Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
24 HR Chick Reviewer
Загружено:
Clarebelle ReyesИсходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
24 HR Chick Reviewer
Загружено:
Clarebelle ReyesАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
EMBRYOLOG
DEVELOPMENT OF THE CHICK EMBRYO
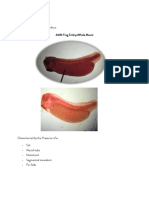
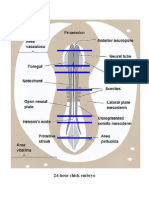
24-HR CHICK EMBRYO
-appears translucent under the
microscope (owed to the thinness of
the blastoderm)
WHOLE MOUNT
Area opaca
-peripheral region of chick blastodisc
-surounds the area pellucida
-in direct contact with the yolk(renders
the area opaque)
-differentiated into 3 zones:
>Peripheral zone
--margin of growth
--cells have proliferated over the
yolk
(w/o becoming adherent)
>Zone junction
--intermediate region
--cells cut free from yolk and
added to
area pellucida
>Inner zone
--germ wall
--cells originate from zone
junction
(contains yolk granules)
--marks transition from area
opaca to
the area pellucida
-area develops into 2 regions:
Area opaca vasculosa
-Inner region of area opaca
-Thickenings of the splanchnic
mesoderm from blood islands
Area opaca vitellina
-outer region of the area opaca
-initially lacks blood
islands/blood
vessels
Area pellucida
-central region of the blastodisc
-where primitive streak forms
-lies directly over the subgerminal
cavity
-2 layers of blastoderm:
>epiblast (outer layer)
--will differentiate into ectoderm
and mesoderm
>hypoblast (inner layer)
Primitive streak
-longitudinal cleft formed on surface of
amniote blastodisc (convergence of
cells)
-gastrulation begins as epiblast cells
migrate towards and into the streak
Primitive groove
-central furrow of the thickening
Primitive ridges
-margins of the primitive streak
-flanking primitive groove on
either
Sides
Primitive pit
-indented region of blastoderm
-anterior end of the primitive
streak
Hensens node (Primitive knot)
-thickened area at anterior end
of the
Streak
-through which cells invaginate
to form
Notochord
-Homologous to dorsal lip of the
blastopore (in amphibian
embryos)
Proamnion
-anterior to developing avian embryo
-surrounding the head
-endoderm and ectoderm
-fate: will be invaded with mesoderm
& become incorporated into amnion
Neural folds
-margins of the neural plate (about to
fuse at the middorsal region)
Neural groove
-median longitudinal groove
-formed by rolling up of the neural
plate
Head fold
-folded region of the blastoderm
-dark crescentic line
-boundary of the heads of the embryo
Notochord
-longitudinal band of cells extending
caudal
-from regions of neural folds to
hensens node
Foregut
-1st part of digestive tract
-definite floor composed of
endodermal cells
-Dome-shaped structure inside head
Anterior intestinal portal
-opening of foregut
-appears like a prominent arched line
beneath the neural folds
-continuous with lateral walls of the
foregut
-as development progresses, it moves
posteriorly & becomes part of the yolk
stalk
Mesenchyme of the head
-lose network of cells
-occupying space betweek foregut and
extoderm (head)
Mesoderm
Anterior border of the
mesoderm
-faint line
-extends across area pellucida
at the
level of anterior end of
notochord
The thickened splanchnic
mesoderm
-darker line
-lateral border of the anterior
intestinal portal
-formed by delamination of
lateral
Plate mesoderm
-will form: heart, part of
circulatory
System, and many other
structure
Somite
-division of dorsal mesoderm
-3 or 4 pairs lie immediately lateral to
the neural folds
Unsegmented mesoderm
-undivided region of mesoderm
-posterior to somites
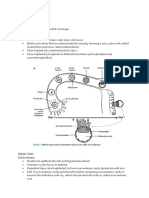
TRANSVERSE SECTION
SECTION THROUGH THE PHARYNGEAL
MEMBRANE
Head ectoderm
-layers of cuboidal cells enclosing the
head
-cells are cuboidal in origin
Neural folds
-margins of neural epithelium
Anterior neuropore
-temporary external opening of
neurocoel
Neural groove
-median longitudinal groove
-formed by the rolling up of neural
plate
Prechordal plate
-mass of chordamesodermal cells
-anterior to notochord
-will form head mesenchyme
Notochord
-small medial mass of cells
-between foregut and neural plate
Foregut
-dorsoventral flattened tube
-walls are made up of endodermal
cells
-located beneath neural plate
Oral plate (Oropharyngeal membrane)
-region where floor of foregut is in
contact with neural ectoderm of head
-will break open to form the mouth (in
lateral development)
Mesenchyme
-loosely scattered cells
-fills up space between foregut and
neural plate
Proamnion
-region of blastoderm beneath
embryos head
-composed of ectoderm and endoderm
layer
Subcephalic pocket
-cavity formed beneath the embryonic
head (as head folds develops)
Somatopleure
-membrane composed of ectoderm
and somatic mesoderm
-forms part of body wall & chorion and
amnion
Splanchnopleure
-cellular layer
-consists of splanchnic mesoderm and
endoderm
-will form body wall & yolk sac and
allantois
Coelom
-cavity formed after separation of
somatic mesoderm and mesoderm
Subgerminal cavity
-space beneath hypoblast within area
pellucida
-give rise to midgut
SECTION THROUGH THE ANTERIOR
INTESTINAL PORTAL
Note:
*neural folds have come together to
form the neural tube
*at the level of the open foregut
*endoderm of the foregut is
continuous with the rest of the
endoderm
*anterior intestinal portal- opening of
the foregut
*region of thickened, splanchnic
mesoderm is prospective cardiac
mesoderm
Neural tube
-formed by thickening and rolling up of
neural plate (during embryonic
neurulation)
-will form the brain and spinal cord
Neural crest
-found at the edges of the neural plate
above the neural tube
-migrate throughout the embryo to
form ganglia, pigment cells, part of
gills arches, etc.
Head fold
-marked by downward bend of
membranes around the head region
Anterior intestinal portal
-opening of the foregut
-as development progresses and gut
elongates, it moves posteriorly and
becomes part of yolk stalk
Amnio-Cardiac vesicle
-region of coelom
-will give rise to amnion and heart
-thickened splanchnic mesoderm,
making up proximal wall of semicardiac vesicle, is the forerunner of
the heart
-somatopleure, making up the dorsal
wall of this vesicle, is involved in the
formation of the amnion
SECTION THROUGH THE MIDGUT
Note:
*midgut- middle part of the gut that
has the yolk for the floor of its cavity
Midgut
-floorless region of the gut
-posterior to the anterior intestinal
portal
SECTION THROUGH THE SOMITE
Note:
*neural folds have no yet closed
together
*somites develop from dorsal
mesoderm & are located on each side
of the neural folds and notochord
*later and adjacent to somites is the
intermediate mesoderm (small region
of mesoderm)
*Intermediate mesoderm will develop
into kidneys
*lateral plate mesoderm, lateral to
intermediate mesoderm, will
delaminate to form somatic and
splanchnic mesodermal layers
Somite
-segmented mesodermal blocks
-located on either side of the
developing spinal cord
-arise from dorsal mesoderm
Nephrotome (Intermediate
mesoderm/mesomere/nephromere)
-stalk-like connection between somites
and lateral plate mesoderm
-anteriorly:forms pronephros;
posteriorly:forms mesenchyme (will
develop into mesonephros and
metanephros
Hypomere
-region of mesoderm distal to
nephrotome
-subdivided into two layers:
>somatic
>splanchnic mesoderm
SECTION THROUGH THE PRIMITIVE
STREAK
Primitive streak
-longitudinal cleft formed of the
surface of the amniote blastodisc by
convergence of cells
-gastrulation begins as the epiblast
cells migrate towards and into the
streak
Hensens node (primitive knot)
-thickened area at the anterior
end of
the streak
-through which cells invaginates
to form
Notochord
-homologous to dorsal lip of
blastopore
Primitive pit
-depression slightly deeper than
primitive groove
-posterior to hensens node
Primitive groove
-central furrow more posterior
to
primitive pit
Primitive ridges
-thickened margins on each side
of the
primitive grovove
Вам также может понравиться
- 24-Hr Chick EmbryoДокумент8 страниц24-Hr Chick EmbryopauОценок пока нет
- 24 HR Chick ReviewerДокумент4 страницы24 HR Chick ReviewerGail AmuraoОценок пока нет
- Dumaguit (2021)Документ12 страницDumaguit (2021)Dimple May Gianne DumaguitОценок пока нет
- 24 33 Hour ChickДокумент9 страниц24 33 Hour ChickMary Grace Tuazon100% (1)
- 24-Hr Chick: Structure Description FateДокумент18 страниц24-Hr Chick: Structure Description FateDimple May Gianne DumaguitОценок пока нет
- 33 HR Chick EmbryoДокумент12 страниц33 HR Chick EmbryoErvin AblazaОценок пока нет
- 24 Hour Chick Embryo - Embryology LabДокумент3 страницы24 Hour Chick Embryo - Embryology LabIvy Cruz50% (2)
- Embryo Lab Exercise 4Документ17 страницEmbryo Lab Exercise 4Karmina SantosОценок пока нет
- Organ Description How Is It Formed? PurposeДокумент6 страницOrgan Description How Is It Formed? PurposeAnna Nicole LazaroОценок пока нет
- Chapter 7Документ7 страницChapter 7Mia Kristhyn Calinawagan SabanalОценок пока нет
- Chick Embryo ReviewerДокумент9 страницChick Embryo ReviewerKeana TapangОценок пока нет
- 33-Hour Chick ReviewerДокумент5 страниц33-Hour Chick ReviewerBeatriceОценок пока нет
- 72-HR ChickДокумент16 страниц72-HR Chick411452123100% (1)
- Ex4 Frog EmbryoДокумент20 страницEx4 Frog EmbryoJan Leightton Laxamana100% (2)
- Neural Tube Formation 4-8 WeeksДокумент56 страницNeural Tube Formation 4-8 WeeksLugembe MasolaОценок пока нет
- Embryonic Period 1Документ35 страницEmbryonic Period 1Riya SinghОценок пока нет
- Embryo Lab Org 2Документ14 страницEmbryo Lab Org 2pauОценок пока нет
- Embryonic Period 4-8weekДокумент25 страницEmbryonic Period 4-8weekaimi BatrisyiaОценок пока нет
- Early Embryology Week OneДокумент14 страницEarly Embryology Week OnelukesqueОценок пока нет
- The Third Week of Development: TH THДокумент8 страницThe Third Week of Development: TH THbarbacumlaudeОценок пока нет
- Tail Neural Tube Notochord Segmented Mesoderm Fin Folds: Epiphysis Olfactory Placodes Lens PlacodeДокумент2 страницыTail Neural Tube Notochord Segmented Mesoderm Fin Folds: Epiphysis Olfactory Placodes Lens PlacodeMarina of The SeaОценок пока нет
- LAB EXERCISE 4 - 4 MM Frog EmbryoДокумент7 страницLAB EXERCISE 4 - 4 MM Frog EmbryoGerald Angelo DeguinioОценок пока нет
- Embryonic Period: Dr. Khin Ma MAДокумент34 страницыEmbryonic Period: Dr. Khin Ma MAIbrahim FoondunОценок пока нет
- Embryology Summary NotesДокумент6 страницEmbryology Summary Notessayeda.raza24Оценок пока нет
- Gas Tru LationДокумент53 страницыGas Tru LationSam MumoОценок пока нет
- 72 HR ReviewerДокумент8 страниц72 HR ReviewerAstrid AmadorОценок пока нет
- Chick EmbryoДокумент95 страницChick EmbryoAllyzha AguilarОценок пока нет
- Seminar 2Документ7 страницSeminar 2gatorssoccer1313Оценок пока нет
- 48hr and 72hr Chick EmbryoДокумент28 страниц48hr and 72hr Chick EmbryoRichelle IgnacioОценок пока нет
- Embryology Notes emДокумент18 страницEmbryology Notes emLuqman AfifОценок пока нет
- 3 EmbryologyДокумент19 страниц3 EmbryologyKennVaneОценок пока нет
- Embryology Notes - emДокумент18 страницEmbryology Notes - emrigario80% (5)
- Anatomy Without Lab Midterm Study GuideДокумент19 страницAnatomy Without Lab Midterm Study GuideChetfalkОценок пока нет
- Chick Embryo (Embryology Lab)Документ9 страницChick Embryo (Embryology Lab)humanupgrade100% (1)
- Uni FileДокумент10 страницUni Filemuqadar khanОценок пока нет
- Exercise 4 Frog Embryo 4mm 7mm 10mmДокумент23 страницыExercise 4 Frog Embryo 4mm 7mm 10mmrexartooz95% (19)
- EmbryologyДокумент39 страницEmbryologyRukshan Ranatunga100% (1)
- EmbryoLab 10mm FrogДокумент13 страницEmbryoLab 10mm FrogpauОценок пока нет
- 8 - Derivatives of Germ Layers-Dr - GosaiДокумент35 страниц8 - Derivatives of Germ Layers-Dr - GosaiDr.B.B.GosaiОценок пока нет
- Universal Embryology SummaryДокумент6 страницUniversal Embryology SummaryJason TonioloОценок пока нет
- Embryology TimelineДокумент3 страницыEmbryology Timelinesayeda.raza24Оценок пока нет
- Dermatomes Lateral Plate Mesoderm Neural CrestДокумент3 страницыDermatomes Lateral Plate Mesoderm Neural CrestÑäd ÉèmОценок пока нет
- 48 & 72 HR Chick PDFДокумент3 страницы48 & 72 HR Chick PDFpinky peachОценок пока нет
- Early Embryological Development: Oral Histology Dent 206 DR Ashraf ShaweeshДокумент26 страницEarly Embryological Development: Oral Histology Dent 206 DR Ashraf ShaweeshAbod NaserОценок пока нет
- Gastrulation and Formation of Germ LayersДокумент53 страницыGastrulation and Formation of Germ LayersRhomizal MazaliОценок пока нет
- Third To Eighth WeekДокумент33 страницыThird To Eighth WeekGeoffreyОценок пока нет
- Weeks 3 - 8Документ32 страницыWeeks 3 - 8Stefan HutsonОценок пока нет
- OrganogenesisДокумент6 страницOrganogenesisnitesh.th15005Оценок пока нет
- Exercise 17 Serial Transverse Section of A 33 Hour Chick Embryo PDFДокумент4 страницыExercise 17 Serial Transverse Section of A 33 Hour Chick Embryo PDFMichaela FayeОценок пока нет
- Development of CNSДокумент84 страницыDevelopment of CNSSamuel frankОценок пока нет
- Development of FaceДокумент19 страницDevelopment of FaceAkhila ReddyОценок пока нет
- 09 - Musculoskeletal DevelopmentДокумент8 страниц09 - Musculoskeletal DevelopmentAXA OFFICIALОценок пока нет
- Gastrulationin MammalsДокумент16 страницGastrulationin MammalsHarsha MaheshwariОценок пока нет
- Ventricles: Dr. Katharina Kian R. Demerre - Bacolod PT 21Документ70 страницVentricles: Dr. Katharina Kian R. Demerre - Bacolod PT 21Cyril Jay G. OrtegaОценок пока нет
- General Embryo-3-011Документ60 страницGeneral Embryo-3-011PragatiОценок пока нет
- Chapter 8Документ4 страницыChapter 8Mia Kristhyn Calinawagan SabanalОценок пока нет
- A Guide for the Dissection of the Dogfish (Squalus Acanthias)От EverandA Guide for the Dissection of the Dogfish (Squalus Acanthias)Оценок пока нет
- David Carreras - A Cunnilinguist's Guide To Mind-Blowing Oral SexДокумент6 страницDavid Carreras - A Cunnilinguist's Guide To Mind-Blowing Oral SexKostyaОценок пока нет
- Essential antenatal care guideДокумент19 страницEssential antenatal care guideSaima KanwalОценок пока нет
- Cestodes: - Phylum Platyhelminthes (Flatworms)Документ23 страницыCestodes: - Phylum Platyhelminthes (Flatworms)ruben6mОценок пока нет
- Unit Test 2with AnswersДокумент22 страницыUnit Test 2with AnswersPhysicshekОценок пока нет
- 132 HealthwiseДокумент9 страниц132 Healthwisemichael.staffordОценок пока нет
- Contraceptive Knowledge, Attitudes and Practice Among Maried Women in Samaru Community, Zaria, NigeriaДокумент5 страницContraceptive Knowledge, Attitudes and Practice Among Maried Women in Samaru Community, Zaria, NigeriaAnivasa KabirОценок пока нет
- PRC Forms NEW GUIDELINEДокумент7 страницPRC Forms NEW GUIDELINEJellyAnnGomezОценок пока нет
- Section: General ObstetricsДокумент15 страницSection: General ObstetricsvarmaОценок пока нет
- Savior Siblings; A Case StudyДокумент4 страницыSavior Siblings; A Case StudyBill BreisОценок пока нет
- I. Human Body OrientationДокумент10 страницI. Human Body OrientationAnn Margarette MoralesОценок пока нет
- Partograph Monitoring Labor ProgressДокумент65 страницPartograph Monitoring Labor ProgressAmyAgustinОценок пока нет
- AnencephalyДокумент2 страницыAnencephalysrust2792Оценок пока нет
- Prenatal Ultrasound Screening GuidelinesДокумент11 страницPrenatal Ultrasound Screening GuidelinesAan Dwi PrasetioОценок пока нет
- Beckwith-Wiedemann SyndromeДокумент6 страницBeckwith-Wiedemann SyndromeAhmad Althof Malihul AdiОценок пока нет
- Prenatal Care for AdolescentsДокумент15 страницPrenatal Care for AdolescentsSara DayonОценок пока нет
- Session #43 SAS - AnaPhy (Lab) (Agdana, Nicole Ken)Документ4 страницыSession #43 SAS - AnaPhy (Lab) (Agdana, Nicole Ken)Nicole Ken AgdanaОценок пока нет
- Content ServerДокумент7 страницContent ServerJames DuncanОценок пока нет
- Klinefelter SyndromeДокумент21 страницаKlinefelter SyndromeClaire GuanteroОценок пока нет
- Pendarahan PostpartumДокумент8 страницPendarahan PostpartumsulviОценок пока нет
- QuestionДокумент5 страницQuestionLyniel Anne de AsisОценок пока нет
- Tubal LigationДокумент3 страницыTubal LigationPal_inОценок пока нет
- Pasien ReadmisiДокумент25 страницPasien ReadmisialbertaОценок пока нет
- Doh Hormone TherapyДокумент32 страницыDoh Hormone TherapyKarla DreamsОценок пока нет
- Destructive Operations FinalДокумент39 страницDestructive Operations Finalsanthiyasandy75% (24)
- 5 Surprising Secrets of Sex, Love, and The Male BrainДокумент6 страниц5 Surprising Secrets of Sex, Love, and The Male BrainJed Diamond100% (4)
- Exstrophy-Epispadias Complex: Current Management: Journal ReadingДокумент64 страницыExstrophy-Epispadias Complex: Current Management: Journal ReadingAnonymous ce3S6XFdwU100% (1)
- Understand female body shapeДокумент9 страницUnderstand female body shapeSergio SchillingОценок пока нет
- Republic V Cagandahan DigestДокумент2 страницыRepublic V Cagandahan DigestJustin Paras100% (1)
- Filipino Masculinity: Camilo A.B. Naraval, MD MSC Health Management and Research GroupДокумент43 страницыFilipino Masculinity: Camilo A.B. Naraval, MD MSC Health Management and Research GroupkimcharriseОценок пока нет
- Unitive and Procreative Health Procreation, Creation and EvolutionДокумент9 страницUnitive and Procreative Health Procreation, Creation and EvolutionJustJ ThingsОценок пока нет