Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Apomixis
Загружено:
Pralex PrajapatiАвторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Apomixis
Загружено:
Pralex PrajapatiАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Apomixis
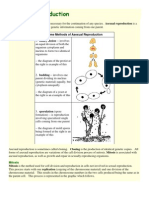
Apomixis is derived from Greek, where "APO" means away from and "mixis" means acts of mingling or mixing.
Generally, apomixis represents the occurence of a different sexual reproductive process in place of normal sexual
processes
which
involves
reduction
division
and
fertilization.
Apomixis is widely seen in higher plants. More 300 species of plants which belong to 35 families show apomixis.
Some of the families where apomixis is seen is gramineae, compositae, rosaceae and rutaceae. Some common
plants
like
maize,
wheat
and
pearl
millet
have
realtives
showing
apomixis.
Hans winkler in 1908 defined it as the substitute process for sexual reproduction or another sexual reproductive
process
and
it
does
not
involve
nuclear
or
cellular
fusion.
Apomixis can help to maintain favorable traits for the survival of an individual but in the linger-time process of
evolution it eliminates the advantage of biparental inheritance.
Definition
Apomixis is defined as the type of sexual reproductive process in which organs or related sexual structures take
part in the process other but there is formation of seeds without the union of gametes.
Apomixis is a process of reproduction by special generative tissues without fertilization in which the generative
tissues can be a sporophytes or gametophyte.
Types of Apomixis
There are four types of apomixis suggested by Maheshwari in 1954.
Recurrent Apomixis
In recurrent apomixis, an embryosac is developed from the megaspore mother cell.
The egg-cell is diploid and the embryo is also diploid.
The embryo-sac develops directly without the process of fertilization.
Some processes like diploid parthenogenesis, diploid apogamy and somatic apospory are recurrent
apomixis.
Diploid parthenogenesis occurs in somatic embryo sacs.
Some of the species which show recurrent apomixis are species of blue grass, onion, and apple.
Non-recurrent apomixis
Non-recurrent apomixis is where an embryo arises directly from a normal egg-cell without the process of
fertilization.
Egg cells is haploid and hence, the resulting embryo is also haploid.
Non-recurrent apomixis includes haploid parthenogenesis, haploid apogamy and adrogamy.
These types of apomixis are rare and are of genetic interest.
Adventive embryony
In adventive embryony, the embryo arises from a cell or a group of cells in the nucleus or in the
integuments. Example - Oranges and roses.
This process takes place in the embryo sac and is regenerated with accuracy.
In addition to adventive embryony process, regular embryo within the embryo sac may also develop
simultaneously resulting in poly-embryony condition.
Example - Citrus, Oputnia.
Vegetative apomixis
In some plants like Poa bulbosa, some Allium, Agave and some grass species, vegetative buds are
produced instead of flowers in the inflorescence.
They can be reproduced without difficulty.
Agamospermy
Agamospermy is process of asexual seed formation, this occurs in flowering plants in many different mechanisms.
Three types of agamospermy exists:
Diplospory is where the dilpoid embryo-sace or the mother cell develops directly into an embryo by the
process known as parthenogenesis.
Apospory is where the embryo is orginated from somatic cell from the surrounding embryo sac mother
cell.
In the above types of agamospermy there is development of gametophyte but there is no meiotic division. Hence, it
is known as gametophytic apomixis.
Adventitious embryony is a type of agamospermy where there is no development of gametophytes. The
embryo is formed from cells of the diploid sporophyte like the integument.
Advantages of Apomixis
The self and cross fertilization processes results in alteration of the genetic composition of plants. Plants bred
through apomixis tend to conserve the genetic structure of their carriers. They can maintain the advantages of
heterozygosity generation after generation. Such a process might offer great advantage in plant breeding where
genetic uniformity can be maintained over generations.
The benefits of apomixis in plant breeding are:
Apomixis results in rapid multiplication genetically similar individuals without risk of segregation.
Heterosis or hybrid vigour can be maintained permanently in crop plants.
There can be efficient exploitation of maternal effect from generation to generation.
Homozygous inbred lines can be rapidly developed as they produce sectors of diploid tissues and
occasional fertile gametes and seeds.
Вам также может понравиться
- Plant and Animal Reproduction 1Документ15 страницPlant and Animal Reproduction 1Ojok Jod100% (1)
- Animals and Plant ReproductionДокумент56 страницAnimals and Plant ReproductionZyan Subaan VacioОценок пока нет
- Techniques Managing StressДокумент6 страницTechniques Managing StressPralex PrajapatiОценок пока нет
- The Phenomenon of ManДокумент12 страницThe Phenomenon of ManPaul Schumann83% (6)
- Classification of FungiДокумент5 страницClassification of FungiSoumit PaulОценок пока нет
- Pollinator Monitoring for Citizen Scientists: A HandbookОт EverandPollinator Monitoring for Citizen Scientists: A HandbookОценок пока нет
- Reproduction of FungiДокумент4 страницыReproduction of FungiVargheseОценок пока нет
- NEBOSH 2007 Jul AllДокумент17 страницNEBOSH 2007 Jul AllRobertProsser19100% (8)
- Microb Monitor 2 Instructions UseДокумент5 страницMicrob Monitor 2 Instructions UseArluky NovandyОценок пока нет
- ApomixisДокумент6 страницApomixisGrt grtОценок пока нет
- ApomixisДокумент6 страницApomixisYekitaSОценок пока нет
- Apomixis - AgrobiosДокумент6 страницApomixis - AgrobiosSripathy KudekalluОценок пока нет
- Class Note (Botany Department) G.P. Women's CollegeДокумент2 страницыClass Note (Botany Department) G.P. Women's CollegeningthoujamsanjayОценок пока нет
- ApomixisДокумент3 страницыApomixisAnonymous yKjxyeLОценок пока нет
- Asexual ReproductionДокумент13 страницAsexual Reproductionkritishaa8100Оценок пока нет
- Asexual ReproductionДокумент3 страницыAsexual ReproductionmohangeneОценок пока нет
- Apomixis Types Definition and AdvantagesДокумент4 страницыApomixis Types Definition and AdvantagesAditya AroraОценок пока нет
- Apomixis Molecular Life of PlantsДокумент3 страницыApomixis Molecular Life of Plantspedro antonioОценок пока нет
- Perpetuation of LifeДокумент48 страницPerpetuation of LifeKimberly Jean EstoqueОценок пока нет
- Comparison of Sexual and Asexual Reproduction Notes in GeneticsДокумент12 страницComparison of Sexual and Asexual Reproduction Notes in GeneticsJestoni BigaelОценок пока нет
- Asexual Reproduction - WikipediaДокумент70 страницAsexual Reproduction - WikipediamacnauldyОценок пока нет
- Apomixis and Its Application in Crop Improvement 2Документ19 страницApomixis and Its Application in Crop Improvement 2shaileshmedicalОценок пока нет
- Asexual Reproduction: An Overview of Key Methods and AdvantagesДокумент11 страницAsexual Reproduction: An Overview of Key Methods and AdvantageskierraleeОценок пока нет
- Plant ReproductionДокумент8 страницPlant ReproductionayanurhidayahОценок пока нет
- Perpetuation of LifeДокумент40 страницPerpetuation of LifeDionne MagnoОценок пока нет
- AsexuAL ReproductionДокумент21 страницаAsexuAL Reproductionkiller_xd09Оценок пока нет
- Types of Reproductive System 2Документ15 страницTypes of Reproductive System 2cristin ungabОценок пока нет
- Modes of ReproductionДокумент33 страницыModes of ReproductionMohaajanan AliОценок пока нет
- Reproduction in Organisms: Hydra and Yeast Chlamydomonas PenicilliumДокумент4 страницыReproduction in Organisms: Hydra and Yeast Chlamydomonas PenicilliumRishi Rao AОценок пока нет
- Ms. Ma. Lourdes S. De BelenDate: March 15, 2022Документ4 страницыMs. Ma. Lourdes S. De BelenDate: March 15, 2022DennisОценок пока нет
- 441 PDFДокумент10 страниц441 PDFFatkurОценок пока нет
- 1 Reproduction in OrganismsДокумент4 страницы1 Reproduction in Organismsis-hakОценок пока нет
- Mode of Reproduction in PlantsДокумент3 страницыMode of Reproduction in PlantsBik BokОценок пока нет
- BIOLOGYДокумент5 страницBIOLOGYRavindraОценок пока нет
- Asexual Reproduction: Cloning and ParthenogenesisДокумент10 страницAsexual Reproduction: Cloning and ParthenogenesisIsmi DahariОценок пока нет
- Modes of ReproductionДокумент4 страницыModes of ReproductionSherilyn ApostolОценок пока нет
- Life Science Module 5 Lesson 1 and 2Документ69 страницLife Science Module 5 Lesson 1 and 2Mae AlfaroОценок пока нет
- Asexual ReproductionДокумент12 страницAsexual ReproductionROWELL LEGASОценок пока нет
- Apomixis Final Ppt-1Документ19 страницApomixis Final Ppt-1SS Rajput100% (2)
- Asexual reproduction methods and typesДокумент8 страницAsexual reproduction methods and typesshehzad AhmedОценок пока нет
- ReproB21Документ33 страницыReproB21SeptiОценок пока нет
- Biology Revision AssignmentДокумент14 страницBiology Revision AssignmentKrishna GovilОценок пока нет
- NEET Biology Reproduction NotesДокумент8 страницNEET Biology Reproduction NotesShubham Aggarwal0% (1)
- Asexual ReproductionДокумент2 страницыAsexual ReproductionShubham SinghОценок пока нет
- Thebiologyprimer Com Plant Reproduction - Text Plant 20reproduction 20is 20the 20production Unique 20from 20the 20parent 20plantsДокумент4 страницыThebiologyprimer Com Plant Reproduction - Text Plant 20reproduction 20is 20the 20production Unique 20from 20the 20parent 20plantsJayce JaxОценок пока нет
- 4Q - Animal Forms Functions 1 - ReproductionДокумент41 страница4Q - Animal Forms Functions 1 - ReproductionMaymayОценок пока нет
- Chapter-8-How Do Organisms ReproduceДокумент8 страницChapter-8-How Do Organisms Reproduceapi-400692183Оценок пока нет
- Biology GeneticsДокумент25 страницBiology GeneticsEsther OlabodeОценок пока нет
- The Reproductive Process: James L, General Biology I (MF009) Foundation in ScienceДокумент30 страницThe Reproductive Process: James L, General Biology I (MF009) Foundation in SciencePikuОценок пока нет
- Apomixis and PolyembryonyДокумент8 страницApomixis and PolyembryonyTushar NathОценок пока нет
- Genbio2 q2 Mod1.1 Reproduction-And-DevelopmentДокумент9 страницGenbio2 q2 Mod1.1 Reproduction-And-DevelopmentHazel AbitriaОценок пока нет
- Reproduction in OrganismsДокумент53 страницыReproduction in OrganismsGopan K GОценок пока нет
- How Organisms Reproduce - Asexual vs Sexual ReproductionДокумент8 страницHow Organisms Reproduce - Asexual vs Sexual ReproductionRishu KaulОценок пока нет
- How Organisms Reproduce: Asexual vs SexualДокумент4 страницыHow Organisms Reproduce: Asexual vs SexualNilkanth PatelОценок пока нет
- Modes of Plant ReproductionДокумент5 страницModes of Plant ReproductionSandeep638Оценок пока нет
- How Do Organisms Reproduce: Chapter - 8Документ8 страницHow Do Organisms Reproduce: Chapter - 8Piyusha MhaiskeyОценок пока нет
- CH 1 ReproductionДокумент9 страницCH 1 ReproductionSandesh RОценок пока нет
- Reproduction in Organisms: o o o o o 5Документ2 страницыReproduction in Organisms: o o o o o 5Abdul SamiОценок пока нет
- Army Public School Gopalpur: Class-Xii Science Subject - Biology Chapter-1 Reproduction in Organisms NotesДокумент5 страницArmy Public School Gopalpur: Class-Xii Science Subject - Biology Chapter-1 Reproduction in Organisms NotesAshok KumarОценок пока нет
- VegetativeДокумент1 страницаVegetativeRaymond LeabresОценок пока нет
- ApomixisДокумент42 страницыApomixisDeepak MewarОценок пока нет
- CBSE NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Biology Chapter 1: Back of Chapter QuestionsДокумент7 страницCBSE NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Biology Chapter 1: Back of Chapter QuestionsSatvik MishraОценок пока нет
- NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Biology Reproduction in OrganismsДокумент5 страницNCERT Solutions For Class 12 Biology Reproduction in OrganismsAnonymous XuiUo2ThОценок пока нет
- Quality Control of Cosmetics: Case of Baby Wipes Sold in YaoundeДокумент6 страницQuality Control of Cosmetics: Case of Baby Wipes Sold in YaoundePralex PrajapatiОценок пока нет
- Biology 2016 Unsloved Paper Outside DelhiДокумент5 страницBiology 2016 Unsloved Paper Outside DelhiPralex PrajapatiОценок пока нет
- Iso 21322 2020Документ12 страницIso 21322 2020Pralex PrajapatiОценок пока нет
- Non-Woven Disposable Wet Wipes - Specification: Kenya Standard DKS 2720Документ11 страницNon-Woven Disposable Wet Wipes - Specification: Kenya Standard DKS 2720Pralex PrajapatiОценок пока нет
- Human Reproduction and Embryonic Development (Recovered) PDFДокумент36 страницHuman Reproduction and Embryonic Development (Recovered) PDFPralex PrajapatiОценок пока нет
- MESOZOAДокумент7 страницMESOZOAPralex PrajapatiОценок пока нет
- Biotechnology and Its ApplicationsДокумент10 страницBiotechnology and Its ApplicationsAlok YadavОценок пока нет
- Food and Drug Administration 7329.001: Compliance Program Guidance ManualДокумент45 страницFood and Drug Administration 7329.001: Compliance Program Guidance ManualPralex PrajapatiОценок пока нет
- Aac Block Quotation For Rohtak Haryana PDFДокумент1 страницаAac Block Quotation For Rohtak Haryana PDFPralex Prajapati100% (1)
- Biology 2012 Unsloved Paper Outside DelhiДокумент5 страницBiology 2012 Unsloved Paper Outside DelhiPralex PrajapatiОценок пока нет
- Food Sources of VitaminДокумент3 страницыFood Sources of VitaminPralex PrajapatiОценок пока нет
- Biotechnology and Its ApplicationsДокумент10 страницBiotechnology and Its ApplicationsAlok YadavОценок пока нет
- MESOZOAДокумент7 страницMESOZOAPralex PrajapatiОценок пока нет
- Biology 2013 Unsloved Paper Outside DelhiДокумент5 страницBiology 2013 Unsloved Paper Outside DelhiPralex PrajapatiОценок пока нет
- Biology 2014 Unsloved Paper Outside DelhiДокумент6 страницBiology 2014 Unsloved Paper Outside DelhiPralex PrajapatiОценок пока нет
- Characteristics of Phylum Porifera (Sponges)Документ15 страницCharacteristics of Phylum Porifera (Sponges)Pralex PrajapatiОценок пока нет
- Biology 2015 Unsloved Paper Outside DelhiДокумент5 страницBiology 2015 Unsloved Paper Outside DelhiPralex PrajapatiОценок пока нет
- Economic ImpДокумент10 страницEconomic ImpPralex PrajapatiОценок пока нет
- ObeliaДокумент7 страницObeliaPralex PrajapatiОценок пока нет
- Characteristics of Phylum Porifera (Sponges)Документ15 страницCharacteristics of Phylum Porifera (Sponges)Pralex PrajapatiОценок пока нет
- LF Vitamins PDFДокумент2 страницыLF Vitamins PDFAgogi_IthosОценок пока нет
- Characteristics of Phylum Porifera (Sponges)Документ15 страницCharacteristics of Phylum Porifera (Sponges)Pralex PrajapatiОценок пока нет
- Economic ImpДокумент10 страницEconomic ImpPralex PrajapatiОценок пока нет
- Plant KingdomДокумент36 страницPlant KingdomPralex PrajapatiОценок пока нет
- Plant KingdomДокумент36 страницPlant KingdomPralex PrajapatiОценок пока нет
- Plant KingdomДокумент36 страницPlant KingdomPralex PrajapatiОценок пока нет
- Plant KingdomДокумент36 страницPlant KingdomPralex PrajapatiОценок пока нет
- Modern Theory On Origin of LifeДокумент13 страницModern Theory On Origin of LifeNorberto R. BautistaОценок пока нет
- KINGDOM ANIMALIA CharacteristicsДокумент7 страницKINGDOM ANIMALIA CharacteristicsPralex PrajapatiОценок пока нет
- Anthropology - Test - Series - Chapter WiseДокумент7 страницAnthropology - Test - Series - Chapter Wisedhivya sankarОценок пока нет
- Activity 5 Type of Root SystemДокумент2 страницыActivity 5 Type of Root SystemPreiy Julian De GuiaОценок пока нет
- Learning Activity Sheet: SUBJECT: Earth and Life Science Mastery Test For Quarter 2 - Week 1&2Документ1 страницаLearning Activity Sheet: SUBJECT: Earth and Life Science Mastery Test For Quarter 2 - Week 1&2Kiara Ash BeethovenОценок пока нет
- Brochure For MapehДокумент4 страницыBrochure For MapehKarl Anthony SuarezОценок пока нет
- NM Annual Report 2011Документ68 страницNM Annual Report 2011Ni ÑoОценок пока нет
- Writing An Organic Chemistry Filename: Writing An Organic Chemistry Lab ReportДокумент6 страницWriting An Organic Chemistry Filename: Writing An Organic Chemistry Lab ReportNikon SinghОценок пока нет
- Kabole 2023Документ12 страницKabole 2023Omoding EmmanuelОценок пока нет
- Assignment 1 BI 602Документ6 страницAssignment 1 BI 602Eneah NaicavacavaОценок пока нет
- East Coast Q3 2014 Letter - Grove of TitansДокумент16 страницEast Coast Q3 2014 Letter - Grove of TitansCanadianValue100% (1)
- Methodology of IAD FrameworkДокумент3 страницыMethodology of IAD FrameworkAna Lalaguna - VargasОценок пока нет
- Hospital Patient Data in HCU RoomДокумент108 страницHospital Patient Data in HCU RoomSri Ratna FitriadewiОценок пока нет
- Concept Strengthening Sheet (CSS-01) Based On AIATS-01 RMДокумент19 страницConcept Strengthening Sheet (CSS-01) Based On AIATS-01 RMB54 Saanvi SinghОценок пока нет
- Palaeopathology and Diagenesis An SEM Evaluation of Structural Changes Using Backscattered Electron ImagingДокумент18 страницPalaeopathology and Diagenesis An SEM Evaluation of Structural Changes Using Backscattered Electron ImagingLucas RossiОценок пока нет
- Interpretation of Histograms and Peripheral Smear FindingsДокумент5 страницInterpretation of Histograms and Peripheral Smear FindingsrezqiОценок пока нет
- Cadmium Tolerance in Schinus Molle Trees Is Modulated by Enhanced Leaf Anatomy and PhotosynthesisДокумент8 страницCadmium Tolerance in Schinus Molle Trees Is Modulated by Enhanced Leaf Anatomy and PhotosynthesisPaulinho TemoteoОценок пока нет
- What is an echinoderm? Key featuresДокумент18 страницWhat is an echinoderm? Key featuresisuru PereraОценок пока нет
- Complete Blood Count and Biochemistry Panel ResultsДокумент8 страницComplete Blood Count and Biochemistry Panel Resultsgunjan pratapОценок пока нет
- Cardiology Ebook Notes PDFДокумент26 страницCardiology Ebook Notes PDFsugisweОценок пока нет
- English 2 Class 02Документ23 страницыEnglish 2 Class 02Bill YohanesОценок пока нет
- Papyrus: The Paper Plant ... Oldest Paper in HistoryДокумент7 страницPapyrus: The Paper Plant ... Oldest Paper in Historynoura_86Оценок пока нет
- Sticky Trap Monitoring of Insect Pests: Steve H. DreistadtДокумент8 страницSticky Trap Monitoring of Insect Pests: Steve H. DreistadtBryan AbarcaОценок пока нет
- Timetable LECTURESДокумент4 страницыTimetable LECTURESRebeccaОценок пока нет
- Behaviour and Ecology of Riparian MammalsДокумент402 страницыBehaviour and Ecology of Riparian MammalsRafael WolfОценок пока нет
- Botany Practical 2022newДокумент21 страницаBotany Practical 2022newSidhОценок пока нет
- Mutah UniversityДокумент13 страницMutah UniversityeyassadailehОценок пока нет
- MIB7Документ6 страницMIB7BLОценок пока нет
- Microbiology List of BooksДокумент3 страницыMicrobiology List of BooksMoazAdelОценок пока нет