Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Hormones and What They Do
Загружено:
Michal GailОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Hormones and What They Do
Загружено:
Michal GailАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
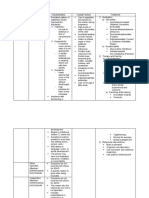
HORMONES
ANTERIOR PITUITARY HORMONES
Human growth hormone (hGH) /
Somatotropin
Thyroid-stimulating hormone
(TSH) / Thyrotropin
Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH)
Luteinizing hormone (LH)
Prolactin (PRL)
Adrenocorticotropic hormone
(ACTH) / Corticotropin
Melanocyte-stimulating hormone
(MSH)
POSTERIOR PITUITARY HORMONES
Oxytocin (OT)
Antidiuretic hormone (ADH) /
Vasopressin
THYROID GLAND HORMONES
T3 (Triiodothyronine) and T4
(Thyroxine) / Thyroid hormones
from follicular cells
PRINCIPAL ACTIONS
Stimulates liver, muscle, cartilage, bone,
and other tissues to synthesize and
secrete insulinlike growth factors (IGFs);
IGFs promote growth of body cells,
protein synthesize, tissue repair,
lipolysis, and elevation of blood glucose
concentration.
Stimulates synthesis and secretion of
thyroid hormones by thyroid gland.
In females, initiates development of
oocytes and induces ovarian secretion of
estrogen. In males, stimulates testes to
produce sperm.
In females, stimulates secretion of
estrogens and progesterone, ovulation,
and formation of corpus luteum. In
males, stimulates testes to produce
testosterone.
Together with other hormones, promotes
milk production by mammary glands.
Stimulates secretion of glucocorticoids
(mainly cortisol) by adrenal cortex.
Exact role in humans is unknown but
many influence brain activity; when
present in excess, can cause darkening
of skin.
Stimulates contraction of smooth muscle
cells of uterus during childbirth;
stimulates contraction of myoepithelial
cells in mammary glands to cause milk
ejection.
Converses body water by decreasing
urine volume; decreases water loss
through perspiration; raises blood
pressure by constricting arterioles.
Increase basal metabolic rate; stimulate
synthesis of proteins; increase use of
glucose and fatty acids for ATP
production; increase lipolysis; enhance
Calcitonin (CT) from parafollicular
cells
PARATHYROID GLAND HORMONE
Parathyroid hormone (PTH) from
chief cells
ADRENAL CORTEX HORMONES
Mineralocorticoids (mainly
aldosterone) from zona
glomerulosa cells
Glucocorticoids (mainly cortisol)
from zona fasciculate cells
Androgens (mainly
dehydroepiandrosterone, or
DHEA) from zona reticularis cells
ADRENAL MEDULLA HORMONES
Epinephrine and norepinephrine
from chromaffin cells
PANCREATIC ISLET HORMONES
Glucagon from alpha cells of
pancreatic islets
Insulin from beta cells of
pancreatic islets
cholesterol excretion; accelerate body
growth; contribute to development of
nervous system.
Lowers blood levels of Ca2+ and HPO42- by
inhibiting bone resorption by osteoclasts
and by accelerating uptake of calcium
and phosphates into bone extracellular
matrix.
Increases blood Ca2+ and Mg 2+ levels
and decreases blood HPO42- level;
increases bone resorption by
osteoclasts; increases Ca2+ reabsorption
and HPO42- excretion by kidneys;
promotes formation of calcitriol (active
form of vitamin D), which increases rate
of dietary CA2+ and Mg2+ absorption
Increase blod levels of Na+ and water;
decrease blood level of K+.
Increase protein breakdown (except in
liver), stimulate gluconeogenesis and
lipolysis, provide resistance to stress,
dampen inflammation, depress immune
responses.
Assist in early growth of axillary and
pubic hair in both sexes; in females,
contribute to libido and are source of
estrogens after menopause.
Enhance effects of sympathetic division
of autonomic nervous system (ANS)
during stress.
Raises blood glucose level by
accelerating breakdown of glycogen into
glucose in liver (glycogenolysis),
converting other nutrients into glucose
in liver (glyconeogenesis), and releasing
glucose into blood.
Lowers blood glucose level by
accelerating transport of glucose into
cells, converting glucose into glycogen
(glycogenesis), and decreasing
Somatostatin from delta cells of
pancreatic islets
Pancreatic polypeptide from F
cells of pancreatic islets
OVARIAN HORMONES
Estrogens and progesterone
Relaxin
Inhibin
TESTICULAR HORMONES
Testosterone
Inhibin
HORMONES PRODUCED BY THE
GASTROINTESTINAL TRACT
Gastrin
Glucose-dependent insulinotropic
peptide (GIP)
Secretin
Cholecystokinin (CCK)
HORMONES PRODUCED BY THE
PLACENTA
Human chorionic gonadotropin
(hCG)
glycogenolysis and gluconeogenesis;
increases lipogenesis and stimulates
protein synthesis.
Inhibits secretion of insulin and
glucagon; slows absorption of nutrients
from gastrointestinal tract.
Inhibits somatosecretion, gallbladder
contraction, and secretion of pancreatic
digestive enzymes.
Together with gonadotropic hormones of
anterior pituitary, regulate female
reproductive cycle and oogenesis,
maintain pregnancy, prepare mammary
glands for lactation, and promote
development and maintenance of female
secondary sex characteristics.
Increases flexability of pubic symphisis
during pregnancy; helps dilate uterine
cervix during labor and delivery.
Inihibits secretion of FSH from anterior
pituitary.
Stimulates descent of testes before
birth; regulates spermatogenesis;
promotes development and maintenance
of male secondary sex characteristics.
Inhibits secretion of FSH from anterior
pituitary.
Promotes secretion of gastric juice;
increases movements of the stomach.
Stimulates release of insulin by
pancreatic beta cells.
Stimulates secretion of pancreatic juice
and bile.
Stimulates secretion of pancreatic juice;
regulates release of bile from
gallbladder; causes feeling of fullness
after eating.
Stimulates corpus luteum in ovary to
continue production of estrogens and
Estrogen and progesterone
Human chorionic
somatomammotropin (hCS)
HORMONES PRODUCED BY THE KIDNEYS
Renin
Erythropoietin (EPO)
Calcitriol* (active form of vitamin
D)
HORMONE PRODUCED BY THE HEART
Atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP)
HORMONE PRODUCED BY THE ADIPOSE
TISSUE
Leptin
progesterone to maintain pregnancy.
Maintain pregnancy; help prepare
mammary glands to secrete milk.
Stimulates development of mammary
glands for lactation.
Part of reaction sequence that raises
blood pressur by bringing about
vasoconstriction and secretion of
aldosterone.
Increases rate of red blood cell
formation.
Aids in absorption of dietary calcium and
phosphorus.
Decreases blood pressure.
Suppresses appetite; may increase FSH
and LH activity.
Reference:
Tortora, G., & Derrickson, B. (2011). Principle of Anatomy & Physiology (13th ed.,
Vol. 1). New Jersey:
John Wiley & Sons.
Вам также может понравиться
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (121)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (266)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (399)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5794)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2259)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (895)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- Harry Stack SullivanДокумент4 страницыHarry Stack SullivanMichal Gail100% (1)
- Cushings Addisons and Acromegaly EdДокумент45 страницCushings Addisons and Acromegaly Edsamehseef100% (1)
- Hard To Find Glossary Oct 2001 PDFДокумент727 страницHard To Find Glossary Oct 2001 PDFCristiano Manzzini50% (2)
- MAIS 615 - Assignment #3 Making Sense of The BrainДокумент14 страницMAIS 615 - Assignment #3 Making Sense of The BrainShelly LasichukОценок пока нет
- 002367889dissecting The USMLE - BookmarkedДокумент629 страниц002367889dissecting The USMLE - BookmarkedPharAway100% (6)
- Elements of A Short StoryДокумент5 страницElements of A Short StoryMichal GailОценок пока нет
- MCQ On EndocrinologyДокумент19 страницMCQ On Endocrinologyolayemi mariam0% (1)
- Cortisol ARCДокумент7 страницCortisol ARCilc67123100% (1)
- Biochemistry Basic Science MCQsДокумент26 страницBiochemistry Basic Science MCQsSidharta Chatterjee50% (2)
- 1.5-DOH Reviewer & Examination-NurseДокумент111 страниц1.5-DOH Reviewer & Examination-NurseRoger CarpisoОценок пока нет
- Effects of Electromagnetic Forces of Earth On HumansДокумент6 страницEffects of Electromagnetic Forces of Earth On HumansArtist MetuОценок пока нет
- Stroop EffectДокумент15 страницStroop EffectMichal GailОценок пока нет
- Multiple-Choice Questions: Chapter 45 Hormones and The Endocrine SystemДокумент15 страницMultiple-Choice Questions: Chapter 45 Hormones and The Endocrine SystemshasagailОценок пока нет
- Demonstration or Showing MethodДокумент1 страницаDemonstration or Showing MethodMichal GailОценок пока нет
- Psychoanalytic Theory CritiqueДокумент1 страницаPsychoanalytic Theory CritiqueMichal GailОценок пока нет
- Theory X and Theory yДокумент14 страницTheory X and Theory yMichal GailОценок пока нет
- Virtual Reality TherapyДокумент2 страницыVirtual Reality TherapyMichal GailОценок пока нет
- ADHDДокумент2 страницыADHDMichal GailОценок пока нет
- Chap3 TestДокумент4 страницыChap3 TestMichal GailОценок пока нет
- Harry Stack Sullivan's Interpersonal TheoryДокумент1 страницаHarry Stack Sullivan's Interpersonal TheoryMichal GailОценок пока нет
- Table TennisДокумент6 страницTable TennisMichal GailОценок пока нет
- Pertemuan 2. Gupta2019Документ28 страницPertemuan 2. Gupta2019MuliasariОценок пока нет
- Frontiers in Neuroendocrinology: SciencedirectДокумент15 страницFrontiers in Neuroendocrinology: SciencedirectFrancisco Javier Luza RamosОценок пока нет
- CHAPTER 10-ReviwerДокумент5 страницCHAPTER 10-ReviwerPhilline ReyesОценок пока нет
- Chemical Coordination and IntegrationДокумент7 страницChemical Coordination and IntegrationAnonymous -Оценок пока нет
- Endo Diseases Oralrev Part IДокумент28 страницEndo Diseases Oralrev Part IRafi AcostaОценок пока нет
- Quiz LetДокумент16 страницQuiz LetMohamed Y AbdallahОценок пока нет
- Endocrinology: Differences Between Nervous and Endocrine SystemДокумент34 страницыEndocrinology: Differences Between Nervous and Endocrine SystemRezaul RazibОценок пока нет
- Chronic Stress and Suicidal Thinking Among Medical Students: Environmental Research and Public HealthДокумент16 страницChronic Stress and Suicidal Thinking Among Medical Students: Environmental Research and Public Healthmuhammad_hanis97Оценок пока нет
- History - CushingДокумент6 страницHistory - CushingNur FadzreenaОценок пока нет
- Glucocorticoid Therapy and Adrenal SuppressionДокумент8 страницGlucocorticoid Therapy and Adrenal SuppressionFan AccountОценок пока нет
- Residency Exam JustДокумент19 страницResidency Exam JustOmar Nayef TaaniОценок пока нет
- IVMS Physiology and Pathophysiology Flash FactsДокумент4 648 страницIVMS Physiology and Pathophysiology Flash FactsMarc Imhotep Cray, M.D.Оценок пока нет
- Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology 6th Edition Scanlon Test BankДокумент15 страницEssentials of Anatomy and Physiology 6th Edition Scanlon Test Bankamitydairyzy100% (28)
- All DrugsДокумент482 страницыAll DrugsJessica IbañezОценок пока нет
- What Is Adrenal InsufficiencyДокумент17 страницWhat Is Adrenal InsufficiencygammuacОценок пока нет
- Addison's DiseaseДокумент6 страницAddison's DiseaseMontasir AhmedОценок пока нет
- The Entire Endocrinology Lectures Set PDFДокумент385 страницThe Entire Endocrinology Lectures Set PDFoakley bartОценок пока нет
- ACTHДокумент4 страницыACTHHassan GillОценок пока нет
- The Endocrinopathies of Anorexia NervosaДокумент13 страницThe Endocrinopathies of Anorexia NervosaCarla MesquitaОценок пока нет
- Sahebkar Panahi 21072017 Proof PDFДокумент16 страницSahebkar Panahi 21072017 Proof PDFJulius PalmaОценок пока нет