Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
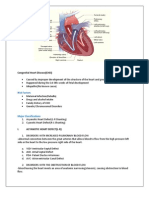
Congenital Heart Diseases
Загружено:
lotd6002Исходное описание:
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Congenital Heart Diseases
Загружено:
lotd6002Авторское право:
Доступные форматы
Congenital Heart Diseases
Abnormalities of the heart or great vessel that are
present from birth
Faulty embryogenesis at weeks 3-8 (eg. Rubella of
mother)
Half cases detect in first year of life, other in
adulthood
Epidemiology
4-50 per 1000 lives birth
Higher in premature infants and in stillborns
Development
28
FHF
cells
SHF
cells
endocardial cushion (delamination of endocardial
cells into ECM become mesenchymal cells)
Day 50th : septation of ventricle,artria and avv
valves & lead formation of 4 chamber
Etiology and Pathogenesis
Sporadic genetic abnormalities
Single gene mutation ( TBX5,GATA4,NKX2-5)
ASD&VSD defects
Notch pathway (JAGGED1,NOTCH1,NOTCH2)
(TOF,Pulmo.Stenosis)
Small chromosomal lesion deleted (22q11.2)
Environmental factors
Congenital rubella infections
Gestational diabetes
Exposures to teratogen (therapeutic drugs)
Clinical features
21
50
Gene
of FHF
(origin: lateral mesoderm)Cardiac crescent
Day 21st : SHF cells migrate to ant. & post
(CT,Atrium)., the FHF cells become tube (mainly left
ventricle) beating tube
Day 28th: looping of the heart tube & neural crest
migration to the outflow tract (form septa and aortic
arches) & ECM enlarges to produces swelling
3 majors categories causes shunt and obstruction
that emits varies CF.
Shunt abnormal comnctn & channels blood down
pressure gradient.
3 categories :
Left to- right shunts
Right to - left shunts
Obstructions
Left to-right shunt
ASD,VSD,PDA & AVSD
septal defects of heart (ASD,VSD,AVSD)
Increase flow volumes and pressures in right heart
(volumes overload)
+
Left
heart
Right ventricular hypertrophy
Right
heart
heart
failure
Dyspnoea
More blood to pulmonary artery
Increase pulmonary pressure
(adapt: medial hypertrophy & vasoconstriction)
Prolonged constriction fibrosis in pulmonary
lumen
Fatigue
Palpitation
Palpable thrill
Parasternal
heave
Pulmonary hypertension
Prolonged right
ventricle
ejection
Pressures at right heart high enough to
time
overcome left heart pressure
Reversal of shunts occur
Cyanosis
Right-to-left
shunt
Left atrium dilate
valve ring
dilate
Incomplete
closure of mitral
valve
Pathophysiology
Left
ventricle
hypertroph
Pressures left > right
Blood flow from left to right
Pansystoli
c murmur
Reduce Regurgitation
VSD
complianc
e
(VSD)
S3
large
heard
volume of
blood
shunted to
right
CLINICAL FEATURES
ASD
Fixed splitting
second heart
sounds (ASD)
Failure of the formation
of the membranous part
of ventricular septum
Fixed opening in atrial septum
due to incomplete tissues
formation
3 major types:
Ostium primum ASD (5%)
Septum primum &
endocardial cushion fails to
fuse
Ostium secundum ASD (90%)
Septum secundum does
not enlarged enough to
cover ostium secundum
Sinus venosus ASD (5%)
Patent Ductus Arteriosus(PDA)
90% occur as isolated anomaly
Communication from left PA to Aorta through
patent ductus arterious
Pathophysiology
Collapsed pulse at
periphery
Left & right shunts at ductus level (bounding)
Wide pulse
Increase pulmonary flow from aorta pressure
PDA
Clinical features
Dyspnoea
Fatigue
Palpitation
Palpable thrill
Parasternal heave
S3
Loud S2
Pansystolic
murmur
Mitral
regurgitation
Sign of congestive
heart failure
Clinical features
Dyspnoea
Fatigue
Palpitation
Palpable thrill
Parasternal heave
Fixed splitting of S2
Mild systolic murmur
Mitral regurgitation
Sign of congestive heart
failure
Turbulent
shunting
Machinery
murmur
Turbulent through
mitral valve
Mid diastolic
murmur
Increase volume
at left heart
Distention of
left heart
Vigorous nonsustained
pulsation
Hyperkinetic apex
beat
Right-to-left shunts
Decreased
diastolic BP
Increased
systolic BP
Delay Lt. ventricle
emptying
Slow closure
of aortic
valve
Reverse
splitting S2
Tetralogy of Fallot (TOF)
Four cardinal features of TOF:
VSD
Pulmonary stenosis
Overriding of aorta
Right ventricular hypertrophy
Morphology
Boot-shaped
Ventricular hypertrophy
Clinical Features
Cyanosis
Clubbing
Polycythaemia
Thrill
Para sternal heave
Mid systolic murmur
Turbulent right
ventricle outflow
Increase pulmonary flow
Right-to-left shunts at ventricular level
Increased deoxygenated blood
Pulmonary
systolic
ejection
Increased
pulmonary art.
pressure
Closure of
pulmonary valve too
soft + late
Single 2nd
heart sound
Central cyanosis
Hypoxia stimulate kidney & liver
Increase erythropoietin
Increased RBC
Polycythaemia
Transposition of Great Arteries
Pathophysiology
Pulmonary stenosis
Infundibular resistance
RightVSD
ventricle
volume loaded
pressure
Right ventricle
hypertrophy
Produces ventriculoarterial discordance
The embryogenic defect is due to abnormal
formation of truncal and aortapulmonary septa
Mixing of blood
Clinical features depend on :
Degree mix of blood
Magnitude of tissue hypoxia
Ability of right ventricle to maintain systemic
circulation
Clinical features
Right ventricular hypertrophy
Left ventricle atrophy
Die in 1st few months of life
Obstructive Congenital
Anomalies
Coarctation of Aorta
Narrowing or constriction of aorta
Two classic form :
infantile
adult
Clinical Features
HTN in upper extremities
Weak pulses
Hypotension in lower extremities
Radiograph notching
undersurfaces of rib
Systolic murmur
Thrill
Cardiomegaly
Pulmonary stenosis and atresia
Obstruct at the pulmonary valve
Clinical features
Right ventricular hypertrophy
Posstenotic dilatation
Aortic stenosis and atresia
Narrow and obstruct of aorta
Three major locations:
Valvular
o HYPOPLASTIC CUSPS
o THICKENED CUSPS
o ABNORMAL NUMBER OF
CUSP
o Hypoplastic- Left -Heart
Syndrome
Subvalvular
o Dense endocardial fibrous
below cusps
Supravalvular
Investigation &
Management
Atrial Septal Defect (ASD)
INVX:
ECG:
Ostium Secundum Right axis
deviation
Ostium primum Left axis deviation
Sinus venosus Invrtd P-wave
Chest X-ray
Dilates PA,RA,RV = Jug handle
appearance
ECG:
Left atrial enlargement
X-ray:
Calcified at ductus
Aneurysm of ductus
Treatment:
Surgical closure (3-6 yr)
ASD close spontaneously upto 2 years
Prosthetic closure by pericardial graft
Ventricular Septal Defect (VSD)
INVX:
ECG changes:
Katz- Watchel phenomenon
(large equiphasic QRS in V2 V3 V4)
X-ray:
Left ventricular enlargement w
pulmonary plethora
Treatment :
Surgical closure
Ideal age < 2yr
Pulm : Sys 1.5:1
Patent Ductus Arteriousus ( PDA)
INVX :
Treatment:
Medical :
Indomethacin 1st -7th day
(MOA: decreased PG-E level
promotes ductal closure)
Surgical :
Ligation & excision of PDA
Ideal age below 2yr
Transcatheter closure
Tetralogy of Fallot (TOF)
INVX:
ECG :
Large R wave
X-ray :
Boot shaped heart
Treatment:
Medical :
Treat
cyanotic:
Squatting
Nasal O2
Morphine
Beta blockers (propanolol)
(MOA: relieve infundibular
spasms)
Sodium bicarb met. Acidosis
Surgical:
Blalock- Taussig procedure
Waterston procedure
Potts procedure
Вам также может понравиться
- Congenital Heart DiseasesДокумент6 страницCongenital Heart Diseasestheglobalnursing100% (2)
- Rheumatic Heart DiseaseДокумент47 страницRheumatic Heart DiseaseGideon K. MutaiОценок пока нет
- Congenital Heart DiseasesДокумент21 страницаCongenital Heart DiseasesfahmiОценок пока нет
- Valvular Heart DiseaseДокумент54 страницыValvular Heart DiseaseKiki RizkyОценок пока нет
- Congenital Heart Disease - Cynotic AcynoticДокумент34 страницыCongenital Heart Disease - Cynotic Acynoticvruttika parmarОценок пока нет
- Congenital Heart Diseases, A Simple Guide to these Medical ConditionsОт EverandCongenital Heart Diseases, A Simple Guide to these Medical ConditionsОценок пока нет
- Abnormal Slow Heart Beats, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsОт EverandAbnormal Slow Heart Beats, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsОценок пока нет
- Valvular Heart Disease 2Документ46 страницValvular Heart Disease 2Topea BogdanОценок пока нет
- Clinical Cardiac EmergenciesДокумент37 страницClinical Cardiac EmergenciesmigalejandroОценок пока нет
- Congenital Heart Defects Test Five Nursing FourДокумент6 страницCongenital Heart Defects Test Five Nursing FourTiffany D'Alessandro GordonОценок пока нет
- Congenital Heart DiseaseДокумент5 страницCongenital Heart Diseasesarguss14100% (1)
- Congenital Heart DefectsДокумент3 страницыCongenital Heart DefectsjbloodDO100% (1)
- Cardiomyopathy and MyocarditisДокумент8 страницCardiomyopathy and Myocarditisoddone_out100% (1)
- Congenital Heart DefectsДокумент8 страницCongenital Heart DefectsJimy C100% (1)
- Patent Ductus ArteriosusДокумент5 страницPatent Ductus ArteriosusAisyahKautsarIlmiОценок пока нет
- Coarctation of The AortaДокумент2 страницыCoarctation of The AortaDavid Cheng0% (1)
- Keynotes Pediatric Cardiology PDFДокумент28 страницKeynotes Pediatric Cardiology PDFBasantkumar SinghОценок пока нет
- Tetralogy of FallotДокумент26 страницTetralogy of FallotGI SanadaОценок пока нет
- Diagnosis and Management of Subarachnoid HemorrhageДокумент25 страницDiagnosis and Management of Subarachnoid HemorrhageMisael ClintonОценок пока нет
- Pediatric CardiologyДокумент30 страницPediatric CardiologyZahra AlaradiОценок пока нет
- Cardiac (Heart) FailureДокумент27 страницCardiac (Heart) FailureSanthoshi Sadhanaa SankarОценок пока нет
- Complications of Acute Myocardial InfarctionДокумент5 страницComplications of Acute Myocardial Infarctionlourdesfercab_at_msn100% (1)
- Post Op CardiacДокумент7 страницPost Op CardiacsimplyputmonicОценок пока нет
- Atrial Septal DefectДокумент12 страницAtrial Septal DefectNurruhaizi Aizi100% (1)
- Rheumatic Heart DiseaseДокумент22 страницыRheumatic Heart DiseasemajdОценок пока нет
- Cardiac DisordersДокумент38 страницCardiac Disordersprototypeallhell100% (1)
- Ventricular Septal DefectДокумент4 страницыVentricular Septal DefectMarina RotaruОценок пока нет
- Cardiac TamponadeДокумент3 страницыCardiac TamponadeKimberly SolisОценок пока нет
- Pedia Cardiology 2Документ5 страницPedia Cardiology 2Medisina101Оценок пока нет
- Quick Reference SheetДокумент2 страницыQuick Reference SheetCGdragonОценок пока нет
- CXR Lecture DR Lenora FernandezДокумент70 страницCXR Lecture DR Lenora Fernandezapi-19431894100% (1)
- TOF Patient EducationДокумент8 страницTOF Patient EducationMia MiaОценок пока нет
- Heart Sounds and MurmursДокумент38 страницHeart Sounds and MurmursLaura Moise100% (5)
- Heart Sounds & MurmursДокумент32 страницыHeart Sounds & MurmursVisruth M Kumar100% (1)
- Congenital Heart 22Документ1 131 страницаCongenital Heart 22Maier Sorina100% (5)
- CXR Made EasyДокумент14 страницCXR Made Easyjaimejm100% (1)
- Congenital Heart DefectsДокумент20 страницCongenital Heart DefectsJanina Loren NeyraОценок пока нет
- Overview of Pediatrics Notes (Dr. Bongalo)Документ3 страницыOverview of Pediatrics Notes (Dr. Bongalo)Angel BataОценок пока нет
- Transcribed By: B7: Francisco, Francisco, Fuentes, Gabriel, Galia, Galindon Merry Christmas Happy New Year Mery Christmas Happy New YearДокумент8 страницTranscribed By: B7: Francisco, Francisco, Fuentes, Gabriel, Galia, Galindon Merry Christmas Happy New Year Mery Christmas Happy New Yearcarlo_nonОценок пока нет
- Cardiac II Study GuideДокумент6 страницCardiac II Study GuiderunnermnОценок пока нет
- Acute Coronary SyndromeДокумент21 страницаAcute Coronary SyndromeNabil Mosharraf Hossain100% (2)
- Management of Cardiac ArrestДокумент12 страницManagement of Cardiac ArrestpunctumlacrimaleОценок пока нет
- CardiologyДокумент62 страницыCardiologyLaura Kathrine Simpson92% (12)
- Cardiac MedsДокумент7 страницCardiac MedsMary Fair DelcidОценок пока нет
- Congenital Heart DiseaseДокумент51 страницаCongenital Heart Diseaseelsa prima putri100% (2)
- ACLS Class Packet PDFДокумент9 страницACLS Class Packet PDFImam GultomОценок пока нет
- Pulmonary HypertensionДокумент54 страницыPulmonary HypertensionpaanarОценок пока нет
- Cardiac AsthmaДокумент12 страницCardiac AsthmaNeupane KsabОценок пока нет
- Manipal Manual of Resuscitation - 4th EditionДокумент73 страницыManipal Manual of Resuscitation - 4th EditionAshlita Mendonca100% (2)
- Congenital Heart DefectsДокумент13 страницCongenital Heart DefectsGheluzee Herrera100% (2)
- Cardiac PacingДокумент4 страницыCardiac PacingmrygnvllОценок пока нет
- Cardiac ArrhythmiasДокумент60 страницCardiac ArrhythmiasMelissa Monique Peart-YatesОценок пока нет
- Pediatric CardiologyДокумент9 страницPediatric CardiologyStephen Pilar Portillo100% (1)
- Pediatric Assessment TriangleДокумент31 страницаPediatric Assessment TriangleblairОценок пока нет
- 25 Cardiovascular DiseaseДокумент35 страниц25 Cardiovascular DiseaseBramantyo NugrosОценок пока нет
- Basics of PacemakerДокумент121 страницаBasics of Pacemakerjeenath justin doss100% (1)
- A Simple Guide to Hypovolemia, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsОт EverandA Simple Guide to Hypovolemia, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsОценок пока нет
- WHO Model List of Essential Medicines For ChildrenДокумент42 страницыWHO Model List of Essential Medicines For Childrenlotd6002Оценок пока нет
- Orthopaedics MCQДокумент4 страницыOrthopaedics MCQlotd6002Оценок пока нет
- Structure of HaemoglobinДокумент12 страницStructure of Haemoglobinlotd6002Оценок пока нет
- Internal FixationДокумент22 страницыInternal Fixationlotd6002Оценок пока нет
- Inotropic Agents. 1Документ38 страницInotropic Agents. 1benny christantoОценок пока нет
- Hypertension Health ChallengeДокумент19 страницHypertension Health ChallengeElijah Tochukwu DavidОценок пока нет
- Cva Case StudyДокумент31 страницаCva Case StudyZoe AnnaОценок пока нет
- Guglielmini 2015Документ15 страницGuglielmini 2015Tỷ PhượngОценок пока нет
- The Health RevolutionДокумент214 страницThe Health RevolutionFisnik Y. Limani0% (1)
- Newborn Adaptation Assessment 2013 FINALДокумент21 страницаNewborn Adaptation Assessment 2013 FINALJennОценок пока нет
- BLOOD PRESSURE Vs HEART RATE From American Heart AssociationДокумент2 страницыBLOOD PRESSURE Vs HEART RATE From American Heart AssociationSyima MnnОценок пока нет
- Date/Time Cues N E E D Nursing Diagnosis Objectives of Care Nursing Interventions EvaluationДокумент4 страницыDate/Time Cues N E E D Nursing Diagnosis Objectives of Care Nursing Interventions EvaluationRczhОценок пока нет
- 2010 Ieee Titb OreskoДокумент7 страниц2010 Ieee Titb OreskoPedro ContrerasОценок пока нет
- QuizДокумент4 страницыQuizampalОценок пока нет
- Acute/Critically Ill Patients in Hemodynamic Monitoring (Assessment)Документ6 страницAcute/Critically Ill Patients in Hemodynamic Monitoring (Assessment)Esmareldah Henry SirueОценок пока нет
- Eet312 Module IДокумент107 страницEet312 Module IAnandu DipukumarОценок пока нет
- The Anatomy of The Coronary SinusДокумент7 страницThe Anatomy of The Coronary Sinusmihalcea alinОценок пока нет
- A P2 1Документ36 страницA P2 1Priya_Vankovic_7963Оценок пока нет
- 2018 2019 Daily Lesson Log AutosavedДокумент322 страницы2018 2019 Daily Lesson Log AutosavedAinah 16Оценок пока нет
- Instant Download Ebook PDF Anatomy Physiology An Integrative Approach 3rd Edition PDF ScribdДокумент41 страницаInstant Download Ebook PDF Anatomy Physiology An Integrative Approach 3rd Edition PDF Scribdheidi.gomez888100% (48)
- Radiology of Chest Wall MassesДокумент11 страницRadiology of Chest Wall MassesDevina BumiОценок пока нет
- How To Care For The Circulatory SystemДокумент31 страницаHow To Care For The Circulatory SystemKim JacintoОценок пока нет
- Datascope Passport 2, 2LT Monitor - User Manual PDFДокумент208 страницDatascope Passport 2, 2LT Monitor - User Manual PDFpaolaОценок пока нет
- Combined Science PDFДокумент57 страницCombined Science PDFRadhika Meher58% (33)
- Cardiac Cycle 0Документ28 страницCardiac Cycle 0ProfMarinho FisiologiaОценок пока нет
- Grade 9 Integrated Science The Human Body - Respiratory SystemДокумент3 страницыGrade 9 Integrated Science The Human Body - Respiratory SystemMarc Jason LanzarroteОценок пока нет
- DR - Tahir Mahmood (PT) IIIRS, SialkotДокумент40 страницDR - Tahir Mahmood (PT) IIIRS, SialkotRabia RaufОценок пока нет
- Heart Attack and EmphysemaДокумент12 страницHeart Attack and EmphysemaKylie Adrianna Bernabe SarmientoОценок пока нет
- Alpha10 описание англ -A10LT-V60-20Документ16 страницAlpha10 описание англ -A10LT-V60-20DenОценок пока нет
- IHDДокумент34 страницыIHDElly Msi ProbolinggoОценок пока нет
- Tani Et Al-2012-EchocardiographyДокумент7 страницTani Et Al-2012-EchocardiographycesareОценок пока нет
- Dictionary of Acupuncture - Read (Index Pag 149)Документ177 страницDictionary of Acupuncture - Read (Index Pag 149)nitsanns84% (19)
- NST1501 Exam Ndou LДокумент7 страницNST1501 Exam Ndou Llufunondou12Оценок пока нет
- Pediatric Nursing-Cardiovascular DisordersДокумент10 страницPediatric Nursing-Cardiovascular Disordershasan ahmd100% (1)