Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Pre-Algebra Study Guide
Загружено:
Jason Sanchez0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
196 просмотров2 страницыStudy Guide
Авторское право
© © All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документStudy Guide
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
196 просмотров2 страницыPre-Algebra Study Guide
Загружено:
Jason SanchezStudy Guide
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 2
7 th Grade Pre-Algebra Study Guide
Number Sense
1) When (+) or (-) integers keep the sign the same
if all the integers have the same sign.
15) To convert a decimal to a percent, move the
decimal two places to the right.
2) When (+) or (-) integers with different signs,
find the difference of the two integers and keep
the sign of the integer with the larger |absolute
value|.
16) To convert a percent to a decimal, move the
decimal two places to the left.
3) When subtracting integers, change to addition
and follow the rules above.
18) Rules for exponents:
* When multiplying numbers with the same
base, add the exponents.
* When dividing numbers with the same
base, subtract the exponents.
* When raising a number to a power
multiply the exponents (34)4 = 316.
4) When (x) or () integers follow these rules:
*(x) or () two negatives equals a positive
*(x) or () two positives equals a positive
17) Order of Operations: follow P, E, M/D, A/S
*(x) or () different signs equals a negative
5) |Absolute value| means the distance a number is
from 0 on a number line & the answer is always
expressed as a positive. The only exception is if
there is a (-) symbol outside the symbols -|4| = 4.
6) Associative Property of (+) or (x)
* 2 + (5 + 8) = (2 + 5) + 8
7) Commutative Property of (+) or (x)
*2x5x8=5x2x8
8) Distributive Property of (x)
* 6(n + 4) = 6n + 24
9) Identity Property of (+)
* 2 + 0 = 2; 56 + 0 = 56
10) Identity Property of (x)
* 2 x 1 = 2; 56 x 1 = 56
11) Zero Property of (x)
* 2 x 0 = 0; 56 x 0 = 0
12) To convert a fraction to a decimal, divide the
numerator by the denominator.
13) To convert a decimal to a fraction, write the
number above the appropriate denominator (ie.
10ths, 100ths, 1000ths, etc.).
14) To convert a fraction to a percent, change it to a
decimal then move the decimal two places to the
right or find a common denominator that is
equal to 10ths or 100ths.
19) When writing numbers in Scientific Notation,
move the decimal behind the first non zero digit
(0.0000768 = 7.68 x 10-5 or 6,534,000 = 6.534 x
106).
20) When calculating the percent of increase or
decrease 1st find the difference, 2nd divide the
difference by the original amount, & 3rd change
the final answer to a percent.
21) When calculating a markup or discount multiply
the beginning amount by the correct decimal
equivalent to the percent then add that amount to
the original amount (% markup or
tax/tip/commission added) or subtract that
amount from the original amount (% decrease)
22) To convert a decimal to a percent, move the
decimal to the right two places.
23) Rational number:
Fractions/Decimals: 2/5, 5/8, 0.3, 0.666.
Integer:
Whole Number: 0, 4, 167, 1,023,000
Negative Integer: -6, -23, -409
Irrational Number:
Non-perfect squares, decimals
24) Most word percent problems can be solved
with a proportion or an equation. The words
rate, per, and unit means that one of the ratios in
the proportion has the number 1 as a divisor.
Algebra & Functions
To solve an equation always use the inverse
operation to isolate the variable:
x+4
x7
2x
x/3
-4
+7
2
3
25) Remember that in a multi-step equation, your
goal is to try to isolate the variable. Begin by
getting rid of the smallest variable term 1st, then
start eliminating the constants:
3x 12 = 9x + 6
-3x
-3x
-12 = 6x + 6
-6
-6
-18 = 6x
6
6
-3 = x
26) When combining like terms follow theses steps:
1) Use the distributive property if you can.
2) Combine any like variable terms and/or
constants on each side of the equation:
2x 6 4x
2x 4x 6
-2x - 6
27) Most problems in algebra can be solved using a
proportion skeleton. Just remember to match
common units the same for both fractions in the
proportion. For example: in = in
ft
ft
28) When solving inequalities your goal is the same
as when you are solving equations. That is you
are trying to isolate the variable. However, in an
inequality, if you (x) or () by a negative you
reverse the < or > sign. You also reverse the sign
if you move the variable from the right side to
the left side.
29) When graphing an inequality remember that a
simple < or > uses an open circle and an or an
uses a closed circle.
30) A unit rate is a comparison of anything to 1. For
example 48 miles driven using 3 gallons of gas
can be written as 16mi/1gal. You can solve most
rate problems using a proportion.
31) To calculate simple interest use the formula:
I = PRT (Interest = Principle x Rate x Time)
32) To calculate compound interest, use the same
formula except that you add the interest to the
principle and re-calculate the next years
interest. Continue to do this until you have
calculated and added interest for the amount of
time it was compounded.
33) To calculate the slope of a line where two sets
of coordinates are given use the formula:
Y2 Y1
X2 X1
34) To determine slope on a graph, find two perfect
interceptions or points and count the rise and
place it over the run (rise/run = slope).
35) Remember that in an equation such as:
y = 3x + 5
The 3 represents the slope and the constant
(+5) represents where the y-intercept will
be.
36) Sometimes you may need to write a function
table to determine the value of y. Always use the
numbers 2, -1, 0, 1, 2 as a value for x.
37) The following rules apply to graphed points
from a linear equation:
1) x will give a positive straight line slope
2) x will give a negative straight line slope
3) x2 will give a positive U shaped slope
4) x2 will give a negative U shaped slope
5) |x| will give a positive V shaped slope
6) -|x| will give a negative V shaped slope
7) x3 will give a positive S shaped slope
8) -x3 will give a negative S shaped slope
Measurement & Geometry
Converting from a LARGE unit to a small unit,
multiply by the conversion factor. Converting from a
small unit to a LARGE unit, divide by the conversion
factor.
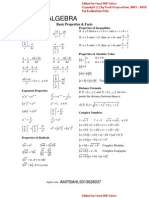
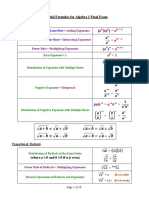
38) Formulas:
1) Pythagorean Theorem: c2 = a2 + b2
2) Area of a Triangle: A = 1/2 bh
4) Area of a Parallelogram: A = bh
5) Volume of a Rectangular Prism: V = lwh
6) Volume of a Cylinder: V = = r2h
7) Volume of a Cone: V = r2 h/3
8) Volume of a Pyramid: V = lwh/3
39) Box and Whisker Plots: the median is the middle
point inside the box, the lower & upper quartiles
are the points at either end of the box not
considered to be an outlier, and the lower/upper
extremes are the farthest points at either end of
the plotted points.
1) Order from least to greatest:
5, 5, 6, 8, 10, 11, 12, 12, 12, 16
2) Find the median:
5, 5, 6, 8, 10, 11, 12, 12, 12, 16
3) Find the upper & lower quartiles:
5, 5, 6, 8, 10, 11, 12, 12, 12, 16
4) 4) Make the Box-and-Whisker Plot:
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16
Вам также может понравиться
- Math Preparedness WorkbookДокумент26 страницMath Preparedness WorkbookAnonymous czkmnf100% (1)
- Linear Equation 1Документ25 страницLinear Equation 1yaw197100% (1)
- Difference Between Rational and Irrational NumberДокумент3 страницыDifference Between Rational and Irrational NumbernishagoyalОценок пока нет
- Day 38 Right Triangle TrigДокумент32 страницыDay 38 Right Triangle TrigArchessОценок пока нет
- 1.3: Determining The Equation of A Line: Learning ObjectivesДокумент6 страниц1.3: Determining The Equation of A Line: Learning ObjectivesZenic TzyОценок пока нет
- Fall Prep Session Materials 2014-15 DraftДокумент216 страницFall Prep Session Materials 2014-15 Draftapi-283319039Оценок пока нет
- Logarithms Practice (SL)Документ2 страницыLogarithms Practice (SL)Firas Ahmad100% (1)
- Fundamentals of Math # 1Документ6 страницFundamentals of Math # 1Brian CbtngnОценок пока нет
- SAT ACT Complex NumbersДокумент8 страницSAT ACT Complex NumbersYb Andik Adi Cahyono100% (1)
- Algebra IДокумент5 страницAlgebra IMatthew SteinОценок пока нет
- Math - Complex Numbers RefresherДокумент5 страницMath - Complex Numbers Refresherhelixate100% (2)
- Basic Number Theory 2017Документ38 страницBasic Number Theory 2017bhushan patil100% (1)
- v2 - Algebra II (Common Core) Regents Review Sheet - Facts You Must Know ColdДокумент19 страницv2 - Algebra II (Common Core) Regents Review Sheet - Facts You Must Know ColdIkhri574Оценок пока нет
- Chapter 1 Quadratic Equations in One UnknownДокумент14 страницChapter 1 Quadratic Equations in One Unknownapi-3704862Оценок пока нет
- 1.3 Perfect Squares and Square RootsДокумент20 страниц1.3 Perfect Squares and Square RootsMAHJABEEN NASEEMОценок пока нет
- Complex NumbersДокумент21 страницаComplex NumbersAditya BansalОценок пока нет
- Pythagorean Theorem Lesson PlanДокумент4 страницыPythagorean Theorem Lesson PlanAnonymousОценок пока нет
- Algebra: Basic Properties & FactsДокумент4 страницыAlgebra: Basic Properties & Factsamitbahl75Оценок пока нет
- Points and Their Coordinates: y AxisДокумент9 страницPoints and Their Coordinates: y AxisMary Ann CrizaldoОценок пока нет
- Algebra 2 Readiness Practice TestДокумент11 страницAlgebra 2 Readiness Practice Testpidmap2Оценок пока нет
- Teaching GeometryДокумент17 страницTeaching Geometryanglo phile100% (1)
- Geometry Rules PDFДокумент21 страницаGeometry Rules PDFVadlamudiMohanKumarОценок пока нет
- Video Math Tutor: Basic Math: Lesson 1 - NumbersДокумент12 страницVideo Math Tutor: Basic Math: Lesson 1 - NumbersThe Video Math TutorОценок пока нет
- Number SystemДокумент74 страницыNumber SystemKrishna SilОценок пока нет
- Number System1 1Документ28 страницNumber System1 1Anonymous Ptxr6wl9DhОценок пока нет
- Sieve of Eratosthenes - WorksheetДокумент1 страницаSieve of Eratosthenes - WorksheetmistryhОценок пока нет
- The Book of Math FormulasДокумент145 страницThe Book of Math FormulasAK67% (3)
- PolynomialsДокумент8 страницPolynomialsRakhi sivanandОценок пока нет
- Basic Rules of AlgebraДокумент4 страницыBasic Rules of AlgebraRogelyn Manalo100% (1)
- Unit ConversionДокумент33 страницыUnit ConversionmukhleshОценок пока нет
- Commutative, Associative and Distributive Laws: Wow! What A Mouthful of Words! But The Ideas Are SimpleДокумент6 страницCommutative, Associative and Distributive Laws: Wow! What A Mouthful of Words! But The Ideas Are SimpleAnnisa RohmahОценок пока нет
- ComplexДокумент33 страницыComplexDipin Preet SinghОценок пока нет
- High School Geometry Days 102-112Документ49 страницHigh School Geometry Days 102-112eclecticOTAОценок пока нет
- Cubes and Cube Roots - NotesДокумент14 страницCubes and Cube Roots - NotesVENKATESH PRABHUОценок пока нет
- Vector Algebra Facts SheetДокумент3 страницыVector Algebra Facts SheetСветлана Дашкевич ЛисовскаяОценок пока нет
- 1 Math Review q1 Place ValueДокумент3 страницы1 Math Review q1 Place Valueapi-318541967Оценок пока нет
- Surface Area and VolumeДокумент48 страницSurface Area and Volumecmnell100% (2)
- Percentage Change TextДокумент3 страницыPercentage Change Textapi-287224366Оценок пока нет
- Review of Linear FunctionsДокумент12 страницReview of Linear FunctionsNut Natthanan100% (1)
- Number SystemДокумент19 страницNumber SystemsansureОценок пока нет
- Arithmetic Sequence and Series: Marija LovrićДокумент9 страницArithmetic Sequence and Series: Marija Lovrićelyas berger100% (1)
- Writing Linear Equations NotesДокумент2 страницыWriting Linear Equations Notesapi-307475527Оценок пока нет
- Geometry Eoc Practice Test 1Документ26 страницGeometry Eoc Practice Test 1api-279522974100% (1)
- FINAL Painless Algebra For DavaoДокумент28 страницFINAL Painless Algebra For DavaozapleekillsОценок пока нет
- Geometry - 02 - TrianglesДокумент152 страницыGeometry - 02 - TrianglesAzizmanvaОценок пока нет
- AlgebraДокумент34 страницыAlgebramansorsabahОценок пока нет
- Golden Sheet For Proofs With Triangle TheoremsДокумент3 страницыGolden Sheet For Proofs With Triangle TheoremseunhaeОценок пока нет
- Essential Formulas For Algebra 2 Final Exam PDFДокумент10 страницEssential Formulas For Algebra 2 Final Exam PDFJustin JeudyОценок пока нет
- 3 - Basic CryptarithmsДокумент12 страниц3 - Basic CryptarithmskevinОценок пока нет
- Solution 2005Документ12 страницSolution 2005BHAAJI0001Оценок пока нет
- 2.6 Using Equations To Solve Word ProblemsДокумент4 страницы2.6 Using Equations To Solve Word ProblemsSherry WangОценок пока нет
- Mensuration Nichod FinalДокумент25 страницMensuration Nichod FinalDCC Bhuna100% (1)
- Basic Trigonometry NotesДокумент14 страницBasic Trigonometry NotesKeri-ann Millar50% (2)
- HS-MATH-ALG2 - Chapter 2 - Relations and FunctionsДокумент64 страницыHS-MATH-ALG2 - Chapter 2 - Relations and FunctionsyuditОценок пока нет
- Algebra ReviewДокумент29 страницAlgebra ReviewKim SmithОценок пока нет
- Chapter1: Square and Square Roots/cubes and Cube Roots ................................................................................. 2Документ2 страницыChapter1: Square and Square Roots/cubes and Cube Roots ................................................................................. 2Rahul KhandelwalОценок пока нет
- Unit Circle!Документ46 страницUnit Circle!Lisa AustinОценок пока нет
- A-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsОт EverandA-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (8)
- Math 8 Unit 6Документ6 страницMath 8 Unit 6api-114939020100% (1)
- Revision Notes P3 0 P7Документ6 страницRevision Notes P3 0 P7Nat GariОценок пока нет
- Blended Learning With Google Toolkit © by Kasey Bell 2Документ15 страницBlended Learning With Google Toolkit © by Kasey Bell 2Laxmi VCОценок пока нет
- Coding in The Classroom Starter Kit Teacher Guide 2022 PDFДокумент54 страницыCoding in The Classroom Starter Kit Teacher Guide 2022 PDFJason SanchezОценок пока нет
- Interactive Math NotebookДокумент11 страницInteractive Math NotebookJason Sanchez0% (1)
- Graphic Organizer To Aid ComprehensionДокумент1 страницаGraphic Organizer To Aid ComprehensionJason SanchezОценок пока нет
- Interactive Math NotebookДокумент11 страницInteractive Math NotebookJason Sanchez0% (1)
- Dangerous Data Sets Lesson Plan PDFДокумент3 страницыDangerous Data Sets Lesson Plan PDFJason SanchezОценок пока нет
- G3 Unususl Jobs All Student ResourcesДокумент12 страницG3 Unususl Jobs All Student ResourcesJason SanchezОценок пока нет
- 240 5th Grade Vocab Words PDFДокумент77 страниц240 5th Grade Vocab Words PDFJason Sanchez100% (1)
- Warmupsgrammar PDF BookДокумент200 страницWarmupsgrammar PDF Bookapi-232647745Оценок пока нет
- Prefix TestДокумент4 страницыPrefix TestJason SanchezОценок пока нет
- Scholastic Skills 01 Month (January) PDFДокумент144 страницыScholastic Skills 01 Month (January) PDFAnna Bianco100% (9)
- English Workbook Grade 4Документ138 страницEnglish Workbook Grade 4Jason Sanchez71% (14)
- 43 Toro DefenseДокумент9 страниц43 Toro DefenseJason SanchezОценок пока нет
- Practice PlanДокумент2 страницыPractice PlanJason SanchezОценок пока нет
- Youth Football ConditioningДокумент2 страницыYouth Football ConditioningJason SanchezОценок пока нет
- 2414 GHW 1 S20Документ2 страницы2414 GHW 1 S20smurfyblueberryОценок пока нет
- AcДокумент3 страницыAcmystery 015Оценок пока нет
- Mat 502Документ290 страницMat 502Kushagra TandonОценок пока нет
- Fourier Transform - Signal ProcessingДокумент366 страницFourier Transform - Signal ProcessingAnonymous UZ5xA8Оценок пока нет
- Assignment 4Документ12 страницAssignment 4jayantsharan jayantОценок пока нет
- Ial Maths Pure 4 CR4Документ15 страницIal Maths Pure 4 CR4nasehaОценок пока нет
- Comparing Riemann and Monte Carlo ApproximationДокумент8 страницComparing Riemann and Monte Carlo ApproximationryanfieldОценок пока нет
- David C. Lay - Study Guide To Linear Algebra and Its Applications, 3rd Edition-Addison Wesley (2005) PDFДокумент349 страницDavid C. Lay - Study Guide To Linear Algebra and Its Applications, 3rd Edition-Addison Wesley (2005) PDFMárcioBarboza75% (4)
- Epi CycloidДокумент4 страницыEpi CycloidKishalaya KunduОценок пока нет
- Mellin Transform Applied To The Problem of Riemann Hypothesis and The Riesz FunctionДокумент8 страницMellin Transform Applied To The Problem of Riemann Hypothesis and The Riesz FunctionJose Javier GarciaОценок пока нет
- Analysis and Design of Algorithms Lab FileДокумент64 страницыAnalysis and Design of Algorithms Lab FilePankhuri JhambОценок пока нет
- A Jacobi Collocation Method For Solving Nonlinear Burgers-Type EquationsДокумент13 страницA Jacobi Collocation Method For Solving Nonlinear Burgers-Type EquationsEduardo SandovalОценок пока нет
- Design Amp Analysis of Algorithm Multiple Choice QuestionsДокумент3 страницыDesign Amp Analysis of Algorithm Multiple Choice QuestionsemirОценок пока нет
- General Mathematics Summative Test 3 2022-2023 - Version 2Документ2 страницыGeneral Mathematics Summative Test 3 2022-2023 - Version 2Mariel VillanuevaОценок пока нет
- MathsДокумент66 страницMathsKousik Mandal40% (10)
- Homogeneous Differential EquationДокумент9 страницHomogeneous Differential EquationSheikh RaselОценок пока нет
- Implicit DifferentiationДокумент26 страницImplicit DifferentiationAhmad MarwadОценок пока нет
- CAT Quadratic Equations Notes+Questions PDFДокумент30 страницCAT Quadratic Equations Notes+Questions PDFFeku PappuОценок пока нет
- 2Q 1st-4th Sum. Test in Math With TOSДокумент8 страниц2Q 1st-4th Sum. Test in Math With TOSDYNA ALTAREJOSОценок пока нет
- Continuity PDFДокумент7 страницContinuity PDFnaveen rajОценок пока нет
- A Note On A New Two Variable Analogue of Hermite PolynomialsДокумент8 страницA Note On A New Two Variable Analogue of Hermite PolynomialsTI Journals PublishingОценок пока нет
- Maxima and Minima of Functions of Two Variables Calculus 3Документ4 страницыMaxima and Minima of Functions of Two Variables Calculus 3Mark Angelo PoliciosОценок пока нет
- Application of Graph Theory To Find Minimal Paths Between Two Places For The Transportation ProblemДокумент9 страницApplication of Graph Theory To Find Minimal Paths Between Two Places For The Transportation ProblemIJRASETPublicationsОценок пока нет
- Sorting Algorithm EssayДокумент2 страницыSorting Algorithm Essayapi-297074626Оценок пока нет
- MEI Structured Mathematics Module Summary Sheets: C3, Methods For Advanced MathematicsДокумент10 страницMEI Structured Mathematics Module Summary Sheets: C3, Methods For Advanced Mathematicsmirali74Оценок пока нет
- Greedy Methods: Manoj Kumar DTU, DelhiДокумент44 страницыGreedy Methods: Manoj Kumar DTU, DelhiAnkit PriyarupОценок пока нет
- (G) G Singular Points of Linear Differential EquationsДокумент3 страницы(G) G Singular Points of Linear Differential EquationsJian's ShahidОценок пока нет
- Multiple Criteria Districting Problems: The Public Transportation Network Pricing System of The Paris RegionДокумент24 страницыMultiple Criteria Districting Problems: The Public Transportation Network Pricing System of The Paris Regiondelia2011Оценок пока нет
- CLASS - XI - Physics NotesДокумент15 страницCLASS - XI - Physics NotesAnuj SharmaОценок пока нет
- Worksheet 1 (Sol)Документ3 страницыWorksheet 1 (Sol)Carlos ArranzОценок пока нет