Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Chapter1 Interaction Design
Загружено:
nnoumanИсходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Chapter1 Interaction Design
Загружено:
nnoumanАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
5/26/2010
Bad designs
Chapter 1:
What is interaction design?
Elevator controls and labels on the bottom row all
look the same, so it is easy to push a label by
mistake instead of a control button
People do not make same mistake for the labels and
buttons on the top row. Why not?
From: www.baddesigns.com
Why is this vending machine
so bad?
Need to push
button first to
activate reader
Normally insert
bill first before
making selection
Contravenes well
known convention
Good design
Marble answering
machine (Bishop,
1995)
Based on how
everyday objects
behave
Easy, intuitive and a
pleasure to use
Only requires onestep actions to
perform core tasks
From: www.baddesigns.com
Good and bad design
What is wrong with
the Apex remote?
Why is the TiVo
remote so much
better designed?
Peanut shaped to fit
in hand
Logical layout and
color-coded,
distinctive buttons
Easy to locate buttons
What to design
Need to take into account:
Who the users are
What activities are being carried out
Where the interaction is taking place
Need to optimize the interactions users have
with a product
So that they match the users activities and needs
5/26/2010
Understanding users needs
Need to take into account what people are
good and bad at
Consider what might help people in the way
they
y currently
y do things
g
Think through what might provide quality
user experiences
Listen to what people want and get them
involved
Activity
How does making a call differ
when using a:
Cell phone
Public phone box?
Consider the kinds of user, type of
activity and context of use
Use tried and tested user-centered methods
What is interaction design?
Designing interactive products to support the
way people communicate and interact in their
everyday and working lives
Sharp, Rogers and Preece (2007)
The design of spaces for human
communication and interaction
Goals of interaction design
Develop usable products
Usability means easy to learn,
effective to use and p
provide an
enjoyable experience
Involve users in the design process
Winograd (1997)
Which kind of design?
HCI and interaction design
Number of other terms used emphasizing
what is being designed, e.g.,
user interface design, software design, user-centered
design, product design, web design, experience
design (UX)
Interaction design is the umbrella term
covering all of these aspects
fundamental to all disciplines, fields, and approaches
concerned with researching and designing computerbased systems for people
5/26/2010
Relationship between ID, HCI
and other fields
Relationship between ID, HCI
and other fields
Academic disciplines contributing
to ID:
Design practices contributing to
ID:
Psychology
y
gy
Social Sciences
Computing Sciences
Engineering
Ergonomics
Graphic
p
design
g
Product design
Artist-design
Industrial design
Film industry
Informatics
Relationship between ID, HCI
and other fields
Interdisciplinary fields that do
interaction design:
HCI
Human Factors
Cognitive Engineering
Cognitive Ergonomics
Computer Supported Co-operative Work
Information Systems
Interaction design in business
Increasing number of ID consultancies, examples of well known ones
include:
Nielsen Norman Group: help companies enter the age of the
consumer, designing human-centered products and services
Cooper: From research and product to goal-related design
Swim: provides a wide range of design services, in each case
targeted to address the product development needs at hand
IDEO: creates
creates products, services and environments for
companies pioneering new ways to provide value to their
customers
QuickTime and a
TIFF (Uncompressed) decompressor
are needed to see this picture.
Working in multidisciplinary
teams
Many people from different
backgrounds involved
Different perspectives
and ways of seeing
and talking about things
Benefits
more ideas and designs
generated
Disadvantages
difficult to communicate and
progress forward the designs being create
What do professionals do in the
ID business?
interaction designers - people involved in the design of all
the interactive aspects of a product
usability engineers - people who focus on evaluating
products, using usability methods and principles
web designers - people who develop and create the visual
design of websites,
websites such as layouts
information architects - people who come up with ideas of
how to plan and structure interactive products
user experience designers (UX) - people who do all the
above but who may also carry out field studies to inform the
design of products
5/26/2010
The User Experience
Why was the iPod user
experience such a success?
How a product behaves and is used by
people in the real world
the way people feel about it and their pleasure and
satisfaction when using it
it, looking at it
it, holding it
it,
and opening or closing it
every product that is used by someone has a user
experience: newspapers, ketchup bottles, reclining
armchairs, cardigan sweaters. (Garrett, 2003)
Cannot design a user experience, only
design for a user experience
What is involved in the process
of interaction design
Identifying needs and establishing requirements
for the user experience
Developing alternative designs to meet these
Building interactive prototypes that can be
communicated and assessed
Evaluating what is being built throughout the
process and the user experience it offers
Why go to this length?
Help designers:
understand how to design interactive
products that fit with what people want,
need and may
y desire
appreciate that one size does not fit all
e.g., teenagers are very different to grown-ups
identify any incorrect assumptions they may
have about particular user groups
e.g., not all old people want or need big fonts
be aware of both peoples sensitivities and
their capabilities
Core characteristics of
interaction design
Users should be involved through the
development of the project
Specific usability and user experience goals
need to be identified,
identified clearly documented and
agreed at the beginning of the project
Iteration is needed through the core activities
Are cultural differences
important?
5/21/1960 versus 21/5/1960?
Which should be used for international
services and online forms?
Why is it that certain products, like the
iPod, are universally accepted by people
from all parts of the world whereas
websites are reacted to differently by
people from different cultures?
5/26/2010
Anna, IKEA online sales agent
Designed to be
different for UK and US
customers
What are the differences
and
d which
hi h iis which?
hi h?
What should Annas
appearance be like
for other countries,
like India, South Africa,
or China?
Usability goals
Activity on usability
How long should it take and how
long does it actually take to:
Using a DVD to play a movie?
Use a DVD to pre-record two
programs?
Using a web browser tool to create a
website?
QuickTime and a
TIFF (Uncompressed) decompressor
are needed to see this picture.
Usability and user experience
goals
Selecting terms to convey a persons feelings,
emotions, etc., can help designers understand
the multifaceted nature of the user experience
How do usability goals differ from user
experience goals?
Are there trade-offs between the two kinds of
goals?
Effective to use
Efficient to use
Safe to use
Have good utility
Easy to learn
Easy to remember how to use
User experience goals
satisfying
enjoyable
engaging
pleasurable
exciting
entertaining
t t i i
helpful
motivating
emotionally fulfilling
aesthetically pleasing
supportive of creativity
supportive of creativity
rewarding
fun
provocative
ti
surprising
enhancing sociability
challenging
boring
frustrating
annoying
cutsey
Design principles
Generalizable abstractions for thinking about
different aspects of design
The dos and donts of interaction design
What to p
provide and what not to p
provide at
the interface
Derived from a mix of theory-based
knowledge, experience and common-sense
e.g. can a product be both fun and safe?
How easy is it to measure usability versus
user experience goals?
5/26/2010
Visibility
This is a control panel for an elevator
Visibility
you need to insert your room card in the slot by the buttons to
get the elevator to work!
How does it work?
Push a button for the floor you want?
Nothing happens. Push any other
button? Still nothing. What do you
need to do?
From:
www.baddesigns.com It
is not visible as to what to do!
What do I do if I am wearing
black?
Invisible automatic
controls can make it
more difficult
to use
How would you make this action more visible?
make the card reader more obvious
provide
id an auditory
di
message, that
h says what
h to do
d (which
( hi h
language?)
provide a big label next to the card reader that flashes
when someone enters
make relevant parts visible
make what has to be done obvious
Feedback
Sending information back to the user about
what has been done
Includes sound, highlighting, animation and
combinations of these
e.g. when screen button clicked on provides sound or
red highlight feedback:
ccclichhk
Constraints
Logical or ambiguous design?
Where do you plug the
mouse?
Restricting the possible actions that can be
performed
Helps prevent user from selecting incorrect
options
Physical objects can be designed to constrain
things
Where do you plug the
y
keyboard?
top or bottom connector?
e.g. only one way you can insert a key into a lock
Do the color coded icons
help?
From: www.baddesigns.com
5/26/2010
How to design them more
logically
Consistency
(i) A provides direct
adjacent mapping
between icon and
connector
Design interfaces to have similar operations
and use similar elements for similar tasks
For example:
(ii) B provides color
coding to associate
the connectors with
the labels
Main benefit is consistent interfaces are easier
to learn and use
always use ctrl key plus first initial of the command
for an operation ctrl+C, ctrl+S, ctrl+O
From: www.baddesigns.com
When consistency breaks
down
What happens if there is more than one
command starting with the same letter?
e.g. save, spelling, select, style
Have to find other initials or combinations of
keys, thereby breaking the consistency rule
e.g. ctrl+S, ctrl+Sp, ctrl+shift+L
Increases learning burden on user, making
them more prone to errors
Internal and external
consistency
Internal consistency refers to designing
operations to behave the same within an
application
Difficult to achieve with complex interfaces
External consistency refers to designing
operations, interfaces, etc., to be the
same across applications and devices
Very rarely the case, based on different
designers preference
Keypad numbers layout
A case of external inconsistency
Affordances: to give a clue
Refers to an attribute of an object that allows
people to know how to use it
e.g. a mouse button invites pushing, a door handle
affords pulling
(a) phones, remote controls (b) calculators, computer keypads
2 3
5 6
1
0
2 3
Norman (1988) used the term to discuss the
design of everyday objects
Since has been much popularised in
interaction design to discuss how to design
interface objects
e.g. scrollbars to afford moving up and down, icons
to afford clicking on
5/26/2010
What does affordance have to
offer interaction design?
Interfaces are virtual and do not have affordances like
physical objects
Norman argues it does not make sense to talk about
interfaces in terms of real
real affordances
Activity
Physical affordances:
How do the following physical objects
afford? Are they obvious?
Instead interfaces are better conceptualized as
perceived affordances
Learned conventions of arbitrary mappings between action
and effect at the interface
Some mappings are better than others
Activity
Virtual affordances
How do the following screen objects
afford?
Wh t if you were a novice
What
i user?
?
Would you know what to do with them?
Usability principles (Nielsen 2001)
Visibility of system status
Match between system and the real world
User control and freedom
Consistency and standards
Help users recognize, diagnose and recover from errors
Error prevention
Recognition rather than recall
Flexibility and efficiency of use
Aesthetic and minimalist design
Help and documentation
Usability principles
Similar to design principles, except
more prescriptive
Used mainly as the basis for
evaluating systems
Provide a framework for heuristic
evaluation
Key points
Interaction design is concerned with designing
interactive products to support the way people
communicate and interact in their everyday
and working lives
It is concerned with how to create quality user
experiences
It requires taking into account a number of
interdependent factors, including context of
use, type of activities, cultural differences, and
user groups
It is multidisciplinary, involving many inputs
from wide-reaching disciplines and fields
Вам также может понравиться
- The Inmates Are Running the Asylum (Review and Analysis of Cooper's Book)От EverandThe Inmates Are Running the Asylum (Review and Analysis of Cooper's Book)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (178)
- Interaction DesignДокумент45 страницInteraction DesignEdin DemicОценок пока нет
- Chapter 1 ID2e SlidesДокумент42 страницыChapter 1 ID2e SlidesDas HuОценок пока нет
- Bahan Uts Sistem InteraksiДокумент297 страницBahan Uts Sistem InteraksiDarien HamidjajaОценок пока нет
- HCI Extra NoteДокумент52 страницыHCI Extra NotemalgahaОценок пока нет
- What Is Interaction Design?Документ51 страницаWhat Is Interaction Design?Vairavel ChenniyappanОценок пока нет
- HCI Slides 4 PDFДокумент51 страницаHCI Slides 4 PDFDr Lokesh SharmaОценок пока нет
- What Is Interaction Design?Документ48 страницWhat Is Interaction Design?luffydmonОценок пока нет
- User Interface Design Course OutlineДокумент52 страницыUser Interface Design Course OutlineParamesh ThangarajОценок пока нет
- W1 L1 COMP1649 Introduction Tran 2021Документ68 страницW1 L1 COMP1649 Introduction Tran 2021Khoa HuỳnhОценок пока нет
- HCI Definition and Interaction DesignДокумент61 страницаHCI Definition and Interaction DesignMuhammad BilalОценок пока нет
- Chapter 1 ID2e SlidesДокумент30 страницChapter 1 ID2e SlidesCarlosОценок пока нет
- IxD#1 - Introduction To IxD - Interaction DesignДокумент57 страницIxD#1 - Introduction To IxD - Interaction DesignDumindu AthukoralaОценок пока нет
- What Is Interaction Design?Документ48 страницWhat Is Interaction Design?SNTCC107CHAITANYA6826Оценок пока нет
- Understanding Interaction Design PrinciplesДокумент39 страницUnderstanding Interaction Design PrinciplesMAITUMELO RADIPODIОценок пока нет
- LN IT 312 01 Human Computer InteractionДокумент22 страницыLN IT 312 01 Human Computer InteractionJay ChalanagОценок пока нет
- Interaction Design Goals and ChallengesДокумент46 страницInteraction Design Goals and ChallengesShaun NyamanjerereОценок пока нет
- Lecture 2 Interaction DesignДокумент46 страницLecture 2 Interaction Designkipkoecharonz korirОценок пока нет
- Interaction Design FundamentalsДокумент46 страницInteraction Design Fundamentalsadeel akramОценок пока нет
- Helen Sharp, Yvonne Rogers, and Jenny Preece (2019)Документ46 страницHelen Sharp, Yvonne Rogers, and Jenny Preece (2019)noOneОценок пока нет
- Design PatternДокумент48 страницDesign PatternRahman RezaeeОценок пока нет
- What Is Interaction Design?Документ44 страницыWhat Is Interaction Design?HahsadasdОценок пока нет
- P03 - What Is Interaction Design - 2Документ27 страницP03 - What Is Interaction Design - 2Fandi Adi PrasetioОценок пока нет
- 411 User ExperienceMobile Applications Development - UI - UX - AdaptedДокумент76 страниц411 User ExperienceMobile Applications Development - UI - UX - Adaptedbed-com-08-19Оценок пока нет
- Midterm HCI Lecture 3Документ23 страницыMidterm HCI Lecture 3Tsuki ninamОценок пока нет
- What is Interaction DesignДокумент52 страницыWhat is Interaction DesignAbdullahi AliОценок пока нет
- Interaction DesignДокумент31 страницаInteraction DesignVery GoodОценок пока нет
- 4040 PDFДокумент311 страниц4040 PDFRabia TabasamОценок пока нет
- What Is Interaction Design?: Human Computer Interaction Teknik Informatika Fakultas Teknik Universitas Surabaya 2020Документ70 страницWhat Is Interaction Design?: Human Computer Interaction Teknik Informatika Fakultas Teknik Universitas Surabaya 2020Andre NotoОценок пока нет
- Chapter 1Документ72 страницыChapter 1Ngô Đăng Trường SaОценок пока нет
- Human Computer InteractionДокумент47 страницHuman Computer Interactionzahra aliОценок пока нет
- Week 2 - Interaction DesignДокумент14 страницWeek 2 - Interaction DesignRaymond RamirezОценок пока нет
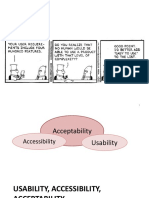
- 1-Usability Acessibility AcceptabilityДокумент46 страниц1-Usability Acessibility AcceptabilityAlmeda AsuncionОценок пока нет
- Design, Prototyping and ConstructionДокумент32 страницыDesign, Prototyping and ConstructionAldoОценок пока нет
- Lecture 1Документ54 страницыLecture 1Radish KumarОценок пока нет
- U I D UID: SER Nterface EsignДокумент22 страницыU I D UID: SER Nterface EsignPurushothama ReddyОценок пока нет
- Understanding and Conceptualizing InteractionДокумент35 страницUnderstanding and Conceptualizing InteractionVairavel ChenniyappanОценок пока нет
- Hci Unit 1Документ53 страницыHci Unit 1khushibansal211Оценок пока нет
- UsabilityДокумент19 страницUsabilityZeeshan FarooqОценок пока нет
- ISYS6619-UX For Digital Business Topik 01Документ69 страницISYS6619-UX For Digital Business Topik 01valdi sОценок пока нет
- Human Computer Interaction: University of HargeisaДокумент34 страницыHuman Computer Interaction: University of HargeisaAidarusОценок пока нет
- ilovepdf_merged (1)Документ17 страницilovepdf_merged (1)gollasainath62Оценок пока нет
- Human Computer Interaction: (Unit - II)Документ34 страницыHuman Computer Interaction: (Unit - II)Vinoth ChandrasekaranОценок пока нет
- Lec#4 Lec#5Документ22 страницыLec#4 Lec#5ahmedhos111111Оценок пока нет
- HCI Slides 5 PDFДокумент35 страницHCI Slides 5 PDFDr Lokesh SharmaОценок пока нет
- User Interface CSE 403: Three Mile IslandДокумент30 страницUser Interface CSE 403: Three Mile IslandGarry MehrokОценок пока нет
- Human Computer Interaction Lecture Notes On UNIT 1Документ29 страницHuman Computer Interaction Lecture Notes On UNIT 1Prabhu AlakannanОценок пока нет
- Interaction Design: Course: COMP6232 / Human - Computer Interaction Year: 2016Документ25 страницInteraction Design: Course: COMP6232 / Human - Computer Interaction Year: 2016FeraSartikaОценок пока нет
- Hci 2Документ35 страницHci 2malgahaОценок пока нет
- HCI Lecture3 18032021 033937pmДокумент24 страницыHCI Lecture3 18032021 033937pmMuhammad Abdul Rehman MustafaОценок пока нет
- Hci Unit - 1Документ19 страницHci Unit - 1Sai KumarОценок пока нет
- Human-Computer Interaction: October 25, 2005 - Intelligent System Design, IT-university - Maria HåkanssonДокумент27 страницHuman-Computer Interaction: October 25, 2005 - Intelligent System Design, IT-university - Maria HåkanssonehsanghaОценок пока нет
- Chapter 2 Conceptualized InteractionДокумент32 страницыChapter 2 Conceptualized InteractionnancyОценок пока нет
- Seminar in Human-Machine Interaction 2011: Teacher: Rosella Gennari Lab: Vladislav Ryzhikov Free University Bozen-BolzanoДокумент47 страницSeminar in Human-Machine Interaction 2011: Teacher: Rosella Gennari Lab: Vladislav Ryzhikov Free University Bozen-Bolzanoعمر اسماعيلОценок пока нет
- OOSE UNIT 4 UI DesignДокумент29 страницOOSE UNIT 4 UI DesignvarunОценок пока нет
- Goals & Evolution of Human-Computer InteractionДокумент50 страницGoals & Evolution of Human-Computer InteractionhhumasОценок пока нет
- UX-UI Design FundamentalsДокумент12 страницUX-UI Design Fundamentalssunil vishwaОценок пока нет
- Chapter 1Документ49 страницChapter 1najonekenobiОценок пока нет
- What Is The Correct Order of UI-UX DesignДокумент14 страницWhat Is The Correct Order of UI-UX DesignKrishna KulkarniОценок пока нет
- Using Language Functions To Learn and Teach EnglishДокумент2 страницыUsing Language Functions To Learn and Teach EnglishAnonymous 38LDTOFkRОценок пока нет
- 1st Point-Check The Subject and Verb Student 2Документ2 страницы1st Point-Check The Subject and Verb Student 2Juan Manuel Martínez RiveraОценок пока нет
- Chapter 3: Verbal Communication SkillsДокумент14 страницChapter 3: Verbal Communication SkillsFares EL DeenОценок пока нет
- B 5 - HubSpot and Motion AI Chatbot Enabled CRMДокумент2 страницыB 5 - HubSpot and Motion AI Chatbot Enabled CRMVasudev GuduriОценок пока нет
- Listening 7 C1Документ2 страницыListening 7 C1Lucía García RuizОценок пока нет
- Edited-Final Demo - Lesson Plan in English 8 - 060154Документ5 страницEdited-Final Demo - Lesson Plan in English 8 - 060154remeceldo dagamacОценок пока нет
- Korean Through FolktalesДокумент104 страницыKorean Through Folktalespizbola100% (2)
- ILFANI ADIRA News Reading PSДокумент3 страницыILFANI ADIRA News Reading PSIlfani AdiraОценок пока нет
- Simplified Chinese Characters Are Standardized ChineseДокумент17 страницSimplified Chinese Characters Are Standardized ChineseSashimiTourloublancОценок пока нет
- Final Task 1 Part E-Planning CommentaryДокумент5 страницFinal Task 1 Part E-Planning Commentaryapi-231342304Оценок пока нет
- ISIFUNDO SOKUQALA Lesson One PDFДокумент12 страницISIFUNDO SOKUQALA Lesson One PDFJulian YellowSan NelОценок пока нет
- Clockwise Pre-Intermediate - Teacher's BookДокумент80 страницClockwise Pre-Intermediate - Teacher's BookRicardoTejada67% (3)
- Speaking: Ielts by Prof. Alexander BДокумент11 страницSpeaking: Ielts by Prof. Alexander BMike PrestonОценок пока нет
- Excl AmatoryДокумент55 страницExcl AmatoryGlory MiondaОценок пока нет
- Grammar Snacks: Question Words - ExercisesДокумент3 страницыGrammar Snacks: Question Words - ExercisesIsabel Llucho Gonzales100% (1)
- Checklist-Remedial Reading On Hiligaynon Basic Sight WordsДокумент3 страницыChecklist-Remedial Reading On Hiligaynon Basic Sight WordsRjGepilanoОценок пока нет
- The Linguist: A Personal Guide To Language Learning by Steve KaufmannДокумент26 страницThe Linguist: A Personal Guide To Language Learning by Steve KaufmannMarcos Bezerra BezerroftОценок пока нет
- Jones Leo, Baeyer C.von. - Functions of American English. Communication Activities For The Classroom. Student's BookДокумент157 страницJones Leo, Baeyer C.von. - Functions of American English. Communication Activities For The Classroom. Student's BookBhanu Pathak75% (4)
- TOEICДокумент2 страницыTOEICMukti AliОценок пока нет
- Learn Punjabi Sentence Structure Made Easy PDFДокумент110 страницLearn Punjabi Sentence Structure Made Easy PDFG S100% (4)
- Hot Spot 3 SBДокумент114 страницHot Spot 3 SBAnalía Villagra89% (19)
- New Trends in Using L1 in EFL ClassroomДокумент10 страницNew Trends in Using L1 in EFL ClassroomtehjavaОценок пока нет
- EDU30001__literacy___Copy.docxДокумент10 страницEDU30001__literacy___Copy.docxnaima fadilyyt7i8 please 0tlОценок пока нет
- Egyptian Arabic Lesson 1: IntroductionsДокумент3 страницыEgyptian Arabic Lesson 1: IntroductionsPakar Kuda LautОценок пока нет
- Purposive Communication Mid-Term Departmental ExamДокумент4 страницыPurposive Communication Mid-Term Departmental ExamFerdinand Pinon90% (20)
- English File: Answer KeyДокумент4 страницыEnglish File: Answer KeyGabriel Castañeda OrdoñezОценок пока нет
- Sindhi Stemmer Using Affix Removal MethodДокумент5 страницSindhi Stemmer Using Affix Removal MethodWARSE JournalsОценок пока нет
- The Page Doctor Supporting DocumentДокумент1 страницаThe Page Doctor Supporting DocumentfilipefbrittoОценок пока нет
- D2 TeribeДокумент1 страницаD2 TeribePeter JohnsonОценок пока нет
- A J Greimas The Perfection of ImperfectionДокумент10 страницA J Greimas The Perfection of ImperfectionManjola BrahajОценок пока нет