Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Obstetric and Clinical Medicine - Gynaecological History and Examination
Загружено:
Shahin KazemzadehАвторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Obstetric and Clinical Medicine - Gynaecological History and Examination
Загружено:
Shahin KazemzadehАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
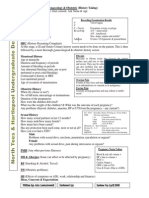
OBSTETRICS AND GYNAECOLOGY
Richard Shaw
Obstetric and Gynaecological History
Formalities
Wash Hands
Introduction - name, age, consent, confidentiality
History of Presenting Complaint
Open Questioning SOCRATES and specific
differential questioning.
o Associated Symptoms
screen for bladder/bowel issues,
vaginal or other orifice discharges
screen for depression (sadness
etc)
Current Pregnancy
o Duration
LMP and EDD from USS
Ngele's Rule: +1 yr, +7d, -3m
How/When did you find out?
o Symptoms
Abnormal
Per vaginal bleeding,
pain/cramps,
dyspareunia
Normal
Fatigue, nausea, vomiting,
urinary frequency, breast
tenderness, constipation,
fluid retention, backache,
weight gain, cravings,
fetal movements after
20w
o Antenatal Care (See Antenatal Visit
Specifics)
USS
18w morphology scan
Vaccinations
MMR
Varicella
Screening Test
Antenatal blood tests
Nuchal Translucency
CVS
Amniocentesis
o Partner
Do you have a partner?
Are they the father?
Was the pregnancy planned?
Was it conceived naturally?
Plans for the future?
Risk Factor Questioning
Specific risk factors to help DDx
Smoking, Alcohol, IDU etc
Menstrual History
Cycle
o Typical cycle length
o Regularity of cycles 21-35d
Bleeding
o 1st day of LMP and duration of menses
3-7d
o Flow
No. pads/tampons used in a day
4/5
Ever needed to double-up?
>80mL/period = heavy
Any flooding or clots?
Post-coital or intermenstrual
bleeding?
Menarche/Menopause ?ranges?
Associated Symptoms
o Primary vs Secondary Dysmenorrhoea
(timing)
o PMS
Obstetric History
Gravidity and Parity (= births >20/52)
o When were these pregnancies?
o Gestations (TermPremAbortLiving/GxPx systems)
o Fetal Outcomes
Ectopics, miscarriages (gestation
at miscarriage) , terminations,
normal birth
o Length of labour
Induced or spontaneous
o Delivery types and fetal presentations
o Sex and birthweight of babies
o Complications (ante, peri, postnatally)
Bleeding, infection, other?
Sexual History
Initial framing question - why and consent.
Are you sexually active?
o No have you ever been sexually active?
o Yes How long have you been sexually
active for? When did you last have a sexual
encounter with someone?
Practices
o Oral, Anal, Vaginal?
o Who does what? Insertive/Receptive,
Ejaculation?
o Do you have sex with men, women or both?
Partner
o Regular or casual?
type of relationship and duration
o Male or female partner? Similar symptoms?
OBSTETRICS AND GYNAECOLOGY
Partner risk assessment
Ethnicity, IDU, Sex workers?
o How many sexual partners have you had
in last 12 months? Male/Female/Both?
o Any sex worker/overseas local contact?
Travel?
o Are you happy with your relationship?
Protection from Pregnancy
o Are you using any form of protection or
contraception?
o Condom
% of times used
When is it put on/taken off?
When did you last have sex
without one?
o Contraceptive devices or medications?
o Are you concerned about getting
pregnant/your partner pregnant?*
o When did you last have unprotected sex?
Protection from STI's
o Have you or your partners ever had an STI?
When? Diagnosis? Treatment?
Partner?
o Ever been screened for HIV or other STIs?
Would you like to be screened?
o Have you or your partners ever injected
drugs?
o Vaccinations? Hep B, HPV, Hep A (for MSM
only)
Is there anything about your current sex life you
are concerned about?
Have you ever been sexually abused or the subject
of domestic violence?
Gynaecological History
Contraception
o Type of contraceptive being taken and
why?
o Are you happy with your current
contraception?
o Planning on having a family in the future?
o COCP
Type/brand, dose
Variation in times taken.
Frequency of missed pills
S/E's and physiological impacts
STIs (5th P of the 5 P's of Sexual History)
o Gonorrhoea, Chlamydia, Syphilis, HIV,
Herpes, HPV, Hepatitis
PIDs
o Salpingitis, endometritis
o
Richard Shaw
Others
o UTIs, Vaginitis, Vulval Dermatitis, Fibroids
etc
Pap Smears
o Last pap smear results
Past Medical/Surgical History
Any surgeries? Gynaecological/Pelvic or otherwise?
Ever required a blood transfusion?
Weight gain/loss?, thyroid disease, epilepsy
DVT, ID-DM, Lung and Heart Disease, H/T,
Jaundice
Medications and Allergies
Drugs
o Prescribed drugs?
o Over the counter drugs?
o Herbs/supplements?
OCP/HRT
Allergies/Drug Allergies
o Penicillin? Latex?
Family History
Any conditions that run in the family?
o Endometriosis, PCOS,
cervical/ovarian/breast/colon cancer
o DM, DVT, H/T, Heart and Lung disease
o Twins in the family?
Timing of menopause in family members if
relevant
Osteoporosis, hirsutism etc as relevant
Psychosocial History
Drugs
o Smoking, Alcohol, Recreational Drugs
Home Supports
o Is there anyone at home to support you?
o Where do you live and what type of
accommodation is it?
o Childcare arrangements?
o Plans for breastfeeding?
Relationship
o Stability?
Education/Employment/Financial WHACS
ADLs and other activities
o Sleep, appetite, micturition, defecation
Exercise/Diet/Community Activities/Other
OBSTETRICS AND GYNAECOLOGY
Richard Shaw
Obstetric and Gynaecological Examinations
Gynaecological Examination
Explain why you want to perform this examination.
Explain what this examination will involve.
Questions to ask beforehand:
o Have you ever had this examination done before?
o Are you currently pregnant?
Can't use brush or combi
o Are you currently on your period?
Makes PV examination difficult
o Have you had any children? Were they vaginal
births?
Alters method of speculum insertion
Would you like someone else to be in the room during the
examination? A chaperone.
Ideally would also ask patient to empty bladder and
bowels beforehand more comfortable examination.
Ensure all equipment is present before starting:
o Speculum
o KY Jelly
o Swabs/Cervical Samplers
Broom and Brush (or Combi)
Brush/Combi not for pregnant women
o Slides and Fixation Spray
Appropriate details must be written on
slide in pencil before beginning
o Lighting
o Gloves
Position and Exposure
Allow patient to undress and put on gown in privacy and
ensure there are plenty of sheets.
Patient supine with legs apart, ankles together and knees
bent (frog-legged position).
Perineum should be brightly illuminated with a lamp.
General Inspection
Mentally alert and orientated
Respiratory distress and/or anxiety
Abdomen (ideally full abdominal examination)
Inspection
Skin quality
Abdominal distension and masses
Scars and Striae
Palpation
Is there pain anywhere in your abdomen? Palpate this area last.
Light Palpation
Deep Palpation
Liver
Spleen
Put on gloves, and re-explain to patient what you intend to do.
Pelvis
Inspection
Pubic hair distribution
Normal anatomy features
o Labia majora
o Labia minora
o Vaginal and urethral openings discharges?
Blood discharge
Menses, cancer, miscarriage,
cervical polyp or erosion
Purulent discharge
Vaginitis, cervicitis,
endometritis, retained
tampon
Physiological discharge
If discharge present, inspect/describe
it, swab it and seal in container.
o Clitoral shape and size
Skin lesions
o Features of thrush or trichomoniasis
Leukoplakia
Redness
Swelling
Excoriation
o Ulceration
o Rashes
o Warts
o Scars
o Sinus openings
Vaginal atrophy (elderly)
Palpation
External genitalia
o Tenderness,
o Lumps and bumps
Bartholin cyst or Abscess
Separate labia and palpate
in posterior part of L. majora
Cough Test
o Stress incontinence
o Cystocoele bulge from anterior
o Rectocoele blge from posterior
o Uterine Prolapse
Cervix (tell patient what you intend to do)
o Put KY Jelly on right index and middle finger
o Separate labia with thumb and forefinger of left
hand and insert right fingers into vagina
OBSTETRICS AND GYNAECOLOGY
o
o
o
o
Position (which way cervix is pointing)
Post (normal), ant or central
Consistency/Surface(nose in nulliparous)
Hard, soft or lumpy
Nabothian cysts
Size, Shape, Mobility
Tenderness
Tactile tenderness
Excitation tenderness
Tender when moved around
External Os
Dilatation/effacement
Fornices
o Anterior, posterior and lateral
Uterus
o Fingers in vagina are kept high up and rotated
to face upwards while left hand presses/rocks
above symphysis (perpendicular to linea alba)
o Fundal height
o Tenderness
Period Pain
Adenomyosis
o Position
Angle between cervix and vagina
Anteversion
Most women, where the
uterus lies on top of the
bladder, pointing
posteroinferiorly
Axial
Uterine lumen is parallel to
vaginal lumen
Retroversion
Majority of uterus lies in
uterorectal pouch rather
than overlying the bladder
o Flexion
Angle between uterine lumen and
cervical canal
Retroflexion
Distal uterus is in normal
position (cervix pointing
posteroinferiorly) but the
body is bent backwards
occupying uterorectal pouch
Anteflexion
Distal portion of uterus is in
normal position but fundus
points anteriorly and
inferiorly. Normal position
o Size
Conveyed as a gravid uterus in weeks
of pregnancy (e.g. 18 week uterus)
Normal size is approximately a fist
o Shape/Surface
Smooth and enlarged
Pregnancy
o
o
Richard Shaw
Adenomyosis
Submucous fibroids
Knobbly
Fibroids
Consistency
Soft pregnancy
Hard fibroids
Mobility
due to adhesions
Masses
Uterine masses move with cervix and
adnexal masses do not
Adnexa
o Turn fingers laterally to each side in turn and
bimanually palpate with left hand
o Attempt to feel for
Fallopian tubes
Broad ligament
Adnexal masses or tenderness
o Ask about tenderness/pain
Withdraw fingers and observe glove for any discharge (+/- smell for
distinctly pungent odour)
Speculum Examination
Warm speculum with warm water during abdominal
examination check temperature on skin
KY jelly can be used but may interfere with some cytology
examinations
Hold speculum with gun grip (handle facing up) and stand
on the right side of the patient - touch speculum to
fourchette (talk to patient the whole way through)
Spread labia with left hand and insert speculum
o Nulliparous - bills parallel to labia
o Multiparous - maybe perpendicular to labia
Turn handle towards ceiling with insertion
o Resistance before complete insertion reached
flexion of vagina as it passes through the pelvic
diaphragm angle speculum more posteriorly
(Warn patient) Open speculum with left hand, visualise
the cervix and lock nut with right hand
Inspection
Vagina
Cervix
o Parity
Nulliparous dot or circle
Multiparous curved line
Pap Smear
Important to get cells samples from
o External cervix (preferably transformation zone)
o Endocervical cells
Remember Pap smear ideal at detected precancerous cells
and cervical cancer detecting sensitivity is only 50%
Do not use brush or combi on a pregnant women
o May rupture the fetal membranes and cause
miscarriage or premature birth
OBSTETRICS AND GYNAECOLOGY
Ensure appropriate details have been written on slide in
pencil beforehand.
With each device:
o Rotate through 360 at the squamous-columnar
junction (transitional zone)
o Remove and sweep across slide twice (one swipe
on each side) (brush roll)
o Fix slide with fixant spray
o If available, put the brush into a thin prep or
short prep container also good when there is
bleeding or discharge
Speculum removal
o Loosen nut
o Keep bill open initially to prevent closure over
the cervix
o Once again rotate the bills back to parallel with
the labia when exiting the introitus
Obstetric Examination
General Inspection
Distress of mother?
Obese
BMI (e.g. height and weight)
BP, HR, Temp.
UA
FHR/CTG
Fetal Movements
Has the baby been moving normally?
o Starts at 18-20 weeks in nulliparous women and
15-17 weeks in multiparous women.
Movements reduce after 36 weeks but should still be
investigated maternal kick chart
Abdominal
Inspection
o Striae
o Linea alba
o Scars
Palpation
o Fundal height (need to know gestation from Hx)
Fundus to pubic symphysis
Most important is increasing height on
serial measurement (until engagement)
12/52 fundus just palpable above
pubic symphysis
20/52 fundus at umbilicus
General rule fundal height is
gestation in weeks from LMP
20-36 weeks +/- 2cm
36-40 weeks +/- 3cm
40 weeks +/- 4cm
o Lie
Relation of fetal long axis to maternal
long axis
Richard Shaw
Left occipito-anterior is most common
position and lie
Longitudinal, Oblique (fetal head in
iliac fossa, usually due to full bladder)
or Transverse
Presentation (Palpable after 26 weeks)
o Fetal part occupying lower segment/pelvis
o Cephalic
Further subdivided by attitude
relationship of fetal head to spine
flexed (best), neutral, extended
o Breech (4%)
Engagement
o "fifths palpable" fraction out of 5
o The fetal head can be palpated bimanually
Both hands placed on imaginary line
between the two ASIS with fingers
pointed inferiorly and medially
Then "ballot" the head between hands
o Usually palpable after 37 weeks
Amniotic Fluid
o "Ballot" the amnion between hands and feel
how tense it is (hands like oven mits)
o Abnormality suspected use USS
o Excess fluid polyhydramnios
o Insufficient fluid oligohydramnios
Uterine Irritability
o Same technique as amniotic fluid palpation but
fingers spread sensitivity to uterine
contractions often an abnormal finding
o Intrauterine growth restriction
Fetal Heart Sounds
o Using Dopper device/Pinar stethoscope
o Like a horse galloping and not the "whooshing"
noise of placental blood flow
o Palpate maternal radial pulse to confirm that
HR found is different to maternal HR
o Fetal HR may undergo decelerations in:
Squeezing of cord
Hypoxia
Cephalic pressure during labour
o Best found over anterior shoulder of fetus
OBSTETRICS AND GYNAECOLOGY
Speculum Examination
Vaginal Examination
Dilatation
Effacement
Position
o Occiput in relation to maternal pelvis
o Assists with finding best location to listen for
fetal heart sounds (over anterior shoulder)
Station
o Level of presenting part in relation to maternal
ischial spines
Bishops Score
o <7 not favourable
o > or = 7 favourable
Richard Shaw
OBSTETRICS AND GYNAECOLOGY
In Addition
Cardiovascular Examination
Respiratory Examination
Breast Examination
Lymph Nodes Examination
Skin Examination
o Oedema
o Spider angioma
o Striae
o Linea nigra
Other examinations as directed by the history
o Oedema of legs
o Reflexes
o Clonus
o Signs of anaemia
Post Partum Assessment
Initial Questioning
What day post partum?
Mode of delivery:
o Caesarean
o Vaginal
o Instrumental
Any perineal trauma sustained at birth?
Passing urine?
Bowels/flatus?
Lochia (PV discharge)
o Blood, mucus, placental tissue
Breasts
Breast or bottle feeding?
Tenderness/redness/cracked nipples?
Educate on mastitis
Antenatal Card
Blood pressure - need BP check with GP
Abnormal LFTs - need repeat
Diabetes - need 75g GTT at 6/52
Ensure appropriate follow-up on discharge
Blood Group
o Does she need anti-D?
Rubella Immunity
o Does she need MMR?
Pap Smear
If not done in past 2 years, need to see GP at 6 weeks
Contraception
Ask about plans
Give options if unsure
Arrange if concerned about patient following up (e.g.
young, multiple unplanned pregnancies)
Can start hormonal contraception ~3-6 weeks post
partum
Examination
BP
Fundus
o Should be firm and below umbilicus
o Perineum if suturing
If 3rd/4th degree tearing, need
referral to pelvic floor clinic
Anything else relevant on history (e.g. complaint of sore
calf muscles)
Richard Shaw
Вам также может понравиться
- Paediatric History and Examination 08092012-2Документ10 страницPaediatric History and Examination 08092012-2Shahin KazemzadehОценок пока нет
- Gynaecological History Taking - Geeky MedicsДокумент6 страницGynaecological History Taking - Geeky MedicsMariam Mohamed100% (1)
- Gynecology - Comprehensive Examination of The Female CheckedДокумент3 страницыGynecology - Comprehensive Examination of The Female CheckedMuhammad AdnanОценок пока нет
- Obstetric Gynaecology Jan 11Документ32 страницыObstetric Gynaecology Jan 11selvie87Оценок пока нет
- Paediatric Examination Handbook 2015Документ66 страницPaediatric Examination Handbook 2015Ulfa Rahmadanti SetiawanОценок пока нет
- Newborn AssessmentДокумент9 страницNewborn AssessmentSusmita HalderОценок пока нет
- 02-History-Taking-In-OBGYN-DrAyman - Copy - PpsДокумент26 страниц02-History-Taking-In-OBGYN-DrAyman - Copy - PpsSworupKhadkaОценок пока нет
- Pediatrics OSCEДокумент3 страницыPediatrics OSCEMoh'd Ghanayem100% (1)
- Gyni History TalkingДокумент61 страницаGyni History TalkingEthiopia TekdemОценок пока нет
- Obstetric History TakingДокумент5 страницObstetric History TakingGirish Waru100% (1)
- Gynaecological History Taking - Geeky MedicsДокумент7 страницGynaecological History Taking - Geeky MedicsJahangir AlamОценок пока нет
- Case Write-Up 1 Obstructive Jaundice With Cholecystitis Secondary To Ampullary TumorДокумент21 страницаCase Write-Up 1 Obstructive Jaundice With Cholecystitis Secondary To Ampullary TumorwhosenahОценок пока нет
- 00 Obs&Gyn Clerkship-1-1Документ9 страниц00 Obs&Gyn Clerkship-1-1samwel daniel100% (1)
- History & Physical Exam in Ob/Gyn: By: - DR AmanuДокумент75 страницHistory & Physical Exam in Ob/Gyn: By: - DR AmanuKåbåñå TürüñåОценок пока нет
- ObsGyn OSCE Notes PDFДокумент52 страницыObsGyn OSCE Notes PDFNorman Ahmad RiyandiОценок пока нет
- Pathology of Female Genital Tract Short NotesДокумент5 страницPathology of Female Genital Tract Short NotesameerabestОценок пока нет
- Case Summary Ovarian CystДокумент4 страницыCase Summary Ovarian CystFrancesca AkanjiОценок пока нет
- Key Points of Obstetrics and Gynaecological HistoryДокумент44 страницыKey Points of Obstetrics and Gynaecological HistoryRoisah Yunan NegariОценок пока нет
- ObsGyn OSCE NotesДокумент52 страницыObsGyn OSCE Notesmysorewala100% (11)
- GynecologyДокумент50 страницGynecologyPhilips55100% (4)
- Obgyn HISTORY TAKING & EXAMINATIONДокумент94 страницыObgyn HISTORY TAKING & EXAMINATIONvalentinemusa218100% (1)
- Surgery History TakingДокумент18 страницSurgery History Takingpranjl100% (2)
- Gastrointestinal History and ExaminationДокумент4 страницыGastrointestinal History and ExaminationAtif Rasool MaharОценок пока нет
- Pediatrics H&P TemplateДокумент3 страницыPediatrics H&P TemplateMark Ma80% (5)
- Problem-based Approach to Gastroenterology and HepatologyОт EverandProblem-based Approach to Gastroenterology and HepatologyJohn N. PlevrisОценок пока нет
- History TakingДокумент3 страницыHistory Takingmkct111100% (1)
- History Taking ObstetricДокумент13 страницHistory Taking ObstetricAnironOrion100% (7)
- Case Write Up FibroidДокумент17 страницCase Write Up FibroidNadsri AmirОценок пока нет
- Case Write UpsДокумент4 страницыCase Write UpsMuhammad AzmanОценок пока нет
- Pediatric History and Physical Exam TemplateДокумент4 страницыPediatric History and Physical Exam TemplateJay Pee Tumaliuan Tumanguil0% (2)
- Ten-Minute History-Taking and Physical Examination Station ExampleДокумент2 страницыTen-Minute History-Taking and Physical Examination Station ExampleMin MawОценок пока нет
- Obstetrics Case Presentation Performa Version 1.5Документ27 страницObstetrics Case Presentation Performa Version 1.5Ajay RajОценок пока нет
- History Taking in ObgynДокумент17 страницHistory Taking in Obgynselvie87100% (1)
- Case Presentation: S. Suchitra 3 Year MBBS MVJ Medical College and Research HospitalДокумент23 страницыCase Presentation: S. Suchitra 3 Year MBBS MVJ Medical College and Research Hospitalwarkhungam khumlo100% (1)
- History Taking ChecklistДокумент3 страницыHistory Taking ChecklistIzzah Zaidun100% (3)
- History Taking and Physical Examination, Level 5Документ48 страницHistory Taking and Physical Examination, Level 5CLEMENTОценок пока нет
- Obstetric Cases For MS-IIIДокумент13 страницObstetric Cases For MS-IIIkukadiyaОценок пока нет
- OSCE Gynae-OSCE-MMSSДокумент24 страницыOSCE Gynae-OSCE-MMSSMohammad Saifullah100% (1)
- Clinical History Taking Format in Medicine - Physical, Systemic ExaminationДокумент3 страницыClinical History Taking Format in Medicine - Physical, Systemic ExaminationNishad PatelОценок пока нет
- Medical History Taking TemplateДокумент2 страницыMedical History Taking TemplateAnwar Hammoud100% (1)
- Obsandgyne Tables 200pagesДокумент221 страницаObsandgyne Tables 200pagesRashed ShatnawiОценок пока нет
- Clerkship Obgyn OsceДокумент6 страницClerkship Obgyn OsceErika Leah Manalo100% (1)
- Ob-Gyn OsceДокумент2 страницыOb-Gyn Oscechristietwong100% (1)
- Obstetrics and Gynecology - 2009Документ45 страницObstetrics and Gynecology - 2009CCGMP100% (1)
- Breast Cancer History TakingДокумент2 страницыBreast Cancer History Takingbloo tomartoОценок пока нет
- Gyne History Taking PDFДокумент6 страницGyne History Taking PDFGokul AdarshОценок пока нет
- Haematological History and Examination 18092012-2Документ8 страницHaematological History and Examination 18092012-2Shahin KazemzadehОценок пока нет
- Uterine Fibroid - Viva VoceДокумент77 страницUterine Fibroid - Viva VoceK Haynes Raja100% (1)
- 01.15.01 Pediatric History Taking and Physical ExamДокумент14 страниц01.15.01 Pediatric History Taking and Physical ExamMikmik DGОценок пока нет
- Long Case O&G-placenta PraeviaДокумент24 страницыLong Case O&G-placenta Praeviasaifulhusni100% (2)
- History Taking Form in Gynecology & ObstetricsДокумент8 страницHistory Taking Form in Gynecology & ObstetricsAbdullah Matar86% (7)
- OSCE Gynae HXДокумент3 страницыOSCE Gynae HXmpage3100% (1)
- OB-GYN Oral Exam Study GuideДокумент34 страницыOB-GYN Oral Exam Study GuidePatrick Sylvester100% (1)
- Cwu Ong Year 5Документ23 страницыCwu Ong Year 5Nurulasyikin MAAОценок пока нет
- History Taking Cheat SheetДокумент1 страницаHistory Taking Cheat SheetLaura ForsythОценок пока нет
- Gynecology History TakingДокумент1 страницаGynecology History TakingSulabh ShresthaОценок пока нет
- OB History Endorsement FormatДокумент6 страницOB History Endorsement FormatVin CustodioОценок пока нет
- Dewhurst's Textbook of Obstetrics & GynaecologyОт EverandDewhurst's Textbook of Obstetrics & GynaecologyChristoph LeesРейтинг: 2 из 5 звезд2/5 (1)
- Comprehensive Handbook Obstetrics & Gynecology 3rd EdОт EverandComprehensive Handbook Obstetrics & Gynecology 3rd EdРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)
- Declarations Brendon BurchardДокумент1 страницаDeclarations Brendon BurchardShahin Kazemzadeh100% (3)
- Haematological History and Examination 18092012-2Документ8 страницHaematological History and Examination 18092012-2Shahin KazemzadehОценок пока нет
- OSCE: Respiratory History and ExaminationДокумент10 страницOSCE: Respiratory History and ExaminationShahin KazemzadehОценок пока нет
- Why UNSWДокумент1 страницаWhy UNSWShahin KazemzadehОценок пока нет
- Strategic Marketing: The University of Lahore (Islamabad Campus)Документ3 страницыStrategic Marketing: The University of Lahore (Islamabad Campus)Sumaira IrshadОценок пока нет
- Taoist Master Zhang 张天师Документ9 страницTaoist Master Zhang 张天师QiLeGeGe 麒樂格格100% (2)
- PNP Ki in July-2017 AdminДокумент21 страницаPNP Ki in July-2017 AdminSina NeouОценок пока нет
- Digital Electronics Chapter 5Документ30 страницDigital Electronics Chapter 5Pious TraderОценок пока нет
- Barrett Beyond Psychometrics 2003 AugmentedДокумент34 страницыBarrett Beyond Psychometrics 2003 AugmentedRoy Umaña CarrilloОценок пока нет
- Paul Wade - The Ultimate Isometrics Manual - Building Maximum Strength and Conditioning With Static Training-Dragon Door Publications (2020) - 120-146Документ27 страницPaul Wade - The Ultimate Isometrics Manual - Building Maximum Strength and Conditioning With Static Training-Dragon Door Publications (2020) - 120-146usman azharОценок пока нет
- Prognostic Factors and Management of Patients With Choanal AtresiaДокумент7 страницPrognostic Factors and Management of Patients With Choanal Atresiafarah maulida martaОценок пока нет
- Masoneilan - 78 Series Air Filter Regulators IOMДокумент8 страницMasoneilan - 78 Series Air Filter Regulators IOMNithyAОценок пока нет
- Play ClawДокумент2 страницыPlay ClawFrenda SeivelunОценок пока нет
- Acetylcysteine 200mg (Siran, Reolin)Документ5 страницAcetylcysteine 200mg (Siran, Reolin)ddandan_2Оценок пока нет
- Contemporary Philippine Arts From The Regions: Quarter 1Документ11 страницContemporary Philippine Arts From The Regions: Quarter 1JUN GERONAОценок пока нет
- Honda IzyДокумент16 страницHonda IzyTerry FordОценок пока нет
- Quanta To QuarksДокумент32 страницыQuanta To QuarksDaniel Bu100% (5)
- Animal Health ChecklistДокумент4 страницыAnimal Health ChecklistcapsfastОценок пока нет
- Cambridge IGCSE: CHEMISTRY 0620/42Документ12 страницCambridge IGCSE: CHEMISTRY 0620/42Khairun nissaОценок пока нет
- Camless EnginesДокумент4 страницыCamless EnginesKavya M BhatОценок пока нет
- Literature Review of Service Quality in RestaurantsДокумент7 страницLiterature Review of Service Quality in RestaurantsuifjzvrifОценок пока нет
- Music 9 Q3 Mod4 Musical Elements of Given Romantic Period PiecesДокумент19 страницMusic 9 Q3 Mod4 Musical Elements of Given Romantic Period PiecesFinn Daniel Omayao100% (1)
- Neet Question Paper 2019 Code r3Документ27 страницNeet Question Paper 2019 Code r3Deev SoniОценок пока нет
- Spring 2010 - CS604 - 1 - SolutionДокумент2 страницыSpring 2010 - CS604 - 1 - SolutionPower GirlsОценок пока нет
- Concrete Specification (BS8500)Документ3 страницыConcrete Specification (BS8500)teh100% (1)
- Reaction Paper FinalДокумент5 страницReaction Paper FinalJelo RoxasОценок пока нет
- Toshiba MotorsДокумент16 страницToshiba MotorsSergio Cabrera100% (1)
- RN42Документ26 страницRN42tenminute1000Оценок пока нет
- Extract The .Msi FilesДокумент2 страницыExtract The .Msi FilesvladimirОценок пока нет
- Erosional VelocityДокумент15 страницErosional VelocityGary JonesОценок пока нет
- Ancient Sumer Flip BookДокумент9 страницAncient Sumer Flip Bookapi-198624210Оценок пока нет
- Reaserch On Effect of Social Media On Academic Performance: Study On The Students of University of DhakaДокумент27 страницReaserch On Effect of Social Media On Academic Performance: Study On The Students of University of DhakaFatema Tuz Johoora88% (114)
- 1 PBДокумент7 страниц1 PBIndah Purnama TaraОценок пока нет
- Module-29A: Energy MethodsДокумент2 страницыModule-29A: Energy MethodsjhacademyhydОценок пока нет