Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Dynamics SYLLABUS
Загружено:
ERKATHIRАвторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Dynamics SYLLABUS
Загружено:
ERKATHIRАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
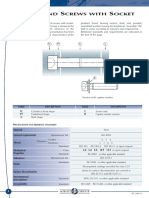
ME6505
DYNAMICS OF MACHINES
LT P C
3003
OBJECTIVES:
To understand the force-motion relationship in components subjected to external forces and analysis of standard
mechanisms.
To understand the undesirable effects of unbalances resulting from prescribed motions in mechanism.
To understand the effect of Dynamics of undesirable vibrations.
To understand the principles in mechanisms used for speed control and stability control.
UNIT I FORCE ANALYSIS
9 Dynamic force analysis Inertia force and Inertia torque D Alemberts principle Dynamic Analysis inreciprocating
engines Gas forces Inertia effect of connecting rod Bearing loads Crank shaft torque Turning moment
diagrams Fly Wheels Flywheels of punching presses- Dynamics of Cam-follower mechanism.
UNIT II BALANCING
9
Static and dynamic balancing Balancing of rotating masses Balancing a single cylinder engine Balancing of
Multi-cylinder inline, V-engines Partial balancing in engines Balancing of linkages Balancing machines-Field
balancing of discs and rotors.
UNIT III SINGLE DEGREE FREE VIBRATION
9
Basic features of vibratory systems Degrees of freedom single degree of freedom Free vibration Equations of
motion Natural frequency Types of Damping Damped vibration Torsional vibration of shaft Critical speeds of
shafts Torsional vibration Two and three rotor torsional systems.
UNIT IV FORCED VIBRATION
9
Response of one degree freedom systems to periodic forcing Harmonic disturbances Disturbance caused by
unbalance Support motion transmissibility Vibration isolation vibration measurement.
UNIT V MECHANISM FOR CONTROL
9
Governors Types Centrifugal governors Gravity controlled and spring controlled centrifugal governors
Characteristics Effect of friction Controlling force curves. Gyroscopes Gyroscopic forces and torques
Gyroscopic stabilization Gyroscopic effects in Automobiles, ships and airplanes.
TOTAL : 45 PERIODS
OUTCOMES:
Upon completion of this course, the Students can able to predict the force analysis in mechanical system and
related vibration issues and can able to solve the problem
TEXT BOOK:
1.Uicker, J.J., Pennock G.R and Shigley, J.E., Theory of Machines and Mechanisms ,3rd Edition, Oxford University
Press, 2009.
2.Rattan, S.S, Theory of Machines, 3rd Edition, Tata McGraw-Hill, 2009.
REFERENCES:
1.Thomas Bevan, "Theory of Machines", 3rd Edition, CBS Publishers and Distributors, 2005.
2.Cleghorn. W. L, Mechanisms of Machines, Oxford University Press, 2005
3.Benson H. Tongue, Principles of Vibrations, Oxford University Press, 2nd Edition, 2007
4.Robert L. Norton, "Kinematics and Dynamics of Machinery", Tata McGraw-Hill, 2009.
5.Allen S. Hall Jr., Kinematics and Linkage Design, Prentice Hall, 1961
6.Ghosh. A and Mallick, A.K., Theory of Mechanisms and Machines", Affiliated East-West Pvt. Ltd., New Delhi, 1988.
7.Rao.J.S. and Dukkipati.R.V. "Mechanisms and Machine Theory", Wiley-Eastern Ltd., New Delhi, 1992.
8.John Hannah and Stephens R.C., "Mechanics of Machines", Viva Low-Prices Student Edition, 1999.
9.Grover. G.T., Mechanical Vibrations, Nem Chand and Bros., 1996
10.William T. Thomson, Marie Dillon Dahleh, Chandramouli Padmanabhan, Theory of Vibration with Application, 5th
edition, Pearson Education, 2011
11.V.Ramamurthi, "Mechanics of Machines", Narosa Publishing House, 2002.
12.Khurmi, R.S.,Theory of Machines, 14th Edition, S Chand Publications, 2005.
Вам также может понравиться
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (121)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (400)
- Kawasaki Bayou 300 Service Manual RepairДокумент678 страницKawasaki Bayou 300 Service Manual RepairMac Thon81% (64)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (266)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5794)
- 3408C & 3412C Electrical System Marine Auxillary Generator SetДокумент2 страницы3408C & 3412C Electrical System Marine Auxillary Generator SetHamid Essarbouti100% (1)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2259)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (345)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (895)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- Hydraulic and Compressible Flow TurbomachinesДокумент146 страницHydraulic and Compressible Flow TurbomachinesPaul Healy100% (3)
- Wear Resistance of Material Used in Slurry TransportДокумент7 страницWear Resistance of Material Used in Slurry TransportwoodoobooОценок пока нет
- SHC 302 FinalДокумент285 страницSHC 302 FinalAmr HassanОценок пока нет
- Cryogenic Heat Exchangers For Process Cooling and Renewable Energy StorageДокумент16 страницCryogenic Heat Exchangers For Process Cooling and Renewable Energy StoragelalithaОценок пока нет
- Report - Maintainability Design ReviewДокумент94 страницыReport - Maintainability Design ReviewNtoko100% (1)
- Thermal Engineering Lab ManualДокумент64 страницыThermal Engineering Lab ManualERKATHIR86% (7)
- C2 - RevAДокумент16 страницC2 - RevAChirag ShahОценок пока нет
- Company Contact DetailsДокумент30 страницCompany Contact DetailsERKATHIRОценок пока нет
- Department of Automobile Engineering At8091 - Manufacturing of Automotive ComponentsДокумент11 страницDepartment of Automobile Engineering At8091 - Manufacturing of Automotive ComponentsERKATHIRОценок пока нет
- Department of Automobile Engineering At8091 - Manufacturing of Automotive ComponentsДокумент3 страницыDepartment of Automobile Engineering At8091 - Manufacturing of Automotive ComponentsERKATHIRОценок пока нет
- How Will You Calculate The Piston Speed If You Know The Stroke Length and Engine Speed?Документ23 страницыHow Will You Calculate The Piston Speed If You Know The Stroke Length and Engine Speed?ERKATHIRОценок пока нет
- Applied Mathematics For Engineering DesignДокумент4 страницыApplied Mathematics For Engineering DesignERKATHIRОценок пока нет
- Form 1 Application For Registration of Designs (Seesection 5 and 44)Документ8 страницForm 1 Application For Registration of Designs (Seesection 5 and 44)ERKATHIRОценок пока нет
- Me8392 Manufacturing Technology L T P CДокумент1 страницаMe8392 Manufacturing Technology L T P CERKATHIRОценок пока нет
- Me 8392 - Manufacturing Technology: 14. Course OutcomesДокумент6 страницMe 8392 - Manufacturing Technology: 14. Course OutcomesERKATHIRОценок пока нет
- AT2401 NotesДокумент58 страницAT2401 NotesERKATHIRОценок пока нет
- Subject Code L P T C 3 0 0 3: Operational ResearchДокумент2 страницыSubject Code L P T C 3 0 0 3: Operational ResearchERKATHIRОценок пока нет
- Hindusthan Institute Technology Department of Automobile EngineeringДокумент3 страницыHindusthan Institute Technology Department of Automobile EngineeringERKATHIRОценок пока нет
- ATHT Course Information SheetДокумент4 страницыATHT Course Information SheetERKATHIRОценок пока нет
- Emission Control: Exhaust Emissions Are Produced by Cars, Buses, andДокумент26 страницEmission Control: Exhaust Emissions Are Produced by Cars, Buses, andERKATHIRОценок пока нет
- aAPC 2marks With AnswerДокумент17 страницaAPC 2marks With AnswerERKATHIR0% (1)
- AT6711Документ83 страницыAT6711ERKATHIRОценок пока нет
- AT2403 Vehicle Maintenance: Layout of An Automobile Repair, Service and Maintenance ShopДокумент58 страницAT2403 Vehicle Maintenance: Layout of An Automobile Repair, Service and Maintenance ShopERKATHIRОценок пока нет
- TL 18 Project Work Schedule - PgugДокумент4 страницыTL 18 Project Work Schedule - PgugERKATHIRОценок пока нет
- Etd 2mark With AnswerДокумент16 страницEtd 2mark With AnswerERKATHIR100% (1)
- 10m703 Power Plant EngineeringДокумент2 страницы10m703 Power Plant EngineeringERKATHIR100% (1)
- HMT Lab ManualДокумент37 страницHMT Lab ManualERKATHIR100% (3)
- Etd 2mark With AnswerДокумент16 страницEtd 2mark With AnswerERKATHIR100% (1)
- HMT 2mark With AnswerДокумент13 страницHMT 2mark With AnswerERKATHIR71% (7)
- Parafusos Com Gargantachapter 3Документ7 страницParafusos Com Gargantachapter 3Miguel QueirosОценок пока нет
- Exercises On Stress StateДокумент4 страницыExercises On Stress StatecusanhОценок пока нет
- Heat Flow Experiment System Specification GenericДокумент2 страницыHeat Flow Experiment System Specification GenericpinkpanterОценок пока нет
- What Is Sewing M/C?: The M/C Which Is Used To Stitch Fabric or Other Material Together With ThreadДокумент48 страницWhat Is Sewing M/C?: The M/C Which Is Used To Stitch Fabric or Other Material Together With ThreadDewan Ajuad Hossain RifatОценок пока нет
- Machining and Machine Tool Operation PI GATE 2020 Previous Year With Ans KeyДокумент21 страницаMachining and Machine Tool Operation PI GATE 2020 Previous Year With Ans Keyhyper meshОценок пока нет
- The Pure Substance:: A Pure Substance Is One That Has A Homogeneous and Invariable Chemical CompositionДокумент113 страницThe Pure Substance:: A Pure Substance Is One That Has A Homogeneous and Invariable Chemical CompositionHrishikesh ReddyОценок пока нет
- Mod. Ct/Ev Mod. Ctc/Ev: Cooling Tower ApparatusДокумент4 страницыMod. Ct/Ev Mod. Ctc/Ev: Cooling Tower Apparatusessam essОценок пока нет
- Research: John W. HutchinsonДокумент25 страницResearch: John W. HutchinsonskcОценок пока нет
- B-191 Operationmanual en A LowresДокумент28 страницB-191 Operationmanual en A LowresDinhtrung TruongОценок пока нет
- Analysis and Design of Prestressed Deck Slab Bridge With IRC 112-2011Документ6 страницAnalysis and Design of Prestressed Deck Slab Bridge With IRC 112-2011Anonymous b9fkTYfEoRОценок пока нет
- SECTION 15010: Handbook of FundamentalsДокумент5 страницSECTION 15010: Handbook of FundamentalsAndy WijayaОценок пока нет
- PSAII Final EXAMДокумент15 страницPSAII Final EXAMdaveadeОценок пока нет
- Primena Application: Belarus DeutzДокумент6 страницPrimena Application: Belarus DeutzDragan LazicОценок пока нет
- 3 - Bar ElementДокумент53 страницы3 - Bar ElementLoo Kai XenОценок пока нет
- Ps-1 Unit 3Документ21 страницаPs-1 Unit 3Prathap VuyyuruОценок пока нет
- Asme Sec Viii D1 Nma App y PDFДокумент15 страницAsme Sec Viii D1 Nma App y PDFADRIANОценок пока нет
- H-3860D - Man - 0816 DesgasteДокумент8 страницH-3860D - Man - 0816 Desgastealvaro almendarezОценок пока нет
- A Multibody Tool For The Optimization of The SuspeДокумент11 страницA Multibody Tool For The Optimization of The SuspeMei Arief HindartoОценок пока нет
- Hilliard Flame Clutch InstallationДокумент4 страницыHilliard Flame Clutch InstallationDavid CarsonОценок пока нет
- 1.daily Report Manufacture Steel Structure. TGL 09.07 2Документ133 страницы1.daily Report Manufacture Steel Structure. TGL 09.07 2Rusman LumbantoruanОценок пока нет
- Sidewinder 24 30 Manual REV 05 2014Документ6 страницSidewinder 24 30 Manual REV 05 2014kirk sutherlandОценок пока нет
- App 05 Drill Rig SpecДокумент8 страницApp 05 Drill Rig SpecTibebu TayeОценок пока нет