Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Prcatice # 10
Загружено:
AfifaFarooqИсходное описание:
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Prcatice # 10
Загружено:
AfifaFarooqАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
10.
PHY 101
Chapter 7
Work & Energy
Practice Problems
Summer 2013
Instructor: Asad Hasan
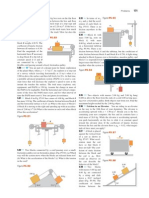
An object of mass m starts from rest and slides a distance d down a frictionless incline of angle
. While sliding, it contacts an unstressed spring of negligible mass as shown in Figure P8.10. The
object slides an additional distance x as it is brought momentarily to rest by compression of the spring
(of force constant k). Find the initial separation d between object and spring. d
kx 2
x .
2mg sin
See also Bridging problem page 231; chapter 7
13.
Two objects are connected by a light string passing over a light frictionless pulley as shown in
Figure P8.13. The object of mass 5.00-kg is released from rest. Using the principle of conservation of
energy, (a) determine the speed of the 3.00-kg object just as the 5.00-kg object hits the ground. (b) Find
the maximum height to which the 3.00-kg object rises. a) v = 4.43 m/s, b) yamx = 5m
24.
A particle of mass m = 5.00 kg is released from point A and slides on the frictionless track
shown in Figure P8.24. Determine (a) the particle's speed at points B and C and (b) the net work done
by the gravitational force in moving the particle from A to C.
31.
The coefficient of friction between the 3.00-kg block and the surface in Figure P8.31 is 0.400.
The system starts from rest.
a) What is the speed of the 5.00-kg ball when it has fallen 1.50 m? v=3.74 m/s
b) What is the acceleration of the 5.00-kg ball when it has fallen 1.50 m?
2
2
to determine the acceleration use v f vi 2ah ; a = 4.66 m/s2
36.
A 50.0-kg block and 100-kg block are connected by a string as in Figure P8.36. The pulley is
frictionless and of negligible mass. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the 50-kg block and
incline is 0.250. Determine the change in the kinetic energy of the 50-kg block as it moves from A to B,
a distance of 20.0 m. K A 3.92 kJ .
48.
A block slides down a curved frictionless track and then up an inclined plane as in Figure
P8.48. The coefficient of kinetic friction between block and incline is k. Use energy methods to show
that the maximum height reached by the block is
ymax
54.
1 k cot
A 2.00-kg block situated on a rough incline is connected to a spring of negligible mass having a
spring constant of 100 N/m (Fig. P8.54). The pulley is frictionless. The block is released from rest
when the spring is unstretched. The block moves 20.0 cm down the incline before coming to rest. Find
the coefficient of kinetic friction between block and incline. k 0.115
57.
A 10.0-kg block is released from point A in Figure P8.57. The track is frictionless except for the
portion between points B and C , which has a length of
6.00 m. The block travels down the track, hits a spring of force constant 2 250 N/m, and compresses
the spring 0.300 m from its equilibrium position before coming to rest momentarily. Determine the
coefficient of kinetic friction between the block and the rough surface between B and C. k = 0.328
Вам также может понравиться
- 2024spring General Physics (1) Problem Set 2 With SolutionsДокумент31 страница2024spring General Physics (1) Problem Set 2 With SolutionspurevnaymbayarjargalОценок пока нет
- Newton's 2nd Law of MotionДокумент14 страницNewton's 2nd Law of MotionGarrey BrionesОценок пока нет
- Physics I ProblemsДокумент1 страницаPhysics I ProblemsbosschellenОценок пока нет
- Tutorial 5Документ4 страницыTutorial 5Cheryl LowОценок пока нет
- All AnswersДокумент22 страницыAll AnswersNadiatul JannahОценок пока нет
- Phys10 Chap7 PotentialEnergy&ConservationДокумент4 страницыPhys10 Chap7 PotentialEnergy&ConservationEngelbert Bicoy AntodОценок пока нет
- Cavendish University Zambia: School of MedicneДокумент2 страницыCavendish University Zambia: School of MedicneMuhau ZvikomboreroОценок пока нет
- Physics I Problems PDFДокумент1 страницаPhysics I Problems PDFbosschellenОценок пока нет
- Problem Set - FinalsДокумент3 страницыProblem Set - FinalsJason TylerОценок пока нет
- CH 07Документ4 страницыCH 07Mohammed Abdul MajidОценок пока нет
- Physics I Problems PDFДокумент1 страницаPhysics I Problems PDFbosschellenОценок пока нет
- Kerja Dan Energi (Work and Energy)Документ29 страницKerja Dan Energi (Work and Energy)Nurul FitriОценок пока нет
- PROBLEM - SOLVING - Friction and 2nd Law UstДокумент34 страницыPROBLEM - SOLVING - Friction and 2nd Law UstMarj Ladica MangaОценок пока нет
- Tutorial 3 WEДокумент5 страницTutorial 3 WE2B Dai Ko DUPLICATEОценок пока нет
- 2b-Dynamics FR Practice ProblemsДокумент24 страницы2b-Dynamics FR Practice ProblemsTiff VoОценок пока нет
- Assignment 3 Solution PDFДокумент10 страницAssignment 3 Solution PDFAhmed AttallaОценок пока нет
- Work Power EnergyДокумент9 страницWork Power EnergySanmati Jain100% (1)
- Module 6Документ5 страницModule 6John Kennedy EvangelistaОценок пока нет
- M1 Supporting Material 3 - Connected Particles Types I - IXДокумент9 страницM1 Supporting Material 3 - Connected Particles Types I - IXTanvir IslamОценок пока нет
- FR MomentumДокумент22 страницыFR MomentumJanel Edwards0% (1)
- General Physics Worksheet For Freshman UnityДокумент3 страницыGeneral Physics Worksheet For Freshman UnityZiyad MohammedОценок пока нет
- Ejercicios de Practica Del Capítulo 6pДокумент5 страницEjercicios de Practica Del Capítulo 6pAbdul singhОценок пока нет
- hw7 ch8Документ8 страницhw7 ch8faisalphyОценок пока нет
- Work and EnergyДокумент124 страницыWork and Energyjack100% (1)
- Tutorial 4Документ4 страницыTutorial 4Farah HananiОценок пока нет
- Mechanics Periodic T2W7 SolvedДокумент13 страницMechanics Periodic T2W7 SolvedigoraketaОценок пока нет
- Newton'S Laws of Motion: Worksheet No.Документ3 страницыNewton'S Laws of Motion: Worksheet No.EUGENE ABULOC100% (1)
- Problem 1) : Homework No. 3 Instructor: Ali BakhshiДокумент4 страницыProblem 1) : Homework No. 3 Instructor: Ali Bakhshiplamss asawdОценок пока нет
- UP HW CH 8Документ5 страницUP HW CH 8Kent Benedict CabucosОценок пока нет
- MecДокумент2 страницыMecsiddharth yadavОценок пока нет
- Physics I ProblemsДокумент1 страницаPhysics I ProblemsbosschellenОценок пока нет
- Tutorial 1: Energy and Momentum Methods of Particle: Applied Mechanics II, Ramesh Khanal, Nepal Engineering College, 2016Документ5 страницTutorial 1: Energy and Momentum Methods of Particle: Applied Mechanics II, Ramesh Khanal, Nepal Engineering College, 2016Romharsh OliОценок пока нет
- Qns For End TermДокумент8 страницQns For End TermNilesh Tanna TannaОценок пока нет
- TB Chapter7 PDFДокумент24 страницыTB Chapter7 PDFAsmaa AhmedОценок пока нет
- Phys10 Chap7 PotentialEnergy&ConservationДокумент14 страницPhys10 Chap7 PotentialEnergy&ConservationRomeo RualesОценок пока нет
- PHYS1020 Practice Test 2 SolutionsДокумент10 страницPHYS1020 Practice Test 2 SolutionsAaisha SiddiquiОценок пока нет
- Lecture 6B - Work and Energy Part 2Документ38 страницLecture 6B - Work and Energy Part 2Mark Alexis AtesorОценок пока нет
- Correl 2 Until MidtermsДокумент23 страницыCorrel 2 Until MidtermsKimberly TacaisanОценок пока нет
- Phy094 Tutorial 9 QДокумент2 страницыPhy094 Tutorial 9 Qhafiz_yusoff1620Оценок пока нет
- Ch8 Review Problems NewДокумент6 страницCh8 Review Problems NewVic VanceОценок пока нет
- Problem Set2 PDFДокумент1 страницаProblem Set2 PDFMr. DummyОценок пока нет
- Applications of Newton's Second Law (Dynamics) : Toboggan Down A Hill (Modified)Документ2 страницыApplications of Newton's Second Law (Dynamics) : Toboggan Down A Hill (Modified)Elma AsagraОценок пока нет
- DynamicsДокумент4 страницыDynamicsSyed ShaulОценок пока нет
- CL4Документ2 страницыCL4Harvey BautistaОценок пока нет
- Kinetics of A Particle - Force and AccelerationДокумент14 страницKinetics of A Particle - Force and AccelerationMeryl RodriguezОценок пока нет
- 4.1.1a TestДокумент31 страница4.1.1a TestutheinsweОценок пока нет
- Examples MomentumДокумент9 страницExamples Momentumettypasewang0% (1)
- Physics Open Yale Course Final ExamДокумент5 страницPhysics Open Yale Course Final ExamScribiPnogОценок пока нет
- Tut Test 4 MemoДокумент8 страницTut Test 4 MemoVogelОценок пока нет
- Homework CH 6Документ2 страницыHomework CH 6Bader Al-AneziОценок пока нет
- Rev2, ENGR 62, StanfordДокумент40 страницRev2, ENGR 62, StanfordsuudsfiinОценок пока нет
- Probset1 PDFДокумент3 страницыProbset1 PDFLee TalierОценок пока нет
- NLM Subjective Problems-SP-NPJC 1-June 13Документ19 страницNLM Subjective Problems-SP-NPJC 1-June 13Mohit GargОценок пока нет
- Assignment 3 PDFДокумент3 страницыAssignment 3 PDFAhmed AttallaОценок пока нет
- TUTORIAL 3 (Kinetics of Particles)Документ6 страницTUTORIAL 3 (Kinetics of Particles)Hareez FarhanОценок пока нет
- Module 10 Dynamics With Problems BoardДокумент33 страницыModule 10 Dynamics With Problems Boardjose santiagoОценок пока нет
- Topic C: Energy - Examples SPRING 2014: V V V V e 0.0 e 0.5 e 1.0Документ9 страницTopic C: Energy - Examples SPRING 2014: V V V V e 0.0 e 0.5 e 1.0ettypasewangОценок пока нет
- Work, Power & Energy (Question)Документ4 страницыWork, Power & Energy (Question)Harika NKОценок пока нет
- Water Temperature: 298K Density: 1000kg/m 3 Viscosity: 0.91 CP 0.00091N.s/m 2 Test Section Diameter: 10.25 MM 0.01025m Area (M) : 0.008252m 2Документ3 страницыWater Temperature: 298K Density: 1000kg/m 3 Viscosity: 0.91 CP 0.00091N.s/m 2 Test Section Diameter: 10.25 MM 0.01025m Area (M) : 0.008252m 2AfifaFarooqОценок пока нет
- Problems - Chapter 29Документ9 страницProblems - Chapter 29AfifaFarooqОценок пока нет
- Practice - Chapter 30Документ7 страницPractice - Chapter 30AfifaFarooqОценок пока нет
- Hydrogen Sulfide StudyДокумент77 страницHydrogen Sulfide StudyAfifaFarooqОценок пока нет
- CHM 217-All Experiments Solution PDFДокумент51 страницаCHM 217-All Experiments Solution PDFAhmad AbdelhakОценок пока нет
- Chicken Corn SoupДокумент2 страницыChicken Corn SoupAfifaFarooqОценок пока нет
- ReferenceДокумент1 страницаReferenceAfifaFarooqОценок пока нет
- Practice # 8Документ9 страницPractice # 8AfifaFarooqОценок пока нет
- HW#2 Textbook QuestionsДокумент4 страницыHW#2 Textbook QuestionsAfifaFarooqОценок пока нет
- Department of Mathematics and Statistics American University of Sharjah Second Midterm Exam - Spring 2012 MTH 221 - Linear AlgebraДокумент8 страницDepartment of Mathematics and Statistics American University of Sharjah Second Midterm Exam - Spring 2012 MTH 221 - Linear AlgebraAfifaFarooqОценок пока нет
- Further Reading: Zenger, J., & Folkman, J. (2012) - Why Invest in LD? Leadership Excellence, 29 (9), 13. Retrieved FromДокумент1 страницаFurther Reading: Zenger, J., & Folkman, J. (2012) - Why Invest in LD? Leadership Excellence, 29 (9), 13. Retrieved FromAfifaFarooqОценок пока нет
- Inventor. (Online) - Available: National Pollutant InventoryДокумент1 страницаInventor. (Online) - Available: National Pollutant InventoryAfifaFarooqОценок пока нет
- Practice 1-Chapter 22Документ2 страницыPractice 1-Chapter 22AfifaFarooqОценок пока нет
- Coordinate System For Tactical MissilesДокумент20 страницCoordinate System For Tactical MissilesD.ViswanathОценок пока нет
- Forms of Electromagnetic Waves and The em SpectrumДокумент6 страницForms of Electromagnetic Waves and The em SpectrumMicah TormonОценок пока нет
- Sma 2322 Fluid Mechanics 1Документ2 страницыSma 2322 Fluid Mechanics 1xtnnjrОценок пока нет
- Force and Laws of MotionДокумент9 страницForce and Laws of MotionsamaОценок пока нет
- Experiment 4: Work, Power and Energy Laboratory ReportДокумент4 страницыExperiment 4: Work, Power and Energy Laboratory ReportRamnuj Orecul SoralcОценок пока нет
- Micro-Nano-Scale Mechanics PDFДокумент48 страницMicro-Nano-Scale Mechanics PDFM.ThirunavukkarasuОценок пока нет
- Drag On A Circular Cylinder: Instructed byДокумент12 страницDrag On A Circular Cylinder: Instructed byKasun Weerasekara100% (1)
- Science 7 Q3 W1Документ12 страницScience 7 Q3 W1Syed FlyntОценок пока нет
- Powell TH Vortex SoundДокумент19 страницPowell TH Vortex SoundAbraham Benjamin BrittoОценок пока нет
- Practical Experiment No. 5: Brewster Angle Determination Physics LabДокумент3 страницыPractical Experiment No. 5: Brewster Angle Determination Physics LabAnirudh SharmaОценок пока нет
- 2011-Using Vibration Signatures Analysis To Detect Cavitation in Centrifugal PumpsДокумент9 страниц2011-Using Vibration Signatures Analysis To Detect Cavitation in Centrifugal Pumpsmortazavi.technicalОценок пока нет
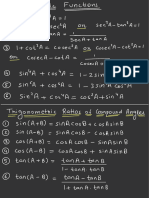
- Trigonometric FormulasДокумент5 страницTrigonometric Formulasanshumansingh042006Оценок пока нет
- Chapter Test A: Teacher Notes and Answers SoundДокумент5 страницChapter Test A: Teacher Notes and Answers SoundWengОценок пока нет
- WavesДокумент160 страницWavesrussell_mahmood0% (1)
- Photo-Electric Effect-Theory & Examples Module-6Документ10 страницPhoto-Electric Effect-Theory & Examples Module-6Raju SinghОценок пока нет
- Winglet Design and Analysis For Low-Altitude Solar Powered UAV PDFДокумент24 страницыWinglet Design and Analysis For Low-Altitude Solar Powered UAV PDFAdit 0110Оценок пока нет
- 09 Fluid Mechanics and Hydraulic Machineries - IДокумент39 страниц09 Fluid Mechanics and Hydraulic Machineries - IManoj PokharelОценок пока нет
- IB PHYSICS 2.2 Forces Presentation All UnitДокумент65 страницIB PHYSICS 2.2 Forces Presentation All UnitJustCallMeLarryОценок пока нет
- Work, Energy and Power-1Документ32 страницыWork, Energy and Power-1Ian HaroldОценок пока нет
- 10th Science (EM)Документ360 страниц10th Science (EM)Murali MohanОценок пока нет
- 5 Sets Model Questions of PhysicsДокумент27 страниц5 Sets Model Questions of Physicsdast DonОценок пока нет
- Answer Sheets - GENERAL PHYSICS 1 - Quarter 2 - Module 1 Rotational Equilibrium and Rotational DynamicsДокумент7 страницAnswer Sheets - GENERAL PHYSICS 1 - Quarter 2 - Module 1 Rotational Equilibrium and Rotational DynamicsJan Lloyd Daquiado GabridoОценок пока нет
- Transonic Design Doc PDFДокумент152 страницыTransonic Design Doc PDFAnkur BhatnagarОценок пока нет
- Relative Velocity - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaДокумент6 страницRelative Velocity - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaZaw Moe KhineОценок пока нет
- S6 Q4 Week-4Документ7 страницS6 Q4 Week-4Zygfred Zain IberoОценок пока нет
- Work Study, Time StudyДокумент21 страницаWork Study, Time StudyShashank SrivastavaОценок пока нет
- Misconceptions About Gyroscopic StabilizationДокумент8 страницMisconceptions About Gyroscopic StabilizationAgniva BhattacharyaОценок пока нет
- Sound and ResonanceДокумент12 страницSound and ResonanceHeart SoulОценок пока нет
- 0625-IGCSE-Formula-List (1) - 1Документ1 страница0625-IGCSE-Formula-List (1) - 1PutorialsОценок пока нет
- BCS & Bank MCQ + Written Math. Speed.16.09.2017Документ38 страницBCS & Bank MCQ + Written Math. Speed.16.09.2017Tareq Anwar Shishir100% (1)