Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Unit 4 Assignment 1
Загружено:
miller44Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Unit 4 Assignment 1
Загружено:
miller44Авторское право:
Доступные форматы
Unit 4 assignment 1: Video summary 2
This video is about motherboards different types of form factors like ATX, BTX, and NLX. Its
also about communication buses, connectors and what a motherboard contains. What to do while
buying a motherboard. Not all CPUS and motherboards are compatible dont buy a motherboard
without knowing a CPU that fits it. Dont even buy the case without knowing your motherboard.
Size and shape are determined by the form factor of the motherboard.
There are three form factors of primary interest today. And one of them is the ATX form factor.
ATX replaced the older AT form factor. Reasons the ATX is better it is smaller, better
organization which makes it easier to work on and it provides much more support for a wide
variety of I/O devices. The BTX form factor is compatible with all of the ATX functions but the
BTX has been designed to promote better air flow. Another form factor is the NLX the NLX is
used on low end personal computers and supports riser cards. Riser cards fit into expansion slots,
provides connectors for additional expansion slots and are also known as daughter boards.
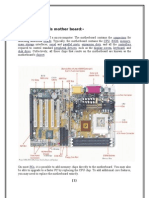
If you look at the bottom of the motherboard youll see copper tracing all across it these tracings
make up the bus system. Buses connects various components and allows delivery of power and
data. The system bus is the largest and fastest bus and connects motherboard to CPU. On the
motherboard you want to be able to identify various connectors like PI power, 40 pin IDE, 34 pin
floppy drive, SATA, and 50 or 68 pin SCSI.
Topics
Motherboards
ATX form factor
BTX form factor
NLX form factor
Communication buses
Connectors
Expansion slots
Terms used in video clip 1.04 with definitions:
CPU: control processor unit
P1: power connector.
DIMM: memory slots.
AGP: accelerated graphics port.
PCI: peripheral component interconnect.
IDE: integrated drive electronics.
SATA: serial advanced technology attachment.
Soft power button: front of computer does not immediately cut
power.
Power switch: back of the computer immediately cuts power.
Wake on LAN is a technology that allows a network professional to
remotely power on a computer or to wake it up from sleep mode.
SCSI: Small Computer System Interface (SCSI) is a set of parallel
interface standards developed by the American National Standards
Institute (ANSI) for attaching printers, disk drives, scanners and
other peripherals to computers.
ISA: Industry Standard Architecture
MCA: Micro Channel Architecture
EISA: (Extended Industry Standard Architecture) is a standard bus
(computer interconnection) architecture that extends the ISA
standard to a 32-bit interface.
VESA local bus: VESA Local Bus (sometimes called the VESA VL
bus) is a standard interface between your computer and its
expansion slot that provides faster data flow between the devices
controlled by the expansion cards and your computer's
microprocessor.
PCIx: faster
PCIe: express fastest expected to replace AGP.
Вам также может понравиться
- PlayStation Architecture: Architecture of Consoles: A Practical Analysis, #6От EverandPlayStation Architecture: Architecture of Consoles: A Practical Analysis, #6Оценок пока нет
- Xbox Architecture: Architecture of Consoles: A Practical Analysis, #13От EverandXbox Architecture: Architecture of Consoles: A Practical Analysis, #13Оценок пока нет
- Types of MotherboardДокумент6 страницTypes of MotherboardmarianneОценок пока нет
- CompTIA A+ Certification (Chapter 01)Документ0 страницCompTIA A+ Certification (Chapter 01)Wasantha KumaraОценок пока нет
- Motherboard ComponentsДокумент24 страницыMotherboard ComponentsCarol MutugiОценок пока нет
- Module - MotherboardДокумент37 страницModule - Motherboardyuva_sriОценок пока нет
- Mother BoardДокумент8 страницMother Boardalphonsocolleen8Оценок пока нет
- Motherboard Form FactorsДокумент3 страницыMotherboard Form FactorsasyrafidzОценок пока нет
- MotherboardДокумент30 страницMotherboardJhan Rhoan Salazar100% (1)
- Mother BoardДокумент29 страницMother BoardSwayamprakash PatelОценок пока нет
- The Main Circuit Board of A MicrocomputerДокумент16 страницThe Main Circuit Board of A Microcomputeramandeep123Оценок пока нет
- MOTHERBOARDДокумент70 страницMOTHERBOARDCha DechavezОценок пока нет
- MotherboardДокумент38 страницMotherboardpiusamantaОценок пока нет
- "Motherboard": Presented by Intramantra Global Solution PVT LTD, IndoreДокумент31 страница"Motherboard": Presented by Intramantra Global Solution PVT LTD, IndoreJimit ShahОценок пока нет
- Experiment:-4: 1) AT (Advanced Technology)Документ4 страницыExperiment:-4: 1) AT (Advanced Technology)Vishv PatelОценок пока нет
- Motherboards: The Main Board On A PCДокумент85 страницMotherboards: The Main Board On A PCUmar SheriffОценок пока нет
- What Is A Motherboard ?Документ13 страницWhat Is A Motherboard ?Ian OffemariaОценок пока нет
- Motherboard The Heart of The Computer: Microprocessors Sockets Soldering Embedded System Main MemoryДокумент8 страницMotherboard The Heart of The Computer: Microprocessors Sockets Soldering Embedded System Main MemoryJhay Consolacion WalkerОценок пока нет
- Components of A MotherboardДокумент14 страницComponents of A MotherboardvcinfotechОценок пока нет
- Practical-3: Specify The Difference Between Desktop Motherboard, Laptop and Server MethodДокумент7 страницPractical-3: Specify The Difference Between Desktop Motherboard, Laptop and Server MethodAarunain PandavdraОценок пока нет
- Unit 1-Mastering Lan and Trouble ShootingДокумент17 страницUnit 1-Mastering Lan and Trouble Shootingbala smileyОценок пока нет
- Inggris MotherboardДокумент4 страницыInggris Motherboards4tr10.d1m4sОценок пока нет
- Motherboard ArchitectureДокумент15 страницMotherboard ArchitectureAbhishek DebОценок пока нет
- Otherhardware Updated Js2019 Clo1 Week3Документ54 страницыOtherhardware Updated Js2019 Clo1 Week3somerandomhedgehog100% (1)
- Hardware BibleДокумент123 страницыHardware BibleMitko JosifoskiОценок пока нет
- CPH Microproject PDFДокумент12 страницCPH Microproject PDFRohanОценок пока нет
- MotherboardДокумент8 страницMotherboardMayank JaiswalОценок пока нет
- Expansion Cards and System Interfaces: MotherboardДокумент21 страницаExpansion Cards and System Interfaces: Motherboardjahan2006Оценок пока нет
- Motherboard and Its ComponentsДокумент5 страницMotherboard and Its ComponentsVenky MudavathОценок пока нет
- CSS 11 Q1 W4-5 Finalized1Документ30 страницCSS 11 Q1 W4-5 Finalized1AC BalioОценок пока нет
- Components of HardwareДокумент9 страницComponents of HardwareNUTS GAMINGОценок пока нет
- Computer Motherboard PresentationДокумент21 страницаComputer Motherboard PresentationKoushal JainОценок пока нет
- Hardware&Networking Manual 231124 165519Документ46 страницHardware&Networking Manual 231124 165519crecbhoomi21Оценок пока нет
- Computer MotherboardДокумент15 страницComputer MotherboardElsabet KindeОценок пока нет
- Class NotesДокумент12 страницClass NotesHeart WeyganОценок пока нет
- Unit 03 The MotherboardДокумент17 страницUnit 03 The MotherboardSneaky peteОценок пока нет
- CSS 11 Q1 W4-5 FinalizedДокумент31 страницаCSS 11 Q1 W4-5 FinalizedAC BalioОценок пока нет
- Practical No. - 1Документ55 страницPractical No. - 1Rashi SharmaОценок пока нет
- Mboard TshootingДокумент29 страницMboard TshootingDrift GeeОценок пока нет
- Css MOTHERBOARD - TRANSESДокумент7 страницCss MOTHERBOARD - TRANSESRonalyn SiaОценок пока нет
- Components of MotherboardДокумент4 страницыComponents of MotherboardMayur GoreОценок пока нет
- 1.2 Explain Motherboard Components, Types and Features: Form FactorДокумент12 страниц1.2 Explain Motherboard Components, Types and Features: Form FactorTuesept Anne Vargas UrgenteОценок пока нет
- Chapter1 04152023Документ41 страницаChapter1 04152023NICDAO, Christine JoyОценок пока нет
- Repair and Maintenance PC System ComponentsДокумент14 страницRepair and Maintenance PC System ComponentsMuvubuka KatimaniОценок пока нет
- CSS PrintДокумент6 страницCSS Printjhazmineiloveyou123Оценок пока нет
- The Motherboard: Form Factors Chipsets Connectors Buses MotherboardДокумент48 страницThe Motherboard: Form Factors Chipsets Connectors Buses MotherboardWilbertJamesEscletoMoralesОценок пока нет
- A MotherboardДокумент4 страницыA MotherboardOttonniel BenОценок пока нет
- Motherboard Parts and FunctionsДокумент52 страницыMotherboard Parts and FunctionsDemart Vermin Tapang100% (1)
- Motherboard: Board or Logic BoardДокумент9 страницMotherboard: Board or Logic BoardappatujuОценок пока нет
- Final Notes of Second Yr 2022Документ269 страницFinal Notes of Second Yr 2022RAM KrishnaОценок пока нет
- Motherboard Lesson - NewДокумент7 страницMotherboard Lesson - NewNeil DuyagОценок пока нет
- Motherboards Routers and SwitchesДокумент3 страницыMotherboards Routers and SwitchesELISABETH KNOLОценок пока нет
- Motherboard Form FactorsДокумент5 страницMotherboard Form FactorsShe Real LeanОценок пока нет
- Ece018 - Digital Electronics 2 - Reflection Paper 1Документ2 страницыEce018 - Digital Electronics 2 - Reflection Paper 1John Wilfredd CurimoОценок пока нет
- Contoh Makalah Dalam Bahasa InggrisДокумент6 страницContoh Makalah Dalam Bahasa InggrisMerry ErawatiОценок пока нет
- Computer Systems / ServicingДокумент406 страницComputer Systems / ServicingMakaha Rutendo0% (1)
- Different Kinds of MotherboardsДокумент9 страницDifferent Kinds of MotherboardsDar N. AgasangОценок пока нет
- Motherboard: Personal Computers Printed Circuit Board Computers Apple Logic BoardДокумент7 страницMotherboard: Personal Computers Printed Circuit Board Computers Apple Logic BoardMustafa MuhammedОценок пока нет
- Chapter-01 (First Look at Computer Parts and Tools) What'S Inside The Case (Casing)Документ10 страницChapter-01 (First Look at Computer Parts and Tools) What'S Inside The Case (Casing)Al Arafat RummanОценок пока нет
- TESDA Assestment Review (Motherboard) 2015Документ77 страницTESDA Assestment Review (Motherboard) 2015Sharalyn P. SiaОценок пока нет
- 7200 C30 5Документ2 страницы7200 C30 5Vasile Popescu0% (1)
- Amba Bus ProtocolДокумент3 страницыAmba Bus Protocolkoti459Оценок пока нет
- 8086 Microprocessor: Dr. M. Gopikrishna Assistant Professor of Physics Maharajas College ErnakulamДокумент116 страниц8086 Microprocessor: Dr. M. Gopikrishna Assistant Professor of Physics Maharajas College ErnakulamgopiikrishnaОценок пока нет
- Crown Notes 2017 PDFДокумент28 страницCrown Notes 2017 PDFAdil MushtaqueОценок пока нет
- K250 Service Manual Part 2 1987Документ70 страницK250 Service Manual Part 2 1987SHARIF LAFFREYОценок пока нет
- E-CCS - LM - Module 3 Lessons 1-2 PDFДокумент117 страницE-CCS - LM - Module 3 Lessons 1-2 PDFKai Me50% (2)
- COA Module2Документ14 страницCOA Module2entertainmentworldyОценок пока нет
- Funds of Distributed Control SystemsДокумент55 страницFunds of Distributed Control SystemsAttreau0% (2)
- Arm STM32H742 PDFДокумент357 страницArm STM32H742 PDFtungОценок пока нет
- 1 Ion30 Installer Guide Latest 0Документ44 страницы1 Ion30 Installer Guide Latest 0maxx1nsaneОценок пока нет
- The 8085 Microprocessor Architecture: Dr. Kuda Nageswara RaoДокумент32 страницыThe 8085 Microprocessor Architecture: Dr. Kuda Nageswara RaoKrishna ChaitanyaОценок пока нет
- Drive LCD - Ks0066uДокумент34 страницыDrive LCD - Ks0066uJose SilvaОценок пока нет
- COMPUTER STUDIES Question N AnswerДокумент134 страницыCOMPUTER STUDIES Question N AnswerAMANANG'OLE BENARD ILENY0% (1)
- DS PDFДокумент49 страницDS PDFTrieeОценок пока нет
- Desktop and Laptop Option Best PracticesДокумент21 страницаDesktop and Laptop Option Best PracticesmogallapuОценок пока нет
- Asus K8AE-LA 754 Rev 1.0 SCHДокумент40 страницAsus K8AE-LA 754 Rev 1.0 SCHSebastian QuaroneОценок пока нет
- Avionics - QBДокумент5 страницAvionics - QBVeeramani ShankarОценок пока нет
- 3D Graphics Content Over OCP: Martti Venell Sr. Verification Engineer BitboysДокумент13 страниц3D Graphics Content Over OCP: Martti Venell Sr. Verification Engineer BitboysSohei LaОценок пока нет
- Timing Diagram of 8085Документ13 страницTiming Diagram of 8085abk_89100% (1)
- Register Organization of 8086 PDFДокумент10 страницRegister Organization of 8086 PDFDevikaОценок пока нет
- Car2x - From Research To Product DevelopmentДокумент6 страницCar2x - From Research To Product DevelopmentSri Natha DesikanОценок пока нет
- Modicon Premium CataДокумент459 страницModicon Premium Cataajrojas1359Оценок пока нет
- Os Ca MCQ'SДокумент5 страницOs Ca MCQ'Ssk khuddusОценок пока нет
- Computer Maintenance Course OutlineДокумент3 страницыComputer Maintenance Course OutlineyonasОценок пока нет
- 8051 Microcontroller TrainingДокумент7 страниц8051 Microcontroller TrainingSarthak SisgainОценок пока нет
- Project Report USB GameboyДокумент70 страницProject Report USB GameboyRambo333Оценок пока нет
- CSE 243: Introduction To Computer Architecture and Hardware/Software InterfaceДокумент27 страницCSE 243: Introduction To Computer Architecture and Hardware/Software Interfaceanilkumarpatil1988Оценок пока нет
- Examples: Disks, Disk Drives, Display Screens, Keyboards, Printers, Boards and Chips, Usb To Midi, Usb HubДокумент2 страницыExamples: Disks, Disk Drives, Display Screens, Keyboards, Printers, Boards and Chips, Usb To Midi, Usb HubJea XeleneОценок пока нет
- Unit 3: Bus Structure, Memory and I/O InterfacingДокумент1 страницаUnit 3: Bus Structure, Memory and I/O Interfacingyogesh deoОценок пока нет
- Hb140e Cpu-Sc 313-6CF23 19-01Документ241 страницаHb140e Cpu-Sc 313-6CF23 19-01Moumene Djafer BeyОценок пока нет