Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
TET 4115 - 2015 Assignment 10
Загружено:
eh2asham1Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
TET 4115 - 2015 Assignment 10
Загружено:
eh2asham1Авторское право:
Доступные форматы
Faculty of Information Technology, Mathematics and Electrical Engineering
Department of Electric Power Engineering
Power Systems Group
TET 4115: Power System Analysis, FALL 2015
Assignment 10
(Based on Lectures 3, 4 and 5 of the Protection System Part)
Released: 02 November 2015
Guidance: 09 November 2015
Submission deadline: 16 November 2015
Task 1. Over-current protection
Objective: Learn about over-current relay coordination
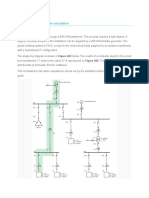
Given the 22 kV distribution system with two feeders shown in Fig. 1. The source
impedance, including the main transformer, is 0.5+j2 ohms referred to the 22 kV side.
Fig. 1 Configuration
a) Calculate the load impedance ZL2 and ZL3 assuming constant impedance load and the
given load flow data.
b) Calculate the load-current seen from relay R1
TET4115: Power System Analysis, 2015.
i)
Using a simplified analysis assuming 1 pu voltage profile
ii)
Using the provided load flow data
Compare and comment the result. Is the load situation worst case?
c) Calculate the 3-phase fault current for faults on bus 1 to 4. Scale to 2-phase faults by
3 /2.
d) What should the time-coordination be between relays R0, R1 and R2? What is the
purpose of this time-coordination?
e) Define fixed time delays and starting currents for relay R0, R1 and R2.
f) Why do we also need instantaneous over-current relays? Suggest an instantaneous
starting-current for relay R1.
Task 2 Distance protection
Objective: Learn about RX-diagrams and plotting of fault currents and load
currents related to distance protection zones.
For simplicity given the same power system as in task 1, where we now want to study
distance protection.
a) Calculate the load impedance seen from the relay R1.
b) Calculate the 3-phase fault impedance for faults on Bus 2 and 4.
c)
Plot an RX-diagram for the impedance seen for relay R1. In this diagram also plot
i) The line representing the impedance of the line Z1
ii) The load current found in Task 1. b ii)
iii) The 3-phase fault current for faults on Bus 2 and 4.
d) Suggest zone 1, 2 and 3 of protection for the distance relay R1.
TET4115: Power System Analysis, 2015.
Task 3 Ground fault protection
Objective: Learn about ground-fault currents and protection in isolate neutral
systems.
Assume that the transformer T1 has an isolated neutral on the 22 kV side. Now consider
a ground fault with fault resistance Rf=0.
a) Calculate the total capacitance to ground for the 22 kV system.
b) Calculate the ground fault current (does not depend deeply on fault location).
c) Calculate the zero-sequence voltage at Bus 1.
d) Assume that the fault is on Bus 2. Calculate the zero-sequence current seen by relays
R1 and R4.
e) Draw the zero-sequence currents in a diagram where the zero-sequence voltage at
bus 1 is assumed to be real. Suggest zones of protection for the ground fault.
TET4115: Power System Analysis, 2015.
Cross-check for some of the questions:
Task 1
a) 43.5
b) i) 262.4 A ii) 276.8 7.50 A
c) Three phase fault currents Bus 1: 6.16 kA; Bus 2: 2.95 kA; Bus 3: 0.148 kA; Bus
4: 1.95 kA
d) The coordination-time is typically 0.2-0.3 seconds
e) Hint: Rule of thumb for starting-current 1.5 I L max I S 0.8 I f min
f) One possibility for instantaneous starting current for R1: 4 kA.
Task 2
a) 44.5+j2
b) Bus 2: 1+j2 ; Bus 4: 2.06+j3.91 (including the load impedance)
Task 3
a)
b)
c)
d)
0.3 F
3.59 A
-12.7 kV
In faulty feeder: j1.2 A; In healthy feeder: -j1.2 A
TET4115: Power System Analysis, 2015.
Вам также может понравиться
- TET 4115 - 2015.solution To Assignment 3Документ5 страницTET 4115 - 2015.solution To Assignment 3eh2asham1Оценок пока нет
- TET 4115 - 2015 Solution To Assignment 7Документ4 страницыTET 4115 - 2015 Solution To Assignment 7eh2asham1Оценок пока нет
- TET 4115 - 2015 Solution To Assignment 8Документ5 страницTET 4115 - 2015 Solution To Assignment 8eh2asham1Оценок пока нет
- TET 4115 - 2015 Assignment 2Документ4 страницыTET 4115 - 2015 Assignment 2eh2asham1Оценок пока нет
- TET 4115 - 2015 Assignment 3Документ3 страницыTET 4115 - 2015 Assignment 3eh2asham1Оценок пока нет
- TET 4115 - 2015 Solution To Assignment 6Документ3 страницыTET 4115 - 2015 Solution To Assignment 6eh2asham1Оценок пока нет
- TET 4115 - 2015 Solution 5Документ11 страницTET 4115 - 2015 Solution 5eh2asham1Оценок пока нет
- Solution To Assignment 4 TET 4115 - 2015Документ7 страницSolution To Assignment 4 TET 4115 - 2015eh2asham1Оценок пока нет
- TET 4115 - 2015 Assignment 2Документ4 страницыTET 4115 - 2015 Assignment 2eh2asham1Оценок пока нет
- TET 4115 - 2015 Assignment 8Документ4 страницыTET 4115 - 2015 Assignment 8eh2asham1Оценок пока нет
- Solution 9Документ1 страницаSolution 9eh2asham1Оценок пока нет
- TET 4115 - 2015 Assignment 3Документ3 страницыTET 4115 - 2015 Assignment 3eh2asham1Оценок пока нет
- TET 4115 - 2015 Assignment 2Документ4 страницыTET 4115 - 2015 Assignment 2eh2asham1Оценок пока нет
- TET 4115 - 2015 Assignment 2Документ4 страницыTET 4115 - 2015 Assignment 2eh2asham1Оценок пока нет
- TET 4115 - 2015 Assignment 2Документ4 страницыTET 4115 - 2015 Assignment 2eh2asham1Оценок пока нет
- Fundamentals of Electromagnetics With Matlab - Lonngren & SavovДокумент699 страницFundamentals of Electromagnetics With Matlab - Lonngren & SavovFirass Mckey100% (1)
- TET 4115 - 2015 Assignment 2Документ4 страницыTET 4115 - 2015 Assignment 2eh2asham1Оценок пока нет
- TET 4115 - 2015 Assignment 1Документ2 страницыTET 4115 - 2015 Assignment 1eh2asham1Оценок пока нет
- Chapter 9 (Magnetization)Документ3 страницыChapter 9 (Magnetization)eh2asham1Оценок пока нет
- Exercise 9Документ2 страницыExercise 9eh2asham1Оценок пока нет
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5794)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (890)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (344)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (265)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2219)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (119)
- Homework8 Solution PDFДокумент5 страницHomework8 Solution PDFDean WinchesterОценок пока нет
- S Ramp CalculationsДокумент4 страницыS Ramp CalculationsRonald PeetersОценок пока нет
- Problems Based On Newton's First Law of Motion Basic LevelДокумент14 страницProblems Based On Newton's First Law of Motion Basic LevelRahul KumarОценок пока нет
- FE Preparation Material 2Документ9 страницFE Preparation Material 2mssaber77Оценок пока нет
- Determination of Ten Percent Fines ValueДокумент6 страницDetermination of Ten Percent Fines ValueMd Tanvir Haider 191-47-915Оценок пока нет
- CVIE3400 Open Channel Hydraulics Saint-Venant EquationsДокумент3 страницыCVIE3400 Open Channel Hydraulics Saint-Venant EquationsTưMãОценок пока нет
- Cable Spacing As A Means of Noise Mitigation - EEPДокумент5 страницCable Spacing As A Means of Noise Mitigation - EEPmahmoud fawzyОценок пока нет
- Melc 1 Applying Quality Standards AqsДокумент29 страницMelc 1 Applying Quality Standards AqsRicky BalceОценок пока нет
- Homemade Electric Motor: I. PurposeДокумент4 страницыHomemade Electric Motor: I. PurposedmejiagaОценок пока нет
- Specific Charge of The Electron - E/m: (Item No.: P2510200)Документ5 страницSpecific Charge of The Electron - E/m: (Item No.: P2510200)Camila Diaz BОценок пока нет
- QuestionsДокумент5 страницQuestionsHarshin MohanОценок пока нет
- High Efficiency Motors Type 2 Coordination Motor Starting - NHPTNL74-IndДокумент8 страницHigh Efficiency Motors Type 2 Coordination Motor Starting - NHPTNL74-IndsimranОценок пока нет
- Reflections and New Directions in Sprinting and HurdlingДокумент25 страницReflections and New Directions in Sprinting and HurdlingFagaras Moni67% (3)
- SJ 155Документ3 страницыSJ 155wendyОценок пока нет
- Cable Calculations Worked Examples.Документ337 страницCable Calculations Worked Examples.Shijumon KpОценок пока нет
- Save My Exams (Physics Notes) - Work, Energy & PowerДокумент38 страницSave My Exams (Physics Notes) - Work, Energy & Powervihaan.nemaniОценок пока нет
- A parallel combination of 𝑅 = 2Ω, L = 1H and C = 1F is connected across a current source 𝐼 = 10𝐴 through a switch. Determine 𝑣 0, 0 𝑎𝑛𝑑 (0) - Given i (0) =0Документ2 страницыA parallel combination of 𝑅 = 2Ω, L = 1H and C = 1F is connected across a current source 𝐼 = 10𝐴 through a switch. Determine 𝑣 0, 0 𝑎𝑛𝑑 (0) - Given i (0) =0Effecure HealthcareОценок пока нет
- EERC-82-09 Fluid-Structure Interactions Added Mass Computations For Incompressible FluidДокумент126 страницEERC-82-09 Fluid-Structure Interactions Added Mass Computations For Incompressible FluidBMWrider1453Оценок пока нет
- MODULE 1 - LES #1 Force SystemДокумент13 страницMODULE 1 - LES #1 Force SystemJake BarettoОценок пока нет
- Lab 2 - Nodal and Mesh AnalysisДокумент1 страницаLab 2 - Nodal and Mesh AnalysisHung NguyênОценок пока нет
- Dynamics PDFДокумент35 страницDynamics PDFLukeman IssahОценок пока нет
- Project ProposalДокумент6 страницProject Proposaloscar100% (2)
- S.C Calculations: Short Circuit StudyДокумент17 страницS.C Calculations: Short Circuit StudyAhmedRaafatОценок пока нет
- A Train Travelling at 40 M / S Takes 2.0 S To Pass The Man. What Is The Length of The Train? M MC 40 MD 80 MДокумент4 страницыA Train Travelling at 40 M / S Takes 2.0 S To Pass The Man. What Is The Length of The Train? M MC 40 MD 80 MDaniel CannywoodОценок пока нет
- Circuit Theory Experiment 2 Lab Report DONE Jen HahnДокумент10 страницCircuit Theory Experiment 2 Lab Report DONE Jen HahnPei Ing100% (1)
- IEC 61643 31 2018 Low Voltage Surge Protective Devices Part 31 Requirements and Test Methods For SPDs For Photovoltaic Installations PDFДокумент112 страницIEC 61643 31 2018 Low Voltage Surge Protective Devices Part 31 Requirements and Test Methods For SPDs For Photovoltaic Installations PDFJefferson PereiraОценок пока нет
- Dokumen - Tips - Physics Module 1 Kinematics Note It It Essential in Kinematics Problems ToДокумент14 страницDokumen - Tips - Physics Module 1 Kinematics Note It It Essential in Kinematics Problems ToTaha Kafil-Hussain100% (2)
- Calculation of PCB Track ImpedanceДокумент6 страницCalculation of PCB Track ImpedanceDurbha RaviОценок пока нет