Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
NSG Care For Pt. With Endocrine Glands Disorders
Загружено:
Wendy EscalanteОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
NSG Care For Pt. With Endocrine Glands Disorders
Загружено:
Wendy EscalanteАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
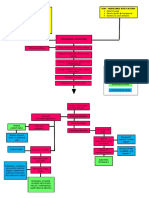
1 NURSING CARE OF PATIENTS WITH ENDOCRINE DISORDERS escalante-saac
Exocrine Glands
Exocrine Glands
Endocrine glands
Endocrine glands
Endocrine glands
Secretions of hormones
Hormone
Target tissue
Pituitary, Adrenal,
Thyroid
Islets of pancreas,
Parathyroid, Gonads
Neuroendocrine circulation
HYPOTHALAMUS
(anatomy)
endocrine glands
Flattened funnel
Third ventricle
Hypothalamus
Pituitary gland
HYPOPHYSIS (pituitary
gland)
infundibulum
Kidney bean
Adenohypophysis(anteri
or)
Neurohypophysis(poster
ior)
Anterior pituitary
AP cells
Posterior Pituitary
Nerve tissue
Posterior Pituitary
Hypothalamic hormones
*Gonadotropin Releasing
Hormone,*Thyrotropin
Releasing Hormone,
*Corticotrophin
Releasing Hormone,
*Prolactin Inhibiting
Hormone, *Growth
ReleasingHormone,*Som
atostatin
*Follicle Stimulating
Hormone,*Luteinizing
Hormone,*Thyroid
Stimulating
Hormone(Thyrotropin),
*Adrenocorticotropic
Hormone,
*Prolactin,*Growth
Ducts carry secretion to epithelial surface or mucosa of
digestive tract external secretions
Extracellular effect (food digestion)
Ductless that contains capillary network to allow easy uptake of
hormones into bloodstream internal secretions
Intracellular effects such as altering target cell metabolism
Interconnected network of glands and nervous system.
Key feature of endocrine glands
Biochemical that exert effect on target tissue
Located some distance from endocrine glands with no direct
physical connection between endocrine and target cells.
Endocrine glands must use circulatory system to transport
secreted hormone to target tissue such as:
Works with nervous system to regulate overall physiologic
function called_
Also regulate environmental changes
Regulate function of _
It is_ shaped
Forms floor and walls of the_ of brain
Regulate primitive function of body from water balance to sex
drive
Carried by_
Suspended from hypothalamus by stalk- _
Size and shape of a_
Composed of 2 structures with independent origins and
separate functions
Composed of of pituitary
Hypothalamic hormones that regulate_
Composed of of pituitary
Compose of_, not a true neuron gland
Hypothalamic secrete hormone that are stored in_ until released
to blood
There are 8 hormones, 6 of these regulate the Anterior P.
glands, and the other 2 hormones release into capillaries in the
Posterior P.
6 hormones releasing and inhibiting
Anterior lobe hormones
2 NURSING CARE OF PATIENTS WITH ENDOCRINE DISORDERS escalante-saac
Hormone
Oxytocin and
Antidiuretic
ANTERIOR PITUITARY
HORMONES
1. FSH (follicle stimulating
hormone)
2. LH (luteinizing hormone)
3.TSH (thyroid stimulating
hormone)
4. ACTH
(adrenocorticotropic
hormone)
5. PRL (prolactin)
2 other hypothalamic hormones
There are 2 gonadotropin hormone that target gonads:
*stimulates secretion of ovarian sex hormones and development
of ovarian follicles and sperm production.
*stimulates ovulation, stimulates corpus luteum to secret
progesterone, stimulates testes to secret testosterone.
*stimulates secretion of thyroid hormone.
*stimulates adrenal cortex to secrete glucocorticoids.
*stimulates mammary glands to synthesize milk, enhance
secretion of testosterone by testes
*stimulates mitosis and cellular differentiation
6. GH (growth hormone)
POSTERIOR PITUITARY
HORMONES
1. ADH (antidiuretic hormone)
2. OT (oxytocin)
CONTROL OF PITUITARY
SECRETION
*not
*hypothalamus
Hypothalamic and cerebral
control
Posterior lobe control
GROWTH HORMONE
bones, muscle, cartilage
and fat
*liver
*insulin like growth
factor(IGF-I or IGF-II)
*increase protein
synthesis
*lipid metabolism
*Carbohydrate
metabolism
*electrolyte balance
*bone growth thickening
and remodeling
*secretion release
during first_ of sleep
*Gradually decrease
with age
*protein
Produced by hypothalamus, released when hypothalamic
neurons are stimulated.
*increases water retention, prevents dehydration
*released during sexual arousal, promotes feeling of sexual
satisfaction and emotional bonding between partners,
stimulates labor and contraction during childbirth, stimulates
flow of milk during lactation, causes uterine contraction.
*rate of secretions are_
*regulated by_ other brain center and feedback from target
organs
Anterior lobe control releasing hormone and inhibiting hormone
from hypothalamus.
Ex. In cold weather, pituitary stimulated by hypothalamus to
release TSH to generate body heat
Neuroendocrine reflex hormone release in response to N.S
signal
Ex. suckling infant-stimulates nerve endings-hypothalamusposterior lobe-oxytocin-milk ejection
Widespread effect of body tissue- _
Induces the _ to produce growth stimulants like_
*provides energy
*makes glucose available for glycogen synthesis and storage
*2 hrs.
*lack of_ synthesis contributes to aging of tissue and wrinkling
of the skin
3 NURSING CARE OF PATIENTS WITH ENDOCRINE DISORDERS escalante-saac
PINEAL GLAND
corpus callosum
Involution(shrinkage)
Circadian rhythm
Melatonin, serotonin
Puberty
THYMUS
Bilobed, superior
Immune defense
Hormone
thymus
THYROID GLAND
*butterfly
*left and right
*T3 (triiodothyronine),T4
(thyroxine)
*calcitonin
*osteoblast
PARATHYROID GLAND
4, posterior
PTH or parathyroid
Hormone
Hypercalcemia
Hypocalcemia
*increase blood calcium
levels
*promotes synthesis of
calcitriol
*increase absorption of
calcium
*decrease urinary excretion
*increase bone
reabsorption
ADRENAL GLANDS
Above(suprarenal) or top
Adrenal cortex and medulla
Medulla
Medulla
Catecholamine, dopamine
Hypertension, increase
digestion
ADRENAL CORTEX
Corticosteroids and
corticoids
1.
mineralocorticosteroids
(aldosterone)
2. glucocorticoids
(cortisol)
3. sex steroids
(androgen)
ALDOSTERONE
Attached to roof of 3rd ventricle beneath the posterior end of _
After age 7, undergoes_
May synchronize physiologic function with 24-hour_of daylight
and darkness
Synthesize _ from_ during the night
Regulate timing of_ in humans
Plays a role in three system- Endocrine, Lymphatic and
Immune
_glands in the mediastinum_ to the heart
Important in_
Secretes_ that affect immune activity
Gland that relate to myasthenia gravis
>_shaped glands
>There are two lobe the_
>Secretes_ and_.
>Para follicular C or clear cells secretes_ with rising blood
calcium.
>stimulates_ activity and bone formation
Are _ glands that are embedded to the _surface of thyroid gland
Release_
Calcitonin is released when there is_. And the effect is to
decrease calcium in blood
PTH id released when there is_. And the effect is to increase
calcium in blood
PT gland uses:
Located_ the kidney
These are formed_
Inner core, 10-20% of gland
Has dual nature, endocrine glands and sympathetic ganglion of
the SNS
When stimulates, releases_ (epinephrine, norepinephrine) and
trace of_ into the bloodstream
Catecholamine causes_
Surrounds medulla and produces more than 25 steroid
hormones called_
Secretes 3 classes of steroid hormones, the_
*sodium retention and water balance
*sugar level
*sexual development
*electrolyte balance
*stimulates sodium retention and potassium secretion
4 NURSING CARE OF PATIENTS WITH ENDOCRINE DISORDERS escalante-saac
CORTISOL
CATEGORIES OF
CORTICOSTEROIDS
1. sex steroids
(androgen)
2. estradiol
PANCREAS
PANCRATIC HORMONE
1-2
98%, digestive enzymes
1. INSULIN
>BETA
>glucose and amino acid
>nutrients
>glycogen, fat and protein
>suppresses
>DM
2. GLUCAGON
>ALPHA
>blood glucose
>glucose
>increase
>fat catabolism
3. SOMATOSTATIN
>DELTA
>glucagon and insulin
>nutrient digestion and
absorption
4. GASTRIN
>GAMMA
>acid secretion
GONADS
*regulates metabolism of glucose and other fuels
*stimulates release of fuels in blood
*helps adapt stress and tissue repair
*anti-inflammatory effect can become immunosuppression in
long term use
*sets libido, prenatal development
*small quantity but important after menopause
Exocrine digestive gland and endocrine cell duster(pancreatic
islets)
_ million pancreatic islets Langerhans produces hormone
Other _ of pancreas cells produces_
*secreted by_ cells
*secreted during and after meals when _blood levels are
RISING
*stimulates cell to absorb_
*promotes synthesis of_
*_use of already used stored fluids
*insufficiency of inactivity causes_
*secreted by_ cells
*released between meals when_ concentration is FALLING
*in liver, stimulates release of_ into circulation
*_blood glucose level in adipose
*stimulates_
*stored by_ cells
*particularly suppresses secretion of_
*inhibits_ which prolongs absorption of nutrients
*secreted by_ cells
*stimulates stomach_ motility and emptying
Ovaries and testes are both endocrine and exocrine
Whole cells eggs and sperm
Exocrine product
Gonadal hormone mostly
steroids
Estradiol and progesterone
Endocrine products
Testosterone,weaker
androgen, estrogen and
inhibin
PROSTAGLANDINS
>PLASMA
>fertility,blood clotting and
body temp
Testicular hormone
Ovarian hormone
Work locally
Released by _ cells
5 NURSING CARE OF PATIENTS WITH ENDOCRINE DISORDERS escalante-saac
Вам также может понравиться
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (895)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (344)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- Complaint - Ventura V CombsДокумент35 страницComplaint - Ventura V CombsNew York Post100% (6)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (121)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (400)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- Weber, Eric - How To Pick Up GirlsДокумент126 страницWeber, Eric - How To Pick Up GirlsMarl Hudson100% (5)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- Simone de Beauvoir - The Second Sex-Vintage Books (1989) PDFДокумент701 страницаSimone de Beauvoir - The Second Sex-Vintage Books (1989) PDFPrashant Sharma93% (14)
- Jet Mykles - Indigo Knights 01 - Squire (Contempory) PDFДокумент165 страницJet Mykles - Indigo Knights 01 - Squire (Contempory) PDFMaria Vasile100% (1)
- Concept Map in Head and Neck CancerДокумент3 страницыConcept Map in Head and Neck CancerWendy EscalanteОценок пока нет
- Cara Urutan Minyak LintahДокумент4 страницыCara Urutan Minyak Lintahaerohel100% (1)
- Japanese Bath EssayДокумент4 страницыJapanese Bath EssayIan KollОценок пока нет
- Course of Automation in IndustrialДокумент3 страницыCourse of Automation in IndustrialWendy EscalanteОценок пока нет
- Nurs1117 AlphaДокумент118 страницNurs1117 AlphaRappler0% (1)
- Cardiac 1.09 Blood Pressure Normal ValuesДокумент1 страницаCardiac 1.09 Blood Pressure Normal ValuesRandy Mar TagudarОценок пока нет
- Birth Rates and Death Rates Etc Formulas PDFДокумент2 страницыBirth Rates and Death Rates Etc Formulas PDFHafiz Zahid MahmoodОценок пока нет
- PATHOДокумент2 страницыPATHOWendy EscalanteОценок пока нет
- NCPДокумент3 страницыNCPWendy EscalanteОценок пока нет
- Classification LFДокумент34 страницыClassification LFAnonymous 4tzR698Оценок пока нет
- Drug StudyДокумент14 страницDrug StudyWendy EscalanteОценок пока нет
- Laboratory Exams and ResultsДокумент15 страницLaboratory Exams and ResultsWendy EscalanteОценок пока нет
- NCP 2 MiДокумент16 страницNCP 2 MiWendy EscalanteОценок пока нет
- Assessment of Kidneys PDFДокумент1 страницаAssessment of Kidneys PDFWendy EscalanteОценок пока нет
- Nasogastric Tube Management and CareДокумент21 страницаNasogastric Tube Management and CareWendy EscalanteОценок пока нет
- Drug StudyДокумент14 страницDrug StudyWendy EscalanteОценок пока нет
- NCP 2 MiДокумент16 страницNCP 2 MiWendy EscalanteОценок пока нет
- 02 Orig Art 02 PDFДокумент3 страницы02 Orig Art 02 PDFWendy EscalanteОценок пока нет
- Integrated Management of Childhood Illness3 1 PDFДокумент78 страницIntegrated Management of Childhood Illness3 1 PDFWendy EscalanteОценок пока нет
- Caring For The Bedridden PatientДокумент1 страницаCaring For The Bedridden PatientWendy EscalanteОценок пока нет
- PATHOДокумент2 страницыPATHOWendy EscalanteОценок пока нет
- Modifiable Risk Factors Non - Modifiable Risk Factors: LegendДокумент2 страницыModifiable Risk Factors Non - Modifiable Risk Factors: LegendWendy Escalante100% (1)
- Nasogastric Tube Management and CareДокумент21 страницаNasogastric Tube Management and CareWendy EscalanteОценок пока нет
- Concept Map of Carotid Artery DiseaseДокумент2 страницыConcept Map of Carotid Artery DiseaseWendy EscalanteОценок пока нет
- Lift CarryДокумент7 страницLift CarryBianca ThereseОценок пока нет
- Assessment of KidneysДокумент1 страницаAssessment of KidneysWendy EscalanteОценок пока нет
- Acid-Ash DietДокумент10 страницAcid-Ash DietWendy Escalante0% (1)
- Brat DietДокумент8 страницBrat DietWendy EscalanteОценок пока нет
- Clear Liquid DietДокумент6 страницClear Liquid DietWendy EscalanteОценок пока нет
- At DietДокумент8 страницAt DietWendy EscalanteОценок пока нет
- Concept Map of CKD Gastrointestinal SymptomsДокумент4 страницыConcept Map of CKD Gastrointestinal SymptomsWendy Escalante0% (1)
- Example of Invitation CardДокумент2 страницыExample of Invitation CardWendy EscalanteОценок пока нет
- Domestic Violence Service Providers ListДокумент13 страницDomestic Violence Service Providers ListLynn TОценок пока нет
- The Women's Movement and FeminismДокумент55 страницThe Women's Movement and Feminismdeep pointОценок пока нет
- People vs. CampuhanДокумент6 страницPeople vs. CampuhanJotmu SolisОценок пока нет
- Prosecution - ISSUE 2Документ5 страницProsecution - ISSUE 2AnakhaОценок пока нет
- Dealing With Sexual Sin and Especially Pornography in The ChurchДокумент5 страницDealing With Sexual Sin and Especially Pornography in The ChurchRob MeintjesОценок пока нет
- Masculine Identities and Male Sex Work Between East Java and BaliДокумент203 страницыMasculine Identities and Male Sex Work Between East Java and BaliKey KusumaОценок пока нет
- Sample ChargeДокумент1 страницаSample ChargeluisОценок пока нет
- Isolating Mechanisms-2Документ20 страницIsolating Mechanisms-2Rupali GuravОценок пока нет
- A View From The BridgeДокумент1 страницаA View From The BridgeDipanОценок пока нет
- Gender Trouble Males Adolescence and Masculinity in The Choral ContextДокумент12 страницGender Trouble Males Adolescence and Masculinity in The Choral ContextRob Saldaña100% (1)
- Last Exit To Brooklyn Rough DraftДокумент8 страницLast Exit To Brooklyn Rough Draftapi-308914094Оценок пока нет
- Case BriefДокумент3 страницыCase BriefShashank JainОценок пока нет
- Justin Martyr - First ApologyДокумент4 страницыJustin Martyr - First ApologyResearchingPubОценок пока нет
- Quotes Ruminations ContemplationsДокумент677 страницQuotes Ruminations ContemplationsBabacar Jean Marie Lawson DiopОценок пока нет
- Can Your Relationship Be SavedДокумент31 страницаCan Your Relationship Be SavedJessicaGonzales100% (1)
- Embryology of Angiosperms PDFДокумент460 страницEmbryology of Angiosperms PDFSudhashree45% (11)
- President's Training PacketДокумент31 страницаPresident's Training PacketKimberly Marie SousaОценок пока нет
- PSYCHOANALYTIC THEORY by FreudДокумент4 страницыPSYCHOANALYTIC THEORY by FreudThis is a GarbageОценок пока нет
- A Critical Approach On Nick JoaquinДокумент6 страницA Critical Approach On Nick JoaquinRachel Ann Olis100% (1)
- Januszczak On Lempicka: Clumsy, Hollow and Contrived...Документ2 страницыJanuszczak On Lempicka: Clumsy, Hollow and Contrived...Begine Was100% (1)
- Kowalski Dilks Wade Book Review PUBLISHEDДокумент3 страницыKowalski Dilks Wade Book Review PUBLISHEDMD SIAMОценок пока нет
- Deviant Eyes, Deviant BodiesДокумент6 страницDeviant Eyes, Deviant BodiesÉrica SarmetОценок пока нет
- Mageo - Jeannette Marie - 2006 - Figurative Dreams Analysis and U.S Traveling IdentitiesДокумент33 страницыMageo - Jeannette Marie - 2006 - Figurative Dreams Analysis and U.S Traveling IdentitiesOscar Plens BravoОценок пока нет
- Pub Best27Документ1 страницаPub Best27AgnieszkaAgayoОценок пока нет