Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
QR Management of Austism Spectrum Disorder in Children and Adolescents PDF
Загружено:
Nydia NadiaИсходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
QR Management of Austism Spectrum Disorder in Children and Adolescents PDF
Загружено:
Nydia NadiaАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Management of Autism Spectrum Disorder in Children and Adolescents
KEY MESSAGES
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is a neurodevelopmental disorder characterised
by impairments in communication, behaviour and social functioning which begin in
childhood.
Early diagnosis and prompt intervention of children with ASD is crucial for the best
outcome.
Modified Checklist for Autism in Toddlers (M-CHAT) may be used as a screening tool
for ASD among children of 18 months and repeat at 24 months if the child passes
the earlier M-CHAT.
It may be used to screen children up until the age of 30 months if the child
misses the earlier screening.
Regardless of the screening result, children suspected of ASD at any age by the
family or other care providers should be referred for evaluation.
Diagnosis of ASD should be made clinically, based on comprehensive history and
observation.
Audiological assessment should be performed in children with or suspected of ASD.
Children with ASD should be managed by a multidisciplinary team.
Parents or carers should actively participate in any intervention offered to children
with ASD.
Children with ASD should receive:
Applied behaviour analysis
Speech, language and communication interventions
Occupational therapy
Parental training should be offered to parents of children with ASD.
Traditional and Complementary Medicine could not be recommended to children
with ASD because of insufficient evidence and potential harmful effects.
This Quick Reference provides key messages and a summary of the main
recommendations in the Clinical Practice Guidelines (CPG) on the Management of
Autism Spectrum Disorder in Children and Adolescents.
Details of the evidence supporting these recommendations can be found in the above
CPG, available on the following websites:
Ministry of Health Malaysia: www.moh.gov.my
Academy of Medicine Malaysia: www.acadmed.org.my
Malaysian Psychiatric Association: www.psychiatry-malaysia.org
Clinical Practice Guidelines Secretariat
Malaysian Health Technology Assessment Section (MaHTAS)
Medical Development Division
Ministry of Health Malaysia
Level 4, Block E1, Precinct 1, 62590, Putrajaya
Tel: 603-8883 1246, E-mail: htamalaysia@moh.gov.my
Management of Autism Spectrum Disorder in Children and Adolescents
Risk Factors
Screening for ASD should be emphasised in children with the following high risk factors: Increased parental age
Maternal age >40 years old
Paternal age >50 years old
First born of mother aged >35 years old and father aged >40 years old
Main Features of ASD
A.
Persistent deficits in social communication and social interaction across multiple
contexts.
B. Restricted, repetitive patterns of behaviour, interests, or activities.
C. Symptoms must be present in the early developmental period (but may not become
fully manifest until social demands exceed limited capacities, or may be masked by
learned strategies in later life).
D. Symptoms cause clinically significant impairment in social, occupational, or other
important areas of current functioning.
E. These disturbances are not better explained by intellectual disability (intellectual
developmental disorder) or global developmental delay.
Comorbidities
Children with ASD can experience a wide range of difficulties with emotional,
attentional, activity, thought, behavioural and medical problems.
Diagnosis of comorbid disorders is of major importance as it may cause significant
clinical impairment in children with ASD.
The comorbidities are:
a) Intellectual disabilities
b) Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD)
c) Sleep disorders
d) Epilepsy
e) Gastrointestinal problems such as feeding problems and constipation
f) Motor incoordination such as poor handwriting
g) Other psychiatric disorderssuch as anxiety and depressive disorder
3
Management of Autism Spectrum Disorder in Children and Adolescents
Audiological Evaluation
Audiological evaluation is an important component of initial assessment to rule out
hearing impairment.
The electrophysiological test is preferably used to evaluate hearing impairment in
children with ASD as compared to behavioural test.
Treatment
i. Applied Behaviour Analysis (ABA)
Lovaas therapy and early intensive behavioural intervention variants improve among
others, social communication skills, language and daily living skills, cognitive performance,
language skills and adaptive behavioural skill.
ii. Speech, Language and Communication Interventions
Interventions
Naturalistic
approach
Types
Benefits
Responsive Education and
Prelinguistic Milieu Teaching
(RPMT)
Improves social communication
& language learning
Reciprocal Imitation Training (RIT) Improves elicited & spontaneous
imitation of objects & gestures
(<5 years old) with a greater play
repertoire
Augmentative
and Alternative
Communication
(AAC)
Video modelling
Picture Exchange Communication Improves communication skills
System (PECS)
& requesting skills
Speech Generating Device (SGD)
SGD with enhanced milieu
teaching & signing improves
requesting skills
Video self-modelling
Improves social communication
skills, functional skills & behavioural
functioning
Video modelling with other as Improves play skills, independent
model
living & social-communicative
skills
Management of Autism Spectrum Disorder in Children and Adolescents
iii. Occupational Therapy
Interventions
Benefits
Sensory integration therapy
Improves in sensory processing, motor skills, social
functioning & autistic mannerisms but further study
required to support current findings
Social skills and self-help skills
Improves overall social competence & friendship quality
Joint attention
Improves joint attention & joint engagement
Perceptual motor training
Increases attention span
iv. Other Interventions
Interventions
Benefits
Social Stories
Improves social skills & reduces inappropriate
behaviours
Developmental, Individualdifference, Relationship-based
(DIR) FloortimeTM
Improves developmental skills & reduces autistic
symptoms
Music therapy
Improves joint attention skills & longer eye contact
Parent education and support
Improves parent-child interaction, parent synchrony,
childs language comprehension & functional verbal
utterances
v. Pharmacotherapy
Children with ASD may be offered:
atypical antipsychotics as a short-term treatment for irritability
o methylphenidate and atomoxetine for hyperactivity
o melatonin for sleep difficulties
o
Social Welfare Service
Children with ASD should be referred to the Department of Social Welfare at their respective
local districts. This will enable the child to be registered for social welfare benefits.
Transition from Adolescent to Adult Services
Transition for adolescents with ASD should be discussed and planned early by all
who are involved in their management.
Care for children and adolescents with ASD should be continued to adult health
services. There is a need for establishment of this service to support adolescents
when they enter adulthood.
5
Management of Autism Spectrum Disorder in Children and Adolescents
Modified Checklist for Autism in Toddlers (M-CHAT)
Answer ALL questions. Circle the appropriate answer.
Jawab SEMUA soalan. Bulatkan jawapan yang sesuai.
1
Adakah anak anda seronok apabila ditimang, dibuai atau dihenjut atas kaki /
paha dan sebagainya?
Does your child enjoy being swung, bounced on your knee, etc?
Ya / Yes
Tidak / No
Adakah anak anda menunjukkan minat terhadap kanak-kanak
lain? (contohnya bergaul, bermain, berkawan)
Does your child take an interest in other children?
Ya / Yes
Tidak / No
Adakah anak anda suka memanjat, contohnya tangga, kerusi, meja dan
lain-lain?
Does your child like climbing on things, such as up stairs?
Ya / Yes
Tidak / No
Adakah anak anda seronok bermain cak-cak atau main sorok-sorok?
Does your child enjoy playing peek-a-boo or hide and seek?
Ya / Yes
Tidak / No
Adakah anak anda pernah bermain-main olok-olok / berlakon, contohnya
menelefon, bermain anak patung atau bermain masak-masak dan
sebagainya?
Does your child ever pretend for example to talk on the phone or take care
of dolls or pretend other things?
Ya / Yes
Tidak / No
Adakah anak anda pernah menunjuk menggunakan jari telunjuk untuk
meminta sesuatu?
Does your child ever use his / her index finger to point, to ask for
something?
Ya / Yes
Tidak / No
Adakah anak anda pernah menunjuk / menggunakan jari telunjuk
terhadap sesuatu yang menarik minatnya?
Does your child ever use his / her index finger to point, to indicate
interest in something?
Ya / Yes
Tidak / No
Bolehkah anak anda bermain dengan alat permainan yang kecil dengan
betul, selain dari memasukkannya ke dalam mulut, membelek-belek atau
menjatuhkan permainan itu? (contohnya kiub, kereta kecil, dan lain-lain)
Can your child play properly with small toys without just mouthing, fiddling
or dropping them?
Ya / Yes
Tidak / No
Pernahkah anak anda membawa objek / benda dan menunjukannya
kepada anda?
Does your child ever bring objects over to you (parent) to show
you something?
Ya / Yes
Tidak / No
10
Adakah anak anda bertentang mata dengan anda lebih daripada dua
saat?
Does your child look you in the eye for more than a second or two?
Ya / Yes
Tidak / No
11
Pernahkah anak anda kelihatan seperti tersangat sensitif / terganggu
terhadap bunyi bising (contohnya: menutup telinga)?
Does your child ever seem oversensitive to noise? (e.g. plugging ears)
Ya / Yes
Tidak / No
12
Adakah anak anda senyum bila melihat anda atau membalas senyuman
anda?
Does your child smile in response to your face or your smile?
Ya / Yes
Tidak / No
13
Adakah anak anda meniru perlakuan anda (contohnya meniru
mimik muka anda dan sebagainya)?
Does your child imitate you? (e.g. if you make a face will your
child imitate it?)
Ya / Yes
Tidak / No
Management of Autism Spectrum Disorder in Children and Adolescents
14
Adakah anak anda bertindak balas apabila namanya
dipanggil?
Does your child respond to his / her name when you call?
Ya / Yes
Tidak / No
15
Sekiranya anda menunjuk pada alat permainan yang jauh dari
anda, adakah anak anda akan melihat kepada alat permainan
tersebut?
If you point at a toy across the room, does your child look at it?
Ya / Yes
Tidak / No
16
Bolehkah anak anda berjalan?
Does your child walk?
Ya / Yes
Tidak / No
17
Adakah anak anda akan melihat pada benda yang sedang anda
lihat?
Does your child look at things you are looking at?
Ya / Yes
Tidak / No
18
Adakah anak anda membuat pergerakan jari yang ganjil / pelik dekat
mukanya?
Does your child make unusual finger movements near his / her face?
Ya / Yes
Tidak / No
19
Adakah anak anda cuba menarik perhatian anda terhadap aktiviti yang
dilakukannya?
Does your child try to attract your attention to his / her own activity?
Ya / Yes
Tidak / No
20
Pernahkah anda terfikir bahawa anak anda ada masalah pendengaran?
Have you ever wondered if your child is deaf?
Ya / Yes
Tidak / No
21
Adakah anak anda dapat memahami percakapan orang?
Does your child understand what people say?
Ya / Yes
Tidak / No
22
Adakah anak anda kadang-kala kelihatan temenung atau merayau /
berjalan tanpa tujuan?
Does your child sometimes stare at nothing or wander with no purpose?
Ya / Yes
Tidak / No
23
Adakah anak anda memandang ke muka anda untuk melihat reaksi /
tindakabalas anda apabila ia menghadapi sesuatu yang baru atau luar
biasa?
Does your child look at your face to check your reaction when faced with
something unfamiliar?
Ya / Yes
Tidak / No
1. No / Tidak
6. No / Tidak
11. Yes / Ya v
16. No / Tidak
2. No / Tidak
3. No / Tidak
21. No / Tidak
7. No / Tidak
12. No / Tidak
17. No / Tidak
22. Yes / Ya v
8. No / Tidak
13. No / Tidak
18. Yes / Ya v
23. No / Tidak
4. No / Tidak
9. No / Tidak
14. No / Tidak
19. No / Tidak
5. No / Tidak
10. No / Tidak
15. No / Tidak
20. Yes / Ya v
Scoring:
The bold items are critical; i.e. 2, 7, 9, 13, 14, 15
A chid requires referral (i.e. fail M-CHAT) for further evaluation if he / she fulfills
the following:
2 or more of critical items
3 or more of any items
Not all children who fail the checklist will meet criteria for a diagnosis on the autism
spectrum disorder. However, children who fail the checklist should be evaluated in more
depth by the relevant specialist.
7
Management of Autism Spectrum Disorder in Children and Adolescents
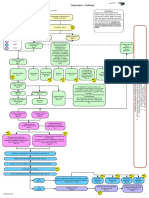
Algorithm on Management of Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder
Growth and developmental
assessment for children
under six years of age at
Maternal & Child Health
Clinic
Referral from
school / community / parent
Referral from
Practitioners / Therapists
M-CHAT screening
(at 18 and 24 months)*
to be completed by parents
assisted if necessary
Scoring**
Refer Pg 6
Fail
Verification by Medical
Practitioner
Follow-up
Diagnosis confirmed by
Family Medicine Specialist /
Paediatrician / Psychiatrist
Multidisciplinary Assessment
and Management***
Speechlanguage
therapy
Occupational
therapy
Psychological
/ behavioural
therapy
Education
Social
welfare
Pharmacotherapy
for comorbidities
Early intervention programme (EIP) is strongly advocated
* M-CHAT may be used to screen children up until 30 months
of age if the child misses the earlier screening
**Regardless of the screening result, children suspected of
ASD by the family or other care provider should be referred
for evaluation
***Multidisciplinary Assessment and Management Team
may include:
Family Medicine Specialist
Paediatrician
Psychiatrist
Clinical Psychologist
Occupational Therapist
Speech-Language Therapist
Audiologist
Medical Social Worker
Вам также может понравиться
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5795)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (895)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (400)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (345)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (266)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1091)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (121)
- Q & A Human BehaviorДокумент189 страницQ & A Human BehaviorAngel King RelativesОценок пока нет
- Theodore DRT Millon Personality-Guided Therapy For Depression Personality-Guided Psychology 2006Документ330 страницTheodore DRT Millon Personality-Guided Therapy For Depression Personality-Guided Psychology 2006Sara86% (7)
- Depression Care PathwayДокумент267 страницDepression Care PathwaydwiОценок пока нет
- Is Mindfulness Useful or Dangerous For Individuals With Psychosis? - Here To HelpДокумент1 страницаIs Mindfulness Useful or Dangerous For Individuals With Psychosis? - Here To HelpRev NandacaraОценок пока нет
- Weirdo. How Misunderstood Human Beings Become MisfitsДокумент2 страницыWeirdo. How Misunderstood Human Beings Become Misfitsandreas.hoferОценок пока нет
- Week 11Документ5 страницWeek 11api-582257412Оценок пока нет
- Cadabams Rehabilitation CenterДокумент6 страницCadabams Rehabilitation CenterDivyaDeepthi18Оценок пока нет
- Personality 1. Film Analysis PDFДокумент2 страницыPersonality 1. Film Analysis PDFCleo-Jill TungolОценок пока нет
- 2.e.case Ctudy On BPADДокумент9 страниц2.e.case Ctudy On BPADManisa Parida100% (1)
- AnxietyДокумент6 страницAnxietyabd ulОценок пока нет
- Local Literature of Sleep DeprivationДокумент3 страницыLocal Literature of Sleep DeprivationEunsang Lee82% (11)
- L 8 NewДокумент13 страницL 8 NewWeronika Tomaszczuk-KłakОценок пока нет
- Bipolar Disorderand TreatmentsДокумент38 страницBipolar Disorderand Treatmentsshahad18Оценок пока нет
- Notes On Dissociative DisordersДокумент7 страницNotes On Dissociative DisordersPrince Rener Velasco PeraОценок пока нет
- A. Factors in Mental Disorders: Name: SCORE: - /91 Intro To Psych Module 22-Assessment and Anxiety DisordersДокумент4 страницыA. Factors in Mental Disorders: Name: SCORE: - /91 Intro To Psych Module 22-Assessment and Anxiety DisorderssusanwhittenОценок пока нет
- Oral Presentation II. Alzheimer Disease.Документ3 страницыOral Presentation II. Alzheimer Disease.Laureta87Оценок пока нет
- Matrix On Somatic Disorders: Luzenne Sanchez Jones PSYC 118X Clinical Psyc TTH 4:30-6:00 March 12, 2020Документ5 страницMatrix On Somatic Disorders: Luzenne Sanchez Jones PSYC 118X Clinical Psyc TTH 4:30-6:00 March 12, 2020Monina JonesОценок пока нет
- Terapi Psikofarmakologi Autisme Spectrum Disorder 2020Документ29 страницTerapi Psikofarmakologi Autisme Spectrum Disorder 2020ian ismeОценок пока нет
- JPBA - 2018 - Multidimensional Schizotypy Scale-Brief and 5FДокумент9 страницJPBA - 2018 - Multidimensional Schizotypy Scale-Brief and 5Fsofian2pОценок пока нет
- Developmental Apraxia of SpeechДокумент4 страницыDevelopmental Apraxia of SpeechStella PapadopoulouОценок пока нет
- A Case ExampleДокумент10 страницA Case ExampleCarole WanОценок пока нет
- BPD Fact SheetДокумент2 страницыBPD Fact Sheetsiknobostu33% (3)
- Do You Know Tyler DurdenДокумент8 страницDo You Know Tyler DurdenRobert ShermanОценок пока нет
- Chapter 17 AP PsychДокумент62 страницыChapter 17 AP PsychEvanSiegel6Оценок пока нет
- Presentation - PsychiatryДокумент21 страницаPresentation - PsychiatrySangkaran KumarОценок пока нет
- Formulation 5P TrainingДокумент19 страницFormulation 5P Trainingkempiniux100% (1)
- Conduct Disorder ToolsДокумент1 страницаConduct Disorder Toolsfuturistzg100% (1)
- Add and Adhd ResearchДокумент25 страницAdd and Adhd Researchapi-520142437100% (1)
- Anwers For NCM 105 TEST QUESTIONS ON MOOD DISORDERS PDFДокумент5 страницAnwers For NCM 105 TEST QUESTIONS ON MOOD DISORDERS PDFDa Bondad100% (1)
- A Look Into Autism, and The Self Admiration: Puzzle Ofthe DisordersДокумент13 страницA Look Into Autism, and The Self Admiration: Puzzle Ofthe DisordersJessica Cisneros100% (1)