Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Problem Set Week 1
Загружено:
cr4zyvi3tАвторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Problem Set Week 1
Загружено:
cr4zyvi3tАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Problem
Set Week 1-Cell Biol 336
1. How do animal cells maintain membrane fluidity, and hence membrane function,
in response to decreased temperature?
2. What are the primary functions of the plasma membrane in all cells?
3. Biomembranes contain many different types of lipid molecules. What are the three
main types of lipid molecules found in biomembranes? How are the three types similar,
and how are they different?
4.
What
are
detergents?
How
do
ionic
and
non-ionic
detergents
differ
in
their
ability
to
disrupt
membrane
structure?
5.
Two
membrane
preparations
have
been
derived
from
the
plasma
membrane
of
erythrocytes
and
are
present
in
a
buffer
solution:
(1)
right-side-out
membrane
vesicles,
in
which
the
exoplasmic
leaflet
of
the
vesicle
faces
the
buffer
(equivalent
in
orientation
to
that
of
the
exoplasmic
leaflet
of
the
intact
plasma
membrane);
and
(2)
inside-out
membrane
vesicles
in
which
the
exoplasmic
leaflet
faces
the
interior
of
the
vesicles.
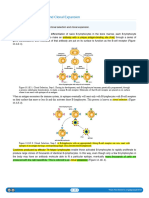
a. Annexin
V
is
a
protein
that
binds
to
phosphatidylserine,
one
of
the
phospholipids
present
in
cell
membranes.
Fluorescently
labeled
annexin
V
is
mixed
with
each
vesicle
preparation.
The
vesicles
are
washed
to
remove
unbound
annexin
V
and
then
examined
by
fluorescence
microscopy.
Presence
of
annexin
V
is
detected
by
green
fluorescence,
as
shown
above.
What
can
be
deduced
from
these
data?
b. A monoclonal antibody has been prepared against band 3, an integral
membrane protein of the erythrocyte plasma membrane. The antibody
recognizes an epitope on the carboxy terminus of band 3. Incubation of the two
membrane vesicle preparations with this antibody following by staining with a
fluorescently labeled secondary antibody generates data similar to that shown in
the micrographs above. What can you deduce about the structure of band 3
from these data?
6. Proteins that for a -barrel pore in the membrane have several strands that
span the membrane. The pore-facing side of each strand carries hydrophilic amino
acid side chains, whereas the bilayer-facing sides carry hydrophobic amino acid side
chains. Which of the three 10-amino acid sequences listed below is the most likely
candidate for a transmembrane strand in a -barrel pore? Explain.
A. ADFKLSVELT
B. AFLVLDKSET
C. AFDKLVSELT
7. Why is it that membrane spanning protein segments are almost always helices
or barrels and never disordered chains?
Вам также может понравиться
- Human Chromosomes: An Illustrated Introduction to Human CytogeneticsОт EverandHuman Chromosomes: An Illustrated Introduction to Human CytogeneticsРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)
- Structure and Function of Biological MembranesОт EverandStructure and Function of Biological MembranesLawrence I. RothfieldОценок пока нет
- CH1131 - Tutorial 2 Questions - Week4 - 01 02 04 Sep 2015Документ3 страницыCH1131 - Tutorial 2 Questions - Week4 - 01 02 04 Sep 2015joshuaОценок пока нет
- Understandings, Applications and Skills (This Is What You Maybe Assessed On)Документ11 страницUnderstandings, Applications and Skills (This Is What You Maybe Assessed On)yara hazemОценок пока нет
- Assignment For Membrane StructureДокумент3 страницыAssignment For Membrane Structurejane austin lynn rebancosОценок пока нет
- Test Bank For Diagnostic Microbiology 4th Edition MahonДокумент15 страницTest Bank For Diagnostic Microbiology 4th Edition Mahonamityharoldv84Оценок пока нет
- SLE206 Cell Biology Practice Exam 2019 - ANSWERSДокумент19 страницSLE206 Cell Biology Practice Exam 2019 - ANSWERSflyingdugong98Оценок пока нет
- Molecular Cell Biology Lodish 7th Edition Test BankДокумент8 страницMolecular Cell Biology Lodish 7th Edition Test BankVictoriaWilliamsegtnm100% (75)
- Molecular Cell Biology 7th Edition Lodish Test BankДокумент8 страницMolecular Cell Biology 7th Edition Lodish Test Bankrosaanqo8100% (33)
- Assignment For Membrane Structure: Ane Austin Lynn N. Rebancos Bsed-Science 3AДокумент9 страницAssignment For Membrane Structure: Ane Austin Lynn N. Rebancos Bsed-Science 3Ajane austin lynn rebancosОценок пока нет
- Problem Set 51-100Документ11 страницProblem Set 51-100Penelope LeizonОценок пока нет
- Molecular Cell Biology 7Th Edition Lodish Test Bank Full Chapter PDFДокумент29 страницMolecular Cell Biology 7Th Edition Lodish Test Bank Full Chapter PDFrorybridgetewe100% (11)
- BT102 Microbiology Current Paper Solved Question Mid Term December DownloadДокумент9 страницBT102 Microbiology Current Paper Solved Question Mid Term December Downloadbc230422430skhОценок пока нет
- Pathophysiology The Biologic Basis For Disease in Adults and Children Mccance 6th Edition Test BankДокумент17 страницPathophysiology The Biologic Basis For Disease in Adults and Children Mccance 6th Edition Test BankAnna Jones100% (22)
- Test Bank For Diagnostic Microbiology 4th Edition MahonДокумент15 страницTest Bank For Diagnostic Microbiology 4th Edition MahonCatherine Smith0% (1)
- Assignment OF PhysiologyДокумент20 страницAssignment OF PhysiologyAhmed KhanОценок пока нет
- HISTOLOGY LaboratoryДокумент5 страницHISTOLOGY LaboratoryFarida GuialelОценок пока нет
- Cell MembraneДокумент2 страницыCell MembraneKim Antonette50% (2)
- Biology Chapter 3Документ2 страницыBiology Chapter 3JUDYОценок пока нет
- Test Bank For Diagnostic Microbiology 4th Edition MahonДокумент36 страницTest Bank For Diagnostic Microbiology 4th Edition Mahonumbrella.intrauofs100% (48)
- Cell Transport Review ANSWERSДокумент7 страницCell Transport Review ANSWERSAnonymous pUJNdQОценок пока нет
- Plant Cell Structure and Importance of Cell Organelles I Post Harvest PhysiologyДокумент10 страницPlant Cell Structure and Importance of Cell Organelles I Post Harvest Physiologychristom karungariОценок пока нет
- Bacteriology Exam IДокумент7 страницBacteriology Exam ITorillo KimОценок пока нет
- Bab 1 2 Biomembran PDFДокумент84 страницыBab 1 2 Biomembran PDFMuh JufriОценок пока нет
- Complement SystemДокумент12 страницComplement Systemdhruvdesai24Оценок пока нет
- Pathophysiology The Biologic Basis For Disease in Adults and Children Mccance 6th Edition Test BankДокумент17 страницPathophysiology The Biologic Basis For Disease in Adults and Children Mccance 6th Edition Test Bankostreajuridicodhs8Оценок пока нет
- Bacteriology DR - NidhalДокумент13 страницBacteriology DR - NidhalAlexandru Ciprian RăduțОценок пока нет
- NSSI Gen Bio 1 Module No Answer KeyДокумент43 страницыNSSI Gen Bio 1 Module No Answer Keygian leepsuОценок пока нет
- Test Bank For Biochemistry A Short Course 3Rd Edition by Tymoczko Test Bank Isbn 1464126135 9781464126130 Full Chapter PDFДокумент36 страницTest Bank For Biochemistry A Short Course 3Rd Edition by Tymoczko Test Bank Isbn 1464126135 9781464126130 Full Chapter PDFcindy.bishop135100% (12)
- Biology Block Test Ganjil Preparation WorksheetДокумент12 страницBiology Block Test Ganjil Preparation WorksheetSMAXICLouis Bintang AlexisОценок пока нет
- Problem Set 1-50Документ12 страницProblem Set 1-50Penelope LeizonОценок пока нет
- Unit 2 Practice Test PDFДокумент5 страницUnit 2 Practice Test PDFCandace LawОценок пока нет
- Please Use Endnote Program To Organize Your ReferencesДокумент25 страницPlease Use Endnote Program To Organize Your ReferencesMy PlanОценок пока нет
- Dwnload Full Human Physiology 2nd Edition Sherwood Test Bank PDFДокумент36 страницDwnload Full Human Physiology 2nd Edition Sherwood Test Bank PDFbogoschollys100% (9)
- Prescotts Microbiology 10th Edition Willey Solutions Manual 1Документ4 страницыPrescotts Microbiology 10th Edition Willey Solutions Manual 1ruth98% (48)
- Prescotts Microbiology 10th Edition Willey Solutions Manual 1Документ35 страницPrescotts Microbiology 10th Edition Willey Solutions Manual 1angelamayqbygsdmeki100% (26)
- Prescotts Microbiology 10Th Edition Willey Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFДокумент25 страницPrescotts Microbiology 10Th Edition Willey Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFbob.morris579100% (14)
- Bab 6 Sruktur Dan Fungsi Sel Bakteria (I)Документ9 страницBab 6 Sruktur Dan Fungsi Sel Bakteria (I)Shakira AmiraОценок пока нет
- Test Bank For Fundamentals of Human Physiology 4th Edition Lauralee SherwoodДокумент23 страницыTest Bank For Fundamentals of Human Physiology 4th Edition Lauralee Sherwooda245141930100% (2)
- Blotting TechniquesДокумент8 страницBlotting TechniquesFitrianiОценок пока нет
- Topic 7.3 Review Practice QuestionsДокумент5 страницTopic 7.3 Review Practice QuestionsGlen JojiОценок пока нет
- 2023-Paper-48 - Marking SchemeДокумент14 страниц2023-Paper-48 - Marking SchemeWijesiri D WОценок пока нет
- Biol120 Lecture 7Документ55 страницBiol120 Lecture 7mooosemnОценок пока нет
- Problems SolutionДокумент3 страницыProblems SolutionJanelle Jabby ReidОценок пока нет
- Functional and Structural Properties of Natural BiomembranesДокумент7 страницFunctional and Structural Properties of Natural BiomembranesAhsan RazaОценок пока нет
- Lecture - Theory of Clonal - Selection - and - Clonal - ExpansionДокумент4 страницыLecture - Theory of Clonal - Selection - and - Clonal - Expansionrockyrawat01012003Оценок пока нет
- Biochimica Et Biophysica Acta: Joel Selkrig, Denisse L. Leyton, Chaille T. Webb, Trevor LithgowДокумент9 страницBiochimica Et Biophysica Acta: Joel Selkrig, Denisse L. Leyton, Chaille T. Webb, Trevor LithgowalkatsumiОценок пока нет
- Cell Bio Assignment - Plasma Membrane and Basement MembraneДокумент2 страницыCell Bio Assignment - Plasma Membrane and Basement Membranerahul mauryaОценок пока нет
- Molecular Cell Biology 7th Edition Lodish Test BankДокумент6 страницMolecular Cell Biology 7th Edition Lodish Test Bankdimyjeba100% (1)
- Csir NotesДокумент61 страницаCsir Noteskammo30Оценок пока нет
- Molecular Cell Biology 7th Edition Lodish Test BankДокумент8 страницMolecular Cell Biology 7th Edition Lodish Test BankLaurenThompsonfpniz100% (15)
- Solution BiotechДокумент54 страницыSolution Biotechkavita sahaiОценок пока нет
- Chapter 6 A Tour of The CellДокумент3 страницыChapter 6 A Tour of The CellMohammad Mahrus Bin AshfaqОценок пока нет
- Full Download Test Bank For Textbook of Diagnostic Microbiology 5th Edition by Mahon PDF Full ChapterДокумент36 страницFull Download Test Bank For Textbook of Diagnostic Microbiology 5th Edition by Mahon PDF Full Chapteruptakespecktaz87n100% (19)
- 4.22 Cell Communication in Class Practice From Past Year Paper (Y11)Документ3 страницы4.22 Cell Communication in Class Practice From Past Year Paper (Y11)Harry CaoОценок пока нет
- Cell Exam Practice Multiple ChoiceДокумент46 страницCell Exam Practice Multiple ChoiceVulneraSanentur67% (3)
- 235022zool H CC T O4 Cell Biology MCQДокумент44 страницы235022zool H CC T O4 Cell Biology MCQIjaz ZoologistОценок пока нет
- The Working Cell: Chapter ObjectivesДокумент12 страницThe Working Cell: Chapter Objectivesirene9tan9ailianОценок пока нет
- 482020104354AM-Class 9 Biology NotesДокумент7 страниц482020104354AM-Class 9 Biology Noteskmdmohideen2297Оценок пока нет
- Initial Velocities of Enzyme Catalyzed Reactions (Experimentally Observed at Low (E) Multiple Turnover Conditions) (Steady State)Документ7 страницInitial Velocities of Enzyme Catalyzed Reactions (Experimentally Observed at Low (E) Multiple Turnover Conditions) (Steady State)cr4zyvi3tОценок пока нет
- Chapter 6 Slides (Part II) CH490Документ33 страницыChapter 6 Slides (Part II) CH490cr4zyvi3tОценок пока нет
- CH 490 Exam 1 NotesДокумент60 страницCH 490 Exam 1 Notescr4zyvi3tОценок пока нет
- Wilderness Remote First Aid ManualДокумент128 страницWilderness Remote First Aid Manualcr4zyvi3t100% (3)
- Biology - Zoology: Practical ManualДокумент24 страницыBiology - Zoology: Practical ManualMohammed umar sheriff100% (1)
- Dengue Test RPT 2 EditДокумент3 страницыDengue Test RPT 2 EditMuhammad KhudriОценок пока нет
- Blood: Blood Transports Everything That Must Be Carried From One Place To Another, Such AsДокумент71 страницаBlood: Blood Transports Everything That Must Be Carried From One Place To Another, Such AsAudrie Allyson GabalesОценок пока нет
- Microbial Carcinogenesis: Dr. Kevin Manuel Assistant Professor Department of Pathology 19.09.18Документ37 страницMicrobial Carcinogenesis: Dr. Kevin Manuel Assistant Professor Department of Pathology 19.09.18Chama TlauОценок пока нет
- Oncology 101: Cancer BasicsДокумент74 страницыOncology 101: Cancer BasicsMary Rose Jose GragasinОценок пока нет
- GlioblastomaДокумент452 страницыGlioblastomaDesmondОценок пока нет
- Int Esws at Y9 Workbook Answers TTPPДокумент37 страницInt Esws at Y9 Workbook Answers TTPPChrystal GraceОценок пока нет
- Cyclin A Protein Specified by Maternal MRNA in Sea Urchin Eggs That Is Destroyed at Each Cleavage DivisionДокумент8 страницCyclin A Protein Specified by Maternal MRNA in Sea Urchin Eggs That Is Destroyed at Each Cleavage Divisionjavi0% (1)
- The Phylum Annelida: A Short IntroductionДокумент3 страницыThe Phylum Annelida: A Short IntroductionTI Journals PublishingОценок пока нет
- Innate Immune SystemДокумент10 страницInnate Immune SystemLydia González del BarrioОценок пока нет
- Angles 2010Документ4 страницыAngles 2010peruchaybeaОценок пока нет
- DNA Profiling: DNA Profiling (Also Called DNA Fingerprinting, DNA Testing, or DNA Typing) IsДокумент3 страницыDNA Profiling: DNA Profiling (Also Called DNA Fingerprinting, DNA Testing, or DNA Typing) IsShaik MoqtiyarОценок пока нет
- FAQs: Dr. Sarojini SahooДокумент4 страницыFAQs: Dr. Sarojini SahooSarojini SahooОценок пока нет
- Flowers Chap17Документ15 страницFlowers Chap17Cheret LengОценок пока нет
- NanoCellect Biomedical Begins Distribution To EuropeДокумент2 страницыNanoCellect Biomedical Begins Distribution To EuropePR.comОценок пока нет
- DNA Fingerprinting - Bio-RadДокумент102 страницыDNA Fingerprinting - Bio-Radebujak100% (3)
- 1651048027class 7 (Science Notes CH 2 Nutrition in Animals)Документ4 страницы1651048027class 7 (Science Notes CH 2 Nutrition in Animals)VijayaLakshmi KuchimanchiОценок пока нет
- Sugarcane Seed Production - Indian ScenarioДокумент13 страницSugarcane Seed Production - Indian ScenarioJournal of Biotechnology and Crop Sciences67% (3)
- Invertebrates in Testing of Environmental Chemicals - Are They AlternativesДокумент19 страницInvertebrates in Testing of Environmental Chemicals - Are They AlternativesTiago TorresОценок пока нет
- New Protocol For in Vitro Propagation of Berry Plants by TIS BioreactorДокумент7 страницNew Protocol For in Vitro Propagation of Berry Plants by TIS BioreactoraguilaquecaeОценок пока нет
- Micro.... Staining TechniquesДокумент74 страницыMicro.... Staining TechniquesArslan AzizОценок пока нет
- Ecology Canadian 4th Edition Molles Test Bank 1Документ10 страницEcology Canadian 4th Edition Molles Test Bank 1joseph100% (36)
- 3rd Term SS1Документ31 страница3rd Term SS1ofurumchinyere9Оценок пока нет
- Photosynthesis and RespirationДокумент7 страницPhotosynthesis and RespirationSofia Romero ReyОценок пока нет
- GMOs and Trials PDFДокумент138 страницGMOs and Trials PDFSamiha AshreenОценок пока нет
- Biochemistry (Chapter 1: A Brief History of Biochemistry) : March 2016Документ31 страницаBiochemistry (Chapter 1: A Brief History of Biochemistry) : March 2016Dinah C FortuitoОценок пока нет
- Human Papilloma VirusДокумент3 страницыHuman Papilloma Virusxwendnla russiaОценок пока нет
- Molecules: Banana Lectin: A Brief ReviewДокумент11 страницMolecules: Banana Lectin: A Brief ReviewVincent William RodriguezОценок пока нет
- 10 Biology Structural Organization of AnimalsДокумент2 страницы10 Biology Structural Organization of AnimalsHasan shaikhОценок пока нет
- Fbioe 08 599674Документ16 страницFbioe 08 599674Tanishka AggarwalОценок пока нет