Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Bungee Jump: Phases of Motion: Phase 1 - Freefall
Загружено:
Dicky DjayadiИсходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Bungee Jump: Phases of Motion: Phase 1 - Freefall
Загружено:
Dicky DjayadiАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
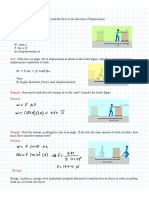
Bungee Jump: Phases of motion
Figures shown are approximate, and based loosely on the Verzasca dam bungee jump from GoldenEye, ignoring loss
of energy from the system due to air resistance, heat, transverse motion (in reality bungee jumpers end up swinging
sideways, which reduces vertical speed).
Note: Displacement, velocity and acceleration values are given as positive in the downwards direction.
Beginning:
Displacement
(min)
increasing
Velocity
increasing
Acceleration
.
constant
GPE
(max)
decreasing
KE
(min)
increasing
EPE
(min)
constant
Phase 1 - Freefall: At the start, the jumper is stationary, and the cord is slack, so all energy is in the form of
gravitational potential. The only force acting is his own weight, hence his acceleration is simply that due to gravity.
During this phase, GPE is being converted directly to KE.
Cord becomes taut:
Displacement
increasing
Velocity
increasing
Acceleration
.
decreasing
GPE
decreasing
KE
increasing
EPE
(min)
increasing
Phase 2 Cord taut, still accelerating: At the instant the cord becomes taut, nearly halfway down, the jumper is
travelling at around , but he is still accelerating (albeit not as rapidly as when in freefall). Nearly half of the
GPE has now been converted into KE, but during this phase GPE will go increasingly into EPE, meaning KE will not
increase as fast as before. The resultant force will still be downwards, as the tension is not as great as the weight.
Max speed:
Displacement
increasing
Velocity
(max)
decreasing
Acceleration
decreasing
GPE
decreasing
KE
(max)
Decreasing
EPE
increasing
Phase 3 Slowing down: Eventually the upward force of tension will exceed the weight, and his downward speed
will begin to drop at last. From now on, energy is being transferred from both GPE and KE to EPE due to the increased
tension in the bungee cord.
Lowest point:
Displacement
(max)
decreasing
Velocity
decreasing
Acceleration
(min)
Increasing
GPE
(min)
increasing
KE
(min)
Increasing
EPE
(max)
decreasing
Phase 4 Bouncing back:
At the lowest point, all GPE and KE has been transferred to EPE. Since the cord is at maximum extension, the
acceleration is now the greatest it will be at any point during the jump, but it is still acting in the upwards direction.
However, since the jumper has lost all downward speed by this point, rather than falling downwards more and more
slowly, he will begin travelling upwards faster and faster. The reverse journey is identical in all respects except the
direction of velocity and acceleration. His maximum speed will be reached once again, for instance, at the same
point (where tension equals weight, giving zero acceleration), but this time he will be travelling up instead of down.
He should end up exactly back at the starting point with zero speed and a slack rope.
Note that due to the inefficiency of this system in real life (see disclaimer at the top!) a jumper wont quite reach
their original height.
Вам также может понравиться
- Question 1060Документ65 страницQuestion 1060Shaikh Usman AiОценок пока нет
- Fluidization 1Документ8 страницFluidization 1Abdul RehmanОценок пока нет
- Materials and Hardware: Gas Turbine EngineДокумент12 страницMaterials and Hardware: Gas Turbine Enginepranav dixitОценок пока нет
- Sample Problems: Potential EnergyДокумент18 страницSample Problems: Potential EnergyJet TejadaОценок пока нет
- Stratosphere Rainbows End ReportДокумент6 страницStratosphere Rainbows End ReportBenedick CruzОценок пока нет
- Lecture 9Документ32 страницыLecture 9HamzahОценок пока нет
- Unit 1: Conservation Laws: Energy ReviewДокумент19 страницUnit 1: Conservation Laws: Energy ReviewbevinjОценок пока нет
- Physics 3Документ2 страницыPhysics 3Jeff BrownОценок пока нет
- Conservation of Energy LabДокумент9 страницConservation of Energy LabTyler50% (2)
- Physics Problem Based Learning (PBL) : DATE: 19/7/2016 TIME: 10:30 A.M. Place: Bt3 PPST Group No.: 4Документ27 страницPhysics Problem Based Learning (PBL) : DATE: 19/7/2016 TIME: 10:30 A.M. Place: Bt3 PPST Group No.: 4dopeОценок пока нет
- Lesson 1 - Kinetic and Gravitational Potential EnergyДокумент20 страницLesson 1 - Kinetic and Gravitational Potential EnergyMouli MishraОценок пока нет
- Roller Coaster PhysicsДокумент157 страницRoller Coaster Physicszzz_monster100% (2)
- Atg Some Ref Notes From SomewhereДокумент34 страницыAtg Some Ref Notes From SomewhereGirish SreeneebusОценок пока нет
- Physique BalanoireДокумент3 страницыPhysique BalanoireRocky KumarОценок пока нет
- Chapter 03 ThermodynamicsДокумент345 страницChapter 03 Thermodynamicsnt83% (6)
- Motion of A Simple Pendulum in A FluidДокумент16 страницMotion of A Simple Pendulum in A FluidGokul JeevaОценок пока нет
- Motion in A Vertical CircleДокумент2 страницыMotion in A Vertical CircleExpertsmindEduОценок пока нет
- Experiment 4 Work Power and EnergyДокумент3 страницыExperiment 4 Work Power and EnergyAllen ZafraОценок пока нет
- 9I Forces & Motion Year 9 NotesДокумент100 страниц9I Forces & Motion Year 9 Notesebrahimb5253Оценок пока нет
- Conservation of Energy, It Is Not Created or DestroyedДокумент2 страницыConservation of Energy, It Is Not Created or DestroyedeisengreenОценок пока нет
- File 46392Документ8 страницFile 46392khangsiean89Оценок пока нет
- Thermodynamics: Equilibrium StateДокумент7 страницThermodynamics: Equilibrium Statemukesh3021Оценок пока нет
- What Is A Conservative Force?Документ2 страницыWhat Is A Conservative Force?Alfred ThomasОценок пока нет
- As Lecture 2Документ4 страницыAs Lecture 2Ujjal Kumar DeyОценок пока нет
- WorkДокумент6 страницWorkjoei ArqueroОценок пока нет
- Law of Conservation of EnergyДокумент25 страницLaw of Conservation of EnergyJireh Ann Mejino100% (1)
- Phys10.02 Expt5 - Conservation of EnergyДокумент7 страницPhys10.02 Expt5 - Conservation of EnergyKenneth BagayasОценок пока нет
- Simple Harmonic Motion, In: Physics Movement EquilibriumДокумент3 страницыSimple Harmonic Motion, In: Physics Movement EquilibriumLyka LykaОценок пока нет
- Mastering Physics - Energy LabДокумент9 страницMastering Physics - Energy Labpalparas100% (1)
- AP Physics: - Gravity WrapupДокумент11 страницAP Physics: - Gravity WrapupCash Cash CashОценок пока нет
- EnergyДокумент33 страницыEnergyapi-3755159100% (1)
- Case Study 14 - Moment of InertiaДокумент5 страницCase Study 14 - Moment of Inertiamushroom0320Оценок пока нет
- Makalah Visual Basic LoopДокумент13 страницMakalah Visual Basic LoopNely UlwiyatiОценок пока нет
- Fluid MechanicsДокумент9 страницFluid MechanicsRegineDagumanFuellasОценок пока нет
- 6 Further Mechanics StudentДокумент30 страниц6 Further Mechanics StudenthuzaОценок пока нет
- RW Ism CH05Документ48 страницRW Ism CH05Ali KozbarОценок пока нет
- Physics For Future Presidents LectureДокумент41 страницаPhysics For Future Presidents LectureJohn CrawfordОценок пока нет
- Physics - WorkДокумент11 страницPhysics - WorkMohammed HassaanОценок пока нет
- G9, 1.3 Forces and MovementДокумент5 страницG9, 1.3 Forces and MovementKinmokusei MyoeОценок пока нет
- Simple Harmonic Motion Mass On SpringДокумент35 страницSimple Harmonic Motion Mass On SpringHisyamAl-Muhammadi100% (1)
- Work, Pe, Ke, GpeДокумент28 страницWork, Pe, Ke, GpeRoscela Mae D. ArizoОценок пока нет
- Physics in Bungee JumpingДокумент9 страницPhysics in Bungee JumpingSamantha Maye EspigaОценок пока нет
- EMMERSON PULLEN - 03.07 Forms of Energy AdvДокумент2 страницыEMMERSON PULLEN - 03.07 Forms of Energy AdvEmme PullenОценок пока нет
- Factors Affecting The Time Period of A Simple PendulumДокумент32 страницыFactors Affecting The Time Period of A Simple PendulumLow Ban HengОценок пока нет
- E201: Work, Energy and Power PALERO JR., Dante MДокумент5 страницE201: Work, Energy and Power PALERO JR., Dante MRamnuj Orecul SoralcОценок пока нет
- Energy Skate ParkДокумент3 страницыEnergy Skate Parkapi-339130050Оценок пока нет
- Complete Igcse Physics PPT CompilationДокумент185 страницComplete Igcse Physics PPT CompilationKareem Elhag100% (4)
- NASA: Calculation1Документ2 страницыNASA: Calculation1NASAdocumentsОценок пока нет
- Ballistic PendulumДокумент9 страницBallistic Pendulumapi-286681510Оценок пока нет
- Statistical Methods in ANNДокумент42 страницыStatistical Methods in ANNelakkadanОценок пока нет
- Artificial Neural NetworksДокумент20 страницArtificial Neural NetworksSreerag Kunnathu SugathanОценок пока нет
- Cheat SheetДокумент2 страницыCheat SheetAnush UnanyanОценок пока нет
- Lesson 12: Electric Potential Energy & VoltageДокумент3 страницыLesson 12: Electric Potential Energy & Voltage140557Оценок пока нет
- Physics FileДокумент4 страницыPhysics FileMaria Socorro Salas VergaraОценок пока нет
- As Level Chapter 5 NotesДокумент17 страницAs Level Chapter 5 NotesVivehaОценок пока нет
- Hydrodynamic Levitation ExplainedДокумент1 страницаHydrodynamic Levitation Explainedl MemoirОценок пока нет
- PHYS101 Lesson10 Momentum Part 2Документ40 страницPHYS101 Lesson10 Momentum Part 2Kyla LoonОценок пока нет
- Physics GRD 12 Wonderland Sky RiderДокумент5 страницPhysics GRD 12 Wonderland Sky RiderHell Razer100% (7)
- FE1073 C1 Formal ReportДокумент9 страницFE1073 C1 Formal ReportDicky DjayadiОценок пока нет
- Bila Komputer Ditinggal MudikДокумент1 страницаBila Komputer Ditinggal MudikDicky DjayadiОценок пока нет
- FE1073-C1 Resultants and Equilibrium of Forces - May 2014 PDFДокумент13 страницFE1073-C1 Resultants and Equilibrium of Forces - May 2014 PDFDicky DjayadiОценок пока нет
- Civil Engineering Contracts, 2nd Edition Practice and ProcedureДокумент1 страницаCivil Engineering Contracts, 2nd Edition Practice and ProcedureDicky DjayadiОценок пока нет
- Letter of UndertakingДокумент1 страницаLetter of UndertakingDicky DjayadiОценок пока нет
- CV2016-Illustration of Table 3-2Документ1 страницаCV2016-Illustration of Table 3-2Dicky DjayadiОценок пока нет
- ToD FullДокумент95 страницToD FullDicky DjayadiОценок пока нет
- GC0001 ABCC 2010 12 004 - WilmarДокумент24 страницыGC0001 ABCC 2010 12 004 - WilmarDicky DjayadiОценок пока нет
- ML0001-Career Management Handout 3Документ5 страницML0001-Career Management Handout 3Dicky DjayadiОценок пока нет
- CV2015 - Tut 5 Q - Specific Energy (1) - Critical Depth & HumpsДокумент1 страницаCV2015 - Tut 5 Q - Specific Energy (1) - Critical Depth & HumpsDicky DjayadiОценок пока нет
- EE1002 Physics Foundation For EEEДокумент2 страницыEE1002 Physics Foundation For EEEDicky DjayadiОценок пока нет
- MH1810 Course Information 1415Документ1 страницаMH1810 Course Information 1415Dicky DjayadiОценок пока нет
- World CurrencyДокумент2 страницыWorld CurrencyDicky DjayadiОценок пока нет
- Prog 1Документ2 страницыProg 1Dicky DjayadiОценок пока нет
- Report of ACI-ASCE Committee 326 Shear and Diagonal Tension Part 3 - Siabs and Footings, Chapter 8, March1962Документ44 страницыReport of ACI-ASCE Committee 326 Shear and Diagonal Tension Part 3 - Siabs and Footings, Chapter 8, March1962Mohamed100% (1)
- Physics Inertial ForceДокумент7 страницPhysics Inertial ForceInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyОценок пока нет
- Transverse Standing Waves On A StringДокумент4 страницыTransverse Standing Waves On A StringSYDNEYОценок пока нет
- Mat Foundations (Part B) : DR Nor Faizah BawadiДокумент20 страницMat Foundations (Part B) : DR Nor Faizah Bawadiabas ibrahimОценок пока нет
- Be Winter 2021Документ2 страницыBe Winter 2021starboyОценок пока нет
- Chap4 3Документ8 страницChap4 3AhmedSeragОценок пока нет
- Structural Connections According To Eurocode 3 PDFДокумент139 страницStructural Connections According To Eurocode 3 PDFZoran Vlašić100% (2)
- Physics SSC-I - (3rd Set)Документ6 страницPhysics SSC-I - (3rd Set)misshi khanОценок пока нет
- Footing Design Calculations: DefinitionsДокумент31 страницаFooting Design Calculations: DefinitionsMark Roger Huberit IIОценок пока нет
- BG C11 Shaft 2019 EN2Документ15 страницBG C11 Shaft 2019 EN2Do Cao DuyОценок пока нет
- BRIDON BAC TechnicalДокумент25 страницBRIDON BAC TechnicalMohamed SidateОценок пока нет
- Mud ViscosityДокумент5 страницMud Viscosityhindn162Оценок пока нет
- Solution To Manometer Problem PDFДокумент5 страницSolution To Manometer Problem PDFMark Augusto V. AgusОценок пока нет
- Effect of Wind Force On Manoeuvrability Chapter - 10Документ7 страницEffect of Wind Force On Manoeuvrability Chapter - 10erudite_0206Оценок пока нет
- Convective Heat Transfer PDFДокумент13 страницConvective Heat Transfer PDFCarlos Eduardo Noreña OssaОценок пока нет
- Mousetrap Technical ReportДокумент6 страницMousetrap Technical ReportCaproci10% (1)
- Teacher Notes and Answers 17 Electrical Energy and CurrentДокумент3 страницыTeacher Notes and Answers 17 Electrical Energy and CurrentMona Mohamed Safwat100% (1)
- Sample Paper ASAT LeaderДокумент30 страницSample Paper ASAT LeadersahniОценок пока нет
- Module1 Thermo Harish PDFДокумент69 страницModule1 Thermo Harish PDFmaanavОценок пока нет
- Solution Assignment 2: Phy 104 Modern PhysicsДокумент24 страницыSolution Assignment 2: Phy 104 Modern PhysicsAhmed AliОценок пока нет
- Internal ForcesДокумент55 страницInternal ForcesBaileyMorgan100% (1)
- NU - Lecture 12 (WATER HAMMER) PDFДокумент1 страницаNU - Lecture 12 (WATER HAMMER) PDFMr. Mark B.Оценок пока нет
- 03 - Pole Foundation Design Calculation PDFДокумент44 страницы03 - Pole Foundation Design Calculation PDFJason Secret100% (2)
- Material PropertiesДокумент42 страницыMaterial PropertiesDr_M_Soliman100% (2)
- Limit Dead PositionsДокумент5 страницLimit Dead PositionsJatin SharmaОценок пока нет
- GATE AEROSPACE FormulasДокумент38 страницGATE AEROSPACE FormulasMust Watch82% (11)
- AP Physics 1 02DynamicsMCQ Quiz1Документ28 страницAP Physics 1 02DynamicsMCQ Quiz1SoulArcher23Оценок пока нет
- CHAPTER 3 Moments and CouplesДокумент6 страницCHAPTER 3 Moments and CouplesQuinton DuvenageОценок пока нет