Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Moving Load Anlaysis As Per En1991-2
Загружено:
sumanОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Moving Load Anlaysis As Per En1991-2
Загружено:
sumanАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
MIDAS
Civil
Moving Load Analysis as per EN 1991-2
Integrated Solution System
For Bridge and Civil Structure
Moving load analysis
(Eurocode 1-2:2003)
Overview
Bridge overview
2 span continuous composite girder
bridge
Span length: 2@24 m
Carriageway width: 9.3 m
Unit system: kN, m
Lane definition
Notional lanes & remaining area
Location and numbering of the lanes
Vehicle load
Load Model 1
Load Model 2
Load Model 3
Moving load analysis option
Concurrent forces
MIDAS IT
Program Version
V7.3.0
Program License
Registered, Trial
Revision Date
1
Result evaluation
Influence line
Moving load tracer
Envelope of member forces
2007.02
2012.7.24
MIDAS Information Technology Co., Ltd.
MIDAS
Civil
Integrated Solution System
For Bridge and Civil Structure
Moving Load Analysis as per EN 1991-2
1. Bridge overview
Bridge type: Straight bridge
Span length: 2@24 m
Carriageway width: 9.3 m
Spacing of cross beams: 4.8 m
MIDAS IT
2007.02
MIDAS Information Technology Co., Ltd.
MIDAS
Civil
Moving Load Analysis as per EN 1991-2
Integrated Solution System
For Bridge and Civil Structure
2. Number and width of notional lanes
EN 1991-2:2003. Table 4.1 Number and width of notional lanes
Carriageway
width w
Number of
notional lanes
Width of a
notional lane w l
Width of the
remaining area
w = 9.3 m
n1 = Int(w/3) = 3
3m
w 3 x n1 = 0.3 m
3. Location and numbering of the lanes of the bridge
For each individual verification, the number of lanes to be taken into account as loaded, their locations on
the carriageway and their numbering should be so chosen that the effects from the load models are the
most adverse. (EN 1991-2:2003, 4.2.4(2) )
In midas Civil, the user directly defines the locations of lanes, and the numbering of the lanes for design is
automatically performed. In this tutorial, the locations of the lanes are shown below.
MIDAS IT
2007.02
MIDAS Information Technology Co., Ltd.
MIDAS
Civil
Moving Load Analysis as per EN 1991-2
Integrated Solution System
For Bridge and Civil Structure
Step 1. Open the model file.
1
1. Click
2. Select Eurocode Moving Load.mcb.
3. Click [Open] button.
This tutorial is intended to introduce the functions of Moving
load analysis. Therefore the procedures of creating elements,
assigning static loads and boundary conditions are omitted
here.
Please refer to the online manual for the detailed usage.
Step2. Define moving load code
MIDAS IT
2
1. Load > Load Type > Moving load > Moving load code
2007.02
2. Moving Load Code: EUROCODE
3. Click [OK] button.
3
4
MIDAS Information Technology Co., Ltd.
MIDAS
Civil
Moving Load Analysis as per EN 1991-2
Integrated Solution System
For Bridge and Civil Structure
Step3-1. Define traffic line lane (Lane_A)
1.
Load > Load Type > Moving Load > Traffic Line
Lane > Add
2. Lane Name: Lane_A
Depending on the
design members,
Lane_A could be
notional lane No. 1,2
or 3. The number of
lanes is determined
when performing
analysis.
For detail
information of
Vehicular Load
Distribution, refer to
the next page.
For the calculation
of the eccentricity,
refer to the page 7 in
this tutorial.
3. Eccentricity : -0.9 m
4. Vehicular Load Distribution : Cross Beam
5. Cross Beam Group: Cross Beam
6. Selection by : 2 Points
7. Click (0,0,0).
8. Click (48,0,0).
9. Click [OK] button.
4
5
6
7
MIDAS IT
2007.02
Cross Beam group
comprises of all the
transverse elements.
9
5
MIDAS Information Technology Co., Ltd.
MIDAS
Civil
Moving Load Analysis as per EN 1991-2
Integrated Solution System
For Bridge and Civil Structure
Tip 1. Vehicular load distribution
Lane element: Apply loads to the traffic line lane elements reflecting the eccentricity.
When defining lanes by the lane element type, the vertical load components (vehicle loads) and the moments due to the eccentricity are
assigned only to the line lane elements. Even though the lanes can be located on cross beam elements, if the lane element type is selected, then
the distribution of the loads onto the cross beams will not be considered.
Cross beam: Apply the traffic loads to the cross beams.
When using Cross Beam type, the eccentricity is used only for locating the lanes from the line lane elements. The vehicle loads are distributed
to the girders via cross beam elements defined as a Cross Beam Group. If the user is modeling a bridge having multiple girders, the Cross
Beam type is recommended for vehicular load distribution.
For example, an axle load of 100kN is located as shown below. Then, concentrated loads, 25kN and 75kN, are applied to point A and point B
respectively. The cross beams themselves are loaded.
100kN
MIDAS IT
2007.02
MIDAS Information Technology Co., Ltd.
MIDAS
Civil
Moving Load Analysis as per EN 1991-2
Integrated Solution System
For Bridge and Civil Structure
Step3-2. Define traffic line lane (Lane B)
1. Lane Name: Lane_B
2. Eccentricity : -3.9 m
1
3. Vehicular Load Distribution : Cross Beam
4. Cross Beam Group: Cross Beam
5. Selection by : 2 Points
3
4
Enter the eccentricity
of a traffic line lane
relative to a traffic line
lane element. Traffic
line lane elements are
defined as the reference
frame elements from
which the eccentricity is
measured.
7. Click (48,0,0).
8. Click [OK] button.
In this tutorial, the
eccentricities are
calculated as shown in
the right figure.
MIDAS IT
8
7
6. Click (0,0,0).
2007.02
7
MIDAS Information Technology Co., Ltd.
MIDAS
Civil
Moving Load Analysis as per EN 1991-2
Integrated Solution System
For Bridge and Civil Structure
Step3-3. Define traffic line lane (Lane C)
1. Lane Name: Lane_C
2. Eccentricity : -6.9 m
1
3. Vehicular Load Distribution : Cross Beam
4. Cross Beam Group: Cross Beam
5. Selection by : 2 Points
6. Click (0,0,0)
7. Click (48,0,0)
8. Click [OK] button.
3
4
5
6
MIDAS IT
2007.02
8
8
MIDAS Information Technology Co., Ltd.
MIDAS
Civil
Moving Load Analysis as per EN 1991-2
Integrated Solution System
For Bridge and Civil Structure
Step3-4. Define remaining area
1. Lane Name: RA
2. Eccentricity : -8.55 m
1
3. Wheel Spacing : 0 m
4. Lane Width : 0.3 m
5. Vehicular Load Distribution : Cross Beam
6. Cross Beam Group: Cross Beam
7. Selection by : 2 Points
2,3,4
8. Click (0,0,0)
9. Click (48,0,0)
5
10. Click [OK] button.
7
8
MIDAS IT
2007.02
10
9
MIDAS Information Technology Co., Ltd.
MIDAS
Civil
Moving Load Analysis as per EN 1991-2
Integrated Solution System
For Bridge and Civil Structure
Step4. Define vehicular load
( Case 1. Check Load Model 1 )
1. Load > Load Type > Moving Load > Vehicles > Add
Standard
2. Standard Name : EN 1991-2:2003 RoadBridge
2
3. Vehicular Load Type : Load Model 1
4. Click [OK] button.
3
Load Model 1 (LM1) : Concentrated and uniformly
distributed loads, which cover most of the effects of the traffic
of lorries and cars.
The user can directly change the Adjustment Factor given in
the National Annex.
Recommended values of factors for road bridge
0
TS
0.75
0.75
UDL
0.40
0.40
Pedestrian +
cycle-track loads
0.40
0.40
gr1b(Single axle)
0.75
gr2 (Horizontal forces)
gr3 (Pedestrian loads)
gr4 (LM4-Crowd loading)
0.75
gr5 (LM3-Special vehicles)
Symbol
grla
(LM1+pedestrian or
cycle-track loads)
MIDAS IT
4
10
0
2007.02
MIDAS Information Technology Co., Ltd.
MIDAS
Civil
Moving Load Analysis as per EN 1991-2
Integrated Solution System
For Bridge and Civil Structure
Step5. Define moving load case
( Case 1. Check Load Model 1 )
1. Load > Load Type > Moving Load > Moving Load
Cases > Add
2
2. Load Case Name : MV-LM1
3. Select Load Model : LM 1, FLM 1
4. Vehicle : Load Model 1
5. Select Lane_A, Lane_B, Lane_C and RA.
6. Click
4
7. Select RA.
8. Click
9. Click [OK] button.
6
Load Model 1 should be applied to each notional lane and to
the remaining area. Load Model 1 is applied only to the
unfavorable parts of the influence line, longitudinally and
transversally.
MIDAS IT
2007.02
11
MIDAS Information Technology Co., Ltd.
MIDAS
Civil
Moving Load Analysis as per EN 1991-2
Integrated Solution System
For Bridge and Civil Structure
Step6. Define vehicular load
( Case 2. Check Load Model 2 )
1. Load > Load Type > Moving Load > Vehicles > Add
Standard
2. Standard Name : EN 1991-2:2003 RoadBridge
2
3. Vehicular Load Type : Load Model 2
4. Click [OK] button.
3
Load Model 2 (LM2) : A single axle load applied to specific
tyre contact areas which covers the dynamic effects of the
normal traffic on short structural members.
The user can directly change the Adjustment Factor given in
the National Annex.
Additional dynamic amplification factor near expansion
joints are not taken into account.
MIDAS IT
2007.02
4
12
MIDAS Information Technology Co., Ltd.
MIDAS
Civil
Moving Load Analysis as per EN 1991-2
Integrated Solution System
For Bridge and Civil Structure
Step7. Define moving load case
( Case 2. Check Load Model 2 )
1. Load > Load Type > Moving Load > Moving Load
Cases > Add
2. Load Case Name : MV-LM2
3. Select Load Model : LM 2,3,4 / FLM 2,3,4 / Footbridge
4. Click [Add] button.
3
5. Vehicle Class : VL:Load Model 2
6. Max. Number of Loaded Lanes: 1
7. Select Lane_A, Lane_B, Lane_C and RA.
8. Click
5
9. Click [OK] button.
10. Click [OK] button.
6
4
Load Model 2 should be applied to any location on the
carriageway.
8
10
MIDAS IT
2007.02
9
13
MIDAS Information Technology Co., Ltd.
MIDAS
Civil
Moving Load Analysis as per EN 1991-2
Integrated Solution System
For Bridge and Civil Structure
Step8. Define vehicular load
( Case 3. Check Load Model 3 with the simultaneous presence of Load Model 1 )
1. Load > Load Type > Moving Load > Vehicles > Add
Standard
2. Standard Name : EN 1991-2:2003 RoadBridge
2
3. Vehicular Load Type : Load Model 3(3600/200)
4. Click [OK] button.
3
Load Model 3 (LM3) : A set of assemblies of axle loads
representing special vehicles which can travel on routes
permitted for abnormal loads.
A dynamic amplification for Load Model 3 is taken into
account automatically.
In this tutorial, special vehicle is assumed to move at normal
speed.
Applicable Axlelines in midas Civil
MIDAS IT
4
14
Axle-lines of 150kN
Axle-lines of 200kN
Available
Available
Axle-lines of
240kN
2007.02
Not Available
MIDAS Information Technology Co., Ltd.
MIDAS
Civil
Moving Load Analysis as per EN 1991-2
Integrated Solution System
For Bridge and Civil Structure
Step9. Define moving load case
( Case 3. Check Load Model 3 with the simultaneous presence of Load Model 1 )
1. . Load > Load Type > Moving Load > Moving Load
Cases > Add
2. Load Case Name : MV-LM3
3. Select Load Model : LM 1 & 3 Multi
4. LM1 : Load Model 1
5. LM3 : Load Model 3 (3600/200)
4
6. Select Lane_A, Lane_B, Lane_C and RA.
7. Click
8. Select RA.
9. Click
10. Click [OK] button.
Load Model 3 is applied to Lane_A, Lane_B or Lane_C .
MIDAS IT
2007.02
10
15
MIDAS Information Technology Co., Ltd.
MIDAS
Civil
Moving Load Analysis as per EN 1991-2
Integrated Solution System
For Bridge and Civil Structure
Tip 2. Simultaneity of Load Model 1 and special vehicle
Key
Axle-line of 150 or 200kN
X: Bridge Axis direction
(1) Lane 1
(2) Lane 2
Standardized vehicle
Area loaded with the frequent model of LM1
Where special vehicles are assumed to move at normal speed, a pair of special vehicles should be used
in the lane(s) occupied by these vehicles. On the other lanes and the remaining area, the bridge deck
MIDAS IT
16
should be loaded by Load Model 1 with its frequent values.
2007.02
MIDAS Information Technology Co., Ltd.
MIDAS
Civil
Moving Load Analysis as per EN 1991-2
Integrated Solution System
For Bridge and Civil Structure
Step10. Moving load analysis option
1. Analysis > Analysis Control > Moving Load
2. Frame : Normal + Concurrent Force
3. Displacements Group : Results
4. Forces/Moments Group : Results
5. Click [OK] button.
Normal + Concurrent Force : If the output of concurrent
forces for max and min values is required for moving load
analysis, select Normal + Concurrent Force .
Note
Concurrent forces are not calculated for LM1 & 3 (Multi) model.
Select the specific group for which analysis results need
to be
2007.02
checked in order to reduce analysis time.
MIDAS IT
5
17
Number/Line Element : Assign the number of reference
points on a line element for moving loads and drawing
influence line in an influence line analysis. The accuracy of
results increases with the increase in the number, but the
analysis time may become excessive.
[Structure Group: Results]
MIDAS Information Technology Co., Ltd.
MIDAS
Civil
Moving Load Analysis as per EN 1991-2
Integrated Solution System
For Bridge and Civil Structure
Step 11. Perform analysis
1. Click
Step 12-1. Shear force diagrams
1. Results > Forces > Beam Diagrams
MVmin : The
minimum force
resulting from
the vehicle load
applied to the
structure.
2. Load Cases/Combinations : Mvall:MV-LM1
4. Display Options : Solid Fill
5. Check on Contour, Legend.
6. Click [Apply] button.
3
MVmax: The
maximum force
resulting from
the vehicle load
applied to the
structure.
MVall: Both
maximum and
minimum force
MIDAS IT resulting from
the vehicle load
applied to the
structure.
18
3. Components : Fz
2007.02
6
MIDAS Information Technology Co., Ltd.
MIDAS
Civil
Moving Load Analysis as per EN 1991-2
Integrated Solution System
For Bridge and Civil Structure
Step 12-2. Shear force tables
1. Click
1
2. Check on MV-LM1(MV:all).
3. Click [OK] button.
MIDAS IT
19
2007.02
MIDAS Information Technology Co., Ltd.
MIDAS
Civil
Moving Load Analysis as per EN 1991-2
Integrated Solution System
For Bridge and Civil Structure
Step 12-3. Shear force tables
(Concurrent forces)
1. Right-click on the Beam Force table.
2. Select View by Max Value Item
3. Check on Shear-z.
4. Click [OK] button.
Calculate the
corresponding member
forces under the
conditions where the
MIDAS IT maximum and
minimum member
forces occur at each
position.
20
2007.02
MIDAS Information Technology Co., Ltd.
MIDAS
Civil
Moving Load Analysis as per EN 1991-2
Integrated Solution System
For Bridge and Civil Structure
Step 13. Bending moment diagrams
1. Results > Forces > Beam Diagrams
2. Load Cases/Combinations : MVall:MV-LM1
3. Components : My
4. Display Options : Solid Fill
5. Check on Legend.
6. Click [Apply] button.
MIDAS IT
2007.02
6
21
MIDAS Information Technology Co., Ltd.
MIDAS
Civil
Moving Load Analysis as per EN 1991-2
Integrated Solution System
For Bridge and Civil Structure
Step 14. Reactions
1. Results > Reactions > Reaction Forces /Moments
2. Load Cases/Combinations : MVmax:MV-LM1
3. Components : Fz
4. Check on Values.
2
5. Check on Legend.
6. Click [Apply] button.
MIDAS IT
22
2007.02
MIDAS Information Technology Co., Ltd.
MIDAS
Civil
Moving Load Analysis as per EN 1991-2
Integrated Solution System
For Bridge and Civil Structure
Step 15. Influence lines
1. Results > Influence Lines > Beam Forces/Moments
2. Key Element: 101
3. Parts: j
4. Components: My
2
5. Check on Legend
6. Click [Apply] button.
3
4
5
Key Element: 101
MIDAS IT
2007.02
i-end j-end
23
MIDAS Information Technology Co., Ltd.
MIDAS
Civil
Moving Load Analysis as per EN 1991-2
Integrated Solution System
For Bridge and Civil Structure
Step 16-1. Moving load tracer
Display moving load location that results in the minimum
moment at the j-end of the element no. 101 due to the
MV-LM2 load case.
1. Results > Moving Load Tracer > Beam Forces/Moment
2. Moving Load Cases: MVmin:MV-LM2
3. Key Element: 101
4. Parts: j
Trace and graphically
display the vehicle
loading condition
(corresponding moving
load case and location)
that results in the
maximum/ minimum
force of a beam element.
The loading condition is
converted into a static
loading and produced as
a model file of the MCT
type by clicking [Write
Min/Max Load to File]
button.
5. Components: My
6. Check on Contour, Legend and Applied Loads.
2
7. Click [Apply] button.
3
5
6
MIDAS IT
2007.02
7
24
MIDAS Information Technology Co., Ltd.
MIDAS
Civil
Moving Load Analysis as per EN 1991-2
Integrated Solution System
For Bridge and Civil Structure
Step 16-2. Moving load tracer
Display moving load location that results in the minimum
moment at the j-end of the element no. 101 due to the
MV-LM3 load case.
1. Results > Moving Load Tracer > Beam Forces/Moment
2. Moving Load Cases: MVmin:MV-LM3
3. Key Element: 101
4. Parts: j
5. Components: My
2
6. Check on Contour, Legend and Applied Loads.
3
7. Click [Apply] button.
MIDAS IT
2007.02
25
MIDAS Information Technology Co., Ltd.
MIDAS
Civil
Moving Load Analysis as per EN 1991-2
Integrated Solution System
For Bridge and Civil Structure
Step 16-3. Moving load tracer
Display moving load location that results in the maximum
reaction of the node no. 103 due to the MV-LM1 load
case.
1. Results > Moving Load Tracer > Reactions
2. Moving Load Cases: MVmax:MV-LM1
3. Key Node: 103
4. Components: Fz
5. Check on Contour, Legend and Applied Loads.
6. Click [Apply] button.
3
RA
Lane (3)
Lane (1)
Lane (2)
MIDAS IT
2007.02
Key Node: 103
Node No. 103
26
MIDAS Information Technology Co., Ltd.
MIDAS
Civil
Moving Load Analysis as per EN 1991-2
Integrated Solution System
For Bridge and Civil Structure
Step 17-1. Converting the moving load into a static load
1. Click [Write Min/Max Load to File] button.
2. Click [OK] button.
3. Select File>Exit in the MIDAS/Text Editor.
MIDAS IT
27
Where moving load analysis has been carried
out, the moving load case, which produces
the maximum or minimum results, is
converted into a static loading and produced
as the MCT type.
2007.02
MIDAS Information Technology Co., Ltd.
MIDAS
Civil
Moving Load Analysis as per EN 1991-2
Integrated Solution System
For Bridge and Civil Structure
Step 17-2. Converting the moving load into a static load
1. Tools>MCT Command Shell
2. Click
2
3. Select the file name MVmaxMV-LM1Fz103.mct.
4. Click [Open] button.
5. Click [Run] button.
6. Click [Yes] button.
7. Click [Close] button.
3
8. Click
MIDAS IT
2007.02
5
28
7
MIDAS Information Technology Co., Ltd.
MIDAS
Civil
Moving Load Analysis as per EN 1991-2
Integrated Solution System
For Bridge and Civil Structure
Step 18-1. Check beam reactions due to the converted static load
1. Results>Reactions>Reaction Forces/Moments
2. Load Cases/Combinations: ST:MVmaxMV-LM1Fz103
3. Components: Fz
2
4. Check on Values and Legend.
5. Click [Apply] button.
MIDAS IT
29
2007.02
MIDAS Information Technology Co., Ltd.
MIDAS
Civil
Moving Load Analysis as per EN 1991-2
Integrated Solution System
For Bridge and Civil Structure
Step 18-2. Check reaction table due to the static load
1. Click
2. Check on MVmaxMV-LM1Fz103(ST).
3. Click [OK] button.
MIDAS IT
2007.02
Reaction table due to static load case MVmaxMV-LM1Fz103
displays the concurrent reactions due to the moving load case
MV-LM1 when the reaction of the node no. 103 is maximum.
3
30
MIDAS Information Technology Co., Ltd.
Вам также может понравиться
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (119)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (265)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (399)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2219)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5794)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (344)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (890)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- Civil Engineering Interview QuestionsДокумент11 страницCivil Engineering Interview QuestionsVishnu Nandakumar100% (1)
- Moving Load Anlaysis As Per EN1991-2Документ30 страницMoving Load Anlaysis As Per EN1991-2tyukgombaОценок пока нет
- Highway Geometric Design Guide (Completed)Документ685 страницHighway Geometric Design Guide (Completed)David Vaca Oyola100% (1)
- KSA MOMRA Parking Design Manual 2019 TranslatedДокумент96 страницKSA MOMRA Parking Design Manual 2019 Translatedsiddeshkumar100% (3)
- UIC 774 3 Code For Track Rail InteractionДокумент76 страницUIC 774 3 Code For Track Rail InteractionReggie Cruz100% (3)
- Design Report for Sambalpur-Rourkela Road (SH-10) ImprovementДокумент124 страницыDesign Report for Sambalpur-Rourkela Road (SH-10) ImprovementBabulalSahuОценок пока нет
- Fundamentals of Safe Intersection DesignДокумент90 страницFundamentals of Safe Intersection DesignPamela JezreelОценок пока нет
- FDOT Design Manual Complete 2022Документ1 325 страницFDOT Design Manual Complete 2022Alvaro BallestasОценок пока нет
- Traffic Engineering Solved Question PaperДокумент27 страницTraffic Engineering Solved Question PaperHanamant Hunashikatti100% (5)
- SE1M54 Course Works P1Документ16 страницSE1M54 Course Works P1Philip Yap100% (2)
- BOX Culvert Load DetailsДокумент7 страницBOX Culvert Load DetailsDhimas Surya Negara100% (1)
- Hilton Design & Construction Standards July 2010Документ265 страницHilton Design & Construction Standards July 2010sardarmkhan80% (10)
- Beam Design Formulas With Shear and MomentДокумент20 страницBeam Design Formulas With Shear and MomentMuhammad Saqib Abrar100% (8)
- Underpass Design and Approval ProcessДокумент36 страницUnderpass Design and Approval ProcessbryantОценок пока нет
- Final Journal of The Indian Roads CongressДокумент97 страницFinal Journal of The Indian Roads CongressSony JsdОценок пока нет
- Phase Relations Explained in Simple TermsДокумент9 страницPhase Relations Explained in Simple TermsHarish Lambadi100% (2)
- Analysis and Design of Under Pass RCC BridgeДокумент7 страницAnalysis and Design of Under Pass RCC Bridgehima_bindu_890% (1)
- 37 DI Go-To Lists RB0812Документ4 страницы37 DI Go-To Lists RB0812arunks4uОценок пока нет
- Reinforced Concrete CourseДокумент25 страницReinforced Concrete CourseAbdissa BekeleОценок пока нет
- MIT1 040s09 Lec01Документ21 страницаMIT1 040s09 Lec01adrianrrccОценок пока нет
- CE5510-Advance Structural Concrete DesignДокумент47 страницCE5510-Advance Structural Concrete Designshish0iitrОценок пока нет
- Analysis and Design of Under Pass RCC BridgeДокумент7 страницAnalysis and Design of Under Pass RCC Bridgehima_bindu_890% (1)
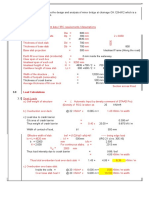
- Analysis and Design of Railway Over Bridge at Kumaranellur-1231Документ4 страницыAnalysis and Design of Railway Over Bridge at Kumaranellur-1231sumanОценок пока нет
- Influence Lines Notes - 06bДокумент5 страницInfluence Lines Notes - 06bWael Shawky BaldawiОценок пока нет
- Influence Lines Notes - 06bДокумент5 страницInfluence Lines Notes - 06bWael Shawky BaldawiОценок пока нет
- Civil and Structural Standards For Intelligent Transportation System (Its) v2 - 0Документ1 страницаCivil and Structural Standards For Intelligent Transportation System (Its) v2 - 0sumanОценок пока нет
- iRAP Model Factsheet 3 - Road Attributes PDFДокумент14 страницiRAP Model Factsheet 3 - Road Attributes PDFqwertОценок пока нет
- List of Jacksonville Infrastructure ProjectsДокумент4 страницыList of Jacksonville Infrastructure ProjectsActionNewsJaxОценок пока нет
- Chapter 3 Loads On BridgeДокумент43 страницыChapter 3 Loads On BridgeAbdulkhaliq AbdulyimahОценок пока нет
- 0041 Geometric Road DesignДокумент51 страница0041 Geometric Road DesignAbdo AlsalmiОценок пока нет
- Standard Details & Specifications: Two-Family Dwellings and Associated StructuresДокумент6 страницStandard Details & Specifications: Two-Family Dwellings and Associated StructuresMakky MakkyОценок пока нет
- Traffic Study Process ManualДокумент12 страницTraffic Study Process ManualRaheel ADNANОценок пока нет
- Getting Started HCS2010 PDFДокумент51 страницаGetting Started HCS2010 PDFJose Luis CabanillasОценок пока нет
- Appendix C: Templates For Traffic Management PlansДокумент26 страницAppendix C: Templates For Traffic Management PlansHamdy KarОценок пока нет
- EsalcalcДокумент28 страницEsalcalcRaul Zapana ZelaОценок пока нет
- Brief Discription of Civil Engineering ProjectДокумент11 страницBrief Discription of Civil Engineering ProjectAmulyaRajbharОценок пока нет
- Francisco Jose Lamiquiz Dauden and Mateus Porto Schettino - Shared Space and Its Application in Madrid (ENG)Документ15 страницFrancisco Jose Lamiquiz Dauden and Mateus Porto Schettino - Shared Space and Its Application in Madrid (ENG)dr.hamdyОценок пока нет
- IRC IH Jan 2018Документ68 страницIRC IH Jan 2018Akash YadavОценок пока нет
- 2012mutcd Ca PG801-1402 PDFДокумент602 страницы2012mutcd Ca PG801-1402 PDFpesc_casiОценок пока нет
- Spatial Separations 2010Документ3 страницыSpatial Separations 2010ARTUROОценок пока нет
- Cycling in NYC: The Official Guide ToДокумент24 страницыCycling in NYC: The Official Guide ToΑυτός είμαι εγώОценок пока нет
- Cross Section Elements for Road DesignДокумент89 страницCross Section Elements for Road DesignYohannes Girma0% (1)
- Banning Rickshaw FRM Dhaka City Is A Major ConcernДокумент33 страницыBanning Rickshaw FRM Dhaka City Is A Major ConcernLamia ShamsОценок пока нет
- Design Loads for Highway Bridge StructuresДокумент33 страницыDesign Loads for Highway Bridge StructuresIvy SeahОценок пока нет