Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
(ST) UGW9811 V900R010C00 ST v1.5
Загружено:
John Cristouv CortezОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
(ST) UGW9811 V900R010C00 ST v1.5
Загружено:
John Cristouv CortezАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Security Target for
UGW9811 V900R010
Version
1.5
Date
2013-11-07
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD.
Huawei
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 2013. All rights reserved.
No part of this document may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means without prior written
consent of Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
Trademarks and Permissions
and other Huawei trademarks are trademarks of Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
All other trademarks and trade names mentioned in this document are the property of their respective holders.
Notice
The purchased products, services and features are stipulated by the contract made between Huawei and the customer.
All or part of the products, services and features described in this document may not be within the purchase scope or
the usage scope. Unless otherwise specified in the contract, all statements, information, and recommendations in this
document are provided "AS IS" without warranties, guarantees or representations of any kind, either express or
implied.
The information in this document is subject to change without notice. Every effort has been made in the preparation
of this document to ensure accuracy of the contents, but all statements, information, and recommendations in this
document do not constitute a warranty of any kind, express or implied.
Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
Address:
Huawei Industrial Base
Bantian, Longgang
Shenzhen 518129
People's Republic of China
Website:
Version 1.5
http://www.huawei.com
Huawei Copyright Huawei Technologies
Co., Ltd.
Huawei UGW9811 Version 900 Release 10 Security Target
Contents
Contents
1 Introduction ..................................................................................................................................... 5
1.1 ST reference ...................................................................................................................................................... 5
1.2 TOE reference ................................................................................................................................................... 5
1.3 TOE overview ................................................................................................................................................... 5
1.3.1 TOE usage and major security features ................................................................................................... 5
1.3.2 TOE type .................................................................................................................................................. 8
1.3.3 Non-TOE hardware/software/firmware required by the TOE ................................................................. 8
1.4 TOE description ................................................................................................................................................ 8
1.4.1 Physical scope .......................................................................................................................................... 8
1.4.2 Logical scope of the TOE ........................................................................................................................ 9
2 Conformance claims ................................................................................................................... 10
3 Security Problem Definition..................................................................................................... 11
3.1 Assets .............................................................................................................................................................. 11
3.2 Threat Agents.................................................................................................................................................. 11
3.3 Threats ............................................................................................................................................................ 12
3.4 Organizational Security Policies ..................................................................................................................... 12
3.5 Assumptions ................................................................................................................................................... 12
4 Security Objectives ..................................................................................................................... 13
4.1 Security Objectives for the TOE ..................................................................................................................... 13
4.2 Security Objectives for the Operational Environment .................................................................................... 13
4.3 Security Objectives rationale .......................................................................................................................... 14
5 Security Requirements for the TOE ........................................................................................ 16
5.1 Conventions .................................................................................................................................................... 16
5.2 TOE Security Functional Requirements ......................................................................................................... 16
5.2.1 Security Audit (FAU) ............................................................................................................................ 16
5.2.2 User Data Protection (FDP) ................................................................................................................... 17
5.2.3 Identification and Authentication (FIA)................................................................................................. 18
5.2.4 Security Management (FMT)................................................................................................................. 19
5.2.5 Protection of the TSF (FPT) .................................................................................................................. 19
5.2.6 Resource utilization (FRU) .................................................................................................................... 20
5.2.7 TOE access (FTA) ................................................................................................................................. 20
5.2.8 Trusted Path/Channels (FTP) ................................................................................................................. 21
Version 1.5
Huawei Copyright Huawei Technologies
Co., Ltd.
ii
Huawei UGW9811 Version 900 Release 10 Security Target
Contents
5.3 Security Assurance Requirements .................................................................................................................. 22
5.4 Rationale for the Security Requirements ........................................................................................................ 22
5.5 Dependencies .................................................................................................................................................. 23
6 TOE Summary Specification .................................................................................................... 26
6.1 Authentication................................................................................................................................................. 26
6.2 Access Control ................................................................................................................................................ 27
6.2.1 Account Locking.................................................................................................................................... 27
6.2.2 SGSN/MME/S-GW Blacklist and Whitelist .......................................................................................... 27
6.2.3 IP-based ACL ........................................................................................................................................ 27
6.3 Communication security ................................................................................................................................. 28
6.4 Auditing .......................................................................................................................................................... 29
6.5 Time ................................................................................................................................................................ 30
6.6 Security function management ....................................................................................................................... 30
Version 1.5
Huawei Copyright Huawei Technologies
Co., Ltd.
iii
Huawei UGW9811 Version 900 Release 10 Security Target
Contents
Revision Record
Revision
Version
Change Description
Author
2013-3-6
0.1
Initial template
Yao Junning
2013-3-13
1.0
Fist version
Chen Xiaoli;Yao Junning
2013-07-25
1.1
Change according to EOR
Jason Chen;Yao Junning
2013-08-26
1.2
Change according
developer comment
2013-09-09
1.3
Change according to EOR
Shirley Chen; Yao Junning
2013-09-18
1.4
Update assurance component and
guidance list
Shirley Chen; Yao Junning
2013-11-07
1.5
Update TOE version
Shirley Chen; Yao Junning
Date
Version 1.5
to
EOR
and
Huawei Copyright Huawei Technologies
Co., Ltd.
Shirley Chen;Yao Junning
Huawei UGW9811 Version 900 Release 10 Security Target
Contents
Introduction
1.1 ST reference
This ST is uniquely identified as below,
Title: Huawei UGW9811 Version 900 Release 10 Security Target
Version: V1.5
Publication date: 2013-11-07
1.2 TOE reference
The TOE is identified as below,
TOE name: Huawei UGW9811
TOE version: V900R010ENGC00SPC200
Developer: Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
TOE release date: 2013-7-10
1.3 TOE overview
In this section, the usage and its major security features are summarised, TOE type and major non-TOE
hardware/software required by the TOE are summarised.
1.3.1 TOE usage and major security features
The mobile network has developed from the 2G global system for mobile communications (GSM), the 2.5G general
packet radio service (GPRS), and the 3G universal mobile telecommunications system (UMTS) to the enhanced 3G
(E3G) long term evolution (LTE). Mobile networks cover wide areas, achieve high-speed wireless data transmission,
and allow access to the Internet.
The UGW9811, a unified packet gateway independently developed by Huawei, can be used in GPRS, UMTS, and EPC
networks. The UGW9811 can function as a gateway GPRS support node (GGSN), serving gateway (S-GW), PDN
gateway (P-GW), or any combination of these three roles, and can be managed individually. The TOE and its
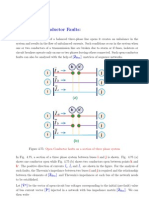
environment are shown in Figure 1.
Version 1.5
Huawei Copyright Huawei Technologies
Co., Ltd.
Huawei UGW9811 Version 900 Release 10 Security Target
Contents
TOE
Figure 1 TOE and its environment
MS:mobilestation
BSS:basestationsubsystem
BTS:basetransceiverstation
BSC:basestationcontroller
RNC:radionetworkcontroller
UTRAN:UMTSterrestrialradioaccessnetwork
EUTRAN:EvolvedUMTSTerrestrialRadioAccess
Network
eNodeB:EnhancedNodeB
SGSN:servingGPRSSupportNode
MME:MobilityManagementEntity
CG:charginggateway
HSGW:HighRatePacketDataServingGateway
OCS:OnlineChargingsystem
PCRF:PolicyandChargingRulesFunction
ReportServer:usedtorecordand
summarizeservicedatareportedby
UGW9811
ICAPserver:InternetContentAdaptation
ProtocolServer
BMSC:BoradcastMulticastService
Center
3GPPAAA:authentication,authorization,
andaccountingfor3GPPnetwork
AAA:authentication,authorization,and
accountingforPDN
LIG:LawfulInterceptGateway
LMT:LocalManagementTerminal
M2000:HuaweiiManagerElement
ManagementSystem
NMS:NetworkManagementSystem
The networks other than the Maintenance network are categorized as the telecommunication service network.
Usage
In the telecommunication service network, the UGW9811 provides the following functions when acted as
GGSN/S-GW/P-GW:
Version 1.5
Huawei Copyright Huawei Technologies
Co., Ltd.
Huawei UGW9811 Version 900 Release 10 Security Target
Contents
1. Acting as an interface between mobile stations (MSs) and external PDNs: The UGW9811 acts as a gateway for MSs
to access an external packet data network (PDN). The UGW9811 acts as GGSN which exchanges routing information
between MSs and PDN. The UGW9811 serves as a router for all IP addresses of MSs in the GPRS/UMTS/EPC
network.
2. Session management: The UGW9811 acts as GGSN which sets up communication between MSs and external PDNs.
3. Mobility management: The UGW9811 acts as a serving-gateway, support Local mobility anchor point for
inter-eNodeB handover.
4. Data receiving and processing: The UGW9811 acts as GGSN which receives data from MSs and routes the data to an
external PDN. It also receives data from the external PDN, and selects a path in the GPRS/UMTS network to forward
the data according to the destination address. Then, it sends the data to the SGSN.
5. Abundant charging functions: The UGW9811 provides the functions of normal charging, hot billing, content-based
charging, and online charging.
6. Service awareness: Service awareness (SA) is an application layer-based traffic inspection and control technique.
The SA technique has wide applications in areas such as flow-based charging (FBC), bandwidth control, service report,
security protection.
TOE major security features
The major security features implemented by the UGW9811 and subject to evaluation are:
Authentication
The authentication feature enables the UGW9811 to identify and authenticate MS users and check the validity of
service requests initiated by the MS users to ensure that only valid users can access network services.
The TOE can authenticate administrative users (referred as users hereafter) by user name and password. The TOE is
able to enforce password policies as well as lockout policies to deter password guessing attacks. Further, it is possible
to limit login of specific users to specific time frames and to define expiry dates for accounts and passwords.
Access Control
The TOE offers the management of network devices.
Role-based access control: The TOE implements role-based access control, limiting access to different management
functionality to different roles as defined in administrator-defined access control associations. The TOE allows the
definition of User Groups, as well as Command Groups in order to define roles that can be assigned to users.
The TOE can limit the user access to the TOE device or application using the ACL (Access Control List) feature by
matching information contained in the headers of connection-oriented or connectionless IP packets against ACL rules
specified.
The TOE can limit the session establishment in the mobile network using the blacklist/whitelist feature by matching the
resource of the session establishment request against the blacklist/whitelist specified.
Communications security
The TOE provides communication security by implementing Secure Sockets Layer (SSL), and Internet Protocol
Security (IPsec).
The TOE offers SSL encryption for the communication between the LMT client and the TOE or between the M2000
(Huawei network management system) and the TOE.
Except the OM interface, the IPsec is used in the interface between the TOE and other non-OM network elements such
as Gn/Gp/S11 interfaces.
Auditing
The TOE generates audit records for security-relevant management actions and stores the audit records in CF card of
the TOE. The audit data can be queried by the authorized user.
Version 1.5
Huawei Copyright Huawei Technologies
Co., Ltd.
Huawei UGW9811 Version 900 Release 10 Security Target
Contents
The TOE classify the audit record into four categories according to the management scope and action: Operation logs,
Security logs, System logs and Diagnosis logs.
Security function management
The following means are provided by the TOE for management of security functionality:
-
User and group management
Access control management (by means of defining command groups, managed object groups, and association
of users with particular managed elements, managed objects, and commands)
Enabling/disabling of SSL/IPsec for communications security.
1.3.2 TOE type
The TOE is a Service and Network Controller and its local management graphical user interface (GUI)
1.3.3 Non-TOE hardware/software/firmware required by the TOE
The server part of the TOE requires the following:
-
At least two L3 switches to connect to the maintenance network and the telecommunication service network
separately
AAA servers for the 3GPP network and the PDN network to perform MS user authentication
Firewalls between the server part of the TOE and the various PDN networks
The management LMT GUI requires:
A PC suitable to run the OS (see below)
Microsoft Windows XP SP3 or later
1.4 TOE description
1.4.1 Physical scope
The hardware components of TOE include cabinets, sub racks, boards, and power supply system. The TOE consists of
five types of boards:
Name
version
Description
SRU/MPU
V900R10C00
Switch and Route Processing Unit/Main Processing Unit, which is the core circuit
board for system management. The SRU/MPU collects routing information and
generates routing tables. The SRU/MPU serves as the operation and maintenance
agent of the system.
SFU
V900R10C00
Switching Fabric Unit, which performs the data exchange function. The SFU
switches service data in the entire system and works in 3+1 backup mode to share
service data load.
SPU
V900R10C00
Service Processing Unit, which performs the service processing function. The SPU
processes all UGW9811 services, including GTP access, charging, and policy
Version 1.5
Huawei Copyright Huawei Technologies
Co., Ltd.
Huawei UGW9811 Version 900 Release 10 Security Target
Contents
enforcement.
LPU
V900R10C00
Line Processing Unit, which provides physical interfaces that connect the
UGW9811 to NEs or external networks.
The TOE comes with the following software:
Name
Version
UGW9811
V900R010ENGC00SPC200
LMT GUI
V900R010C00
The TOE comes with the following guidance:
Name
Version
HUAWEI UGW9811 Unified Gateway V900R010C00 Product Documentation
06(GGSN&S-GW&P-GW)
V900R010C00, 2013/06/08
UGW9811 NPE Solution Documentation
V900R009C01, 2011/12/15
Common Criteria Security Evaluation Certified Configuration
V1.2, 2013/11/07
1.4.2 Logical scope of the TOE
See section 1.3.1 TOE major security features
Version 1.5
Huawei Copyright Huawei Technologies
Co., Ltd.
Huawei UGW9811 Version 900 Release 10 Security Target
Contents
Conformance claims
This ST and the TOE conform to the version of CC as below:
Part 1: Introduction and general model Version 3.1 Revision 4
Part 2: Security functional components Version 3.1 Revision 4
Part 3: Security assurance components Version 3.1 Revision 4
This ST conforms to CC Part 2 conformant
This ST conforms to CC Part 3 conformant
This ST conforms to no Protection Profile
This ST confirms to EAL 3 augmented with ALC_CMC.4 (instead of ALC_CMC.3), and no other packages
Version 1.5
Huawei Copyright Huawei Technologies
Co., Ltd.
10
Huawei UGW9811 Version 900 Release 10 Security Target
Security Problem Definition
3.1 Assets
All data from and to the interfaces available on the TOE is categorized into user data and TSF data.
User Data: The TOE provides the packet service for the mobile user. The user data includes the user data packet of the
user to access PDN network and the information of the user such as user identity and user location.
TSF data: The TSF data includes the following type:
1) Audit records.
2) Configuration parameters for the security features such as audit, authentication and authorization, access control,
communication etc.
3) Network traffic destined to the TOE processed by security feature and functions.
4) Routing and other network forwarding-related tables, including the following security attributes,
Network layer routing tables
Link layer address resolution tables
BGP, OSPF databases.
5) Management User account data, including the following security attributes
Management User identities
Locally managed passwords
Locally managed access levels
3.2 Threat Agents
The Assets are threatened by the following threat agents:
TA.ROGUE_MS_USER:
A MS user seeking to act outside his/her authorization
TA.ROGUE_USER:
A management user seeking to act outside his/her authorization
TA.ROGUE_SYSTEM:
A SGSN/MME/S-GW seeking to connect to the server part of the TOE while there is no
resource or they are not allowed to
TA.NETWORK_M:
An attacker who can access the management network that the TOE is connected to
Version 1.5
Huawei Copyright Huawei Technologies
Co., Ltd.
11
Huawei UGW9811 Version 900 Release 10 Security Target
TA.NETWORK_T:
An attacker who can access the telecommunication network that the TOE is connected
to
TA.PHYSICAL:
An attacker with physical access to the TOE
3.3 Threats
The combination of assets and threat agents gives rise to the following threats:
T.UNAUTHORIZED_MS:
TA.ROGUE_MS_USER tries to access the telecommunication service network/PDN
that he/she is not authorized to
T.UNAUTHORIZED:
TA.ROGUE_USER tries to access the TOE management function that he/she is not
authorized to
T.AUTHORIZED:
TA.ROGUE_USER performs actions on the TOE that he/she is allowed to but not
desired and these actions cannot be traced back to that specific user
T.UNKNOWN_USER:
TA.NETWORK_T or TA.NETWORK_M gains unauthorized access to the TOE and is
able to perform actions on the TOE
T.NETWORK_M:
TA.NETWORK_M is able to modify/read external network traffic originating from /
designated for the TOE and thereby:
Perform actions on the TOE
Gain unauthorized knowledge about the traffic between the LMT and the server
T.NETWORK_T:
TA.NETWORK_T is able to modify/read external network traffic originating from
designated for the TOE and thereby gain unauthorized knowledge about the traffic
between the server and LIG, SGSN, MME, RNC, eNodeB, PGW, SGW, PCRF, OCS,
3GPP-AAA server, AAA server, DHCP server, Report server, CHR server, BM-SC,
HSGW, ICAP server
T.UnwantedTraffic:
TA.NETWORK_T, TA.ROGUE_MS_USER or TA.ROGUE_SYSTEM sends
unwanted network traffic to the TOE which consumes the TOEs processing capacity
for incoming network traffic, thus fails to process traffic expected to be processed. This
may further causes the TOE fails to respond to system control and security management
operations.
T.PHYSICAL:
TA.PHYSICAL gains physical access to the TOE (either LMT or UGW9811 Server)
and is able to perform actions on the TOE.
3.4 Organizational Security Policies
P.ISOLATION: The user must provide security domain isolation of the networks. Different security policies should be
deployed for different security domains. In addition, the isolation of the management/control/end-user planes should be
designed, in such a way that events on one Security Plane are kept totally isolated from the other Security Planes.
3.5 Assumptions
A. NetworkSegregation: It is assumed that the network interfaces that allow access to the TOEs user interfaces are in
a management network that is separate from the application (or, public) networks that the
network device hosting the TOE serves.
Version 1.5
Huawei Copyright Huawei Technologies
Co., Ltd.
12
Huawei UGW9811 Version 900 Release 10 Security Target
Security Objectives
4.1 Security Objectives for the TOE
O.IDAUTH: The TOE must uniquely identify and authenticate the claimed identity of all users, before granting a
user access to TOE functions or, for certain specified services, to a connected network.
O.IDAUTHMS:
The TOE shall support MS user authentication, allowing the TOE to accept/reject the non-3GPP
MS users based on the response of the 3GPP AAA servers, and accept/reject MS users accessing PDN networks based
on the response of the PDN AAA servers.
O.Resource: The TOE shall provide functionalities and management configuration to prevent traffic overload.
O.Connect: The TOE shall provide functionality to limit other devices (e.g., MS, SGSN/MME/S-GW) from connecting
to it
O.Audit: The TOE shall provide functionality to generate audit records for security-relevant administrator actions.
O.Authorization: The TOE shall implement different authorization levels that can be assigned to administrators in
order to restrict the functionality that is available to individual administrators.
O.Communication: The TOE must implement logical protection measures for network communication between the
server and LMT part of the TOE, and the server part of the TOE and various devices in the telecommunication
network1.
4.2 Security Objectives for the Operational Environment
The following security objectives, in addition to those assumptions, are to be satisfied without imposing technical
requirements on the TOE. That is, they will not require the implementation of functions in the TOE hardware or
software. Thus, they will be satisfied largely through application of procedural or administrative measures.
OE.PHYSECThe operator shall ensure the TOE is protected against unauthorized physical access.
OE.Person: Personnel working as authorized administrators shall be carefully selected for trustworthyness and trained
for proper operation of the TOE.
OE.TrustedSystems: The operator shall correctly configure the TOE such that only trusted devices can connect to the
TOE
OE.NetworkElementsThe operator shall provide:
See T.Network_T
Version 1.5
Huawei Copyright Huawei Technologies
Co., Ltd.
13
Huawei UGW9811 Version 900 Release 10 Security Target
At least two L3 switches to separate the management network and the telecommunication service network
3GPP-AAA server to authenticate the non-3GPP MS user to use the 3GPP network
PDN AAA server to authenticate the MS user to the PDN network
Firewall between the server part of the TOE and the PDN networks
OE.NetworkSegregationThe operational environment shall provide segregation by deploying the Ethernet interface
on MPU/SRU in TOE into a local sub-network, compared to the interfaces on LPU in TOE serving the application (or
public) network.
OE.NetworkSecurityThe operational environment shall provide network security. Different security policies should
be deployed for different security domains. In addition, the isolation of the management/control/end-user planes should
be designed, in such a way that events on one Security Plane are kept totally isolated from the other Security Planes.
4.3 Security Objectives rationale
The tracing shows how the security objectives trace back to the threats, OSPs and assumptions as described in the
security problem definition. The security objectives rationale also demonstrates that all the given threats, OSPs and
assumption are addressed.
Threat / OSPs/Assumption
Objectives
T.UNAUTHORIZED_MS
The threat of unauthorized access to access the
telecommunication service network or the PDN is
countered by a requirement that the TOE will
authenticate the MS user (O.IDAUTHMS) according to
the 3GPP AAA server for the non-3GPP user or the PDN
AAA server for users who want to access the PDN.
These servers are provided by the operational
environment (OE.NetworkElements).
T.UNAUTHORIZED
The threat of unauthorized access to the management
function of the TOE or related data is countered by
requiring the TOE to implement an authentication and
authorization
functionality
(O.IDAUTH,
O.Authorization)
In addition, OE.Person ensures that only users that are
carefully selected and properly trusted can gain access to
certain roles.
T.AUTHORIZED
The threat of users may perform undesired action is
countered by OE.Person, which ensures that only users
that are carefully selected and properly trusted can gain
access to certain roles. Should this prove insufficient,
O.Audit will ensure that the actions of the user can be
traced back to him.
T.UNKNOWN_USER
The threat that TA.NETWORK_M may gain
unauthorized access to the TOE and perform actions on
the TOE is countered by requiring the TOE implements
authentication mechanism (O.IDAUTH).
The
Version 1.5
threat
that
Huawei Copyright Huawei Technologies
Co., Ltd.
TA.NETWORK_T
may
gain
14
Huawei UGW9811 Version 900 Release 10 Security Target
unauthorized access to the TOE is countered by
providing functionality to limit other devices to connect
to the TOE (O.Connect) and the operator shall configure
the TOE correctly to only allow trusted systems in the
telecommunication network to connect to the TOE
(OE.TrustedSystems).
T.NETWORK_M
This threat is countered by providing the SSL to protect
the communication between the TOE and the LMT
(O.Communication )
T.NETWORK_T
This threat is countered by providing the IPSec to protect
the communication between the TOE and the other
devices in the telecommunication service network
(O.Communication )
T.UnwantedTraffic
This threat is countered by requiring the TOE to prevent
internal collapse due to traffic overload (O.Resource)
and providing functionality to limit other devices to
connect to the TOE (O.Connect), and to request the
operator to correctly configure the TOE such that only
trusted
system
can
connect
to
the
TOE
(OE.TrustedSystems)
T.PHYSICAL
This threat is countered by requiring the operational
environment to provide adequate physical security to the
TOE (OE.PHYSEC)
P.ISOLATION
This policy is expressed by a corresponding requirement
in OE.NetworkSecurity. The devices needed to provide
network separation and policy (L3 switches, firewalls)
are fulfilled by OE.NetworkElements.
A.NetworkSegregation
The assumption is expressed by a corresponding
requirement in OE.NetworkSegregation. The devices
needed to provide network segregation is fultilled by
OE.NetworkElements.
Version 1.5
Huawei Copyright Huawei Technologies
Co., Ltd.
15
Huawei UGW9811 Version 900 Release 10 Security Target
Security Requirements for the TOE
5.1 Conventions
The following conventions are used for the completion of operations:
Strikethrough indicates text removed as a refinement
(underlined text in parentheses) indicates additional text provided as a refinement.
Bold text indicates the completion of an assignment.
Italicized and bold text indicates the completion of a selection.
Iteration/N indicates an
number/character/name.
element
of
the
iteration,
where
is
the
iteration
5.2 TOE Security Functional Requirements
5.2.1 Security Audit (FAU)
FAU_GEN.1 Security audit data generation
FAU_GEN.1.1 The TSF shall be able to generate an audit record of the following auditable events:
a)
Start-up and shutdown of the audit functions;
b)
All auditable events for the not specified level of audit; and
c)
the following auditable events:
i. user activity
1. login, logout
2. operation requests
ii. user management
1. add, delete, modify
2. password change
3. operation authority change
4. online user query
5. session termination
iii. authentication policy modification
iv. system management
Version 1.5
Huawei Copyright Huawei Technologies
Co., Ltd.
16
Huawei UGW9811 Version 900 Release 10 Security Target
1. reset to factory settings
v. log management
1. log policy modification
FAU_GEN.1.2 The TSF shall record within each audit record at least the following information:
FAU_GEN.2
a)
Date and time of the event, type of event, subject identity (if applicable), and the outcome
(success or failure) of the event; and
b)
For each audit event type, based on the auditable event definitions of the functional
components included in the PP/ST, interface (if applicable), workstation IP (if applicable),
User ID (if applicable), CLI command name (if applicable), and MML command name
(if applicable).
User identity association
FAU_GEN.2.1 For audit events resulting from actions of identified users, the TSF shall be able to associate each
auditable event with the identity of the user that caused the event.
FAU_SAR.1
Audit review
FAU_SAR.1.1 The TSF shall provide users authorized per FDP_ACF.1 with the capability to read all information
from the audit records.
FAU_SAR.1.2 The TSF shall provide the audit records in a manner suitable for the user to interpret the information.
FAU_SAR.3
Selectable audit review
FAU_SAR.3.1/a The TSF shall provide the ability to apply selection of audit data based on log level, slot-id for the
system log.
FAU_SAR.3.1/b The TSF shall provide the ability to apply querying of audit data based on date and time range, user
ID for the operator log and security log.
FAU_STG.1
Protected audit trail storage
FAU_STG.1.1 The TSF shall protect the stored audit records in the audit trail from unauthorized deletion.
FAU_STG.1.2 The TSF shall be able to prevent unauthorised modifications to the stored audit records in the audit trail.
FAU_STG.3 Action in case of possible audit data loss
FAU_STG.3.1 The TSF shall delete the oldest files if the audit trail exceeds the size of store device.
5.2.2 User Data Protection (FDP)
FDP_ACC.1
Subset access control
FDP_ACC.1.1 The TSF shall enforce the access control policy on users as subjects, and commands issued by the
subjects targeting the objects.
FDP_ACF.1
Security attribute based access control
FDP_ACF.1.1 The TSF shall enforce the access control policy to objects based on the following:
a)
users and their following security attributes: user level
b)
commands and their following security attributes: Command Groups
FDP_ACF.1.2 The TSF shall enforce the following rules to determine if an operation among controlled subjects and
controlled objects is allowed:
Version 1.5
the user has been granted authorization for the commands targeted by the request, and
Huawei Copyright Huawei Technologies
Co., Ltd.
17
Huawei UGW9811 Version 900 Release 10 Security Target
the user is associated with a Command Group that contains the requested command
FDP_ACF.1.3 (Refined away)
FDP_ACF.1.4 (Refined away)
5.2.3 Identification and Authentication (FIA)
FIA_AFL.1
Authentication failure handling
FIA_AFL.1.1 The TSF shall detect when an administrator configurable positive integer within 1 and 5 unsuccessful
authentication attempts occur related to login event since the last successful authentication of the indicated user
identity and before the counter for these attempts is reset after an administrator configurable time frame either
between 1 and 60 minutes or never for the LMT user.
FIA_AFL.1.2 When the defined number of unsuccessful authentication attempts has been surpassed, the TSF shall
lockout the account for an administrator configurable duration either between 1 and 1440 minutes or
indefinitely for the LMT user.
FIA_ATD.1 User attribute definition
FIA_ATD.1.1 The TSF shall maintain the following list of security attributes belonging to individual users:
FIA_SOS.1
a)
user ID
b)
user level
c)
password
d)
unsuccessful authentication attempt since last successful authentication attempt counter
e)
login start and end time.
f)
account expiration date for LMT user
g)
password expiration date for LMT user
Verification of secrets
FIA_SOS.1.1 The TSF shall provide a mechanism to verify that secrets meet:
FIA_UAU.2
a)
A user name consists of a maximum of 32 letters and numerals and must start with a
letter. The user name is case insensitive.
b)
A password is a 6- to 32-character string that contains letters and numerals. The letters
are case sensitive. The password must adhere to the password policy.
User authentication before any action
FIA_UAU.2.1 The TSF shall require each user to be successfully authenticated before allowing any other
TSF-mediated actions on behalf of that user.
FIA_UID.2
User identification before any action
FIA_UID.2.1 The TSF shall require each user to be successfully identified before allowing any other TSF-mediated
actions on behalf of that user.
FIA_UAU.2/MS
User authentication before any action
FIA_UAU.2.1 The TSF shall require each (MS) user to be successfully authenticated (by the 3GPP-AAA server or
PDN AAA server) before allowing any other TSF-mediated actions on behalf of that user.
Application note: the 3GPP-AAA server authenticates the MS users form the non-3GPP network (such as CDMA-2000
network), and the PDN AAA server authenticates the MS users who want to access the PDN
FIA_UID.2/MS
Version 1.5
User identification before any action
Huawei Copyright Huawei Technologies
Co., Ltd.
18
Huawei UGW9811 Version 900 Release 10 Security Target
FIA_UID.2.1 The TSF shall require each (MS) user to be successfully identified (by the 3GPP-AAA server or PDN
AAA server) before allowing any other TSF-mediated actions on behalf of that user.
Application note: the 3GPP-AAA server identifies the MS users form the non-3GPP network (such as CDMA-2000
network), and the PDN AAA server identifies the MS users who want to access the PDN
5.2.4 Security Management (FMT)
FMT_MSA.1
Management of security attributes
FMT_MSA.1.1 The TSF shall enforce the access control policy to restrict the ability to query, modify the security
attributes identified in FDP_ACF.1 and FIA_ATD.1 to Admin user and administrator-defined roles.
FMT_MSA.3
Static attribute initialization
FMT_MSA.3.1 The TSF shall enforce the access control policy to provide restrictive default values for security
attributes (Command Group and User Group associations) that are used to enforce the SFP.
FMT_MSA.3.2 The TSF shall allow the nobody to specify alternative initial values to override the default values when
an object or information is created.
FMT_SMF.1
Specification of Management Functions
FMT_SMF.1.1 The TSF shall be capable of performing the following management functions:
FMT_SMR.1
FMT_SMR.1.1
a)
authentication, authorization, encryption policy
b)
user management
c)
definition of IP addresses and address ranges that will be accepted as source addresses
in client session establishment requests
d)
IP-Based ACL policy
e)
APN-specific packet filtering based on ACL
f)
SGSN/MME/S-GW blacklist and whitelist
g)
IPSEC configuration
h)
SSL configuration
Security roles
The TSF shall maintain the roles:
a)
Admin user
b)
administrator-defined roles
FMT_SMR.1.2 The TSF shall be able to associate users with roles.
5.2.5 Protection of the TSF (FPT)
FPT_ITT.1 Basic internal TSF data transfer protection
FPT_ITT.1.1 The TSF shall protect TSF data from disclosure, modification when it is transmitted between separate
parts of the TOE.
FPT_STM.1 Reliable time stamps
FPT_STM.1 The TSF shall be able to provide reliable time stamps.
Version 1.5
Huawei Copyright Huawei Technologies
Co., Ltd.
19
Huawei UGW9811 Version 900 Release 10 Security Target
5.2.6 Resource utilization (FRU)
FRU_PRS.1 Limited priority of service
FRU_PRS.1.1 The TSF shall assign a priority (used as configured bandwidth) to each subject (ME user) in the TSF.
FRU_PRS.1.2 The TSF shall ensure that each access to bandwidth shall be mediated on the basis of the subjects (ME
users) assigned priority.
FRU_RSA.1 Maximum quotas
FRU_RSA.1.1 The TSF shall enforce maximum quotas of the following resources: bandwidth that (ME users) can use
simultaneously.
5.2.7 TOE access (FTA)
FTA_MCS.1 Basic limitation on multiple concurrent sessions
FTA_MCS.1.1 The TSF shall restrict the maximum number of concurrent sessions that belong to the (TSF).
FTA_MCS.1.2 The TSF shall enforce, by default, a limit of 16 sessions per (TSF).
FTA_SSL.1 TSF-initiated session locking
FTA_SSL.1.1 The TSF shall lock an interactive session after a time interval which can be configured by:
a)
Clearing or overwriting display devices, making the current contents unreadable;
b) Disabling any activity of the users data access/display devices other than unlocking the
session
FTA_SSL.1.2 The TSF shall require the following events to occur prior to unlocking the session: user
re-authentication
FTA_TSE.1 TOE session establishment
FTA_TSE.1.1 The TSF shall be able to deny session establishment based on
a)
authentication
b)
source IP address
c)
account expiration date
d)
password expiration date
e)
login start and end time
f)
VRF network
g)
VLAN network
FTA_TSE.1/NE TOE session establishment
FTA_TSE.1.1 The TSF shall be able to deny (NE) session establishment based on
a)
IP-based ACL
b)
VRF network
c)
VLAN network
FTA_TSE.1/MS TOE session establishment
FTA_TSE.1.1 The TSF shall be able to deny (MS) session establishment based on
Version 1.5
Huawei Copyright Huawei Technologies
Co., Ltd.
20
Huawei UGW9811 Version 900 Release 10 Security Target
a)
Access Point Name
b)
The SGSN/MME/S-GW on blacklist
c)
The SGSN/MME/S-GW not on white list
d)
Source IP address
e)
VRF network
f)
IP-based ACL
5.2.8 Trusted Path/Channels (FTP)
FTP_ITC.1/M2000 Inter-TSF trusted channel
FTP_ITC.1.1 The TSF (server part of the TOE) shall provide a communication channel between itself and another
trusted IT product (M2000) that is logically distinct from other communication channels and provides assured
identification of its end points and protection of the channel data from modification or disclosure.
FTP_ITC.1.2 The TSF (server part of the TOE) shall permit (M2000) to initiate communication via the trusted channel.
FTP_ITC.1.3 The TSF (server part of the TOE) shall initiate communication via the trusted channel for performing
M2000 related actions.
FTP_ITC.1/LI Inter-TSF trusted channel
FTP_ITC.1.1 The TSF (server part of the TOE) shall provide a communication channel between itself and another
trusted IT product (the LIG) that is logically distinct from other communication channels and provides assured
identification of its end points and protection of the channel data from modification or disclosure.
FTP_ITC.1.2 The TSF (server part of the TOE) shall permit (the LIG) to initiate communication via the trusted channel.
FTP_ITC.1.3 The TSF (server part of the TOE) shall initiate communication via the trusted channel for performing
LIG related actions.
FTP_ITC.1/NE Inter-TSF trusted channel
FTP_ITC.1.1 The TSF (server part of the TOE) shall provide a communication channel between itself and another
trusted IT product2 that is logically distinct from other communication channels and provides assured identification of
its end points and protection of the channel data from modification or disclosure.
FTP_ITC.1.2 The TSF (server part of the TOE) shall permit another trusted IT product to initiate communication via
the trusted channel.
FTP_ITC.1.3 The TSF (server part of the TOE) shall initiate communication via the trusted channel for performing
another trusted IT product related functions.
See T.Network_T
Version 1.5
Huawei Copyright Huawei Technologies
Co., Ltd.
21
Huawei UGW9811 Version 900 Release 10 Security Target
5.3 Security Assurance Requirements
The development and the evaluation of the TOE shall be done in accordance to the following security assurance
requirements:
EAL3+ augmented by ALC_CMC.4.
This level has been chosen because it is commensurate with the threat environment that is experienced by typical
consumers of the TOE.
5.4 Rationale for the Security Requirements
The following table provides a mapping of SFR to the security objectives, showing that each security functional
requirement addresses at least one security objective.
The following rationale provides justification for each security objective for the TOE, showing that all security
objectives are addressed and the security functional requirements are suitable to meet and achieve the security
objectives:
Security Objectives
Security Functional Requirements
O.IDAUTH
User
authentication
is
implemented
by
FIA_UAU.2/FIA_UID.2. The necessary user
attributes (passwords) are spelled out in
FIA_ATD.1. The authentication mechanism
supports
authentication
failure
handling
(FIA_AFL.1), restrictions as to the validity of
accounts for logon (FTA_TSE.1), and a password
policy (FIA_SOS.1). The TOE prevents a user
having too many sessions (FTA_MCS.1) and locks
session when they are inactive for a configured
period of time (FTA_SSL.1). Management
functionality for all of these is provided in
FMT_SMF.1.
O.IDAUTHMS
MS user authentication is implemented
FIA_UAU.2/MS and FIA_UID.2/MS.
O.Resource
The requirement for assigning a priority (used as
configured bandwidth)
is spelled out in
FRU_PRS.1, enforcing the maximum quotas for
bandwidth and limited the bandwidth (used by the
MS) is spelled out in FRU_RSA.1
by
The requirement for limiting other device to access
the TOE is spell out in
O.Connect
FTA_TSE.1, where connection can be refused based
on security attributes like authentication, IP address,
account expiration date, and so on.
FTA_TSE.1/NE: where connection can be refused
based on IP address
FTA_TSE.1/MS: where connection can be refused
based on Access Point Name (APN)
Version 1.5
Huawei Copyright Huawei Technologies
Co., Ltd.
22
Huawei UGW9811 Version 900 Release 10 Security Target
Security Objectives
Security Functional Requirements
Management functionality of configuring who is
allowed to connect is spell out in FMT_SMF.1
O.Audit
The generation of audit records is implemented by
FAU_GEN.1. Audit records are supposed to include
user identities (FAU_GEN.2) where applicable,
which are supplied by the authentication mechanism
(FIA_UID.2). Since the TOE generates audit records
in a binary format, tools are provisioned to read and
search these records (FAU_SAR.1, FAU_SAR.3).
The loss of audit log is protected (FAU_STG.1,
FAU_STG.3). The time stamp required is provided
by the TOE (FPT_STM.1). Management
functionality for the audit mechanism is spelled out
in FMT_SMF.1.
O.Authorization
The requirement for authorization is spelled out in
FDP_ACC.1, and the access control policies are
modelled in FDP_ACF.1. Unique user IDs and user
authentication are necessary for access control
provisioning (FIA_UID.2, FIA_UAU.2), and
user-related attributes are spelled out in FIA_ATD.1.
Access control is based on the definition of roles
(FMT_SMR.1), and management functionality for
the definition of access control policies is provided
(FMT_MSA.1,
FMT_MSA.3,
FMT_MSA.3,
FMT_SMF.1).
O.Communication
The requirement to provide secure connection
between the LMT and the server part of the TOE is
spell out in FPT_ITT.1. The requirements to provide
secure communication between the server part of the
TOE and other devices (M2000, LIG, devices in the
telecommunication networks) are spell out in
FTP_ITC.1/M2000,
FTP_ITC.1/LI,
and
FTP_ITC.1/NE. Management functionality to enable
these mechanisms is provided in FMT_SMF.1
5.5 Dependencies
SFR
Dependencies
FAU_GEN.1
FPT_STM.1:
FAU_GEN.2
FAU_SAR.1
Version 1.5
met
FAU_GEN1: met
FIA_UID.2: met by FIA_UID.2
FAU_GEN.1: met
Huawei Copyright Huawei Technologies
Co., Ltd.
23
Huawei UGW9811 Version 900 Release 10 Security Target
SFR
Dependencies
FAU_SAR.3
FAU_SAR.3: met
FAU_STG.1
FAU_GEN.1: met
FAU_STG.3
FAU_STG.1: met
FPT_STM.1
FDP_ACC.1
FDP_ACF.1: met
FDP_ACF.1
FDP_ACC.1: met
FMT_MSA.3: met
FIA_AFL.1
FIA_UAU.1: met by FIA_UAU.2
FIA_ATD.1
FIA_SOS.1
FIA_UAU.2
FIA_UID.1: met by FIA_UID.2
FIA_UID.2
FIA_UAU.2/MS
FIA_UID.1: met by FIA_UID.2/MS
FIA_UID.2/MS
[FDP_ACC.1 or FDP_IFC.1]: met by FDP_ACC.1
FMT_MSA.1
FMT_SMR.1: met
FMT_SMF.1: met
FMT_MSA.3
Version 1.5
FMT_MSA.1: met
FMT_SMR.1: met
FMT_SMF.1
FMT_SMR.1
FIA_UID.1: met by FIA_UID.2
FPT_ITT.1
FRU_PRS.1
Huawei Copyright Huawei Technologies
Co., Ltd.
24
Huawei UGW9811 Version 900 Release 10 Security Target
Version 1.5
SFR
Dependencies
FRU_RSA.1
FTA_MCS.1
FIA_UID.1: met by FIA_UID.2
FTA_SSL.3
FTA_TSE.1
FTA_TSE.1/NE
FTA_TSE.1/MS
FTP_ITC.1/M2000
FTP_ITC.1/LI
FTP_ITC.1/NE
Huawei Copyright Huawei Technologies
Co., Ltd.
25
Huawei UGW9811 Version 900 Release 10 Security Target
TOE Summary Specification
6.1 Authentication
The TOE provides Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP) security verification by the Password Authentication Protocol (PAP)
and Challenge Handshake Authentication Protocol (CHAP) modes for MS users authentication
The TOE authenticates the users based on individual user IDs and passwords. User IDs are unique within the TOE and
stored together with associated passwords and other (security) attributes in the memory. A user must enter the correct
user name and password to log in to the UGW9811, which prevents unauthorized access to the UGW9811.
A user name consists of a maximum of 32 letters and numerals and must start with a letter. The user name is case
insensitive.
The authorized administrators are able to configure a system-wide password policy that is then enforced by the TOE.
Besides the minimum length of the password, which can be set to be between 6 and 32 characters, administrators have
the option to enforce the use of specific characters (numeric, alphanumeric low or capital, and special characters).
To meet the requirements for assigning rights to different users and prevent unauthorized access and operations, the
users are categorized into different levels by role and are assigned the corresponding operation rights.
A user group defines a set of rights for different user type. A command group is a set of commands. A user group can
be authorized rights via command groups, an user group may include more than one command groups. Commands are
classified into command groups, and then the command groups are assigned to users with different authorities, realizing
authority management.
Commands are classified into command groups and command groups are assigned to users with different rights. One
command belongs to only one specific command group. The system provides eight predefined command groups. The
commands contained in these command groups cannot be modified. This means that a command group to which a
command belongs cannot be changed, and rights can be assigned only by specifying command groups.
The TOE supports max attempts due to authentication failure within certain period of time. This function is achieved by
providing counts on authentication failure.
The TOE also offers the enforcement of permanent or timer-based account lockouts: administrators can specify after
how many consecutively failed authentication attempts an account will be permanently or temporarily locked, and
whether the counter for failed attempts will be reset automatically after a certain amount of minutes.
When a session is inactive for a configured period of time, the TOE will lock this session and the user needs to re-enter
his password to unlock the session.
(FDP_ACC.1, FDP_ACF.1, FIA_AFL.1, FIA_ATD.1, FIA_SOS.1, FIA_UAU.2, FIA_UID.2, FIA_UAU.2/MS,
FIA_UID.2/MS, FTA_SSL.1, FMT_SMR.1, FMT_MSA.1, FMT_MSA.3)
Version 1.5
Huawei Copyright Huawei Technologies
Co., Ltd.
26
Huawei UGW9811 Version 900 Release 10 Security Target
6.2 Access Control
The access control feature enables carriers to manage user authorities to ensure that only authorized users are allowed to
operate the UGW9811 within the authorization range, such as adding, modifying, or deleting users, logging in or
logging out users, and assigning rights to users.
The access control feature is implemented in the three planes: management plane, control plane and end-user plane.
In the management plane, the TOE can enforce the account locking function for the LMT user access control.
In the control plane, the access control feature includes:
Different access control policies for subscribers. These control policies have different priorities, which ensure
that subscribers with a higher priority level have priority access to network resources.
Supports to control the subscriber capacity and the bandwidth. When the number of subscribers or the
bandwidth usage reaches the maximum limit, the TOE does not allow new subscribers to access.
Supports to deny the session establishment request from the blacklisted SGSNs, MMEs, and S-GWs,APN.
In the end-user plane, the TOE supports:
Bandwidth management to restrict the maximum bandwidth for the specific service(eg, P2P) of the subscriber
group.
IP-based ACL, Blacklist and Whitelist, APN-specific Packet Filtering Based on ACLs
Anti-spoofing function to check the uplink and downlink user-plane traffic and discards packets from spoofed
source IP addresses.
VRF (Virtual routing and forwarding) and the VLAN(virtual local area network) functions to separate the
different network from each other to ensure network security.
6.2.1 Account Locking
The UGW9811 supports a maximum of 16 actives sessions for the LMT login.
For LMT login, when a user is absent, the account can be locked to prevent unauthorized access to the system.
If an administrator has specified values for these parameters for a specific user, the TOE will deny authentication of the
user if the number of account valid days configured for the user has been exceeded, if the password has not been
changed within the timeframe specified in the password valid days configuration for the user, or if the user tries to
authenticate in a timeframe that lies outside of the login start time and login end time specified for the user.
Support limiting access by IP address. This function is achieved by comparing IP address of requesting session with
configured value stored in memory.
6.2.2 SGSN/MME/S-GW Blacklist and Whitelist
The UGW9811 supports adding specific IP address ranges of serving GPRS support nodes (SGSNs), mobility
management entities (MMEs), and serving gateways (S-GWs) to whitelists or blacklists. The UGW9811 grants access
to whitelisted SGSNs, MMEs, and S-GWs and rejects access to blacklisted ones.
By specifying the SGSNs, MMEs, and S-GWs on which subscribers can be activated, carriers can restrict the service
usage by or roaming behaviors of subscribers.
The TOE supports to deny the MS session establishment request from the blacklisted SGSNs, MMEs, and S-GWs.
6.2.3 IP-based ACL
The TOE supports IP-based Access Control List (ACL) to filter traffic destined to TOE to prevent internal traffic
Version 1.5
Huawei Copyright Huawei Technologies
Co., Ltd.
27
Huawei UGW9811 Version 900 Release 10 Security Target
overload and service interruption.
The TOE also uses the ACL to identify flows and perform flow control to prevent the CPU and related services from
being attacked
1) Support enabling ACLs by associating ACLs to whitelist, blacklist, user-defined-flow. This function is achieved by
interpreting ACL configurations then storing interpreted value in memory.
2) Support screening, filtering traffic destined to CPU. This function is achieved by downloading ACL configurations
into hardware.
3) Support rate limiting traffic based on screened traffic. This function is achieved by downloading configuration of rate
into hardware.
The TOE can use the ACL to deny the networks data packet based on some criteria defined in the ACL such as
destination ip address, destination port number, ip protocol.
The TOE can flexibly set the ACL rules for the user-defined flows to prevent unidentified attacks in the network. In
addition, you can specify the characteristics of the attack data flows and set rules for filtering the data flows of these
characteristics.
Besides the above IP-based ACL function for the received IP data packets, the TOE supports the APN-specific packet
filtering Based on ACLs. With this function, the UGW9811 checks the uplink and downlink traffic at the user-plane of
an access point name (APN) based on an ACL packet filtering policy. The UGW9811 forwards or discards packets that
match specific ACL rules. This feature enables the UGW9811 to prevent unauthorized access of UEs or servers on the
PDN, therefore protecting the network and subscribers from malicious attacks.
The TOE can use the APN based on ACL to deny the users data packet based on some criteria defined in the ACL such
as destination IP address, destination port number, IP protocol.
(FIA_AFL.1, FTA_MCS.1, FTA_TSE.1, FTA_TSE.1/NE, FTA_TSE.1/MS. FRU_PRS.1, FRU_RSA.1)
6.3 Communication security
The LMT log in the UGW9811 can use the SSL.
The TOE provides a trusted communication channel between the TOW and the SGSNs, MMEs, and S-GWs which are
defined in the whitelist.
The TOE provides a trusted communication channel between the TOW and the LIG.
When using maintenance terminals to perform OM operations for the UGW9811, carriers can use SSL to ensure the
security of data transmission and maintenance interfaces on the UGW9811.
SSL
SSL provides the following security services:
Identity authentication
Identity authentication means checking whether the individual in communication is an expected
object. SSL authenticates servers and clients based on digital certificates to check whether the
servers and clients are authorized. Both clients and servers have their own identifiers, which are
numbered with the public key. To verify that a user is authorized, SSL requires digital
authentication during data exchange in the handshake stage.
Connection privacy
Connection privacy means that data is encrypted before transmission to prevent data from being
hacked by malicious users. SSL enables confidentiality by using encryption algorithms. Common
encryption algorithms are DES, 3DES, RC2, and RC4.
Version 1.5
Data integrity
Huawei Copyright Huawei Technologies
Co., Ltd.
28
Huawei UGW9811 Version 900 Release 10 Security Target
Data integrity means that any modification to data during transmission can be detected. SSL
establishes a secure channel between the client and the server and uses message digest algorithms to
ensure data integrity so that all the data processed by SSL can reach the destination without being
modified. Common message digest algorithms are message digest 5 (MD5) and secure hashing
algorithm-1 (SHA-1).
The UGW9811 supports SSL versions SSLv3, TLS1.0, and TLS1.1.
IPsec
The UGW9811 supports IPsec. IPsec provides two security protocols to ensure the privacy, integrity, authenticity, and
anti-replay of data packets during transmission: Authentication Header (AH) and Encapsulating Security Payload (ESP).
Internet Key Exchange (IKE) can automatically negotiate key exchange, and establish and maintain security
associations (SAs) to simplify the use and management of IPsec.
(FTP_ITT.1, FTP_ITC.1/M2000, FTP_ITC/LI, FTP_ITC.1/NE)
6.4 Auditing
The logs of the TOE include:
1) Operation logs: Operation logs record the information about operations performed by the user, such as the task
name, user name, client IP address, and operation time. An administrator can query for and save users' logs based on
specified parameters.
2) Security logs: Security logs record all security events, including user login events, user authentication events, and
management events.
3) System logs: System logs record system information, including the black box information, process status, and OS
operating error. System logs are used to locate and analyse faults.
4) Diagnostic logs: Application software operation logs (DEBUG_LOG) record the operation log information about the
OMU software and NE software. The operation log information includes error information and operation information.
Application software operation logs are used to commission the application software and locate faults.
The TOE can provide auditing ability by receiving all types of logs and processing them according to users
configuration:
The TOE generates audit records for security-relevant events (for example, Operation logs, Security logs, System logs,
Application software operation logs). Attempt to access regardless success or failure is logged, along with user id,
source IP address, timestamp etc.
For system logSupport classification based on severity level. This function is achieved where logging messages are
encoded with severity level and output to log buffer. Support enabling, disabling log output. This function is achieved
by interpreting enable/disable commands and storing results in memory. Log output is performed based on this result.
Where appropriate, the data recorded with each audit record includes the unique user ID associated with a subject
during authentication. (for example, Operation logs, Security logs)
Audit review
Users can query for operation logs and security logs only after an administrator assigns related rights to the users. By
regularly checking logs, an administrator can trace and audit operators' behaviours, find attack behaviours in time, and
take measures, such as changing the password and locking the account.
Review functionality is provided via the command line interface, which allows administrators to inspect the audit log.
The TOE supports the authorized users to query for operation logs and security logs based on the query criteria such as
operator, start time and end time.
For system log
Version 1.5
Huawei Copyright Huawei Technologies
Co., Ltd.
29
Huawei UGW9811 Version 900 Release 10 Security Target
1) Support log output screening, based on severity level, regular expression. This function is performed by providing
filtering on output.
2) Support querying log buffer. This function is achieved by performing querying operation with conditions input.
3) Support redirecting logs to various output channels: monitor, log buffer, trap buffer, log file. This function is
achieved by interpreting commands and storing results in memory or in log files in CF card. Log channel for output is
selected prior to execution of redirecting.
Audit Storage
These logs are stored on the hard disk of the SRU/MPU board of the TOE. Only users which have G_6 and G_7 can
access these logs files
Each type of log file defines the maximum number of audit records supported to be stored. If the audit record number of
the log file exceeds the maximum number threshold, the latest audit record will be dropped. If the storage capacity
reached the threshold, the latest log will overwrite the earliest log.
(FAU_GEN.1, FAU_GEN.2, FAU_SAR.1, FAU_SAR.3, FAU_STG.1, FAU_STG.3)
6.5 Time
The TOE supports its own clock, to support logging and timed log-outs.
(FPT_STM.1, FTA_SSL.3)
6.6 Security function management
The TOE offers management functionality for its security functions, where appropriate. This is partially already
addressed in more detail in the previous sections of the TSS, but includes:
1) User management, including user name, password, User Group memberships, including the association of users and
corresponding privileged functionalities. etc.
2) Access control management, including the blacklists.
3) Enabling/disabling and configuring of SSL.
4) Enabling/disabling and configuring of IPsec
5) Support configuration on session lock when no operation is performed on the user session within a given interval;
6) Support configuration on max attempts due to authentication failure within certain period of time;
7) Support configuration on limiting access by IP address;
8) Support configuration ACLs based on IP protocol number, source and/or destination IP address, source and/or
destination port number if TCP/UDP;
9) Support configuration on APN-specific packet filtering Based on ACLs.
10) Support configuration on SGSN/MME/S-GW blacklist and whitelist.
Above functions are achieved by providing interpreting input commands and storing result of interpreting in memory.
Some results like routes generated, ACLs will be downloaded into hardware to assist forwarding and other TSF
functions.
(FMT_SMF.1)
Version 1.5
Huawei Copyright Huawei Technologies
Co., Ltd.
30
Huawei UGW9811 Version 900 Release 10 Security Target
Acronyms and Abbreviations
A
ATCA
advanced telecommunications computing architecture
ATM
asynchronous transfer mode
B
BG
border gateway
BSC
base station controller
BSS
base station subsystem
BTS
base transceiver station
C
CG
charging gateway
CDR
charging data record
CGP
carrier grade platform
CS
circuit switched
D
DNS
domain name server
E
EIR
equipment identity register
G
GGSN
Gateway GPRS support node
GPRS
General Packet Radio Service
GSM
Global System Mobile
GTP
GPRS Tunnel Protocol
Version 1.5
Huawei Copyright Huawei Technologies
Co., Ltd.
31
Huawei UGW9811 Version 900 Release 10 Security Target
H
HA
home agent
HLR
home location register
I
IP
Internet Protocol
ICMP
Internet control message protocol
IPv4
Internet Protocol version 4
ISDN
integrated services digital network
M
MME
mobility management entity
MS
mobile station
O
OMU
operation and maintenance unit
OS
operating system
P
PDP
Packet Data Protocol
PDU
Packet Data Unit
P-GW
PDN gateway
P-TMSI
packet temporary mobile subscriber identity
Q
QoS
quality of service
R
RADIUS
remote authentication dial-in user service
RAN
radio access network
RNC
radio network controller
Version 1.5
Huawei Copyright Huawei Technologies
Co., Ltd.
32
Huawei UGW9811 Version 900 Release 10 Security Target
SGSN
serving GPRS support node
S-GW
serving gateway
SS7
signaling system No.7
SSH
secure shell
SMS
short message service
SOL
serial over LAN
T
TCP
Transmission Control Protocol
U
UDP
User Datagram Protocol
UE
user equipment
UMTS
Universal Mobile Telecommunications System
W
WAP
Version 1.5
wireless access protocol
Huawei Copyright Huawei Technologies
Co., Ltd.
33
Вам также может понравиться
- Cybersecurity Insights Report Ninth EditionДокумент32 страницыCybersecurity Insights Report Ninth EditionmmjОценок пока нет
- Security Overview (SRAN11.1 01)Документ21 страницаSecurity Overview (SRAN11.1 01)Sameh GalalОценок пока нет
- S1.3 (IMDA Singapore) Update On 5G Development in Singapore PDFДокумент9 страницS1.3 (IMDA Singapore) Update On 5G Development in Singapore PDFdtvt40Оценок пока нет
- Iridium SecurityДокумент9 страницIridium SecurityOlly PediaОценок пока нет
- En Day1-Liu Gui Qing-Accelerating Cloud Network Convergence Enabling Digital Transformation-EnДокумент16 страницEn Day1-Liu Gui Qing-Accelerating Cloud Network Convergence Enabling Digital Transformation-EnMohammod FaisolОценок пока нет
- (Ptsecurity, 2016) Positive Research 2016 EngДокумент104 страницы(Ptsecurity, 2016) Positive Research 2016 EngrossloveladyОценок пока нет
- Ddos Mitigation Service: Public Document 2 Aug 2013Документ17 страницDdos Mitigation Service: Public Document 2 Aug 2013Amanda HammondОценок пока нет
- Wireless and Mobile Network Security 9780070700246 0070700249 - Compress PDFДокумент244 страницыWireless and Mobile Network Security 9780070700246 0070700249 - Compress PDFRonak MakwanaОценок пока нет
- U2000 Northbound Alarm SNMP Interface Technical PosterДокумент1 страницаU2000 Northbound Alarm SNMP Interface Technical Posterishtiaq3any1Оценок пока нет
- IPLOOK IKEPC 500 Series Product InformationДокумент4 страницыIPLOOK IKEPC 500 Series Product InformationIPLOOK TechnologiesОценок пока нет
- HUAWEI SAE-HSS9820 归属用户服务器: IPLOOK NetworksДокумент11 страницHUAWEI SAE-HSS9820 归属用户服务器: IPLOOK NetworksIPLOOK TechnologiesОценок пока нет
- Eudemon8000E X PDFДокумент2 страницыEudemon8000E X PDFgaryОценок пока нет
- Framework To Conduct 5G Testing 508Документ64 страницыFramework To Conduct 5G Testing 508Turgut AlpОценок пока нет
- Security challenges in 5G and beyondДокумент41 страницаSecurity challenges in 5G and beyondzayyanu yunusaОценок пока нет
- Telecommunications Infrastructure Security Getting in the SS7 KingdomДокумент44 страницыTelecommunications Infrastructure Security Getting in the SS7 Kingdomashish_dewan_bit9090% (1)
- IPLOOK HSS Product Information V1.3Документ13 страницIPLOOK HSS Product Information V1.3IPLOOK TechnologiesОценок пока нет
- Mobile Network Operator Infrastructure Security SolutionДокумент46 страницMobile Network Operator Infrastructure Security SolutionQuang Thịnh LêОценок пока нет
- Scurity in LTE NetworksДокумент27 страницScurity in LTE NetworksyassminbgОценок пока нет
- Cellusys Report Signalling Security - Sizing The Operator ThreatДокумент20 страницCellusys Report Signalling Security - Sizing The Operator ThreatAmine ElmekkiОценок пока нет
- IPLOOK GGSN Product Information V1.3Документ14 страницIPLOOK GGSN Product Information V1.3IPLOOK TechnologiesОценок пока нет
- Transmission Security Overview (SRAN11.1 - 02)Документ21 страницаTransmission Security Overview (SRAN11.1 - 02)waelq2003Оценок пока нет
- Pro Curve Network Security Student GuideДокумент414 страницPro Curve Network Security Student GuideyemlawzОценок пока нет
- Migrating Mobile Networks To 5G: A Smooth and Secure ApproachДокумент11 страницMigrating Mobile Networks To 5G: A Smooth and Secure ApproachDương HàОценок пока нет
- Equipment Security (SRAN16.1 01)Документ83 страницыEquipment Security (SRAN16.1 01)VVLОценок пока нет
- Security For Mobile Broadband Webinar Presentation PDFДокумент27 страницSecurity For Mobile Broadband Webinar Presentation PDFRendi NazaharОценок пока нет
- F5 5G WP BuildingBetter5GSecurity Final 120720Документ14 страницF5 5G WP BuildingBetter5GSecurity Final 120720Jussein TorresОценок пока нет
- HUAWEI SAE-HSS9820 归属用户服务器: IPLOOK NetworksДокумент12 страницHUAWEI SAE-HSS9820 归属用户服务器: IPLOOK NetworksIPLOOK TechnologiesОценок пока нет
- The Telecom Paradigm Shift Needed For 5G AutomationДокумент14 страницThe Telecom Paradigm Shift Needed For 5G AutomationIkunduОценок пока нет
- SECPDS - 004 - EN-1901 - Arbor Threat Mitigation System (TMS) PDFДокумент5 страницSECPDS - 004 - EN-1901 - Arbor Threat Mitigation System (TMS) PDFGeorge GuОценок пока нет
- 5 GToolbox Implementation ReportpdfДокумент44 страницы5 GToolbox Implementation ReportpdfLjube BabunskiОценок пока нет
- SYE AI and Cyber Security WP 190925Документ6 страницSYE AI and Cyber Security WP 190925JhonathanОценок пока нет
- Huawei UCC Solution Overview V6Документ47 страницHuawei UCC Solution Overview V6M H Khan RonyОценок пока нет
- Rethinking RadioДокумент14 страницRethinking RadioSercan Sari100% (1)
- SE2900 Product: ForewordДокумент34 страницыSE2900 Product: ForewordOluwole OlamideОценок пока нет
- Network Security Case StudyДокумент13 страницNetwork Security Case StudyshankugeetuОценок пока нет
- TS 270 LTE Security and InsecurityДокумент4 страницыTS 270 LTE Security and Insecurityclu5t3rОценок пока нет
- Technology Solution for 4G-LTEДокумент62 страницыTechnology Solution for 4G-LTEBuchi ReddyОценок пока нет
- Core Security Consulting Services Data SheetДокумент2 страницыCore Security Consulting Services Data SheetSamuelAvalosОценок пока нет
- Avaya Etisalat SIPДокумент29 страницAvaya Etisalat SIPNoorul Haque0% (1)
- Converged Policy PCRFДокумент19 страницConverged Policy PCRFhuytd100% (1)
- IPLOOK 64 Bit GW WEB Operation Manual-20200408-V1.2Документ58 страницIPLOOK 64 Bit GW WEB Operation Manual-20200408-V1.2IPLOOK TechnologiesОценок пока нет
- Network Security v1.0 - Module 5Документ26 страницNetwork Security v1.0 - Module 5Ernesto Silverio FloresОценок пока нет
- 5g Security PDFДокумент22 страницы5g Security PDFSaahil MathewsОценок пока нет
- The Futu RE With 5 G: Volume 3, Issue 2Документ27 страницThe Futu RE With 5 G: Volume 3, Issue 2MAURICIO MARINОценок пока нет
- Long Term Evolution and Its Security InfrastructureДокумент26 страницLong Term Evolution and Its Security InfrastructureyekoyesewОценок пока нет
- Cloud-based BNG Architecture Testing PerformanceДокумент16 страницCloud-based BNG Architecture Testing PerformanceSebastian Ariel NardiОценок пока нет
- Security Testing Services SciencesoftДокумент17 страницSecurity Testing Services SciencesoftWondachew WoldeyesusОценок пока нет
- SS7 Security ReportДокумент16 страницSS7 Security Reportrico6Оценок пока нет
- ORAN - O2 IMS AlignmentДокумент7 страницORAN - O2 IMS AlignmentRandhir kumar SinhaОценок пока нет
- 5g, Mobile NetworkДокумент37 страниц5g, Mobile NetworkAagam ShahОценок пока нет
- HCIA-AI V1.0 Lab GuideДокумент124 страницыHCIA-AI V1.0 Lab Guidemulte123Оценок пока нет
- 5G Security Report-2020Документ22 страницы5G Security Report-2020KrzysztofОценок пока нет
- Huawei Certification Training Flyer-En-SecurityДокумент4 страницыHuawei Certification Training Flyer-En-SecurityPaulo CorreiaОценок пока нет
- Multicast Video AppДокумент39 страницMulticast Video AppSurekha SundarrОценок пока нет
- ZXWN EIR Technical SpecificationДокумент35 страницZXWN EIR Technical SpecificationCoachArun MishraОценок пока нет
- IPLOOK HSS HLR Product InformationДокумент29 страницIPLOOK HSS HLR Product InformationIPLOOK TechnologiesОценок пока нет
- LogRhythm7 OverviewДокумент23 страницыLogRhythm7 OverviewNguyen Tuan NgocОценок пока нет
- Optimizing and Testing WLANs: Proven Techniques for Maximum PerformanceОт EverandOptimizing and Testing WLANs: Proven Techniques for Maximum PerformanceОценок пока нет
- Third Quarter Course Guide in Computer Iii Date No. of Meetings Chapter/Unit Lessons Reference Performance Task/Products/ProjectsДокумент4 страницыThird Quarter Course Guide in Computer Iii Date No. of Meetings Chapter/Unit Lessons Reference Performance Task/Products/ProjectsJohn Cristouv CortezОценок пока нет
- Load Flow - CompleteДокумент4 страницыLoad Flow - CompleteJohn Cristouv CortezОценок пока нет
- Fourth Quarter Course Guide in Computer Iii Date No. of Meetings Chapter/Unit Lessons Reference Performance Task/Products/ProjectsДокумент3 страницыFourth Quarter Course Guide in Computer Iii Date No. of Meetings Chapter/Unit Lessons Reference Performance Task/Products/ProjectsJohn Cristouv CortezОценок пока нет
- Second Quarter Course Guide in Computer Iii Date No. of Meetings Chapter/Unit Lessons Reference Performance Task/Products/ProjectsДокумент2 страницыSecond Quarter Course Guide in Computer Iii Date No. of Meetings Chapter/Unit Lessons Reference Performance Task/Products/ProjectsJohn Cristouv CortezОценок пока нет
- SC TNS - CompleteДокумент89 страницSC TNS - CompleteJohn Cristouv CortezОценок пока нет
- TEST - CompleteДокумент89 страницTEST - CompleteJohn Cristouv CortezОценок пока нет
- SC TNS - CompleteДокумент89 страницSC TNS - CompleteJohn Cristouv CortezОценок пока нет
- Project Load Flow AnalysisДокумент24 страницыProject Load Flow AnalysisJohn Cristouv CortezОценок пока нет
- First Quarter Course Guide in Computer Iii Date Chapter/Unit Lessons References Performance Task/Products/ProjectsДокумент4 страницыFirst Quarter Course Guide in Computer Iii Date Chapter/Unit Lessons References Performance Task/Products/ProjectsJohn Cristouv CortezОценок пока нет
- Installation GuideДокумент4 страницыInstallation GuideAnonymous ugAY1fsF0aОценок пока нет
- ETAP Short-Circuit Analysis IEC 60909 Standard 3-Phase Fault CurrentsДокумент91 страницаETAP Short-Circuit Analysis IEC 60909 Standard 3-Phase Fault CurrentsJohn Cristouv CortezОценок пока нет
- SC MIN C - 1 - CompleteДокумент94 страницыSC MIN C - 1 - CompleteJohn Cristouv CortezОценок пока нет
- Rockwell Basis Forperforming Insulationpower FactortestingДокумент4 страницыRockwell Basis Forperforming Insulationpower FactortestingJohn Cristouv CortezОценок пока нет
- Lecture 12Документ12 страницLecture 12ranjish_007Оценок пока нет
- Ieee 519Документ15 страницIeee 519peterchoong63100% (3)
- Etap Coordination 01Документ38 страницEtap Coordination 01John Cristouv Cortez50% (6)
- ETAP System Theo Yeu CauДокумент1 страницаETAP System Theo Yeu CauNguyenDinhLyОценок пока нет
- 5 Motors Damage CurvesДокумент7 страниц5 Motors Damage Curvesrobertovm2002Оценок пока нет
- SasoДокумент24 страницыSasoJohn Cristouv CortezОценок пока нет
- 04443726aa Micrologic P User ManualДокумент96 страниц04443726aa Micrologic P User ManualandyОценок пока нет
- Micrologic 5 6 2Документ188 страницMicrologic 5 6 2MatijaDebogovićОценок пока нет
- IEEE - 0241 - 1990 Gray Electric Power Systems in Commercial BДокумент19 страницIEEE - 0241 - 1990 Gray Electric Power Systems in Commercial BJohn Cristouv CortezОценок пока нет
- BSF Earthing System Calculation 1Документ29 страницBSF Earthing System Calculation 1Veerasamy KarikalvalavanОценок пока нет
- Lecture 12Документ12 страницLecture 12ranjish_007Оценок пока нет
- KW Eff PF HP: - IEEE STD 141-1993, P. 131-132Документ6 страницKW Eff PF HP: - IEEE STD 141-1993, P. 131-132John Cristouv CortezОценок пока нет
- Tia 607 B 2011Документ72 страницыTia 607 B 2011Elizabeth P0% (1)
- Short Circuit CalculationsДокумент10 страницShort Circuit CalculationsBalan DanielОценок пока нет
- Power Systems Study SpecificationsДокумент15 страницPower Systems Study Specificationsペレス ネスターОценок пока нет
- Electrical Engineer PRIMER (REE)Документ2 страницыElectrical Engineer PRIMER (REE)Harry King Corral AvenidoОценок пока нет
- Opinions B1Документ1 страницаOpinions B1Ainhoa Paute MontalbanОценок пока нет
- PCT GuidelinesДокумент205 страницPCT GuidelinesOla SvenssonОценок пока нет
- Owen Performance DataДокумент8 страницOwen Performance Dataunduh100% (1)
- Figures of Romantic Anti-Capitalism (Sayre & Löwy)Документ52 страницыFigures of Romantic Anti-Capitalism (Sayre & Löwy)dfgsgstrhsrОценок пока нет
- ISO 13849-1 PL Calculations SimplifiedДокумент119 страницISO 13849-1 PL Calculations SimplifiedAnonymous jW9BkgbQmEОценок пока нет
- Mathematics Upper Secondary4Документ5 страницMathematics Upper Secondary4fvictor1Оценок пока нет
- Animalism Argument QuestionedДокумент2 страницыAnimalism Argument QuestionedJustin HorkyОценок пока нет
- Why Arabic World Turned from ScienceДокумент14 страницWhy Arabic World Turned from ScienceLynne LarsenОценок пока нет
- List of Disqualified CandidatesДокумент4 страницыList of Disqualified CandidatesMuhammad BilalОценок пока нет
- Bioethanol Production From Breadnut (Artocarpus Camansi) ProposalДокумент46 страницBioethanol Production From Breadnut (Artocarpus Camansi) ProposalIvan ArcenaОценок пока нет
- Sub GradeДокумент12 страницSub GradeMiaОценок пока нет
- Chp1 - Measurements of Length and TimeДокумент26 страницChp1 - Measurements of Length and Timejonathan tungalОценок пока нет
- Torrent Downloaded FromДокумент2 страницыTorrent Downloaded Fromcena3135Оценок пока нет
- 2011 0720 RT5370 RT5372 RT5390U Linux SoftAP v2.6.0.0 ReleaseNotes DPA PDFДокумент173 страницы2011 0720 RT5370 RT5372 RT5390U Linux SoftAP v2.6.0.0 ReleaseNotes DPA PDFdraseoneОценок пока нет
- BIM Implementation for Construction Projects and DeveloperДокумент29 страницBIM Implementation for Construction Projects and DevelopergrtunaОценок пока нет
- Marxist View of ColonialismДокумент9 страницMarxist View of ColonialismEhsan VillaОценок пока нет
- Maxillary Sinus Pneumatization and Its Relationship With Vitamin D Deficiency A Cross Sectional Study Jodh 19Документ5 страницMaxillary Sinus Pneumatization and Its Relationship With Vitamin D Deficiency A Cross Sectional Study Jodh 19sidraОценок пока нет
- New Open Source Ansys Solidworks Flac 3D Geometry Conversion Program PDFДокумент9 страницNew Open Source Ansys Solidworks Flac 3D Geometry Conversion Program PDFSonОценок пока нет
- Israa Hadi ResumeДокумент1 страницаIsraa Hadi Resumeapi-301344062Оценок пока нет
- Alis Advencha Ina WandalanДокумент3 страницыAlis Advencha Ina WandalanMDRMОценок пока нет
- Risk ManagementДокумент101 страницаRisk ManagementAizuddin Sugara100% (1)
- Global Developmental DelayДокумент4 страницыGlobal Developmental DelayPaulina Kristiani BangunОценок пока нет
- WLU PS463 - Seminar in Biopsychology - Brain Maps of Meaning - Fall 2016 Course Outline - Manwell PDFДокумент28 страницWLU PS463 - Seminar in Biopsychology - Brain Maps of Meaning - Fall 2016 Course Outline - Manwell PDFJesse PiniciveroОценок пока нет
- Meditation - Russ Michael PDFДокумент139 страницMeditation - Russ Michael PDFWarrior Soul100% (2)
- Alternative MedicineДокумент2 страницыAlternative MedicineEddi HCОценок пока нет
- ERPH 2022 EnglishДокумент14 страницERPH 2022 EnglishSarveena MurugiahОценок пока нет
- Chapter 4. CyclonesДокумент17 страницChapter 4. CyclonesHatem SalahОценок пока нет
- PreCalc graph transformations and trigonometryДокумент6 страницPreCalc graph transformations and trigonometrygreen286Оценок пока нет
- 11 Edition: Mcgraw-Hill/IrwinДокумент11 страниц11 Edition: Mcgraw-Hill/IrwinmanahilОценок пока нет
- JSS MAHAVIDYHAPEETHA Fluid Machinery CIA 1 Results and AnalysisДокумент18 страницJSS MAHAVIDYHAPEETHA Fluid Machinery CIA 1 Results and Analysisamit621988Оценок пока нет