Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Chapter Nine Homework
Загружено:
Michelle Murphy0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
160 просмотров2 страницыNeuroscience, Exploring the Brain
Авторское право
© © All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документNeuroscience, Exploring the Brain
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
160 просмотров2 страницыChapter Nine Homework
Загружено:
Michelle MurphyNeuroscience, Exploring the Brain
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 2
Chapter Nine Homework
1. What physical property of light is most closely related to the
perception of color?
Light is electromagnetic radiation, which has three properties:
wavelength, frequency, and amplitude. Wavelength is closely
related to the perception of color because wavelengths of 400700 nm are visible to the naked eye. Within this visible spectrum,
different wavelengths appear as different colors.
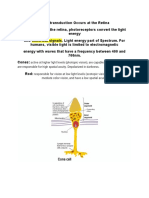
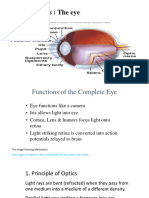
2. Name eight structures in the eye that light passes through before
it strikes the photoreceptors?
The eight structures of the eye through which light passes before
striking the photoreceptors are the cornea, the aqueous humor,
the lens, the vitreous humor, the ganglion cell layer, the inner
plexiform layer, the inner nuclear layer and the outer plexiform
layer.
3. What is myopia, and how is it corrected?
Myopia is commonly referred to as nearsightedness, which
occurs when the eyeball is too long. When the eyeball is too long,
the rays of light converge and cross before the retina, therefore
the image on the retina is blurred. The amount of refraction that
the cornea and the lens provide is too large to focus distant
objects on the retina. To correct this, the use of artificial concave
lenses are used to help focus the image on the retina.
4. Give three reasons explaining why visual acuity is best when
images fall on the fovea.
Visual acuity is best when it falls on the fovea for three reasons.
The first being that visual acuity improves as the ratio of
photoreceptors to ganglion cells decreases. Few photoreceptors
feed each ganglion cell in the fovea, creating a low ration which
maximizes visual acuity. Secondly, the fovea sits in a pit that the
lateral displacement of the ganglion and bipolar cells creates
above the photoreceptors. This allows light to strike the
photoreceptors without passing through the other layers of
retinal cells, minimizing light scatter that can blur the image.
Finally, visual space is not mapped to the targets of visual input
uniformly. The central few degrees of the retina are overrepresented in neural space. Signals from individual cones in
the fovea are represented in a larger volume of brain tissue than
input from photoreceptors in peripheral regions of the retina. This
specialization contributes to high acuity in central vision.
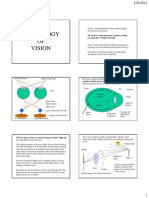
5. What happens in the retina when you get used to the dark?
Why cant you see color in the dark?
Getting used to the dark is called dark adaptation. This capability
is a consequence of a duplex retina, in which cones function best
at high levels of illumination and rods function best at low levels
of illumination. When moving from high to low levels of
illumination, the retina must be adapted to the dark before the
rods are maximally sensitive. Dark adaptation is a biochemical
process in which rhodopsin, the rod photopigment, regenerates
after being bleached in the light. The functional circuitry of the
retina also readjusts as rhodopsin regenerates. Consequently,
information from more rods is available to ganglion cells. The
regeneration of unbleached rhodopsin and the resulting changes
in functional circuitry take about 20-25 minutes. At night, it is
difficult to detect colors because the cones, which have three
photopigments with different spectral sensitivities, are inactive.
Only cones are capable of color vision. At low levels of
illumination, only rods are active and they contain only one
photopigment. Rhodopsins peak sensitivity is 500 nm.
Вам также может понравиться
- Low Vision: Assessment and Educational Needs: A Guide to Teachers and ParentsОт EverandLow Vision: Assessment and Educational Needs: A Guide to Teachers and ParentsОценок пока нет
- Jahandar Hajiyev-1Документ33 страницыJahandar Hajiyev-1aze2005aze2020Оценок пока нет
- Phototransduction Occurs at The RetinaДокумент13 страницPhototransduction Occurs at The RetinaKathleen RussellОценок пока нет
- Ophthalmic Dispensing Revision Guide: First Year Part OneОт EverandOphthalmic Dispensing Revision Guide: First Year Part OneРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (3)
- W1-6 Biochemistry of Vision and Hearing Lecture PDFДокумент75 страницW1-6 Biochemistry of Vision and Hearing Lecture PDFSAHIL AGARWALОценок пока нет
- MDT - Illu - Lecture1Документ14 страницMDT - Illu - Lecture1Madhura TuljapurkarОценок пока нет
- Vision: Written ReportДокумент25 страницVision: Written Reportloan kimОценок пока нет
- Human Visual System (Disowner)Документ4 страницыHuman Visual System (Disowner)Christelle ZuluetaОценок пока нет
- The Main Parts of The Eye and Their FunctionДокумент5 страницThe Main Parts of The Eye and Their FunctionJoshuaОценок пока нет
- Bio Psychology Lecture Notes Chapter 6 The Visual SystemДокумент7 страницBio Psychology Lecture Notes Chapter 6 The Visual SystemGeneric_Persona50% (2)
- Sensory and Perceptual Process NotesДокумент10 страницSensory and Perceptual Process NotesSarah KimОценок пока нет
- The Eye and VisionДокумент70 страницThe Eye and VisionLedkos SLОценок пока нет
- CHP 2Документ22 страницыCHP 2Muskaan ShaikhОценок пока нет
- Structure and Function of EyesДокумент11 страницStructure and Function of EyesSamar Ameen SialОценок пока нет
- 2-Special SensesДокумент63 страницы2-Special Sensestmqt2fbnzgОценок пока нет
- Chapter 3 Sensation & Perception (A)Документ13 страницChapter 3 Sensation & Perception (A)Sidra.kОценок пока нет
- Presentation1 EyeДокумент12 страницPresentation1 EyesujithaОценок пока нет
- Special SensesДокумент23 страницыSpecial SensesÑäd ÉèmОценок пока нет
- The Human EyeДокумент3 страницыThe Human EyeKajetano GraucosОценок пока нет
- 1295188730neuro Essay 2 - Compare The Properties of Rods and Cones, and Their Retinal Pathways EssayДокумент4 страницы1295188730neuro Essay 2 - Compare The Properties of Rods and Cones, and Their Retinal Pathways EssayscholifyОценок пока нет
- Explain About Elements of Visual PerceptionДокумент8 страницExplain About Elements of Visual PerceptionYagneshОценок пока нет
- The Visual SystemДокумент9 страницThe Visual SystemLaura SalidoОценок пока нет
- Sensation: I. Eye: VisionДокумент15 страницSensation: I. Eye: VisionAvie Tablatin De LeonОценок пока нет
- Vision - : The EyeДокумент17 страницVision - : The EyeVaishali GuptaОценок пока нет
- Neurostiinte - Eye, Brain, Vision - David Hubel (Cap 3,4 p32-83) PDFДокумент52 страницыNeurostiinte - Eye, Brain, Vision - David Hubel (Cap 3,4 p32-83) PDFgicutaОценок пока нет
- The Physiology of Human Vision: Steven M. LavalleДокумент17 страницThe Physiology of Human Vision: Steven M. LavalleAdson AlcantaraОценок пока нет
- Lecture Notes 5Документ3 страницыLecture Notes 5Carol RiveraОценок пока нет
- The Photochemistry of VisionДокумент82 страницыThe Photochemistry of VisionSyedaNaveenBatool100% (4)
- 0 OphthalmologyДокумент12 страниц0 OphthalmologyParsaant SinghОценок пока нет
- Chapter 4 - Perception and SensationДокумент6 страницChapter 4 - Perception and Sensationecaber.a12343991Оценок пока нет
- Light & Eyes: - Vision Begins When Light Comes Into The Eye - LightДокумент31 страницаLight & Eyes: - Vision Begins When Light Comes Into The Eye - LightfouadОценок пока нет
- Biology Eye NotesДокумент12 страницBiology Eye NotesBalakrishnan MarappanОценок пока нет
- The Physics of Light and Color - Human Vision and Color Perception - Olympus LSДокумент14 страницThe Physics of Light and Color - Human Vision and Color Perception - Olympus LSmarialopezmartinez424Оценок пока нет
- Human SensesДокумент6 страницHuman Sensesvicky7Оценок пока нет
- Bionic Eye EB KNS 2019Документ58 страницBionic Eye EB KNS 2019Lalitaditya DivakarlaОценок пока нет
- Chapter 18 PDFДокумент53 страницыChapter 18 PDFMencam AsongОценок пока нет
- What Is Vision?Документ6 страницWhat Is Vision?mwxОценок пока нет
- Color PhysicsДокумент85 страницColor PhysicsThe GentlemanОценок пока нет
- CNS 03 VisualДокумент15 страницCNS 03 VisualJeff ParkОценок пока нет
- Sensory and Perceptual ProcessesДокумент8 страницSensory and Perceptual ProcessesKika EspejoОценок пока нет
- Special SensesДокумент152 страницыSpecial SensesCor GuerreroОценок пока нет
- 5 - VisionДокумент7 страниц5 - VisionJamesMontisОценок пока нет
- Structure of Eye !Документ11 страницStructure of Eye !Leonora KadriuОценок пока нет
- VisionДокумент49 страницVisionSOFIA SALGADO SILVAОценок пока нет
- Vision ResearchДокумент4 страницыVision ResearchMichael SmithОценок пока нет
- CommunicationДокумент16 страницCommunicationbitchass niggaОценок пока нет
- Chapter4 Sensation and PerceptionДокумент6 страницChapter4 Sensation and PerceptionJenelyn Ponce AguiloОценок пока нет
- Eye PDFДокумент19 страницEye PDFDebbie MeyerОценок пока нет
- HME 2209-wk - 2Документ7 страницHME 2209-wk - 2frank kipkoech bettОценок пока нет
- Vision:: 1-Outer LayerДокумент3 страницыVision:: 1-Outer LayerAimal IhsasОценок пока нет
- Unit 2 Windows of KnowledgeДокумент9 страницUnit 2 Windows of Knowledgesajith kumar VariathОценок пока нет
- اخطاء انكسار 3&4Документ6 страницاخطاء انكسار 3&4Hassan AljaberiОценок пока нет
- Sensing and Perceiving 4.2Документ18 страницSensing and Perceiving 4.2Dami TepedeОценок пока нет
- Chapter 3Документ102 страницыChapter 3Womens Program Assosciation100% (1)
- The Eye and Its DiseasesДокумент33 страницыThe Eye and Its DiseasesbeedgaiОценок пока нет
- Sec 8 BДокумент3 страницыSec 8 BShiela Marie RodrigoОценок пока нет
- Psychology 100Документ10 страницPsychology 100extraordinarygirl99Оценок пока нет
- Chapter 5. VisionДокумент33 страницыChapter 5. Visionyamquim01Оценок пока нет
- Sensation and PerceptionДокумент3 страницыSensation and PerceptionjdmacatuladОценок пока нет
- Macular Function Test: Dr. PushpanjaliДокумент53 страницыMacular Function Test: Dr. Pushpanjalipushpanjali ramteke83% (6)
- Lecture 8 Special Senses Part 3-VisionДокумент32 страницыLecture 8 Special Senses Part 3-VisionMoses Jr KazevuОценок пока нет
- Byron L.-Electrophysiology of Vision - Clinical Testing and Applications (2005) PDFДокумент532 страницыByron L.-Electrophysiology of Vision - Clinical Testing and Applications (2005) PDFSabrina Fermano100% (1)
- US Navy Course NAVEDTRA 12968D - Lookout Training HandbookДокумент81 страницаUS Navy Course NAVEDTRA 12968D - Lookout Training HandbookGeorges50% (4)
- Ergonomics in Computerized OfficesДокумент238 страницErgonomics in Computerized Officestinhcoonline100% (3)
- Sensation and Perception - PsychologyДокумент105 страницSensation and Perception - PsychologyJet EstefaniОценок пока нет
- IE 5790 - HUMAN Factor Engineering: Lecturer Set 4 - Visual Sensory SystemДокумент37 страницIE 5790 - HUMAN Factor Engineering: Lecturer Set 4 - Visual Sensory SystemattaurrehmanОценок пока нет
- M-9 Human Factors: Aviation Training HubДокумент104 страницыM-9 Human Factors: Aviation Training HubMuhammad SubhanОценок пока нет
- Laboratory Exercise in Sensory Physiology: Student Lab ManualДокумент17 страницLaboratory Exercise in Sensory Physiology: Student Lab ManualChippy RabeОценок пока нет
- Physiology of VisionДокумент12 страницPhysiology of VisionAlexis Bondad100% (1)
- Electroretinogram (Erg)Документ33 страницыElectroretinogram (Erg)Rani Mahita AjiОценок пока нет
- Vision: - Carlene S. Solidum, MD, DPPSДокумент98 страницVision: - Carlene S. Solidum, MD, DPPSJimell ObradorОценок пока нет
- Psychology Final NotesДокумент266 страницPsychology Final NotesTanay SinghОценок пока нет
- Neuroscience For Kids - Vision Exp PDFДокумент23 страницыNeuroscience For Kids - Vision Exp PDFAr Hitesh ParmarОценок пока нет
- Physiology of Vision: Adeline Joseph Ii MSC ZoologyДокумент14 страницPhysiology of Vision: Adeline Joseph Ii MSC Zoologyadeline JosephОценок пока нет
- Knowing The World: Functional Limitations of Sense OrgansДокумент12 страницKnowing The World: Functional Limitations of Sense Organsramya anil nairОценок пока нет
- LegibilityДокумент49 страницLegibilitytakahiroshimadaОценок пока нет
- Perception Ch2-3 - The Eye and RetinaДокумент70 страницPerception Ch2-3 - The Eye and Retina楊楨琳Оценок пока нет
- Westinghouse Electric Corporation 0002Документ262 страницыWestinghouse Electric Corporation 0002Carlos MolinaОценок пока нет
- Insect Vision: Zales Promo Code GemstoneДокумент11 страницInsect Vision: Zales Promo Code Gemstonejohn cenaОценок пока нет
- Photo Chemistry of VisionДокумент107 страницPhoto Chemistry of VisionPhysiology by Dr Raghuveer100% (1)
- Special Senses) 3. Photoreceptors - Rods and Cones - KeyДокумент1 страницаSpecial Senses) 3. Photoreceptors - Rods and Cones - Keyranag59100Оценок пока нет
- Clinical OpticsДокумент88 страницClinical OpticsKris ArchibaldОценок пока нет
- Studio PilotДокумент8 страницStudio PilotAnonymous fyN6ueOОценок пока нет
- Physiology of Eye. Physiology of VisionДокумент27 страницPhysiology of Eye. Physiology of VisionSmartcool So100% (1)
- Sensory and Perceptual Process NotesДокумент10 страницSensory and Perceptual Process NotesSarah KimОценок пока нет
- Indoor Lighting Design Incorporating Human PsychologyДокумент13 страницIndoor Lighting Design Incorporating Human PsychologyNatthamol Toey PhumchanОценок пока нет
- The Photochemistry of VisionДокумент82 страницыThe Photochemistry of VisionSyedaNaveenBatool100% (4)
- The EyeДокумент173 страницыThe Eyejamaica dangaОценок пока нет
- ADHD is Awesome: A Guide to (Mostly) Thriving with ADHDОт EverandADHD is Awesome: A Guide to (Mostly) Thriving with ADHDРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (3)
- The Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityОт EverandThe Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (30)
- Think This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeОт EverandThink This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeРейтинг: 2 из 5 звезд2/5 (1)
- Love Life: How to Raise Your Standards, Find Your Person, and Live Happily (No Matter What)От EverandLove Life: How to Raise Your Standards, Find Your Person, and Live Happily (No Matter What)Рейтинг: 3 из 5 звезд3/5 (1)
- LIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionОт EverandLIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (404)
- The Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsОт EverandThe Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (4)
- Summary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisОт EverandSummary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (42)
- Raising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsОт EverandRaising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)
- By the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsОт EverandBy the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsОценок пока нет
- Summary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedОт EverandSummary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (81)
- Raising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsОт EverandRaising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (170)
- The Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaОт EverandThe Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (266)
- Dark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.От EverandDark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (110)
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityОт EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5)
- Summary: Limitless: Upgrade Your Brain, Learn Anything Faster, and Unlock Your Exceptional Life By Jim Kwik: Key Takeaways, Summary and AnalysisОт EverandSummary: Limitless: Upgrade Your Brain, Learn Anything Faster, and Unlock Your Exceptional Life By Jim Kwik: Key Takeaways, Summary and AnalysisРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (8)
- Empath: The Survival Guide For Highly Sensitive People: Protect Yourself From Narcissists & Toxic Relationships. Discover How to Stop Absorbing Other People's PainОт EverandEmpath: The Survival Guide For Highly Sensitive People: Protect Yourself From Narcissists & Toxic Relationships. Discover How to Stop Absorbing Other People's PainРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (95)
- The Courage Habit: How to Accept Your Fears, Release the Past, and Live Your Courageous LifeОт EverandThe Courage Habit: How to Accept Your Fears, Release the Past, and Live Your Courageous LifeРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (253)
- Mindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessОт EverandMindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (328)
- Summary: Thinking, Fast and Slow: by Daniel Kahneman: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedОт EverandSummary: Thinking, Fast and Slow: by Daniel Kahneman: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (61)
- The Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossОт EverandThe Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (6)
- The Marshmallow Test: Mastering Self-ControlОт EverandThe Marshmallow Test: Mastering Self-ControlРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (59)
- Manipulation: The Ultimate Guide To Influence People with Persuasion, Mind Control and NLP With Highly Effective Manipulation TechniquesОт EverandManipulation: The Ultimate Guide To Influence People with Persuasion, Mind Control and NLP With Highly Effective Manipulation TechniquesРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (1412)
- Cult, A Love Story: Ten Years Inside a Canadian Cult and the Subsequent Long Road of RecoveryОт EverandCult, A Love Story: Ten Years Inside a Canadian Cult and the Subsequent Long Road of RecoveryРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)