Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
STI Male
Загружено:
Doxo RubicinОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
STI Male
Загружено:
Doxo RubicinАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
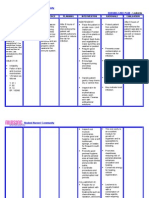
Fact sheet 2- Dysuria and urethral discharge in males
Risk assessment and symptoms
Ask a few direct questions in a sensitive manner in private to
check if any other symptoms or a risk history are present as
this may guide testing, treatment and management.
1. Past history - Check medical records and ask about any
past history of STI
2. Sexual history - Include the follow questions:
Regular partner and/or casual sexual partners
Treat for chlamydia and gonorrhoea
Repeat Treatment
Do not wait for test results - treat with:
Azithromycin 1g orally as single dose
Azithromycin 1g as a single dose
AND
AND
Ceftriaxone 500mg IMI as a single dose AND
Tinidazole 2g orally as a single dose
Treat contacts with the same treatment as above3
Amoxycillin 3g AND Probenecid 1g as a single dose3
Replace Amoxycillin and Probenecid with Ceftriaxone
500mg IMI if infection was acquired outside the region3.
Contact tracing and follow up
New partners in the last 6 months
Complete the STI case management form
If their partner has other sexual partners
Test and treat contacts as soon as possible for both
chlamydia and gonorrhoea as above
3. Symptoms - Check for:
Advise to abstain from sex until contact(s) are treated
Burning, stinging or pain on passing urine
Discharge from the penis or anus
Testicular pain or swelling
Genital sores or rashes
If sores are present check protocols for genital ulcers and
discuss with a medical officer or KPHU
Take blood as above if not done at the initial visit
Enter on recall system for a follow up STI check (PCR
and blood tests) in 3 months time
Condom use
Urethritis
If a male has the following symptoms test and treat during
initial consult:
Burning, stinging or pain on passing urine and/or
Urethral discharge
Recurrent or persistent urethritis
If symptoms recur or do not resolve with treatment consider
re-infection, resistant gonorrhoea or another cause of
urethritis.
Re-infection is likely
if discharge is present ALSO take:
External urethral swab for MCS to check for
gonococcal antibiotic sensitivities
Note- The swab should be taken before passing urine and
can be self collected
Blood tests
Syphilis serology, HIV Ab, Hep B cAb sAb sAg2
Hep C Ab if indicated (eg: history of injecting drug use
or unsafe tattooing, body piercing, incarceration etc)
Check if any other blood tests are due
Discuss with a doctor (MO).
Torsion excluded- epididymitis likely
Risk assessment and tests as for urethritis
Initiate treatment
Azithromycin 1g as a single dose
AND
Ceftriaxone 500mg as a single dose3
Second day
Doxycycline 100mg bd for 10 days OR repeat Azithromycin
1g in 7 days if adherence to doxycycline is unlikely
Contact(s) should be treated to cover chlamydia and
gonnorhoea
New partner since treatment was given
Follow up in 7 days to check response to treatment,
contact(s) have been treated and to provide ongoing
management as appropriate.
Test again (as above) if it is more than one month since
the previous test. Take another urethral swab for MCS if
discharge is present. Repeat treatment for urethritis as above
and test and treat contacts.
AND
Exclude torsion of the testes (medical emergency).
Presents with pain and swelling of the testis
Contact trace and follow up as for urethritis.
First void urine for chlamydia and gonorrhoea PCR
Epididymo-orchitis
Symptoms resolved quickly with treatment but have
recurred and contact(s) were not treated at the same
time
Take the following tests with consent
If no response to this treatment, discuss with KPHU or a
sexual health physician
1 Check general fact sheet for how to collect specimens
Resistant gonorrhoea or another cause is likely
2 Hep B testing is not needed if Hep B immune (cAb positive and sAg negative) or if
adequately vaccinated.
3 Do not give Amoxycillin or Ceftriaxone to people allergic to penicillin discuss with
MO. Alternative treatment for gonorrhoea is Ciprofloxacin 500mg as a single dose or
No or little response of symptoms to initial treatment
Contact(s) were treated at the same time
No new partners since treatment given.
Azithromycin 2g as a divided dose
Test again (as above) if it is more than one month since
the previous test. Take another urethral swab for MCS if
discharge is present.
VC - Last Modified: October 4, 2010 8:50 AM
F
A
C
T
S
H
E
E
T
2
Flow chart 2- Dysuria and urethral discharge in males
Presents with:
- Urethral discharge and/ or dysuria- (stinging/burning or pain on passing urine)
Ask about
Presents with:
AND
/OR
Testicular pain or swelling
- Sexual history and risk assessment
- Check for other symptoms
Testing:
Talk to a medical officer:
1) First void urine (FVU) for chlamydia, gonorrhoea and trichomonas PCR1 AND
Exclude torsion of the testes
(medical emergency)
2) If urethral discharge present - Urethral swab (external) MCS2
Plus
TEST
Obtain informed consent and take blood for:
Torsion excluded:
3) HIV, syphilis, Hep B3 (Hep C if indicated)
- Test as for urethritis
- Treat for epididymo-orchitis
4) Throat and/or rectal swabs for chlamydia and gonorrhoea (PCR and MCS)
if indicated4
Treatment for epididymo-orchitis- check allergies2
Treatment for urethritis- check allergies before treatment5
Initial treatment
1) Azithromycin 1g as a single dose
1) Azithromycin 1g as a single dose
AND
AND
2) Amoxycillin 3g and Probenecid 1g as a single dose
Or Ceftriaxone 500mg IM if infection acquired outside the region3
2) Ceftriaxone 500mg IMI stat
Ongoing Treatment
3) Doxycycline 100mg bd for 14 days OR repeat Azithromycin
1g in 7 days if adherence to doxycycline is unlikely
Contact tracing and follow up
- Test and treat contacts for both chlamydia and gonorrhoea as soon as possible
- Enter on recall system for a repeat STI check in 3 months
Represents with recurrent or persistent dysuria and /or discharge?
3
YES
Symptoms- should resolve quickly with appropriate antibiotics.
If symptoms recur assess if re-infection or another cause is likely - refer to symptomatic male factsheet
Resistant gonorrhoea or another cause
- Test as above if more than 1 month since the previous test
- Take another urethral swab for MCS if discharge is present
Re-infection
- Test as above if more than 1
month since the previous test
- Repeat treatment as above
- Test and treat contacts
Treat with:
1) Azithromycin 1g orally,
2) Ceftriaxone 500mg IMI stat
AND
3) Tinidazole 2g orally
- Treat contacts with above5
Footnotes
1
Always take FVU on any male the presents with symptoms.
2
If discharge present, then take urethral swab BEFORE Urine sample - the client can self collect urethral swab.
3
Hep B testing is not necessary if immune or history of vaccination
4
Refer to WA Guidelines for managing Sexually Transmitted Infections. http://silverbook.health.wa.gov.au
5
Do NOT give Amoxycillin or Ceftriaxone to people allergic to penicillin discuss with a MO. Alternative treatment for gonorrhoea is Ciprofloxacin 500mg as a single
dose or Azithrromycin 2g as a divided dose
Kimberley Aboriginal Medical Services Council (KAMSC) and WA Country Health Service (WACHS) Kimberley Vc - Last Updated: 24Sep10
Вам также может понравиться
- TAFE MapДокумент1 страницаTAFE MapDoxo RubicinОценок пока нет
- Hepatitis C: New Treatments: Gps at The FrontlineДокумент1 страницаHepatitis C: New Treatments: Gps at The FrontlineDoxo RubicinОценок пока нет
- Examination Sequence As Follows: Claw HandДокумент4 страницыExamination Sequence As Follows: Claw HandDoxo RubicinОценок пока нет
- 15 March Reminders and RecallsДокумент1 страница15 March Reminders and RecallsDoxo RubicinОценок пока нет
- 9 March Annual ImmunisationДокумент1 страница9 March Annual ImmunisationDoxo RubicinОценок пока нет
- Mifepristone Use Medical TOPДокумент5 страницMifepristone Use Medical TOPDoxo RubicinОценок пока нет
- Non Accidental Injury in ChildrenДокумент2 страницыNon Accidental Injury in ChildrenDoxo RubicinОценок пока нет
- Diabetes in PregnancyДокумент5 страницDiabetes in PregnancyDoxo RubicinОценок пока нет
- Antenatal RecordДокумент7 страницAntenatal RecordDoxo Rubicin100% (2)
- Metro Communicable Disease Statutory Notification FormДокумент2 страницыMetro Communicable Disease Statutory Notification FormDoxo RubicinОценок пока нет
- Making Ordinary, Extraordinary: CV Writing 101Документ8 страницMaking Ordinary, Extraordinary: CV Writing 101Doxo RubicinОценок пока нет
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5795)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (895)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (400)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (345)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2259)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (266)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (121)
- Herpes ZosterДокумент3 страницыHerpes ZosterjotayuОценок пока нет
- L30 - FPSC Paper Mill Colony C38/1, Gurdwara Road, Siddheshwar LucknowДокумент4 страницыL30 - FPSC Paper Mill Colony C38/1, Gurdwara Road, Siddheshwar LucknowShamsuddin ShamsОценок пока нет
- ImmunisationДокумент29 страницImmunisationOjambo FlaviaОценок пока нет
- 1150 3362 1 PBДокумент6 страниц1150 3362 1 PBRoni HasibuanОценок пока нет
- Health and Its FailureДокумент10 страницHealth and Its FailureAmit KasniaОценок пока нет
- Digging Up The Bones - MicrobiologyДокумент31 страницаDigging Up The Bones - MicrobiologyMossa Di Base100% (1)
- MCQ's For TrainingДокумент52 страницыMCQ's For TrainingYalvant YadavОценок пока нет
- Orbital CellulitisДокумент21 страницаOrbital CellulitisElsa Octavia100% (1)
- Solowska Et Al DX and MGT of COVID Vaccine ReactionsДокумент31 страницаSolowska Et Al DX and MGT of COVID Vaccine ReactionsJoshua TamayoОценок пока нет
- Tatalaksana ARV - Efek Samping - IRIS - Monitoring Terapi - PEPДокумент95 страницTatalaksana ARV - Efek Samping - IRIS - Monitoring Terapi - PEPtriiОценок пока нет
- Fletcher - Diagnostic Histopathology of Tumors, 4th Edition (Dragged)Документ1 страницаFletcher - Diagnostic Histopathology of Tumors, 4th Edition (Dragged)gianneОценок пока нет
- Tetanus and MeningicoccalДокумент9 страницTetanus and MeningicoccalAce FabrigasОценок пока нет
- Pathophysiology of Meningococcal Meningitis and SepticaemiaДокумент8 страницPathophysiology of Meningococcal Meningitis and SepticaemiaEugen TarnovschiОценок пока нет
- K1. Elektif ParasitДокумент34 страницыK1. Elektif ParasitUu'ayu UnyuОценок пока нет
- Determine Hbsag 2: Infectious DiseasesДокумент1 страницаDetermine Hbsag 2: Infectious DiseasesJose IrulaОценок пока нет
- Overview of Mucocutaneous Symptom ComplexДокумент5 страницOverview of Mucocutaneous Symptom ComplexDaphne Jo ValmonteОценок пока нет
- Otitis Externa: Journal ReadingДокумент22 страницыOtitis Externa: Journal ReadingRizka FadilahОценок пока нет
- 2018 - DR Nerissa Hannink - What Are The Long-Term Health Risks of Having Your Tonsils Out - Pursuit by The University of Melbourne (News)Документ4 страницы2018 - DR Nerissa Hannink - What Are The Long-Term Health Risks of Having Your Tonsils Out - Pursuit by The University of Melbourne (News)n3v3rmor33Оценок пока нет
- Antiphospholipid Antibody SyndromeДокумент273 страницыAntiphospholipid Antibody SyndromeGeorgiana Murgu100% (2)
- Nursing Care Plan LeukemiaДокумент2 страницыNursing Care Plan Leukemiaderic87% (30)
- Colds & Flu: A Clinical Doctor/Patient ManualДокумент142 страницыColds & Flu: A Clinical Doctor/Patient ManualKemal Salkic100% (2)
- Tugas Sosioantropologi - Ahmad Sadewo Putro Iskandar - 211000098Документ115 страницTugas Sosioantropologi - Ahmad Sadewo Putro Iskandar - 211000098DeworldsОценок пока нет
- Fimmu 10 01078Документ24 страницыFimmu 10 01078ArieОценок пока нет
- Body Defence MechanismsДокумент11 страницBody Defence MechanismsJoyce TaiОценок пока нет
- Common Skin DisordersДокумент10 страницCommon Skin DisordersPaul Vincent Alfonso100% (1)
- HIVCombiPT English V4 PDFДокумент5 страницHIVCombiPT English V4 PDFFelixColindresОценок пока нет
- Systemic Lupus ErythematosusДокумент10 страницSystemic Lupus ErythematosuszkxxyyОценок пока нет
- Swine DiseasesДокумент28 страницSwine DiseasesTsel KoncetОценок пока нет
- Tugas Keperawatan AnakДокумент9 страницTugas Keperawatan Anakiliyin wahinaОценок пока нет
- Disorders of White Blood: CellsДокумент2 страницыDisorders of White Blood: CellsIberisОценок пока нет