Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Common Neurotransmitters - Their Functions and Malfunctions
Загружено:
idjacobs0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
409 просмотров2 страницыThis document summarizes common neurotransmitters, their functions, and examples of malfunctions associated with irregular levels of each neurotransmitter. Acetylcholine enables muscle action, learning, and memory, and its deficiency is linked to Alzheimer's and its excess to conditions like botulism. Dopamine influences movement, learning, attention, and emotion, and its excess or deficiency is associated with disorders like schizophrenia and Parkinson's. Serotonin affects mood, sleep, and arousal, and its irregular levels can cause mood disorders, insomnia, and OCD.
Исходное описание:
transmitters
Оригинальное название
Neurotransmitters CHART
Авторское право
© © All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
DOC, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документThis document summarizes common neurotransmitters, their functions, and examples of malfunctions associated with irregular levels of each neurotransmitter. Acetylcholine enables muscle action, learning, and memory, and its deficiency is linked to Alzheimer's and its excess to conditions like botulism. Dopamine influences movement, learning, attention, and emotion, and its excess or deficiency is associated with disorders like schizophrenia and Parkinson's. Serotonin affects mood, sleep, and arousal, and its irregular levels can cause mood disorders, insomnia, and OCD.
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате DOC, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
409 просмотров2 страницыCommon Neurotransmitters - Their Functions and Malfunctions
Загружено:
idjacobsThis document summarizes common neurotransmitters, their functions, and examples of malfunctions associated with irregular levels of each neurotransmitter. Acetylcholine enables muscle action, learning, and memory, and its deficiency is linked to Alzheimer's and its excess to conditions like botulism. Dopamine influences movement, learning, attention, and emotion, and its excess or deficiency is associated with disorders like schizophrenia and Parkinson's. Serotonin affects mood, sleep, and arousal, and its irregular levels can cause mood disorders, insomnia, and OCD.
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате DOC, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 2
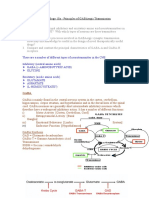
Common Neurotransmitters - KEY
Neurotransmitter
Function
Examples of Malfunctions
Acetylcholine (Ach)
Enables Muscle Action (movement),
Learning, Memory
Alzheimers disease: too little effects
memory, Ach-producing neurons deteriorate
in hippocampus deteriorate causing memory
problems
Excitatory
Botulism poison blocks Ach leads to paralyze
of respiratory muscles
Black Widow bite too much - muscles in
violent convulsions
Dopamine
Inhibitory
Influences movement, learning,
attention, and emotion
Movement and reward
Strongly associated with reward
mechanisms in brain
Excess dopamine receptor activity linked to
schizophrenia (positive symptoms)
Starved of dopamine, the brain produces
tremors and decreased mobility of
Parkinsons disease
Play part of rewarding property in
drugs like cocaine, alcohol, opium,
heroin, nicotine THESE
INCREASE DOPAMINE
Serotonin
Affects mood, hunger, sleep, and
arousal, impulsivity
Inhibitory
Undersupply linked OCD, anxiety, mood
disorders(depression), anger control,
insomnia, and suicide
Prozac and other antidepressant increase
serotonin levels
Drink warm milk at night help you sleep
because contains and amino acid that brain
uses to make serotonin (relax)
Plays a role in schizophrenia, may interact
with dopamine system to alter the way it
operates.
Norepinephrine
Excitatory
Aka Noradrenaline
Helps control alertness and arousal
Mood, sleep, learning
*Role in perception: LSD attaches to
serotonin receptor cites blocking perceptual
paths
Undersupply can depress mood
Oversupply insomnia
Increases heart rate and slows
digestion during stress
Common Neurotransmitters - KEY
Neurotransmitter
GABA (gammaaminobutyric acid)
Inhibitory
Function
Examples of Malfunctions
A major (best known) inhibitory
neurotransmitter
Undersupply linked to seizures, tremors, and
insomnia
Sleep; movement
Anxiety, Huntingtons disease, epilepsy
Seems needed to keep neuron
activity in check
Too little GABA also may be anxiety drugs
Valium works by enhancing effects of GABA
Too little GABA in some brain areas can be
epilepsy
Glutamate
Excitatory
Major excitatory neurotransmitter
Involved in memory
Most common in CNS as much as
of all brain neurons
CuriouslyActually toxic to neurons
and an excess will kill them
Oversupply over stimulate brain leading to
migraines or seizures (why some avoid
MSG, monosodium glutamate, in food)
Damage after stroke
Sometimes brain damage or stroke leads to
excess and many more brain cells die than
from original trauma
ALS (Lou Gehrigs Disease) excessive
glutamate production.
Schizophrenia lack of glutamate
production. (negative symptoms)
Many neurologists feel this is responsible for
many CNS diseases
Endorphins
(endogenous
(produced within)
morphine)
Released in response to pain or
vigorous exercise
If brain is flooded with opiates like heroin
and morphine the brain may stop producing
these natural opiates
Pain control
Short for Endogenous
morphine built in
morphine
Structurally similar to heroin and has
similar functions: pain reduction,
pleasure
Opiods work by attaching at
endorphin receptor site
AGONISTS
Lack of no established disorder
This is the neurotransmitter responsible for
allowing bears and other animals to
hibernate. Heroin slows heart rate,
respiration, and metabolism in general
exactly what you need to hibernate if you
were a bear. Heroin can slow it to nothing
death or Permanent Hibernation
Вам также может понравиться
- "Neurotransmitter": Supporting Lecturer: NOVIA SINATA, M.Si, AptДокумент24 страницы"Neurotransmitter": Supporting Lecturer: NOVIA SINATA, M.Si, AptAmoxicilliartha RivanolaОценок пока нет
- NeurotransmitterДокумент1 страницаNeurotransmitterZeeham EscalonaОценок пока нет
- Inhibitory NeurotransmittersДокумент11 страницInhibitory NeurotransmittersAi NeeriОценок пока нет
- PsychopharmacologyДокумент160 страницPsychopharmacologyInah Sarita100% (1)
- 9 NeurotransmittersДокумент48 страниц9 NeurotransmittersYolanda UlmiОценок пока нет
- Depression Medications ExplainedДокумент5 страницDepression Medications ExplainedxyzОценок пока нет
- Topic 7 - Neurobiologic ComponentДокумент44 страницыTopic 7 - Neurobiologic ComponentJemimah Adaclog100% (1)
- Major Neurotransmitters and Their FunctionsДокумент29 страницMajor Neurotransmitters and Their FunctionsashupathakaОценок пока нет
- Introduction To Neurotransmitters: BY: Mudasir Maqbool Mohmad Amin DarДокумент24 страницыIntroduction To Neurotransmitters: BY: Mudasir Maqbool Mohmad Amin DarKAMYA SRIDHARAN 20214044100% (1)
- Central Nervous System Pharmacology: Elly Nurus SakinahДокумент64 страницыCentral Nervous System Pharmacology: Elly Nurus Sakinahkareem92Оценок пока нет
- Neurotransmitter Release and ProcessДокумент14 страницNeurotransmitter Release and ProcessRain TolentinoОценок пока нет
- BIOCHEM Types of Neurotransmitters PDFДокумент7 страницBIOCHEM Types of Neurotransmitters PDFTammy StephanieОценок пока нет
- Biological Bases Study GuideДокумент13 страницBiological Bases Study Guideapi-421695293Оценок пока нет
- Functional Neuroanatomy of BrainДокумент50 страницFunctional Neuroanatomy of BrainAsim ShresthaОценок пока нет
- Introduction To NeuropharmacologyДокумент6 страницIntroduction To Neuropharmacologyammarhafez78100% (1)
- Psychotherapeutic Drugs GuideДокумент12 страницPsychotherapeutic Drugs Guidecamile buhanginОценок пока нет
- Treatment Modalities For Mood DisordersДокумент55 страницTreatment Modalities For Mood DisordersGlory MimiОценок пока нет
- Understanding Antipsychotic Drugs for SchizophreniaДокумент34 страницыUnderstanding Antipsychotic Drugs for SchizophreniamariaОценок пока нет
- CNS Drugs Acting on GABA and Sodium ChannelsДокумент27 страницCNS Drugs Acting on GABA and Sodium Channelsashokvishnoi29pОценок пока нет
- PHARMACOLOGY OF PSYCHOSIS AND MANIAДокумент53 страницыPHARMACOLOGY OF PSYCHOSIS AND MANIAlavanyakakarlaОценок пока нет
- Glutamate & Gaba: NeurotransmittersДокумент33 страницыGlutamate & Gaba: NeurotransmittersPanchitaJuarezОценок пока нет
- PSY1011 - Psychological Disorders LectureДокумент61 страницаPSY1011 - Psychological Disorders LectureeeОценок пока нет
- Neurotransmitters-Classification, Relevance in The Etiology and Treatment of Mental IllnessДокумент22 страницыNeurotransmitters-Classification, Relevance in The Etiology and Treatment of Mental Illnessneethus10Оценок пока нет
- Biological Treatments in PsychiatryДокумент56 страницBiological Treatments in PsychiatryNurul AfzaОценок пока нет
- Cognitive Disorders PresentationДокумент70 страницCognitive Disorders PresentationWasiu AfoloabiОценок пока нет
- Antipsychotic DrugsДокумент47 страницAntipsychotic DrugsIkram UddinОценок пока нет
- CEP BPSD Discussion Guide ENG RFCG Updated2019 PDFДокумент8 страницCEP BPSD Discussion Guide ENG RFCG Updated2019 PDFM.DalaniОценок пока нет
- Antipsychotic Drugs - Wafa Bin ShamlanДокумент8 страницAntipsychotic Drugs - Wafa Bin ShamlanSara AbdoОценок пока нет
- Drug Summary Drug Fill-In-The-Blank Ws NT Drug Review Key 2Документ3 страницыDrug Summary Drug Fill-In-The-Blank Ws NT Drug Review Key 2api-261267976Оценок пока нет
- Dr. Jagan Associate Professor of Pharmacology HOD - para Clinical Department Texila American UniversityДокумент41 страницаDr. Jagan Associate Professor of Pharmacology HOD - para Clinical Department Texila American UniversityredderdatОценок пока нет
- PsychopharmacologyДокумент53 страницыPsychopharmacologypujarze4100% (1)
- Sleep Disturbances: Presented By, Maria JacobДокумент61 страницаSleep Disturbances: Presented By, Maria Jacobmaria jacob100% (1)
- Psychopharmacology in PsychiatryДокумент94 страницыPsychopharmacology in PsychiatryOslo SaputraОценок пока нет
- Types of DepressionДокумент12 страницTypes of DepressionKADAMBARIОценок пока нет
- SSRI (Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitor)Документ1 страницаSSRI (Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitor)Mike EveretteОценок пока нет
- NeurotransmittersДокумент11 страницNeurotransmittersapi-286518624100% (1)
- CNS StimulantsДокумент26 страницCNS StimulantsShivaОценок пока нет
- INTRODUCTION TO NEUROPHARMACOLOGYyyДокумент27 страницINTRODUCTION TO NEUROPHARMACOLOGYyyEbad RazviОценок пока нет
- Neurobiologic Theories AND Psychopharmacology: BY Group 1Документ15 страницNeurobiologic Theories AND Psychopharmacology: BY Group 1PALEN, DONNA GRACE B.Оценок пока нет
- 7 Major Neurotransmittersm HandoutДокумент1 страница7 Major Neurotransmittersm HandoutRolland LeeОценок пока нет
- Pharmacology of Sedative-HypnoticsДокумент49 страницPharmacology of Sedative-HypnoticsGeorge AbrahamОценок пока нет
- LECTURE 1 The Nature of PsychologyДокумент59 страницLECTURE 1 The Nature of PsychologyColossal HeartОценок пока нет
- Role of Vitamin D in Schizophrenia in Elderly PatientДокумент3 страницыRole of Vitamin D in Schizophrenia in Elderly PatientJAVED ATHER SIDDIQUIОценок пока нет
- Psychopharmacology NewestДокумент43 страницыPsychopharmacology NewestRegina PunОценок пока нет
- 2019 Mood Disorders and AntidepressantsДокумент29 страниц2019 Mood Disorders and Antidepressantsgowod86101Оценок пока нет
- Table of NeurotransmittersДокумент20 страницTable of NeurotransmittersJhost Clinton PurbaОценок пока нет
- Intro To Clinical PsychiatryДокумент26 страницIntro To Clinical PsychiatryNoelle Grace Ulep Baroman100% (1)
- Atypical Antidepressants - Pharmacology, Administration, and Side Effects - UpToDateДокумент16 страницAtypical Antidepressants - Pharmacology, Administration, and Side Effects - UpToDateMelissandreОценок пока нет
- Anti PsychoticsДокумент34 страницыAnti Psychotics88AKKОценок пока нет
- Abnormal Psychology Module 11 Schizophrenia Spectrum and Other Psychotic DisordersДокумент23 страницыAbnormal Psychology Module 11 Schizophrenia Spectrum and Other Psychotic DisordersSumriddhi SrivastavaОценок пока нет
- Guide to Antipsychotics for SchizophreniaДокумент24 страницыGuide to Antipsychotics for SchizophreniaKhadija ArshadОценок пока нет
- Adrenergic AgentsДокумент57 страницAdrenergic AgentsAn Lo100% (1)
- Pharmacology of Autonomic Nervous System 2013Документ166 страницPharmacology of Autonomic Nervous System 2013Adimera TsehayeОценок пока нет
- Brain Disorders: A2 Biology Unit 5 Topic 8Документ16 страницBrain Disorders: A2 Biology Unit 5 Topic 8Yasmin FarhanОценок пока нет
- Serotonin and Ergot Alkaloids: Zain Ul ArfeenДокумент50 страницSerotonin and Ergot Alkaloids: Zain Ul ArfeenRuva Oscass JimmyОценок пока нет
- Adrenergic DrugsДокумент20 страницAdrenergic DrugsEdwardRoshanОценок пока нет
- EE 671 - Neural Networks: Nervous System Source: Ulty/farabee/biobk/biobooktoc - HTMLДокумент29 страницEE 671 - Neural Networks: Nervous System Source: Ulty/farabee/biobk/biobooktoc - HTMLtmkiran100% (1)
- Psych Ch. 5 NotesДокумент7 страницPsych Ch. 5 NotesHaylle ThomasОценок пока нет
- NeurotransmittersДокумент5 страницNeurotransmittersJoezerk Jhon Biel100% (1)
- Types of NeurotransmittersДокумент1 страницаTypes of NeurotransmittersAileen AblanОценок пока нет
- Oxytocin Spray Boosts Social Skills Children AutismДокумент3 страницыOxytocin Spray Boosts Social Skills Children AutismidjacobsОценок пока нет
- Oxytocin Pathways and The Evolution of Human BehaviorДокумент36 страницOxytocin Pathways and The Evolution of Human BehavioridjacobsОценок пока нет
- ZR 12088Документ7 страницZR 12088idjacobsОценок пока нет
- Sleep GabaДокумент16 страницSleep GabaidjacobsОценок пока нет
- The Medicinal Chemistry of PsychedelicsДокумент6 страницThe Medicinal Chemistry of PsychedelicsidjacobsОценок пока нет
- Pratt, W. E., & Kelley, A. E. (2004) - Nucleus Accumbens Acetylcholine Regulates AppetitiveДокумент38 страницPratt, W. E., & Kelley, A. E. (2004) - Nucleus Accumbens Acetylcholine Regulates AppetitiveidjacobsОценок пока нет
- Oxytocin and Serotonin Brain Mechanisms in The Nonhuman PrimateДокумент10 страницOxytocin and Serotonin Brain Mechanisms in The Nonhuman PrimateidjacobsОценок пока нет
- Anxiety Disorders and Gaba NeutransmiterДокумент11 страницAnxiety Disorders and Gaba Neutransmitercitra dewiОценок пока нет
- Thesis SerotoninДокумент42 страницыThesis SerotoninidjacobsОценок пока нет
- Happy Chemicals01 PDFДокумент43 страницыHappy Chemicals01 PDFidjacobs100% (1)
- Depression SerotoninДокумент5 страницDepression SerotoninidjacobsОценок пока нет
- CH12 159-168 PDFДокумент10 страницCH12 159-168 PDFidjacobsОценок пока нет
- Learningmemory PDFДокумент8 страницLearningmemory PDFidjacobsОценок пока нет
- Acetyl DesДокумент38 страницAcetyl DesidjacobsОценок пока нет
- Gais04 PDFДокумент5 страницGais04 PDFidjacobsОценок пока нет
- Brainstem Acetylcholine Release and REM SleepДокумент6 страницBrainstem Acetylcholine Release and REM SleepidjacobsОценок пока нет
- RBDДокумент20 страницRBDsavvy_as_98Оценок пока нет
- Pi Is 1364661310001865Документ9 страницPi Is 1364661310001865idjacobsОценок пока нет
- Corrections: USA (100, 15806-15811 First Published December 12, 2003Документ4 страницыCorrections: USA (100, 15806-15811 First Published December 12, 2003idjacobsОценок пока нет
- Cognition and MemoryДокумент6 страницCognition and MemoryidjacobsОценок пока нет
- Acetyl C NeuronДокумент14 страницAcetyl C NeuronidjacobsОценок пока нет
- Chapter 15: The Autonomic Nervous SystemДокумент7 страницChapter 15: The Autonomic Nervous SystemidjacobsОценок пока нет
- 8 1483638611Документ1 страница8 1483638611idjacobsОценок пока нет
- Acetate AcetylcholineДокумент1 страницаAcetate AcetylcholineidjacobsОценок пока нет
- 05 07 08MK 0777protocol2.1Документ23 страницы05 07 08MK 0777protocol2.1idjacobsОценок пока нет
- Gabas Intro 2002Документ12 страницGabas Intro 2002idjacobsОценок пока нет
- Alzheimer's Disease and Acetylcholine Receptors: Neu Obiologi E Expe Iment LisДокумент7 страницAlzheimer's Disease and Acetylcholine Receptors: Neu Obiologi E Expe Iment LisidjacobsОценок пока нет
- Pharmacology 18a Priciples of GABAergic TransmissionДокумент2 страницыPharmacology 18a Priciples of GABAergic TransmissionidjacobsОценок пока нет
- GABA Receptors and The Immune System-012012Документ23 страницыGABA Receptors and The Immune System-012012idjacobsОценок пока нет
- Pharmacology 18a Priciples of GABAergic TransmissionДокумент2 страницыPharmacology 18a Priciples of GABAergic TransmissionidjacobsОценок пока нет
- YSA'ların Tarihçesi ve Temel KavramlarıДокумент82 страницыYSA'ların Tarihçesi ve Temel Kavramlarıuyelikicin3737100% (1)
- Visual Closure Cierre VisualДокумент221 страницаVisual Closure Cierre VisualBlanca Espinal100% (3)
- Internet Addiction and Depression, Anxiety and Stress: I O J E SДокумент11 страницInternet Addiction and Depression, Anxiety and Stress: I O J E SShari' Si WahyuОценок пока нет
- ReferencesДокумент4 страницыReferencesapi-290353359Оценок пока нет
- Day 3 MSN 1Документ13 страницDay 3 MSN 1Ramzen Raphael DomingoОценок пока нет
- 13 Phacomatoses: Sturge-Weber SyndromeДокумент3 страницы13 Phacomatoses: Sturge-Weber SyndromesoumenОценок пока нет
- Fonseca Toscano Wermke Melodies That HelpДокумент13 страницFonseca Toscano Wermke Melodies That HelpAle Alonso100% (1)
- Psychology - Article 38Документ1 страницаPsychology - Article 38piping stressОценок пока нет
- Soothing The Traumatized Brain: WorksheetsДокумент5 страницSoothing The Traumatized Brain: WorksheetsAlguémОценок пока нет
- Endocrine System-Lesson PlanДокумент2 страницыEndocrine System-Lesson PlanMark Joseph DiazОценок пока нет
- How Choices Shape Our Freedom and FutureДокумент42 страницыHow Choices Shape Our Freedom and FutureStephanie Castillon100% (1)
- Case Presentation Psych PDFДокумент11 страницCase Presentation Psych PDFNorsakinah Mohd AhmadОценок пока нет
- MCQ Pathways9th.IДокумент4 страницыMCQ Pathways9th.Iareej alblowi100% (1)
- A Safe, Natural Way To End AddictionДокумент9 страницA Safe, Natural Way To End AddictionnupathwaysОценок пока нет
- Esmé Weijun Wang's Insightful Look at Mental HealthДокумент4 страницыEsmé Weijun Wang's Insightful Look at Mental Healthgghyo88Оценок пока нет
- Nerve CellДокумент45 страницNerve Cellapi-420631518Оценок пока нет
- Definitions of Stress: DR Gillian Butler PHDДокумент5 страницDefinitions of Stress: DR Gillian Butler PHDHawraa HawraaОценок пока нет
- Self Confedence in SportsДокумент5 страницSelf Confedence in Sportsapi-254541038Оценок пока нет
- Techathon-2k23 230607 151215Документ2 страницыTechathon-2k23 230607 151215christojames 1482Оценок пока нет
- The Effects of Sleep Deprivation To Students' Academic Performance at Batasan Hills National High SchoolДокумент13 страницThe Effects of Sleep Deprivation To Students' Academic Performance at Batasan Hills National High SchoolAngela ErandioОценок пока нет
- 4 Hbo Module 3 - Lesson 1-3Документ18 страниц4 Hbo Module 3 - Lesson 1-3Ron TrimillosОценок пока нет
- Neuro NotesДокумент10 страницNeuro NotesPatrickОценок пока нет
- EMG Biofeedback Techniques for Muscle Re-educationДокумент38 страницEMG Biofeedback Techniques for Muscle Re-educationSreeraj S RОценок пока нет
- Reading As A Cognitive ProcessДокумент16 страницReading As A Cognitive ProcessgatuskevinОценок пока нет
- Brockport Brain Gym Study Effects on LearningДокумент95 страницBrockport Brain Gym Study Effects on LearningmuthoharohОценок пока нет
- Keywords: Birth Order, Early Recollection, Style of Life, Adolescents, Group CounsellingДокумент22 страницыKeywords: Birth Order, Early Recollection, Style of Life, Adolescents, Group CounsellingSheza FarooqОценок пока нет
- A Powerful Way To Unleash Your Natural Creativity by Tim HarfordДокумент2 страницыA Powerful Way To Unleash Your Natural Creativity by Tim HarfordYla ReyesОценок пока нет
- Activity 5Документ2 страницыActivity 5Haezil MioleОценок пока нет
- The Search For Existential Identity Patient-Therapist Dialogues in Humanistic Psychotherapy (Bugental, James F. T)Документ360 страницThe Search For Existential Identity Patient-Therapist Dialogues in Humanistic Psychotherapy (Bugental, James F. T)Ricardo Canales RojasОценок пока нет
- Top 50 Brain Teasers and Mind GamesДокумент4 страницыTop 50 Brain Teasers and Mind GamesSharpBrains100% (23)