Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Bearing Selection
Загружено:
Kenneth ChawАвторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Bearing Selection
Загружено:
Kenneth ChawАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
[Pg 1 / 6]
Bearing V12.xmcd
The Units used as standard: m, kg, N, Pa, sec, watts
N, kg, m, Pa, sec/min, watts/kW
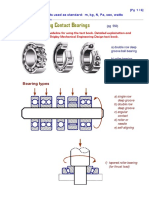
Rolling Contact Bearings
(pg 550)
This note is only a guideline for using the text book. Detailed explaination and
tables are found in Shigley Mechanical Engineering Design text book.
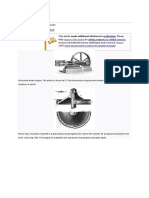
a) double row deep
groove ball bearing
b) roller bearing
c) angular contact
bearing
Bearing types
a) single row
deep groove
b) double row
deep groove
c) angular
contact
d) roller or
needle
e) self-aligning
f) tapered roller bearing
(for thrust load)
[Pg 2 / 6]
Bearing V12.xmcd
Bearing Load
Pg 554
Ball bearings are designed to support high radial load and limited axial load.
Roller bearings, however, support extremely high radial load but no axial load.
Other bearings are beyond the scope of this subject.
Bearing Life
Pg 553
The objective of this analysis is to determine the life of a bearing before the first
tangible evidence of fatigue.
Common life measures are
1. Number of revolutions of the inner ring (outer ring stationary) or
2. Number of hours of use at a standard angular speed
AFBMA standard states that the first evidence of fatigue is the spalling or pitting of
an area of 0.01 in2 (by Timken Company laboratories).
The AFBMA (and most other manufactures) term rating life as the life span of 90%
of a batch of bearings.
Bearing Load-life trade-off at constant reliability
For 90% reliability (R = 0.9) (std value for most bearing), the regression equation form is
1
a
F L = constant
this is the basic load-rating eqn for bearing
where
F is steady radial load, and
L is the desired life
and
a=3
a=
Fr
=
Lr Fd
Ld
10
3
for ball bearing
for roller bearings
where Lr, Fr refer to RATED specs provided by manufacturers
and Ld, Fd are the DESIGNER values.
[Pg 3 / 6]
Bearing V12.xmcd
From the equation above, a catalog load rating known as C10 is use to represent the
standard 90% reliability (10th percentile rating life where the reliability R = 0.90 ).
1
Hence the catalog rating
(unit: kN) is given by
LD nD 60
C10 = Af Fr
LR nR 60
Fr
LD
- radial load (in kN) applied to the bearing
- designed life (in hours) --> the expected life of the bearing
nD
LR
- designed rotational speed of the bearing in RPM
- rated life (in hours) provided by manufacturer of the bearing
nR
Af
- rated rotational speed of the bearing (RPM)
- application (safety) factor of the bearing system
The value (LR x nR) provide the rated life in revolutions for 1 minute. Most bearing
manufacturer chooses a rated cycles value of 1,000,000 revolutions in a 1 hr period to
correspond to a basic load rating in the catalog. Hence for most class of bearing
where R = 0.90, the catalog rating is given by:
1
LD nD 60
C10 = Af Fr
6
10
N.B: If reliability is not mentioned,
then the default value of R = 0.90 is
assumed.
Sample 1A
A ball bearing is to be selected to carry a radial load of 6.5 kN. The designed life is
5000 hr with a rotation rate of 900 rpm. For a bearing reliability of 0.90, find the
suitable bearing.
Designed load (radial),
Designed life,
Fr = 6.5kN
Af = 1.15
nD = 900rpm
1
a
LD nD 60
= 48.31 kN
6
10
C10 = Af Fr
a = 3
Application factor,
LD = 5000
Inner ring rotates,
Ball bearing,
Refer to Table 11-2 pg 571 , column for
Deep Groove Load Ratings. The next
higher C rating C10 = 55.9 kN
corresponding to Bore 65mm.
The selected bearing is 65mm 02-series deep groove ball bearing !
[Pg 4 / 6]
Bearing V12.xmcd
Reliability of the Bearings
The Reliability-Life Trade-Off [bearing survival and load-life] :
Reliability R > 0.9
Empirical formulaes had been used for higher accuracy of the calculation for
Bearing Life based on reliability analysis. The formula below is the most accurate for
bearing analysis.
1
Xd =
LD nD 60
6
10
Xd
C10 = Fr
1
x
+
x
log
0 (
o)
Based on experimental data, the equation above had been refined and finally for
academic purposes, it was simplified further. The final equation for load rating of
reliability R 0.9 is shown below:
1
Xd =
LD nD 60
6
10
Xd
C10 = Af Fr
1
1.483
0.02 + 4.439 ( 1 R)
If Application factor (safety factor ) if not mentioned, Af = 1.0
[Pg 5 / 6]
Bearing V12.xmcd
Sample 1B
If reliability in Sample 1A is R = 0.95 , and safety factor Af = 1.15 , find the new load
rating and the correct bearing? Find the suitable bearing if it is to be mounted on a
65mm round shaft.
1
C10
Xd
= 1.15 6.5 10
1
1.483
0.02 + 4.439 ( 1 0.95 )
Answer:
C10 = 57 kN
The next higher C load rating is ( C10 = 61.8 kN) for a
70mm bore deep groove ball bearing.
However the shaft diameter is only 65mm. It will be rocking within the bearing bore
because of the generous tolerance (i.e. the bearing is too big for the shaft)
Comments: 70mm ball-bearing - Not recommended
Solution: Use the alternative:- Angular Contact bearing.
The next higher Angular Contact C rating ( C10 = 63.7 kN) corresponding to a 65mm
bearing. This bearing will slip perfectly on the 65mm shaft.
Recommended: 65mm Angular Contact ball bearing
Overall Reliability (or combined reliability) for multi-bearings system
Most shaft are supported by at least 2 bearings. If the overall reliability of the
bearings supporting the shaft is given as R' , then
Individual bearing reliability,
R=
where n is the number of bearings
supporting the shaft.
(used at least 2 more decimal points)
R'
For a 3 bearings system with overall reliability R' = 0.99 then
the individual reliability is given by R =
If R' = 0.999 then
If R' = 0.9999 then
R =
R =
0.99 = 0.9967
0.999 = 0.99967 with 2 decimal points added.
3
0.9999 = 0.999967 with 2 decimal points added.
[Pg 6 / 6]
Bearing V12.xmcd
Combined radial and thrust loading
A ball bearing is capable of resisting radial loading, Fr and thrust (axial) loading, Fa.
To consider both loads, an equivalent radial load, Fe is obtained that does the same
damage as combined radial and thrust load. The equation is given as below:
Fe = X1 V Fr + Y1 Fa
or
Fe = X2 V Fr + Y2 Fa
To correct for various rotating-ring conditions, a rotation factor, V is used.
V=1
inner ring rotates
V = 1.2
outer ring rotates
The X and Y factors depends on several conditions including number of balls
and its diameter.
The Equivalent Radial load factors for ball-bearing is shown in Table 11-1.
The Y = 0 for straight and cylindrical roller bearings because it does not take
any axial load.
If
If
Fa
V Fr
Fa
V Fr
then use X1 and Y1 in Table 11-1
>e
then use X2 and Y2 in Table 11-1
To get the accurate value of e and Y2, tabulation may be needed.
1
Fe = X2 V Fr + Y2 Fa
LD nD 60
C10 = Fe
6
10
Sample 2
An ball bearing is to be selected to carry a radial load of 8 kN and thrust load of 4 kN.
The desired life LD is to be 5000 h with an inner-ring rotation rate of 900 rpm What is
the basic load rating that should be used in selecting a bearing for reliability of 0.95?
Sample 3
A bearing is to be selected to carry a radial load of 5.0 kN. The designed life is 2500 hrs
with a rotation rate of 500 rpm. For a bearing reliability of 0.99, find the suitable bearing if
it is to be mounted on a 35mm round shaft. Application factor = 1.15
Вам также может понравиться
- Bearing SelectionДокумент22 страницыBearing SelectionAbhishek ShindeОценок пока нет
- RTA 03.4 Fuel Injection NozzlesДокумент5 страницRTA 03.4 Fuel Injection NozzlesAlexis Barnabás Collins100% (1)
- Diesel Engine ConstructionДокумент53 страницыDiesel Engine ConstructionLasse HansenОценок пока нет
- Types of Lubrication: BoundaryДокумент20 страницTypes of Lubrication: BoundaryAbishek Abi100% (1)
- Steam Turbine: Navigation SearchДокумент42 страницыSteam Turbine: Navigation Searchh_imdad23Оценок пока нет
- Diesel Engine and Steam BoilerДокумент0 страницDiesel Engine and Steam BoilerChathuranga ManukulaОценок пока нет
- Piston Stress AnalysisДокумент13 страницPiston Stress Analysisducatiss900100% (3)
- Thrust BearingДокумент5 страницThrust BearinghardaniОценок пока нет
- Man New Piston RingsДокумент3 страницыMan New Piston RingsMario AndrewОценок пока нет
- Boiler Module VДокумент23 страницыBoiler Module VdeepanckОценок пока нет
- Trunk Piston Engine The Crank ShaftДокумент10 страницTrunk Piston Engine The Crank ShaftAayush AgrawalОценок пока нет
- Couplings - A Basic Introduction To Different Types of CouplingsДокумент38 страницCouplings - A Basic Introduction To Different Types of CouplingsMohsin MurtazaОценок пока нет
- ValvesДокумент40 страницValvesMizta KunaОценок пока нет
- Sulzer Turbocharging 00Документ18 страницSulzer Turbocharging 00ozakyusОценок пока нет
- Mechanical Foam Type ExtinguisherДокумент2 страницыMechanical Foam Type ExtinguisherAayush AgrawalОценок пока нет
- Grease Sampling Procedure For Slew BearingДокумент4 страницыGrease Sampling Procedure For Slew BearingSCISTRTОценок пока нет
- Firing Order of CylindersДокумент17 страницFiring Order of CylindersSaurav KumarОценок пока нет
- MAN-Service Experience Small Bore Four-Stroke Engines PDFДокумент20 страницMAN-Service Experience Small Bore Four-Stroke Engines PDFvangeliskyriakos8998Оценок пока нет
- Training Book-CE Aung BaДокумент176 страницTraining Book-CE Aung BaPhyo Thiha KyawОценок пока нет
- Flow Profile For Reciprocating Pumps - Chemical Engineering ProcessingДокумент3 страницыFlow Profile For Reciprocating Pumps - Chemical Engineering ProcessingVILLANUEVA_DANIEL2064Оценок пока нет
- Crankshaft TerminologyДокумент16 страницCrankshaft TerminologySathistrnpcОценок пока нет
- Air Start ExplosionДокумент12 страницAir Start ExplosionsahilimuОценок пока нет
- Cylinder Liner TheoryДокумент85 страницCylinder Liner TheoryMuhammad Nasim Abbas100% (1)
- 3D Modeling of Crankshaft Using Catia Software: Chapter-1Документ33 страницы3D Modeling of Crankshaft Using Catia Software: Chapter-1naveen mylapilli0% (1)
- Completely Describe The Iron-Carbon Diagram With HelpingДокумент5 страницCompletely Describe The Iron-Carbon Diagram With HelpingwaqarОценок пока нет
- TT401 GearДокумент45 страницTT401 GearDurjoy Roy100% (1)
- Gas Turbines and Its ModificationsДокумент29 страницGas Turbines and Its ModificationsHamza NeweraОценок пока нет
- Countermeasure For SurgingДокумент3 страницыCountermeasure For SurgingParthiban Nagarajan100% (1)
- Stern Tube BoringДокумент2 страницыStern Tube BoringMedha Jog KatdareОценок пока нет
- Exhaust Valve MaterialsДокумент2 страницыExhaust Valve MaterialsRannier CazagrandeОценок пока нет
- Tie Bolts or Tie RodsДокумент8 страницTie Bolts or Tie RodsAayush AgrawalОценок пока нет
- Machine Design Case StudyДокумент30 страницMachine Design Case StudyJoe Felice100% (3)
- Bearing Instal at Ion and Maintenance GuideДокумент130 страницBearing Instal at Ion and Maintenance GuideTeodoru Horia Adrian75% (4)
- 19 - Wartsila - Turbocharging 2 Stroke Engine - Existing & Future DemandsДокумент18 страниц19 - Wartsila - Turbocharging 2 Stroke Engine - Existing & Future DemandsCháu Bác HồОценок пока нет
- Types of Piston RingsДокумент10 страницTypes of Piston RingsJa Phe TiОценок пока нет
- Detailed 3D Ring Pack Analysis by Federal MogulДокумент13 страницDetailed 3D Ring Pack Analysis by Federal MogulthisisjineshОценок пока нет
- Fuel Injector NozzlesДокумент10 страницFuel Injector NozzlesHenrik KunzkeОценок пока нет
- BearingДокумент24 страницыBearingniteen_mulmule485Оценок пока нет
- Cylinder Liner Gauging 1Документ5 страницCylinder Liner Gauging 1Vinay Kumar Neelam100% (1)
- Appendix ThermodynamicsДокумент50 страницAppendix ThermodynamicsRiteshMandaliyaОценок пока нет
- Dresser-Rand Group Inc - FinalДокумент24 страницыDresser-Rand Group Inc - FinalMatt JonesОценок пока нет
- GeislingerДокумент5 страницGeislingerSameh Jeep100% (1)
- Marine Diesel EngineДокумент5 страницMarine Diesel Enginemy generalОценок пока нет
- Hydraulic CylindersДокумент7 страницHydraulic Cylinderspacopil34Оценок пока нет
- Piston RingДокумент8 страницPiston RingashokkumarОценок пока нет
- 5 Exhaust ValveДокумент7 страниц5 Exhaust ValveAhamed RasheenОценок пока нет
- Service Details Man BW PDFДокумент7 страницService Details Man BW PDFTapas ChaudhuriОценок пока нет
- Engine Construction: Bed PlateДокумент25 страницEngine Construction: Bed PlatenareshОценок пока нет
- 1d Dvs Sulzer Rta48t Codebook 812Документ812 страниц1d Dvs Sulzer Rta48t Codebook 812BorysОценок пока нет
- Bearings: Scraping of The Bearing Surfaces Is Strictly ProhibitedДокумент46 страницBearings: Scraping of The Bearing Surfaces Is Strictly ProhibitedKumarОценок пока нет
- Gearboxes: Gearbox ApplicationДокумент8 страницGearboxes: Gearbox Applicationrizviabbas2012Оценок пока нет
- ViFlow Funke GB PDFДокумент8 страницViFlow Funke GB PDFukalОценок пока нет
- Four Stroke Diesel EngineДокумент9 страницFour Stroke Diesel Engineteguh arif pratama adi putraОценок пока нет
- CHAPTER 2 CrankshaftДокумент19 страницCHAPTER 2 CrankshaftAUNG0% (1)
- Engine Crankshaft Deflection Measurement Guide - IIMSДокумент9 страницEngine Crankshaft Deflection Measurement Guide - IIMSNyan ThutaОценок пока нет
- FlywheelДокумент62 страницыFlywheelSudarson KarthikeyanОценок пока нет
- Types of Internal Combustion EnginesДокумент18 страницTypes of Internal Combustion EnginesMoayadОценок пока нет
- Rolling Contact Bearings: Bearing TypesДокумент6 страницRolling Contact Bearings: Bearing Typessofyan samОценок пока нет
- 1 B Roll No 2Документ1 страница1 B Roll No 2himanshugarg979Оценок пока нет
- Strategy Tester PDFДокумент20 страницStrategy Tester PDFKenneth ChawОценок пока нет
- Hello PDFДокумент3 страницыHello PDFKenneth ChawОценок пока нет
- 06-Mydin DoneДокумент12 страниц06-Mydin DoneKenneth Chaw100% (1)
- Create 3D Solid Primitives:: Switch To The 3D Modeling WorkspaceДокумент4 страницыCreate 3D Solid Primitives:: Switch To The 3D Modeling WorkspaceKenneth ChawОценок пока нет
- Strategy Tester PDFДокумент20 страницStrategy Tester PDFKenneth ChawОценок пока нет
- 19-08-2018Документ1 страница19-08-2018Kenneth ChawОценок пока нет
- Power Supply Box Chassis - SheeДокумент1 страницаPower Supply Box Chassis - SheeKenneth ChawОценок пока нет
- Orientation Test-01 - IndexДокумент1 страницаOrientation Test-01 - IndexKenneth ChawОценок пока нет
- SolidWorks For Sheet MetalДокумент15 страницSolidWorks For Sheet MetalCodreanu Petru100% (2)
- Lock Box Bottom - InCH - Sheet1Документ1 страницаLock Box Bottom - InCH - Sheet1Kenneth ChawОценок пока нет
- Examples BoilerДокумент5 страницExamples BoilerKenneth ChawОценок пока нет
- Cylinder DrawingДокумент1 страницаCylinder DrawingKenneth ChawОценок пока нет
- Toy Box2 - SolidworksДокумент1 страницаToy Box2 - SolidworksKenneth ChawОценок пока нет
- Practical Paper Model PDFДокумент2 страницыPractical Paper Model PDFKenneth ChawОценок пока нет
- Part 2Документ1 страницаPart 2Kenneth ChawОценок пока нет
- Sheet Metal BoxДокумент1 страницаSheet Metal BoxKenneth ChawОценок пока нет
- Steel Tube Structure-Test2 - SHДокумент1 страницаSteel Tube Structure-Test2 - SHKenneth ChawОценок пока нет
- cls17 DMD Forcst PDFДокумент32 страницыcls17 DMD Forcst PDFamenstoОценок пока нет
- Identifying Customer Needs SweetwaterДокумент26 страницIdentifying Customer Needs SweetwaterKenneth ChawОценок пока нет
- Fluent Tut Mixing ElbowДокумент58 страницFluent Tut Mixing Elbowgp1707Оценок пока нет
- Academy Award: Current Special CategoriesДокумент1 страницаAcademy Award: Current Special CategoriesKenneth ChawОценок пока нет
- Steel Tube Structure-Test2 - SHДокумент1 страницаSteel Tube Structure-Test2 - SHKenneth ChawОценок пока нет
- Steel Tube Structure-Test2 - SHДокумент1 страницаSteel Tube Structure-Test2 - SHKenneth ChawОценок пока нет
- Cs WP Sample Exam Question Part 1Документ2 страницыCs WP Sample Exam Question Part 1Kenneth ChawОценок пока нет
- Revision 1Документ1 страницаRevision 1Kenneth ChawОценок пока нет
- Fuel of Give Out of Calorific Ofoxygen, ofДокумент17 страницFuel of Give Out of Calorific Ofoxygen, ofKenneth ChawОценок пока нет
- Uhas 2122 Course Outline - 2016Документ4 страницыUhas 2122 Course Outline - 2016Kenneth ChawОценок пока нет
- Sources of Energy - Malaysian Scenario Part 1Документ11 страницSources of Energy - Malaysian Scenario Part 1Kenneth ChawОценок пока нет
- Limit - Switch Test1 Sheet1Документ1 страницаLimit - Switch Test1 Sheet1Kenneth ChawОценок пока нет
- CLA Brochure - 2022-3Документ10 страницCLA Brochure - 2022-3Streamer AccountОценок пока нет
- Honda IzyДокумент16 страницHonda IzyTerry FordОценок пока нет
- Rotating Equipment & ServiceДокумент12 страницRotating Equipment & Servicenurkasih119Оценок пока нет
- CCДокумент5 страницCCnazmulОценок пока нет
- Acetylcysteine 200mg (Siran, Reolin)Документ5 страницAcetylcysteine 200mg (Siran, Reolin)ddandan_2Оценок пока нет
- Bench-Scale Decomposition of Aluminum Chloride Hexahydrate To Produce Poly (Aluminum Chloride)Документ5 страницBench-Scale Decomposition of Aluminum Chloride Hexahydrate To Produce Poly (Aluminum Chloride)varadjoshi41Оценок пока нет
- Lab Manual Switchgear and Protection SapДокумент46 страницLab Manual Switchgear and Protection SapYash MaheshwariОценок пока нет
- Action ResearchДокумент2 страницыAction ResearchGeli BaringОценок пока нет
- Newsletter 1-2021 Nordic-Baltic RegionДокумент30 страницNewsletter 1-2021 Nordic-Baltic Regionapi-206643591100% (1)
- SICHEM Brochure 2023Документ8 страницSICHEM Brochure 2023krishnarao badisaОценок пока нет
- Group 2 ITI Consensus Report: Prosthodontics and Implant DentistryДокумент9 страницGroup 2 ITI Consensus Report: Prosthodontics and Implant DentistryEsme ValenciaОценок пока нет
- Cambridge IGCSE: CHEMISTRY 0620/42Документ12 страницCambridge IGCSE: CHEMISTRY 0620/42Khairun nissaОценок пока нет
- Masoneilan - 78 Series Air Filter Regulators IOMДокумент8 страницMasoneilan - 78 Series Air Filter Regulators IOMNithyAОценок пока нет
- Ethical Conflicts in Psychology PDF DownloadДокумент2 страницыEthical Conflicts in Psychology PDF DownloadAvory0% (2)
- PetrifiedДокумент13 страницPetrifiedMarta GortОценок пока нет
- Notice: Premerger Notification Waiting Periods Early TerminationsДокумент5 страницNotice: Premerger Notification Waiting Periods Early TerminationsJustia.comОценок пока нет
- Lenovo NotebooksДокумент6 страницLenovo NotebooksKamlendran BaradidathanОценок пока нет
- Sanskrit Subhashit CollectionДокумент110 страницSanskrit Subhashit Collectionavinash312590% (72)
- Aribah Ahmed CertificateДокумент2 страницыAribah Ahmed CertificateBahadur AliОценок пока нет
- Jpedal ManualДокумент20 страницJpedal ManualDamián DávilaОценок пока нет
- Women Are Better Managers Than MenДокумент5 страницWomen Are Better Managers Than MenCorazon ValdezОценок пока нет
- Pelayo PathopyhsiologyДокумент13 страницPelayo PathopyhsiologyE.J. PelayoОценок пока нет
- Vocabulary FceДокумент17 страницVocabulary Fceivaan94Оценок пока нет
- June 2017 (IAL) MS - Unit 1 Edexcel Physics A-LevelДокумент16 страницJune 2017 (IAL) MS - Unit 1 Edexcel Physics A-LevelNyraStardollОценок пока нет
- CTS2 HMU Indonesia - Training - 09103016Документ45 страницCTS2 HMU Indonesia - Training - 09103016Resort1.7 Mri100% (1)
- Nescom Test For AM (Electrical) ImpДокумент5 страницNescom Test For AM (Electrical) Impشاہد یونسОценок пока нет
- William Hallett - BiographyДокумент2 страницыWilliam Hallett - Biographyapi-215611511Оценок пока нет
- What You Need To Know About Your Drive TestДокумент12 страницWhat You Need To Know About Your Drive TestMorley MuseОценок пока нет
- BSH 7005-15Документ129 страницBSH 7005-15Mark InnesОценок пока нет
- Green Dot ExtractДокумент25 страницGreen Dot ExtractAllen & UnwinОценок пока нет
- CATIA V5-6R2015 Basics - Part I : Getting Started and Sketcher WorkbenchОт EverandCATIA V5-6R2015 Basics - Part I : Getting Started and Sketcher WorkbenchРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (10)
- Practical Reservoir Engineering and CharacterizationОт EverandPractical Reservoir Engineering and CharacterizationРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (3)
- SketchUp Success for Woodworkers: Four Simple Rules to Create 3D Drawings Quickly and AccuratelyОт EverandSketchUp Success for Woodworkers: Four Simple Rules to Create 3D Drawings Quickly and AccuratelyРейтинг: 1.5 из 5 звезд1.5/5 (2)
- Pocket Guide to Flanges, Fittings, and Piping DataОт EverandPocket Guide to Flanges, Fittings, and Piping DataРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (22)
- Certified Solidworks Professional Advanced Weldments Exam PreparationОт EverandCertified Solidworks Professional Advanced Weldments Exam PreparationРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)
- FreeCAD | Step by Step: Learn how to easily create 3D objects, assemblies, and technical drawingsОт EverandFreeCAD | Step by Step: Learn how to easily create 3D objects, assemblies, and technical drawingsРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)
- Autodesk Fusion 360: A Power Guide for Beginners and Intermediate Users (3rd Edition)От EverandAutodesk Fusion 360: A Power Guide for Beginners and Intermediate Users (3rd Edition)Рейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (2)
- Autodesk Inventor 2020: A Power Guide for Beginners and Intermediate UsersОт EverandAutodesk Inventor 2020: A Power Guide for Beginners and Intermediate UsersОценок пока нет