Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Common Metallurgical Defects in Ductile Iron English
Загружено:
edgarestevessАвторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Common Metallurgical Defects in Ductile Iron English
Загружено:
edgarestevessАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
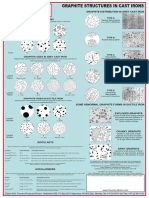
Common Metallurgical
Defects in Ductile Iron
Compacted Graphite
Exploded Graphite
Chunky Graphite
Spiky Graphite
Potential Causes:
Low residual magnesium and/or rare earth from
poor nodularisation practice, high temperatures
or long holding time.
Excess sulphur in the base iron not balanced
by sufficient magnesium.
Potential Causes:
Excess rare earth additions, particularly when high
purity charges are used. Normally found in thick
section castings or at higher carbon equivalents.
Potential Causes:
Excess rare earth additions, particularly when high
purity charges are used. Normally found in thick
section castings or at higher carbon equivalents.
Note that once the rare earth addition is reduced, it may
take time to dilute the residual rare earth in return metal,
particularly in induction melted iron.
Note that once the rare earth addition is reduced, it may
take time to dilute the residual rare earth in return metal,
particularly in induction melted iron.
Potential Causes:
Very small amounts of lead which have not been
neutralised by rare earths result in spiky graphite.
This has a catastrophic effect on mechanical
properties.
Bismuth, titanium and antimony can give similar
structures but can also be neutralised with rare
earths.
Flake Graphite
Surface Structure
Nodule Alignment
Carbides
Potential causes:
High carbon equivalent.
Excess pouring temperature.
Slow cooling rate in thicker sections.
Insufficient inoculation.
Potential causes:
Excess sulphur build-up in moulding sand.
This causes reversion to flake as the magnesium
in the iron reacts with the sulphur. The use of
higher magnesium / rare earth in the nodulariser or
a cerium containing inoculant can overcome this.
Potential causes:
Low carbon equivalent
Under inoculation causing growth of large
dendrites with nodules aligned between
arms of the dendrite.
High pouring temperature.
Potential causes:
Low carbon equivalent.
Excess magnesium and/or rare earth.
Carbide promoting elements such as Mn, Cr, V, Mo.
Insufficient inoculation.
Rapid cooling rate.
Irregular Graphite
Slag Inclusions
Shrinkage
Gas
Potential causes:
High holding temperature.
Long holding time which can result in "dead" irons.
Poor inoculation or excessive fading of inoculation.
Graphite shape may be improved by a late addition
of a powerful speciality inoculant.
Potential causes:
Inadequate slag control from pouring system.
Lack of slag traps or filter.
Low pouring temperature.
Excess additions of slag forming materials.
Turbulent mould filling.
Potential causes:
Insufficient mould strength causing dilation.
Inadequate feed metal available.
Poor gating design.
Excess magnesium.
Low carbon equivalent.
Under inoculation or over inoculation.
Gas holes are a totally separate subject and can be
influenced by melting procedures, metal handling,
refractory conditions, mould moisture, sand permeability,
core resins, hot spots near cores, slag handling, metal
temperature, base metal composition, mould venting,
Ti and Al contents amongst other sources.
Specialist advice should be sought in cases of gas once
the above have been investigated.
Graphite Flotation
The photomicrograph given here shows dendrite arms
growing inside a hydrogen pinhole.
Elkem produces a complete range of nodularisers and inoculants for the treatment
of ductile iron. MgFeSi alloys are available for applications such as sandwich treatments,
tundish cover ladles and flow through systems. They are graded so as to be suited
for different ladle sizes. Products for in-the-mould processes are also available.
Ultraseed inoculant is designed for pure Mg produced ductile iron, irons of low oxygen
and sulphur levels and dead iron which has been held for extended periods of time.
This inoculant will give high nodule counts in ductile iron which is normally difficult to
inoculate and will help to prevent micro-shrinkage.
Preseed is a powerful preconditioning agent for all cast irons to improve consistency in
melting and increase mechanical properties
Please refer to your local Elkem representative for further information on the range
of Elkem products for grey, compacted and ductile cast irons.
Ultraseed is a Registered Trademark of Elkem AS. Preseed is a trademark of Elkem AS.
Elkem AS, Foundry Products Division, Hoffsveien 65 b, P.O. Box 5211 Majorstua, N-0303 Oslo, Norway, www.foundry.elkem.com
Вам также может понравиться
- Technical InformationДокумент78 страницTechnical InformationCarlos Barrachina Martínez100% (2)
- ISO 9001:2015 Explained, Fourth Edition GuideДокумент3 страницыISO 9001:2015 Explained, Fourth Edition GuideiresendizОценок пока нет
- 26-ELKEM - Poster-Graphite Structures in Cast IronsДокумент1 страница26-ELKEM - Poster-Graphite Structures in Cast IronsSalvador Rocha100% (2)
- ELMAGДокумент2 страницыELMAGthomazfabricioОценок пока нет
- O HC HCДокумент101 страницаO HC HCIndustrial Infra Jobs100% (1)
- Chunky GraphiteДокумент16 страницChunky GraphitesachinguptachdОценок пока нет
- Seminar S.G IronДокумент32 страницыSeminar S.G Ironravikataria02Оценок пока нет
- Common Metallurgical Defects in Ductile Cast Iron PDFДокумент1 страницаCommon Metallurgical Defects in Ductile Cast Iron PDFsskiitb100% (2)
- Common Metallurgical Defects in Ductile Iron English (1Документ1 страницаCommon Metallurgical Defects in Ductile Iron English (1sateeshkori100% (2)
- SG Iron ProductionДокумент20 страницSG Iron ProductionShreyashri Nayak100% (1)
- MagnesiumДокумент3 страницыMagnesiumIsidoro LópezОценок пока нет
- Common Metallurgical Defects in Grey Iron English (1Документ1 страницаCommon Metallurgical Defects in Grey Iron English (1sateeshkori100% (2)
- SG Iron CompositionДокумент5 страницSG Iron CompositionamirgukharОценок пока нет
- Recovery of Magnesium in A Ductile Iron Process.: AbstractДокумент8 страницRecovery of Magnesium in A Ductile Iron Process.: AbstractJorge Prado DiazОценок пока нет
- Thermal Analysis Optimization of Gray and Ductile Iron ProductionДокумент18 страницThermal Analysis Optimization of Gray and Ductile Iron ProductionslagmercuryОценок пока нет
- Late Metal Stream InoculationДокумент2 страницыLate Metal Stream Inoculationarnaldorcr8646Оценок пока нет
- Elkem 13 Compacted Graphite IronДокумент2 страницыElkem 13 Compacted Graphite Ironmarcotulio123Оценок пока нет
- Shrinkage in Iron CastingsДокумент10 страницShrinkage in Iron CastingskarthikkandaОценок пока нет
- Surface Graphite Degeneration in Ductile Iron CastДокумент8 страницSurface Graphite Degeneration in Ductile Iron CastKhairul MuzafarОценок пока нет
- Sampling of Liquid Cast IronДокумент2 страницыSampling of Liquid Cast Ironarnaldorcr8646Оценок пока нет
- Partition of Slag Phases in The Treatment and Pouring of Ductile IronДокумент2 страницыPartition of Slag Phases in The Treatment and Pouring of Ductile Ironarnaldorcr8646Оценок пока нет
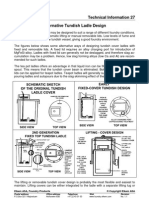
- Alternative Tundish Ladle DesignДокумент2 страницыAlternative Tundish Ladle Designarnaldorcr8646Оценок пока нет
- Selection of Inoculants For Grey Cast IronДокумент2 страницыSelection of Inoculants For Grey Cast Ironarnaldorcr8646Оценок пока нет
- KB Alloys Foundrymans Guide To SR and TiBorДокумент7 страницKB Alloys Foundrymans Guide To SR and TiBorfoundryjoeОценок пока нет
- Shrinkage in Ductile IronДокумент5 страницShrinkage in Ductile Ironkarthikkanda100% (1)
- 26-ELKEM Poster-Graphite Structures in Cast IronsДокумент1 страница26-ELKEM Poster-Graphite Structures in Cast IronsHOSSIENОценок пока нет
- Common Metallurgical Defects in Grey Cast Irons 2Документ1 страницаCommon Metallurgical Defects in Grey Cast Irons 2Rasool MohammadiОценок пока нет
- Effect of Bismuth in Ductile IronДокумент4 страницыEffect of Bismuth in Ductile Ironmarcotulio123100% (2)
- Elkem 10 Tundish Cover Ladle NodularizationДокумент2 страницыElkem 10 Tundish Cover Ladle Nodularizationmarcotulio123Оценок пока нет
- AFS Thermal Analysis of CupsДокумент12 страницAFS Thermal Analysis of Cupsyash_ganatraОценок пока нет
- FP240Документ28 страницFP240igorisakovОценок пока нет
- Effect of Minor and Trace Elements in Cast IronДокумент2 страницыEffect of Minor and Trace Elements in Cast IronsachinguptachdОценок пока нет
- Carbide Dissolution in Thin Wall Ductile Iron PDFДокумент8 страницCarbide Dissolution in Thin Wall Ductile Iron PDFsachinguptachdОценок пока нет
- Back to BASICS: Nitrogen fissures defects in iron castingsДокумент2 страницыBack to BASICS: Nitrogen fissures defects in iron castingsJustin DixonОценок пока нет
- Manganese, Sulfur and Manganese-Sulfur Ratio Effects in Gray Cast IronДокумент30 страницManganese, Sulfur and Manganese-Sulfur Ratio Effects in Gray Cast IronNetoОценок пока нет
- Fading of InoculationДокумент2 страницыFading of Inoculationarnaldorcr8646Оценок пока нет
- Tundish Cover Ladle Nodularization Technical InfoДокумент2 страницыTundish Cover Ladle Nodularization Technical InfoAnonymous iztPUhIiОценок пока нет
- Home About Us Products Quality Control Representation Useful Links Contact UsДокумент5 страницHome About Us Products Quality Control Representation Useful Links Contact Ustushak mОценок пока нет
- Casting Defect - Fissure DefectsДокумент3 страницыCasting Defect - Fissure Defectsvivek1312Оценок пока нет
- Effect of Minor and Trace Elements in Cast IronДокумент2 страницыEffect of Minor and Trace Elements in Cast IronsachinguptachdОценок пока нет
- Ductile Dross Formation MonitoringДокумент27 страницDuctile Dross Formation MonitoringsachinguptachdОценок пока нет
- Mapa MetalograficoДокумент1 страницаMapa MetalograficoBreno DellaОценок пока нет
- Elkem 07 Magnesiun Contents in Ductile IronДокумент2 страницыElkem 07 Magnesiun Contents in Ductile Ironmarcotulio123Оценок пока нет
- Lecture - Magnesium Alloys - Hue'sДокумент29 страницLecture - Magnesium Alloys - Hue'sMurali ManuОценок пока нет
- Oxidation of Ferrosilicon Alloys During StorageДокумент1 страницаOxidation of Ferrosilicon Alloys During Storagearnaldorcr8646Оценок пока нет
- Common Metallurgical Defects in Grey Cast IronДокумент9 страницCommon Metallurgical Defects in Grey Cast IronRolando Nuñez Monrroy100% (1)
- Factors Influencing The Recovery and Addition of MagnesiumДокумент4 страницыFactors Influencing The Recovery and Addition of Magnesiumarnaldorcr8646Оценок пока нет
- Magnesium Contents in Ductile IronДокумент2 страницыMagnesium Contents in Ductile Ironarnaldorcr8646Оценок пока нет
- Cold Mounting EnglishpdfДокумент6 страницCold Mounting EnglishpdfJorge BonillaОценок пока нет
- Compression MountingДокумент12 страницCompression MountingEden HazardОценок пока нет
- BCIRA Broadsheet 41Документ4 страницыBCIRA Broadsheet 41Justin Dixon100% (1)
- Ferroalloy Storage Bin DesignДокумент2 страницыFerroalloy Storage Bin Designarnaldorcr8646Оценок пока нет
- Introduction in Alloys and Influence of Elements: Alloys and Melting 01 - Alloys - and - Melting - EN - Docx 1/13Документ13 страницIntroduction in Alloys and Influence of Elements: Alloys and Melting 01 - Alloys - and - Melting - EN - Docx 1/13luisA1923Оценок пока нет
- Defects in Ductile IronДокумент12 страницDefects in Ductile IronSerdar çevikОценок пока нет
- 3 Inoculant Alloy CompositionДокумент2 страницы3 Inoculant Alloy CompositionAdams GodoyОценок пока нет
- GraphiteStructuresInCI PDFДокумент1 страницаGraphiteStructuresInCI PDFAnonymous B3I6zYNhqdОценок пока нет
- Cast Iron SolidificationДокумент12 страницCast Iron Solidificationkatchani123100% (1)
- 5 Mechanisms Graphite Nucleation Cast IronДокумент2 страницы5 Mechanisms Graphite Nucleation Cast Ironmarcotulio123Оценок пока нет
- Engineering Equipment for Foundries: Proceedings of the Seminar on Engineering Equipment for Foundries and Advanced Methods of Producing Such Equipment, Organized by the United Nations Economic Commission for EuropeОт EverandEngineering Equipment for Foundries: Proceedings of the Seminar on Engineering Equipment for Foundries and Advanced Methods of Producing Such Equipment, Organized by the United Nations Economic Commission for EuropeОценок пока нет
- Steam Turbine Theory and Practice by Kearton PDF 35Документ4 страницыSteam Turbine Theory and Practice by Kearton PDF 35KKDhОценок пока нет
- Accomplishment Report 2021-2022Документ45 страницAccomplishment Report 2021-2022Emmanuel Ivan GarganeraОценок пока нет
- Iso 9001 CRMДокумент6 страницIso 9001 CRMleovenceОценок пока нет
- August 03 2017 Recalls Mls (Ascpi)Документ6 страницAugust 03 2017 Recalls Mls (Ascpi)Joanna Carel Lopez100% (3)
- Column Array Loudspeaker: Product HighlightsДокумент2 страницыColumn Array Loudspeaker: Product HighlightsTricolor GameplayОценок пока нет
- SEO-Optimized Title for Python Code Output QuestionsДокумент2 страницыSEO-Optimized Title for Python Code Output QuestionsTaru GoelОценок пока нет
- Mission Ac Saad Test - 01 QP FinalДокумент12 страницMission Ac Saad Test - 01 QP FinalarunОценок пока нет
- Software Requirements Specification: Chaitanya Bharathi Institute of TechnologyДокумент20 страницSoftware Requirements Specification: Chaitanya Bharathi Institute of TechnologyHima Bindhu BusireddyОценок пока нет
- Wi FiДокумент22 страницыWi FiDaljeet Singh MottonОценок пока нет
- Energy AnalysisДокумент30 страницEnergy Analysisca275000Оценок пока нет
- CAS-GEC04 Module11 Food-SecurityДокумент6 страницCAS-GEC04 Module11 Food-SecurityPermalino Borja Rose AnneОценок пока нет
- Complete Guide To Sports Training PDFДокумент105 страницComplete Guide To Sports Training PDFShahana ShahОценок пока нет
- Reader's Digest (November 2021)Документ172 страницыReader's Digest (November 2021)Sha MohebОценок пока нет
- Three-D Failure Criteria Based on Hoek-BrownДокумент5 страницThree-D Failure Criteria Based on Hoek-BrownLuis Alonso SAОценок пока нет
- ABP - IO Implementing - Domain - Driven - DesignДокумент109 страницABP - IO Implementing - Domain - Driven - DesignddoruОценок пока нет
- BPL Millipacs 2mm Hardmetrics RarДокумент3 страницыBPL Millipacs 2mm Hardmetrics RarGunter BragaОценок пока нет
- Iq TestДокумент9 страницIq TestAbu-Abdullah SameerОценок пока нет
- Trading As A BusinessДокумент169 страницTrading As A Businesspetefader100% (1)
- FINAL A-ENHANCED MODULES TO IMPROVE LEARNERS - EditedДокумент22 страницыFINAL A-ENHANCED MODULES TO IMPROVE LEARNERS - EditedMary Cielo PadilloОценок пока нет
- Bharhut Stupa Toraa Architectural SplenДокумент65 страницBharhut Stupa Toraa Architectural Splenအသွ်င္ ေကသရОценок пока нет
- Traffic LightДокумент19 страницTraffic LightDianne ParОценок пока нет
- Decision Maths 1 AlgorithmsДокумент7 страницDecision Maths 1 AlgorithmsNurul HafiqahОценок пока нет
- Evolution of Bluetooth PDFДокумент2 страницыEvolution of Bluetooth PDFJuzerОценок пока нет
- Cold Rolled Steel Sections - Specification: Kenya StandardДокумент21 страницаCold Rolled Steel Sections - Specification: Kenya StandardPEng. Tech. Alvince KoreroОценок пока нет
- Clark DietrichДокумент110 страницClark Dietrichikirby77Оценок пока нет
- Lecture Ready 01 With Keys and TapescriptsДокумент157 страницLecture Ready 01 With Keys and TapescriptsBảo Châu VươngОценок пока нет
- UNIT FOUR: Fundamentals of Marketing Mix: - Learning ObjectivesДокумент49 страницUNIT FOUR: Fundamentals of Marketing Mix: - Learning ObjectivesShaji ViswambharanОценок пока нет
- TDS Sibelite M3000 M4000 M6000 PDFДокумент2 страницыTDS Sibelite M3000 M4000 M6000 PDFLe PhongОценок пока нет
- PandPofCC (8th Edition)Документ629 страницPandPofCC (8th Edition)Carlos Alberto CaicedoОценок пока нет