Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Antibiotic Summary - Draft
Загружено:
Strept PneumoniaИсходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Antibiotic Summary - Draft
Загружено:
Strept PneumoniaАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
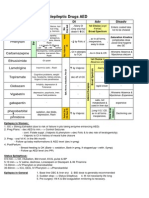
[SPECTRUM , EFFECTS AND USES]
Antibiotics
Antibiotic spectrum according
to class
1. Penicillin :
Strept. Except viridans
MSSA(Methicillin-sensitive Staphylococcus aureus)
Enterococcus
2. Ampicillin and amoxicillin :
MSSA but only with added clav. Acid/sulbactam
Strept. Except viridans
Enterococcus
Anaerobes
Gm ve but only with clav. Acid /sulbactam
3. Anti-staph penicillin (naficillin/dicloxacillin)
MSSA
Strept. Except viridans
4. Anti-pseudomonas penicillin (pipracillin/tazobactam)
MSSA
Strept. Except viridans
Enterococcus
Gm ve
Anaerobes
Pseudomonas
5. Cephalosporins 1st gen:
Gm +ve except enterococci
Gm ve
Anaerobes
6. Cephalosporins 2nd gen:
Gm +ve except enterococci
Gm ve
Anaerobes
1
Summary of classes of antibiotics in clinical use | Stanford school
of medicine
[SPECTRUM , EFFECTS AND USES]
7. Cephalosporins 3rd gen :
Gm +ve except enterococcus
Gm ve
Anaerobes
Pseudomonas : only ceftazidime(fortum)
8. Cephalosporins 4th gen:
Gm +ve except enterococci
Gm ve
Anaerobes
Pseudomonas
9. Cephalosporins 5th gen (Ceftaroline ) :
Gm +ve except enterococcus
Gm ve
MRSA
10.
Carbapenems (imipenem
/meropenem/ertapenem):
They cover all organisms except
MRSA
Vancomycin resistant enterococcus (VRE)
Acinetobacter
Atypicals
Stenotrophomonas
11.
Quinolones (ciprofloxacin)
MSSA
Gm ve
Pseudomonas
Atypicals
12.
Quinolones (levofloxacin)
Gm +ve
Gm ve
Atypicals
Anaerobes
13.
Quinolones (moxifloxacin)
Gm +ve
Gm ve
2
Summary of classes of antibiotics in clinical use | Stanford school
of medicine
[SPECTRUM , EFFECTS AND USES]
Atypicals
Anaerobes
MRSA
14.
Aminoglycosides
Used for serious aerobic gm ve infections including
pseudomonas , used with vancomycin/ lactams in
cases of endocarditis
Contraindicated in renal failure and myasthenia gravis
Ototoxic-nephrotoxic : tobramycin is the safest
Summary and notes
- Main use for cephalosporins in summary
1. 1st gen : gm +ve except MRSA
2. 2nd gen : anaerobes
3. 3rd gen : gm ve + pseudomonas (fortum only)
4. 4th gen : pseudomonas
5. 5th gen : MRSA
- Cephalosporins do not cover enterococci
- Fortum is the only 3rd gen against pseudomonas
- Imipenem and meropenem active against pseudomonas
- Imipenem doesnt cross BBB
- Imipenem is always combined with cilstatin that inhibit
human dehydropeptidas enzyme
- Carbapenems only IV route
- Ertapenem is not active against enterococcus fecalis
- Penicillin G : strept A/B, strept pneumonia
- Ampicillin/amoxicillin : strept A/B , strept pneumonia ,
enterococcus fecalis, listeria
- Ampicillin/amoxicillin + clav. Acid/sulbactam: MSSA, strept
A/B, strept pneumonia , enterococcus fecalis, listeria
3
Summary of classes of antibiotics in clinical use | Stanford school
of medicine
[SPECTRUM , EFFECTS AND USES]
- Anti-staph penicillins : MSSA mostly
- Anti-pseudomonal penicillins : MSSA, strept A/B, strept
pneumonia, enterococcus fecalis
- Quinolones : strept A/B, strept pneumonia , enterococcus
fecalis
- Quinolones are bactericidal antibiotics mostly and dont
cross BBB
- Macrolides : weak cover for strept A/B , pneumonia , listeria
- Tetracyclines : strept pneumonia
- Sulpha : MSSA, strept A/B, strept pneumonia , strept viridans
, listeria
- Clindamycin : strept A/B, strept pneumonia , anaerobes
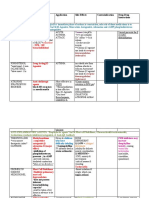
Generally preferred drugs for gm
+ve organisms
MSSA
Coagulase-ve
staph
Strept A/B
Strept
pneumonia
Strept viridans
Enterococcus
fecalis
Enterococcus
4
Naficillin
Cefazolin
Vanco
Naficilli
Vanco
Carbapenems
Penicillin + clindamycin for A
Any lactams
Vanco
Penicillin G
Any lactams
Vanco
Penicillin G
Ceftriaxone
Vanco
Ampicillin
Penicillin G
Vanco
Ampicillin
Summary of classes of antibiotics in clinical use | Stanford school
of medicine
[SPECTRUM , EFFECTS AND USES]
facium
listeria
NB:
-
Penicillin G
Vanco
Ampicillin gentamicin
Sulpha
Carbapenems
Staph = naficillin (except MRSA)
Strept = penicillin G / ceftriaxone
Enterococcus/listeria = ampicillin
For cases of severe allergy against ampicillin , vanco is a
good choice
Resistant bacteria
Risk factors:
- Recent excess use of cephalosporins/quinolones for MRSA or
vanco for VRE
- Longterm hospitalization
- Hemodialysis
Drug of choice:
- Vancomycin :
MRSA
Side effects: red man syndrome , nephrotoxic ,
ototoxic ,neutropenia
Poor BBB crossing
- Daptomycin:
MRSA
VRE
Side effects : myopathy , neuropathy , esinophilia
- Linezolid:
MRSA
VRE
5
Summary of classes of antibiotics in clinical use | Stanford school
of medicine
[SPECTRUM , EFFECTS AND USES]
Side effects : lactic acidosis , serotonin syndrome
,neuropathy, optic neuritis
- Ceftaroline
Generally preferred drugs for gm ve
organisms
2nd gen cephalosporins
3rd gen cephalosporins
4th gen cephalosporins
Amoxicillin/ampicillin+ clav.
Acid/sulbactam
Anti-spseudomonal penicillins
Carbapenems
Aztreonam
Quinolones
Aminoglycosides
E-coli
H.influenza
Klebsiella
Proteus
The same+
Neisseria
- The same
+citrobacteria and
neisseria
- As 3rd gen
-
As 4th gen
As 4th gen
As 2nd gen
All except Neisseria
All except neisseria
Resistant negative
strains
Pseudomonas mainly
Others: stenotrophomonas ,ESBL
Drug of choice:
6
Summary of classes of antibiotics in clinical use | Stanford school
of medicine
[SPECTRUM , EFFECTS AND USES]
Ceftazidime : pseudomonas , only one in 3rd gen
Cefipime: pseudomonas , false +ve coombs test
Pipracillin/tazobactam: pseudomonas , PLT
Carbapenems except ertapenem : pseudomonas and ESBL
- Aztreonam : weak anti-pseudomonal
- Aminoglycosides : pseudomonas , poor lung
penetration , ototoxic , nephrotoxic
NB:
1. Ciprofloxacin & levofloxacin have good anti-pseudomonal
activity
2. Ampicillin sulbactam has good cover for acinetobacter
3. Sulpha is good for stenotrophomonas and can be used if no
contraindications
Generally preferred drugs for
anaerobic infections
When should we cover anaerobes even if theres no growth?
-
periodontal infections
Infections of deep spaces of neck
Aspiration pneumonia
Lung abscess
Empyema
Intra-abdominal abscess
Secondary peritonitis
metronidazole
carbapenems
lactams + clav.
Acid/sulbactam
7
Bacteroids
Clostridia
Metallic taste
Fair for all organisms but
ertapenem is not preferred
- Fair against all organisms
- PLT
Summary of classes of antibiotics in clinical use | Stanford school
of medicine
[SPECTRUM , EFFECTS AND USES]
clindamycin
2nd gen cephalosporins
moxifloxacin
chloramphenicol
Fair for all organisms
Q 6hrs compliance
Fair against all
Fair against actinomyces
QT prolongation
Not recommended for
pediatrics
- Excellent against all except
c. difficile
NB:
- If infection above diaphragm use clindamycin
- If infection below diaphragm use metronidazole
- If generalized use lactams + clav. Acid/sulbactams
&moxifloxacin
- Metronidazole should never be used as monotherapy except
for c. difficile that is the most common cause for infection
colitis due to antibiotic use
- Most gut flora is gm ve
- Vanco can be used for TTT of c. difficile but only oral because
IV route is poorly absorbed in GIT
Generally preferred drugs for
atypical organisms
Mycoplasma pneumonia
Chlamydia trachomatis
Chlamydophila pneumonia
Chlamydophila pisittaci
rickettsia
legionella
8
Atypical pneumonia
PID
Urethritis
Prostatitis
Pneumonia in neonates
Atypical pneumonia
Bird transmission
Typhus
Atypical pnemonia
Summary of classes of antibiotics in clinical use | Stanford school
of medicine
[SPECTRUM , EFFECTS AND USES]
Drug of choice:
1. Macrolides :
all except rickettsia
Side effects : QT prolongation , hepatic injury ,
exacerbate myasthenia gravis
2. Tetracycline :
all except legionella
Side effects: esophagitis , hyperpigmentation
Should be taken with plenty of fluids
3. Quinolones:
for all except rickettsia
Side effects : QT prolongations , exacerbate myasthenia
gravis
4. Chloramphenicol:
for all except legionella
Side effects : aplastic anemia
mycoplasma
chlamydia
rickettsia
legionella
Doxycycline
Azithromycin
Quinolones
Doxycycline
Azithromycin
Levofloxacin
Doxycycline
Azithromycin
Quinolones
Levofloxacin
Moxifloxacin
Azithromycin
Summary of classes of antibiotics in clinical use | Stanford school
of medicine
[SPECTRUM , EFFECTS AND USES]
Key
means
excellent
activity
means good
activity
means not
always active
1
0
Summary of classes of antibiotics in clinical use | Stanford school
of medicine
Вам также может понравиться
- Egyptian Fellowship of Emergency MedicineДокумент144 страницыEgyptian Fellowship of Emergency MedicineStrept PneumoniaОценок пока нет
- Top 300 Drugs Pocket Reference Guide (2021 Edition)От EverandTop 300 Drugs Pocket Reference Guide (2021 Edition)Рейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)
- Pharmacology of Volume and Vascular Tone RegulationДокумент2 страницыPharmacology of Volume and Vascular Tone RegulationgraycorypОценок пока нет
- Pharmacology MapsДокумент18 страницPharmacology MapsPERUBATAN Cawangan Zagazig100% (1)
- OB Power Point Presentation 002Документ57 страницOB Power Point Presentation 002RitamariaОценок пока нет
- Ericksonian Approaches To Pain ManagementДокумент6 страницEricksonian Approaches To Pain Managementosher2650% (2)
- Chemotherapy NДокумент28 страницChemotherapy NFaisal MehboobОценок пока нет
- Mu 002Документ10 страницMu 002chandanОценок пока нет
- Antibiotics 9Документ11 страницAntibiotics 9Beth Morales100% (1)
- Quinolones, Folic Acid Antagonist and Urinary Tract Antitb and LeprosyДокумент124 страницыQuinolones, Folic Acid Antagonist and Urinary Tract Antitb and LeprosyrenОценок пока нет
- AntiemeticsДокумент25 страницAntiemeticsPridho GaziansyahОценок пока нет
- Vancomycin Pharmacology Indications, Mechanism, and Side Effects! PDFДокумент1 страницаVancomycin Pharmacology Indications, Mechanism, and Side Effects! PDFFrancis PasayОценок пока нет
- Northern Ireland Management of Infection Guidelines For Primary and Community Care 2016Документ48 страницNorthern Ireland Management of Infection Guidelines For Primary and Community Care 2016dreneavalentinstefanОценок пока нет
- AntimicrobialsДокумент1 страницаAntimicrobialsRomaine Barrett100% (1)
- SAR of Macrolides, Penicillins, and Other AntibioticsДокумент36 страницSAR of Macrolides, Penicillins, and Other AntibioticsBen Paolo Cecilia RabaraОценок пока нет
- Antibiotic GuideДокумент6 страницAntibiotic GuideAnnTran100% (1)
- Common infections and recommended antibioticsДокумент3 страницыCommon infections and recommended antibioticsNicole BerryОценок пока нет
- Warfarin Sodium: INR Levels 4.0 or Less Ok To Carry Out Procedure Test Atleast 72 Hrs Prior To ProcedureДокумент6 страницWarfarin Sodium: INR Levels 4.0 or Less Ok To Carry Out Procedure Test Atleast 72 Hrs Prior To ProcedureVimi GeorgeОценок пока нет
- Pharmacology of The GITДокумент31 страницаPharmacology of The GITmarviecute22Оценок пока нет
- Pharma ChartsДокумент33 страницыPharma ChartsNooreen Hussain100% (1)
- Treatment guidelines for common infectionsДокумент1 страницаTreatment guidelines for common infectionsJoseph De JoyaОценок пока нет
- DrugsДокумент155 страницDrugsAkankshaОценок пока нет
- Classification of AntibioticsДокумент5 страницClassification of AntibioticsdenaОценок пока нет
- Antibiotic Classification & Indications OverviewДокумент16 страницAntibiotic Classification & Indications Overviewdaven100% (1)
- AntibioticsДокумент2 страницыAntibioticsPGI Custodio, Ed KristianОценок пока нет
- Pharmacology Drug ChartДокумент50 страницPharmacology Drug ChartEssentialForLivingОценок пока нет
- Pharmacology OverviewДокумент95 страницPharmacology OverviewMiguel CuevasОценок пока нет
- Classification of Drugs PDFДокумент15 страницClassification of Drugs PDFmuhammad ihtisham ul hassanОценок пока нет
- Pharmacology Mnemonics (Part 01) by M IhtishamДокумент32 страницыPharmacology Mnemonics (Part 01) by M Ihtishammuhammad ihtisham ul hassan100% (1)
- Generic Name Brand Names Common Uses Possible Side Effects Mechanism of ActionДокумент13 страницGeneric Name Brand Names Common Uses Possible Side Effects Mechanism of Actionangel3424Оценок пока нет
- Pharmacology SummaryДокумент16 страницPharmacology Summaryshenric16Оценок пока нет
- AntibioticsДокумент6 страницAntibioticsOccamsRazor100% (1)
- List of antibiotics: generic names, brands, classes and usesДокумент9 страницList of antibiotics: generic names, brands, classes and usesprince1500100% (1)
- Adrenergics & Adrenergic BlockersДокумент5 страницAdrenergics & Adrenergic Blockersapi-3739910100% (4)
- Pharmacology of DiureticsДокумент75 страницPharmacology of DiureticsAhmed BassettОценок пока нет
- Antidiarrheal DrugsДокумент4 страницыAntidiarrheal DrugsNadhirah ZulkifliОценок пока нет
- Chapter 43 - Beta-LactamДокумент7 страницChapter 43 - Beta-LactamErika De JesusОценок пока нет
- Pharm Drug Outline AdrДокумент1 страницаPharm Drug Outline AdrCess Lagera YbanezОценок пока нет
- AntibioticsДокумент5 страницAntibioticsLaureece Salm ApduhanОценок пока нет
- RX Cheat Sheet Pharmacy CrackДокумент1 страницаRX Cheat Sheet Pharmacy Crackramesh kumar100% (1)
- Cholinergics and Cholinergic BlockersДокумент5 страницCholinergics and Cholinergic Blockersapi-3739910100% (3)
- Classification of AntibioticsДокумент4 страницыClassification of AntibioticsNico AvellanaОценок пока нет
- Microbiology Summary 13 - 14 Part 1Документ13 страницMicrobiology Summary 13 - 14 Part 1Jessica MalinОценок пока нет
- Review Handouts For Medical Pharmacology: Terriann Crisp, PH.DДокумент28 страницReview Handouts For Medical Pharmacology: Terriann Crisp, PH.Dmus zaharaОценок пока нет
- Mechanism of Action For Each Class of AntiДокумент146 страницMechanism of Action For Each Class of AntiReynaldo RiveraОценок пока нет
- Drug Interactions of Antianginal Drugs..Документ40 страницDrug Interactions of Antianginal Drugs..Kamal SikandarОценок пока нет
- PHARMA SupertableДокумент2 страницыPHARMA SupertablelpanatalioОценок пока нет
- Family Names of DrugsДокумент1 страницаFamily Names of DrugsangelОценок пока нет
- Antiinfectives Drug TableДокумент5 страницAntiinfectives Drug Tablecdp1587100% (3)
- Anti-Viral Drugs AltДокумент42 страницыAnti-Viral Drugs AltSidraОценок пока нет
- Anti EmeticsДокумент29 страницAnti EmeticsBezawit Tsige100% (1)
- Basic Pharmacology OverviewДокумент42 страницыBasic Pharmacology OverviewWin Htet0% (1)
- Bumetanide Torsemide: Desmopressin - V2Документ1 страницаBumetanide Torsemide: Desmopressin - V2med testОценок пока нет
- Classification of DrugsДокумент10 страницClassification of DrugsSafura IjazОценок пока нет
- ChemotherapyДокумент11 страницChemotherapyNedaAbdullahОценок пока нет
- Antiepileptic Drugs AED: D' DI Disadv SE AdvДокумент1 страницаAntiepileptic Drugs AED: D' DI Disadv SE Advrayooona88Оценок пока нет
- Drug Name Mechanism Application Side Effects Contraindication Drug-Drug InteractionsДокумент3 страницыDrug Name Mechanism Application Side Effects Contraindication Drug-Drug Interactionsazhar hussinОценок пока нет
- Mechanisms of Drug Toxicity: Proceedings of the Third International Pharmacological MeetingОт EverandMechanisms of Drug Toxicity: Proceedings of the Third International Pharmacological MeetingH. RaškováОценок пока нет
- Therapeutic Hypothermia - Principles, Indications, Practical ApplicationОт EverandTherapeutic Hypothermia - Principles, Indications, Practical ApplicationОценок пока нет
- Ion Channels in Health and DiseaseОт EverandIon Channels in Health and DiseaseGeoffrey S. PittОценок пока нет
- Overview of Mechanical Ventilation Settings, Modes, TroubleshootingДокумент24 страницыOverview of Mechanical Ventilation Settings, Modes, TroubleshootingRochim CoolОценок пока нет
- NICU Nutrition GuideДокумент22 страницыNICU Nutrition GuideStrept PneumoniaОценок пока нет
- CroupДокумент26 страницCrouptamaОценок пока нет
- Blood Gas Analysis GuideДокумент42 страницыBlood Gas Analysis GuideStrept PneumoniaОценок пока нет
- Post - Resuscitation Management of An Asphyxiated Neonate: Perinatal AsphyxiaДокумент19 страницPost - Resuscitation Management of An Asphyxiated Neonate: Perinatal AsphyxiaAmit KinareОценок пока нет
- Respiratory Distress ChildrenДокумент38 страницRespiratory Distress ChildrenStrept PneumoniaОценок пока нет
- Fluoroquinolone ReviewДокумент13 страницFluoroquinolone ReviewStrept Pneumonia100% (1)
- Neonatal Physiology: Teka Siebenaler RRT Cardiopulmonary Services University of Minnesota Amplatz Children's HospitalДокумент29 страницNeonatal Physiology: Teka Siebenaler RRT Cardiopulmonary Services University of Minnesota Amplatz Children's HospitalStrept PneumoniaОценок пока нет
- Practical Pediatric تحفهДокумент25 страницPractical Pediatric تحفهStrept PneumoniaОценок пока нет
- Neonatal SeizuresДокумент26 страницNeonatal SeizuresStrept PneumoniaОценок пока нет
- Newborn AbnormalДокумент29 страницNewborn AbnormalStrept PneumoniaОценок пока нет
- Fluid Electrolyte NutritionДокумент40 страницFluid Electrolyte NutritionStrept PneumoniaОценок пока нет
- Hyperkalemia: Samir El AnsaryДокумент43 страницыHyperkalemia: Samir El AnsaryStrept PneumoniaОценок пока нет
- Best Review of Ventilators and VentilationДокумент7 страницBest Review of Ventilators and VentilationStrept PneumoniaОценок пока нет
- Acute BronchitisДокумент1 страницаAcute BronchitisDr.G.Bhanu PrakashОценок пока нет
- Fetal Circulation Vs Neonatal CirculationДокумент1 страницаFetal Circulation Vs Neonatal CirculationStrept PneumoniaОценок пока нет
- EMLc 4 EngДокумент35 страницEMLc 4 EngMarina MihailescuОценок пока нет
- Weingart Vent HandoutДокумент4 страницыWeingart Vent HandoutStrept Pneumonia100% (1)
- Antibiotic Summary - DraftДокумент10 страницAntibiotic Summary - DraftStrept Pneumonia100% (1)
- Paediatric Chest X-RayДокумент10 страницPaediatric Chest X-RayIdha KurniasihОценок пока нет
- Antibiotic Summary - DraftДокумент10 страницAntibiotic Summary - DraftStrept Pneumonia100% (1)
- Tier 4 of The Points Based SystemДокумент93 страницыTier 4 of The Points Based SystemStrept PneumoniaОценок пока нет
- Child Approp TreatmtДокумент1 страницаChild Approp Treatmtzenagit123456Оценок пока нет
- Tier 4 VisaДокумент8 страницTier 4 VisaStrept PneumoniaОценок пока нет
- VAF9 - Self Assessment FormДокумент8 страницVAF9 - Self Assessment FormDiabloОценок пока нет
- External Gestational Age CharachteristicsДокумент1 страницаExternal Gestational Age CharachteristicsStrept PneumoniaОценок пока нет
- Tier 4 of The Points Based SystemДокумент93 страницыTier 4 of The Points Based SystemStrept PneumoniaОценок пока нет
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective: Short Term Goals: Independent: Short Term GoalsДокумент2 страницыAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective: Short Term Goals: Independent: Short Term GoalskyawОценок пока нет
- Preboard Exam Np3 Medical Surgical NursingДокумент19 страницPreboard Exam Np3 Medical Surgical NursingDavid LopezОценок пока нет
- Christian Rupal's ResumeДокумент2 страницыChristian Rupal's ResumesaumiljoshilondonОценок пока нет
- Acute Compartment SyndromeДокумент44 страницыAcute Compartment Syndromeasi basseyОценок пока нет
- Submission For The Reclassification of A Medicine: Topical MinoxidilДокумент33 страницыSubmission For The Reclassification of A Medicine: Topical MinoxidilMoneimul IslamОценок пока нет
- NBEMS announces DNB/DrNB practical exam datesДокумент2 страницыNBEMS announces DNB/DrNB practical exam datesShivaraj S AОценок пока нет
- Cvek Pulpotomy: Report of A Case With Five-YearДокумент4 страницыCvek Pulpotomy: Report of A Case With Five-YearKaren SandovalОценок пока нет
- Loneliness and Social Isolation in Older Adults-The Effects of A PandemicДокумент8 страницLoneliness and Social Isolation in Older Adults-The Effects of A Pandemicmadalena limaОценок пока нет
- Aneroxia Research PaperДокумент34 страницыAneroxia Research PaperDuaa HammadОценок пока нет
- Antibodies To Sars-Cov-2 Are Associated With Protection Against ReinfectionДокумент30 страницAntibodies To Sars-Cov-2 Are Associated With Protection Against ReinfectionJimmy A. Camones ObregonОценок пока нет
- Social Participation of People With Chronic Wounds - A Systematic ReviewДокумент25 страницSocial Participation of People With Chronic Wounds - A Systematic ReviewcumbredinОценок пока нет
- EMedicine - Oral Hemangiomas - Article by Steven Brett SloanДокумент19 страницEMedicine - Oral Hemangiomas - Article by Steven Brett SloanDr Monal YuwanatiОценок пока нет
- The Rubik's Cube Approach To Clinical MedicineДокумент2 страницыThe Rubik's Cube Approach To Clinical Medicinehenrygoldstein100% (1)
- Nursing Grand Rounds Reviewer PDFДокумент17 страницNursing Grand Rounds Reviewer PDFAlyssa Jade GolezОценок пока нет
- PharmacovigilanceДокумент45 страницPharmacovigilancepavani valluriОценок пока нет
- DM GerontikДокумент15 страницDM GerontikPuji Affan Dwi MiriyantoОценок пока нет
- Radiographic Special Procedures: Kenneth M. Luciano, RRTДокумент36 страницRadiographic Special Procedures: Kenneth M. Luciano, RRTKaye A. JardinicoОценок пока нет
- Bill Receipt for Super Extn Health Male TestДокумент1 страницаBill Receipt for Super Extn Health Male TestSiddhant choudharyОценок пока нет
- N.favisim 2012cДокумент9 страницN.favisim 2012cIsmail Bazly ZarirОценок пока нет
- Cleft Lip and Cleft PalateДокумент27 страницCleft Lip and Cleft Palatenamah odatОценок пока нет
- Gen EpidemiologyДокумент88 страницGen EpidemiologyShibu Sebastian100% (1)
- Ecg ReviewДокумент155 страницEcg ReviewVimal Nishad100% (5)
- Combined Dental Management of Patients With Medical ConditionsДокумент65 страницCombined Dental Management of Patients With Medical ConditionsJenny WangОценок пока нет
- UNAIDS Core Epidemiology Slides enДокумент11 страницUNAIDS Core Epidemiology Slides enTabarcea VitaliОценок пока нет
- Asthma Aware KitДокумент33 страницыAsthma Aware KitEkzHa Noctis CaeleumОценок пока нет
- Pe 1 Module 1Документ11 страницPe 1 Module 1Joanna Valerie A. IboñaОценок пока нет
- MapehasdasdДокумент2 страницыMapehasdasdAmiel Angelo BaliosОценок пока нет
- Cpe Common Diagnoses 6-4-2021Документ9 страницCpe Common Diagnoses 6-4-2021Shubham HarishОценок пока нет