Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Rigid Body Statics Chapter 3
Загружено:
rafiah bazlaaОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Rigid Body Statics Chapter 3
Загружено:
rafiah bazlaaАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Tutorial Chapter 3: Statics of Rigid Body
Resultants of a Force and Couple System
1. List the characteristics of force by the aid of appropriate diagram.
2. Explain the conditions to preserve the static equilibrium for a rigid body.
3. Define the moment of a force about a point for two-dimensional objects. Describe the
moment equation by the help of sketch.
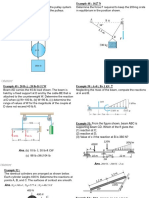
4. The two forces and a moment are applied to an angle bracket as shown in Figure 1.
Determine:
a. The resultant of this system of forces
b. The distance from the resultant force to the point A
[ans: a) FR =154.9 N, = 18.83 b) d = 0.179 m ]
Figure 1
5. A beam is loaded as shown in Figure 2. Neglecting the reactions at supports, determine
the equivalent force couple system at point A.
Figure 2
[ans: a) FR =-150 N, MA = 250 N.m ]
6. A post AB is subjected with three forces as shown in Figure 3.
a. Determine the resultant force and couple moment that is acting at point A.
1
Prepared by Adila Nalisa Mohd Roslan
Tutorial Chapter 3: Statics of Rigid Body
b. If those three forces are replace with the resultant force obtained from part a),
determine the distance of this resultant force from point A along AB
[ans: a) FR =15.62 kN, =39.8, MA = 22 kN.m , b) d = 1.833 m from point A]
Figure 3
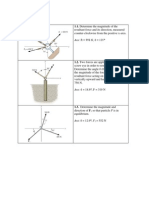
7. Three forces are acting on a post as shown in Figure 4. Replace the forces by a single
resultant force and determine the point of application of the resultant force that is
measured from point A.
Figure 4
[ans: a) FR =1.676 kN, =28.5, MA = -2.167 kN.m , b) d = 1.471 m from point A]
8. Replace the two forces in Figure 5 by an equivalent resultant force and couple moment
at point O if given F= 30 N.
2
Prepared by Adila Nalisa Mohd Roslan
Tutorial Chapter 3: Statics of Rigid Body
Figure 5
[ans: FR =127.12 N, =73.55, MO = 27.23 N.m]
3
Prepared by Adila Nalisa Mohd Roslan
Tutorial Chapter 3: Statics of Rigid Body
Reactions at Supports and Connections // Equilibrium of a 2-Force and 3-Force Body
1. Explain the concepts of equilibrium of two-force member and three-force member.
Sketch appropriate diagrams.
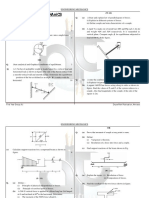
2. Figure 6 shows a light rod AB, hinge at A and B and attached at B to a short link BD.
Draw the free body diagram of the two-force and three-force members if the system is in
static equilibrium.
Figure 6
3. A horizontal beam is supported by a hinge and pulley and is loaded as shown in Figure
7. Neglecting the weight of the beam and the friction of the pulley, determine the tension
in cable ADEB and the component of the reaction at C.
Figure 7
[ans: TADEB =156.17 N, CX = 266.23N, Cy= -9.744 N]
4
Prepared by Adila Nalisa Mohd Roslan
Tutorial Chapter 3: Statics of Rigid Body
4. A beam shown in Figure 8 is supported by a pin at A and a roller at B. Determine the
reaction forces at the pin A and the roller B.
Figure 8
[ans: By =5 k N, AX = 0 N, Ay= 13 kN]
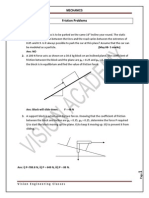
5. A beam is loaded as shown in Figure 10. Neglecting the thickness of the beam,
calculate the horizontal and vertical component of reactions at supports A and B.
Figure 9
[ans: By =348.1 N, AX = 230.77 N, Ay= - 51.95 N]
6. Three loads and a 8 kN tension are applied to a beam as shown in Figure 10. The beam
is supported by a pin at A and roller at B.
a. Draw the free body diagram of the beam.
b. By neglecting the thickness of the beam, determine the reactions at A and B.
5
Prepared by Adila Nalisa Mohd Roslan
Tutorial Chapter 3: Statics of Rigid Body
Figure 10
[ans: By =84.051 kN, AX = -5.657kN, Ay= - 3.394kN]
6
Prepared by Adila Nalisa Mohd Roslan
Вам также может понравиться
- CSU-Cabadbaran Advance Review For EE: Topic: Mechanics 1 - StaticsДокумент10 страницCSU-Cabadbaran Advance Review For EE: Topic: Mechanics 1 - StaticsCinderella WhiteОценок пока нет
- Summative 1 ReviewerДокумент11 страницSummative 1 ReviewerJuli BakerОценок пока нет
- Chapter 7 Linkage, Recombination, and Eukaryotic Gene MappingДокумент20 страницChapter 7 Linkage, Recombination, and Eukaryotic Gene MappingSiamHashan100% (1)
- Equivalent Force Systems and Free Body Diagrams Solved ProblemsДокумент14 страницEquivalent Force Systems and Free Body Diagrams Solved ProblemsYun RamОценок пока нет
- Rigid Body Statics Concepts and ProblemsДокумент43 страницыRigid Body Statics Concepts and ProblemsJC CABESOОценок пока нет
- Engineering Mechanics Lecture Slides for Statics CourseДокумент213 страницEngineering Mechanics Lecture Slides for Statics CourseradniksrbijeОценок пока нет
- Approximate Derivatives Using Finite DifferencesДокумент13 страницApproximate Derivatives Using Finite DifferencesEugene Embalzado Jr.100% (1)
- ES 12 - Chapter 17 - Plane Motion of Rigid Bodies - Energy and Momentum MethodsДокумент50 страницES 12 - Chapter 17 - Plane Motion of Rigid Bodies - Energy and Momentum Methodscriscab12345Оценок пока нет
- Equilibrium SystemsДокумент12 страницEquilibrium SystemsEmilio Joaquin FloresОценок пока нет
- RMK Engineering College mechanical engineering tutorial problemsДокумент22 страницыRMK Engineering College mechanical engineering tutorial problemskalirajgurusamy33% (3)
- CENGR 3140 - Numerical Differentiation MethodsДокумент4 страницыCENGR 3140 - Numerical Differentiation MethodsBry RamosОценок пока нет
- STATICS ProblemsДокумент6 страницSTATICS Problemsdesertfox1943Оценок пока нет
- Center of GravityДокумент33 страницыCenter of GravitynellaОценок пока нет
- Mechanics QuestionsДокумент6 страницMechanics QuestionsPranjalShankhdharОценок пока нет
- Dynamics Worksheet 2 - ForcesДокумент2 страницыDynamics Worksheet 2 - ForcesJennifer Moore100% (1)
- Overviews of StaticsДокумент70 страницOverviews of StaticsJacous WcyОценок пока нет
- Engineering Mechanics QUESTION PAPERSДокумент31 страницаEngineering Mechanics QUESTION PAPERSgotu123Оценок пока нет
- Dynamics of Rigid BodiesДокумент3 страницыDynamics of Rigid BodiesRalph Lauren RodriguezОценок пока нет
- Chap 3-EquilibriumДокумент23 страницыChap 3-Equilibriumafnene1Оценок пока нет
- Fundamentals of geotechnical engineering: Weight-volume relationships and soil propertiesДокумент2 страницыFundamentals of geotechnical engineering: Weight-volume relationships and soil propertiesJustin Carlo Domingo100% (1)
- Direct Instruction 1Документ6 страницDirect Instruction 1api-314997078100% (1)
- Rigid Body Equilibrium ExamplesДокумент27 страницRigid Body Equilibrium ExamplesCarla Vernice SolidorОценок пока нет
- FrictionДокумент5 страницFrictionmishra_rakesh161989Оценок пока нет
- Vectors Scalars PPTДокумент14 страницVectors Scalars PPTDaniel LeeОценок пока нет
- UNIFORM CIRCULAR MOTION - Notes PDFДокумент5 страницUNIFORM CIRCULAR MOTION - Notes PDFJohnston ThevarajahОценок пока нет
- Integral Calculus: Engr. Anacleto M. Cortez JRДокумент10 страницIntegral Calculus: Engr. Anacleto M. Cortez JRPanfilo Diaz LacsonОценок пока нет
- STR ModuleДокумент10 страницSTR ModuleViamae Avellana CabutajeОценок пока нет
- Module 2 - Equilibrium of Rigid BodiesДокумент21 страницаModule 2 - Equilibrium of Rigid BodiesJoyce AsisОценок пока нет
- Mechanics of Rigid BodiesДокумент15 страницMechanics of Rigid BodiessoulcivicОценок пока нет
- Mechanics CH-3 MarkosДокумент16 страницMechanics CH-3 MarkosGadisaОценок пока нет
- QUIZ ASSIGNMENT NO. 2 Dynamic of Rigid Bodies Answer Key 1Документ26 страницQUIZ ASSIGNMENT NO. 2 Dynamic of Rigid Bodies Answer Key 1AicelleОценок пока нет
- Module 6 Plane GeometryДокумент2 страницыModule 6 Plane GeometryGlenn Frey LayugОценок пока нет
- Equillibrium of Coplanar Concurrent ForcesДокумент17 страницEquillibrium of Coplanar Concurrent Forcessalman husainОценок пока нет
- Engineering Mechanics: SolutionДокумент4 страницыEngineering Mechanics: SolutionasluznetОценок пока нет
- 2.3 LabДокумент11 страниц2.3 LabJanno Acayen100% (1)
- Exer1322 PDFДокумент21 страницаExer1322 PDFNelva CSОценок пока нет
- Viriable Separable Differential EquationsДокумент12 страницViriable Separable Differential EquationsrootveshmehtaОценок пока нет
- QUIZ ASSIGNMENT NO. 1 Dynamic of Rigid Bodies Answer KeyДокумент15 страницQUIZ ASSIGNMENT NO. 1 Dynamic of Rigid Bodies Answer KeyAicelleОценок пока нет
- 1) Dynamics of Rigid BodiesДокумент18 страниц1) Dynamics of Rigid Bodiesnicolo agustinОценок пока нет
- Differential EquationsДокумент65 страницDifferential EquationsRayhan BОценок пока нет
- Chapter 14 Kinetics of Particle - Work & EnergyДокумент37 страницChapter 14 Kinetics of Particle - Work & Energyحزيفہ اعظمОценок пока нет
- Homework 1 3Документ6 страницHomework 1 3inisdeprawn100% (2)
- Coplanar Parallel Force SystemДокумент5 страницCoplanar Parallel Force Systemclarissa ordonoОценок пока нет
- ES 11 Formula Sheet v1Документ3 страницыES 11 Formula Sheet v1Sam RuelosОценок пока нет
- Equilibrium of Particles ChapterДокумент6 страницEquilibrium of Particles ChapterRhey LuceroОценок пока нет
- Statics of Rigid Bodies Problem Set 1 SolutionsДокумент2 страницыStatics of Rigid Bodies Problem Set 1 SolutionsGillian AmbaОценок пока нет
- Rigid Body Dynamics Lecture HandoutsДокумент4 страницыRigid Body Dynamics Lecture HandoutsJaya Mae Mañago0% (1)
- Assignment-3 - Engg Mech PDFДокумент6 страницAssignment-3 - Engg Mech PDFNiteshОценок пока нет
- Dynamics - Chapter - 2 - Kinematics - of - Particles Rectilinear Motion To Normal Tangential Coordinates PDFДокумент56 страницDynamics - Chapter - 2 - Kinematics - of - Particles Rectilinear Motion To Normal Tangential Coordinates PDFJP NielesОценок пока нет
- Resultant Force Systems ExplainedДокумент2 страницыResultant Force Systems Explainedmerj05Оценок пока нет
- Acceleration Analysis of MechanismsДокумент32 страницыAcceleration Analysis of MechanismsThahir Shah100% (1)
- Normal and Tangential ComponentsДокумент19 страницNormal and Tangential ComponentsGarrey BrionesОценок пока нет
- Banking of Highway Curves:: W G V R W V GRДокумент10 страницBanking of Highway Curves:: W G V R W V GRRetro GamerОценок пока нет
- Lecture 4 - QuadrilateralsДокумент29 страницLecture 4 - QuadrilateralsSandra Enn BahintingОценок пока нет
- MODULE 3. Kinetics of ParticlesДокумент40 страницMODULE 3. Kinetics of ParticlesAron H OcampoОценок пока нет
- GE 104 - Lecture 2.2Документ40 страницGE 104 - Lecture 2.2Jigg PelayoОценок пока нет
- Rectilinear Motion ExplainedДокумент22 страницыRectilinear Motion ExplainedJamie MedallaОценок пока нет
- Statics FundamentalsДокумент142 страницыStatics FundamentalsDean Ackles100% (1)
- NCESQ 2018 QuestionsДокумент3 страницыNCESQ 2018 QuestionsKhent Alfred B. DerechoОценок пока нет
- Strategy and Planning For Sponsorship CSRДокумент3 страницыStrategy and Planning For Sponsorship CSRrafiah bazlaaОценок пока нет
- Report CSRДокумент3 страницыReport CSRrafiah bazlaaОценок пока нет
- Schematic Diagram of The Adsorption Cooling SystemДокумент1 страницаSchematic Diagram of The Adsorption Cooling Systemrafiah bazlaaОценок пока нет
- Part B: Sungai TekalaДокумент7 страницPart B: Sungai Tekalarafiah bazlaaОценок пока нет
- 3.2 Crisis Management MAC 2020Документ53 страницы3.2 Crisis Management MAC 2020rafiah bazlaaОценок пока нет
- 3.1 Engineering Ethics SEPT 2018 PDFДокумент105 страниц3.1 Engineering Ethics SEPT 2018 PDFfarhannaim15Оценок пока нет
- 3.3 Practicing Ethics As An Engineering Student PDFДокумент20 страниц3.3 Practicing Ethics As An Engineering Student PDFمحمد فائزОценок пока нет
- Analysis For Common Problems in Solar Domestic Hot Water System Field Testing in ChinaДокумент7 страницAnalysis For Common Problems in Solar Domestic Hot Water System Field Testing in Chinasurajss8585Оценок пока нет
- Ent 600Документ1 страницаEnt 600rafiah bazlaaОценок пока нет
- 1274WKS 2 Noise Control Guide Management of Noise at Work PDFДокумент216 страниц1274WKS 2 Noise Control Guide Management of Noise at Work PDFrafiah bazlaaОценок пока нет
- Ent 600Документ1 страницаEnt 600rafiah bazlaaОценок пока нет
- ENT300 StudentMarksДокумент1 страницаENT300 StudentMarksrafiah bazlaaОценок пока нет
- Report MaterialДокумент17 страницReport Materialrafiah bazlaaОценок пока нет
- JJ 103 Fitting ReportДокумент11 страницJJ 103 Fitting Reportrafiah bazlaaОценок пока нет
- ME PDC Course PlanДокумент6 страницME PDC Course PlanBabitha DhanaОценок пока нет
- Operations Management: Supplement 10 - Work MeasurementДокумент39 страницOperations Management: Supplement 10 - Work MeasurementSupriya NandaОценок пока нет
- En Co2a MSSДокумент23 страницыEn Co2a MSSNicaur Dan PopescuОценок пока нет
- Assignment Channel CodingДокумент2 страницыAssignment Channel CodingLakshitha Prabath WijesingheОценок пока нет
- Monbukagakusho Physics 2010 SolutionДокумент26 страницMonbukagakusho Physics 2010 SolutionIskandar Setiadi100% (11)
- Trig2 Tutorial VДокумент2 страницыTrig2 Tutorial VSabrina LinuxОценок пока нет
- Structural Design of Multi-Storeyed Building by U H VaryaniДокумент5 страницStructural Design of Multi-Storeyed Building by U H VaryanidineshОценок пока нет
- Verification and ValidationДокумент22 страницыVerification and Validationapi-3806986Оценок пока нет
- QPCSEON16Документ929 страницQPCSEON16Farhan Sheikh MuhammadОценок пока нет
- Rational Numbers on the Number LineДокумент4 страницыRational Numbers on the Number LineESTEPHANIE TUMAGANОценок пока нет
- Details of Fluid MechanicsДокумент25 страницDetails of Fluid MechanicsJeevan RoyОценок пока нет
- GATE Questions On Laplace TransformДокумент6 страницGATE Questions On Laplace Transformgautam100% (1)
- Knit 3Документ189 страницKnit 3adnan100% (1)
- Ia Ha 2Документ4 страницыIa Ha 2Er Shubham RaksheОценок пока нет
- ProposalДокумент9 страницProposalAsaad iqbalОценок пока нет
- LSI Layout Using Hierarchical Design With Compaction: Liudvikas Abraitis and Arvydas BarilaДокумент4 страницыLSI Layout Using Hierarchical Design With Compaction: Liudvikas Abraitis and Arvydas BarilaNirmal KushwahaОценок пока нет
- ANALYSIS OF SERVICE QUALITY PERFORMANCE IMPACT ON STUDENT SATISFACTIONДокумент12 страницANALYSIS OF SERVICE QUALITY PERFORMANCE IMPACT ON STUDENT SATISFACTIONfadlyОценок пока нет
- Mathematics - Class 6 CH - 5Документ35 страницMathematics - Class 6 CH - 5RUPali KUMARIОценок пока нет
- Voice Based Application As Medicine Spotter For Visually ImpairedДокумент5 страницVoice Based Application As Medicine Spotter For Visually ImpairedCh.pranushaОценок пока нет
- FFT convolution stepsДокумент19 страницFFT convolution stepsAbishek RajeshОценок пока нет
- Structural and Design Specific of Space Grid SystemДокумент11 страницStructural and Design Specific of Space Grid SystemClaudia Kristell Mattos RivasОценок пока нет
- Investigation on Pole-Slot Combinations for PM Machines with Concentrated WindingsДокумент6 страницInvestigation on Pole-Slot Combinations for PM Machines with Concentrated WindingsAnna DrKiss SzűcsnéОценок пока нет
- Statistics - Mean - 700 - 800 Level QuestionsДокумент4 страницыStatistics - Mean - 700 - 800 Level QuestionsSumalya BhattaacharyaaОценок пока нет
- CS 302 PDFДокумент7 страницCS 302 PDFMaz Har UlОценок пока нет
- Jean PiagetДокумент23 страницыJean PiagetSachini PonweeraОценок пока нет
- Electromagnetic Induction Lesson PlanДокумент5 страницElectromagnetic Induction Lesson PlanRenz CruzОценок пока нет
- 19MT1201 MFE Session Problems 2019 - 20Документ22 страницы19MT1201 MFE Session Problems 2019 - 20sai tejaОценок пока нет