Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
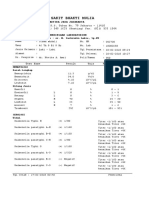
Bacte Lec
Загружено:
Judith Dianne IgnacioОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Bacte Lec
Загружено:
Judith Dianne IgnacioАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
I.
Other E.coli infections
UTI- caused by Uropathogenic E. coli
a. Adhesins/ Pili- mediates the
adherence of urethrogenic E.coli to
the epithelial cells lining the urinary
tract
b. Hemolysins- kill leukocytes and inhibit
phagocytosis and chemotaxis
c. Aerobactin- an extracellular iron
complex; allows bacterial cell to
chelate iron
Septicemia & Meningitis
- Newborns acquire the infection in the
birth canal before or during delivery
when the mothers vagina is colonized
- Infection also results if contamination
of the amniotic fluid takes place
V.
HAFNIA
- Not known to cause gastroenteritis
- Possesses delayed (+) citrate reaction
a. Hafnia alvei- the only sp
VI.
PROTEUS
- Dienes Phenomenon- 2 species in 1
medium: produce demarcation line
a. Proteus mirabilis b. Proteus vulgaris
- Widely recognized human pathogens
- Isolated from urine, wounds and ear &
bacteremic infections
- Produce swarming colonies or nonselective media such as sheeps blood
agar
- Colonies produce burned chocolate
odor
- Produce H2S
- Hydrolyze urea-pink
* K1 Ag- the most documented virulenceassociated factor of neonatal meningeal
infections; capsular antigen
II.
*P.Mirabilis is differentiated from P.vulgaris
by the indole and ornithine decarboxylase
tests:
KLEBSIELLA
- GI tract of human and animals
- -large, very mucoid colonies- presence
of capsule
a. Klebsiella pneumoniae most common
spp
- with a polysaccharide capsule
- a frequent cause of lower respiratory
tract infections
- also causes wound infections, UTI and
bacteremia
b. Klebsiella oxytoca- identical to K.
pneumoniae
- indole (+)
c. K. ozaenae isolated from nasal
secretions and cerebral abcesses
d. K. rhinoscleromatis- isolated from
patients with rhinoscleroma infection of
the nasal cavity
III.
ENTEROBACTER
- Motile
- (+) in Simmons citrate
- (+) in KCN broth
- Methyl red (-)
- Voges-Proskauer test (+)
- Produces ornithine decarboxylase
a. Enterobacter cloacae
b. Enterobacter aerogenes
IV.
SERRATIA
- Opportunistic pathogens - nosocomial
outbreaks
- Ferment lactose slowly
- Resistant to a wide range of
antimicrobials
- Produce pigment
a. Serratia marcescens produce
characteristic
b. Serratia rubiaea
prodigiosin pinkred pigment
c. Serratia odorifera- gives off a dirty musty
odor like potatoes
P. mirabilis- indole (-), ornithine (+)
P. vulgaris indole (+), ornithine (-)
*P. vulgaris- sucrose (+)
- gives an acid/acid reaction in TSI agar
*Rose Waalers test- diagnostic stage using
Proteus to differentiate Rickettsiae sp
VII.
MORGANELLA has only 1 sp
a. M. morganii formerly known as P.
morganii
- Has been implicated in diarrheal
illness
- Its role as a etiologic agent of diarrhea
disease remains to be further
examined however, it is a documented
cause of UTI
VIII.
PROVIDENCIA consists of 4 spp
a. P. alcalifaciens found in the feces of
children with diarrhea
b. P. stuartii- nosocomial outbreaks in
burn units
- Isolated from urine cultures
c. P. rettgeri-UTI pathogen
- Has caused occasional
nosocomial outbreaks
d. P. rustigianii rarely isolated
IX.
EDWARDSIELLA
(-) for urea
- (+) for lysine decarboxylase
- (+) for H2S
- (+) for indole
- (-) for Simmons citrate
a. Edwardsiella tarda- opportunistic;
cause bacteremia & wound infections
b. Edwardsiella ictaluri- cause enteric
septicemia in fish
c. Edwardsiella hoshinae- isolated from
snakes, birds and water
X.
XI.
ERWINIA & PECTOBACTERIUM
- both are plant pathogens
- Erwinia- grows poorly at 37oC
- Fails to grow on selective media such
as EMB agar, MAC agar and other
differentia media used for the isolation
of enteric
CITROBACTER
- Methyl red test (+)
- Simmons citrate (+)
- Mistaken as Salmonella
a. Citrobacter freundii diarrheal stool
cultures
o UTI
o Penumonia
o Intra-abdominal abcesses
o Infectious diseases acquired in
hospital setting
o Endocarditis- IV drug abusers
Aortic valve replacement
Вам также может понравиться
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (119)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (265)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5794)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2219)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (344)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (894)
- 02 PEDIA250 (5) Pediatric History Taking PDFДокумент11 страниц02 PEDIA250 (5) Pediatric History Taking PDFJudith Dianne Ignacio100% (1)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- 09 PEDIA250 (5) Developmental Pediatrics PDFДокумент5 страниц09 PEDIA250 (5) Developmental Pediatrics PDFJudith Dianne IgnacioОценок пока нет
- Microbiologics Information Manual-9020-7751 PDFДокумент190 страницMicrobiologics Information Manual-9020-7751 PDFbogdan.tomosОценок пока нет
- Tableau: Classement Des BactériesДокумент1 страницаTableau: Classement Des BactériesCharlotte Taton100% (2)
- VITEK2 CardsДокумент4 страницыVITEK2 CardsNidia MaradiagaОценок пока нет
- MUST KNOW CLINICAL CHEMISTRY QUALITY CONTROLДокумент56 страницMUST KNOW CLINICAL CHEMISTRY QUALITY CONTROLRyan Pan95% (19)
- Gram-Negative Enteric Bacteria Classification and IdentificationДокумент40 страницGram-Negative Enteric Bacteria Classification and IdentificationCharmaine Corpuz GranilОценок пока нет
- Hasil Lab Edit-2Документ3 страницыHasil Lab Edit-2Anonymous zAebekT2yОценок пока нет
- Vitek Ast gn70Документ4 страницыVitek Ast gn70Mike Gesmundo100% (1)
- Doctors OrderДокумент2 страницыDoctors OrderkeithОценок пока нет
- (PEDIA) 2.04 Pediatric Neurologic Exam - Dr. Rivera PDFДокумент15 страниц(PEDIA) 2.04 Pediatric Neurologic Exam - Dr. Rivera PDFJudith Dianne IgnacioОценок пока нет
- (PHA) 4.08 Geriatric Pharmacology - Dr. GuevarraДокумент4 страницы(PHA) 4.08 Geriatric Pharmacology - Dr. GuevarraJudith Dianne IgnacioОценок пока нет
- Pedia 3.1 - Bacte A 2 PDFДокумент23 страницыPedia 3.1 - Bacte A 2 PDFJudith Dianne IgnacioОценок пока нет
- (PEDIA) History Taking and Physical ExamДокумент14 страниц(PEDIA) History Taking and Physical ExamJudith Dianne IgnacioОценок пока нет
- 3.2 Head and Neck I Gomez JMSalesДокумент8 страниц3.2 Head and Neck I Gomez JMSalesJudith Dianne IgnacioОценок пока нет
- Pedia 2 3.04 Pediatric NephrologyДокумент11 страницPedia 2 3.04 Pediatric NephrologyJudith Dianne IgnacioОценок пока нет
- 4.3 Intestinal FlagellatesДокумент7 страниц4.3 Intestinal FlagellatesJudith Dianne Ignacio100% (1)
- Physical Diagnosis Group 3: Gicaro Gustilo Gromea Gutierrez Ignacio JacintoДокумент11 страницPhysical Diagnosis Group 3: Gicaro Gustilo Gromea Gutierrez Ignacio JacintoJudith Dianne IgnacioОценок пока нет
- Format Health HistoryДокумент3 страницыFormat Health HistoryJudith Dianne Ignacio100% (1)
- Mtech315 AlphaДокумент29 страницMtech315 AlphaJudith Dianne IgnacioОценок пока нет
- Coagulation FactorsДокумент4 страницыCoagulation FactorsJudith Dianne IgnacioОценок пока нет
- Adrenal Glands (Notes)Документ5 страницAdrenal Glands (Notes)Judith Dianne IgnacioОценок пока нет
- CC ReviewДокумент11 страницCC ReviewJudith Dianne IgnacioОценок пока нет
- Skripsi Tanpa Pembahasan PDFДокумент68 страницSkripsi Tanpa Pembahasan PDFfellafaronaОценок пока нет
- 152 Experiment 3Документ2 страницы152 Experiment 3Earl CañoneroОценок пока нет
- Detection and Identification of Enterobacter sakazakii in Raw Milk and Fresh Dairy Products in YogyakartaДокумент14 страницDetection and Identification of Enterobacter sakazakii in Raw Milk and Fresh Dairy Products in YogyakartaNespi LeorensiОценок пока нет
- Karakterisasi Dan Identifikasi Bakteri Enterobacteriaceae Pada Telur Penyu Lekang (Lepidochelys Olivacea) Asal Lhok Pante Tibang, Banda AcehДокумент8 страницKarakterisasi Dan Identifikasi Bakteri Enterobacteriaceae Pada Telur Penyu Lekang (Lepidochelys Olivacea) Asal Lhok Pante Tibang, Banda Acehparkc6922Оценок пока нет
- The Resistance Test of 10 Rice Plant of Banten Local Variety To The Bacterial Leaf Blight Disease (Xanthomonas Oryzae Pv. Oryzae) Seedling Phase OlehДокумент7 страницThe Resistance Test of 10 Rice Plant of Banten Local Variety To The Bacterial Leaf Blight Disease (Xanthomonas Oryzae Pv. Oryzae) Seedling Phase OlehAmel RahmaОценок пока нет
- AeromonasДокумент9 страницAeromonasDorota Pietras-OżgaОценок пока нет
- TABLE Microbial ID 11Документ3 страницыTABLE Microbial ID 11Emmy Segovia MurilloОценок пока нет
- Pseudomonas aeruginosa lipase gene sequenceДокумент6 страницPseudomonas aeruginosa lipase gene sequenceLani PuspitaОценок пока нет
- Gram Negative Rods Identification GuideДокумент1 страницаGram Negative Rods Identification Guidenaura ghinaОценок пока нет
- Pseudomonas Fluorescens Peronosclerospora Maydis Zea MaysДокумент9 страницPseudomonas Fluorescens Peronosclerospora Maydis Zea MaysAhri KolaОценок пока нет
- PHM321Y Antibiotics: Amoxicillin Amoxicillin-ClavulanateДокумент3 страницыPHM321Y Antibiotics: Amoxicillin Amoxicillin-Clavulanatejrubin83669Оценок пока нет
- Identification of Aerobic Pathogenic Bacteria Isolated From Ready-to-Eat Cakes Sold in Traditional Markets in Manado CityДокумент3 страницыIdentification of Aerobic Pathogenic Bacteria Isolated From Ready-to-Eat Cakes Sold in Traditional Markets in Manado CityVenita NapitОценок пока нет
- Vaccin AriДокумент1 страницаVaccin ArighinsavitОценок пока нет
- Enterobacterias 2361 100222195611 Phpapp02Документ90 страницEnterobacterias 2361 100222195611 Phpapp02clau lizОценок пока нет
- BM099 Agar+Glucoza FioleДокумент3 страницыBM099 Agar+Glucoza FioleKeep CalmОценок пока нет
- Biochem Test 1.2Документ9 страницBiochem Test 1.2Angela ReyesОценок пока нет
- Bacterial identification guide with mnemonicsДокумент4 страницыBacterial identification guide with mnemonicsMica SaeronОценок пока нет
- Enterobacteriaceae Family Characteristics and AntigensДокумент4 страницыEnterobacteriaceae Family Characteristics and AntigensADIОценок пока нет
- Blue - Carba - Prueba Bioquímica para Detección de Carbapenemasas Directamente Desde CultivosДокумент3 страницыBlue - Carba - Prueba Bioquímica para Detección de Carbapenemasas Directamente Desde CultivosDavian Araujo PumarejoОценок пока нет
- Colilert RaportДокумент22 страницыColilert RaportAlina CatrangiuОценок пока нет
- Chromocult Coliform Agar AOAC - FOOD 2016Документ6 страницChromocult Coliform Agar AOAC - FOOD 2016jhonni sigiroОценок пока нет
- Bacterii Identificate Cu VITEKДокумент4 страницыBacterii Identificate Cu VITEKGeoemilia1Оценок пока нет
- Enteropluri Code Book 7-2013Документ229 страницEnteropluri Code Book 7-2013bobОценок пока нет
- Key Reactions of EnterobacteriaceaeДокумент3 страницыKey Reactions of EnterobacteriaceaeMare5Der5Оценок пока нет