Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
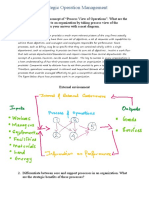
OIS 5000 Case Project Marketing Advantage Deliverable 1 Overview
Загружено:
Numair KhanАвторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
OIS 5000 Case Project Marketing Advantage Deliverable 1 Overview
Загружено:
Numair KhanАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
OIS 5000
Case Study Deliverable 1
Deliverables:
The first project deliverable includes the two critical items:
Process Hierarchy
Using the list of processes that was compiled by your junior coworker, organize the processes at
Marketing Advantage into a meaningful hierarchy. Please structure the hierarchy according to a
Value Chain (Functional) view. Since the list contains varying levels of granularity, you are
allowed to create additional process grouping units, rename existing, or delete existing. Process
hierarchy should be grouped according to a clear numbering reference.
Project Prioritization Matrix (aka QFD)
Based on interviews with owners, management, and staff, we have identified 4 processes at
Marketing Advantage that are particularly important and are also struggling right now. The
following table summarizes notes and observations about these 4 processes. Your job is to create
a prioritization matrix (QFD) to help the team know where to focus attention on process
improvement. Please label assumptions and provide additional comments on the evaluation
scores. Write 2-3 paragraphs about your recommendations and justifications for your
recommendations.
The following processes should be prioritized using the template for Process Prioritization Matrix
(published online at Canvas). The criteria for prioritization are:
Internal Impact (employees)
External Impact (Customers)
Improvement Feasibility
Current State Performance
Financial Value from Improvement
Rick (the owner) expressed the relative importance of these criteria as follows:
Internal Impact (20%)
External Impact (40%)
Improvement Feasibility (10%)
Current State Performance (10%)
Financial Value from Improvement (20%)
Proposed Scope of Improvement Project
Based on discussions with members of Marketing Advantages management team,
the processes related to Wholesale Large Format Accounts will be area of first focus.
These customer accounts struggle with the following challenges:
1. Inventory Management
2. Rush Orders Management
3. Workflow Management
4. Quality Assurance
Process Name &
Description
Interview Notes
Inventory
Management:
The fulfillment of
orders for Large
Format Printing
generally requires
two main inventory
items:
1. Media. This is
the fabric
material upon
which the
clients logo
and design are
printed
2. Hardware.
These are the
structural parts
required for the
tent or
marketing
stand.
In conversations with several employees, the process of
Inventory Management was raised repeatedly as being a main
problem. Since issues with inventory touch so many different
people in the company, it causes widespread frustration when
inventory is not available. One employee even estimated that
50% of orders experience some issue with inventory not being
available at the right time.
Even though this process is critically important to the smooth
flow of the business, it is unclear how Inventory is managed in
the current environment. The process is performed in an ad-hoc
and inconsistent way. Sometimes, the sales team will place an
order for the media and hardware and other times the production
team will place orders with their inventory suppliers.
Large Format orders for wholesalers are generally extremely time sensitive and
most often a rush. When inventory is not available to fulfill promised orders, the
sales team often must rely upon expensive rush orders with their suppliers. The
media and hardware suppliers often need to overnight material to Marketing
Advantage. The cost of overnight shipment quickly deteriorates the already-thin
profit margin on Wholesale orders.
Inventory issues also cause unnecessary rescheduling by the Production
Management team. When items are not available, they will need to reschedule all
jobs to work on those items where inventory exists.
Generally speaking, the end client is not aware of the inventory
issues that Marketing Advantage faces. The team generally
scrambles enough that the client is shielded from the pain of
mismanagement. However, the end client is impacted in a
negative way when the extra rushing caused by inventory leads
to poor quality on the finished product.
Process Name &
Description
Interview Notes
Rush Order
Management:
The expedited
processing of an
order is intended to
be used on a rare
exception basis.
Rush orders bypass
the typical work
queue and are
placed at front of
the priority list.
Rush orders also
involve shipment
with overnight
services.
Wholesalers who place orders with Marketing Advantage on
behalf of their end clients often misunderstand the Large Format
printing process. Wholesalers underestimate the work involved
with creating Large Format items (such as tents and display
stands). Very often, the end customer (the client of the
wholesaler) does not have the right graphics and logos for use
with large format items. Usually, their logo works great on small
items (like pens and other trinkets), but does not work well on
large items.
This lack of understanding by the Wholesaler about Large Format
can occasionally create the need for Rush Orders. These rush
orders play an important role in servicing the needs of
wholesalers and the ability to deal with rush orders effectively is
a key part of Marketing Advantages strategy to become a
flexible and responsive partner for Wholesalers.
Rush Orders were originally intended to be an exception to the
normal process, but lately the number of rush orders has made
them more the norm than the exception. If not managed
effectively, these Rush Orders have an extremely disruptive
impact on the entire work flow for Large Format printing. As one
order gets prioritized as a rush order, that necessarily means
that the other orders in the queue get disrupted.
The Wholesaler and the end customer are often unaware of the
internal challenges required to effectively deal with rush orders.
Marketing Advantage generally does a good job of hiding and
covering the amount of disruption caused by rush orders.
Rush orders have both direct and indirect cost impact. Direct
costs involve overnight shipment and occasional overtime hours
to ensure the order gets completed. Indirect costs involve a
delay to other orders which then turns a normal order into a rush
order as the company deals with the shuffling of internal
prioritization. Other indirect costs involve an inefficient use of
machines and people as they are reallocated and reconfigured to
work on a rush order.
Process Name &
Description
Interview Notes
Workflow
Management:
The process
involved with
managing the flow
of individual orders
from inception to
completion. Also
involves the
interaction of
multiple orders as
they compete with
other orders for
priority, time, and
resources.
Marketing Advantage has seen such strong growth in recent
years that the processes involved with workflow management
have not been well defined. In the current environment,
customer orders flow in a halting, inconsistent, nonstandardized,
and ad-hoc way.
As a sales representative takes an order from a wholesaler for an
end customer there is no standardized way that the order will be
completed as it flows through the various stages of design,
printing, finishing, shipping, and invoicing. The sales
representative generally works with each group individually to
make sure his/her order gets completed. There is no centralized
queue management process that guides the priority and flow of
orders through all stages of the fulfillment process.
The lack of a standardized workflow process creates direct
challenges for internal employees. First, employees constantly
feel the pressure of pleasing individual sales representatives who
come and advocate for the priority of their individual orders.
Employees are often torn between pleasing one representative
and disappointing another.
Second, employees are interrupted
by sales representatives who come asking about the status and
progress of their individual orders. Since sales representatives
have no system that captures the progress of an order through
the lifecycle, they must bother and interrupt each fulfillment
group to get a status.
Customers dont directly feel the negative impact of a poor
workflow process. However, the lack of standardized and robust
workflow management contributes to quality issues and timing
pressures when the company isnt able to effectively balance the
internal inefficiencies of an inconsistent process.
Process Name &
Description
Interview Notes
Quality Assurance:
In the current
process, each order
is inspected for
quality issues by
the finishing team.
After sewing the
material onto the
hardware, the
finishing team
inspects for
printing problems
and other
formatting
problems. If they
identify problems,
they notify sales
representatives
who work to
correct or recreate
the order.
In a recent interview, Rick the owner of Marketing Advantage expressed concern
that too many orders experience problems that are ultimately detected by the end
customer. The finishing team has been given a quality assurance role, but they do
not detect and prevent all defects from reaching the end customer.
The sales, design, and printing groups have come to rely too much on the
finishing team for quality assurance. These teams are not intentionally negligent
or careless with quality, but they trust that mistakes will be caught by the
finishers. This overreliance on a manual quality check at the end of the process
causes about 15% of orders to experience rework and defect correction.
The end customer ultimately discovers quality issues when the order arrives.
Unfortunately, given the sensitive and urgent nature of marketing campaigns, it is
often too late to correct problems with orders before the marketing event.
Internal employees experience the frustration of rework when quality issues arise.
It becomes demoralizing and discouraging when a job or order must be done
twice (or more). This is especially true considering the amount of urgent work
that already exists in the queue.
Evaluation:
This first project/case study deliverable will scored on a scale of 50 possible points (25 for hierarchy and
25 for prioritization matrix).
The process hierarchy will be graded on the following points:
Logical structure and organization of processes. There is no absolute best way to organize
these processes, but your approach should be rational and logical and show that you understand
the relationship among these processes and their placement in a hierarchy.
Formatting. Is the hierarchy clear and understandable? Does the hierarchy follow a consistent
numbering structure?
Hierarchy Consistency. Is there consistency in the granularity among the processes at each
hierarchy unit? For example, are the units at Level 2 consistent in the level of granularity?
The Process Prioritization Matrix will be graded on the following points:
Scoring is Reasonable. Scoring is not an exact science, but you should demonstrate that the
scores reflect the areas of emphasis from the interview notes. Scoring involves both the correct
weighting on the relative priority of criteria and the scoring of each individual process against the
criteria.
Labeled Assumptions. Ensure that you offer some context about the assumptions you made on
the scoring. Use the Comments column for these notes and assumptions.
Recommendation. Write 2-3 paragraphs that describe the recommendations for action (with
justification for the recommendation)
Вам также может понравиться
- 5 Ways For Lead Time ReductionДокумент5 страниц5 Ways For Lead Time ReductionYamini ShamiОценок пока нет
- Staple Yourself - Article 1Документ7 страницStaple Yourself - Article 1Rishikesh BaddiОценок пока нет
- Managing FMEA'sДокумент8 страницManaging FMEA'sFalando de FMEAОценок пока нет
- Lean Six Sigma (Part A)Документ17 страницLean Six Sigma (Part A)Punniavel PОценок пока нет
- Texto Examen Gop2Документ11 страницTexto Examen Gop2monohhxxОценок пока нет
- Staple Yourself To Order - CritqueДокумент4 страницыStaple Yourself To Order - Critquexebra100% (2)
- OPMAN Midterm ExamДокумент2 страницыOPMAN Midterm ExamLalosa Fritz Angela R.Оценок пока нет
- Process Level of PerformanceДокумент16 страницProcess Level of PerformanceRenato GutierrezОценок пока нет
- Strategic Operation ManagementДокумент6 страницStrategic Operation ManagementFaiza ShaikhОценок пока нет
- Question 1aДокумент7 страницQuestion 1aAssignments HelperОценок пока нет
- Top Company ReportДокумент6 страницTop Company ReportManjesh RОценок пока нет
- Domain Certification HP GBS: Order Management Case Study - Level 2Документ4 страницыDomain Certification HP GBS: Order Management Case Study - Level 2DanОценок пока нет
- Chapter 1 - Operations As A Competitive WeaponДокумент9 страницChapter 1 - Operations As A Competitive WeaponVasudevan R DОценок пока нет
- Customer ServiceДокумент23 страницыCustomer ServiceMohinderSinghОценок пока нет
- Change Management: Raja Rocky MBA HR - 500088081Документ3 страницыChange Management: Raja Rocky MBA HR - 500088081raja rockyОценок пока нет
- Optimizing Efficiency: FabricationДокумент7 страницOptimizing Efficiency: FabricationVivek Kumar SinghОценок пока нет
- Business Process Reengineering: Jump To Any SectionДокумент53 страницыBusiness Process Reengineering: Jump To Any SectionDeepak Venkatesh SОценок пока нет
- Background Information For LearnersДокумент2 страницыBackground Information For LearnersAndrew DefensorОценок пока нет
- Customer Centric Organisations & NPSДокумент4 страницыCustomer Centric Organisations & NPSVenessa BooneОценок пока нет
- 01) What Is SAP - Meaning and Definition of SAP ERP SoftwareДокумент4 страницы01) What Is SAP - Meaning and Definition of SAP ERP SoftwareBoppineti Naga RajuОценок пока нет
- CHAPTER 2 Review of Related Literature AДокумент9 страницCHAPTER 2 Review of Related Literature AChristian Rey HinayОценок пока нет
- Assignment - Ranpath ToolsДокумент8 страницAssignment - Ranpath ToolsNayana WeerasingheОценок пока нет
- AnswersДокумент16 страницAnswersDhufera JabesaОценок пока нет
- Chapter I.2 - Report 3Документ13 страницChapter I.2 - Report 3Gellie Mae Bonilla-IranОценок пока нет
- Module-V Customer FocusДокумент11 страницModule-V Customer FocusPrashant JhaОценок пока нет
- Furniture Management SystemДокумент27 страницFurniture Management Systemanadhan45% (11)
- 12 Manageing Customers Quality ServicesДокумент12 страниц12 Manageing Customers Quality ServicesSamuel AdamuОценок пока нет
- Thesis About Business Process ImprovementДокумент8 страницThesis About Business Process ImprovementRichard Hogue100% (2)
- PDD 5Документ15 страницPDD 5A SaaviОценок пока нет
- Vendor ManagementДокумент5 страницVendor Managementapi-3701207Оценок пока нет
- Operations Management PlanningДокумент3 страницыOperations Management Planninghannabee00Оценок пока нет
- Designing The Operations SystemДокумент3 страницыDesigning The Operations Systemmusicoustic1Оценок пока нет
- The Eight Building Blocks of CRM: Processes: Key FindingsДокумент11 страницThe Eight Building Blocks of CRM: Processes: Key Findingscindy quekОценок пока нет
- CRM Project Format Greated by Dharmarajan TrichyДокумент46 страницCRM Project Format Greated by Dharmarajan TrichydupakkurОценок пока нет
- What Is SAPДокумент4 страницыWhat Is SAPRohit TripathiОценок пока нет
- What Is VC?: 1. General Implementation Concepts For VCДокумент22 страницыWhat Is VC?: 1. General Implementation Concepts For VCV S Krishna AchantaОценок пока нет
- Operational ManagementДокумент7 страницOperational ManagementSabbir_07Оценок пока нет
- Procurement Challenges and Solutions - Fleet and Transport ManagementДокумент22 страницыProcurement Challenges and Solutions - Fleet and Transport Managementtonderai mangozheОценок пока нет
- Concepts in Enterprise Resource Planning, Fourth Edition 1-1Документ21 страницаConcepts in Enterprise Resource Planning, Fourth Edition 1-1tuanОценок пока нет
- TQM DrunkerДокумент7 страницTQM DrunkerAnkit JainОценок пока нет
- Challenges That Face Operation ManagersДокумент13 страницChallenges That Face Operation ManagersOmosh Ja DiasporaОценок пока нет
- JSW AssignmentДокумент6 страницJSW AssignmentSONALI HОценок пока нет
- Methodology To Implement BPR: Ramkumar.K 12MBA036Документ26 страницMethodology To Implement BPR: Ramkumar.K 12MBA036Ram KumarОценок пока нет
- A Day in Life of Frederic GodeДокумент5 страницA Day in Life of Frederic Godebhjbhjk50% (2)
- Benefits OF ERP: Reduction of Lead-TimeДокумент4 страницыBenefits OF ERP: Reduction of Lead-TimeRag LakОценок пока нет
- Milestone OneДокумент10 страницMilestone Onesivaabhilash100% (1)
- What Is SAP? Definition of SAP ERP SoftwareДокумент10 страницWhat Is SAP? Definition of SAP ERP SoftwarethenameisvijayОценок пока нет
- Improve Your Sales ProcessДокумент12 страницImprove Your Sales ProcessSandip GhoshОценок пока нет
- 1.1 Significant Shaping Operations, Management, and MarketingДокумент2 страницы1.1 Significant Shaping Operations, Management, and MarketingDorin RoscaОценок пока нет
- Assignment - 2: "Case Study-Sanolabor "Документ4 страницыAssignment - 2: "Case Study-Sanolabor "Nepali Dravin PoudyalОценок пока нет
- Debritu AssignДокумент5 страницDebritu Assigngetamesay assefaОценок пока нет
- Freeing Up The Sales Force For Selling: JULY 2011Документ5 страницFreeing Up The Sales Force For Selling: JULY 2011technocratsumit9794Оценок пока нет
- Role of Product ManagerДокумент13 страницRole of Product Manager9013126157Оценок пока нет
- Business Process Reengineering (BPR) : de Nition, Steps, ExamplesДокумент7 страницBusiness Process Reengineering (BPR) : de Nition, Steps, ExamplesMilan PatelОценок пока нет
- Assignment Module 1 OMДокумент5 страницAssignment Module 1 OMAkash Singh Rajput0% (1)
- 08-Power of Cross Functional Teams PDFДокумент0 страниц08-Power of Cross Functional Teams PDFsunilbholОценок пока нет
- Getting Started On The Lean JourneyДокумент2 страницыGetting Started On The Lean JourneyGunawan tОценок пока нет
- Final PaperДокумент5 страницFinal Paperapi-366064574Оценок пока нет
- RCD ManagementДокумент6 страницRCD ManagementPindoterOОценок пока нет
- Tema & Htri by Bert BoxmaДокумент5 страницTema & Htri by Bert Boxmabloodterry2284Оценок пока нет
- Introduction To Physiotherapy PracticeДокумент22 страницыIntroduction To Physiotherapy PracticejОценок пока нет
- Esp8285 Datasheet enДокумент29 страницEsp8285 Datasheet enJohn GreenОценок пока нет
- Quizlet Table 7Документ1 страницаQuizlet Table 7JosielynОценок пока нет
- Introduction To Regional PlanningДокумент27 страницIntroduction To Regional Planningadeeba siddiquiОценок пока нет
- Module 1Документ64 страницыModule 1Jackyson RajkumarОценок пока нет
- CA-idms Ads Alive User Guide 15.0Документ142 страницыCA-idms Ads Alive User Guide 15.0svdonthaОценок пока нет
- Why You MeДокумент18 страницWhy You MeFira tubeОценок пока нет
- 95 935 Dowsil Acp 3990 Antifoam CompДокумент2 страницы95 935 Dowsil Acp 3990 Antifoam CompZhan FangОценок пока нет
- UniFi Quick GuideДокумент2 страницыUniFi Quick GuideAndhika TharunaОценок пока нет
- Federal Government Employees Housing FoundationДокумент2 страницыFederal Government Employees Housing FoundationMuhammad Shakil JanОценок пока нет
- Intermediate Programming (Java) 1: Course Title: Getting Started With Java LanguageДокумент11 страницIntermediate Programming (Java) 1: Course Title: Getting Started With Java LanguageRickCy Perucho PccbsitОценок пока нет
- SET UP Computer ServerДокумент3 страницыSET UP Computer ServerRicHArdОценок пока нет
- K To 12 Math 7 Curriculum Guide PDFДокумент15 страницK To 12 Math 7 Curriculum Guide PDFEdmar Tan Fabi100% (1)
- Advancement of SGДокумент2 страницыAdvancement of SGkailasasundaramОценок пока нет
- APS PresentationДокумент32 страницыAPS PresentationRozack Ya ZhackОценок пока нет
- Preliminary Voters ListДокумент86 страницPreliminary Voters Listمحمد منيب عبادОценок пока нет
- Applied Computational AerodynamicsДокумент15 страницApplied Computational AerodynamicsjoereisОценок пока нет
- Combat Storm - Shipping ContainerДокумент6 страницCombat Storm - Shipping ContainermoiОценок пока нет
- Kobelco CK1100G Spec BookДокумент38 страницKobelco CK1100G Spec BookEjeantengОценок пока нет
- UntitledДокумент17 страницUntitledSedat100% (1)
- Day 1 Training Material FlowДокумент200 страницDay 1 Training Material FlowGhazouani AymenОценок пока нет
- Articles About Social Issues - Whiter SkinДокумент9 страницArticles About Social Issues - Whiter Skinf aОценок пока нет
- Taxonomy: Family StaphylococcaceaeДокумент40 страницTaxonomy: Family StaphylococcaceaeMarissa Terrado SorianoОценок пока нет
- Keira Knightley: Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchДокумент12 страницKeira Knightley: Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchCrina LupuОценок пока нет
- Analyse Bacterologique de L EauДокумент6 страницAnalyse Bacterologique de L Eaupeguy diffoОценок пока нет
- AMX Prodigy Install ManualДокумент13 страницAMX Prodigy Install Manualsundevil2010usa4605Оценок пока нет
- Classical School of Thought: Ms. Salma ShaheenДокумент62 страницыClassical School of Thought: Ms. Salma ShaheenQasim Ali100% (1)
- Trend in Agricultural ProductivityДокумент1 страницаTrend in Agricultural ProductivityGiaОценок пока нет
- 24 Assets: Create a digital, scalable, valuable and fun business that will thrive in a fast changing worldОт Everand24 Assets: Create a digital, scalable, valuable and fun business that will thrive in a fast changing worldРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (20)
- The Millionaire Fastlane, 10th Anniversary Edition: Crack the Code to Wealth and Live Rich for a LifetimeОт EverandThe Millionaire Fastlane, 10th Anniversary Edition: Crack the Code to Wealth and Live Rich for a LifetimeРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (88)
- ChatGPT Side Hustles 2024 - Unlock the Digital Goldmine and Get AI Working for You Fast with More Than 85 Side Hustle Ideas to Boost Passive Income, Create New Cash Flow, and Get Ahead of the CurveОт EverandChatGPT Side Hustles 2024 - Unlock the Digital Goldmine and Get AI Working for You Fast with More Than 85 Side Hustle Ideas to Boost Passive Income, Create New Cash Flow, and Get Ahead of the CurveОценок пока нет
- Summary of Zero to One: Notes on Startups, or How to Build the FutureОт EverandSummary of Zero to One: Notes on Startups, or How to Build the FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (100)
- 12 Months to $1 Million: How to Pick a Winning Product, Build a Real Business, and Become a Seven-Figure EntrepreneurОт Everand12 Months to $1 Million: How to Pick a Winning Product, Build a Real Business, and Become a Seven-Figure EntrepreneurРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (2)
- Summary of The Four Agreements: A Practical Guide to Personal Freedom (A Toltec Wisdom Book) by Don Miguel RuizОт EverandSummary of The Four Agreements: A Practical Guide to Personal Freedom (A Toltec Wisdom Book) by Don Miguel RuizРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (112)
- SYSTEMology: Create time, reduce errors and scale your profits with proven business systemsОт EverandSYSTEMology: Create time, reduce errors and scale your profits with proven business systemsРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (48)
- To Pixar and Beyond: My Unlikely Journey with Steve Jobs to Make Entertainment HistoryОт EverandTo Pixar and Beyond: My Unlikely Journey with Steve Jobs to Make Entertainment HistoryРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (26)
- The Master Key System: 28 Parts, Questions and AnswersОт EverandThe Master Key System: 28 Parts, Questions and AnswersРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (62)
- The Millionaire Fastlane: Crack the Code to Wealth and Live Rich for a LifetimeОт EverandThe Millionaire Fastlane: Crack the Code to Wealth and Live Rich for a LifetimeРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (58)
- Startup: How To Create A Successful, Scalable, High-Growth Business From ScratchОт EverandStartup: How To Create A Successful, Scalable, High-Growth Business From ScratchРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (114)
- Take Your Shot: How to Grow Your Business, Attract More Clients, and Make More MoneyОт EverandTake Your Shot: How to Grow Your Business, Attract More Clients, and Make More MoneyРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (22)
- Cryptocurrency for Beginners: A Complete Guide to Understanding the Crypto Market from Bitcoin, Ethereum and Altcoins to ICO and Blockchain TechnologyОт EverandCryptocurrency for Beginners: A Complete Guide to Understanding the Crypto Market from Bitcoin, Ethereum and Altcoins to ICO and Blockchain TechnologyРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (300)
- Brand Identity Breakthrough: How to Craft Your Company's Unique Story to Make Your Products IrresistibleОт EverandBrand Identity Breakthrough: How to Craft Your Company's Unique Story to Make Your Products IrresistibleРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (48)
- Creating Competitive Advantage: How to be Strategically Ahead in Changing MarketsОт EverandCreating Competitive Advantage: How to be Strategically Ahead in Changing MarketsРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (2)
- Summary: Who Not How: The Formula to Achieve Bigger Goals Through Accelerating Teamwork by Dan Sullivan & Dr. Benjamin Hardy:От EverandSummary: Who Not How: The Formula to Achieve Bigger Goals Through Accelerating Teamwork by Dan Sullivan & Dr. Benjamin Hardy:Рейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (2)
- The Kingdom Driven Entrepreneur's Guide: Doing Business God's WayОт EverandThe Kingdom Driven Entrepreneur's Guide: Doing Business God's WayРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (42)
- Anything You Want: 40 lessons for a new kind of entrepreneurОт EverandAnything You Want: 40 lessons for a new kind of entrepreneurРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (46)
- Secrets of the Millionaire Mind: Mastering the Inner Game of WealthОт EverandSecrets of the Millionaire Mind: Mastering the Inner Game of WealthРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (1026)
- Enough: The Simple Path to Everything You Want -- A Field Guide for Perpetually Exhausted EntrepreneursОт EverandEnough: The Simple Path to Everything You Want -- A Field Guide for Perpetually Exhausted EntrepreneursРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (24)
- Your Next Five Moves: Master the Art of Business StrategyОт EverandYour Next Five Moves: Master the Art of Business StrategyРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (799)
- What Self-Made Millionaires Do That Most People Don't: 52 Ways to Create Your Own SuccessОт EverandWhat Self-Made Millionaires Do That Most People Don't: 52 Ways to Create Your Own SuccessРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (24)
- Level Up: How to Get Focused, Stop Procrastinating, and Upgrade Your LifeОт EverandLevel Up: How to Get Focused, Stop Procrastinating, and Upgrade Your LifeРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (22)
- WEALTH EXPO$ED: This Short Argument Made Me a Fortune... Can It Do The Same For YouОт EverandWEALTH EXPO$ED: This Short Argument Made Me a Fortune... Can It Do The Same For YouРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (87)
- The E-Myth Revisited: Why Most Small Businesses Don't Work andОт EverandThe E-Myth Revisited: Why Most Small Businesses Don't Work andРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (709)