Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Metodo Xenosep
Загружено:
Jenny Chavez AlarconОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Metodo Xenosep
Загружено:
Jenny Chavez AlarconАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Oil and Grease, SPE, 10300
Oil and Grease
USEPA1 Solid Phase Extraction Method
5 to 1000 mg/L HEM and SGT-HEM
DOC316.53.01186
Method 10300
Hexane Extractable Gravimetry
Scope and Application: For water and wastewater
1
Equivalent to USEPA Method 1664A, Solid Phase Extraction (SPE)
Test preparation
Before starting the test:
Follow the instructions for sample collection and acidification in Sample collection, preservation and storage.
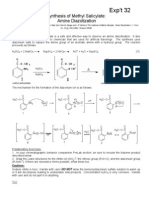
Assemble the Xenosep SPE apparatus as shown in Figure 14. Be sure to put the waste collection tube in the large flask
before installing the funnel assembly. Put the pattern side of the SPE filter down in the SPE filter support (Figure 15).
Wash all glassware in hot water with detergent, rinse with tap and distilled water and rinse with acetone or n-hexane.
Rinse all glassware thoroughly with hexane to make sure the analyte is not retained on the apparatus. Inadequate rinsing will
result in low recovery.
Determine a blank value (1 liter of distilled or deionized water) with each new lot of reagents. If the blank result is greater
than 5 mg, resolve the source of error or remove interferences before performing this procedure.
If analyzing for SGT-HEM, rinse the inner cavity of the aluminum dish with a few milliliters of acetone and then with a few
milliliters of hexane to remove any potential artifacts.
Label the aluminum dish and heat in an oven for one hour at 105 C. Cool the dish in a dessicator for 30 minutes. Weigh the
dish on an analytical balance to the nearest 0.1 mg. Record this weight as "B" for HEM step 22 or SGT-HEM step 12.
Make sure that the aluminum dish is removed from the hot plate before the solution has completely evaporated. Heating the
solution too long will result in low recovery.
Use a vacuum pump that can generate a Free Air Flow of at least 1 CFM (3 CFM preferred). Insufficient SPE disk drying will
result in low recovery.
Collect the following items :
Description
Hydrochloric acid, 1:1
Quantity
6 mL
Hexane (n-hexane) in Teflon-FEP wash bottle
1 wash bottle
Methanol in PE wash bottle
1 wash bottle
Deionized water in PE wash bottle
1 wash bottle
SPE Starter Kit, EPA Method 1664A
1 kit
SPE Consumables Kit
1 kit
SPE Solvent Recovery Kit
1 kit
Aluminum weighing dish
Hot plate
Vacuum pump
Oil and Grease
Page 1 of 12
Oil and Grease
Collect the following items (continued):
Description
Quantity
pH paper, 014 pH units
Lab stand
Clamp, swivel
Desiccator
For SGT-HEM:
Silica gel
1 bottle
125-mL Erlenmeyer flask
100-mL volumetric flask (for HEM results over 1000 mg/L)
Magnetic stir plate
Aluminum weighing dish
Additional sodium sulfate column
See Consumables and replacement items for reorder information.
Figure 14 Solid phase extraction assembly
1.
Hot plate
7.
Eluter tube
2.
Aluminum dish
8.
Clamp, tubing
3.
Glass dome
9.
3-way valve
Oil and Grease
Page 2 of 12
Oil and Grease
4.
Solvent recovery assembly
10. 2-way valve
5.
Funnel assembly (see Figure 15)
11. To vacuum
6.
Sodium sulfate column
12. Waste collection tube with O-Ring
1.
Aluminum clamp
4.
SPE filterpattern side down
2.
Funnel
5.
Stainless steel support
3.
Coupler with O-Rings
6.
SPE starter holder
Figure 15 Funnel assembly
Solid phase extraction for HEM
1. Add approximately
10 mL of hexane to the
funnel. Wait 5 seconds.
Turn the vacuum on and
off to pull the solvent into
the waste collection tube.
Repeat with a second
10-mL portion of hexane.
2. Turn the vacuum on
for 1 minute to dry the
filter. Turn off the vacuum.
3. Add approximately
10 mL of methanol to the
funnel. Wait 5 seconds.
Turn the vacuum on and
off to pull the solvent into
the waste collection tube.
4. Remove the tube and
discard the solvent waste.
Refer to the MSDS and
local regulations for safe
disposal of the solvent.
Do not allow the filter to
become dry.
Make sure the valves are
set to pull vacuum from
the funnel holder and the
tubing clamp is open.
Oil and Grease
Page 3 of 12
Oil and Grease
Solid phase extraction for HEM (continued)
5. Add approximately
20 mL of deionized water
to the funnel. Wait 5
seconds. Turn the vacuum
on and off to pull the water
into the flask.
Do not allow the filter to
become dry.
If the filter becomes dry,
repeat steps 35.
9. Turn the valve to apply
vacuum to the eluter tube.
Close the tubing clamp on
the funnel holder tube.
6. Slowly pour the
acidified sample into the
funnel and turn on the
vacuum. Use deionized
water to rinse any debris
from the walls of the
funnel.
7. Leave the vacuum on
for 4 to 8 minutes to air dry
the filter. Turn off the
vacuum.
Do not leave the vacuum
on for more than
8 minutes.
See Sample collection,
preservation and storage
for sample acidification.
10. Add 10 mL of hexane
to the empty sample
bottle. Shake the bottle in
a horizontal, circular
motion for 10 seconds to
rinse the bottle.
11. Use a transfer pipet to
collect the hexane from
the shoulder of the sample
bottle. Slowly rinse the
walls of the funnel with the
hexane. Go around the
funnel at least 3 times.
Repeat steps 1011 two
more times.
Oil and Grease
Page 4 of 12
8. Put the funnel
assembly on the eluter
tube.
12. Turn the vacuum on
and off to pull the solvent
into the flat-sided flask.
Rinse the walls of the
funnel with approximately
10 mL of hexane. Wait 5
seconds. Turn the vacuum
on and off.
Oil and Grease
Solid phase extraction for HEM (continued)
13. Remove the flat-sided
flask from the eluter tube.
14. Pour the hexane into
a pre-weighed aluminum
dish.
15. Rinse the flat-sided
flask with approximately
5 mL of hexane. Add the
hexane to the dish.
16. Put the dish on the hot
plate and place the glass
cover over the dish.
17. Close the 3-way valve
and open the 2-way valve
to pull vacuum from the
solvent recovery
apparatus.
18. Turn on the vacuum.
Turn the hot plate on low
heat (3585 C). Heat for
approximately 2 minutes.
19. Examine the dish for
dry spots. As soon as
there is a dry spot remove
the dish from the hot plate.
Put the dish in a fume
hood until the rest of the
hexane has evaporated.
20. When the dish is dry,
put the dish in a desiccator
for 30 minutes.
21. After 30 minutes,
weigh the dish to the
nearest 0.1 mg. Repeat
steps 20 and 21 until the
weight loss is less than
0.5 mg from the previous
weight. Record the weight.
22. Calculate the test
results:
Example:
AB
---------------------------------------- 1000
sample volume
B= 6.2318 g
A= weight of dish with
residue (g) (step 21)
B= weight of dish (g)
A= 6.2394 g
sample volume = 0.950 L
6.2394 g 6.2318 g
----------------------------------------------------- 1000 =
0.950 L
8.0 mg/L HEM
Oil and Grease
Page 5 of 12
Oil and Grease
Solid phase extraction for SGT-HEM (HEM < 1000 mg/L)
1. Add hexane to the
residue in the aluminum
dish from the HEM test
until the dish is
approximately half full
(approximately 60 mL).
2. Heat slightly to
dissolve all of the residue.
3. Pour the mixture into a
125-mL Erlenmeyer flask.
Rinse the pan and funnel
several times with hexane
and add to the flask. Add
hexane to approximately
the 100-mL mark.
4. Add 3 ( 0.3) g of
silica gel for every 100 mg
of HEM or fraction thereof:
3 mg/L HEM
-------------------------------------- =
100
silica gel (g)
Example: if the HEM value
was 735 mg, round 7.35 g up
to the next whole gram
increment (8 g or 800 mg)
and add 3 x 800/100= 24 g of
silica gel.
Do not add more than 30 g
silica gel.
5. Add a stir bar to the
flask and stir for 5 minutes.
Oil and Grease
Page 6 of 12
6. Put a new sodium
sulfate column into the
eluter tube. Put the funnel
on the eluter tube.
7. Install a clean
flat-sided flask.
8. Adjust the valves to
pull vacuum from the
eluter tube.
Oil and Grease
Solid phase extraction for SGT-HEM (HEM < 1000 mg/L) (continued)
Go to the HEM
procedure.
9. Pour the solution from
the Erlenmeyer flask into
the funnel. Turn the
vacuum on and off to pull
the solution into the flatsided flask.
10. Rinse the Erlenmeyer
flask with 5 mL hexane.
Add the hexane to the
funnel. Turn the vacuum
on and off.
11. Complete steps 1321
under Solid phase
extraction for HEM to
evaporate the solvent.
12. Calculate the test
results:
AB
---------------------------------------- 1000
sample volume
A= weight of dish with
residue (g) (step 21)
Rinse the walls of the
funnel with approximately
5 mL of hexane. Turn the
vacuum on and off.
B= weight of dish (g)
Example:
A= 6.2360 g
B= 6.2320 g
sample volume = 0.950 L
6.2360 g 6.2320 g
----------------------------------------------------- 1000 =
0.950 L
4.2 mg/L SGT-HEM
Report result as 5 mg/L
SGT-HEM
Solid phase extraction for SGT-HEM (HEM > 1000 mg/L)
1. Add hexane to the
residue in the aluminum
dish from the HEM test
until the dish is
approximately half full
(approximately 60 mL).
Heat slightly to dissolve all
of the residue.
2. Pour the mixture into a
100-mL volumetric flask.
Rinse the pan and funnel
several times with hexane
and add to the flask.
3. Dilute to the mark with
hexane and mix well.
4. Calculate the volume
to remove for the silica gel
treatment:
100,000
V 1000 = ----------------------------HEM value
V1000 = volume that
contains 1000 mg HEM
Oil and Grease
Page 7 of 12
Oil and Grease
Solid phase extraction for SGT-HEM (HEM > 1000 mg/L) (continued)
Go to the SGT-HEM
(HEM < 1000 mg/L)
procedure.
5. Remove the amount
calculated in step 4 from
the volumetric flask and
add it to a 125-mL
Erlenmeyer flask. Add
hexane to approximately
the 100-mL mark.
6. Add 30 g of silica gel
to the flask.
If the volume added in
step 5 contained less than
1000 mg HEM, calculate
the amount of silica gel to
add based on the mg HEM
that was added to the
flask.
3 mg HEM in aliquot
---------------------------------------------------------- =
100
silica gel (g)
7. Complete steps 512
in the procedure for Solid
phase extraction for SGTHEM (HEM < 1000 mg/L).
8. Correct the test result
for the reduced volume
that was treated with the
silica gel:
100
W d -------------- = W c
V 1000
where:
Wd = result from step 12
V1000 = volume removed
for silica gel treatment
Wc = corrected SGT-HEM
result
Interferences
For samples that are known to contain extremely high levels of oil and grease, use a smaller
sample volume and correct for the volume difference to give the result as a 1-L sample.
High concentrations of particulates in the water sample can clog the SPE filter or retain high levels
of water, which can lower the extraction efficiency. Inorganic particulates are easier to filter than
organic particulates. The following techniques may help to filter samples containing high levels of
particulates:
Decantingallow the sample to settle and pour the top portion into the funnel first. Just before
dryness, add the rest of the sample. Remove any sediment from the bottle and add it to the
SPE filter. Use deionized water to rinse any sediment that remains in the bottle.
Prefilters or prefilter fibersplace the prefilter or prefilter fibers into the coupler before the
funnel is attached.
Drying agentsadd magnesium sulfate to the SPE filter or to the prefilter to remove water that
may be trapped in the particulates.
Filtration aidsadd materials such as sodium chloride, sand, diatomaceous earth or glass
beads to help speed the complete filtration of samples that contain organic particulates.
This method is not applicable to materials that volatilize at temperatures below approximately
85 C (185 F). Petroleum fuels from gasoline through #2 fuel oil may be partially lost in the solvent
removal operation. Some crude oils and heavy fuel oils contain a significant percentage of
materials that are not soluble in n-hexane. Recoveries of these materials may be low.
Oil and Grease
Page 8 of 12
Oil and Grease
Sample collection, preservation and storage
Collect 1 L (9501050 mL) of sample in a wide-mouth glass bottle. Do not rinse the bottle with
sample before collection. The sample must be at room temperature before the test.
Sample volume
Complete the steps that follow to measure the sample volume.
6. Use a laboratory pen to mark on the sample bottle the liquid level of the sample.
7. When the test is complete, fill the bottle to this mark with tap water.
8. Pour the tap water into a 1-L graduated cylinder and write down the volume. Use this volume
for the sample volume in the final step of the test procedure for HEM or SGT-HEM.
Acidification
The sample must be acidified with 1:1 hydrochloric acid (HCl) solution to a pH of 2 or less before
the test is started. To find the volume of HCl to use, collect a separate aliquot, add HCl until the pH
is less than 2 and add this volume of acid to each sample bottle before collection. Do not dip pH
paper, a pH electrode, a glass rod or other materials into the sample because oil and grease in the
sample may adhere to these items.
If the test can not be started for more than a few hours after collection, cool and store the sample
at 04 C (3239 F). Acidified samples can be stored for 28 days.
Accuracy check
For USEPA reporting, each laboratory must first measure an acceptable MDL (Minimum Detection
Limit) and IPR (Initial Precision and Recovery) before samples can be measured. Before
measuring the MDL or IPR, run laboratory reagent water blanks to eliminate interferences.
Standard solution preparation
Required items:
Stearic acid, 98% minimum
Hexadecane, 98% minimum
Acetone for Organic Residue Analysis, residue less than 1 mg/L
100-mL Class A volumetric flask
10.0-mL Class A volumetric pipet
15.0-mL Class A volumetric pipet
1. Put 200 ( 2) mg stearic acid and 200 ( 2) mg hexadecane into a 100-mL volumetric flask.
2. Add 7585 mL of acetone and shake vigorously until all material has dissolved.
3. Allow to equilibrate to room temperature and fill to volume with acetone. Mix well. The
concentration of this stock solution is 4000 mg/L HEM (2000 mg/L SGT-HEM).
4. Use a volumetric pipet to dilute the stock solution for use in MDL, IPR or OPR measurements:
MDL standard solution:
a. Add 15 mL of the stock solution into a clean 100-mL volumetric flask. Dilute to the mark
with acetone and mix well.
b. Pipet 10 mL for HEM (or 20 mL for SGT-HEM) into a 1-L volumetric flask. Dilute to the
mark with deionized water at pH < 2 and mix well. The concentration of this standard
solution is 6 mg/L HEM (or 6 mg/L SGT-HEM).
Oil and Grease
Page 9 of 12
Oil and Grease
IPR or OPR standard solution:
Add 10 mL of the stock solution into 1 liter of deionized water and mix well. The concentration
of this solution is 40 mg/L HEM (20 mg/L SGT-HEM).
Note: To verify the concentration of the IPR/OPR standard, use a pipet to add 10 mL of the standard
solution into a pre-weighed flask or dish. Allow the acetone to evaporate in a fume hood. When dry,
weigh the flask or dish. The weight of the residue should be 40 (1) mg.
EPA requirements for MDL and IPR
MDL: measure seven replicates of a 6 mg/L standard solution, find the standard deviation and
multiply the standard deviation by 3.143 (Students t test). The acceptable limits are:
HEM: 1.4 mg/L
SGT-HEM: 1.6 mg/L
IPR: follow the procedure for HEM and SGT-HEM (if necessary) four separate times using a
40 mg/L HEM (20 mg/L SGT-HEM) standard solution. Report the average percent recovery (x)
and the standard deviation for both HEM and SGT-HEM. The acceptable limits are:
HEM: Precision(s) 11%; Recovery (x) 83101%
SGT-HEM: Precision(s) 28%; Recovery (x) 83116%
A low result can be an indication of loss during quantitative transfers or loss during heating. A high
result can be an indication of incomplete drying or contamination. Run a blank before running
samples. If the blank result is more than 5 mg, identify and remove the source of contamination.
After acceptable values are obtained for the MDL and IPR, keep records for USEPA verification.
Oil and grease reporting to USEPA
Include the following data with the HEM and/or SGT-HEM results for each set of up to 20 samples
per discharge source.
1. Blank value: must be less than 5.0 mg/L for HEM and SGT-HEM.
Note: It may be necessary to use a standard that matches the regulatory concentration limit, is 1 to 5
times higher than the concentration of the sample (B) or is at the concentration of the Ongoing
Precision and Recovery, whichever is highest. Divide the concentration of the spike (T) by 2 for
SGT-HEM if using the 40 mg/L HEM (20 mg/L SGT-HEM) standard.
2. OPR (Ongoing Precision and Recovery): add 10 mL of the 40 mg/L HEM (20 mg/L SGTHEM) standard to a 1-liter sample and run the test. The acceptable limits for recovery are:
HEM: 78114%
SGT-HEM: 64132%
3. MS and MSD (matrix spike and matrix spike duplicate): measure the HEM and SGT-HEM
concentration of the sample (B). Spike two 1-L samples with 10 mL of the 40 mg/L HEM
(20 mg/L SGT-HEM) standard and measure the concentration after spiking (A).
Calculate the Percent Recovery (P) as follows:
100 ( A B )
P HEM (40 mg/L) = ----------------------------------T
100 ( A B )
P SGT HEM = ----------------------------------T2
where:
A = concentration of the unspiked sample
B = concentration of the spiked sample
T = concentration of the spike solution
Oil and Grease
Page 10 of 12
Oil and Grease
If the recovery for HEM and SGT-HEM is within the acceptable limits for OPR (step 2), then
calculate the Relative Percent Difference (RPD).
Conc MS Conc MSD
RPD = ---------------------------------------------------- 200
Conc MS + Conc MSD
If the RPD for HEM is 18 and for SGT-HEM 34, then continue with step 4. If the recovery is
lower than the RPD, an interference may be present. Identify and correct the interference,
then repeat MS and MSD.
After every five MS/MSD tests, calculate the average percent recovery (Pa) and standard
deviation of the percent recovery (sp). Record these numbers as Pa 2sp. Update the
accuracy assessment on a regular basis (e.g., after five to ten new accuracy measurments).
4. Balance calibration: measure a 2 mg and a 1000 mg class S weight on the analytical
balance before and after each analytical batch. If the values are not within 10% of the actual
weight, recalibrate the balance.
Summary of method
Oil and Grease & Total Petroleum Hydrocarbons (TPH) include any material that may be
recovered as a substance that is soluble in the n-hexane extractant. These include substances
such as relatively non-volatile hydrocarbons, vegetable oils, animal fats, waxes, soaps, greases
and related materials. When measuring oil and grease (HEM) gravimetrically, the substances are
extracted from the sample with n-hexane, then the n-hexane is evaporated. The residue left is
weighed to determine the concentration of oil and grease materials in mg/L.
When measuring Total Petroleum Hydrocarbons (SGT-HEM) gravimetrically, the substances are
extracted from the sample with n-hexane, then mixed with silica gel to absorb non-TPH
components. Then the n-hexane is evaporated. Like the HEM, the residue left is weighed to
determine the concentration of total petroleum hydrocarbons.
Definition of HEM and SGT-HEM
Oil and grease is the conventional term used to define pollutants of this nature. The newer term
n-Hexane Extractable Materials (HEM) indicates this method may be applied to materials other
than oils and greases.
Likewise, the term Total Petroleum Hydrocarbons (TPH) was traditionally used to classify aliphatic
hydrocarbon materials. The newer term Silica Gel Treated n-Hexane Extractable Material
(SGT-HEM), indicates that this method may be applied to materials other than aliphatic petroleum
hydrocarbons that are not adsorbed by silica gel.
Consumables and replacement items
Required reagents
Description
Quantity/Test
Unit
6 mL
500 mL
88449
100200 mL
1L
2510253
Methanol, ACS grade
10 mL
500 mL
1446449
Silica Gel, 100200 mesh (for SGT-HEM)
130 g
500 g
2665034
Hydrochloric Acid Standard Solution, 1:1 (6 N)
Hexane, for Organic Residue Analysis
Catalog number
Oil and Grease
Page 11 of 12
Oil and Grease
Required apparatus
Description
Quantity/Test
Unit
Catalog number
Balance, Analytical, 115 VAC 60 Hz.
each
2936801
Bottle, wash, 500-mL Teflon, FEP
each
2505100
Bottle, wash, 500-mL
3/pkg
2927204
Bottle, wide-mouth, 1-L
each
2951401
Clamp, swivel
each
2503400
Cylinder, graduated, 1-L
each
108153
Desiccator
each
2088800
1428400
Desiccator Plate
each
Flask, Erlenmeyer, 125-mL (for SGT-HEM)
each
50543
Hot Plate (Thermolyne), 120 VAC, 50 Hz
each
2344100
Marker, laboratory
each
2092000
Oven, drying, 120 VAC, 50 Hz
each
1428900
Pump, vacuum, 27 in. Hg, 1.3 CFM
each
2824800
SPE Consumables Kit
24/pkg
2943800
SPE Starter Kit, EPA Method 1664A
each
2943231
SPE Solvent Recovery Kit
each
2514300
Stirrer, magnetic, 120 VAC
each
2343600
Stir Bar, 22.2 x 7.9 mm
each
2095350
Support stand
each
2504900
Tongs, crucible, 9-inch
each
56900
Unit
Catalog number
Recommended standards
Description
Hexadecane, 99%
Stearic acid
100 mL
2664842
500 g
2664934
Unit
Catalog number
Optional reagents and apparatus
Description
Acetone, for Organic Residue Analysis
Flask, volumetric, Class A, 100-mL
Flask, volumetric, Class A, 1-L
pH Paper, 014 pH units
1L
2510153
each
1457442
each
1457453
100/pkg
2601300
Pipet filler, safety bulb
each
1465100
Pipet, serological, 10-mL
each
53238
Pipet, volumetric, Class A, 10 mL
each
1451538
Pipet, volumetric, Class A, 15 mL
each
1451539
Silica Gel with indicator (for desiccator)
454 g
1426901
FOR TECHNICAL ASSISTANCE, PRICE INFORMATION AND ORDERING:
In the U.S.A. Call toll-free 800-227-4224
Outside the U.S.A. Contact the HACH office or distributor serving you.
On the Worldwide Web www.hach.com; E-mail techhelp@hach.com
Hach Company, 2007, 2010, 2012. All rights reserved. Printed in the U.S.A.
HACH COMPANY
WORLD HEADQUARTERS
Telephone: (970) 669-3050
FAX: (970) 669-2932
Edition 7
Вам также может понравиться
- Organic Chemistry Laboratory II. Preparation of TriphenylmethanolДокумент3 страницыOrganic Chemistry Laboratory II. Preparation of Triphenylmethanolmario840Оценок пока нет
- M976 26 PDFДокумент3 страницыM976 26 PDFdanzan1Оценок пока нет
- Determination of Oil and GreaseДокумент5 страницDetermination of Oil and GreaseobliviategibiОценок пока нет
- Synthesis of Acetylferrocene F19Документ3 страницыSynthesis of Acetylferrocene F19Terhemba IningevОценок пока нет
- Steam Distillation ExperimentДокумент4 страницыSteam Distillation ExperimentibnyasseenОценок пока нет
- SteamDistДокумент4 страницыSteamDistgnaequiОценок пока нет
- 14-Friedel Crafts Acylation FerroceneДокумент10 страниц14-Friedel Crafts Acylation FerroceneNguyen Minh Duc100% (1)
- TrimyristinДокумент3 страницыTrimyristindinna_dinunОценок пока нет
- Nickel Experiment XWДокумент4 страницыNickel Experiment XWKhairul Anwar Abd HamidОценок пока нет
- 24 AspirinДокумент4 страницы24 AspirinAyoeYoeRamndaniОценок пока нет
- International Olive Council Method for Determining StigmastadienesДокумент12 страницInternational Olive Council Method for Determining StigmastadienesSlaw Ben AissaОценок пока нет
- The Gravimetric Determination of NickelДокумент7 страницThe Gravimetric Determination of Nickelswathi_ravi_5Оценок пока нет
- S946 05 PDFДокумент3 страницыS946 05 PDFdanzan1Оценок пока нет
- USP-FCC Sugar Beet FiberДокумент3 страницыUSP-FCC Sugar Beet FiberMAXОценок пока нет
- Mandelic Acid: 1. ProcedureДокумент4 страницыMandelic Acid: 1. ProcedureKangal PothikОценок пока нет
- Preparative TLC MosherДокумент4 страницыPreparative TLC MosherThoa BùiОценок пока нет
- Friedel-Crafts Acylation of TolueneДокумент6 страницFriedel-Crafts Acylation of TolueneKybernetikumОценок пока нет
- Analgesic Separation Column LabДокумент3 страницыAnalgesic Separation Column Labapi-178321548Оценок пока нет
- Laboratory Manual For Determining Oil and Grease For Raw and Treated EffluentДокумент3 страницыLaboratory Manual For Determining Oil and Grease For Raw and Treated EffluentAnas YuzairiОценок пока нет
- Aldol Condensation Between Benzaldehyde and AcetoneДокумент5 страницAldol Condensation Between Benzaldehyde and Acetonevicky_law_2Оценок пока нет
- Miscellaneous ChemicalsДокумент8 страницMiscellaneous Chemicalsgbonger100% (8)
- Experiment 12 Preparation of Adipic Acid From CyclohexeneДокумент6 страницExperiment 12 Preparation of Adipic Acid From Cyclohexenesaransh1994Оценок пока нет
- CetanalideДокумент2 страницыCetanalideSaubie AslamiahОценок пока нет
- 935.38 Absorcion de Grasa AOACДокумент1 страница935.38 Absorcion de Grasa AOACIsmael Morales PuenteОценок пока нет
- Western BlotДокумент4 страницыWestern Blotme_dayakarОценок пока нет
- Acid Detergent Fiber Procedure (ADF) : 1. ApplicationДокумент4 страницыAcid Detergent Fiber Procedure (ADF) : 1. ApplicationFarai FaustosОценок пока нет
- ObjectivesДокумент6 страницObjectivesTtalgis CartОценок пока нет
- Scope: CautionДокумент7 страницScope: CautionJavier Oswaldo Gonzalez AceroОценок пока нет
- Lieberman NДокумент3 страницыLieberman NTitis Adisti HapsariОценок пока нет
- CHEM 165 Lab Manual Spring 2000Документ41 страницаCHEM 165 Lab Manual Spring 2000Leon AFОценок пока нет
- English AFL ProcedureДокумент5 страницEnglish AFL ProcedureDaniel CristinaОценок пока нет
- Separating The Components of Panacetin PrelabДокумент5 страницSeparating The Components of Panacetin PrelabAmy LaPointe100% (2)
- Oil & Grease TestДокумент16 страницOil & Grease TestRohini GadhaweОценок пока нет
- Amine Test ProcedureДокумент2 страницыAmine Test ProcedureAvinash NegiОценок пока нет
- CHEM2054 B9 FlowchartДокумент4 страницыCHEM2054 B9 FlowchartBowie ChongОценок пока нет
- Aplication Fat Extraction FoodДокумент6 страницAplication Fat Extraction FoodKu BonОценок пока нет
- 9-Simple Distillation (P)Документ3 страницы9-Simple Distillation (P)Gezem GigantoОценок пока нет
- ASTM D 1065 - 96 (Reapproved 2001) Unsaponifiable Matter in Naval Stores, Including Rosin, TallДокумент3 страницыASTM D 1065 - 96 (Reapproved 2001) Unsaponifiable Matter in Naval Stores, Including Rosin, Tallalin2005Оценок пока нет
- Exp7 PDFДокумент4 страницыExp7 PDFAshkan AbbasiОценок пока нет
- Caution: Oil Will Be Hot, and May Splatter or Catch Fire. Wear Goggles at All TimesДокумент4 страницыCaution: Oil Will Be Hot, and May Splatter or Catch Fire. Wear Goggles at All TimesRodil ChipanaОценок пока нет
- Experiment 17b 1bДокумент27 страницExperiment 17b 1bRajeev GangwarОценок пока нет
- Analysis Methods Spices CondimentsДокумент24 страницыAnalysis Methods Spices CondimentssureshhmaxОценок пока нет
- Figure 5.1 Preparation of CyclohexeneДокумент5 страницFigure 5.1 Preparation of CyclohexeneMark Cliffton BadlonОценок пока нет
- Appendix B - Analytical MethodsДокумент9 страницAppendix B - Analytical MethodsRebecca SchroederОценок пока нет
- Chem 315 - Extraction of CaffeineДокумент18 страницChem 315 - Extraction of CaffeinekОценок пока нет
- DistillationДокумент6 страницDistillationpremise5274Оценок пока нет
- The Synthesis of Ethyl Ethanoate: A2 Experiment 13.5 (3) Teachers' GuideДокумент3 страницыThe Synthesis of Ethyl Ethanoate: A2 Experiment 13.5 (3) Teachers' GuideRudyОценок пока нет
- Re CrystallizationДокумент25 страницRe CrystallizationMarol CerdaОценок пока нет
- DAK Revised SOPДокумент10 страницDAK Revised SOPazlinkadirОценок пока нет
- Synthesis of Aspirin Lab ReportДокумент12 страницSynthesis of Aspirin Lab ReportJasmeetSingh63% (8)
- 4 GrignardReactionДокумент5 страниц4 GrignardReactionامیرحسین محمدیОценок пока нет
- Santa Monica College Chem 22 Lab ManualДокумент59 страницSanta Monica College Chem 22 Lab ManualMide Ogundipe100% (1)
- AcetaminophenДокумент4 страницыAcetaminophenSamushonga TendaiОценок пока нет
- Pressure Canning for Beginners: The Ultimate Guide on How to Can Meals, Vegetables and Meat in a JarОт EverandPressure Canning for Beginners: The Ultimate Guide on How to Can Meals, Vegetables and Meat in a JarРейтинг: 3 из 5 звезд3/5 (2)
- The Chemistry of Dairy Products - A Chemical Analysis of Milk, Cream and ButterОт EverandThe Chemistry of Dairy Products - A Chemical Analysis of Milk, Cream and ButterОценок пока нет
- Methods and Instruments Used in Brewing Control - Selected QuestionsОт EverandMethods and Instruments Used in Brewing Control - Selected QuestionsОценок пока нет
- LEED V4.1 Score CardДокумент1 страницаLEED V4.1 Score CardAsad YousafОценок пока нет
- New Zealand Soakage Design Manual - Auckland CityДокумент11 страницNew Zealand Soakage Design Manual - Auckland CityFree Rain Garden ManualsОценок пока нет
- Minesite Water Management HandbookДокумент128 страницMinesite Water Management Handbookedatgka100% (1)
- NRW Manager's HandbookДокумент110 страницNRW Manager's HandbookGigih Yuli AsmaraОценок пока нет
- Pollution Prevention and ControlДокумент33 страницыPollution Prevention and Controljohns josephОценок пока нет
- ETRATA, CHRISTIAN ANGELO (Part 1,2,3 and Related Appendices)Документ62 страницыETRATA, CHRISTIAN ANGELO (Part 1,2,3 and Related Appendices)AngeloEtrataОценок пока нет
- Oxygen Sag Model and DO DeficitДокумент2 страницыOxygen Sag Model and DO DeficitkatoОценок пока нет
- L 2: Environmental Impact AssessmentДокумент34 страницыL 2: Environmental Impact AssessmentVaidh Prakash ChoudharyОценок пока нет
- Marine Safety Information BulletinДокумент1 страницаMarine Safety Information BulletincaptaksahОценок пока нет
- Analysis of The Requirements of Change in Function and Principles of Building Conversion ToДокумент2 страницыAnalysis of The Requirements of Change in Function and Principles of Building Conversion Tosubhashie weerasingheОценок пока нет
- Multiple-Choice Test Chapter 22: Humans and The Environment: 1 A B C D 2 A B C D 3 A B C D 4 A B C D 5 A B C DДокумент2 страницыMultiple-Choice Test Chapter 22: Humans and The Environment: 1 A B C D 2 A B C D 3 A B C D 4 A B C D 5 A B C DsybejoboОценок пока нет
- Organica FCR BrochureДокумент2 страницыOrganica FCR BrochureAhmed AsemОценок пока нет
- Soil Characteristics and Soil PollutionДокумент58 страницSoil Characteristics and Soil PollutionKaren Johnson100% (1)
- Module-5 Social Issues & The EnvironmentДокумент17 страницModule-5 Social Issues & The Environmentrushi C SОценок пока нет
- Cryogenic Air Separation For The Production of NitrogenДокумент24 страницыCryogenic Air Separation For The Production of NitrogenJackie_Demyan_7107100% (1)
- 459 - 04-Nov-2019 - BUIDCO Final EOIДокумент12 страниц459 - 04-Nov-2019 - BUIDCO Final EOISourabhAgarwalОценок пока нет
- Transformer Oil Containment: Substation Design InstructionДокумент24 страницыTransformer Oil Containment: Substation Design Instructionplavi10Оценок пока нет
- Wat RM 08 Regulation of Sustainable Urban Drainage Systems SudsДокумент30 страницWat RM 08 Regulation of Sustainable Urban Drainage Systems SudsChris FindlayОценок пока нет
- HAazopДокумент35 страницHAazopSaravanan ElangovanОценок пока нет
- Math Sample Paper SolutionsДокумент12 страницMath Sample Paper Solutionskeshav bankaОценок пока нет
- Caline4 PrsentationДокумент16 страницCaline4 PrsentationIancovici Sasha100% (1)
- Environments Key Terms Matching ExerciseДокумент2 страницыEnvironments Key Terms Matching Exerciselisa langstonОценок пока нет
- The Impact of Environmental Pollution On HumanДокумент6 страницThe Impact of Environmental Pollution On HumanErdi 'Day' SidhartaОценок пока нет
- List of Clearances, Approvals Required For Power Projects in IndiaДокумент3 страницыList of Clearances, Approvals Required For Power Projects in Indiapandetarun100% (1)
- Products DatabaseДокумент104 страницыProducts DatabaseAlexОценок пока нет
- DrVinitha DhupkarДокумент35 страницDrVinitha DhupkarBajibabu ProdduturiОценок пока нет
- EMP-Umreth-Vasad & Kapadvanj-Ladvel PDFДокумент100 страницEMP-Umreth-Vasad & Kapadvanj-Ladvel PDFJasarat AtakishiyevОценок пока нет
- Ravenswood Business District Specific Plan Development ProjectsДокумент26 страницRavenswood Business District Specific Plan Development ProjectsAkin A. OkupeОценок пока нет
- Misamis Occidental Plans to Protect Aquamarine ResourceДокумент8 страницMisamis Occidental Plans to Protect Aquamarine ResourcejelosalisaliОценок пока нет