Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Relays
Загружено:
Rajeev RawatАвторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Relays
Загружено:
Rajeev RawatАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
6/26/2014
relays - | FaaDoOEngineers.com
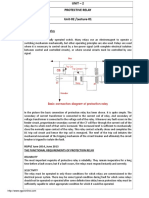
Types of Relays
Types of protection relays are mainly based on their characteristic, logic, on actuating parameter and operation mechanism.
Based on operation mechanism protection relay can be categorized as electro magnetic relay, static relay and mechanical relay.
Actually relay is nothing but a combination of one or more open or closed contacts. These all or some specific contacts the relay
change their state when actuating parameters are applied to the relay. That means open contacts become closed and closed
contacts become open. In electromagnetic relay these closing and opening of relay contacts are done by electromagnetic action
of a solenoid.
In mechanical relay these closing and opening of relay contacts are done by mechanical displacement of different gear level
system.
In static relay it is mainly done by semiconductor switches like thyristor.
In digital relay on and off state can be referred as 1 and 0 state.
Based on Characteristic the protection relay can be categorized as1. Definite time relays
Definite Time Over Current Relay
This relay is created by applying intentional time delay after crossing pick up value of the current. A definite time over current
relay can be adjusted to issue a trip output at definite amount of time after it picks up. Thus, it has a time setting adjustment
and pick up adjustment.
1. Inverse time relays with definite minimum time(IDMT)
Ideal inverse time characteristics can not be achieved, in an over current relay. As the current in the system increases, the
secondary current of the current transformer is increased proportionally. The secondary current is fed to the relay current coil.
But when the CT becomes saturated, there would not be further proportional increase of CT secondary current with increased
system current.
From this phenomenon it is clear that from trick value to certain range of faulty level, an inverse time relay shows exact inverse
characteristic. But after this level of fault, the CT becomes saturated and relay current does not increase further with increasing
faulty level of the system. As the relay current is not increased further, there would not be any further reduction in time of
operation in the relay. This time is referred as minimum time of operation.
Hence, the characteristic is inverse in the initial part, which tends to a definite minimum operating time as the electric current
becomes very high. That is why the relay is referred as inverse definite minimum time over current relay or simply IDMT
relay.
Sponsored Ads
http://www.faadooengineers.com/threads/35620-relays
1/7
6/26/2014
relays - | FaaDoOEngineers.com
1. Instantaneous relays.
Instantaneous over current relay, which operates very fast with no intentional time delay and the operating time of these relay can
be as low as 0.01sec . These relay operates only when the impedance between the relay and the source z s is very small
compared to the impedance to the impedance of the protected section z l .
7. Voltage restraint over current relay.
The voltage restrained over current protection function(51V) is used to protect generators. The operation set point is adjusted
according to the voltage to take into account cases of faults close to the generator which cause voltage dips and short circuit
current. This protection function is three-pole. It picks up if one ,two or three phase currents reach the voltage-adjusted operation
set point.
Based on of logic the protection relay can be categorized as1. Differential.
Principle of Differential Protection scheme is one simple conceptual technique. The differential relay actually compares
between primary current and secondary current of power transformer, if any unbalance found in between primary and secondary
currents the relay will actuate and inter trip both the primary and secondary circuit breaker of the transformer.
[IMG]file:///C:\Users\arptst\AppData\Local\Temp\msohtmlclip1\01\clip_image001.gif[/IMG]
2. Unbalance.
3. Neutral displacement.
4. Directional.
The over-current protection can be given directional feature by adding directional element in the protection system.
Directional over-current protection responds to over-currents for a particular direction flow. If power flow is in the
opposite direction, the directional over-current protection remains un-operative.
Directional over-current protection comprises over-current relay and power directional relay- in a single relay casing.
The power directional relay does not measure the power but is arranged to respond to the direction of power flow.
Directional operation of relay is used where the selectivity can be achieved by directional relaying. The directional
relay recognizes the direction in which fault occurs, relative to the location of the relay. It is set such that it actuates
for faults occurring in one direction only. It does not act for faults occurring in the other direction. Consider a feeder
AC (Fig. 9) passing through sub-section B. The circuit breaker CB3 is provided with a directional
[IMG]file:///C:\Users\arptst\AppData\Local\Temp\msohtmlclip1\01\clip_image002.emz[/IMG](Fig. 9) Principle of directional
protection
Relay `R' which will trip the breaker CB3 if fault power flow in direction C alone. Therefore for faults in feeder AB,
the circuit breaker CB3 does not trip unnecessarily. However for faults in feeder BC the circuit-breaker CB3 trips
Because it's protective relaying is set with a directional feature to act in
http://www.faadooengineers.com/threads/35620-relays
2/7
6/26/2014
relays - | FaaDoOEngineers.com
direction AC
Another interesting example of directional protection is that of reverse power protection of generator (Fig. 10). If the
prime mover fails, the generator continues to run as a motor and takes power from bus-bars.
[IMG]file:///C:\Users\arptst\AppData\Local\Temp\msohtmlclip1\01\clip_image003.emz[/IMG](Fig. 10) Reverse powers protection
against motoring action of a generator
Directional power protection operates in accordance with the direction of power flow.
Reverse power protection operates when the power direction is reversed in relation to the normal working direction.
Reverse power relay is different in construction than directional over-current relay.
In directional over-current relay, the directional element does not measure the magnitude of power. It senses only
direction of power flow. However, in Reverse Power Relays, the directional element measures mag
nitude and
direction of power flow.
1. Restricted earth fault.
An external fault in the star side will result in current flowing in the line current transformer of the affected phase and at the same
time a balancing current flows in the neutral current transformer, hence the resultant electric current in the relay is therefore zero.
So this REF relay will not be actuated for external earth fault. But during internal fault the neutral current transformer only carries
the unbalance fault current and operation of Restricted Earth Fault Relay takes place. This scheme of restricted earth fault
protection is very sensitive for internal earth fault of electrical power transformer. The protection scheme is comparatively
cheaper than differential protection scheme
6. Over fluxing.
7. Distance schemes.
8. Bus bar protection.
9. Reverse power relays.
10.Loss of excitation.
11.Negative phase sequence relays etc.
Based on actuating parameter the protection relay can be categorized as1.Current relays.
2. Voltage relays.
3. Frequency relays.
4. Power relays etc.
Based on application the protection relay can be categorized as1.Primary relay.
2. Backup relay.
Primary relay or primary protection relay is the first line of power system protection whereas backup relay is operated only when
primary relay fails to be operated during fault. Hence backup relay is slower in action than primary relay. Any relay may fail to be
operated due to any of the following reasons,
1) The protective relay itself is defective.
2) DC Trip voltage supply to the relay is unavailable.
3) Trip lead from relay panel to circuit breaker is disconnected.
4) Trip coil in the circuit breaker is disconnected or defective.
5) Current or voltage signals from CT or PT respectively is unavailable.
As because backup relay operates only when primary relay fails, backup protection relay should not have anything common with
primary protection relay.
Some examples of Mechanical Relay are1. Thermal
(a) OT trip (Oil Temperature Trip)
http://www.faadooengineers.com/threads/35620-relays
3/7
6/26/2014
relays - | FaaDoOEngineers.com
(b) WT trip (Winding Temperature Trip)
(C) Bearing temp trip etc.
2. Float type
(a) Buchholz
(b) OSR
(c) PRV
(d) Water level Controls etc.
3. Pressure Switches.
4. Mechanical Interlocks.
5. Pole discrepancy Relay.
WORKING OF SINGLE-POLE DOUBLE-THROW RELAY
SPDT relay is an electromagnetic switch consisting of a coil (terminals 85 & 86), 1 common terminal (30), 1 normally closed
terminal (87a) and a normally open terminal (87).
[IMG]file:///C:\Users\arptst\AppData\Local\Temp\msohtmlclip1\01\clip_image004.jpg[/IMG]
Fig1. Poles of a SPDT Relay Switch
When the coil of the relay is at rest (not energized), the common terminal (30) and the normally closed terminal (87a) have
continuity.
[IMG]file:///C:\Users\arptst\AppData\Local\Temp\msohtmlclip1\01\clip_image005.jpg[/IMG]
Fig2. Un-energized Relay Position
When the coil is energized, the common terminal (30) and the normally open terminal (87) have continuity.
[IMG]file:///C:\Users\arptst\AppData\Local\Temp\msohtmlclip1\01\clip_image006.jpg[/IMG]
Fig3. Energized Relay Position
Basically, the coil is an electromagnet that causes the arm that is always connected to the common (30) to pivot when
energized thereby breaking contact with the normally closed terminal (87a) and making it with the normally open terminal (87).
Below is an example of how the connections are made to a load in a circuit using a SPDT relay switch?
[IMG]file:///C:\Users\arptst\AppData\Local\Temp\msohtmlclip1\01\clip_image007.jpg[/IMG]
Fig4. Connection of an SPDT Relay to Load
When the relay coil is energized, contact is established between the common (COM) and normally-open (NO) terminal thereby
completing the supply connections to the load. Hence, the load is switched on when the relay is energized. Also check this
article to understand the working of relays with the help of pictures, here - How Relay works
Different Types of Relay
1. Single Pole Single Throw (SPST)- these types of relay comprise of 4 terminals. Two terminals are used as coil points and
other two can be used to connect or disconnect the circuit (A and B).
2. Single Pole Double Throw (SPDT)- these types of relay comprise of 5 terminals two for coil one for common terminal(C)
and rest two can be connected to the common terminal.
3. Double Pole Single Throw (DPST)- these types of relay comprise of 6 terminal two for coil and other four for connecting and
disconnecting two device. In other words it contains two SPST relay in one package.
4.DoublePole Double Throw(SPDT)- these types of relay comprise of 8 terminal two for coil and another two as common point
and rest for connecting and disconnecting devices. In another words in this two SPDT relay are connected in one package.
[IMG]file:///C:\Users\arptst\AppData\Local\Temp\msohtmlclip1\01\clip_image008.png[/IMG]
Comparison of Different Type Relay:
Characteristic
Electro Mechanical
Static Relay
Digital Relay
Numerical Relay
Present generation Relays.
Present generation Relays.
Relay
Technology
1st generation
2nd generation
Standard
Relays.
Relays.
http://www.faadooengineers.com/threads/35620-relays
4/7
6/26/2014
relays - | FaaDoOEngineers.com
Operating
They use principle of
In this relays
They use Microprocessor. Within built
They use Microprocessor. W
Principle
electromagnetic
transistors and ICs
software with predefined values
software with predefined valu
principle.
r been used
Measuring
Induction
R, L, C, Transistors,
Microprocessors, Digital ICs, Digital
Microprocessor s,Digital ICs
elements/
disc,Electromagnets,
Analogue ICs
Signal Processors
processors
Hardware
Induction cup,
comparators
Balance Beam
Measuring
Electrical
Level
A/D
A/D
method
Qtysconverted
detects,comparison
conversion,Numericalalgorithmtechniques
conversion,Numericalalgorit
intomechanical
withreference value
force, torque
in analogue
Comparator
Surrounding
Depend upon
There value may
Environment
gravitation and the
vary with respect to
value changes to the
temperature also.
surrounding
magnetic fields also.
Relay Size
Bulky
Small
Small
Compact
Speed of
Slow
Fast
Fast
Very Fast
Timing
Mechanical clock
Static timers
Counter
Counter
function
works, dashpot
Time of
Temp .Dependant
Temp. Dependant
Stable
Stable
Reliability
High
Low
High
High
Vibration Proof
No
Yes
Yes
Yes
Characteristics
Limited
Wide
Wide
Wide
Requirement
Required
Required
Not Required
Not Required
Response
Accuracy
http://www.faadooengineers.com/threads/35620-relays
5/7
6/26/2014
relays - | FaaDoOEngineers.com
of Draw Out
CT Burden
High
Low
Low
Low
CT Burden
8 to 10 VA
1 VA
<0.5 VA
<0.5 VA
Reset Time
Very High
Less
Less
Less
Auxiliary supply
Required
Required
Required
Required
Range of
Limited
Wide
Wide
Wide
Low
High
High
High
Function
Single Function
Single Function
Multi Function
Single Function
Maintenance
Frequent
Frequent
Low
Very Low
Resistance
100 mille ohms
10 Ohms
10 Ohms
10 Ohms
Output
< 1 Pico Farad
> 20 Pico Farads
> 20 Pico Farads
> 20 Pico Farads
Yes
No
No
No
No
Partially
Programmable
Programmable
No
No
Possible
Yes
Not Possible
Possible
Possible
Possible
Flags, targets
LEDs
LEDs, LCD
LEDs, LCD
No
Yes
Yes
Yes
settings
Isolation
Voltage
Capacitance
Deterioration
due to
Operation
Relay
Programming
SCADA
Compatibility
Operational
value
indication
Visual
indication
Self monitoring
http://www.faadooengineers.com/threads/35620-relays
6/7
6/26/2014
relays - | FaaDoOEngineers.com
Parameter
Plug setting, dial
Thumb wheel,dual
Keypad for numeric values,through
Keypad for numeric values,th
setting
setting
in line switches
computer
computer
Fault
Not possible
Not possible
possible
possible
Disturbance
Recording
http://www.faadooengineers.com/threads/35620-relays
7/7
Вам также может понравиться
- DAF CF Electrical System (To Chassis 0E621376) Service ManualДокумент792 страницыDAF CF Electrical System (To Chassis 0E621376) Service ManualAlex100% (2)
- Fault Detection in TM LineДокумент25 страницFault Detection in TM Linenaveen gОценок пока нет
- Door Monitor ProjectДокумент4 страницыDoor Monitor Projectlekhs_tim10% (1)
- Relays and C BДокумент33 страницыRelays and C BRachit KhannaОценок пока нет
- Eaton EX 2200-3000 Product ManualДокумент24 страницыEaton EX 2200-3000 Product ManualGabriel GonzalezОценок пока нет
- PCR049 MGDS 2 17 0001Документ11 страницPCR049 MGDS 2 17 0001DharmenderSinghChoudharyОценок пока нет
- Xrio Converter Manual Abb Ref615 v1.0 Enu Tu2.22 v1.000Документ11 страницXrio Converter Manual Abb Ref615 v1.0 Enu Tu2.22 v1.000m_dh87129Оценок пока нет
- RelayДокумент12 страницRelaytai58Оценок пока нет
- Harmonics MCPQG Ieee 2005Документ54 страницыHarmonics MCPQG Ieee 200523OtterОценок пока нет
- Reles Eletromecanicos Formulas de CurvasДокумент3 страницыReles Eletromecanicos Formulas de CurvasLUCELINO DA COSTA LARANJEIRAОценок пока нет
- Goldwind GW165-5.25.6MW-Product BrochureДокумент2 страницыGoldwind GW165-5.25.6MW-Product BrochureVictor SОценок пока нет
- FINAL HG 11 02 08 enДокумент64 страницыFINAL HG 11 02 08 enDarko MiticОценок пока нет
- Snubber Circuits ExplainedДокумент9 страницSnubber Circuits ExplainedcoolsinghrkОценок пока нет
- Over Current RelayДокумент42 страницыOver Current Relayyousafali15100% (1)
- CH 1 Intro 2 InstrumentationДокумент22 страницыCH 1 Intro 2 InstrumentationNorkarlina Binti Khairul AriffinОценок пока нет
- Abb UpsДокумент16 страницAbb Upsbiya saraОценок пока нет
- 1Документ15 страниц1Saravanaraja KumaresanОценок пока нет
- 4 - Types of DC Chopper PDFДокумент38 страниц4 - Types of DC Chopper PDFPrem KumarОценок пока нет
- Few Words About Digital Protection RelayДокумент5 страницFew Words About Digital Protection RelayPierre Enrique Carrasco FuentesОценок пока нет
- 2307882Документ116 страниц2307882Jimmy McynsОценок пока нет
- Experiment 4 - Three Phase Uncontrolled RectifierДокумент13 страницExperiment 4 - Three Phase Uncontrolled RectifierAaaa DdddОценок пока нет
- Practical Power System Protection - Book ReviewДокумент2 страницыPractical Power System Protection - Book Reviewحمزة الفيتوريОценок пока нет
- 3rd Harmonic FilterДокумент2 страницы3rd Harmonic Filterserban_el100% (1)
- p122 Micom Relay ManualДокумент3 страницыp122 Micom Relay ManualThuy DinhОценок пока нет
- GSM Based Fault Monitoring SystemДокумент23 страницыGSM Based Fault Monitoring SystemSanjana Singh100% (1)
- EI2203 - Electronic Devices and Circuits - 2 Marks With AnswersДокумент16 страницEI2203 - Electronic Devices and Circuits - 2 Marks With AnswersASPCN 2017Оценок пока нет
- DC ChoppersДокумент94 страницыDC ChoppersRaghu Raman100% (3)
- Unit-I Circuit BreakersДокумент13 страницUnit-I Circuit Breakerspurushg62Оценок пока нет
- Single Line Diagram (SLD) Or, One Line DiagramДокумент3 страницыSingle Line Diagram (SLD) Or, One Line DiagramFedilino P. FornollesОценок пока нет
- Over Under VoltДокумент1 страницаOver Under Voltapi-3747180100% (1)
- GATE EE 2015 Solved Paper PDFДокумент629 страницGATE EE 2015 Solved Paper PDFohioОценок пока нет
- BSNL (Bharat Sanchar Nigam Limited) : A Presentation OnДокумент25 страницBSNL (Bharat Sanchar Nigam Limited) : A Presentation OnMahesh Kumar NigamОценок пока нет
- Whirlpool FL 242Документ11 страницWhirlpool FL 242Claudio Luciano KupfersteinОценок пока нет
- Waste HandlerДокумент8 страницWaste HandlerDharmesh patelОценок пока нет
- Relay - Schneider Electric - Micom Serie20 - P115Документ259 страницRelay - Schneider Electric - Micom Serie20 - P115Jeffrey ChavezОценок пока нет
- Microprocessor Based Impedance RelayДокумент11 страницMicroprocessor Based Impedance RelayS Bharadwaj ReddyОценок пока нет
- Over and Under Voltage Relay CharacteriticsДокумент24 страницыOver and Under Voltage Relay CharacteriticsKashif RehmanОценок пока нет
- Medium Voltage Ac Drives Selection Guide: Powerflex 7000 - Direct-To-Drive™ Technology - Air-Cooled - Liquid-CooledДокумент36 страницMedium Voltage Ac Drives Selection Guide: Powerflex 7000 - Direct-To-Drive™ Technology - Air-Cooled - Liquid-CooledRamesh Gandhasiri50% (2)
- CEB Training Report 2Документ15 страницCEB Training Report 2Lakshan Walpita100% (1)
- Selection Criteria of Motors For Various Applications: - by R.PrasanthДокумент15 страницSelection Criteria of Motors For Various Applications: - by R.PrasanthOlusegun OlugbadeОценок пока нет
- PRS-778 X Instruction Manual en Overseas General X 2.04 20200814Документ275 страницPRS-778 X Instruction Manual en Overseas General X 2.04 20200814Quang Bình TrầnОценок пока нет
- Course Outline: 1. Introduction To WECC 2. Fundamentals of ElectricityДокумент51 страницаCourse Outline: 1. Introduction To WECC 2. Fundamentals of ElectricityWoldemariam WorkuОценок пока нет
- 2004 Corolla Electrical Diagram - Glossary of Terms and SymbolsДокумент2 страницы2004 Corolla Electrical Diagram - Glossary of Terms and SymbolsNick BaptisteОценок пока нет
- Uploads Product Rishmaster EM3490 1PH Manual PDFДокумент2 страницыUploads Product Rishmaster EM3490 1PH Manual PDFKo PaukОценок пока нет
- Life Cycle Testing of Electrical Loads by Down Counter: AbstractДокумент4 страницыLife Cycle Testing of Electrical Loads by Down Counter: AbstractTRIAD TECHNO SERVICESОценок пока нет
- Department of Electrical & Electronics Engg.: BEV Sem (Ex) Experiment No - 1 Aim: Apparatus RequiredДокумент44 страницыDepartment of Electrical & Electronics Engg.: BEV Sem (Ex) Experiment No - 1 Aim: Apparatus Requiredvkdkris75% (4)
- UniMasr.com 79e3983af376cc3e0a3c7adef354815eДокумент60 страницUniMasr.com 79e3983af376cc3e0a3c7adef354815eBala MОценок пока нет
- Motor Protection ToshibaДокумент24 страницыMotor Protection ToshibaAriesFranandaPanjaitanОценок пока нет
- Auto Selection of Any Available PhaseДокумент16 страницAuto Selection of Any Available PhaseRyan HarrisОценок пока нет
- 45 - 60055 - EE512 - 2015 - 5 - 2 - 1 - Experiment 2 PLC PDFДокумент7 страниц45 - 60055 - EE512 - 2015 - 5 - 2 - 1 - Experiment 2 PLC PDFkrishnandrkОценок пока нет
- Motion Controller BES-516-604, Typical Applications: Balluff Zero Speed Controller On A Grinding MachineДокумент8 страницMotion Controller BES-516-604, Typical Applications: Balluff Zero Speed Controller On A Grinding MachinenorbertoОценок пока нет
- Auto Transformer StarterДокумент13 страницAuto Transformer StarterarunОценок пока нет
- Shubham SeminarДокумент19 страницShubham SeminarShubham BodadeОценок пока нет
- 3locked Rotor TestДокумент5 страниц3locked Rotor TestAlpagut Sencer KaracaОценок пока нет
- AEG GC14 K ACBsДокумент18 страницAEG GC14 K ACBsPaulo H TavaresОценок пока нет
- Soft StarterДокумент24 страницыSoft StarterAli AhmadОценок пока нет
- Lab Notes Overcurrent GroundFault Protection v1Документ7 страницLab Notes Overcurrent GroundFault Protection v1srinivasaphanikiranОценок пока нет
- Types and Revolution of Electrical RelaysДокумент23 страницыTypes and Revolution of Electrical RelaysKishan DarjiОценок пока нет
- Lect 1 e 1435 Power System ProtectionДокумент41 страницаLect 1 e 1435 Power System ProtectionabdullahОценок пока нет
- Notes Switchgear and Protection Unit 2Документ32 страницыNotes Switchgear and Protection Unit 2Pratik SinghОценок пока нет
- Necessity of a protection systemДокумент29 страницNecessity of a protection systemarmanmanyata010299Оценок пока нет
- Current AffairsДокумент17 страницCurrent AffairsRajeev RawatОценок пока нет
- SSR-02/2015 BATCH APPLICATIONДокумент1 страницаSSR-02/2015 BATCH APPLICATIONRajeev RawatОценок пока нет
- Nov 2011 Atul1Документ10 страницNov 2011 Atul1Rajeev RawatОценок пока нет
- Nov 2011 Atul1Документ10 страницNov 2011 Atul1Rajeev RawatОценок пока нет
- AjjuДокумент1 страницаAjjuRajeev RawatОценок пока нет
- Mohsin Ansari - 9179957278 Carrier Objective:: E-Mail: ContactsДокумент2 страницыMohsin Ansari - 9179957278 Carrier Objective:: E-Mail: ContactsRajeev RawatОценок пока нет
- Basin Creek Power Plant Provides Clean EnergyДокумент2 страницыBasin Creek Power Plant Provides Clean EnergyMuhammad IshfaqОценок пока нет
- Noc18 Ee35 Assignment11Документ4 страницыNoc18 Ee35 Assignment11harsh chaudharyОценок пока нет
- Electrical Service Manual Original Manual Issue Date: 4/2010Документ51 страницаElectrical Service Manual Original Manual Issue Date: 4/2010Marcyo LimaОценок пока нет
- SC EleДокумент153 страницыSC EleKukinjosОценок пока нет
- Ucc 28750Документ52 страницыUcc 28750eneas.baroneОценок пока нет
- 9071 - Transformers - Pad-Mounted - Single-Phase PDFДокумент7 страниц9071 - Transformers - Pad-Mounted - Single-Phase PDFAlexis AguillonОценок пока нет
- Simulation Study Using SIMULINK/MATLAB On THD For PV Grid Connected SystemДокумент5 страницSimulation Study Using SIMULINK/MATLAB On THD For PV Grid Connected SystemsaraswatthiОценок пока нет
- Commissioning Sample: 1. Service EntranceДокумент6 страницCommissioning Sample: 1. Service EntranceEmmerОценок пока нет
- Premium - Datasheet - LVS V2.1 ENДокумент2 страницыPremium - Datasheet - LVS V2.1 ENClem CZОценок пока нет
- Meters Requirement NigeriaДокумент16 страницMeters Requirement NigeriaMatousОценок пока нет
- Dynamic Voltage Regulator Operation With Demand Side Management For Voltage ControlДокумент6 страницDynamic Voltage Regulator Operation With Demand Side Management For Voltage ControlRezhaОценок пока нет
- 1.1 Earthing: Product Manual GIS Type EXK-0Документ10 страниц1.1 Earthing: Product Manual GIS Type EXK-0Dipen SoniОценок пока нет
- Flat Pack 1800Документ2 страницыFlat Pack 1800Beeboy Ekkachon0% (1)
- Electromechanical Systems Ee-352 Instructor: DR Mashood Nasir Spring 2018-19 Assignment 1 Due Date: 8 February, 2019Документ4 страницыElectromechanical Systems Ee-352 Instructor: DR Mashood Nasir Spring 2018-19 Assignment 1 Due Date: 8 February, 2019Shiza ShakeelОценок пока нет
- Short Circuit Calculation DetailsДокумент15 страницShort Circuit Calculation DetailsSabir NaseerОценок пока нет
- (RES) Back Up Prot. Isolation and Normalization List - Sejingkat 132-33Kv 80MVA TXF No.2Документ9 страниц(RES) Back Up Prot. Isolation and Normalization List - Sejingkat 132-33Kv 80MVA TXF No.2ericОценок пока нет
- SUN2000-100KTL-M1 DatasheetДокумент2 страницыSUN2000-100KTL-M1 DatasheetInnozon EnergyОценок пока нет
- Bu1.2-2002 (R2008, R2013) WatermarkedДокумент19 страницBu1.2-2002 (R2008, R2013) WatermarkedfernandoОценок пока нет
- Four Layer Diode, Diac, SCR & TriacДокумент28 страницFour Layer Diode, Diac, SCR & Triaczeeshan aslam 19-Arid-31Оценок пока нет
- Durabrand DCT1303R - DCT1903R Manual de ServicioДокумент55 страницDurabrand DCT1303R - DCT1903R Manual de ServicioaldoОценок пока нет
- ET Tut2 Ans AUT2016-17Документ6 страницET Tut2 Ans AUT2016-17Tirumala Rao Yalla100% (1)
- CMX 007 Adjustable Frequency DriveДокумент9 страницCMX 007 Adjustable Frequency DriveJESUSCALVILLOОценок пока нет
- Quick Warping CapstansДокумент11 страницQuick Warping CapstansartemОценок пока нет
- Ansi C84Документ6 страницAnsi C84Ramiro Magbanua FelicianoОценок пока нет
- Smart Building Using Pir & IotДокумент10 страницSmart Building Using Pir & IotRitesh VeeraniОценок пока нет
- PIX Easy FR With Easy Pact EXE CB User Guide - PHA3627800Документ65 страницPIX Easy FR With Easy Pact EXE CB User Guide - PHA3627800Rajesh NayakОценок пока нет