Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Glycolipids
Загружено:
Ruchini EdiriweeraОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Glycolipids
Загружено:
Ruchini EdiriweeraАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
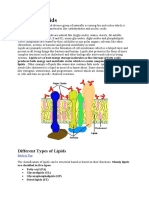
GLYCOLIPIDS
The glycolipids are yet another division of lipids that is utilised by the human as well as other forms of life.
Glycolipids are named in reference to their chemical structure: practically all glycolipids are derivatives of
ceramides. Ceremides are a fatty acid bonded or connected to the amino alcohol sphingosine. In fact, although
the class of lipids we discussed called phospholipids, are chemically different from glycolipids, the
phospholipid we call sphingomyelin, also is derived from ceramides. Glycolipids, however, are different as
well, because they contain no phosphates in comparison to phospholipids. What also puts glycolipids in a class
of their own is the fact that the fat is connected to a sugar molecule. Hence, the name glycolipid (glyco=sugar,
lipid=fat). Therefore, glycolipids are simply fats that are bonded to sugars. So, since glycolipids are built from
sphingosine, fat, and a sugar, we can be more exact in our naming and call them "glycosphingolipids".
In common with the phospholipids, the glycolipids are an essential part of cell membranes. Glycolipids also
help determine the blood group of an individual. In regards to blood grouping, glycolipids act as receptors at the
surface of the red blood cell. This is important as we can use this principle to classify our blood type, which is
critical during transfusions, etc .In microorgansims, certain glycolipids even help ensure their survival by
"tricking" our immune system into thinking they are not foreign. This helps them to evade immune survelllence.
On the other hand, some viruses, bacteria (eg., cholera) use glycolipids on their cell surface as well. This helps
the immune system destroy and clear the pathogen from the body.
Types of glycolipids
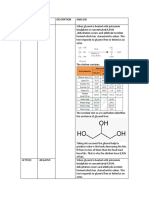
Cerebrosides-Cerebroside (from cerebro=brain) are glycolipids that are found primarily in the brain and
peripheral (other areas of the body) nervous tissue. There are different types of glycolipids, each characterised
by the sugar that they are bonded to and the type of fatty acid that is used to bond to the sugar. Sugars such as
galactose and glucose are bonded to the lipid. When a galactose or glucose molecule is bonded to the lipid, the
glycolipid is called a galactocerebroside or glucocerebroside, respectively.
Ceramide oligosaccharides-Just as we discussed ceremides, another group of glycolipids is termed the ceremide
oligosaccharides (ceremide="ceremide", oligo="short", saccharide="sugar"). Basically, these are ceremides
with short chains of sugars, in comparison to cerebrosides with only "one" sugar attached.
Sulfoglycosphingolipids-These cerebrosides are also called sulfatides, They are simply cerebrosides with a
sulfate residue on the sugar portion of glycolipid. This long name simply implies a cerebroside that contains a
sulfated galactose. As you can see, galactosyl, contains the word "galact" meaning the sugar galactose. The
difference here, is that the galactose has sulfate added to it,
Synthesis and degradation of glycolipids
Synthesis of glycolipids occurs with the help of enzymes that sequentially add sugars to the lipid. When the
lipids are required to be broken down, enzymes in the lysosome of the cell help to remove the sugar subunits.
This is important medically, because a deficiency of any of the enzymes involved in these processes cause an
accumulation of a particular glycolipid that cannot be further broken down. When this accumulation occurs, the
excess lipid remains trapped in the plasma or the cells and deposits in various organ/tissue systems and
unfortunately, damages them.
Вам также может понравиться
- Lipid Metabolism - WikipediaДокумент31 страницаLipid Metabolism - WikipediaTomiwa AdeshinaОценок пока нет
- Catalog Maritim CPLДокумент219 страницCatalog Maritim CPLPamellaОценок пока нет
- Pleiger Centralized HydraulicДокумент8 страницPleiger Centralized HydraulicPamellaОценок пока нет
- IndometacinДокумент47 страницIndometacinSava1988Оценок пока нет
- Metabolic Interrelationships Rev 07-11-2014Документ82 страницыMetabolic Interrelationships Rev 07-11-2014algutОценок пока нет
- IHC - InterpretareДокумент185 страницIHC - InterpretareAnca NeaguОценок пока нет
- Types and Classification of LipidsДокумент9 страницTypes and Classification of LipidsEdin AbolenciaОценок пока нет
- Curs 1 Introducere MetabolismДокумент56 страницCurs 1 Introducere MetabolismCristina FlorentinaОценок пока нет
- Farmacie Anul V Arad Lista Referatelor La Farmacie ClinicaДокумент12 страницFarmacie Anul V Arad Lista Referatelor La Farmacie ClinicaMisoaga ElenaОценок пока нет
- Medicatia HipolipemiantaДокумент77 страницMedicatia HipolipemiantaAlexandra G. CazanОценок пока нет
- Pleiger Electro Hydraulic System (EHS)Документ8 страницPleiger Electro Hydraulic System (EHS)PamellaОценок пока нет
- Acid Citric 1Документ45 страницAcid Citric 1Ioana-Mihaela Toma100% (1)
- Farmacie ClinicaДокумент2 страницыFarmacie ClinicaViorel PopОценок пока нет
- 1 - AntibioticeДокумент31 страница1 - AntibioticeAnca GuțuОценок пока нет
- Separanda Si VenenaДокумент3 страницыSeparanda Si VenenaGeta Deleanu Obradovici100% (1)
- Lista Medicamente Cu Card PHARMACCESДокумент3 страницыLista Medicamente Cu Card PHARMACCESPITICINFURIATОценок пока нет
- KristinaMarieTurnerGossypolPresentation HandoutsДокумент4 страницыKristinaMarieTurnerGossypolPresentation HandoutsKristina TurnerОценок пока нет
- Neuroprotection-WPS OfficeДокумент4 страницыNeuroprotection-WPS OfficeabdoОценок пока нет
- Metabolism UlДокумент17 страницMetabolism Ulmmmbbb100% (1)
- Toxicologie Clinica 1Документ29 страницToxicologie Clinica 1Andrei Marica100% (1)
- lp4+5 Farmaco AntihipertensiveДокумент9 страницlp4+5 Farmaco Antihipertensivededeyutza123Оценок пока нет
- Acidul UricДокумент25 страницAcidul UricAndreea ChiochiuОценок пока нет
- Licență Pulberi Farmaceutice PDFДокумент35 страницLicență Pulberi Farmaceutice PDFcristi cristiОценок пока нет
- 09 Taste Masking and Evaluation MethodsДокумент11 страниц09 Taste Masking and Evaluation MethodsKamran Alam100% (1)
- Docetaxel MonographДокумент13 страницDocetaxel MonographAmeliaОценок пока нет
- Aspirin Aspirină: "Asprin" Redirecţionează Aici. For The Author, See - Pentru Autor, A Se VedeaДокумент30 страницAspirin Aspirină: "Asprin" Redirecţionează Aici. For The Author, See - Pentru Autor, A Se VedeaIonela IordacheОценок пока нет
- ToxicologieДокумент29 страницToxicologieRazvan FumeaОценок пока нет
- Integrarea MetabolismuluiДокумент29 страницIntegrarea MetabolismuluiMunteanu DoruОценок пока нет
- Indicatii ExamenДокумент4 страницыIndicatii ExamenЕкатерина КостюкОценок пока нет
- Alimentatia Pacientului LitiazicДокумент92 страницыAlimentatia Pacientului LitiazicRosca MarcelОценок пока нет
- Curs 1 Farmacologia Generala: A. Farmacologie Pharmakon (Medicament) + Logos (Stiinta, Discurs)Документ4 страницыCurs 1 Farmacologia Generala: A. Farmacologie Pharmakon (Medicament) + Logos (Stiinta, Discurs)Claudia Stanis100% (1)
- General Medicine PDFДокумент28 страницGeneral Medicine PDFsubramaniam krishnamoorthiОценок пока нет
- Denumiri MedicamenteДокумент4 страницыDenumiri MedicamenteFlorin PostolacheОценок пока нет
- 24) Glycerol - A Review of Its Pharmacology, Pharmacokinetics, Adverse Reactions, and Clinical Use PDFДокумент14 страниц24) Glycerol - A Review of Its Pharmacology, Pharmacokinetics, Adverse Reactions, and Clinical Use PDFkevin steve velandia avilaОценок пока нет
- Journal of Biomedical SciencesДокумент37 страницJournal of Biomedical SciencesumairОценок пока нет
- Desmi Pump DISCOMДокумент36 страницDesmi Pump DISCOMVasile IonОценок пока нет
- AX M1 5000VA 24V ManualДокумент52 страницыAX M1 5000VA 24V Manualalexandru juncuОценок пока нет
- Power PointДокумент4 страницыPower Pointlarisa_2493100% (1)
- A Review On Current Trends in Oral Drug Delivery-Fast Dissolving TabletsДокумент16 страницA Review On Current Trends in Oral Drug Delivery-Fast Dissolving TabletsIJAR JOURNAL100% (1)
- Compatibility Atenolol With Excipients PDFДокумент9 страницCompatibility Atenolol With Excipients PDFelektron2010Оценок пока нет
- Anti Hyperlipidemic Agent PDFДокумент11 страницAnti Hyperlipidemic Agent PDFStefanus Surya100% (1)
- Structure of Membrane LipidsДокумент41 страницаStructure of Membrane LipidsStanley ChikoveОценок пока нет
- Group 2 GlycolipidsДокумент8 страницGroup 2 GlycolipidsMarvin JeaОценок пока нет
- LipidДокумент97 страницLipidNasar ullahОценок пока нет
- Properties and Significance of Complex LipidsДокумент47 страницProperties and Significance of Complex LipidsSatyabrat DuttaОценок пока нет
- Chemistry of COMPOUND LipidsДокумент46 страницChemistry of COMPOUND LipidsQueenОценок пока нет
- L8 - Structure Functions of Various LipidsДокумент23 страницыL8 - Structure Functions of Various Lipidsbilawal khanОценок пока нет
- Al Biology Carbohydrate LipidsДокумент8 страницAl Biology Carbohydrate LipidsDr.CharinОценок пока нет
- 03 CarbohydrateДокумент45 страниц03 CarbohydrateManojitОценок пока нет
- GlycerophospholipidsДокумент2 страницыGlycerophospholipidsHANNA CASANDRA GARCIAОценок пока нет
- Carbohydrate Classification of Carbohydrate Metabolism and Regulation of CarbohydrateДокумент14 страницCarbohydrate Classification of Carbohydrate Metabolism and Regulation of CarbohydratesukОценок пока нет
- LipidsДокумент10 страницLipidsFrancis Ryannel S. De CastroОценок пока нет
- VojoyДокумент7 страницVojoyFerds SalvatierraОценок пока нет
- Different Types of LipidsДокумент7 страницDifferent Types of LipidsNESLIHAN ERSOYAKОценок пока нет
- Lecture 17 - Glycosides Intro, ClassificationДокумент6 страницLecture 17 - Glycosides Intro, Classificationahsanonweb1983Оценок пока нет
- Lecture Research BiochemДокумент16 страницLecture Research BiochemDianne MaeОценок пока нет
- CarbohydratesДокумент112 страницCarbohydratesmaryam ijazОценок пока нет
- Lipids and Lipid Metabolism ReviewerДокумент14 страницLipids and Lipid Metabolism ReviewerKiela Therese LabroОценок пока нет
- Metabolism of Phospholipids: Gandham - Rajeev Email:gandhamrajeev33@gmaДокумент32 страницыMetabolism of Phospholipids: Gandham - Rajeev Email:gandhamrajeev33@gmaOnSolomonОценок пока нет
- Lipid: Endah PuspitasariДокумент13 страницLipid: Endah Puspitasaritnep21Оценок пока нет
- Aryl Halides: By:-Dr - Harpreet Kaur Pggcg11 CHDДокумент21 страницаAryl Halides: By:-Dr - Harpreet Kaur Pggcg11 CHDyeateshwarriorОценок пока нет
- Organic Compounds Containing NitrogenДокумент9 страницOrganic Compounds Containing NitrogenAUM S. PATELОценок пока нет
- Gluco Neo GenesisДокумент36 страницGluco Neo GenesisAmalia DarwisОценок пока нет
- Chapter 3 - Structure Characteristics - StarchДокумент22 страницыChapter 3 - Structure Characteristics - StarchVanessa LimОценок пока нет
- Vehicle WashДокумент12 страницVehicle Washyilmaz_uuurОценок пока нет
- Acrolein Test Fede RДокумент5 страницAcrolein Test Fede RLaura MartinezОценок пока нет
- Dna Vs Rna and Protein Synthesis Updated Recap by Amoeba SistersДокумент2 страницыDna Vs Rna and Protein Synthesis Updated Recap by Amoeba SistersJaneОценок пока нет
- Vinyl AcetateДокумент3 страницыVinyl AcetatechristopheОценок пока нет
- CH 243. AromaticityДокумент63 страницыCH 243. Aromaticityjob omyОценок пока нет
- Qb-Msc-301-Org. Chem. - 5Документ3 страницыQb-Msc-301-Org. Chem. - 5ftfdvcnОценок пока нет
- 1.1 Synthesis and Metabolism of AcetylcholineДокумент1 страница1.1 Synthesis and Metabolism of AcetylcholineDRxNaveen Maurya012Оценок пока нет
- Physical Science Grade 11 - St. Lorenzo Module 2 - : Saint Louis School of Pacdal, IncДокумент10 страницPhysical Science Grade 11 - St. Lorenzo Module 2 - : Saint Louis School of Pacdal, IncNo nameОценок пока нет
- Oxygen Containing CompoundsДокумент15 страницOxygen Containing Compoundsguia macatangayОценок пока нет
- ExamДокумент3 страницыExamJason TulipatОценок пока нет
- Heterocycles ScaffoldsДокумент25 страницHeterocycles ScaffoldsMoreno MarcatiОценок пока нет
- Hexose Monophosphate ShuntДокумент18 страницHexose Monophosphate ShuntAbdul Jabbar Abdul JabbarОценок пока нет
- Class 12 Important Questions For Chemistry - Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers - AglaSem Schools PDFДокумент11 страницClass 12 Important Questions For Chemistry - Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers - AglaSem Schools PDFvishwanathzОценок пока нет
- PhikalДокумент4 страницыPhikalDennis OptionalОценок пока нет
- Nutrition and Diet Therapy - Lecture Notes, Study Material and Important Questions, AnswersДокумент58 страницNutrition and Diet Therapy - Lecture Notes, Study Material and Important Questions, AnswersM.V. TV50% (2)
- Soal CC StrokeДокумент1 страницаSoal CC StrokeAngeline BudimanОценок пока нет
- Experiment 5a Pre Post LabДокумент9 страницExperiment 5a Pre Post LabRue Cheng Ma100% (1)
- Systematic NomenclatureДокумент12 страницSystematic NomenclatureSanjib Mal100% (1)
- Lab - Evaporation and Inter Molecular AttractionsДокумент3 страницыLab - Evaporation and Inter Molecular Attractionsscoop71288% (8)
- W6 Medicinal Chemistry of Analgesics - May2023Документ70 страницW6 Medicinal Chemistry of Analgesics - May2023CMuhammad FurqonОценок пока нет
- Drug Names - Stems, Prefixes, Roots and Suffixes - NCLEX MasteryДокумент5 страницDrug Names - Stems, Prefixes, Roots and Suffixes - NCLEX MasteryMarcel YoungОценок пока нет
- Chapter 19 Ver 1Документ101 страницаChapter 19 Ver 1jsaddsa jsasdОценок пока нет
- Sachin Rana (Iitb) : Answer The FollowingДокумент32 страницыSachin Rana (Iitb) : Answer The FollowingAkshat SoniОценок пока нет
- Enzymes ClassДокумент152 страницыEnzymes ClassPrasthuthi Chowdary100% (2)
- Organic Chemistry Past Papers by SKNДокумент5 страницOrganic Chemistry Past Papers by SKNMuhammad IshaqueОценок пока нет
- Chapter 3, 4 5 HopmeworkДокумент5 страницChapter 3, 4 5 HopmeworkDanОценок пока нет