Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Little Lfo Manual
Загружено:
isshmangАвторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Little Lfo Manual
Загружено:
isshmangАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
1
Little LFO
User Manual
Little LFO
by Little IO Co.
Contents
Overview
OscillatorStatus
Switch
StatusLight
OscillatorLabel
VolumeandEnvelope
Volume
Envelope
Attack(ATT)
Decay(DEC)
Sustain(SUS)
Release(REL)
Legato
OscillatorShapeSection
WaveSelector
Amplitude(AMP)
Phase(PHS)
PulseWidth(PW)
KeyboardSync(SNC)
OscillatorFrequencySection
SettingFrequencyControlSource
KeyboardFrequencyControl
MajorControl(SEMI):Semitoneoffset
MinorControl(PORT):Portamento
TempoFrequencyControl
Major(TEMPO):Tempo
Minor(CORR):PhaseCorrection
FreeFrequencyControl
Major(FRQ):Frequency
Minor(FINE):FineControl
ModulationSection
(SNC)Synchronization
(AMP)AmplitudeModulation
(FRQ)FrequencyModulation
(PHS)PhaseModulation
InternalModulationCycle
AudioOutputs
+ALLKEYS+
Oscillator Audio Outputs
AntiAliasing
PerformanceCVPorts(AsinPerformanceArts)
GateCV Input and Output
NoteCV Input and Output
EnvelopeCV Outputs
OscillatorCVInputs
Trim Knobs
Amplitude CV Input
Frequency CV Input
Phase CV Input
PulseWidth CV Input
OscillatorCVOutputs
BipolarOutput
UnipolarOutput
EnvelopedOutput
Overview
LittleLFOisamultiusesemimodularRackExtension.Itcanbeusedasasoundand/or
modulationsourceforReason.Asasoundsource,thereisahugevarietyofpossibilities.It
comeswith125Combinatorpatchesmadeby9patchdesigners,withinstrumentssuchas
synths,basses,drumkitsandsoundeffects.Asamodulationsource,thecombinationof
variousinternalmodulationandwaveformsgivesawiderangeofmodulationpossibilities.
CommonUses
Oscillatorsectionforasynthesizer
Modulationsectionforsynthesizeroreffects
Weirdnoisemakerforsoundeffectsorfun
CoolFeatures
Separateportamentoforeachoscillator
Pulsewidthcanbeusedonanywaveform
Allactiveoscillatorsarehookedintoamodulationcycle(SeeInternalModulationCycle
section)
Adjustablephasecorrectionfortemposyncedoscillators(SeePhaseCorrectioninthe
Tempo Frequency Controlsection)
MoreStandardFeatures
4Oscillators
15waveforms
Frequencycanbecontrolledbykeyboard,tempo,orfreelyset
Optionalantialiasing
Amplitude,frequency,phase,andpulsewidthcontrolsforeachoscillator
Keyboardsynchronizationforeachoscillator
Amplitude,frequencyandphasemodulationbetweenoscillators
Oscillatorsynchronization
ADSRenvelopeisautomaticallyhookeduptoamplitude,butalsohas2CVoutputs
CVinputsforoscillatoramplitude,frequency,phase,andpulsewidth
Audiooutputswithandwithoutenvelope
BipolarandunipolarCVoutputs,eachwithandwithoutenvelope
GateandnoteCVinputandoutput/throughput
Oscillator Status
Switch
Thisswitchturnstheoscillatoronandoff.Whentheoscillatorisoff,itisremovedfromthe
modulationcycle.
Status Light
Whentheoscillatorisatthetopofthewaveform,thelightisallthewayon.Whentheoscillator
isatthebottomofthewaveform,thelightisallthewayoff.Thisisausefulvisualizationwhen
theoscillatorsfrequencyisbelow10Hz.
Oscillator Label
Theoscillatorsarelabeled1,2,3,and4.
Volume and Envelope
Volume
TheVolumeslidercontrolstheoutputtoallaudiosources.
Minimum: dBFS(Allaudiosignalssilent)
Maximum: 0dBFS(Unalteredaudiosignals)
Envelope
ThereisasingleADSRenvelope(Attack>Decay>Sustain>Release)inLittleLFO.It
internallycontrolstheamplitudeofallsignalssenttotheenvelopedAudioandCVoutputs(See
OscillatorCVOutputsandAudioOutputs).
Attack (ATT)
064seconds
Decay (DEC)
064seconds
Sustain (SUS)
01scalingofamplitude
Release (REL)
064seconds
Theenvelopewillaffecttheamplitudeofallenvelopedoutputports.
Whenlegatoisoff,hittinganyMIDInotewillalwaysjumptotheattackpartoftheenvelope.When
legatoison,onlytriggernoteswilljumptotheattackpartoftheenvelope.
Legato
LegatochangesafewcontrolsthroughoutLittleLFO.Whenlegatoisoff,eachMIDInoteis
consideredadistincttrigger.Whenlegatoison,onlyMIDInotesthatareprecededbynoactive
notesareconsideredatrigger.Triggernotesretriggertheenvelopetoimmediatelyrestartfrom
theattack.Notesthatoverlaporoccurcontinuouslyareconsideredtied.Inlegatomode,tied
notesdonotrestarttheenvelope.Thiscanbeusefulfortyingnotestogetherintophrases.
Oscillator Shape Section
Thewaveshapesectionofeachoscillatorletsyouchoosefrom15differentwaveformssettheir
amplitude,phase,pulsewidthandkeyboardsynchronization.
Wave Selector
Choosefrom15differentwaveformsbyscrollingthroughthemwithup/downbuttons:
sine
downcurve
3pyramid
triangle
upcurve
5pyramid
square
3step
9pyramid
downsaw
4step
noise
upsaw
8step
smoothnoise
Ifyouwantantialiasedversionsofthesewaveforms,thereisatoggleonthebackthatyoumust
enable.
Amplitude (AMP)
ThiscontrolstheamplitudeoftheaudioandCVoutputsandaffectstheamountofinternal
modulationgiventothenextactiveoscillatorinthemodulationcycle.
Minimum: 0%
Maximum: 100%
Phase (PHS)
Thiscontrolsthepointinthewaveformatwhichitwillbeginplaying.
Minimum: 180(1halfwaveformbackward)
Maximum: +180(1halfwaveformforward)
Pulse Width (PW)
Pulsewidthchangesthelengthofthefirstandsecondhalvesofthewavelinearly,whilekeeping
theoverallwavelengththesame.Anywaveformwillbeaffectedbythepulsewidthcontrolofits
waveformsection.
Minimum: 0%
Maximum: 100%
Asanexample,hereishowpulsewidthaffectssquareandsinewaves.
PulseWidth
Amount
SquareWave
SineWave
PW:50%
Unchanged
Waveform
PW:20%
PW:80%
Keyboard Sync (SNC)
ThiswillresettheoscillatortothebeginningofitswaveformwhenthereisanewMIDIkeyhitor
thereisnewgateinput.Thiscontroldoesnotchangethefrequencyoftheoscillator.Keyboard
Syncisaffectedbythelegatocontrolonthetoprightofthedevice(seeLegatoinVolumeand
Envelope).Iflegatoisoff,allkeyhitsmaketheoscillatorrestartfromthebeginningofits
waveform.Iflegatoison,onlytriggernotesmaketheoscillatorrestart.
Note:Currently,oscillatorsfasterthan64Hzarenotkeyboardsyncediftheenvelopeis
engaged.Thismaychangeinafuturerelease.
10
Oscillator Frequency Section
Thefrequencysectionletsyoucontrolthefrequencybyselectingacontrollingsourceand
modifyingitwithtwoknobs.
Setting Frequency Control Source
Youcancontrolthefrequencyofeachoscillatorinthreedifferentways:throughthekeyboard,
throughthetemposyncedfrequencies,orbyfreelysettingtheexactfrequency.Tosetthe
frequencycontrolsource,clickonthebuttonnexttothedesiredfrequencycontrolsource:
Keyboard,TempoorFree.TheMajor(larger)andMinor(smaller)knobschangefunctionality
dependingonwhichfrequencycontrolsourceisselected.
Keyboard Frequency Control
Inthissetting,thefrequencyiscontrolledbyMIDInotesandnotestriggeredthroughthenoteand
gateCVinput.
Note:BeforeanynoteiseversenttoLittleLFO,keyboardfrequencycontrolledoscillatorswill
defaulttoMIDInote0,whichisabout8.18Hz.
Major Control (SEMI): Semitone offset
ForeverynotesenttoLittleLFO,theoscillatorsfrequencywillbesettothespecified
numberofsemitonesawayfromthatnotesfrequency.Forexample,settingthisknobto
+7willcausethisoscillatorsfrequencytobeamusicalfifthabovethenotesenttoLittle
LFO.Thisisusefulforharmonizingoscillatorsandaddingsuboscillators.
Minimum: 32semitones
Maximum: +32semitones
Minor Control (PORT): Portamento
11
Portamentoisaglidebetweennotes.Playingonenoteandthenanotherwillcausethe
frequencyglidefromthefirstnotetothesecondcontinuously.Theportamentoknobsets
thetimeittakestomakethefullglidefromthelowestMIDInotepossibletothehighest
MIDInotepossible.Smallernotechangeswilltakelesstime.
Minimum: 0seconds
Maximum: 10seconds
Iflegatoison,therewillonlybeaglidebetweentiednotes(seeLegatoinVolumeand
Envelope).
Tempo Frequency Control
Inthissetting,thefrequencyiscontrolledrelativetotheoveralltempo(BPM).
Major (TEMPO): Tempo
Thisknobsetsthefrequencytoafractionofthetempo.Forexample,4/4meansonce
every4beats.So,theperiodis4beats,andthefrequencyissetaccordingly.Asanother
example,1/4meansonceeverybeat,sotheperiodis1beat.Asanotherexample,4/4T
means3timesforevery2timesthatthe4/4wouldplay.Inotherwords,4/4Tis1.5times
thefrequencyof4/4.The24possibletemposyncedvaluesare32/4,16/4,12/4,8/4,7/4,
6/4,8/4T,5/4,4/4,3/4,4/4T,2/4,3/8,2/4T,1/4,3/16,1/4T,1/8,1/8T,1/16,1/16T,1/32,
1/32T,and1/64.
Notethattheoscillatorkeepsplayingitdoesnotstartorstoponparticularbeats.The
beatsarejustusedtodeterminetheperiodofthewaveform,whichequivalentlysetsthe
frequency.So,inthe4/4example,theoscillatorsfrequencyissetsothatthebeginning
ofthewaveformoccursatthebeginningofthefirstbeatoffourbeats.
Minor (CORR): Phase Correction
Theoscillatorsbasefrequencyissetbyfrequencysectionontheoscillatoritself,
whetherbykeyboardfrequencycontrol,tempofrequencycontrol,orfreefrequency
control.TheoscillatorsfrequencycanbemodulatedbyanotheroscillatororCV
frequencyinput.Thus,collectively,theinfluencesthataffecttheoscillatorsfrequencyare
thefrequencycontrolknobontheoscillatoritself,frequencymodulationfromanother
oscillator,orfrequencymodulationfromCVinput.
Atemposyncedoscillatorisinphasewiththetempowhenthebeginningofthe
oscillatorswaveformoccursatthepointsintimespecifiedbytheTEMPOknob.For
example,iftheTEMPOknobissetto4/4andtheoscillatorisinphasewiththetempo,
thenthebeginningofthewaveformwilloccuronceeveryfourbeats,atthebeginningof
thefirstbeat.
12
Ifthetemposyncedoscillatorsfrequencyisbeingchangedbytheinfluencesmentioned
above,itispossibleforittogetoutofphasewiththetempo.Thismayormaynotbe
desirable.Phasecorrectionpullstheoscillatorbackinphasewiththetempo.
TheCORRknobsetshowlongittakestocorrectthephaseoftheoscillator.
Minimum: 0seconds(immediatecorrection)
Maximum: (nocorrection)
WhentheCORRknobissetto0,correctionhappensimmediately.Whenitssetto,
thecorrectiontakesforever,or,inotherwords,thereisnocorrection.
Withimmediatecorrection,thentheoscillatorwillimmediatelybesetinphasewiththe
tempo.Inthiscase,frequencymodulationfromanotheroscillatororfromCVinputhave
noeffect.ChangingtheTEMPOknoboftheoscillatoritselfresultsinclickingbecausethe
phaseisimmediatelychanged.
Withnocorrection,theoscillatorsfrequencywillbethenormalresultofallinfluenceson
thefrequencyacombinationoftheTEMPOknobsbasefrequency,thefrequency
modulationfromanotheroscillator,andthefrequencymodulationfromtheCVinput.This
allowstheoscillatortogetoutofphasewiththetempo.
Withsomecorrection,e.g.iftheCORRknobissetto1second,thentheoscillators
phasewillbepulledbackinphasewiththetempooveratimespanof1second.So,ifthe
TEMPOknobischangedtoanewposition,thenwithin1secondtheoscillatorsphase
willsmoothlyshifttobeinphasewiththetempo.Thiswillnotcauseclicking.Ifthe
oscillatorsfrequencykeepschangingmorethanonceasecond,eitherduetofrequency
modulationormultiplechangestotheTEMPOknob,thenthephasewillnevercatchup.
Thiscanbeaninterestingeffect.
TryThis:Settheoscillatortoalowfrequency,modulateitsfrequency,andchangethe
CORRknobtocreatedifferenttypesofrepeatingwaveforms.
Free Frequency Control
Inthissetting,thefrequencyisspecifiedinHz.
Major (FRQ): Frequency
Minimum:
0Hz
13
Maximum:
4096Hz
Minor (FINE): Fine Control
ThisknobalsosetsthefrequencyinHz,givingfingergrainedcontrolwithinasmaller
range.ItsvalueisaddedtothevalueoftheFRQknobtodeterminethefrequency.
Minimum: 12semitones(1octave)
Maximum: +12semitones(1octave)
Note:BysettingboththeFRQandFINEknobstotheirmaximumvalues,itispossibletosetthe
oscillatorfrequencytoamaximumof8192Hz.
14
Modulation Section
Themodulationsectioncontrolsfrequency,amplitude,andphasemodulationaswellas
synchronization.Theinternalmodulationcycledetermineswhichoscillatorismodulatingwhich
(seeInternalModulationCycle).Whendescribingmodulation,itisimportanttodistinguish
betweenthemodulationandcarrierfrequencies.Forexample,ifOscillator2ismodulating
Oscillator1,thenOscillator2isthemodulatorandOscillator1isthecarrier.Inthisexample,the
modulationsectionhighlightedbelowdetermineshowOscillator2modulatesOscillator1.
Ingeneral,amodulationsectionhasamodulatorandacarrier.Themodulatorisalwaysthe
oscillatorimmediatelytotherightofthemodulationsection.Thecarrierisdeterminedbythe
internalmodulationcycle.
Note:Intheknobcontrolsforamplitude,frequency,andphasemodulation,negative
percentagesactasifthemodulatorsignalwasinverted.
Synchronization (SNC)
TurningSNConmakeitsothat,wheneverthemodulatorarrivesbackatthebeginningofits
waveform,itforcesthecarrierwavetojumptothebeginningofitswaveform.Thiscausesthe
carrierwavetohavethesamebasefrequencyofthemodulatorwave.
Amplitude Modulation (AMP)
Thecarrieramplitudeismodulatedby,atamaximum,thepercentageofitsfrequencyspecified
setbytheAMPknob.Whenthemodulatorisatitstrough,itwillreducetheamplitudeofthe
carrierbytheAMPknob.Whenthemodulatorisatitspeak,itwillnotreducetheamplitudeofthe
carrieratall.
Minimum: 100%
Maximum: 100%
NotethatthemaximumamplitudeofthecarrierissetbytheAMPknobintheWaveShape
sectionofthecarrieroscillator.Together,thesetwocontrolssettheminimumandmaximum
amplitudeofthecarrierfrequency.Forexample,withtheamplitudemodulationat50%andthe
carrieramplitudeat60%,thecarrieramplituderangesfrom60%whenthemodulatorisatits
15
peakto30%whenthemodulatorisatitstrough.
Frequency Modulation (FRQ)
Thecarrierfrequencyismodulatedby,atamaximum,thepercentageofitsfrequencysetbythe
FRQknob.
Minimum: 100%
Maximum: 100%
Forexample,ifthecarrierbasefrequencyis400Hzandthefrequencymodulationknobissetto
100%,thenthecarriermodulatesbetween800Hzwhenthemodulatorisatitspeakto0Hz
whenthemodulatorisatitstrough.Withthemodulationknobat50%,thecarrierwouldmodulate
between600Hzand200Hz.
Phase Modulation (PHS)
Thecarrierphaseismodulatedby,atamaximum,thepercentageofhalfaperiod(180)setby
thePHSmodulationknob.Thecarrierphasecanbeshiftedforward180andbackward180,
enablingfull360modulation.
Minimum: +100%(180ahead)
Maximum: 100%(180behind)
IfthePHSknobissettoapositivevalue,then,whenthemodulatorisatitspeak,thecarrieris
aheadofitsbasephasebythatvalue,and,whenthemodulatorisatitstrough,thecarrieris
behinditsbasephasebythatvalue.IfthePHSknobissettoanegativevalue,thereverseis
true.
Note:Inthemodulationcycle,ifalloscillatorsarephasemodulatingeachother,youmaycreate
phasemodulationfeedbackwhichsoundslikeverynoisystatic(similartowhitenoise).
16
Internal Modulation Cycle
Allactiveoscillatorsareautomaticallyhookedintoamodulationcycle.Themodulationgoesright
toleftandwrapsaroundendtoend.
Forexample,ifalloscillatorsareturnedon,thenOscillator4willmodulateOscillator3,whichwill
modulateOscillator2,whichwillmodulateOscillator1,whichwillmodulateOscillator4.
Anyinactiveoscillatorisleftoutofthecycle.
Asanotherexample,ifonlyOscillators1and3areturnedon,thenOscillator3willmodulate
Oscillator1,andOscillator1willmodulateOscillator3.
Bydefault,themodulationcontrolsareallsetto0,sonomodulationwilloccuruntiltheseare
changed.Forspecificsonmodulationcontrols,seeModulation Section.
17
Audio Outputs
Audiooutputsprovidetheaudiodataindifferentformats.
Note:Trianglesonbothsidesofanoutputmeanthatitisenveloped.
+ALL KEYS+
The+ALLKEYS+outputisasumofalloscillatorsinkeyboardfrequencycontrolmode.This
audiooutputisenveloped,asindicatedbytheenvelopetriangles.+ALLKEYS+isconvenientfor
usingLittleLFOasasynth.
Oscillator Audio Outputs
Oscillatoraudiodataisavailableenvelopedorunenveloped.Theenvelopedaudiooutputison
therightunenvelopedisontheleft.
18
Anti Aliasing
Bydefault,antialiasingisoff.Turningitonremovesaparticularkindofdissonancefromthe
audiooutputswhenplayinghighernotes.
Note:Evenifantialiasingisturnedon,aliasingmaystilloccurwithoscillatorsyncing,pulsewidth
modification,andaggressivemodulation.Thismaychangeinalaterrelease.
19
Performance CV Ports
(AsinPerformanceArts)
Gate CV Input and Output
ThereisaGateCVinputporttocontroltheenvelopeonLittleLFO.ThiscanbepairedwithNote
CVinputlikeinmanyotherdevicestocreatemonophonickeyboardinput.
ThereisalsoaGateCVoutputportthatcanactasathroughputoftheGateCVinput.GateCV
inputandthegateinformationofMIDInotessentdirectlytoLittleLFOalsocomesoutthrough
thisport.GateCVoutputdatacanbesenttootherCVinputportstocreatevelocitytracking.
TryThis:CreateavelocitytrackedoscillatorbyconnectingthegateCVoutputtoanoscillator
AMPCVinput.Thefasteryouhitanote,thelouderthatoscillatorwillbe.Maybeturndownthe
baseamplitudeofthatoscillatoronthefrontofthedevice.
Note CV Input and Output
ThereisaNoteCVinputporttocontrolthefrequencyofkeyboardcontrolledoscillators.Thiscan
bepairedwithGateCVinputlikeinmanyotherdevicestocreatemonophonickeyboardinput.
ThereisalsoaNoteCVoutputportthatactsasathroughputoftheNoteCVinput.NoteCVinput
andthenoteinformationofMIDInotessentdirectlytoLittleLFOcomeoutthroughthisport.Note
CVoutputdatacanbesenttootherCVinputportstocreatekeyboardtracking.
TryThis:CreateakeyboardtrackedvibratoortremolobyconnectingthenoteCVoutputtoa
temposyncedoscillatorsFREQCVinput.Thehigherthenote,thehighertheoscillators
frequency.UsethetrimknoboftheFREQCVinputtolimittheeffecttowithinthedesired
range.
Envelope CV Outputs
LittleLFOhasasingleADSRenvelopewhichcontrolstheamplitudeoftheenvelopedCV
outputs.TheEnvelopeCVoutputsprovidesjusttheenvelopeinformationitself.Thevalueranges
between0and1asspecifiedbytheattack,decay,sustain,andreleasevalues.Withthe
20
EnvelopeCVout,thisdatacanalsobesenttootherinputportstocontrolthingssuchas
frequency,pulsewidth,etc.
21
Oscillator CV Inputs
Inadditiontotheinternalmodulationonthefrontofthedevice,theoscillatorscanbemodulated
usingtheCVinputsonthebackofthedevice.Theamplitude,frequency,phase,andpulsewidth
ofeachoscillatorcanbemodulatedviatheseCVinputs.
Trim Knobs
EachoscillatorCVinputhasatrimknobthatreducestherangeoftheeffect.
Minimum: 0(0%)
Maximum: 127(100%)
Bydefault,thetrimknobsaresetto127andthusallowthemaximumrangeoftheeffect.Ifthe
trimknobissetto,forexample,63,thentherangeoftheeffectisreducedbyabouthalf.
Amplitude CV Input (AMP)
TheAMPCVinputaddsorsubtractsfromtheoscillatorsbaseamplitudesetonthefrontofthe
device.Themaximumrangeoftheeffectis100%oftheoscillatorsbaseamplitude.For
example,withthetrimknobsetto127andtheoscillatorsbaseamplitudeat50%,thenthe
maximumAMPCVinputwillraisetheoscillatorsamplitudeto150%andtheminimumAMPCV
inputwillreducetheoscillatorsamplitudeto50%.
Note:Percentagesover100%arehardclipped.Negativepercentagesinvertthewaveform.
Frequency CV Input (FREQ)
TheFREQCVinputaddsorsubtractsfromtheoscillatorsbasefrequencysetonthefrontofthe
device.Thisporthasnoteresolution,sothemaximumrangeoftheeffectis127semitones
fromtheoscillatorsbasefrequency.IfthetrimknobissettoNsemitones,thentherangeofthe
effectisNsemitones.
Note:SincetheFREQCVinputporthasnoteresolution,plugginginnoteCVoutputfromthe
MatrixPatternSequencer,RPG8,orotherdeviceswillcausetheoscillatortoshiftitsbase
frequencybythatmanysemitones.
22
TryThis:Plugintwofrequencycontrolsourcestotwodifferentoscillatorstocreate
nonstandardpolyphony.
TryThis:TurnonOscillators1and2andsetthemtokeyboardfrequencycontrolmode.For
eachoscillator,turnonaMatrixSequencerandhookitsnoteCVoutputintotheoscillators
FREQCVinputanditsgateCVoutputintotheoscillatorsAMPCVinput.Thencreatesome
modulationbetweentheoscillators.WhenbothMatrixesareplayingnotesatthesametime,
theoscillatorsaremodulating,butwhenonlyoneMatrixisplayinganotethereisno
modulation.DistributororOchenKspolysplittercanbeusedaswell.
Phase CV Input (PHS)
ThePHSCVinputshiftsthephaseoftheoscillatorfromtheoscillatorsbasephasesetonthe
frontofthedevice.Themaximumrangeoftheeffectis180.
Pulse Width CV Input (PW)
ThePWCVinputaddsorsubtractstofromtheoscillatorsbasepulsewidthsetonthefrontof
thedevice.Themaximumrangeoftheeffectis50%.Forexample,withthetrimknobsetto127
andtheoscillatorsbasepulsewidthat50%,thenthemaximumPWCVinputwillincreasethe
oscillatorspulsewidthto100%andtheminimumPWCVinputwilldecreasetheoscillators
pulsewidthto0%.Pulsewidthiscappedbetween0%and100%.
23
Oscillator CV Outputs
OscillatorCVoutputisavailableinfourforms.Theaudiodatacanbeadjustedbytheenvelopeor
not,anditcanbebipolarorunipolar.Thesixoscillatoraudiooutputportsarehighlightedabove.
Theyformtworowsandthreecolumnswhichcorrespondtothetablebelow.
NotEnveloped
NotEnveloped
Enveloped
Bipolar
Notenveloped,
bipolarCVoutput
Notenveloped,
bipolarCVoutput
Enveloped,
bipolarCVoutput
Unipolar
Notenveloped,
unipolarCVoutput
Notenveloped,
unipolarCVoutput
Enveloped,
unipolarCVoutput
Bipolar
BipolarCVoutputvaluescanrangefrom1to1.Thecenterofthewaveformcorrespondstothe
value0.Forexample,iftheoscillatoramplitudeis80%,thenitsbipolarCVoutputrangesfrom
0.8to0.8.
ExamplebipolarCVoutputforawaveformwithamplitude80%
OnepossiblewaytousethisistoplugtheCVoutputofoneoscillator,callitOscillatorA,intothe
24
frequencyCVinputofanotheroscillator,callitOscillatorB.ThenOscillatorBwillhaveahigher
frequencywhenOscillatorAsCVoutputispositiveandlowerfrequencieswithOscillatorAsCV
outputisnegative.
Unipolar
UnipolarCVoutputvaluescanrangefrom0to1.Thewaveformisbottomalignedat0and
verticallyscaleddownbyhalftofitwithinthe0to1range.Forexample,ifthewaveforms
amplitudeis80%,thenthenitsunipolarCVoutputrangesfrom0to0.8.
ExampleunipolarCVoutputforawaveformwithamplitude80%
Enveloped
EnvelopedCVoutputvaluesareamplitudeadjustedbytheenvelope.
TryThis:PluganenvelopedCVoutputfromoneoscillatorintothefrequencyCVinputof
anotheroscillator.Thiswillcauseavibratoeffectinthesecondoscillatorwhichslowlycomes
inwiththeattackoftheenvelope.
Вам также может понравиться
- NEL Spectral Suite For Kyma - Class Descriptions (1st Draft)Документ25 страницNEL Spectral Suite For Kyma - Class Descriptions (1st Draft)Cristian VogelОценок пока нет
- Waldorf Microwave Masterclass PDFДокумент10 страницWaldorf Microwave Masterclass PDFdaneОценок пока нет
- Digital Audio EffectsДокумент111 страницDigital Audio EffectsJosep M ComajuncosasОценок пока нет
- MOLEKULAR Manual EnglishДокумент159 страницMOLEKULAR Manual EnglishpabloansonОценок пока нет
- Generate Algorithmic Music in ReaktorДокумент8 страницGenerate Algorithmic Music in ReaktorBeturbio VturvioОценок пока нет
- Modal Synthesis of Weapon Sounds PDFДокумент7 страницModal Synthesis of Weapon Sounds PDFDmitry NemtsoffОценок пока нет
- Nord Modular G2 English User Manual v1.4 Edition 1.4x PDFДокумент291 страницаNord Modular G2 English User Manual v1.4 Edition 1.4x PDFAlejo JavierОценок пока нет
- Drum Machine VSTДокумент51 страницаDrum Machine VSTIstok JugОценок пока нет
- Kyma Capsules Volume 1Документ31 страницаKyma Capsules Volume 1Cristian Vogel100% (1)
- CMPT 468 Final Project Instrument SynthesizerДокумент3 страницыCMPT 468 Final Project Instrument SynthesizerdialauchennaОценок пока нет
- Real-Time Sound Similarity Synthesis by PDFДокумент6 страницReal-Time Sound Similarity Synthesis by PDFStefano FranceschiniОценок пока нет
- M2-104-UM v1-0 UMP and MIDI 2-0 Protocol SpecificationДокумент84 страницыM2-104-UM v1-0 UMP and MIDI 2-0 Protocol SpecificationBrandy ThomasОценок пока нет
- Yamaha SY77 Display UpgradeДокумент18 страницYamaha SY77 Display UpgradeAntónio GomesОценок пока нет
- Matlab Implementation of Reverberation AlgorithmsДокумент6 страницMatlab Implementation of Reverberation AlgorithmsJo E Fran RodriguesОценок пока нет
- Cottle Computer Music Using SC3Документ403 страницыCottle Computer Music Using SC3GLVОценок пока нет
- Demystifying Maxmsp PDFДокумент47 страницDemystifying Maxmsp PDFaliloia1Оценок пока нет
- NEL FFT Suite User GuideДокумент18 страницNEL FFT Suite User GuideCristian VogelОценок пока нет
- Toby Newman How To Write A VST PluginДокумент77 страницToby Newman How To Write A VST Pluginshannonoram5050Оценок пока нет
- Power Amplifiers: Phase Shift OscillatorДокумент3 страницыPower Amplifiers: Phase Shift OscillatorAli DurazОценок пока нет
- Bome's Midi Translator Tutorial: MT Pro with AbletonДокумент11 страницBome's Midi Translator Tutorial: MT Pro with AbletonDean Nguyen100% (1)
- Reaktor Instructions Coursework 1 090815 v2Документ9 страницReaktor Instructions Coursework 1 090815 v2ARITOSOUL341Оценок пока нет
- The Nord Modular ExperienceДокумент10 страницThe Nord Modular ExperienceKasimir BlaumilchОценок пока нет
- OCTOGRIS Manual en 64bitsДокумент31 страницаOCTOGRIS Manual en 64bitsAnonymous anQLg1aОценок пока нет
- Digital Sound Synthesis by Physical ModellingДокумент12 страницDigital Sound Synthesis by Physical ModellingBrandy ThomasОценок пока нет
- A Paradigm For Physical Interaction With Sound in 3-D Audio SpaceДокумент9 страницA Paradigm For Physical Interaction With Sound in 3-D Audio SpaceRicardo Cubillos PeñaОценок пока нет
- MAX 6 IntroДокумент22 страницыMAX 6 IntroemviverosОценок пока нет
- Week 7 - Sound Cards & Digital AudioДокумент10 страницWeek 7 - Sound Cards & Digital Audiorafiqueuddin93Оценок пока нет
- Stilson-Smith - Alias-Free Digital Synthesis of Classic Analog Waveforms (BLIT)Документ12 страницStilson-Smith - Alias-Free Digital Synthesis of Classic Analog Waveforms (BLIT)HangTheBankersОценок пока нет
- Wishart, Trevor - Computer Sound Transformation PDFДокумент11 страницWishart, Trevor - Computer Sound Transformation PDFvalsОценок пока нет
- 926 Music DSPДокумент265 страниц926 Music DSPeircom100% (1)
- The Music21 Stream: A New Object Model For Representing, Filtering, and Transforming Symbolic Musical StructuresДокумент8 страницThe Music21 Stream: A New Object Model For Representing, Filtering, and Transforming Symbolic Musical Structuresifen_michaelОценок пока нет
- Synthetic Instruments: Concepts and ApplicationsОт EverandSynthetic Instruments: Concepts and ApplicationsРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1)
- HD Recording and Sampling TipsДокумент16 страницHD Recording and Sampling TipsBrian NewtonОценок пока нет
- Audio Processing Using MatlabДокумент51 страницаAudio Processing Using MatlabYogyogyog PatelОценок пока нет
- Micro-MIDI: A Real Time, Dynamic Microtonal MIDI ApplicationДокумент7 страницMicro-MIDI: A Real Time, Dynamic Microtonal MIDI ApplicationinventionjournalsОценок пока нет
- A Tutorial On Spectral Sound Processing Using Max/MSP and JitterДокумент16 страницA Tutorial On Spectral Sound Processing Using Max/MSP and Jittertramazio0% (1)
- Faust TutorialДокумент78 страницFaust TutorialMatt WallОценок пока нет
- MIDI Short For Musical Instrument Digital Interface) Is A TechnicalДокумент10 страницMIDI Short For Musical Instrument Digital Interface) Is A TechnicalJomark CalicaranОценок пока нет
- Chord-O-Mat 3 Manual - Guide to Triggering ChordsДокумент36 страницChord-O-Mat 3 Manual - Guide to Triggering ChordsMr JasОценок пока нет
- New Perspectives On Distortion Synthesis For Virtual Analog OscillatorsДокумент13 страницNew Perspectives On Distortion Synthesis For Virtual Analog OscillatorsAlfonso SantimoneОценок пока нет
- Reverb Design for Improved Intelligibility and Spacial ImpressionДокумент9 страницReverb Design for Improved Intelligibility and Spacial ImpressionSerj PoltavskiОценок пока нет
- HALion 3 ManualДокумент252 страницыHALion 3 ManualBorralla LixoОценок пока нет
- Audio Signal ProcessingДокумент35 страницAudio Signal ProcessingTejanshu DarjiОценок пока нет
- Spectrogram Using Short-Time Fourier Transform - MATLAB Spectrogram PDFДокумент25 страницSpectrogram Using Short-Time Fourier Transform - MATLAB Spectrogram PDFÁlvaro Quintana CarvachoОценок пока нет
- Wavetable Synthesis Basic IntroductionДокумент1 страницаWavetable Synthesis Basic IntroductionBen GraysonОценок пока нет
- FFT Computation and Generation of SpectrogramДокумент32 страницыFFT Computation and Generation of Spectrogramps1188Оценок пока нет
- Ultimate Midi Guide From PDFДокумент4 страницыUltimate Midi Guide From PDFnetzah2padre100% (1)
- Patch Design for Diva: How to Create Mono Lead SoundsДокумент8 страницPatch Design for Diva: How to Create Mono Lead SoundsMichael WeinsteinОценок пока нет
- Immersive Audio Signal ProcessingДокумент3 страницыImmersive Audio Signal ProcessingSubhaОценок пока нет
- Mdegranular : Granular Synthesis External For Max:mspДокумент7 страницMdegranular : Granular Synthesis External For Max:mspcubb8387Оценок пока нет
- Digital Signal Processing for Audio Applications: Volume 2 - CodeОт EverandDigital Signal Processing for Audio Applications: Volume 2 - CodeРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)
- Audio Coding ThesisДокумент126 страницAudio Coding ThesisKhaqan TahirОценок пока нет
- Met A Plug in ManualДокумент6 страницMet A Plug in ManualdienteОценок пока нет
- AN INVERTED ENVELOPE ‘FLIPS’ THE ENVELOPE IN QUESTIONДокумент4 страницыAN INVERTED ENVELOPE ‘FLIPS’ THE ENVELOPE IN QUESTIONdradetoxОценок пока нет
- Mozzi Interactive Sound Synthesis On The Open Source ArduinoДокумент7 страницMozzi Interactive Sound Synthesis On The Open Source ArduinojfkОценок пока нет
- Algorithmic Composer: Openmusic and Chaos - Omchaos LibraryДокумент11 страницAlgorithmic Composer: Openmusic and Chaos - Omchaos LibrarysophochaОценок пока нет
- The Ambisonic Decoder Toolbox: Extensions For Partial Coverage Loudspeaker ArraysДокумент36 страницThe Ambisonic Decoder Toolbox: Extensions For Partial Coverage Loudspeaker ArraysAaron J. HellerОценок пока нет
- Digital Audio EffectsДокумент47 страницDigital Audio Effectscap2010100% (1)
- Eti 4M09 4 09 04 29 GM TacДокумент8 страницEti 4M09 4 09 04 29 GM TaclaurianОценок пока нет
- The 10 Modes of OBDIIДокумент6 страницThe 10 Modes of OBDIIisshmangОценок пока нет
- Heavy-Duty Circuit Tester: Item 30779Документ4 страницыHeavy-Duty Circuit Tester: Item 30779isshmangОценок пока нет
- Fastec Diagnosis by Isshman GarciaДокумент5 страницFastec Diagnosis by Isshman GarciaisshmangОценок пока нет
- Hologram USA Media KitДокумент27 страницHologram USA Media KitisshmangОценок пока нет
- 500 Amp Carbon Pile Load Tester PDFДокумент8 страниц500 Amp Carbon Pile Load Tester PDFisshmangОценок пока нет
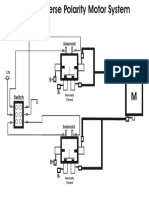
- Reverse Polarity Motor SchematicДокумент1 страницаReverse Polarity Motor SchematicisshmangОценок пока нет
- Ideal Industries, Inc. Technical Manual MODEL: 61-340 MODEL: 61-342 Multimeter Service InformationДокумент25 страницIdeal Industries, Inc. Technical Manual MODEL: 61-340 MODEL: 61-342 Multimeter Service InformationisshmangОценок пока нет
- K-Meter: User ManualДокумент12 страницK-Meter: User ManualisshmangОценок пока нет
- S&G Short Finder 25300 InstructionsДокумент2 страницыS&G Short Finder 25300 InstructionsisshmangОценок пока нет
- Obdtester Manual enДокумент25 страницObdtester Manual en2791957100% (1)
- Autel MaxiDAS DS808 Full Kit User Manual V1.00Документ114 страницAutel MaxiDAS DS808 Full Kit User Manual V1.00obd365Оценок пока нет
- SRF39FPДокумент2 страницыSRF39FPisshmangОценок пока нет
- InstructionsДокумент1 страницаInstructionsisshmangОценок пока нет
- 5 Day Bodybuilding Workout Schedule PDFДокумент3 страницы5 Day Bodybuilding Workout Schedule PDFVenkat Chowdary YamparalaОценок пока нет
- Exercise-Log 5daysДокумент1 страницаExercise-Log 5daysapi-361058314Оценок пока нет
- 194C-LA-232722 Section 1 - 161Документ165 страниц194C-LA-232722 Section 1 - 161isshmangОценок пока нет
- 9.2 Whats NewДокумент2 страницы9.2 Whats NewisshmangОценок пока нет
- 194C-LA-232722 Section 3 - 162Документ168 страниц194C-LA-232722 Section 3 - 162isshmangОценок пока нет
- 194C-LA-232722 Section 4 - 22Документ26 страниц194C-LA-232722 Section 4 - 22isshmangОценок пока нет
- Evap Theory and Operation - 2004 4.2l - Bravada, Envoy & TrailblazerДокумент2 страницыEvap Theory and Operation - 2004 4.2l - Bravada, Envoy & TrailblazerisshmangОценок пока нет
- 2004 Trailblazer P0442 (From My GM Software)Документ4 страницы2004 Trailblazer P0442 (From My GM Software)isshmangОценок пока нет
- K-Meter: User ManualДокумент12 страницK-Meter: User ManualisshmangОценок пока нет
- 13 Q Driveability Questionaire PDFДокумент1 страница13 Q Driveability Questionaire PDFisshmangОценок пока нет
- 2004 Evap System Repair Instructions - 4.2l - Bravada, Envoy & TrailblazerДокумент29 страниц2004 Evap System Repair Instructions - 4.2l - Bravada, Envoy & Trailblazerisshmang100% (2)
- IRig Keys 37 PRO User ManualДокумент13 страницIRig Keys 37 PRO User Manualkankucho78Оценок пока нет
- Mitchell 1 Article - 2004 Evap, Fuel System, Fittings... Etcand More 4.2l - Bravada, Envoy & TrailblazerДокумент117 страницMitchell 1 Article - 2004 Evap, Fuel System, Fittings... Etcand More 4.2l - Bravada, Envoy & TrailblazerisshmangОценок пока нет
- Start TestДокумент29 страницStart TestisshmangОценок пока нет
- 7 Key Elements of Music ProductionДокумент39 страниц7 Key Elements of Music Productionisshmang100% (2)
- MPC2000XL ManualДокумент209 страницMPC2000XL ManualRoparapera AmericanaОценок пока нет
- Python and Matlab Project Course On Design and Performance Analysis of 5G Wireless Systems: Mmwave, Massive Mimo, Noma, FBMC, Full Duplex and IotДокумент8 страницPython and Matlab Project Course On Design and Performance Analysis of 5G Wireless Systems: Mmwave, Massive Mimo, Noma, FBMC, Full Duplex and IotSandeep VermaОценок пока нет
- Digital Communications LaboratoryДокумент25 страницDigital Communications Laboratorysunny756Оценок пока нет
- Kennedy 4th EditionДокумент14 страницKennedy 4th EditionJesmar PosadasОценок пока нет
- Courses EECE DeptДокумент33 страницыCourses EECE Deptshahzad pervezОценок пока нет
- PLC 1790 Technical ManualДокумент48 страницPLC 1790 Technical ManualAghil Ghiasvand MkhОценок пока нет
- Voltage Controller OscillatorДокумент9 страницVoltage Controller OscillatorAlan WahyudiОценок пока нет
- r05220405 Analog CommunicationsДокумент8 страницr05220405 Analog CommunicationsandhracollegesОценок пока нет
- Cascadia Manual 2023.04.12Документ109 страницCascadia Manual 2023.04.12Sfx WillowОценок пока нет
- Anna University Trichy B.Tech Information Technology SyllabusДокумент84 страницыAnna University Trichy B.Tech Information Technology SyllabusvelklncitОценок пока нет
- Yaesu System FusionДокумент21 страницаYaesu System Fusionapi-330110643Оценок пока нет
- Hull Penetrator Replacement System (HPRS)Документ7 страницHull Penetrator Replacement System (HPRS)doom55Оценок пока нет
- Chapter12 Power AmplifiersДокумент107 страницChapter12 Power AmplifiersNikunj ShahОценок пока нет
- BK4811B Datasheet V1.2 PDFДокумент37 страницBK4811B Datasheet V1.2 PDFFlorian NicolaeОценок пока нет
- Unit - IV - Spread Spectrum ModulationДокумент16 страницUnit - IV - Spread Spectrum ModulationPrisha SinghОценок пока нет
- MODUL II: AM Modulation and DemodulationДокумент16 страницMODUL II: AM Modulation and DemodulationI Komang SulastraОценок пока нет
- Ece-V-Information Theory & Coding (10ec55) - NotesДокумент217 страницEce-V-Information Theory & Coding (10ec55) - NotesRaghu N GowdaОценок пока нет
- Lecture 2 - Overview of Optical Fiber CommunicationДокумент12 страницLecture 2 - Overview of Optical Fiber Communicationsamarth100% (1)
- GPS Signals (C)Документ23 страницыGPS Signals (C)indika2222Оценок пока нет
- Computer Networks MCQ - Basics & Access NetworksДокумент309 страницComputer Networks MCQ - Basics & Access NetworksAlem GirmaОценок пока нет
- Key Features of OPTIMOD-FM 5700i: Two Optimized Processing ChainsДокумент8 страницKey Features of OPTIMOD-FM 5700i: Two Optimized Processing ChainsFelipe QuindeОценок пока нет
- Report GSM Based Remote Monitoring of 3 Parameters On TransformersДокумент16 страницReport GSM Based Remote Monitoring of 3 Parameters On TransformersJilly ArasuОценок пока нет
- An Introduction To Frequency ModulationДокумент11 страницAn Introduction To Frequency ModulationHevidar JankirОценок пока нет
- 01 WDM PrinciplesДокумент55 страниц01 WDM PrinciplesFaris Azhari AbdulfattahОценок пока нет
- Iptv BroadcasterДокумент12 страницIptv BroadcasterZeljko TrnjanacОценок пока нет
- Kamus ItДокумент2 432 страницыKamus ItNurhasim HasanОценок пока нет
- ASK Experiment Recovers Digital SignalДокумент8 страницASK Experiment Recovers Digital SignalShiela Monique Fajardo100% (1)
- AFG320 Service ManualДокумент128 страницAFG320 Service ManualmanyergsОценок пока нет
- Seminar Report Seminar ReportДокумент22 страницыSeminar Report Seminar Reportksm cherryОценок пока нет
- Mock Board Examination in Esat CДокумент8 страницMock Board Examination in Esat CspidyanОценок пока нет
- SK200-1W Lora Anti-Interference Wireless Single-Channel Switch Module v1.1Документ10 страницSK200-1W Lora Anti-Interference Wireless Single-Channel Switch Module v1.1Вадим МкртчянОценок пока нет