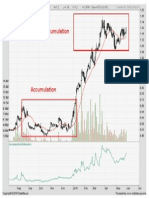
Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
ICSA
Загружено:
tenglumlowАвторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
ICSA
Загружено:
tenglumlowАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Examination Syllabus
CHARTERED SECRETARIES MALAYSIA
Examination Syllabus
contents
INDEX TO SYLLABI
CERTIFICATE IN CORPORATE ADMINISTRATION
Part 1
Business Writing and Communication
Fundamentals of Accounting
Basic Business Law
Business Organisation and Administration
6
7
9
10
Part 2
Compliance and Statutory Forms
Corporate Regulatory Framework
Meetings and Minutes Writing
11
12
13
PROFESSIONAL DIPLOMA IN CORPORATE
ADMINISTRATION
Part 1
Business Law
Business Organisation and Management
Business Accounting
Business Ethics
15
17
18
19
Part 2
Business Finance
Business Strategies
Corporate Compliance and Practice
Law and Practice of Meetings
20
21
23
24
ICSA INTERNATIONAL QUALIFYING SCHEME
Professional Part 1
Strategic and Operations Management
Corporate Law
Financial Accounting
Taxation
26
28
30
32
Professional Part 2
Corporate Governance
Corporate Secretaryship
Corporate Financial Management
Corporate Administration
35
38
40
42
Please visit our website www.maicsa.org.my
for more updates
3
CHARTERED SECRETARIES MALAYSIA
THE INSTITUTE OF CHARTERED
SECRETARIES AND ADMINISTRATORS
The Institute of Chartered Secretaries and
Administrators is the leading recognised
professional body for Chartered Secretaries
and Administrators in the United Kingdom
and throughout the world. The Institute was
formed in 1891 when a small group of company
secretaries saw the need for a company secretary to be professionally
qualied and to have specic education and training for such an
appointment.
The Institute was granted the Royal Charter in 1902, which set the
seal of authority and royal recognition on that belief. Nearly 70 years
later the importance of the company secretarys role was conrmed in
the Court of Appeal where it was stated that Nowadays the secretary
is a much more important person than in 1887; he is an ofcer of the
company with great responsibility.....
Chartered Secretaries are qualied in company law, accounting,
corporate governance, administration, company secretarial practice
and management and are trained to chart a course through
regulation, legislation and best practice in order to deliver effective
operations. The Institute has 44,000 members and 28,000 students
in over 90 countries.
THE MALAYSIAN INSTITUTE OF
CHARTERED SECRETARIES AND
ADMINISTRATORS
The Malaysian Institute of Chartered Secretaries
and Administrators, in short, MAICSA was
founded in 1959 as an affiliated body to
The Institute of Chartered Secretaries and
Administrators, United Kingdom. Membership
of the Institute is limited only to members of the Institute residing
in Malaysia, namely Fellows and Associates, Graduates and
students.
MAICSA as a premier professional body in company secretaryship
and administration exists to serve the needs of the various sectors
of society, in particular, the corporate sector. As betting a dynamic
organisation, the Institute strives to be sensitive to changes and
changing socio-economic developments within the country, and
actively participates in the enhancement of corporate governance
in all its manifold activities centred around greater transparency,
accountability, integrity and professionalism. MAICSA aims not only
to generate a cadre of professional and trained manpower but also
acts as a catalyst for the growth and development of the commercial
and industrial sectors of our country.
As the premier professional body in corporate secretaryship and
administration, MAICSA is committed to ensuring the following
objectives :
Maintenance of the highest standards of integrity and ethical
values incorporating the element of best practice in all its
endeavours.
Raising the prole of the members it represents through an
increased awareness of the contribution made by professional
administrators in various organisations which inter alia
increases the recognition accorded to Chartered Secretaries.
Contributing to the development and well-being of the people
and the nation of which it remains a vital vibrant and integral
component.
In line with its mission and objectives the corner-stone of which is
continuous education to enhance professional skills, the Institute
places great emphasis on the holistic development of the individual.
A continuous learning culture is fostered by the Institute through
continuing professional education and training to ensure the
systematic development and extension of members professional
and managerial knowledge and to better serve both the private and
public sectors of Malaysia.
SYLLABI
The detailed syllabi for all modules are outlined on the following
pages.
All syllabuses are based on Malaysian Law, Standard and
Practice. Therefore, examination questions must be answered
in reference to Malaysian Law, Standard and Practice.
The standard of knowledge and understanding required in
the Institutes examinations is high and it is therefore most
important that students should read around the subject areas as
widely as possible. The reading lists, which are not exhaustive,
contain recommended reading together with other suggested
associated texts.
Students are expected to keep abreast of changes in the law
affecting the modules which they are studying. Generally,
however, a detailed knowledge of new legislation will not be
expected in examinations held within six months of the passing
of the relevant Act. Syllabus changes will be notied to teaching
establishments, and will be published for the information of
students in the Institutes Newsletter and website.
Please visit our website www.maicsa.org.my for more updates
Examination Syllabus
contents
INDEX TO SYLLABI
CERTIFICATE IN CORPORATE ADMINISTRATION
Part 1
Business Writing and Communication
Fundamentals of Accounting
Basic Business Law
Business Organisation and Administration
6
7
9
10
Part 2
Compliance and Statutory Forms
Corporate Regulatory Framework
Meetings and Minutes Writing
11
12
13
Please visit our website www.maicsa.org.my
for more updates
CHARTERED SECRETARIES MALAYSIA
Certicate In Corporate Administration (CCA): Part 1
BUSINESS WRITING AND COMMUNICATION
SYLLABUS
DESCRIPTION
With globalisation and increasing multi-diversity in the workforce, the
ability to communicate well is one of the key factors for success in
any business organisation. In fact, people who communicate well
have a distinct advantage over those who dont.
This course is designed to provide students with an understanding of
basic communication as well as the appropriate tools and conventions
to be applied in good written and oral communication. The human and
psychological aspects of communication are also emphasised.
LEARNING OUTCOME
Upon completion of this module, the student should be able to:
Appreciate the importance of personal skills (listening, writing,
speaking) in communication
Write effective business letters, memos, e-mails, bulletins and
other brief messages using the correct format, salutations and
closings.
Communicate effectively and be critical of their own work.
Maintain trust and goodwill even when required to write negative
(bad) news messages.
Make effective and forceful presentations using appropriate
visuals/technological tools.
Written Communication II
Writing business reports and proposals.
Types and purpose of reports
Format, approach, structure and layout of reports
Usage of visuals in enhancing reports.
Distinguish between fact and opinion, and making them clear
in report.
Presentation Skills and Public Speaking
Planning, Writing and Completing oral presentations
Learning to speak with condence and making an effective
sales pitch
Effective use of facial expressions, body language, humour
and visuals in making effective presentations
Employment Messages & Interviewing for Employment
Planning and writing effective resumes
How to perform well during interviews
The Dos and Donts during interviews
Follow up after the interviews
RECOMMENDED READING
1.
2.
3.
LEARNING CONTENTS
4.
Introduction to Communication Theory
Denition of business communication
Nature and function of communication
The communication process, channels and communication
barriers
Guidelines for overcoming communication barriers
FURTHER READING
1.
2.
Personal Skills in Communication
Effective communication in teams
The art of listening
Verbal (face-to-face) communication
Non-verbal communication (use of face, body language, para
language, time etc.)
Written Communication I
Language, style, tone, readability and grammar
Writing letters, memos, e-mails, bulletins and other brief
messages
Strategies for writing routine, positive, bad-news and persuasive
messages
Applying the correct formats and conventions to the various
types of communication.
Thill, J. V. & Bovee, C. L. (2005), Excellence in Business
Communication, 6th Edition. Prentice Hall.
Guffey, M. E., Rhodes, K. & Rogin, P. (2005), Business
Communication: Process & Products. 4th Edition. South
Western.
Young, D. J. (2006), Foundations of Business Communication:
An Integrative Approach. McGraw Hill Irwin.
Bovee, C. L. & Thill, J. V. (2005), Business Communication
Today. 8th Edition. Prentice Hall.
Chaney, L. H. & Jeanette, S. M. (2004), Intercultural Business
Communication. 3rd Edition. Prentice Hall.
Guffey, M. E. (2003), Business Communication. 4th Edition.
South Western.
Examination Syllabus
Certicate In Corporate Administration (CCA): Part 1
FUNDAMENTALS OF ACCOUNTING
SYLLABUS
DESCRIPTION
This syllabus is designed for candidates who have little or no
knowledge of accounting. It provides the elementary knowledge
essential for the accounting practice of bookkeeping and preparation
of ledger accounts, trial balance, prot and loss accounts and
balance sheet. It provides the underpinning knowledge for the
subject Business Accounting for candidates who aspire to pursue the
Professional Diploma in Corporate Administration programme.
LEARNING OUTCOME
On completion of this subject, the student should be able to:
Discuss the basic accounting principles, concepts and rules
that underpin the preparation of accounts
Identify the source documents that provide the necessary
nancial information for recording purposes
Explain the process of how financial transactions are
recorded and accounted for from source documents to ledger
accounts
Use specialized journals to record credit transactions
Apply general journal entries on certain transactions and post
them to the ledger accounts
Record bank and cash transactions based on sound internal
control procedures
Use control accounts to record credit transactions
Prepare a simple trial balance, prot and loss account and
balance sheet
LEARNING CONTENTS
Introduction to basic accounting principles and its
applications
Denition of accounting
Types of businesses
Basic accounting principles
Business operating cycle
Financial periods and balance sheet date
Accrual concept of accounting
Basic book entry
Denition of bookkeeping
Five groups of accounts
Inventories
Chart of accounts and classication of accounts
Accounting equation
Rules governing double entry
Cash and credit transactions
Source documents and specialized journals
Denition of source documents
Sales invoices
Receipts
Purchase invoices
Cheques
Adjustment notes
Entries in the accounts and overview of trial balance
Sales journal
Sales returns journal
Purchase journal
Purchase returns journal
Cash payments journal
Cash receipts journal
Accounting for inventories
General Journal entries
Introduction
Narrations
Opening general journal entry
Recording transactions in the general journal and posting them
to the ledger accounts
Benets of journal entries
Introduction to ledger accounts
Denition of ledger entries
Types of ledger accounts
Balancing ledger accounts
Control accounts and subsidiary accounts
Denitions
Understanding accounts receivable control account
Understanding accounts payable control account
Posting between control accounts and subsidiary accounts
Posting to ledger accounts
Cash Account and Bank Account
Introduction
Purpose of cash book
The two-column cash book and three-column cash book
Source documents for cash book
Cash discounts
Contra entries
Dishonoured cheques
Recording transactions in the three-column cash book
Petty cash book
Purpose of petty cash book
The imprest system and its features
Columnar petty cash book
Source documents for petty cash
Posting to ledger accounts
The importance of cash control
Internal control procedures for cash receipts and cash
disbursements
CHARTERED SECRETARIES MALAYSIA
Certicate In Corporate Administration (CCA): Part 1
FUNDAMENTALS OF ACCOUNTING
Preparing the Trial Balance
Denition of trial balance
Purpose of trial balance
Checklist for posting to ledger accounts
Detecting errors in trial balance
Rules of contras
Steps of posting to the general and subsidiary accounts
Preparation of a trial balance
Limitations of a trial balance
Final accounts
Components of trading account
Presentation of trading account
Components of prot and loss account
Presentation of prot and loss account
Capital account and its components
Preparation of balance sheet
Preparing nal accounts from trial balance
RECOMMENDED READING
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
David, W. (2003), Introductory Accounting, 2nd Edition,
McGraw-Hill.
Loh, B.F. and Ng K.H. (2006), Accounting: Principles and
Applications, Pearson Education South Asia Pte Ltd.
Wood, F. & Sangster A. (2005), Business Accounting 1, 10th
Edition, FT Prentice Hall.
Dyson, J.R. (2004), Accounting for Non-Accounting Students,
6th Edition, Financial Times Press.
Isa, Shaari (2004), Accounting Principles, Pearson Malaysia
Sdn Bhd.
Examination Syllabus
Certicate In Corporate Administration (CCA): Part 1
BASIC BUSINESS LAW
SYLLABUS
DESCRIPTION
In this globalised world, commerce has become increasingly
important. Both businessmen and businesswomen will, in the
course of their work, enter into many different legal relationships
with other parties. For example a manager of a business enterprise
may enter into a contract of employment with his or her employer. It
is therefore vital that we understand the law, and how it affects our
work and business. Without a sound knowledge of the basic elements
of Business Law, one may not be able to function efciently and
effectively in todays business environment. This subject provides
an overview of the major aspects of business law, namely: law of
contract, law of agency, sales of goods, hire purchase, negotiable
instruments and basic employment law.
Sale of Goods
Elements of contract for sale. Terms of contract i.e. conditions
and warranties. Implied terms including sale by description, sale
by sample, undertaking as to quality and undertaking as to tness.
Transfer of risk, Transfer of title (nemo dat quad non habet rule).
Remedies for breach to the sellers and buyers.
Hire Purchase
Nature of hire purchase agreement. Formalities for a valid hire
purchase agreement. Terms of hire-purchase agreement. Statutory
rights of hirers. Repossession Termination of hire purchase
agreement.
Negotiable Instruments
Introduction to negotiable instruments. Nature, characteristics,
negotiation, and acceptance of bills of exchange, Indorsements,
delivery, liability of parties. Holders of bills payment of bills of
exchange. Cheques.
LEARNING OUTCOME
Upon completion of this subject, students will be able:
to understand the essentials of a contract and remedies for its
breach
to examine the creation of an agency, duties and liabilities of
agents and principals
to appreciate the terms of sales of goods and hire purchase
agreements, and the rights and liabilities of purchasers, sellers,
hirers and owners respectively
to observe the nature of negotiable instruments in particular
bills of exchange and cheques
to appreciate the employment relationship between an employer
and an employee
Employment Law
Denition of an employee. The contract for service and contract of
service. Termination of the employment relationship through unfair
dismissal, constructive dismissal, redundancy and lay-off.
RECOMMENDED READING
1
2
3
Abdul Majid and Krishnan Arjunan, Business Law in
Malaysia, Lexis Nexis, Malayan Law Journal, 2005
Lee Mei Pheng, General Principles of Malaysian Law, 5th
edition, Fajar Bakti, 2005
Nuraisyah Chua Abdullah, Business Law in Malaysia, Pusat
Penerbitan Universiti (UPENA), Universiti Teknologi MARA,
2003
Wu Min Aun and Beatrix Vohrah, Commercial Law of
Malaysia, Longman, 2nd edition, 1991, Updated 2000
LEARNING CONTENTS
Introduction
Denition of law, classication of law, sources of business law
FURTHER READING
Law of Contract
Elements of a contract including offer and acceptance, consideration,
capacity to contract, consent, intention to create legal relations and
certainty. Terms of contracts i.e. express, implied and exclusion
clauses. Void, voidable and illegal contracts. Discharge of contract
by performance, agreement between two parties, frustration and
breach. Remedies for breach of contract i.e. damages, specic
performance and injunction.
1
2
3
4
ER Hardy Ivamy and Vincent Powell Smith, Malaysian Law
of Sale of Goods-Cases and Materials, Butterworths, 1995
Lee Mei Pheng and Detta Samen, Commercial Law in
Malaysia, Malayan Law Journal, 1997
Maimunah Aminuddin, Malaysian Industrial Relations and
Employment Law, McGraw Hill, 5th edition, 2006
Poh Chu Chai, Law of Negotiable Instruments, Malayan Law
Journal, 5th edition, 2001
Law of Agency
Denition of agency and the general nature of an agency. Creation
of agency by express and implied agreement, ratication, estoppel
and necessity. Termination of agency through act of parties and
operation of law.
CHARTERED SECRETARIES MALAYSIA
Certicate In Corporate Administration (CCA): Part 1
BUSINESS ORGANISATION AND
ADMINISTRATION
SYLLABUS
DESCRIPTION
This subject provides an introduction to the theories and practice of
management as well as organisations. This subject is also designed
to allow students to understand behaviour in the organisations at the
individual and group levels. The ultimate objective of this subject is
to provide introductory knowledge and understanding on the ways
in which people manage and are managed in organisations. A range
of concepts, theories, methods of enquiry and paradigms on the
processes of organisations will be explored.
LEARNING OUTCOME
On completion of this module, the student should be able to
understand:
The principles and concepts of management and
organisation.
The various theories of management.
The basic functions and roles performed by a manager.
The management functions and processes within a business
organisation.
Individual processes and behaviour in terms of personality,
perceptions, attitudes, motivation, learning and performance.
Group processes and behaviour in terms of communication,
work teams, decision making and conict.
The effective leadership in business organisation
Organisational processes in terms of job design, culture, ethics,
change and innovation and organisational power and politics.
LEARNING CONTENTS
Introduction to Business Organisation.
Denition of Organisation. Types of Business Organisation. Functional
Areas in Business Organisation Production, Research & Development,
Marketing, Human Resource, Finance and Accounting.
Theories of Management.
Scientic Management theory, Behavioural Management Theory,
Systems Theory and Contingency Theory.
Management and Manager.
Denitions of Management. Importance of Management. Levels of
Management Top, Middle and First-line. Management Functions:
Planning, Organising, Leading and Control. Mintzbergs Managerial
Roles. Managerial Skills - Conceptual, Human and Technical.
Individuals in Organisation.
Personality and Individual Differences. Personality Theories.
Personality Traits. Emotional Intelligence. Atitudes. Perception.
Stress. Individual Learning and Performance. Learning Process.
Learning Styles. Rewarding and Correcting Performance.
Motivation.
The Concept of Motivation. Foundations of Motivation. Motivation
10
Theories - Needs, Equity, Expectancy and Goal Setting. Job Design
and Empowerment for Motivation.
Work Teams and Group Conict.
Group and Work Team. Types of Teams Formal, Informal,
Temporary, and Permanent. Team Processes. Group Behaviour.
Team Building Activities. Managing Team Conict. Group Decision
Making. Groupthink and Group Polarisation.
Organisational Structure.
Definition of Organisational Structure. Types of Organisation
Structure. Fundamentals in Organising, Authority in Organisations.
Span of Control. Delegation.
Communication.
The Communication Process and Channels. Communication Model.
Barriers to Communication. Differences in Communication between
Genders and across Cultures. Open Communication. Dialogue. Crisis
Communication. Feedback and Learning.
Leadership.
The Nature of Leadership. Theories of Leadership Trait, Behaviour
and Contingency. Types of Leaders Charismatic, Visionary,
Transactional and Transformational. Issues in Leadership Cultural
and Gender.
Organisational Culture and Ethics.
Denition of Organisational Culture. Types and Functions of Organisational
Culture. Denition of Ethics. Developing an Ethical Culture.
Organisational Change and Innovation.
Lewins Force-Field Theory to Change. Managing Reaction and
Resistance to Change. Denition of Innovation. Innovation as a
Change Process. Creating a Culture for Innovation.
Organisational Power and Politics.
Denition of Power. Sources of Power Authority, Vertical and
Horizontal. Denition of Organisational Politics. Managing Political
Behaviour in Organisations. Impression Management Techniques.
RECOMMENDED READING
1
2
5
6
Daft, R.L. (2005), Management. 7th edition Publisher
Thomson-South-Western
Jones, G. R. & George. J. M (2006), Contemporary
Management: Creating Value in Organisations. 4th edition
Publisher McGraw Hill/Irwin.
Hellriegel, D. & Slocum, J. W. (2007), Fundamentals
of Organisational Behaviour. Publisher - ThomsonSouthWestern.
Jones, G. R. & George. J. M (2005), Understanding and
Managing Organisational Behaviour. 4th edition Publisher
Prentice Hall.
Manning, G. & Curtis, K. (2007), The Art of Leadership. 2nd
edition Publisher McGraw Hill/Irwin.
Yulk, G. (2006), Leadership in Organisation. 6th edition
Publisher Prentice Hall
Examination Syllabus
Certicate In Corporate Administration (CCA): Part 2
COMPLIANCE AND STATUTORY FORMS
12
SYLLABUS
DESCRIPTION
This is an introductory course designed to provide fundamental
understanding of the basic compliance with the Companies Act 1965
and other Regulatory Bodies. This course also will help to expose
students on how to deal with the statutory forms.
RECOMMENDED READING
1.
LEARNING OUTCOME
2.
On completion of this subject, the student should be able to
3.
i)
ii)
iii)
Understand the basic principles of corporate law and other
regulatory bodies regulations.
Identify the different types of statutory forms, know the principal
contents and understand the importance of each one of the
forms.
Recognize the importance of complying with the Companies
Act and Regulatory Bodies regulations especially in relation to
ling of the statutory forms with the Registrar of Companies.
Regulatory bodies:
Companies Commission of Malaysia
Bursa Saham Malaysia Berhad
Securities Commission
Bursa Central Depository Sdn Bhd
4.
5.
6.
Best Practice Series. The Company Secretary: A Reference
Kit.(2000). MAICSA.
Best Practice Series. A Guide to Annual General Meetings.(2000).
MAICSA.
Kang Shew Meng (2005), Handbook on Company Secretarial
Practice in Malaysia, 4th edition, Kuala Lumpur: LexisNexis
Business Solutions.
Company Secretarial Practice Manual, Kuala Lumpur:
MAICSA.
Guidebook on Completing Prescribed Forms.(2006) SSM and
MAICSA
Malaysian Companies Act 1965.
LEARNING CONTENTS
1
Types of companies
Incorporation of companies
Memorandum and Articles of Association
Company meetings
Directors, company secretaries, auditors
Shares, preference shares and debentures
Share certicate, transfer and transmission of shares
Charges
Prospectus
10
Receivers and managers
11
Winding-up
11
CHARTERED SECRETARIES MALAYSIA
Certicate In Corporate Administration (CCA): Part 2
CORPORATE REGULATORY FRAMEWORK
SYLLABUS
DESCRIPTION
This module introduces the student to the general principles
of corporate law and the general corporate framework in the
administration of a corporation.
LEARNING OUTCOME
Upon completion of the module, the student should be able to
Understand the general principles of corporate law
Apply the knowledge and understanding of the principles in the
administration and secretarial practice of a corporation
LEARNING CONTENTS
Introduction
Types of business entity sole proprietorship, partnership,
company
Differences between a partnership and a company
Differences between a company and a corporation
Sources of corporate law
Legislation
Subsidiary legislation
English cases
Listing requirements of Bursa Malaysia Securities Bhd
Self regulation
Regulatory bodies
Companies Commission of Malaysia
Registrar of Companies
Bursa Malaysia Securities Bhd
Securities Commission
Classication of companies
Statutory company
Registered company
unlimited company and limited company
private company and public company
exempt private company and its advantages
Related companies
Holding company
Ultimate holding company
Subsidiary
Wholly owned subsidiary
Sister company
Registration of foreign companies
Name of company
Certicate of registration of foreign company
Agent in Malaysia
Cessation of business in Malaysia
Company secretary
Qualication
Removal
Functions and authority
Appointment
Resignation
Administration of company
Registered ofce
Service of documents
Statutory books
Register of members/ shareholders
Register of directors, managers and secretary
Register of debenture holders
Register of substantial shareholders
Register of directors shareholding, debentures and
interests
Register of charges
Register of participatory interest holders
The minutes books
Books of accounts
Common seal
Issuance of shares
Transfer of shares
Account
Directors
Qualication
Appointment
Auditors
Qualication
Appointment
Voluntary winding-up
Liquidation
Striking off the register
Compulsory winding-up
RECOMMENDED READING
1.
2.
3.
Cheah Foo Seong (2006), Guide to Company Law and
Secretarial Practice in Malaysia, Singapore: CCH.
Kang Shew Meng (2005), Handbook on Company Secretarial
Practice in Malaysia, 4th edition, Kuala Lumpur: LexisNexis
Business Solutions.
R Shanty, P. Janine and J Anil (2005), Concise Principles of
Company Law in Malaysia, Kuala Lumpur: MLJ.
FURTHER READING
Incorporation of companies
Name of company
Certicate of incorporation
Commencement of business
Memorandum and Articles of Association
1.
2.
3.
12
Aiman Nariman Mohd Sulaiman (2005), Commercial
Applications of Company Law in Malaysia, Singapore: CCH.
Ben Chan, Philip Koh and Peter Ling (2006), Chan & Koh on
Malaysian Company Law, Kuala Lumpur: Sweet & Maxwell.
Walter Woon (2005), Walter Woon on Company Law,
Singapore: Sweet & Maxwell.
Examination Syllabus
Certicate In Corporate Administration (CCA): Part 2
MEETINGS AND MINUTES WRITING
SYLLABUS
DESCRIPTION
Meetings play an important role in community life, social groupings,
clubs and societies, and most importantly in businesses. It is at
meetings that decisions are made and carried out by operational
people. The syllabus covers principles and practices of the different
types of meetings held within a variety of social groupings, clubs and
societies, most importantly in registered companies.
During meetings the proceedings and transactions should be
properly recorded by suitably appointed recording-secretary to
become minutes and resolutions that are referred to by others as
conclusive evidence that authority or permission has been given.
Thus, students should learn how minutes and resolutions are drafted
and kept permanently as evidence inference and verications by
third parties.
Association and Society Meetings
What is an Association and Society that is registered under a
Societies Act 1966. The Constitution or Rules for internal regulation
of a Society, particularly rules regulating conduct, convening Meetings
such as Annual General Meeting, Extraordinary General Meetings.
The functions of the Management Committee, Ofce-Bearers, Hon.
Secretary and Hon Treasurer, and Committee Members.
Essentials of Public Meetings
Terms and denition used for a public meeting, public places for
holding public meetings and importance of preserving public order.
Public Meetings held in private places.
Minutes Writing
Drafting of minutes of meetings and resolutions as a record of the
proceeding and transactions at Meetings. Techniques in writing
minutes and the importance of keeping minutes properly.
RECOMMENDED READING
LEARNING OUTCOME
1.
On completion of this module, students should be able to :(i)
Understand meetings in general and the various types of
meetings relating to different situations;
(ii) Know that convening meetings have rules and procedures that
have legal consequences;
(iii) Gain an understanding of the specic rules and procedures for
holding company meetings, society and club meetings;
(iv) Know that public meetings have a different set of laws, rules
and regulations;
(v) Understand the importance of giving notice correctly and the
purpose of agenda;
(v) Understand the essential of writing minutes and resolutions;
and
(vi) Appreciate the important practices involved in Meetings.
2.
3.
4.
5.
Lawton P. & Rigby E., - Meetings, Their Law and Practice,
M & E Handbook, 5th Edition (1992).
Priscilla Yap, Company Meetings: Law & Practice in Malaysia,
2nd Edition, CCH 2005.
Kang S.M., Directors & Shareholders Guide on AGM, MLJ
2002.
Societies Act 1966
Companies Act 1965
FURTHER READING
1.
2.
3.
Cheah F S, Company Law & Secretarial Practice, Malaysia
CCH 2006
The Chartered Secretary, Malaysia journal published by
MAICSA
Shearman I., Shackleton on Law & Practice of Meetings, Sweet
& Maxwell 8th Edition (2006)
LEARNING CONTENTS
Terms Used in Meetings
The denition of meetings and the types of regulations governing
Meetings. The paper work involved in the preparation of Notices and
Agenda for private Meetings of organisations. Terms that are normally
used in Meetings like The Chairman, Quorum, Inquorate,
Motions and Resolutions. A general appreciation of the conduct
and procedure at a Meeting
Company Meetings
The types of company Meetings that must be carried out in
accordance to Companies Act 1965 and the Companys Articles of
Association. A clear understanding of the ways in which business
meetings of companies are conducted, incorporating those terms
mentioned earlier.
13
CHARTERED SECRETARIES MALAYSIA
contents
INDEX TO SYLLABI
PROFESSIONAL DIPLOMA IN CORPORATE
ADMINISTRATION
Part 1
Business Law
Business Organisation and Management
Business Accounting
Business Ethics
15
17
18
19
Part 2
Business Finance
Business Strategies
Corporate Compliance and Practice
Law and Practice of Meetings
20
21
23
24
Please visit our website www.maicsa.org.my
for more updates
14
Examination Syllabus
Professional Diploma In Corporate Administration (PDCA): Part 1
BUSINESS LAW
SYLLABUS
DESCRIPTION
This subject aims to educate the student on the core elements of the
principal areas of Business Law. Business Law plays a central and
vital role in the operation of modern trade and commerce.
A person occupying a managerial position in the business world
will invariably discover that some knowledge of the main areas of
Business Law is essential for the discharge of his duties. A corporate
manager or corporate administrator will nd that his work involves,
directly or indirectly, with problems associated with the law of contract,
agency, sale of goods, banking, employment and other areas of
Business Law. Without a sound understanding of the basic elements
of the principal areas of Business Law, a modern corporate manager
or administrator may not be able to function efciently and effectively
in todays business environment.
LEARNING OUTCOME
On completion of this module, the student should be able to:
To provide a thorough knowledge of the core elements of
Malaysian Business
Law together with a good understanding of other selected topics
which are related and important to business organizations.
LEARNING CONTENTS
Introduction
Definition of law. Classification of Law. Sources of Malaysian
Business Law
Agency
The general nature of agency. Creation of agency including subagents. Duty of principal to agent. Duty and authority of agent. Effect
of agents act on third parties including disclosed and undisclosed
principal. Termination of agency.
Commercial Disputes
Arbitration. Nature and purpose. Arbitrator appointment, powers
and authority. Arbitration award. Mareva injunction and Anton Pillar
orders.
Consumer Protection
Principles of consumer protections including the following:
Hire-Purchase - Nature of a hire-purchase agreement.
Formation and contents of hire-purchase agreement. Protection
of hirers including implied conditions and warranties, hrers rights
including assignment, early completion, right o determine hire,
repossession. Exemption clauses.
Trade Descriptions - Denition of a trade description.
Offences involving trade descriptions. Defences.
Direct Sales - Denition of direct sales as opposed to illegal
pyramid schemes.
Control of direct sales through licensing, contents of direct sales
contract, cooling-off period,
Employment Law
Denition of employee. Contract of employment. Duties of employer
and employee. Statutory benefits and protection accorded to
employees. Termination of employment including unfair dismissal,
wrongful dismissal, constructive dismissal, Redundancy.
Industrial and Intellectual Property
Law of Contract
Essential elements of a valid contract including offer, acceptance,
intention to create legal relations, consideration, capacity, certainty.
Contractual terms and conditions, exclusion clauses. Void, voidable
and illegal contracts. Vitiating factors which will set aside contracts
including mistake, misrepresentation, undue influence, fraud,
coercion/duress.
Termination /discharge of contracts through mutual agreement,
performance, frustration, breach. Remedies for breach of contract
including damages, specic performance, injunction, quantum meruit.
Limitation of actions
Sale of Goods
Essential elements of a contract for the sale of goods. Implied terms
and conditions.Passing of property in goods. Transfer of title including
the nemo dat rule and its exceptions. Performance of contract
including delivery and acceptance of goods. Remedies for breach of
contract including breach by the buyer and the unpaid sellers rights.
Breach by seller and the remedies of the buyer.
Copyright protection
Works eligible for protection including performers rights. Duration
of copyright protection.What constitutes infringement of copyright.
Defences for infringement of copyright. Remedies for infringement
of copyright.
Patents
Denition of patents and patentable inventions. Duration of protection.
Rights of patentee. Termination of patents.
Trade marks
Registrable trade marks. . Duration of protection. Restrictions on
registration of trade marks. Effects of registration.
Negotiable Instruments
The law relating to negotiable instruments and bills of exchange with
particular reference to cheques.
15
CHARTERED SECRETARIES MALAYSIA
Professional Diploma In Corporate Administration (PDCA): Part 1
BUSINESS LAW
Bankruptcy Law
General principles of bankruptcy law
Syariah Law
Concepts and principles; commercial transactions in accordance
with Syariah
RECOMMENDED READING
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
12.
13.
14.
15.
16.
17.
18.
16
Abdul Majid bin Nabi Baksh & Krishnan Arjunan, Business
Law in Malaysia, Lexis Nexis, Malayan Law Journal, 2005
Wu Min Aun & Beatrit Vohrah, Commercial Law of Malaysia,
Longman, 2nd edition 1991, Updated 2000
Lee Mei Pheng, General Principles of Malaysian Law, Fajar
Bakti, 5th edition, 2005
Khaw Lake Tee, Copyright Law in Malaysia An Outline,
Butterworths Asia, 2001
Teo Bong Kwang, Trade Mark Law and Practice in Malaysia,
Malaysian Law Journal, 2001
ER Hardy-Ivamy & Vincent Powell-Smith, Malaysian Law of
Sale of Goods Cases and Materials, Butterworths 1995
Poh Chu Chai, Law of Negotiable Instruments, Malaysian Law
Journal, 5th edition, 2001
Sudin Haron & Bala Shanmugam, Islamic Banking System
Concepts and Applications, Pelanduk Publications, 2001
Visu Sinnadurai, Law of Contract, Malayan Law Journal, 3rd
edition, 2004
Syed Ahmad Alsagoff, Principles of the Law of Contract in
Malaysia, Malayan Law Journal, 2nd edition, 2003
Lee Mei Pheng & Detta Samen, Commercial Law in Malaysia,
Malayan Law Journal, 1997
Salleh Buang, Malaysian Law on Hire-Purchase, Sweet and
Maxwell Asia, 2nd edition, 2001
Arthur Wineburg, Intellectual Property Protection in Asia,
Butterworths Asia, 1991
Ida Madieha Abdul Ghani Azmi, Patent Law in Malaysia:
Cases and Commentary, Sweet and Maxwell Asia, 2003
Dunstan Ayadurai, Industrial Relations in Malaysia Law and
Practice Malayan Law Journal, 2nd edition, 2001
Maimunah Aminuddin, Malaysian Industrial Relations and
Employment Law, McGraw-Hill, 5th edition, 2006
K. Rajkumar, Malaysian Labour Laws made Simple, Pelanduk
Publications, 1999
Ayadurai, The Employer, the Employee and the law in
Malaysia, Butterworths Asia, 1985
STATUES:
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
Arbitration Act 1952
Bills of Exchange Act 1949
Consumer Protection Act 1999
Contracts Act 1950
Copyright Act 1987
Direct Sales Act 1993
Employment Act 1955
Examination Syllabus
Professional Diploma In Corporate Administration (PDCA): Part 1
BUSINESS ORGANISATION AND
MANAGEMENT
SYLLABUS
DESCRIPTION
Communication.
The communication model, barriers in communication, the
grapevine, differences in communication between genders and
across cultures.
This subject educates students on the functions and desirable
attitudes of an effective manager. A manager in order to be effective
has to understand how individuals differ from one another, and how
to use varying motivational techniques to improve the productivity
of workers, whether they work in groups or individually. This subject
educates students on how to be an effective leader and how to use of
power and politics in order to advance ones career in a rm. Finally,
the latest trends in changes in organisational structure and culture in
todays volatile business environment are explained.
Leadership.
Trait theories of leadership, behaviour theories of leadership such
as Ohio and Michigan studies and Blake and Moutons Managerial
grid, contingency theories of leadership such as Fiedler, Hersey and
Blanchard, Path-goal theory and Vrooms decision making model of
leadership.
LEARNING OUTCOME
Denition of organisational politics.
Causes and techniques and how to reduce politics in the organisation.
Impression management techniques.
On Completion of this module, the student should be able to
understand:
The duties and the desirable attributes of an effective
manager.
How individuals differ from one another.
What motivates individuals and groups.
The art of communication
Effective leadership in business organisations.
The prevalence of power and politics in organisations.
The organisational structure and culture.
The factors responsible for resistance to change.
Power and Politics. Denition of power.
French & Ravens ve bases of power.
Organisational Structure.
Division of labour, span of control, centralisation and decentralisation,
mechanistic vs organic structure, simple structure, functional
structure, divisional structure and matrix structure. Contingencies of
organisational design such as size, technology, external environment,
and strategy.
Organisational Culture.
Denition. Rituals, myths, structures and symbols. Is culture an
asset or liability?
LEARNING CONTENTS
Denition of management.
Planning Organising Leading and Controlling. Mintzbergs managerial
roles.
Organisational Change.
Lewins force eld analysis model. Resistance to change. Team and
individual interventions in organisational design. Change agents.
RECOMMENDED READING
Theories of management
Frederick Taylors Scientic Management, Henri Fayol, Systems
theory, and Contingency perspectives of management.
1.
2.
Personality and Individual Differences.
Understanding Personality, Attitudes, Perceptions, Emotions, Values
and Beliefs.
Motivation and expectancy theory.
Motivation theories such as Maslow, Herzberg, Aldefer, McGregor,
Adams equity theory and Vrooms expectancy theory. Applied
motivational practices in the workplace such as reward practices,
job design practices and empowerment.
3.
4.
5.
6.
Hellriegel,D. & Slocum, J.W. (2003), Organisational behaviour.
10th edition Publisher- Thomson Learning
Robbins, S. (2003). Organisational behaviour. 10th edition
Publisher-Prentice Hall.
Plunkett, W. R., Attner, R.F., & Allen, G.S (2002),
Management-meeting & exceeding customer expectations.
7th edition Publisher- Thomson Learning.
Daft, R. L. (2002), The Leadership Experience. 2nd edition
Publisher-Thomson Learning.
Graetz, F., Rimmer, M., Lawrence, A. & Smith, A. (2002),
Managing Organisational Change. 1st ed. Publisher- Wiley.
Yukl, G. (1988), Leadership in Organizations. 4th edition
Publisher - Prentice Hall.
Team dynamics.
Types of groups such as formal, informal, temporary and permanent.
Stages of group development. Factors affecting team performance.
Comparison of individual vs group decision-making. Problems with
group decisions such as groupthink and group polarisation.
17
CHARTERED SECRETARIES MALAYSIA
Professional Diploma In Corporate Administration (PDCA): Part 1
BUSINESS ACCOUNTING
SYLLABUS
DESCRIPTION
This is an introductory course designed to provide fundamental
understanding of the basic accounting principles, techniques and
concepts as well as the ability to apply these principles and concepts
in the preparation of nancial statements. This course also deals with
an introduction to cost and management accounting.
LEARNING OUTCOME
On completion of this subject, the student should be able to:
Discuss the functions and role of accounting in business.
Explain the accounting principles and concepts underlying the
preparation of nancial statements.
Analyse the effects of business transactions on the accounting
equation and to record these transactions using double entry
system.
Identify the basic steps in the recording process and develop
skills in recording business transactions systematically.
Develop skills in preparing nancial statements of sole traders
and companies.
Derive elementary ratios
Develop an understanding of the language and mechanics of
cost and management accounting.
LEARNING CONTENTS
The Nature and Objectives of Financial Accounting
Types of business entities sole traders, partnerships and
companies
Nature, purpose and scope of accounting
Main user groups of nancial statements.
Differences between nancial and management accounting.
Accounting principles and The Regulatory Framework
Accounting concepts, conventions and principles
Introduction to the standard setting process
Non-current Assets
Dene non-current tangible and intangible assets.
Distinguish between capital and revenue expenditure items.
Concept of depreciation (and amortisation)
Methods of depreciation (and amortisation).
Accounting entries to record depreciation.
Show how depreciation is presented in the income statement
and balance sheet.
Preparing Financial Statements
Preparing the income statement and balance sheet for sole
traders.
Errors and Suspense Accounts
Types of errors
Suspense accounts and correcting the errors.
Single Entry and Incomplete Records
Preparing nancial statements from incomplete and single entry
records.
Introduction to Company accounts
Capital structure of companies
Types of shares and debentures
Issue of shares
Types of reserves; capital and revenue, share premium
Appropriation of prots
Preparing simple income statement and balance sheet for
internal use.
Interpretation of Financial Statements
Accounting ratios for protability, liquidity and asset utilisation
Signicance of the ratios.
Introduction to cost and Management Accounting
Fundamentals of costing
Elements and classication of costs
Marginal and absorption costing
Cost-volume-prot-analysis
Budgeting
Accounting Cycle
The basic accounting equation and its effect on accounting
process.
Classication of accounts
The double entry system
Introduction to the prime books of entry
Ledgers
Cash book and bank reconciliation
Preparing the trial balance
Adjustment for accruals and prepayments including accounting
for depreciation and bad debts
RECOMMENDED READING
Accounting for Inventory
Dene and classify inventories using FIFO, weighted average
and LIFO methods
Valuing inventory at lower of cost and net realizable value.
6.
18
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
Thomas, A., An Introduction to Financial Accounting, 4th
Edition, McGraw-Hill.
Wood, F., Business Accounting, Volume 1, 8th Edition, Pitman
Publishing.
Gillespie, Lewis and Hamilton, Principles of Financial
Accounting, Prentice Hall, 1997.
Dyson J.R., Accounting for Non-Accounting Students, Financial
Times Management, 4th Edition 1997.
Wong S.V. and Leong A.F.C., Business Accounting, Prentice
Hall 2002.
Jane Lazar and Tan Lay Leng, Company Accounts and
Reporting, 5th Edition Prentice Hall 2002.
Examination Syllabus
Professional Diploma In Corporate Administration (PDCA): Part 1
BUSINESS ETHICS
SYLLABUS
DESCRIPTION
The aim of this course is to highlight key concepts of ethics and ethical
reasoning as they are applied in anticipating and solving complex ethical
problems such as ethical dilemmas faced by the business organizations
and their ofcers. It discusses issues of right and wrong actions or
decisions from all levels of decision making. Integrity requires many
pillars of support one of which is mindful analysis of facts, contexts and
cultures when applying guidelines or principles for ethical judgement
and decisions. The other important factor is leadership with its
constituent constellation reasoning and stakeholder analysis. Keen
awareness of the complexity of ethical decision making is important for
the management of ethics and integrity within an organization.
LEARNING OUTCOME
Understanding of concepts and ethical reasoning for ethical
decision making.
Strategies, shared values, leadership process, system, stafng
and structure are among the key determinants of integrity and
ethical climate of any organization.
Evaluation or judgements of right and wrong actions or
decisions are guided by principles or standards that emphasize
consequence of the act, nature of the act and the character of
decision maker.
Ethical decision making process involves awareness, judgement
and behavior. This process is also influenced by ethical
environment and the cognitive development of decision maker.
Ethics management systems are usually values based rather
than compliance based, requiring continuous reinforcement and
improvements.
LEARNING CONTENTS
Importance of ethics for managers:
Stakeholders competing expectations and claims are making
ethical decision making more complex.
Corporate governance, compliance and regulatory requirements
are increasingly enforced.
Ethical competencies no longer optional to handle complexities
in decision making.
Development of character and integrity critical in performing roles
and responsibilities.
Globalization and cross cultural relationships in business require
awareness of other values and norms.
Evolution of Business Ethics
Adam Smith and moral sentiments in business.
Cooperation and competition in business.
Market success and market failures.
Impact of business sector decisions on stakeholders and
environment.
Corporate social responsibility.
The increasing role of regulations in business affairs.
Corporate governance and long term shareholder value.
Business ethics and the law
Overlap between ethics and law.
Ethical concepts in Business Law.
Why laws are inadequate for business ethics.
The need for self governance over and above compliance.
Importance of trust
Ethical dimensions in Business Decisions
Common ethical problems.
Factors contributing to unethical conduct in organizations
Ethical decision making process; awareness, judgement and
behavior.
Role of values and character.
Importance of principles, facts and context.
Ethics as organizational culture.
Moral guidelines for dealing with ethical dilemmas
Clear cut ethical decisions versus ethical dilemmas.
Moral guidelines for business in different religions and cultures.
Application of moral guidelines for ethical dilemmas in
business.
Consequences, compliance and character as guiding
principles.
Practical guide to sound ethical decision making in business.
Cognitive factors, cognitive barriers and environmental factors
in ethical decision making
Stages of moral awareness and development.
Emotions reason in decision making.
Cognitive barriers to sound ethical judgement.
Organizational culture, core values, policies, systems and
processes.
Types of ethical climate.
Stakeholders and peers.
Managing ethics and integrity in global environment
Cross cultural ethics.
Ethics / integrity management system.
Managing ethics in global environment.
Corporate guidelines and policies for global business ethics.
Coax round table principles for business.
RECOMMENDED READING
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
Weiss J.W., Business Ethics, A Stakeholder and issues
management approach. (Dryden Press 2006)
Steiner and Steiner, Business Government and Society,
Managerial Perspective, 11th edition (McGraw Hill -2006)
Shaw and Barry, Moral Issues in Business, 9th edition
(Wadsworth 2004)
Frederick R., ed., A Companion to Business Ethics (Malden,
Mass.: Blackwell, 1999)
Mahbob Sulaiman, et al, Proceedings of the World Ethics and
Integrity Forum 2005 (Malaysian Institute of Integrity 2005)
19
CHARTERED SECRETARIES MALAYSIA
Professional Diploma In Corporate Administration (PDCA): Part 2
BUSINESS FINANCE
Stocks and Their Valuation
SYLLABUS
DESCRIPTION
This course introduces the student to the fundamentals of business
nance. The course requires an understanding of mathematics as
well as economic concepts and accounting principles. The course
is corporate-oriented with emphasis on practical applications and
problem solving techniques. The primary objective is to provide the
student with the tools to understand and solve the basic nancial
problems confronting business today. The topics covered include
the time value of money, valuation of assets, capital budgeting
techniques, capital structure theory and dividend policy assessment.
The application of the topics to international markets will be made
whenever possible.
Investing in Long-Term Assets: Capital Budgeting
The Cost of Capital
The Basics of Capital Budgeting
Cash Flow Estimation and Risk Analysis
Other Topics in Capital Budgeting
Capital Structure and Dividend Policy
Capital Structure and Leverage
Distribution to Shareholders: Dividends and Share
Repurchases
Working Capital Management
Managing Current Assets
Financing Current Assets
RECOMMENDED READING
LEARNING OUTCOME
1.
The successful student of Business Finance should understand
and be able to apply the basic time value methodology to general
valuation and other cash ow applications and employ the traditional
evaluation techniques of capital budgeting analysis in business and
personal capital investment decisions.
Upon successful completion of this course the student should be
able to:
understand and apply basic time value methodology to general
valuation and integrated cash ow applications;
understand and apply the conceptual relationship between the
expected return and the relevant risk of individual assets and
portfolios of assets;
understand and apply the traditional evaluation techniques of
capital budgeting analysis in business and personal capital
investments;
understand the concept of cost of capital and nancial leverage
and apply those concepts in the determination of the optimal
capital structure; and,
understand the current nancial environment in which business
decisions are made.
2.
3.
4.
FURTHER READING
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
LEARNING CONTENTS
Introduction to Financial Management
An Overview of Financial Management
Financial Statements, Cash Flow, and Taxes
Analysis of Financial Statements
The Financial Environment: Markets, Institutions, and Interest
Rates
Fundamental Concepts in Financial Management
Risk and Rates of Return
Time Value of Money
Financial Assets
Bonds and Their Valuation
20
Brigham, E.F. and Houston, J.F., (2004), Fundamentals
of Financial Management, Tenth Ed., South - Western,
Thomson.
Moffett M.H., Stonehill A.I. and Eitemen D.K., 2006, Essentials
of Global Finance, Second Ed., Pearson Addison Wesley.
Besley S. and Brigham E.F., 2005, Essentials of Managerial
Finance, 13 Ed., South Western, Thomson.
Securities Industry Development Centre, 2002, The Malaysian
Capital Market: Examination Study Guide, Module 12,
Investment Management and Corporate Finance, Securities
Commission, Malaysia.
8.
Ross, S.A., Westerfield, R, and Jordan, (2005), B.D.,
Essentials of Corporate Finance, Fifth Ed., McGraw-Hill.
Arnold, G., 2005, Corporate Financial Management, Third Ed.,
Prentice Hall, Pearson Education.
Business Times, Malaysia
Wall Street Journal
Financial Times
Economists
Articles from Journals
The International Journal of Finance & Banking,
Malaysia
Bankers Journal Malaysia
Financial Management
Journal of Finance
Journal of Financial Economics
Journal of Financial and Quantitative Analysis
Journal of Financial Research
Journal of Business
Review of Financial Studies
Websites
www.btimes.com.my
www.ssrn.com
www.nber.org
www.yahoonance.com
Examination Syllabus
Professional Diploma In Corporate Administration (PDCA): Part 2
BUSINESS STRATEGIES
iii.
SYLLABUS
iv.
Critical Success Factors (CSF) and Key Performance Indices
(KPIs)
Six Sigma
DESCRIPTION
Overview and objective
This module is drawn up to prepare and provide prospective
Chartered Secretaries with the necessary skills and tools to apply
business strategies in practice.
This module will provide a foundation to students for the
International Qualifying Scheme (IQS). The aim of the module is to
help Chartered Secretaries to develop knowledge and understanding
of key principles and practices in business strategies, as well as to
enable them to participate more meaningfully in the strategic and
operational stages in a business.
Students will be exposed to key concepts, principles and
theories in business strategies and will be assessed on their ability
to use these concepts, principles, theories and theoretical knowledge
in practical situations.
The students approach and assessment of resolving conicts
between theory and practice will also be part of the overall module
evaluation.
Pre-requisite learning
The module specication is based on the assumption that students
have relevant prior knowledge of the fundamentals of management
and business environment. This level must have been demonstrated
through the Institutes examinations of the MAICSA Professional
Diploma in Corporate Administration, or those of equivalent
qualications, approved as compliant to the Institutes required
curriculum and standards.
Approaches to formulating business strategies
i.
Benets and aws of business strategy
ii.
Strategy and small businesses
iii.
Setting strategic objectives
iv.
Contemporary thinking on strategy including promotions and
marketing
Change management
i.
Current developments in business environment
ii.
The need for change
iii.
Managing change
People issues and culture in organisations
i.
Principles of organizing and managing projects
ii.
Human factor in projects qualities, motivation, ethics
iii.
Conicts and disciplines
iv.
Leadership, group work and team building
Effective controls in organizations
i.
Control levels
ii.
Performance evaluation
iii.
Monitoring system
iv.
Time management
RECOMMENDED READING
1.
LEARNING OUTCOME
2.
Upon completion of this module, and as a whole, students should
be able to apply the essential knowledge, skills and understanding
of business strategies in practice.
Students should be able to:
1.
explain and apply the process of strategy formulation
2.
discuss and use concepts in contemporary thinking on
strategy
3.
understand and relate change management to practice
4.
apply theories on people issues in managing projects
5.
understand the purpose of effective controls in organisations
and to apply them to business scenarios
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
LEARNING CONTENTS
Johnson, G., Scholes, K. & Whittington, R., Exploring
Corporate Strategy, 7th edition, Financial Times Prentice Hall,
2005
Applegate, A., Lynda M., Robert P., McFarlan, F.W.,
Corporate Information Strategy and Management 7th edition
Text and Cases, Thomson, 2006
Handy, C., Understanding Organisations Penguin, 4th edition,
1993
Huczynski, A. and Buchanan, D., Organisational Behaviour:
An Introductory Text. 5th edition. Financial Times Prentice Hall,
2003.
Ireland, Hokinson and Hitt, Understanding Concepts of
Business Strategy, International Student edition, Thomson
South Weston U.S.A, 2006
Mullins, L., Management and Organisational Behaviour, 7th
edition, Financial Times Prentice Hall, 2004
Naylor, J., Management. 2nd edition, 7th edition, Financial
Times Prentice Hall, 2004
The nature of strategic management
i.
Mission and objectives
ii.
SWOT analysis
21
CHARTERED SECRETARIES MALAYSIA
Professional Diploma In Corporate Administration (PDCA): Part 2
BUSINESS STRATEGIES
FURTHER READING
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
12.
13.
14.
15.
16.
17.
18.
19.
20.
21.
22.
23.
22
Belbin R.M., Beyond the Team. London, ButterworthHeineman, 2000
Bennis, W., On Becoming a Leader. London: Hutchinson
Business Books, 1989
Brue, G., Six Sigma for Small Business, Entrepreneur Press
U.S.A. 2006
Carreira, B. and Trudell, B., Lean Six Sigma, McGrawhill,
U.S.A. 2006
Collision, C. and Parcell, G., Learning to Fly. Oxford, Capstone
Publishing, 2004
Garratt, B., The Fish Rots from the Head-The Crisis in our
Boardrooms. 2nd edition, London, Harper Collins Business,
2003
Goleman, D., Emotional Intelligence. 10th edition, New Year,
Bantam Books, 2005
Handy, C., Inside Organisations. London, Penguin Books
1999
Holbeche, Linda., Understanding Change Theory,
Implementation and Success. U.S.A, Elsenia ButterworthHeinemann 2006
Hooley, G.S., Cox, A.S. and Adams, A. (1992), Our ve
years mission: To foldly go where no man has gone before
Journal of Marketing Management. Volume 8, pp. 35-48. Cited
in Corporate Performance Evaluation in Multinationals (1993).
London: CIMA.
Johnson, G. and Scholes, K., Explaining Corporate Strategy,
4th edition, Hemel Hampstead, Prentice Hall, 1997
Koch, R., The Financial Times Guide to Strategy, FT Prentice
Hall, U.K., 3rd edition
Martin, G., Managing People and Organisations in Changing
Contexts, Butterworth-Heinemann, 2006
Mintzberg, H., The Rise and Fall of Strategic Planning. London,
Prentice Hall 2000
Moore, J.I., Writers on Strategy and Strategic Management,
2nd edition, Penguin Books Ltd, 2001
Myers, K.N., Business Continuity Strategies, 3rd edition Wiley,
2006
Obeng, E., All Change-The Project Leaders Handbook,
London, Financial Times/Prentice Hall, 1995
Pascale, R., Managing on the Edge. Penguin Books Ltd,
1991
Peters, T.J. and Waterman, R.H., In Search of Excellence.
Harper and Row, 1982
Porter, M.E., Competitive Strategy: Techniques for Analysis
Industries and Competitions, New York, Free Press, 1980
Porter, M.E., Competitive Advantage: Creating and Sustaining
Superior Performance. New York, Free Press, 1985
Senge, P.M., The Fifth Discipline. London, Currency 1st edition,
1994
Stacey, R.D., Strategic Management and Organisation
Dynamics. 4th edition, London, Financial Times/Pearson
Education, 2003
24.
25.
26.
27.
Temporal, P., Strategic Positioning, Oxford University, U.K.,
2006
Trompenaars, F. & Hampden-Turner, C., Riding the Waves
of Culture. 2nd edition, McGraw-Hill, 1997
Warren, K., Competitive Strategy Dynamics, Wiley, 2003
Williams, H., The Essence of Managing Groups and Teams.
London, Pearson Educational (Academic), 1996.
Examination Syllabus
Professional Diploma In Corporate Administration (PDCA): Part 2
CORPORATE COMPLIANCE AND PRACTICE
SYLLABUS
Prospectus
Brief denition of prospectus and its contents, the civil liability for
misstatement and the penalties and remedies for misstatements.
DESCRIPTION
The persons who aspire to be a Chartered Secretary should be
acquainted at the beginning with the general regulatory framework
in the administration of a corporation so that the person is able to
understand the implementation of the said regulatory framework into
the day to day running of a corporation at a later stage.
Arrangements and Reconstructions
Procedures for application to court for arrangements and
reconstructions.
Receivers and managers
Qualication and liabilities of receivers and the priority of payment
by the receiver.
LEARNING OUTCOME
On completion of this module, the student should be able to:
Understand the general principles of corporate law
Identify what must be done and/or what must not be done
to comply with the legal requirements set out by the various
regulatory bodies
Relate better in the subsequent courses that he or she
undertake in the Professional Level.
LEARNING CONTENTS
Types of companies
Denition and characteristics of companies limited by shares, limited
by guarantee, unlimited companies exempt private companies and
foreign companies and the differences between the private and
public companies.
Process of incorporation
Reservation of the name of the company, ling in the relevant
documents (annual return, forms 24, 44 and 49), stamp duties and
fees payable for the incorporation, returns to be made, rst directors
meeting and commencement of business.
Winding up
Types, the procedures in brief and the consequences of winding
up.
Regulatory bodies
The roles and functions of the Foreign Investment Committee, the
Securities Commission, the Companies Commission of Malaysia, the
Kuala Lumpur Stock Exchange, the Malaysian Exchange of Securities
Dealing & Automated Quotation Berhad, the Employees Provident
Fund, the Social Security Organisation, the Inland Revenue Board
and Pengurusan Danaharta Nasional Berhad.
Corporate Governance
Definition of corporate governance, the brief overview on The
Malaysian Code on Corporate Governance, its aims and the
compliance of the Code
RECOMMENDED READING
1.
2.
Memorandum and Articles of Association
Contents of the memorandum and articles of association, alteration of
the memorandum of association, alteration to the companys name,
company number and registered ofce, alteration to the objects
clause, alteration to the capital clause.
3.
FURTHER READING
Directors & Ofcers
The qualication and disqualication of directors, company secretary
and auditors, the common law and statutory duties of the director,
secretary and auditor, brief overview of the directors and secretarys
code of conduct.
1.
Shares
Types of shares and procedure for its transfer, the procedure for
alteration of share capital and the procedures for share buy back.
4.
Charges
Types of registrable charges, the procedure for registration of charges
and the consequences of not registering the charges.
Kang Shew Meng (2002), Handbook on Company Secretarial
Practice in Malaysia 3rd Edition. Kuala Lumpur : Lexis Nexis
Business Solutions.
Woon W.C., M. Company Law FT Law & Tax Asia Pacic 1997
(2nd Edition).
Rachagan, Pascoe, Joshi on Principles of Company in
Malaysia MLJ.
2.
3.
5.
6.
Company Secretarial Practice Manual, Kuala Lumpur:
MAICSA.
CCH Asia Guide to Company Law in Malaysia and Singapore
CCH Asia Ltd 1995 (3rd Edition).
Business & Company Law A Study Text for MICPA Students
The Malaysian Institute of Certied Public Accountants 2003.
MAICSA Best Practice Guide Series. Code of Ethics for
Directors and Code of Ethics for Company Secretaries:
ROC.
Malaysian Code on Corporate Governance.
Malaysian Companies Act 1965.
23
CHARTERED SECRETARIES MALAYSIA
Professional Diploma In Corporate Administration (PDCA): Part 2
LAW AND PRACTICE OF MEETINGS
SYLLABUS
DESCRIPTION
Law and practice of meetings is an important subject matter for
Chartered Secretaries to understand and master. Meetings are
important in the administration of companies, rms, organisations,
societies, municipalities, town councils and the parliamentary system
of governments. In this respect, the student is required to under basic
elements that constitute meetings in general, the way meeting are
convened and held, the mechanisms employed for voting to obtain a
decision, types of representations in meetings, the roles and powers
of chairmen and the importance of keeping minutes.
This subject will be broad in nature and requires the student to know
different laws and practices of meeting relating to:
Public Meetings;
Local Authorities like Municipalities and Town Councils;
Registered Societies and Associations;
Company Meetings involving the board of directors;
shareholders or members general meeting, class meeting and
statutory meeting.
LEARNING OUTCOME
On completion of this module, the student should be able to:
develop an understanding of the law and practices involved
in all types of meetings, so that whether they should be in
public practice as Chartered Secretaries or employed by
organisations, rms and companies they are able to contribute
towards convening and holding meetings.
LEARNING CONTENTS
Public gathering and meetings in the street
The streets and public places for gatherings and holding of meetings.
The rights of public holding meetings in the street. Obstruction of
streets, public nuisance under common law. Police permit and local
authorities requirements for holding public meetings under the Police
Act 1967. Unlawful assembly, demonstrations and marches and riot
in relation to Public Order (Preservation) Act 1958.
General principles of meetings
Meaning of notice, kinds of notice. Essential of a valid notice.
Authority for calling for a meeting. Length of time or period of time
to be given. Agenda items. Quorum and effect where a quorum is
not present. Common law requirement of quorum. Case of Sharpe v.
Dawes. The chairman of meeting and his appointment. Minutes and
its legal implications. Societies and associations meetings.
Company Meetings
Different types of meeting of a company. Statutory meeting,
class meeting and debenture holder meetings. Types of general
meeting, namely annual general meeting and extraordinary general
24
meeting. Chairmans role, and company secretarys role in company
meetings.
The provisions of Companies Act 1965 in relation to general
meetings, particularly sections 143,144, and 145 requirements.
Quorum, voting mechanism, and procedures of convening company
meetings. Proxy and corporate representative. Procedures for
demand of poll. Other forms of passing directors and members
resolutions deemed to be meetings, i.e. circular resolution by
directors and section 152A members resolution. Electronic and
teleconferencing type of meeting. Types of resolutions, ordinary
and special resolution. Special Notice and its meaning under the
Companies Act 1965. Meetings connected with court ordered
meetings in reconstruction, rearrangement and compromises.
Members winding-up.
RECOMMENDED READING
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
Hands on Guide - Company Secretarial Essentials, CCH Asia
Pte. Ltd.
Ian Shearman, Shackleton on The Law and Practice of
Meetings, Sweet and Maxwell, 8th edition
Rachagan P. & Joshi, Principles of Company Law in Malaysia,
MLJ
L.H. Hall, Meetings: Law and Procedure, M & E
Taggart W.J. Horsleys, Meetings Procedures, Law and
Practice, Butterworths, 2nd edition
FURTHER READING
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
Priscillia Yap P.Y., Company Meetings: Law & Practice in
Malaysia, 2nd edition, CCH, 2005
Directors & Shareholders Guide on AGM by Kang Shew Meng,
Malayan Law Journal 2002
Local Government Act 1976
Societies Act 1966
Strata Title Act 1985
Table A of the Companies Act 1965;
Police Act 1967
Public Order (Preservation) Act 1958
Examination Syllabus
contents
INDEX TO SYLLABI
ICSA INTERNATIONAL QUALIFYING SCHEME
Professional Part 1
Strategic and Operations Management
Corporate Law
Financial Accounting
Taxation
26
28
30
32
Professional Part 2
Corporate Governance
Corporate Secretaryship
Corporate Financial Management
Corporate Administration
35
38
40
42
Please visit our website www.maicsa.org.my
for more updates
25
CHARTERED SECRETARIES MALAYSIA
ICSA International Qualifying Scheme (IQS): Professional Part 1
STRATEGIC AND OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT
SYLLABUS
AIM
The aim of the module is to develop knowledge and understanding
of key principles and practices in management, to equip the aspiring
Chartered Secretary for both the strategic and operational contexts
of the professional role.
LEARNING OUTCOME
At the conclusion of this module, the candidate will be able to:
Understand and apply strategy theory, models and language
to contribute to boardroom decision making
Understand and apply operations theory and best practice in
contributing to corporate management.
Understand and apply leadership theory and best practice in
the functional role and leadership of teams.
PRE-REQUISITE LEARNING
Corporate Management
The management of change: growth, stability and contraction.
Business process re-engineering. Organisational culture: types
and characteristics. The management and mobilisation of culture.
Organisational development. The management of quality: total quality
management and audit approaches. Benchmarking.
Cycle time reduction. Just in Time and Manufacturing Recourse
Planning techniques. Knowledge and information management:
dissemination and feedback. The Internet and Intranets. Networking,
cascading and team brieng. Formal management communications:
reports, minutes, directives, standing orders, working manuals,
communications technology.
Team Leadership
The concepts of morale, motivation, leadership, authority and
responsibility: theoretical models an their application. Emotional
intelligence, empowerment, self-directed and cross-functional
teams. Project management and team leadership. Techniques in
team building. Enhancing the performance of teams and individuals.
Performance appraisal and measurement: organisation, team and
individual.
This module is designed to enable aspiring Chartered Secretaries to
(a) demonstrate required standards of competence for professional
practice in a key discipline, and (b) acquire essential knowledge
and skills to underpin the relevant components of the Professional
Programme. Evidence of assessed knowledge and understanding
must be demonstrated through the Institutes examinations, or those
of equivalent qualications which have been approved as meeting
the Institutes required curriculum and standards. The module
specication is based on the assumption of some relevant prior
learning in management.
RECOMMENDED READING
LEARNING CONTENTS
5.
Strategic Management
The nature of strategy. Strategic choice, analysis and evaluation:
the balanced scorecard and the strategic balance sheet. Strategic
alliances. Analytical techniques: portfoilio analysis, competitor
analysis, value chain analysis, market migration analysis.
The Boardroom strategic role. Mission, ethics and values.
Social responsibility. The corporate environment and systems theory.
Environmental factors: the impact of law, regulation, the market, and
other PEST factors. Internal factors.
The distinction between strategy and policy. Planning:
short, medium and long term. Targets. Resources. Planning
techniques, including scenario planning. Strategy: effective corporate
performance; strategic options for direction, change and growth.
Policymaking and implementation. Supply chain management and
logistics. The virtual organisation.
Creative and rational models in strategic management:
applications and limitations. The rational cycle: corporate needs,
decision making, implementation, monitoring and review, feedback.
Measurement of corporate performance; concepts of output and
outcome. Contingency management and agile strategies.
6.
26
1.
2.
3.
4.
Handy, C., Understanding Organisations. Penguin, 4th edition,
1993
Huczynski, A.and Buchanan, D., Organizational Behaviour:
An Introductory Text. 5th edition, Financial Times Prentice Hall,
2003
Johnson, Scholes & Whittington, Exploring Corporate
Strategy. 7th edition, Financial Times Prentice Hall, 2005
Mullins, L., Management and Organisational Behaviour. 7th
edition, Financial Times Prentice Hall, 2004
Naylor, J., Management. 2nd edition, Financial Times Prentice
Hall, 2004
Slack, N., Stuart, C. & Johnston, R., Operations Management.
4th edition, London, Financial Times/Prentice Hall, 2003
FURTHER READINGS
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
Belbin, R.M., Beyond the Team. London, ButterworthHeineman, 2000
Bennis, W., On Becoming a Leader. London: Hutchinson
Business Books, 1989
Collison, C. and Parcell, G., Learning to Fly. Oxford, Capstone
Publishing, 2004.
Garratt, B., The Fish Rots from the Head The Crisis in our
Boardrooms. 2nd edition, London, Harper Collins Business,
2003
Goleman, D,. Emotional Intelligence. 10th edition, New York,
Bantam Books, 2005
Handy, C., Inside Organisations. London, Penguin Books
1999
Mintzberg, H., The Rise and Fall of Strategic Planning. London,
Prentice Hall 2000
Examination Syllabus
ICSA International Qualifying Scheme (IQS): Professional Part 1
STRATEGIC AND OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT
8.
9.
10.
11.
12.
13.
14.
15.
16.
Pascale, R., Managing on the Edge. Penguin Books Ltd,
1991
Moore, J.I., Writers on Strategy and Strategic Management,
2nd edition, Penguin Books Ltd, 2001
Obeng, E., All Change-The Project Leaders Handbook,
London, Financial Times/Prentice Hall, 1995
Peters, T.J. and Waterman, R.H., In Search of Excellence.
Harper and Row, 1982
Porter, M.E., Competitive Strategy. New York, Free Press,
1980
Senge, P.M., The Fifth Discipline. London, Currency 1st edition,
1994
Stacey, R.D., Strategic Management and Organisational
Dynamics. 4th edition, London, Financial Times/Pearson
Education, 2003
Trompenaars, F. & Hampden-Turner, C., Riding the Waves
of Culture. 2nd edition, McGraw-Hill, 1997
Williams, H., The Essence of Managing Groups and Teams.
London, Pearson Education (Academic), 1996.
27
CHARTERED SECRETARIES MALAYSIA
ICSA International Qualifying Scheme (IQS): Professional Part 1
CORPORATE LAW
SYLLABUS
AIM
To provide an understanding of the principles of Corporate Law and a
thorough knowledge of the regulation of companies by law, including
statutes and case laws.
LEARNING OUTCOME
Students who have successfully completed the modules on this
subject will be able to understand the core principles of corporate
law and these include:
The nature and functions of companies;
The concept of a company as a corporate entity;
The relationship between the two major organs in the company,
namely the general meeting and the board of directors;
The relationship between the members inter se and the
protection of minorities;
The law and procedure relating to meetings and the rights of
shareholders during meetings;
The concept of corporate liability,
The concept and meaning of corporate governance, in particular,
the duties of directors and the limits on their powers;
The law relating to corporate nance and corporate control
transactions; and
The effect and consequences when companies undergo the
reconstruction, receivership or winding-up process.
capital. Issue of shares at a premium and at a discount. Acquisition
and redemption by a company of its own shares. Methods of otation,
prospectus, Kuala Lumpur Stock Exchange listing requirements.
Dividends.
Shares.
Nature and types of shares. Variation of class rights. Membership and
the register of members. Disclosure of substantial and nominee share
holdings. Share Certicates - transfer and transmission of shares.
Restrictions on transfer. Mortgage of shares. Calls, liens, surrender
and forfeiture of shares. Share warrants. Effects of shares deposited
with the Central Depository.
Loan Capital.
Borrowing powers of a company. Debentures and debenture
stock. Charges securing debentures - xed and oating charges.
Registration of charges. Remedies of debenture-holders.
Corporate Governance.
Directors - Qualication; appointment and remuneration; disclosure;
service contracts; removal; retirement and disqualication; powers
and duciary duties; loans by company to directors and contracts in
which directors are interested. Role and duties of directors in relation
to good corporate governance.
Company Secretary.
Qualification, appointment, vacation of office, duties and
responsibilities.
LEARNING CONTENTS
Auditors.
Appointment and removal; powers and duties.
Nature of registered companies.
The process and effect of registration - the principles of corporate
personality and of limited liability. The distinction between companies
and partnerships.
Meetings and shareholders rights.
Types of meetings; convening of and proceedings at meetings;
resolutions; majority control rule; protection of minority
shareholders.
Classication of companies.
Classication by limitation of liability, by method of formation, by size
-public and private companies. Holding and subsidiary companies.
Insider Dealing.
Types; elements of insider trading; remedies and statutory relief.
Constitution of a company.
The memorandum of association; doctrine of ultra vires. The articles
of association, effects of alterations. Promoters.
Flotation.
Methods of otation. Prospectus - form and content. Misrepresentation
and omissions. Allotment of shares and commencement of business.
Underwriting and commission.
Corporate transactions.
Capacity of companies and the concept of agencies as applied to
companies. Pre-incorporation contracts. The Corporate seal.
Share Capital.
Raising, maintenance and reduction of share capital. The principle of
28
Reconstruction, Disputes and Liquidation.
Reconstruction and takeovers; reconstruction Compulsory acquisition
of shares on takeover and schemes of arrangements.
Compulsory and voluntary liquidation.
Including grounds for winding up, order of application of assets of
insolvent companies, preference and avoidance of transactions,
fraudulent trading and wrongful trading, outline of powers and duties
of liquidator and consequences of winding-up.
NOTE
A detailed knowledge of the Malaysian Companies Act 1965, and
subsequent amendments, the Malaysian Code on Takeover and
Mergers, the Kuala Lumpur Stock Exchange Listing Requirements
and the Securities Commission Act 1992 is expected of students.
Examination Syllabus
ICSA International Qualifying Scheme (IQS): Professional Part 1
CORPORATE LAW
RECOMMENDED READING
1.
2.
3.
4.
Chartered Secretaries Malaysia: Study Manual Corporate
Law
Rachagan, Pascoe & Joshi, Concise Principles of Company
Law (Malayan Law Journal)
Cheah Foo Seong, Guide to Company Law & Secretarial
Practice, Malaysia (CCH Asia)
Ben Chan Chong Choon, Philip Koh Tong Ngee & Peter
SW Ling, Chan & Koh on Malaysian Company Law: Principles
and Practice 2nd Edition (Thomson/Sweet & Maxwell Asia)
FURTHER READING
1.
2.
Company Law in England
(i) Farrar, Hannigan & Wylie, Farrars Company Law
(Butterworths)
(ii) Gower, Prentice & Pettet, Gowers Principles of Modern
Company Law (Sweet & Maxwell)
(iii) Sealy, Cases and Materials in Company Law
(Butterworths)
STATUTES:
1.
2.
The primary statute governing Company Law in Malaysia is
teh Companies Act 1965.
Other relevant statutes are the Securities Industry Act 1983
and teh Securities Commission Act 1993.
Company Law in Malaysia
(i)
Loh Siew Cheang, Corporate Powers: Accountability
(Butterworths)
(ii) Krishnan Arjunan, Company Law in Malaysia: Cases
and Commentary (Malayan Law Journal)
(iii) Woon W.C.M, Company Law (FT Law & Tax Asia
Pacic)
29
CHARTERED SECRETARIES MALAYSIA
ICSA International Qualifying Scheme (IQS): Professional Part 1
FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING
LEARNING CONTENT
SYLLABUS
AIM
In professional practice, the Chartered Secretary has to be competent
in Financial Accounting to a high standard, and in a number of
different contexts.
Expertise is demanded in the boardroom setting to contribute to
the analysis and interpretation of corporate nancial performance and
results. Corporate reporting in compliance with legal and stakeholder
requirements, including nancial statements, is a core responsibility
of the Chartered Secretary.
In public practice, and in many organisations, the Chartered
Secretary is also sometimes called upon to full the role of Corporate
Accountant. The aim of the module is to develop the knowledge
and skills necessary for the Chartered Secretary to carry out these
professional responsibilities.
LEARNING OUTCOME
At the conclusion of this module, the candidate will be able to:
Understand the language, concepts and use of financial
accounts and reports.
Identify and utilise the sources of accounting data and
information.
Understand and apply standards of accounting practice.
Prepare nancial statements for different forms of organisation
in compliance with legal and regulatory requirements.
Apply financial information and statements in corporate
reporting.
Undertake the corporate accounting role for employers and
clients.
Contribute to boardroom analysis of corporate financial
performance.
PRE-REQUISITE LEARNING
This module is a component of the ICSA Bridging Programme. It is
designed to enable aspiring Chartered Secretaries to (a) demonstrate
required standards of competence for professional practice in a key
discipline, and (b) acquire essential knowledge and skills to underpin
the relevant components of the Professional Programme.
Evidence of assessed knowledge and understanding must
be demonstrated through the Institutes examinations, or those of
equivalent qualications which have been approved as meeting the
Institutes required curriculum and standards.
The module specication is based on the assumption of some
relevant prior certicated knowledge, and candidates will nd it helpful
to have familiarised themselves particularly with:
30
An introduction to the principles of book-keeping and
accountancy.
Methods of Financial Measurement
Financial goals; prot and surplus. The recognition of prot: matching
revenue with expenditure; and increase in the value of the business.
Prot measurement and asset valuation on the basis of historical
cost, replacement (current) cost, fair value and current purchasing
power, asset impairment and recoverable amount.
Accounting Regulations
Market imperfections and the need for regulations. Substance versus
form. Sources of regulation. Requirements of the Companies Acts and
other regulatory sources. Form and content of published accounts.
Calculation of distributable prots. Maintenance of permanent capital.
Capital reduction and reorganisation.
Accounting Reports
The preparation and presentation of cash ow statements; fund
accounting; value added statements; segmental reports; prot and
loss accounts; income and expenditure accounts; balance sheets.
Operating and nancial review. Related party disclosures. The
limitations of published accounts.
Valuation of Assets and Liabilities
Accounting concepts, bases and policies. Treatments of: stocks
and long term contracts; xed assets and depreciation; research
and development; foreign currency translations; leases and hire
purchase contracts; goodwill and intangibles; provisions; contingent
liabilities and contingent assets; capital instruments, pensions costs
and taxation.
Consolidated Accounts
Denitions of holding, subsidiary and associated companies and joint
ventures. The nature, purpose and preparation of group accounts.
Merger, acquisition and equity methods of accounting.
Interpretation of Accounts
The examination and analysis of nancial information in relation
to protability, liquidity, gearing, asset utilisation and cash ows.
Uses and limitations of ratio analysis. The preparation for reports
in appropriate style for management, investors, creditors and other
user groups.
RECOMMENDED READING
1.
2.
3.
4.
Approved accounting standards and other pronouncements,
exposure drafts and discussions documents issued by MASB
(available at www.masb.org.my)
Barry Elliott and James Elliott, (2005), Financial Accounting
& Reporting, 9th edition, Pearson Prentice Hall, England
Ng Eng Juan, (2004), A Practical Guide to MASB Standards
(Malaysia) CCH Asia Pte Ltd.
Jane Lazar & Tan Lay Leng, (2003), Company Accounts &
Reporting, 5th edition, Pearson Prentice Hall, Malaysia
Examination Syllabus
ICSA International Qualifying Scheme (IQS): Professional Part 1
FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING
ADDITIONAL REFERENCES
FURTHER READING
1.
1.
2.
3.
4.
Barry J. Epstein, Abbas Ali, Mirza, Peter Walton (2005),
Wiley 2005: Interpretation and Application of International
Accounting and Financial Reporting Standards (REV), Wiley
Tan Liong Tong (2000), Financial Accounting and Reporting in
Malaysia, Volume 1, 2nd edition, Kuala Lumpur, Professional
Advancement Centre Sdn Bhd
Tan Liong Tong (2001), Financial Accounting and Reporting in
Malaysia, Volume 2, 2nd edition, Kuala Lumpur, Professional
Advancement Centre Sdn Bhd
Periodicals of Professional Accounting Bodies
OTHER RECOMMENDED READING
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
MASB Standards
6.
Accounting Standards Board
Financial Reporting Standards and Board Financial Reporting
Exposure Drafts as issued and published in Accountancy
Davies , Paterson R and Wilson A
Generally Accepted Accounting Practice in the United
Kingdom (Longman, 6th edition)
Elliot B and Elliot J
Financial Accounting and Reporting, (Prentice Hall Europe, 3rd
edition, 1998)
Patterson R, Watson A
UK GAAP, Tolley Publishing, 6th edition, 1999 (Sept)
Pizzey AB
Accounting and Finance - A Firm Foundation, (Cassell, 4th
edition, 1994)
Choping D, Skerratt L
Applying GAAP 1999/2000, (Accountancy Books, 1999)
31
CHARTERED SECRETARIES MALAYSIA
ICSA International Qualifying Scheme (IQS): Professional Part 1
TAXATION
SYLLABUS
AIM
To impart a thorough knowledge of the current law relating to taxation
and its practical application to companies, partnerships, trust, estate
settlement, body of persons and individuals.
LEARNING OUTCOME
After completing the Malaysian taxation module, the candidates
should be able to:
determine the resident status of individuals, be able to ascertain
their eligibility for personal reliefs and rebates and compute
their income tax liability;
understand the specic tax provisions related to businesses
enacted in the Income Tax Act 1967, Real Property Gains Act
1976, Promotion of Investment Act, 1986 as well as Stamp Act
1949;
compute the tax liability of companies and determine the section
108 balances;
explain the tax incentives that are available to specialized
industries and compute their tax liability; and understand
the tax and non-tax incentives that are available to Labuan
International Offshore Financial Centre.
LEARNING CONTENTS
SECTION A: INCOME TAX - INCOME TAX ACT 1967
Tax Administration In Malaysia
Taxation as a source of Government revenue
Understanding of the tax system in Malaysia
Scope Of Taxation
Scope of charge
Chargeable persons
Resident status
Basis period and change of accounting date
Capital and revenue receipts/expenses
Badges of trade
Classes of income
Exempt Income
Taxation Of Individual
Residence Status
Ascertainment of gross income, adjusted income, statutory
income, aggregate income, total income and chargeable
income.
Personal reliefs and rebates
Separate taxation and combined assessment
32
Taxation Of Business/partnership
Denition
Commencement and cessation of business
Computation of divisible income/loss and capital allowance
Deductibility of expenses
Taxation Of Company Under Self-assessment
Computation of chargeable income/repayment
Treatment of losses
Allowances pertaining to Schedules 2-4 and controlled sales
provisions
Franking of dividend, imputation system and section 108
account
Taxation Of Other Sources Of Income
Dividend
Interest
Discount
Rent
Royalties
Premium
Pension
Annuities
Other gains or prots
Special classes of income
Tax Compliance, Appeals, Collections & Penalties
Submission of returns
Assessment and appeals
Collections, recovery and refund of tax
Offences and penalties
Public rulings
Taxation Of Non-resident And Double Tax Relief
Principles of avoidance of double taxation
Double Taxation Agreements
Unilateral tax relief
Non-resident relief
Withholding tax provisions
Tax Planning, Anti-avoidance And Investigation
Tax planning for individuals and companies
Anti-avoidance provisions
Events that trigger investigation
Capital statement and ascertainment of income understated
and/or omitted
Tax audit
SECTION B: CAPITAL GAINS TAX - REAL PROPERTY GAINS
TAX ACT 1976
Real Property Gains Tax
Principles and scope of charge
Chargeable assets and persons
Examination Syllabus
ICSA International Qualifying Scheme (IQS): Professional Part 1
TAXATION
No gain no loss transactions and exemptions
Computation of chargeable gains and treatment of losses
Tax rates
Returns and assessment
Payment and recovery of tax
Real property companies
Transfer of assets within group of companies
ii)
Service Tax Act, 1975
Scope of charge
Taxable persons
Taxable services
Rate of Tax, invoicing and records
Licensing requirement
Exemptions
Returns and assessment
Collection and penalties
Disputes and Appeals
iii)
Stamp Act, 1949
Scope of charge
General principles
Specic instruments
Exemptions: Sections 15 and 15A
Duty payable
Adjudication of instruments
SECTION C: TAX INCENTIVES - PROMOTION OF INVESTMENTS
ACT 1986 - INCOME TAX ACT 1967
Tax Incentives
Promotion of Investments Act, 1986 (PIA)
Pioneer status
Investment tax allowance
Industrial adjustment allowance
Double deduction
Income Tax Act, 1967 (1TA)
Reinvestment allowance
Approved service projects
Operational headquarters
Foreign fund management companies
Double deduction
Any other legislation which may be enacted pursuant to PIA and
ITA.
SECTION D: LABUAN TAX HAVEN
- LABUAN OFFSHORE BUSINESS ACTIVITY TAX ACT 1990
Labuan As An Offshore Financial Centre
Principles and scope
Administration
Abatement of Tax
Computation of tax
Tax concessions
SECTION E: INDIRECT TAXES
- SALES TAX ACT 1972
- SERVICE TAX ACT 1975
- STAMP ACT 1949
Indirect Taxation And Stamp Duty
i)
Sales Tax Act, 1972
Scope of charge
Taxable persons
Rate of tax
Exemptions, drawbacks and refunds
Returns
Collections and penalties
WTO method of valuation
Appeals
SECTION F: SPEClALISED INDUSTRIES - INCOME TAX ACT
1967
Speclalised Industries
Sea and air transport undertakings
Banking
Insurance
Trade associations
Co-operatives societies/clubs
Leasing
Housing/developers and contractors
Trust, estate and settlement
Unit trusts
Venture capital companies
Investment holding companies
RECOMMENDED READING
1.
2.
3.
4.
Dr. Jeyapalan Kasipillai
A Comprehensive Guide to Malaysian Taxation 2nd Edition,
2006, McGraw-Hill, Kuala Lumpur
Dr. Veerinderjeet Singh
Malaysian Taxation - Administrative & Technical Aspects
Pearson Malaysia, 7th Edition, 2005
Dr. Arjunan Subramaniam
Malaysian Income Tax Manual Pelanduk Publications
Dr. Arjunan Subramaniam
Malaysian Taxation System 2003
CCH Publisher
Malaysian Master Tax Guide 22nd edition, 2005
33
CHARTERED SECRETARIES MALAYSIA
ICSA International Qualifying Scheme (IQS): Professional Part 1
TAXATION
FURTHER READING
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
Yeo Miow Cheng
Malaysian Taxation
PAAC Sdn Bhd, 15th Edition, 2002
Yeo Miow Cheng
Advanced Malaysian Taxation
PAAC Sdn Bhd, 12th Edition, 2002
Subramaniam A.
Malaysian Tax Handbook, Thompson, 2nd Edition, 2003
Y. K. Chin
Malaysian Taxation, Butterworths Asia, 5th Edition, 2003
Veerinderjeet Singh
Malaysian Taxation - Administrative & Technical Aspect,
Longman Malaysia, 6th Edition, 2003
NOTE:
Includes all amendments to the Finance Acts for the various years.
34
Examination Syllabus
ICSA International Qualifying Scheme (IQS): Professional Part 2
CORPORATE GOVERNANCE
LEARNING CONTENTS
SYLLABUS
AIM
Corporate Governance has emerged on the global agenda in pursuit
of proper and efcient practice in the administration of the business
entity. The objective is probity in business activity, compliance with
law and regulation, and the securing of reputation and condence
towards the attraction of inward investment. The Chartered Secretary
is the key corporate player and the global Profession has emerged
as a benchmark for the development of best practice.
The aim of the module is to instil the knowledge and key skills
necessary for the Chartered Secretary to act as chief adviser to
the Board on best practice in corporate governance, and as the
catalyst for systematic application in the major global forms of
organization.
LEARNING OUTCOME
At the conclusion of this module, the candidate will be able to:
Research and apply the growing global information sources on
corporate governance.
Promote awareness of, and be responsible for continuing
self and personnel development on corporate governance
themes.
Promulgate corporate governance principles and best practice
in the employing or client organisation.
Apply professional knowledge and skills to the resolution of
practical issues and problems in the proper governance of the
employing or client organisation.
Understand and apply the concepts of probity and ethical
standards in governance.
Understand and advise on the impact of corporate governance
principles on the role of Directors, the Secretary, and the audit
function.
Understand the corporate governance mechanisms and
regulatory framework in the Malaysian context
Apply professional knowledge and skills to the resolution of
practical issues and problems in the proper governance of the
employing or client organization within the context of Malaysian
corporate governance and regulatory framework
The Denitions and Objectives of Corporate Governance
The corporate entity; legality, separation of ownership and operation.
The concepts of ownership and accountability, ethics and performance.
The enlightened shareholder and stakeholder concepts. The state
as shareholder. Models of hierarchic and functional relationships in
sound governance. One-tier and two-tier Boards.
The external and internal pressures for sound governance.
History and ongoing developments in corporate governance.
The Reports: from Cadbury and King onwards; national and
international sources. The Combined Code. Corporate governance
guidelines: OECD; the Commonwealth Association. The governance
agenda in the developing and developed economies. International
networking.
The Regulatory and Ethical Framework
The role of legislation and regulation in corporate governance. The
nature and importance of compliance. Compliance statements.
The ethical dimension: codes and practices. The assessment of
corporate performance: yardsticks and measurement; corporate
review; disclosure. Key concepts: inclusion; openness; honesty;
transparency; probity; accountability; judgement; reputation; social
and environmental responsibility.
Sound Governance
The concept of best practice in governance: in companies,
statutory corporations and trusts. Understanding the distinct and
separate roles, duties and responsibilities of corporate ofcers and
stakeholders: chairman, chief executive ofcer, directors, secretary
and shareholders/members. Shareholders: majority control;
minority rights; the rights of members in guarantee companies. The
importance of the proper mix of appointments to the Board. Service
contracts. Induction, orientation and training. Responsibilities of the
Board. Committees and their role: Audit, Remuneration, Nomination.
Internal controls. Overall business risk management and review.
Internal structural relationships in the organisation.
The Secretary and Corporate Governance
The importance and special position of the secretary; the role in sound
and effective governance. Appointment and qualication. Control of
corporate information and corporate reporting: the annual report; the
website. Communication with stakeholders. The whistleblowing
concept: issues and problems, protection.
PRE-REQUISITE LEARNING
Evidence of assessed pre-requisite knowledge and understanding
in the following disciplines must be demonstrated through the
Institutes examinations, or those of equivalent qualications which
have been approved as meeting the Institutes required curriculum
and standards:
Corporate Law
Strategic and Operations Management
Financial Accounting
Management Accounting
Directors
Executive and non-executive directors. Chairman, managing director.
Shadow and alternate directors. The concept of independent
directors. Commonality of legal duty. Comparison of roles, needs,
powers and duties; appointment, reappointment and rotation,
remuneration, removal, retirement and disqualication. Directors
liabilities, indemnity and insurance. Borrowing powers. Conict and
disclosure of interest. Share dealing; model codes; insider dealing.
Company records. Directors disclosures, service contracts and
agreements.
35
CHARTERED SECRETARIES MALAYSIA
ICSA International Qualifying Scheme (IQS): Professional Part 2
CORPORATE GOVERNANCE
Audit
The contribution of internal and external audit to sound governance.
Audit reports and their use. Appointment, removal. Independence
and remuneration: rights, powers and duties in the governance
framework.
Directors and Boards
Corporate Governance in Malaysia
Corporate regulatory framework in Malaysia i.e. Registrar of
Companies (ROC), Kuala Lumpur Stock Exchange (KLSE),
Securities Commission (SC) etc. Comparative perspectives of
corporate regulatory framework between UK & Malaysia. Malaysian
Code of Corporate Governance. Roles, Responsibilities and Powers
of SC. Roles, Responsibilities and Powers of the KLSE. Revamped
listing requirements of KLSE
3.
1.
2.
4.
5.
6.
7.
FURTHER READING
8.
Malaysian Corporate Governance
1.
ICSA (2004), Corporate Governance, ICSA Professional
Development Series, ICSA Publishing Ltd.: London.
2.
KLSE, Revamped Listing Requirement (2001)
3.
MAICSA, Directors & Corporate Ofcers: Case Summaries
(CCH Asia Pte. Ltd. 2003)
4.
Ministry of Finance, Report on Corporate Governance
(Finance Committee on Corporate Governance, 1999)
5.
MICG, Malaysian Code of Corporate Governance (Malayan
Law Journal Sdn. Bhd., 2001),
6.
MICG, 3 Rs of Corporate Governance (MICG Publication,
2001)
7.
Ruin, J.E, Essentials of Corporate Management (MICG
Publication, 2001) General Bingham, K. Corporate Governance
Handbook (Gee Publishing) A looseleaf subscription service
dedicated to corporate governance issues.
8.
Chambers, A., Tolleys Corporate Governance Handbook
(Tolleys, 2002)
9.
Charkham, J., Keeping Good Company: A Study of Corporate
Governance in Five Countries (Oxford University Press,
1995)
10. Monks, A G & Minow, N. (eds), Corporate Governance
(Blackwells, 2001)
11. TIAA-CREF, Policy Statement on Corporate Governance
(1997)
12. Tricker, R.I., Corporate Governance (Gower, 1984)
13. Walmsley, K., Company Secretarial Practice, chapter 8A (ICSA
Publishing) Includes a wide range of useful appendices.
14. Corporate Social Responsibility - ABI Disclosure Guidelines
on Corporate Social responsibility (ABI, 2001). Available at
www.abi.org.uk.
15. Whistleblowing - ICSA, Establishing a Whistleblowing
Procedure (ICSA, 1999)
36
9.
10.
11.
12.
13.
ABI Guidelines on Long-Term Remuneration for Senior
Executives (ABI, 1996)
ABI, Statement of Principles on Share Incentive Schemes (ABI,
1999)
Bingham, K., The Professional Board (Gee Publishing,
2001)
Bruce, M., The ICSA Directors Guide (ICSA Publishing,
2003)
Bruce, M., Tolleys Rights and Duties of Directors (5th edition,
Tolleys, 2002)
Cadbury, A., Corporate Governance and Chairmanship: A
Personal View (Oxford University Press, 2002)
Dunne, Patrick, Running Board Meetings (Kogan Page,
1997)
ICSA, The Appointment and Induction of Directors (ICSA,
1998).
ICSA, Code on Good Boardroom Conduct. See www.icsa.org.
uk/news/guidance.php.
ICSA, Matters Reserved for the Board. See www.icsa.org.
uk/news/guidance.php.
ICSA, Terms of Reference Board Committees. See www.
icsa.org.uk/news/guidance.php.
Stiles, P. & Taylor, B., Boards at Work (Oxford University
Press, 2001)
UK Listing Authority, The Model Code (Appendix to The UK
Listing Rules) (FSA, updated annually).
Shareholder relations
1.
2.
3.
4.
Charkham, J. & Simpson, A., Fair Shares: The Future of
Shareholder Power and Responsibility (Oxford University
Press, 1999)
Hermes, Hermes Statement on Corporate Governance and
Voting Policy (Hermes, 1998). Available at www.hermes.
co.uk.
ICSA, Electronic Communications with Shareholders: A Guide
to Best Practice (ICSA, 2000). An update to this guide is
available at www.icsa.org.uk/news/guidance.php.
PIRC, Shareholder Voting Guidelines (PIRC, 1994)
Reports and Codes of Practice (Additional & Optional)
1.
2.
3.
Report of the Committee on the Financial Aspects of Corporate
Governance: The Code of Best Practice (Cadbury Code) (Gee
Publishing, 1992).
King Report on Corporate Governance (South African Institute
of Directors, 1994)
Directors Remuneration: Report of a Study Group chaired by Sir
Richard Greenbury (Greenbury Committee Report) (Gee
Publishing 1995)
Examination Syllabus
ICSA International Qualifying Scheme (IQS): Professional Part 2
CORPORATE GOVERNANCE
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
Committee on Corporate Governance: Final Report (Hampel
Committee report) (Gee Publishing, 1998).
The text of the Combined Code can also be downloaded from
www.fsa.gov.uk.
Internal Control: Guidance for Directors on the Combined Code
(the Turnbull report) (Croner CCH, 1999). The report is also
available in .pdf format via www.icaew.co.uk.
OECD Principles of Corporate Governance (OECD, 1999).
Available in .pdf format on www.oecd.org.
Principles for Corporate Governance in the Commonwealth:
To w a r d s G l o b a l C o m p e t i t i v e n e s s a n d E c o n o m i c
Accountability (Commonwealth Association for Corporate
Governance, 1999).
OECD Principles of Corporate Governance (OECD, 1999).
Available at www.oecd.org.
Myners, Paul, Institutional Investment in the UK: A Review
(HM Treasury, 2001)
King Report on Corporate Governance for South Africa 2002
(South African Institute of Directors, 2002)
37
CHARTERED SECRETARIES MALAYSIA
ICSA International Qualifying Scheme (IQS): Professional Part 2
CORPORATE SECRETARYSHIP
SYLLABUS
Types of directors. Roles, duties, responsibilities and liabilities.
Appointment, reappointment and rotation. Removal, retirement
and disqualication.
AIM
A core responsibility of the Chartered Secretary is as Secretary to the
Board. The aim of the module is to specify and assess the essential
knowledge and skills involved in taking overall responsibility for
the corporate secretarial function in small, medium and large scale
organisations. The practice of corporate secretaryship in this module
extends to both the strategic and functional contexts, in advising
the Board, in leading teams in secretarial best practice, in ensuring
compliance with law and regulation, and in establishing efcient
internal communication of Board decisions and external reporting.
LEARNING OUTCOME
At the conclusion of this module, the candidate will be able to:
Understand the scope, role and functions of corporate
secretaryship and apply them within the employing or client
organisation.
Understand the law and best practice in meetings, apply
them in the secretaryship function, and ensure corporate
compliance.
Ensure effective communication and dissemination of
information to and from the Board, both internally and externally,
for the optimum benet of the organisation and its needs.
Be aware of the ongoing responsibilities of the Secretary as an
independent professional practitioner within the organisation,
and be responsible for continuing personnel development within
the secretariat.
Be aware of, and be responsible for continuing self-development
in corporate secretaryship as a professional practitioner.
PRE-REQUISITE LEARNING
Corporate Compliance
Company formation, memorandum and articles of association. Filing
of company returns. Offences under the Companies Act. Company
governance overview, including the Code on Corporate Governance.
The annual report. Auditors: appointment and removal. Rights of the
auditor. Listing Requirements of the Kuala Lumpur Stock Exchange
(KLSE). Retention of records. Statutory registers.
Law and Practice of Meetings
Board meetings: composition, roles, chairman and procedures
(including frequency, notice, agenda and papers, quorum,
voting). Role of the company secretary before, during and
after board meetings. Delegation of authority and responsibility.
Committees: types and purposes; composition. Matters
reserved for the Board. Executive discretion. Cooption.
General meetings: Annual General Meetings, Extraordinary
General Meetings, Statutory Meeting, Class Meetings.
Regulations governing general meetings: Role of chairman;
Notice, agenda and papers; Quorum; Standing orders;
Rules of order; Motions; Amendments; Resolutions; Proxies;
Attendance; Voting. Role of the company secretary before,
during and after general meetings. Resolutions in writing.
Minutes and minute books.
Share Registration
Regulation of the securities industry. Types of shares and loan
capital. KLSE and listing requirements.
The company registrar: principles and procedures in share
and membership registration. Register of members, including
software applications. Technology based applications (CDS).
Allotment of shares. Share transfer: forms and registration
procedures. Transmission of shares and registration of
documents affecting title. Membership in companies limited
by guarantee. Issue of share certicates; lost certicates.
Dividends and interest. Employee share option schemes. New
issues and takeovers.
Purchase of own shares. Redemption of shares. Rights issues.
Capital events and the registrars role in capital events.
Evidence of assessed pre-requisite knowledge and understanding
in the following disciplines must be demonstrated through the
Institutes examinations, or those of equivalent qualications which
have been approved as meeting the Institutes required curriculum
and standards:
Malaysian Corporate Law
Strategic and Operations Management
LEARNING CONTENT
The Secretary, the Board, and the Members
The role of the secretary; functions and duties. Appointment
and vacation of ofce. Relationship with chairman and directors.
The secretary as advisor to the chairman and the board.
38
Dissemination of information and decisions. Communications
with shareholders and other stakeholders, including electronic
communications.
RECOMMENDED READING
1.
2.
Kang, Shew Meng (2005), Handbook on Company Secretarial
Practice in Malaysia. 4th Edition. Kuala Lumpur: Lexis Nexis
Business Solutions.
Lawton, P. & Rigby, E. (1992), Meetings: Their Law and
Practice. UK: M & E Handbooks
Examination Syllabus
ICSA International Qualifying Scheme (IQS): Professional Part 2
CORPORATE SECRETARYSHIP
REFERENCES
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
Company Secretarial Practice Manual. Kuala Lumpur:
MAICSA
Malaysia & Singapore Company Secretarys Practice.
Singapore: CCH
MAICSA Best Practice Guide Series
Yap, Priscilla P.Y., (2001). Company Meetings: Law & Practice
in Malaysia. Singapore: CCH
Code of Ethics for Directors and Code of Ethics for
Secretaries: ROC
Malaysian Code on Corporate Governance
Statutes, Regulations and Guidelines:
Companies Act 1965
Companies Regulations 1966
Companies Commission Act 2001
Securities Commission Act 1993
Policies and Guidelines of the Securities Commission
Securities Industry Act 1983
Securities Industry Regulations
Corporate Secretaryship
The Bursa Securities Berhad Listing Requirements &
Practice Notes
Rules of the Malaysian Central Depository Sdn Bhd
Malaysian Code on Corporate Governance
Malaysian Code on Take-overs and Mergers 1998
Foreign Investment Committee Guidelines
Unclaimed Moneys Act 1965
Journals of ICSA and MAICSA
39
CHARTERED SECRETARIES MALAYSIA
ICSA International Qualifying Scheme (IQS): Professional Part 2
CORPORATE FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT
SYLLABUS
Domestic and international sources. The nature of debt. Corporate
debentures and debenture stock, convertibles, warrants. Bank loans
and overdrafts. Retention and self-generated nance.
AIM
The aim of this module is to address the need for the Chartered
Secretary to be knowledgeable and competent in the skills of
corporate nancial planning, and in understanding the impact of the
scal environment on the organisation and its decision making.
LEARNING OUTCOME
At the conclusion of this module, the candidate will be able to:
Understand the nancial sources and requirements of the
employing or client organisation.
Understand the role and efciency of the capital markets.
Understand the nature and importance of capital structure and
the cost of capital.
Understand and apply the principles of working capital
management.
Understand the impact of global and multi-national operations
on corporate nancial management.
PRE-REQUISITE LEARNING
Evidence of assessed pre-requisite knowledge and understanding
in the following disciplines must be demonstrated through the
Institutes examinations, or those of equivalent qualications which
have been approved as meeting the Institutes required curriculum
and standards:
Financial Accounting
Management Accounting
Corporate Law
Management Practice
LEARNING CONTENTS
Financial Objectives and Requirements
The nancial objectives of the main types of organisation: public
and private limited companies, statutory companies, trusts,
and companies limited by guarantee. Determination of nancial
requirements and their impact on business planning and decision
taking. The role of nancial audit.
Sources of Finance
Financial markets: role of the New Issues Market and Stock
Exchange, including the Alternative Investment Market. The
operating institutions on the markets. Inuence of Markets on market
decisions. State funding, corporate donations, sponsorship, grants,
subscriptions, fund raising sources.
Share and Loan Capital
The raising and maintenance of share capital: issue pricing and
methods. Authorised and issued capital. Dividend policy, including
scrip dividends and share re-purchases. Finance and loan capital.
40
Capital Structure, the Cost of Capital
Costs of individual types of nance. Weighted average cost of capital.
Portfolio theory and the Capital Asset Pricing Model. The cost of
capital. Capital gearing. Capital structure theory and decisions.
Working Capital Management
Working capital and its importance. Planning and control of cash and
marketable securities, debtors, current liabilities and stock. Future
expansion and contraction.
Capital Investment Appraisal
Payback. Net Present Value, Internal Rate of Return and their
comparison. Implications of taxation and ination. Capital rationing.
Capital budgeting under uncertainty. Lease or buy decisions.
Business Restructuring
Business expansion and nancial growth. Sources of expansion and
contraction. Restructuring strategies: bids, acquisitions and mergers,
capital reconstructions. Divestment: sell-offs, spin-offs, management
buyouts. Business failure, prediction and rescue packages.
International Aspects
Multi-national operations. Managing exchange risk. The foreign
investment decision. Financing overseas investment.
RECOMMENDED READING
Textbooks
1.
Principles of Managerial Finance by Lawrence J. Gitman; 11th
edition, Pearson Publishing
2.
Corporate Finance: Theory & Practice by Aswath Damodaran;
Wiley Publishing
3.
Capital Investment & Valuation by Brealey & Myers; McGrawHill
4.
International Financial Management by Jeff Madura; Thompson
South-Western
Manuals & Guides
1.
Securities Commission Examination Study Guide Investment
Management & Corporate Finance (Module 12)
2.
Reports from Bursa Saham Malaysia, Bank Negara Malaysia
& Securities Commission
3.
Articles by HSBC Amanah & Citibank
Journals
1.
Global Finance Journal
2.
Journal of Corporate Finance
3.
International Review of Finance
Examination Syllabus
ICSA International Qualifying Scheme (IQS): Professional Part 2
CORPORATE FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT
ADDITIONAL READING
FURTHER READING
1.
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
Investors guide to Analyzing Companies & Valuing Shares by
Michael Cahill; Financial Times- Prentice Hall; 2003
Banking & Financial Services Certicate (BFSC) Study Manual;
Operations by Jee Tzin Kit & K. Loghandran
Intermediate Financial Management by Eugene F. Brigham
& Philip R. Daves; Thompson South-Western 8th Edition
Financial Management and Real Options by Jack Broyles;
Wiley; 2003
Emerging Financial Markets by David o. Biem & Charles W.
Calomiris; Mc Graw-Hill International Edition: 2001
Corporate Financial Investment by Richard Pike & Bill Neale;
Prentice Hall; 4th Edition
Business Finance-Value-Based Approach by Bill Neale &
Trefor McElroy; Prentice Hall; 2004
Corporate Financial Management by Michael Potton; ICSA
International
The Central Bank & The Financial System In Malaysia
A Decade of Change 1989-1999 by Bank Negara Malaysia
Various websites of government agencies
Related articles from local and international newspapers,
magazines, periodicals and academic publications.
2.
3.
Arnold, G.C. (1998), Corporate Financial Management,
Financial Times Pitman: London.
Valdez, S. (2nd edn 1997), An Introduction to Global Financial
Markets, Macmillan: London.
Weston, J.F. and Brigham, E.T. (1990), Essentials of
Managerial Finance, Dryden: London
41
CHARTERED SECRETARIES MALAYSIA
ICSA International Qualifying Scheme (IQS): Professional Part 2
CORPORATE ADMINISTRATION
SYLLABUS
AIM
The Chartered Secretary is regularly employed in a position of
strategic responsibility for administrative operations within and across
the organisation. The aim of the module is to instill knowledge and
key skills in handling the responsibilities of corporate administration
in both the strategic and functional contexts, to develop competence
in advising the Board and leading teams in administrative best
practice, and in ensuring compliance with external regulation and
internal procedures.
LEARNING OUTCOME
At the conclusion of this module, the candidate will be able to:
Understand the scope of strategic and functional administration
and apply it within the employing or client organisation.
Access information sources and deliver knowledge and
information internally to the optimum benet of the organisation
and its needs.
Evaluate the requirements of the legal and regulatory
environment in corporate administration, advise the Board
accordingly, and ensure compliance.
Take responsibility for the administration of corporate
knowledge and information, the human resource, pension
schemes insurance and risk, and physical corporate assets.
PRE-REQUISITE LEARNING
Evidence of assessed pre-requisite knowledge and understanding
in the following disciplines must be demonstrated through the
Institutes examinations, or those of equivalent qualications which
have been approved as meeting the Institutes required curriculum
and standards:
Strategic and Operations Management
Corporate Law
The Human Resource
Employment law and regulation. The employment contract. Concepts
of added value and continuous improvement. Securing and monitoring
the people resource: human resource planning, recruitment and
selection, job descriptions and person specications. Maximizing
performance: job design; job enrichment; reward and recognition
systems; job evaluation. Training and development. Coaching and
counseling. Performance appraisal. Working with consultants and
volunteers. Disciplinary rationale, dismissal constructive dismissal,
grievance procedure, redundancy. Health and safety policy. Risk
assessments, re precaution, rst aid, bullying and violence in the
workplace.
Legislation: Employment Act 1955 (Act 265); Workmen Compensation
Act 1952 (Act 273); Trade Unions Act 1959 (Act 262); Industrial
Relations Act 1967 (Act 177); Occupational Safety and Health Act
1994; Factories and Machinery Act 1967
Insurance, Risk Management and Pensions
The nature of corporate and business risks; management and control.
Corporate liability and insurance: classes and types. The insurance
market; brokers and intermediaries. The use of consultants and
advisers. Disaster planning. Pension scheme, public sector scheme.
Pensions scheme administration, industry wide and other scheme.
Legislation: Insurance Act 1996 (Act 553); Financial Procedure Act
1957 (Act 61); Pension Act 1980 (Act 227).
Corporate Assets
The management of physical assets. Facilities administration: role
and functions. Security and the application of systems. Business
location and relocation. Accommodation and space planning.
Outsourcing management.
RECOMMENDED READING
1.
2.
LEARNING CONTENTS
3.
Role and Functions
The role and functions of the corporate administrator. Administration
as a support service in organisations. The concept of best practice.
The sources and application of guides to best practice.
Knowledge and Information
The sources of information on law, regulation and administrative
best practice. Copyright and intellectual property, including asset
protection. Trademarks and patents. Information, data and technology
as a corporate resource. Technological change and innovation:
internet and website application and management. Security and
integrity of information; control of access. Data protection legislation.
Condentiality.
Legislation: Trademarks Act 1976 (Act 175); Patent Act 1983 (Act
291); Copyright Act 1987 (Act 332); Geographical Indications Act
2000 (Act 602)
42
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
Norsaidatul Akmar Mazelan, Corporate Management Styles
Case Study of Malaysian Companies, Pelanduk Publications
(2000)
David Birchall & Laurence Lyons, Creating Tomorrows
Organisation: Unlocking the Benets of Future Work, FT Pitman
Publication (1995)
Subir Chowdhury, Management Twenty-first Century:
Someday We Will All Manage This Way, Prentice-Hall (2000)
Subir Chowdhury, Organisation Twenty-rst Century, PrenticeHall (2003)
Premeaux Human Resource Management Simon & Schuster
(2002)
Ian Beardwell & Len Holden, Human Resource Management:
A Contemporary Perspective, Pitman Publishing (1994)
Neil Crockford, The Administration of Insurance, ICSA
Publishing, 1987
S.R. Diacon & R.L. Carter, Success in Insurance, John Murray
(1984)
Catherine Tay Swee Kian, A Guide to Protecting Your Ideas,
Inventions, Trademarks & Products, Times Book International
(1997)
Examination Syllabus
43
CHARTERED SECRETARIES MALAYSIA
44
Вам также может понравиться
- GST 02 - Application For Group or Joint Venture RegistrationДокумент8 страницGST 02 - Application For Group or Joint Venture RegistrationtenglumlowОценок пока нет
- Pav CourseДокумент30 страницPav CoursetenglumlowОценок пока нет
- Analyzing Gaps For Profitable Trading StrategiesДокумент31 страницаAnalyzing Gaps For Profitable Trading StrategiestenglumlowОценок пока нет
- Gst-01c - Details of Overseas PrincipalДокумент7 страницGst-01c - Details of Overseas PrincipaltenglumlowОценок пока нет
- Gst-01 - Application For Goods and Services Tax Registration Revised 3 Okt 2014Документ9 страницGst-01 - Application For Goods and Services Tax Registration Revised 3 Okt 2014tenglumlowОценок пока нет
- Cop Safely Remove AsbestosДокумент72 страницыCop Safely Remove AsbestostenglumlowОценок пока нет
- White Card Online - CPCCOHS1001A - WhiteCard Online - Narbil White CardДокумент3 страницыWhite Card Online - CPCCOHS1001A - WhiteCard Online - Narbil White CardtenglumlowОценок пока нет
- Strategy Note - Must-Own Stocks For Long-Term InvestingДокумент139 страницStrategy Note - Must-Own Stocks For Long-Term InvestingtenglumlowОценок пока нет
- 1MDB Wants Money To Come Back To Malaysia But What Kind of Returns Would The Investments Have Yielded - Business News - The Star OnlineДокумент13 страниц1MDB Wants Money To Come Back To Malaysia But What Kind of Returns Would The Investments Have Yielded - Business News - The Star OnlinetenglumlowОценок пока нет
- Royal Malaysian Customs: Guide Approved Toll Manufacturer SchemeДокумент15 страницRoyal Malaysian Customs: Guide Approved Toll Manufacturer SchemetenglumlowОценок пока нет
- SSM Illustration of FS MFRSДокумент76 страницSSM Illustration of FS MFRStenglumlowОценок пока нет
- Royal Malaysian Customs: Guide Approved Trader SchemeДокумент16 страницRoyal Malaysian Customs: Guide Approved Trader SchemetenglumlowОценок пока нет
- Guidebook Import Export 1Документ279 страницGuidebook Import Export 1tenglumlowОценок пока нет
- DoorsДокумент18 страницDoorstenglumlow100% (1)
- EvergreenДокумент1 страницаEvergreentenglumlowОценок пока нет
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (895)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5794)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (266)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (400)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (345)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2259)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (121)
- Executive SummaryДокумент3 страницыExecutive SummaryBenchinoune Abderrahim0% (1)
- Wipro WInsights Sustainability ReportingДокумент3 страницыWipro WInsights Sustainability ReportingHemant ChaturvediОценок пока нет
- Differences Between QuickBooks Pro Premier and EnterpriseДокумент7 страницDifferences Between QuickBooks Pro Premier and Enterpriseathancox5837Оценок пока нет
- Intramuros Adminstration - Exec Summary 06Документ9 страницIntramuros Adminstration - Exec Summary 06Anonymous p47liBОценок пока нет
- Write UpДокумент5 страницWrite UpAli Tariq ButtОценок пока нет
- Casey Loop's Whistleblower Lawsuit vs. The CTAДокумент18 страницCasey Loop's Whistleblower Lawsuit vs. The CTAChadMerdaОценок пока нет
- Confirmation Form: Pillar Regional Conference (NCR)Документ1 страницаConfirmation Form: Pillar Regional Conference (NCR)Llano Multi-Purpose CooperativeОценок пока нет
- ICON Brochure Low ResДокумент4 страницыICON Brochure Low ResLuis Adrian Gutiérrez MedinaОценок пока нет
- Q1. Comment On The Future of Rural Marketing in The Lights of This Case StudyДокумент5 страницQ1. Comment On The Future of Rural Marketing in The Lights of This Case StudySarthak AroraОценок пока нет
- Reviewer in AgencyДокумент13 страницReviewer in AgencyKrissie Guevara100% (2)
- Financial Analysis Hoa Phat Joint Stock Company: Lecture By: Tran Thi Nga Presented byДокумент22 страницыFinancial Analysis Hoa Phat Joint Stock Company: Lecture By: Tran Thi Nga Presented byMinh NguyệtОценок пока нет
- Chart of AccountzsДокумент22 страницыChart of AccountzsMuddser ShahidОценок пока нет
- Bilal PDF DissertationДокумент115 страницBilal PDF DissertationkamilbismaОценок пока нет
- MR Smart Has 75 000 Invested in Relatively Risk Free Assets ReturningДокумент1 страницаMR Smart Has 75 000 Invested in Relatively Risk Free Assets ReturningAmit PandeyОценок пока нет
- 15 Bankers and Manufacturers Vs CA DigestДокумент2 страницы15 Bankers and Manufacturers Vs CA DigestCharisseCastilloОценок пока нет
- HBO Jieliang Home PhoneДокумент6 страницHBO Jieliang Home PhoneAshish BhalotiaОценок пока нет
- Risk/Opportunity Analysis: DOH - National Capital Regional OfficeДокумент3 страницыRisk/Opportunity Analysis: DOH - National Capital Regional Officejai ebuenОценок пока нет
- 120 OcmugДокумент176 страниц120 Ocmugatiwari_45Оценок пока нет
- Auditing NotesДокумент1 страницаAuditing NotesEhsan Umer FarooqiОценок пока нет
- Interesting Cases HbsДокумент12 страницInteresting Cases Hbshus2020Оценок пока нет
- Objectives of DumpingДокумент6 страницObjectives of Dumpingmuhammad usamaОценок пока нет
- Study Online,: Graduate On CampusДокумент28 страницStudy Online,: Graduate On CampusattackcairoОценок пока нет
- ASSIGNMENT 407 - Audit of InvestmentsДокумент3 страницыASSIGNMENT 407 - Audit of InvestmentsWam OwnОценок пока нет
- PDF Rq1 With AnswersДокумент9 страницPDF Rq1 With AnswersCaleb GetubigОценок пока нет
- Supernova Muhammad AliДокумент19 страницSupernova Muhammad AliZafar NawazОценок пока нет
- Stock Investing Mastermind - Zebra Learn-80Документ2 страницыStock Investing Mastermind - Zebra Learn-80RGNitinDeva100% (1)
- Chart of AccountsДокумент22 страницыChart of AccountsaddyОценок пока нет
- Amtrak Dining RFPДокумент54 страницыAmtrak Dining RFPdgabbard2Оценок пока нет
- Bills of Material: Rev. Date Description by CHK'D Reviewed ClientДокумент5 страницBills of Material: Rev. Date Description by CHK'D Reviewed ClientChaitanya Sai TОценок пока нет
- How To Become An Entrepreneur Part 1Документ18 страницHow To Become An Entrepreneur Part 1aries mandy floresОценок пока нет