Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Attapulgite From USP
Загружено:
Nofa PuspitaАвторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Attapulgite From USP
Загружено:
Nofa PuspitaАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Accessed from 128.83.63.
20 by nEwp0rt1 on Mon Nov 21 22:45:44 EST 2011
USP 35
Official Monographs / Aurothioglucose 2273
atropine sulfate [(C 17H23NO3)2 H2SO4 H2O] in the portion of
Tablets taken by the formula:
(694.85 / 676.83)(W / 10)(RU / RS)
in which 694.85 and 676.83 are the molecular weights of atropine sulfate monohydrate and anhydrous atropine sulfate, respectively; W is the weight, in mg, of USP Atropine Sulfate RS
in the Standard preparation; and RU and RS are as defined
therein.
Activated Attapulgite
.
Activated Attapulgite is a highly heat-treated,
processed, native magnesium aluminum silicate.
Packaging and storagePreserve in well-closed containers.
IdentificationActivated Attapulgite responds to the Identification test for Colloidal Activated Attapulgite, the characteristic
peak, however, being much less intense.
Loss on drying 731Dry it at 105 to constant weight: it
loses not more than 4.0% of its weight.
Loss on ignition 733When ignited at 1000 for 1 hour, it
loses between 4.0% and 12.0% of its weight.
Volatile matterWhen ignited at 600 for 1 hour, it loses
between 3.0% and 7.5% of its weight on the dried basis.
Powder finenessProceed as directed in the test for Powder
fineness under Colloidal Activated Attapulgite. The dr y weight of
the residue is not more than 0.10% of the weight of the specimen taken.
Acid-soluble matterBoil 2.0 g with 100 mL of 0.2 N hydrochloric acid for 5 minutes, and cool. Add water to adjust the
volume to 100 mL, and filter. Evaporate 50 mL of the filtrate so
obtained to dr yness, and ignite the residue at 600 : not more
than 0.25 g is found (25%).
Other requirementsIt meets the requirements of the tests
for Microbial limits, pH, Carbonate, Arsenic and Lead, and Adsorptive capacity under Colloidal Activated Attapulgite.
Colloidal Activated Attapulgite
.
Colloidal Activated Attapulgite is a purified native magnesium aluminum silicate.
Packaging and storagePreserve in well-closed containers.
IdentificationAdd 2 g in small portions to 100 mL of water,
with vigorous agitation. Allow to stand for at least 12 hours to
ensure complete hydration. Place 2 mL of the resulting mixture
on a suitable glass slide, and allow to air-dr y at room temperature to produce a uniform film. Place the slide in a vacuum
desiccator over a free sur face of ethylene glycol. Evacuate the
desiccator, and close the stopcock so that the ethylene glycol
saturates the desiccator chamber. Allow to stand for 12 hours.
Record the X-ray diffraction pattern (see X-Ray Diffraction
941), and calculate the d values: several peaks are obser ved;
the characteristic peak corresponds to a d value between 10.3
and 10.7 Angstrom units.
Microbial enumeration tests 61 and Tests for specified
microorganisms 62It meets the requirements of the test
for absence of Escherichia coli.
pH 791Disperse 1.0 g in 10 mL of carbon dioxide-free
water, and mix: the pH of the mixed dispersion so obtained is
between 7.0 and 9.5.
Loss on drying 731Dry it at 105 to constant weight: it
loses between 5.0% and 17.0% of its weight.
Loss on ignition 733When ignited at 1000 for 1 hour, it
loses between 17.0% and 27.0% of its weight.
Volatile matterWhen ignited at 600 for 1 hour, it loses
between 7.5% and 12.5% of its weight on the dried basis.
Powder finenessAdd 50 g to 450 mL of water containing
5 g of sodium pyrophosphate, and stir for 10 minutes. Pour the
resulting dispersion slowly through a No. 325 standard sieve
(see Particle Size Distribution Estimation by Analytical Sieving
786), and carefully wash the residue until clean. Dr y the residue at 105 to constant weight: the dr y weight of the residue
so obtained is not more than 0.30% of the weight of the specimen taken.
Acid-soluble matterBoil 2.0 g with 100 mL of 0.2 N hydrochloric acid for 5 minutes, and cool. Add water to adjust the
volume to 100 mL, and filter. Evaporate 50 mL of the filtrate so
obtained to dr yness, and ignite the residue at 600 : not more
than 0.15 g is found (15%).
CarbonateMix 1.0 g with 15 mL of 0.5 N sulfuric acid: no
effervescence occurs.
Arsenic and LeadTo 5.0 g add 50 mL of 1 N nitric acid,
and boil for 30 minutes, adding 1 N nitric acid at times to
maintain the volume. Filter into a 100-mL volumetric flask,
wash the filter with water, and dilute the combined filtrate and
washings with water to volume.
ArsenicDetermine the arsenic in the solution by atomic absorption spectrometry (see Spectrophotometry and Light-scattering 851), using a graphite furnace to volatilize the arsenic, as
directed by the manufacturer of the instrument used, and
measuring the absorbance at 189.0 nm against a standard: not
more than 2 ppm is found.
LeadDetermine the lead in the solution by atomic absorption spectrometry (see Spectrophotometry and Light-scattering
851), using a graphite furnace to volatilize the lead, as directed by the manufacturer of the instrument used, and measuring the absorbance at 283.3 nm against a standard: not more
than 0.001% is found.
Adsorptive capacityTo 10 mL of a 1 in 10 suspension of
the specimen in water add 80 mL of methylene blue solution (1
in 1000), and shake. Add 10 mL of barium chloride solution (1
in 50), and shake. Allow to stand for 15 minutes. T ransfer 40
mL of the supernatant to a 50-mL centrifuge tube, and centrifuge. To 5 mL of the clear supernatant add 495 mL of water,
and mix: the color of the solution so obtained is not deeper
than that of a solution containing 1.5 g of methylene blue per
mL.
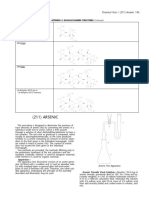
Aurothioglucose
.
C6H11AuO5S 392.18
Gold, (1-thio- D-glucopyranosato)-.
(1-Thio-D-glucopyranosato)gold [12192-57-3].
Aurothioglucose contains not less than 95.0
percent and not more than 105.0 per cent of
C6H11AuO5S, calculated on the dried basis. It is
stabilized by the addition of a small amount of
Sodium Acetate.
Packaging and storagePreserve in tight, light-resistant
containers. Store at room temperature.
USP Reference standards 11
USP Aurothioglucose RS
Official from May 1, 2012
Copyright (c) 2011 The United States Pharmacopeial Convention. All rights reserved.
Accessed from 128.83.63.20 by nEwp0rt1 on Mon Nov 21 22:45:44 EST 2011
2274 Aurothioglucose / Official Monographs
Identification
A: Dissolve a suitable quantity in water to obtain a solution
containing 4 mg per mL. Apply 10 L of this solution and 10
L of an aqueous Standard solution of USP Aurothioglucose RS
containing 4 mg per mL to a suitable thin-layer chromatographic glass microfilament sheet (see Chromatography 621)
impregnated with silicic acid and a suitable fluorescing substance. Allow the spots to dr y, and develop the chromatogram
in a solvent system consisting of a mixture of n-propyl alcohol,
water, and ethyl acetate (3:3:1) until the solvent front has
moved about three-fourths of the length of the plate. Remove
the sheet from the developing chamber, mark the solvent front,
and allow the solvent to evaporate. Locate the spots on the
plate by examination under short-wavelength UV light: the RF
value of the principal spot obtained from the solution under
test corresponds to that obtained from the Standard solution.
B: To a portion of the filtrate obtained in the Assay add
barium chloride TS: a heavy, white precipitate is formed.
Specific rotation 781S: between +65 and +75 .
Test solution: 10 mg per mL, in water.
Loss on drying 731Dry it over phosphorus pentoxide for
24 hours: it loses not more than 1.0% of its weight.
AssayAccurately weigh about 1 g of Aurothioglucose, and
dissolve in 100 mL of water in a 300-mL Kjeldahl flask. Slowly
add 10 mL of nitric acid, and when the reaction has subsided,
boil the mixture for 5 minutes. Filter, wash well the separated
gold with hot water, dr y, and ignite to constant weight. The
weight of the gold so obtained, multiplied by 1.991, represents
the weight of C 6H11AuO5S in the portion of Aurothioglucose
taken.
Aurothioglucose Injectable Suspension
.
Aurothioglucose Injectable Suspension is a sterile suspension of Aurothioglucose in a suitable
vegetable oil. It contains not less than 90.0 percent and not more than 110.0 per cent of the
labeled amount of C 6H11AuO5S. It may contain
suitable thickening agents.
Packaging and storagePreserve in single-dose or in multiple-dose containers, preferably of T ype I glass. Protect from
light.
USP Reference standards 11
USP Aurothioglucose RS
IdentificationTransfer a volume of Injectable Suspension,
equivalent to about 200 mg of aurothioglucose, to a centrifuge
separator containing 20 mL of ethyl acetate and 50 mL of
water. Shake the mixture thoroughly, and centrifuge until the
liquid phases have been clearly separated. W ithdraw the lower,
aqueous phase, and filter, discarding the first 10 mL of the
filtrate. Collect the filtrate in a glass-stoppered vessel, and proceed as directed in Identification test A under Aurothioglucose,
beginning with apply 10 L of this solution.
Bacterial endotoxins 85It contains not more than 7.14
USP Endotoxin Units per mg of aurothioglucose.
Sterility 71It meets the requirements.
Other requirementsIt meets the requirements under Injections 1.
AssayTransfer with a pipet, calibrated to contain rather than
to deliver, an accurately measured volume of Injectable Suspension, equivalent to about 200 mg of aurothioglucose, to a
beaker containing 400 mL of acetone. W ash the pipet into the
beaker with a small quantity of acetone, mix, allow the solids to
settle, and decant the supernatant through a filter. W ash the
solids with another 400-mL portion of acetone, and repeat the
decantation. Transfer the solids to the filter with the aid of ace-
USP 35
tone, then transfer the filter and its contents to a short-necked,
300-mL Kjeldahl flask, add 5 mL of water, and proceed as directed in the Assay under Gold Sodium Thiomalate, beginning
with add 20 mL of nitric acid. The weight of gold so obtained, multiplied by 1.991, represents the weight of
C6H11AuO5S in the portion of Injectable Suspension taken.
Avobenzone
.
C20H22O3 310.40
1,3-Propanedione, 1-[4-(1,1-dimethylethyl)phenyl]-3-(4-methoxyphenyl)-.
1-(p-tert-Butylphenyl)-3-(p-methoxyphenyl)-1,3-propanedione
[70356-09-1].
Avobenzone contains not less than 95.0 percent and not more than 105.0 per cent of
C20H22O3, calculated on the dried basis.
Packaging and storagePreserve in tight, light-resistant
containers.
USP Reference standards 11
USP Avobenzone RS
Identification
A: Infrared Absorption 197K.
B: Ultraviolet Absorption 197U
Solution: 5 g per mL.
Medium: alcohol.
Absorptivities at 360 nm do not differ by more than 3.0%.
Melting range, Class I 741: between 81 and 86 .
Loss on drying 731Dry it in vacuum at 70 for 4 hours: it
loses not more than 0.5% of its weight.
Chromatographic purity
Test solutionProceed as directed for Assay preparation in
the Assay.
Chromatographic system (see Chromatography 621)Proceed as directed in the Assay.
ProcedureInject a volume (about 1 L) of Test solution into
the chromatograph, record the chromatogram, and measure
the peak responses. Calculate the per centage of each impurity
in the portion of A vobenzone taken by the formula:
100(rI / rS)
in which rI is the response of each individual peak, other than
the avobenzone peak, in the chromatogram of the Test solution;
and rS is the sum of the responses of all of the peaks in the
chromatogram of the Test solution: not more than 3.0% of any
individual impurity is found, and the sum of all of the impurities
is not more than 4.5%.
Assay
Standard preparationDilute an accurately measured quantity of USP A vobenzone RS in acetone, and dilute quantitatively,
and stepwise if necessar y, with acetone to obtain a solution
having a known concentration of about 50 mg per mL.
Assay preparationTransfer about 500 mg of A vobenzone,
accurately weighed, to a 10-mL volumetric flask, dilute with
acetone to volume, and mix.
Chromatographic system (see Chromatography 621)The
gas chromatograph is equipped with a flame-ionization detector
and a 0.32-mm 25-m fused silica capillar y column coated
with phase G1. The column temperature is maintained at about
Official from May 1, 2012
Copyright (c) 2011 The United States Pharmacopeial Convention. All rights reserved.
Вам также может понравиться
- Caddy Arc 251i Service ManualДокумент52 страницыCaddy Arc 251i Service Manualrikycien100% (8)
- Robbie Hemingway - Text God VIP EbookДокумент56 страницRobbie Hemingway - Text God VIP EbookKylee0% (1)
- UOP 326 Diene Value by Maleic Anhydre Addition ReactionДокумент4 страницыUOP 326 Diene Value by Maleic Anhydre Addition ReactionMauricio Huerta JaraОценок пока нет
- 2245-2246 AspirinДокумент2 страницы2245-2246 AspirinPhoenixОценок пока нет
- USP Monographs Lysine HydrochlorideДокумент2 страницыUSP Monographs Lysine HydrochlorideFahmi NasrullahОценок пока нет
- Iodine ValueДокумент4 страницыIodine ValueRobert Gilmore100% (4)
- METHOD of ANALYSIS - Allium Cepae ExtractДокумент9 страницMETHOD of ANALYSIS - Allium Cepae ExtractJames AkibonОценок пока нет
- Advanced Pharmaceutical analysisОт EverandAdvanced Pharmaceutical analysisРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (2)
- 07 EPANET Tutorial-SlidesДокумент26 страниц07 EPANET Tutorial-SlidesTarhata Kalim100% (1)
- Acute Leukemia The Scientist's Perspective and ChallengeДокумент438 страницAcute Leukemia The Scientist's Perspective and ChallengemedskyqqОценок пока нет
- Differential Calculus ExamДокумент6 страницDifferential Calculus ExamCaro Kan LopezОценок пока нет
- 121ferrous GluconateДокумент3 страницы121ferrous GluconateAira Jherese MarcosОценок пока нет
- Gelatin Bloom StrengthДокумент3 страницыGelatin Bloom StrengthmeongОценок пока нет
- Usp36-Nf31 01 38Документ2 страницыUsp36-Nf31 01 38Salsabil Nurazizah TAОценок пока нет
- Magnesium Aluminium SilicateДокумент5 страницMagnesium Aluminium SilicateWanguОценок пока нет
- Homap Health & OTC Manufacturing Associates Pakistan: IslamabadДокумент11 страницHomap Health & OTC Manufacturing Associates Pakistan: IslamabadHafiz Ali shanОценок пока нет
- CPCB - So2Документ11 страницCPCB - So2Sudipto GhoshОценок пока нет
- Arsen.01 ImprimirДокумент6 страницArsen.01 ImprimirLautaro Valentin QuirogaОценок пока нет
- Rhenium in Catalysts by SpectrophotometryДокумент7 страницRhenium in Catalysts by SpectrophotometryDavinОценок пока нет
- A - Performance Tests Salt in Desalted Oil, Cameron Method C-010-CДокумент6 страницA - Performance Tests Salt in Desalted Oil, Cameron Method C-010-CSathish RajanОценок пока нет
- PH Euro 3.1.3 PolyolefinesДокумент9 страницPH Euro 3.1.3 Polyolefinesryad bmzaОценок пока нет
- LCMS Trouble ShootingДокумент4 страницыLCMS Trouble Shootingsoma_zoeОценок пока нет
- Polyvinyl AlcoholДокумент3 страницыPolyvinyl Alcoholhossam salahОценок пока нет
- Isosorbide Concentrate: 2266 Isoproterenol / Official Monographs USP 41Документ2 страницыIsosorbide Concentrate: 2266 Isoproterenol / Official Monographs USP 41Clarissa PutriОценок пока нет
- Experiment 12 Preparation of Adipic Acid From CyclohexeneДокумент6 страницExperiment 12 Preparation of Adipic Acid From Cyclohexenesaransh1994Оценок пока нет
- USP - Choline ChlorideДокумент3 страницыUSP - Choline Chloridehh.8968Оценок пока нет
- AP LACTOSE MonohydrateДокумент4 страницыAP LACTOSE MonohydrateAde YuLianiОценок пока нет
- 2334-2335 Betahistine HydrochlorideДокумент2 страницы2334-2335 Betahistine HydrochlorideShady Ashraf LatifОценок пока нет
- 0227-0232 (581) Vitamin D AssayДокумент6 страниц0227-0232 (581) Vitamin D AssayRajesh RaviОценок пока нет
- Ferric Ammonium Citrate BPДокумент3 страницыFerric Ammonium Citrate BPJai MurugeshОценок пока нет
- Standard Analytical ProceduresДокумент80 страницStandard Analytical Proceduresengr_afsoomro3147Оценок пока нет
- Hialuronato de SodioДокумент6 страницHialuronato de SodiozombiecorpОценок пока нет
- 9.2.27 AOAC Official Method 988.11 Mercury (Methyl) in Fish and ShellfishДокумент2 страницы9.2.27 AOAC Official Method 988.11 Mercury (Methyl) in Fish and ShellfishLêXuânThắngОценок пока нет
- Total Dissolved Solids ProcedureДокумент13 страницTotal Dissolved Solids Procedurehemavathi jayОценок пока нет
- P-NitroacetanilideДокумент5 страницP-NitroacetanilideNuratiqah SalamОценок пока нет
- MOA - Faropenam Sodium (In-House) AkumsДокумент9 страницMOA - Faropenam Sodium (In-House) AkumsUsman AshrafОценок пока нет
- USP-NF Oxidized Regenerated CelluloseДокумент2 страницыUSP-NF Oxidized Regenerated CelluloseVõ Đức TrọngОценок пока нет
- PH Euro 3.1.6Документ10 страницPH Euro 3.1.6ryad bmzaОценок пока нет
- Water For InjectionsДокумент4 страницыWater For InjectionsAlvina Arum PuspitasariОценок пока нет
- M976 26 PDFДокумент3 страницыM976 26 PDFdanzan1Оценок пока нет
- YeoKal - Standard CalibrationsДокумент2 страницыYeoKal - Standard Calibrationsjasvinder kumarОценок пока нет
- YeoKal - Standard CalibrationsДокумент2 страницыYeoKal - Standard Calibrationsm daneshpourОценок пока нет
- Crospovidone PDFДокумент2 страницыCrospovidone PDFstselvaОценок пока нет
- 30208EДокумент3 страницы30208EAvinash KumarОценок пока нет
- Expression and Purification of His-Tagged Proteins Expressed in E. Coli (Price Lab)Документ3 страницыExpression and Purification of His-Tagged Proteins Expressed in E. Coli (Price Lab)Raja GunalanОценок пока нет
- Carbomer (Carbomerum) : The International Pharmacopoeia - Ninth Edition, 2019Документ1 страницаCarbomer (Carbomerum) : The International Pharmacopoeia - Ninth Edition, 2019Riska MellindaОценок пока нет
- Usp31nf26s1 - c211, General Chapters - 211 - ARSENICДокумент2 страницыUsp31nf26s1 - c211, General Chapters - 211 - ARSENICEfsha KhanОценок пока нет
- UOP682Документ11 страницUOP682Abu WildanОценок пока нет
- Albumin Solution, HumanДокумент3 страницыAlbumin Solution, HumanMulayam Singh Yadav67% (3)
- ION EXCHANGE Analysis Testing Procedures GeneralДокумент50 страницION EXCHANGE Analysis Testing Procedures GeneralJinalОценок пока нет
- Estimation Protocol Antinutrional Factors in OilseedsДокумент33 страницыEstimation Protocol Antinutrional Factors in OilseedsnarayananОценок пока нет
- 1855-1857 MaltodextrinДокумент3 страницы1855-1857 MaltodextrinsadiaОценок пока нет
- Expt 05 - CyclohexeneДокумент5 страницExpt 05 - CyclohexeneMark Cliffton BadlonОценок пока нет
- Frequently Asked Questions: Pectin Assay Using M-HydroxydiphenylДокумент2 страницыFrequently Asked Questions: Pectin Assay Using M-HydroxydiphenylRodrigosqmОценок пока нет
- NF Monographs - GelatinДокумент2 страницыNF Monographs - GelatinLyadelou FortuОценок пока нет
- Nitrogen, Nitrate (Colorimetric, Brucine)Документ4 страницыNitrogen, Nitrate (Colorimetric, Brucine)envirocompОценок пока нет
- The Chemistry of Fertilisers and Manure - Including Information on the Chemical Constituents and Types of Fertilisers and ManuresОт EverandThe Chemistry of Fertilisers and Manure - Including Information on the Chemical Constituents and Types of Fertilisers and ManuresРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)
- Plant and Animal Bio-Chemistry - Including Information on Amino Acids, Proteins, Pigments and Other Chemical Constituents of Organic MatterОт EverandPlant and Animal Bio-Chemistry - Including Information on Amino Acids, Proteins, Pigments and Other Chemical Constituents of Organic MatterОценок пока нет
- Standard methods for the examination of water and sewageОт EverandStandard methods for the examination of water and sewageОценок пока нет
- The Chemistry of Dairy Products - A Chemical Analysis of Milk, Cream and ButterОт EverandThe Chemistry of Dairy Products - A Chemical Analysis of Milk, Cream and ButterОценок пока нет
- Chemistry at Home - A Collection of Experiments and Formulas for the Chemistry EnthusiastОт EverandChemistry at Home - A Collection of Experiments and Formulas for the Chemistry EnthusiastОценок пока нет
- Legal Chemistry: A Guide to the Detection of Poisons, Examination of Tea, Stains, Etc., as Applied to Chemical JurisprudenceОт EverandLegal Chemistry: A Guide to the Detection of Poisons, Examination of Tea, Stains, Etc., as Applied to Chemical JurisprudenceОценок пока нет
- Recover Gold from Gold Plated Items, And Turn It Into 99.995% Pure GoldОт EverandRecover Gold from Gold Plated Items, And Turn It Into 99.995% Pure GoldОценок пока нет
- Transition Metal Catalyzed Furans Synthesis: Transition Metal Catalyzed Heterocycle Synthesis SeriesОт EverandTransition Metal Catalyzed Furans Synthesis: Transition Metal Catalyzed Heterocycle Synthesis SeriesОценок пока нет
- Firing OrderДокумент5 страницFiring OrderCurtler PaquibotОценок пока нет
- Maintenance Performance ToolboxДокумент6 страницMaintenance Performance ToolboxMagda ScrobotaОценок пока нет
- Propp Function's Types:: 1-Absentation: One of The Members of A Family Absents Himself From HomeДокумент10 страницPropp Function's Types:: 1-Absentation: One of The Members of A Family Absents Himself From HomeRohith KumarОценок пока нет
- Acronyms and AbbreviationsДокумент875 страницAcronyms and AbbreviationsLacky KrishnanОценок пока нет
- M.T Nautica Batu Pahat: Clean Product Tanker 4,497 BHPДокумент1 страницаM.T Nautica Batu Pahat: Clean Product Tanker 4,497 BHPSuper 247Оценок пока нет
- Present Perfect Tense ExerciseДокумент13 страницPresent Perfect Tense Exercise39. Nguyễn Đăng QuangОценок пока нет
- GSM Radio ConceptsДокумент3 страницыGSM Radio ConceptsMD SahidОценок пока нет
- Daily Plankton Agrabinta CianjurДокумент141 страницаDaily Plankton Agrabinta CianjurPutra Cahya GemilangОценок пока нет
- Heisenberg, "Über Den Anschaulichen Inhalt Der Quantentheoretischen Kinematik Und Mechanik"Документ16 страницHeisenberg, "Über Den Anschaulichen Inhalt Der Quantentheoretischen Kinematik Und Mechanik"Benjamin Crowell0% (1)
- Thesis Topics in Medicine in Delhi UniversityДокумент8 страницThesis Topics in Medicine in Delhi UniversityBecky Goins100% (2)
- Tugas Inggris Text - Kelas 9Документ27 страницTugas Inggris Text - Kelas 9salviane.theandra.jОценок пока нет
- AYUSH Warli Art 100628Документ10 страницAYUSH Warli Art 100628adivasi yuva shakti0% (1)
- Adigrat University: College of Engineering and Technology Department of Chemical EnginneringДокумент39 страницAdigrat University: College of Engineering and Technology Department of Chemical EnginneringSeid Aragaw100% (1)
- Data Structures and Algorithms SyllabusДокумент9 страницData Structures and Algorithms SyllabusBongbong GalloОценок пока нет
- Geography NotesДокумент2 страницыGeography NotesMinethegroundОценок пока нет
- AT10 Meat Tech 1Документ20 страницAT10 Meat Tech 1Reubal Jr Orquin Reynaldo100% (1)
- PDFДокумент3 страницыPDFvaliОценок пока нет
- The Consulting Industry and Its Transformations in WordДокумент23 страницыThe Consulting Industry and Its Transformations in Wordlei ann magnayeОценок пока нет
- Reservoir Bag Physics J PhilipДокумент44 страницыReservoir Bag Physics J PhilipJashim JumliОценок пока нет
- HUAWEI PowerCube 500Документ41 страницаHUAWEI PowerCube 500soumen95Оценок пока нет
- MFD16I003 FinalДокумент16 страницMFD16I003 FinalAditya KumarОценок пока нет
- Ezpdf Reader 1 9 8 1Документ1 страницаEzpdf Reader 1 9 8 1AnthonyОценок пока нет
- USA Nozzle 01Документ2 страницыUSA Nozzle 01Justin MercadoОценок пока нет
- Chanakya: For The Indian Television Series Based On His Life, SeeДокумент11 страницChanakya: For The Indian Television Series Based On His Life, SeeTrinadh CrazyguyОценок пока нет
- Sample Valuation ReportДокумент15 страницSample Valuation Reportayush singlaОценок пока нет