangОценок пока нет
- Definitions To Learn For O Level PhysicsДокумент3 страницыDefinitions To Learn For O Level PhysicsWilliam SkyОценок пока нет
- Circular Motion (Chap.7) :: 1 - Physics (A-Level)Документ18 страницCircular Motion (Chap.7) :: 1 - Physics (A-Level)shimoni rathoreОценок пока нет
- Class: BS Second SemesterДокумент15 страницClass: BS Second SemesterAbdullah ZafarОценок пока нет
- Circular Motion (Chap.7) :: Physics (A-Level)Документ18 страницCircular Motion (Chap.7) :: Physics (A-Level)Major warriorОценок пока нет
- PhysicsДокумент7 страницPhysicsNightmareОценок пока нет
- Physics DefinitionsДокумент4 страницыPhysics DefinitionsRhichelle StraussОценок пока нет
- Physics Part 1 e 51Документ62 страницыPhysics Part 1 e 51study materialОценок пока нет
- Moving Charges & Magnetism CH4 Part 1Документ26 страницMoving Charges & Magnetism CH4 Part 1Rishab SharmaОценок пока нет
- The WTF A Level Package Physics Cheat SheetДокумент7 страницThe WTF A Level Package Physics Cheat Sheet7063673nasОценок пока нет
- Physics Notes Zahid I. B. Khan: EchanicsДокумент6 страницPhysics Notes Zahid I. B. Khan: EchanicsZahid IbkОценок пока нет
- Physics AS FactsДокумент5 страницPhysics AS FactsTamzidОценок пока нет
- Force 1Документ13 страницForce 1api-3731257Оценок пока нет
- ZPPD Lecturephysics1430261805Документ179 страницZPPD Lecturephysics1430261805Ps Ak100% (1)
- Kinetics - Force & Acceleration Part 1Документ25 страницKinetics - Force & Acceleration Part 1Jihan GorayahОценок пока нет
- AS Level Physics: Terms & Definitions:-: MeasurementДокумент13 страницAS Level Physics: Terms & Definitions:-: MeasurementJacklynlim LkcОценок пока нет
- Physics 2 PDFДокумент23 страницыPhysics 2 PDFFranchezca ChavezОценок пока нет
- Lectures 1 and 2 Intro and PhotelecДокумент9 страницLectures 1 and 2 Intro and PhotelecNabil IshamОценок пока нет
- General Physics I Essay by Farid MammadovДокумент24 страницыGeneral Physics I Essay by Farid MammadovФарид МамедовОценок пока нет
- Physics - I PDFДокумент179 страницPhysics - I PDFRENGANATHAN PОценок пока нет
- Physics Lab Report 6: ForcesДокумент14 страницPhysics Lab Report 6: ForcesJustin PedrozaОценок пока нет
- Basicconcepct 160405173954Документ38 страницBasicconcepct 160405173954rajkumaresanОценок пока нет
- Physics A Level DefinitionsДокумент12 страницPhysics A Level DefinitionsNaillah Saba100% (1)
- Grade 11 Physics Exam Cheat SheetДокумент3 страницыGrade 11 Physics Exam Cheat SheetEduardo0% (1)
- Chapter 13: Vibrations and Waves Simple Harmonic Motion: X A M K VДокумент7 страницChapter 13: Vibrations and Waves Simple Harmonic Motion: X A M K VJohnBenardОценок пока нет
- General Science For WbcsДокумент95 страницGeneral Science For WbcsMITHUN CHATTERJEE100% (1)
- (Phys) Compiled Definitions and Principles For ASlevel Paper 1/paper 2Документ10 страниц(Phys) Compiled Definitions and Principles For ASlevel Paper 1/paper 2qidamadani100% (1)
- EE8409 Electromagnetic Theory: Dr. Shazzat HossainДокумент32 страницыEE8409 Electromagnetic Theory: Dr. Shazzat HossainMd Shazzat HossainОценок пока нет
- Glossary of Physics - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaДокумент13 страницGlossary of Physics - Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopediadidodido_67Оценок пока нет
- SHM PDFДокумент13 страницSHM PDFHasleen BeniОценок пока нет
- UNIT-2Документ2 страницыUNIT-2Azra HumićОценок пока нет
- Lectures Notes On Engineering Mechanics: Name-Manoranjan Behera Branch-MechanicalДокумент30 страницLectures Notes On Engineering Mechanics: Name-Manoranjan Behera Branch-MechanicalGarfieldsОценок пока нет
- Physics Unit 4 Summary: Further MechanicsДокумент8 страницPhysics Unit 4 Summary: Further MechanicsTravisJohn-JohnsonReadОценок пока нет
- Motion Forces and EnergyДокумент13 страницMotion Forces and EnergyAbid KhanОценок пока нет
- Physics FormulasДокумент20 страницPhysics Formulasbrandon100% (1)
- PHY 331 - F21 - Ch5 - MagnetostaticsДокумент49 страницPHY 331 - F21 - Ch5 - Magnetostaticsنور وائلОценок пока нет
- Handout 1Документ64 страницыHandout 1Sonam AlviОценок пока нет
- Measurements: ForceДокумент6 страницMeasurements: ForceroshОценок пока нет
- Chapter 6 - Work and EnergyДокумент5 страницChapter 6 - Work and EnergyDatu Sarip Azeemkhan Ampatuan-BernanОценок пока нет
- The SI Unit of Energy Is The Joule (J) or Newton-Meter (N M) - TДокумент1 страницаThe SI Unit of Energy Is The Joule (J) or Newton-Meter (N M) - TJason HarrisonОценок пока нет
- Archimedes: The SI Unit of Energy Is The Joule (J) or Newton-Meter (N M) - TДокумент1 страницаArchimedes: The SI Unit of Energy Is The Joule (J) or Newton-Meter (N M) - TJason HarrisonОценок пока нет
- Archimedes: The SI Unit of Energy Is The Joule (J) or Newton-Meter (N M) - TДокумент1 страницаArchimedes: The SI Unit of Energy Is The Joule (J) or Newton-Meter (N M) - TJason HarrisonОценок пока нет
- Database Management System: Additional InformationДокумент2 страницыDatabase Management System: Additional InformationJason HarrisonОценок пока нет
- Write An Assignment On Avalanche Photodiode. 2. Write An Assignment On LEDДокумент1 страницаWrite An Assignment On Avalanche Photodiode. 2. Write An Assignment On LEDJason HarrisonОценок пока нет
- VTT Btuo45-041224Документ58 страницVTT Btuo45-041224Khrystenn Mesias SerapioОценок пока нет
- Interface: Recommended Configuration TableДокумент54 страницыInterface: Recommended Configuration TableTrần ĐìnhОценок пока нет
- Alokaya 1Документ20 страницAlokaya 1joker boyОценок пока нет
- Electrostatics Summary PDFДокумент10 страницElectrostatics Summary PDFKaushal kumarОценок пока нет
- Scada IO ListДокумент3 страницыScada IO ListSaraswatapalitОценок пока нет
- Experiment 5Документ5 страницExperiment 5dummy008Оценок пока нет
- Kedah Fizik Modul 1 T5 P2 2014 SkemaДокумент5 страницKedah Fizik Modul 1 T5 P2 2014 SkemaHelmi TarmiziОценок пока нет
- Natural Draught and Chimney - 1Документ1 страницаNatural Draught and Chimney - 1Sam RagОценок пока нет
- Substation Engineering & LayoutДокумент4 страницыSubstation Engineering & Layoutgulatimanish1985Оценок пока нет
- Eti Ohe 16 - 1 94Документ27 страницEti Ohe 16 - 1 94Abhishek Pandey100% (1)
- June 2014 (R) MA - M1 EdexcelДокумент9 страницJune 2014 (R) MA - M1 EdexcelKollol KolllolОценок пока нет
- NNSN SD6x8Документ44 страницыNNSN SD6x8Patrice PaulОценок пока нет
- Basic Operations With Force Systems (Short)Документ40 страницBasic Operations With Force Systems (Short)Kirk JamisonОценок пока нет
- Electrical Vendor Directory Jan 2020 To Jun 2020Документ231 страницаElectrical Vendor Directory Jan 2020 To Jun 2020sumitshyamal0% (1)
- Imaginary TimeДокумент2 страницыImaginary TimeSally MoremОценок пока нет
- Bahagian A: Kertas 2Документ17 страницBahagian A: Kertas 2wahidms84Оценок пока нет
- 11B Exam Practice: Suggested Calculation: F FДокумент3 страницы11B Exam Practice: Suggested Calculation: F FsalmaОценок пока нет
- CRKTCT - 19. A Capacitor With Capacitance 0.1F in An RC Circuit Is Initially Charged Up ToДокумент5 страницCRKTCT - 19. A Capacitor With Capacitance 0.1F in An RC Circuit Is Initially Charged Up ToWilburОценок пока нет
- Mid - 1 Atd-2Документ1 страницаMid - 1 Atd-2Bhlp RajuОценок пока нет
- Experiment 01Документ15 страницExperiment 01frank samndomiОценок пока нет
- Conradi Probe ExercisesДокумент13 страницConradi Probe ExercisesEray ArıkОценок пока нет
- 26 Solution of TriangleДокумент20 страниц26 Solution of TriangleSachin KumarОценок пока нет
- Maxon ConfigДокумент12 страницMaxon ConfigFurkan YAŞARОценок пока нет
- 9709 w15 QP 41Документ4 страницы9709 w15 QP 41yuke kristinaОценок пока нет
- Typical Limiting Values of SubStation Equipments.Документ10 страницTypical Limiting Values of SubStation Equipments.Jeya KannanОценок пока нет
- Thermal Performance of A Micro Combustor With Heat RecirculationДокумент10 страницThermal Performance of A Micro Combustor With Heat RecirculationHERDI SUTANTOОценок пока нет
- Schematic Diagram of 220 /132 /54 KV Traction SubstationДокумент1 страницаSchematic Diagram of 220 /132 /54 KV Traction SubstationjitendraОценок пока нет
- Speed QuizДокумент2 страницыSpeed QuizKhairi SharifuddinОценок пока нет
- 06 Dielectrics Capacitance 2018mkДокумент41 страница06 Dielectrics Capacitance 2018mkTrần ĐứcAnhОценок пока нет
- SF 17 Sect 14 ALL WebДокумент94 страницыSF 17 Sect 14 ALL WebcachiletОценок пока нет