Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
10CV33 - June 2015
Загружено:
nvnrev0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
40 просмотров2 страницыVTU 10CV33_JUNE 2015
Оригинальное название
10CV33_JUNE 2015
Авторское право
© © All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
PDF или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документVTU 10CV33_JUNE 2015
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PDF или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
40 просмотров2 страницы10CV33 - June 2015
Загружено:
nvnrevVTU 10CV33_JUNE 2015
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PDF или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 2
pages.
:
a
z
gE
2
.
compulsorily draw diagonal cross lines on the re
on, appeal to evaluator and /or equations writen eg, 4248.
2. Any reve
Important Note : 1. On compl
l 10CV/EV/CT33
USN |
Time:
eas
b.
©,
ean
b.
en
b.
4a
b.
Third Semester B.E. Degree Examination, June/July 2015
Strength of Materials
3 hrs. Max. Marks: 100
Note: 1. Answer any FIVE full questions, selecting
atleast TWO questions from each part.
2. Missing data, if any, may be suitably assumed.
PART-A
Define: i) Stress ii) Strain. (04 Marks)
Derive the relation between modulus of rigidity and Young’s modulus of Elasticity and
define elastic constants. (08 Marks)
The modulus of rigidity for a material is 51GPa. A 10mm diarteter rod of the material was
subjected to an axial load of 10KN and the change ip diameter was observed to be
3x 10°mm, Calculate the Poisson’s ratio and the modulus of elasticity. (08 Marks)
A reinforced concrete column 300mm x 300mm(has 4 reinforcement bars of steel each
20mm in diameter. Calculate the safe load the,column can take if the permissible stress in
concrete 5.2 N/mm? and coe =18. C (08 Marks)
A compound bar made of steel plate 60mim wide and 10mm thick to which the copper plate
60mm wide and Smm thick are rigidly connected to each other. The length of the bar is
0.7m. If the temperature is raigedby 80°C. Determine the stress in each metal and the
change in the length.
Take: E,=200 GPa a= 12 x 10%/°C
Eca= 100 GPa Cu = 17 x 10°C. (12 Marks)
Derive expressions for principal stresses and their planes for two dimensional stress systems.
(08 Marks)
At a point in a-strained material, the state of the stress is as shown in the Fig.Q.3(b).
Calculate the normal and the shearing stress on the plane AC. Also find the principal stresses
and their planes. Determine the maximum shear stress and their planes. (12 Marks)
0 at
E) pat
Fig.Q.3(b) : 108
ig.Q.3(b) 160 Nut aa
x ty: 20 Nome!
0 un
Define: i) Shear force ii) Bending moment _ iii) Point of contra flexure, (06 Marks)
A beam ABCD, 8m long has supports at ‘A’ and at ‘C’ which is 6m from ‘A’. The beam
carries a UDL of 10kN/m between ‘A’ and ‘C’ at point B a 30KN concentrated load acts 2m
from the support A and a point load of 15KN acts at the free end “D'. Draw the SED and
BMD giving salient values. Also locate the point of contra-flexure if any. (14 Marks)
1 of2
10CV/EV/CT33
PART-B
ta
y R
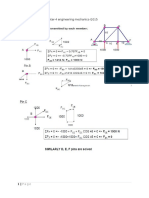
b. The cross section of a beam is shown in Fig.Q.5(b). The shear force on the section is 410kN,
Estimate the shear stresses at various points and plot the shear distribution diagram
(14 Marks)
a. Derive Bernoulli-Euler bending equation aM (06 Marks)
le——}.0m ——
x
Olam
J
OSM
¥
i 0-95 m
le osm a}
Fig.Q.5(b) |
a. Derive the equation BS = M, with usuabhotation. (06 Marks)
ix
b. A beam of constant C/S 10m long is\fgely supported at its ends and loaded with 2 loads of
GOKN each at 3m from either end. Riad the slope at the support and the deflection under any
one load. Take El constant... / (14 Marks)
List the assumptions made‘di the theory of pure torsion (04 Marks)
Explain: i) Polar modulis;"ii) Torsional rigidity; iii) Polar moment of inertia. (06 Marks)
¢. A solid shaft is to tranémit 340 KN-m at 120rpm. If the shear stress of the material should
not exceed 80MPa)Find the diameter required. What percentage saving in weight would be
obtained if this'shaft is replaced by a hollow one whose d; = 0.6d,, the length, material and
oe
shear stress Femaining same. (10 Marks)
a. Distinguish between short column and long column. (04 Marks)
b. Explain:
i) Effective length of column
ii) — Slenderness ratio
iii) Buckling load, (06 Marks)
¢. Determine the Euler's crushing load for a hollow cylindrical cast iron column 150mm
external diameter and 20mm thick. If it is hinged at both the ends and 6m long compare this
toad with the crushing load as given by Rankine’s formula. Use the constants:
1
f= SSOMP: =—— —_E=80GPa, 10 Marks)
SSOMPa c= aa a, (10 Marks)
thee
2of2
Вам также может понравиться
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (890)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (344)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (119)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (399)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2219)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (265)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- Solucionario Estatica Meriam 4th EdicionДокумент991 страницаSolucionario Estatica Meriam 4th EdicionRonald Cruz RomeroОценок пока нет
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- Engineering Mechanics NotesДокумент100 страницEngineering Mechanics NotesRagothsingh Ramadoss67% (3)
- Eijaer1005 PDFДокумент11 страницEijaer1005 PDFnvnrevОценок пока нет
- Engineering-Mechanics by North 2Документ3 страницыEngineering-Mechanics by North 2nvnrevОценок пока нет
- Important SoilДокумент14 страницImportant Soilnamsy ramsyОценок пока нет
- Hadoop Final For PublicationДокумент20 страницHadoop Final For PublicationnvnrevОценок пока нет
- CHAPTER.7 Engineering Mechanics-I2015Документ9 страницCHAPTER.7 Engineering Mechanics-I2015nvnrevОценок пока нет
- TESTДокумент2 страницыTESTnvnrevОценок пока нет
- B OverallДокумент12 страницB OveralldearsaswatОценок пока нет
- Eerc91 17Документ140 страницEerc91 17Ma GhОценок пока нет
- Problem SolutionДокумент15 страницProblem SolutionnvnrevОценок пока нет
- Simple Problem On MOIДокумент2 страницыSimple Problem On MOInvnrevОценок пока нет
- Problems Chapter 1Документ1 страницаProblems Chapter 1nvnrevОценок пока нет
- Worked Example of Chapter-5 Engineering Mechanics-I 2015Документ5 страницWorked Example of Chapter-5 Engineering Mechanics-I 2015nvnrevОценок пока нет
- Into To MechДокумент142 страницыInto To MechnvnrevОценок пока нет
- Shear Force and Bending Moment Work SheetsДокумент5 страницShear Force and Bending Moment Work SheetsnvnrevОценок пока нет
- Allowable Strength DesignДокумент5 страницAllowable Strength DesignnvnrevОценок пока нет
- CHAPTER.7 Engineering Mechanics-I2015Документ7 страницCHAPTER.7 Engineering Mechanics-I2015nvnrevОценок пока нет
- Chapter IДокумент12 страницChapter InvnrevОценок пока нет
- Chapter 6 Engineering Mechanics I2015Документ8 страницChapter 6 Engineering Mechanics I2015nvnrevОценок пока нет
- Worked Example of Chapter - 4 Engineering Mechanics-I 2015Документ9 страницWorked Example of Chapter - 4 Engineering Mechanics-I 2015nvnrevОценок пока нет
- Worked Example of Chapter - 4 Engineering Mechanics-I 2015Документ9 страницWorked Example of Chapter - 4 Engineering Mechanics-I 2015nvnrevОценок пока нет
- Homework solutions for forces and momentsДокумент1 страницаHomework solutions for forces and momentsnvnrevОценок пока нет
- Chapter 2 Worked Examples Force SystemsДокумент17 страницChapter 2 Worked Examples Force Systemsnvnrev100% (1)
- Worked Example of Chapter - 4 Engineering Mechanics-I 2015Документ9 страницWorked Example of Chapter - 4 Engineering Mechanics-I 2015nvnrevОценок пока нет
- Groupwork-II Engineering Mechanics-I 2015Документ1 страницаGroupwork-II Engineering Mechanics-I 2015nvnrevОценок пока нет
- Chapter 6 Engineering Mechanics I2015Документ8 страницChapter 6 Engineering Mechanics I2015nvnrevОценок пока нет
- CHAPTER.7 Engineering Mechanics-I2015Документ7 страницCHAPTER.7 Engineering Mechanics-I2015nvnrevОценок пока нет
- Engineering Mecha-I Assignment-II 2015Документ3 страницыEngineering Mecha-I Assignment-II 2015nvnrevОценок пока нет