Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
MIS 310 Tutorial
Загружено:
Shàhríàrõ Dã RàkínskìИсходное описание:
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
MIS 310 Tutorial
Загружено:
Shàhríàrõ Dã RàkínskìАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
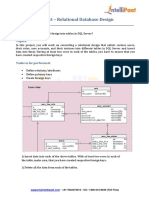
MIS 310
Management Information System
SQL Database
TUTORIAL
Mohammed Rashed Uzzaman(RZZ)
Faculty, North South University
Management Information System
MIS 310 Tutorial (RZZ)
School of Business
Hello everyone!! Welcome to MIS 310 SQL Tutorial!! In this tutorial we will learn the basics of SQL. We
will start from the installation of local server in your pc.
INSTALLING LOCAL SERVER
We will use Xampp in this tutorial,there are also other servers available like Wamp and Mamp.
Wamp is for windows, Mamp is for Mac OS. Xampp is available for both Windows and Mac OS.
XAMPP is a popular all-in-one kit that installs Apache, MySQL, and PHP in one procedure. XAMPP also
installs phpMyAdmin, a Web application you can use to administer your MySQL databases.
So, lets first install Xampp in your PC. If you dont have the installation file or if you havent collected
it yet, no need to worry, you can download it form http://www.apachefriends.org/en/xamppwindows.html .
Lets start the process. First open the folder where you saved your Xampp installation file.
1. Now, double click the installation file as shown in the Figure 1 and follow the process
Figure 1: Xampp installation file.
2|P a ge
MIS 310 Tutorial (RZZ)
2. Click the ok button (Figure 2).
Figure 2: Language selection.
3. Click the next button to start installation as shown in the figure 3.
Figure 3: Start installation.
4. In this step you have to select a folder from your directory. Its c:\ xampp by default. Just click
the Install button if you dont want to install it anywhere else.
Figure 4: Select folder
3|P a ge
MIS 310 Tutorial (RZZ)
Figure 5: Installation in progress.
Figure 6: Finish Installation.
5. Finally click the Finish Button to complete the installation process.
Now youve successfully installed Xampp server in your pc. Go to your desktop and double click the
Xampp icon to open the Xampp control panel (Figure 7).
Figure 7: Xampp Control Panel.
4|P a ge
MIS 310 Tutorial (RZZ)
Figure 7 is a Xampp control panel, from where you have to start Apache and Mysql by pressing the start
buttons. You can start all the services provided by Xampp together, but make sure that you started
Apache and Mysql at least. After starting the services your Xampp server control panel will look like
figure 8.
Figure 8: Start Apache, Mysql.
Ok.. So, finally your computer is ready for Mysql. Now open you web browser and in the address bar
type localhost to open your Xampp server.
Figure 9
A page like Figure 10 will appear in the screen where you will be asked to select a language. Select
English from the list.
Figure 10: Select Language.
5|P a ge
MIS 310 Tutorial (RZZ)
After clicking English you will see a page like the one in figure 11.
Figure 11: Select phpMyAdmin.
Click the phpMyAdmin link to open phpMyAdmin window. Your phpMyAdmin window will be exactly
like the figure 12.
Figure 12: phpMyAdmin page.
Now we are ready to start our next section where wewill cover basic and some advance features of sql.
6|P a ge
MIS 310 Tutorial (RZZ)
SQL
As we are going to use Mysql, it is important to let you know that when you will deal with database and
you have to create, update, select or delete data from your database, you may have to write lines and
lines of sql codes and queries.MysqlsGUI(Graphical User Interface) made it easy for its user to do all
these complex jobs even without knowing a single sql syntax. But for the advance users it also provides
sql code typing area. As a student of MIS 310 database course we must learn to write sql queries first.
But dont worry we will see the use of GUI too.
SQL is not case sensitive. So its actually doesnt matter whether yoursql syntaxs are in capital letter
or not. Though professionalsmaintain a standard of capitalizing sql keywords or syntaxs and putting ;
after finishing a query as a Good Practice, its not actually required. So you can write a sql query like
you write an English sentence. But its important to put the spaces and commas perfectly.
First we will learn how to create a new database.
Creating New Database:
Lets create our first database. To create a new database we have to use the CREATE DATABASE
statement. So, from your phpMyAdmin click SQL as shown in the Figure 13.
Figure 13: Select SQL.
After clicking SQL a new page like Figure 14 will appear. You will see a blank space where we are
7|P a ge
MIS 310 Tutorial (RZZ)
Figure 14: SQL page.
going to write our sql statements. Now type,
CREATE DATABASE `student`;
Again, its not important to capitalize the CREATE DATABASEstatement and putting grave accentmark
(`) before and after of our database name or putting ; after the statement. But you can follow it if you
want, because its a good practice and it reduces the chance of doing mistakes while writing queries.
Dont mix (``) with quotation mark ( ). ` is used only before and after of database names and table
names. If you put database or table name inside quotation mark, Mysql database will show error and
not going to take your statement. So, make sure that you dont make these mistakes.
Figure 15: CREATE DATABASE
After typing the statement click GO button, right down corner of the window.
8|P a ge
MIS 310 Tutorial (RZZ)
Figure 16: GO Button
So, we have created our first database!! Now if you look at the database list which is at the left side of
the window youll see the student database as shown in the Figure 17.
Figure 17: Select Database from list.
Click and open the student database.
Creating New Table:
Now click and open SQL page again and type:
CREATETABLE`student` (
`id`INTNOTNULLPRIMARY KEY,
`first_name`VARCHAR(100),
`last_name` VARCHAR(100),
`dept`varchar (3),
9|P a ge
MIS 310 Tutorial (RZZ)
`address`VARCHAR(255)
);
Here we used CREATE TABLE statement to create a new table named student. You probably have
noticed that this CREATE TABLE statement has two parts. In the first part we mentioned our table name
which is student, and in the second part we wrote the column names that we want to see in our table.
We also have to mention the type and length of the data we are going to insert into these columns. Here
in the id column we will insert Integers which is INT in sql. Forfirst_name and last_name, the data type
is VARCHAR which means Variable Character and inside the brackets we mentioned the length of the
data (100) which means database will not accept more than 100 characters in this field.You must be
wondering why we have not specified the character length for id; we did that because when we mention
INT as data type, database automatically sets the character length to 11.Last two columns of this table
are department (dept) and address of the student.
Its really easy to write SQL statement, all you have to do is just to put spacesperfectly. For id we also
specified that, it is NOT NULL, it means this field cannot be left empty when inserting data, otherwise
database is not going to accept data and this is the primary key for this table. PRIMARY KEY is a unique
key for the entries of a table that differentiates contents of each row from each other. Primary Key
cannot be same for multiple entries of a table.
Afterwriting the statement press GO button like before. A new table will be created and will be visible
in the left side bar.
Figure 18: Opening Student Table.
Click the student table to open the table. A new page will appear where you will see list of columns you
specified for your table with proper description.
10 | P a g e
MIS 310 Tutorial (RZZ)
Figure 19: Table Details.
As you can see id is the primary key of this table which we nominated while we were creating the
table. Our statement was:
`id` INT NOT NULL PRIMARY KEY,
It is also possible to write the statement like below:
CREATE TABLE `student` (
`id` INT NOT NULL,
`first_name` VARCHAR(100),
`last_name` VARCHAR(100),
`dept` varchar (3),
`address` VARCHAR(255),
primary key(`id`)
);
We can also add the auto increment feature to our id field. If we want to add auto increment, then we
just have to add auto_increment in the statement where we specified our id field, like below:
`id` NOT NULL auto_increment,
11 | P a g e
MIS 310 Tutorial (RZZ)
Inserting Data Into Tables:
Now we are going to insert data into our student table. To insert data we have to use INSERT INTO
statement. Data insertion can be done in two ways. We will see both of them with an example. Lets
insert a students data in our table.
Lets say, we want to insert a students information in our student table whos Name is Faisal Jahan,
Department: BBA, and Address: 41 Rampura, Dhaka.
Now, go to the sql page again and type:
INSERT INTO `student` (id, first_name, last_name, dept, address)
VALUES ('', 'Faisal', 'Jahan', 'BBA', '41 Rampura, Dhaka');
Click GO button.
Figure 20: Insert Data.
As you can see, in this SQL statement we first typed the statement we want to execute which is INSERT
INTO, then typed our table name student and after that we typed all the attributes/fields/column
names of our table inside bracket and finally typed the values we want to insert into our table using the
VALUESsyntax. After the VALUES syntax we specified all the data, separated by comma and order by
the column names that we specified before. You must remember, when youre writing a VARCHAR
element or text you always have to write it inside single quotation marks. But its not important when
you are inserting INT data. In this table our id field is auto increment enabled. Thats why we dont
have to write the id but you have to leave empty quotation marks.
This is a form of writing INSERT INTO statement. This form is very useful when you want to insert data
into specific columns. All you have to do is just to specify the column name/names where you want to
insert data. But if you want to insert data into all the columns, then you can just write,
INSERT INTO `student` VALUES ('', 'Faisal', 'Jahan', 'BBA', '41 Rampura, Dhaka');
Inserting Multiple rows:
Go to SQL page and write:
INSERT INTO `student`
12 | P a g e
MIS 310 Tutorial (RZZ)
VALUES ('', 'Tanveer', 'Khan', 'EEE', '11 Bashundhara, Dhaka'),
('', 'Anik', 'Hasan', 'BBA', '63/1 Uttara, Dhaka'),
('', 'Nazmul', 'Islam', 'BBA', '30 Gulshan, Dhaka'),
('', 'Shajib', 'Khan', 'CSE', '21 Dhanmondi, Dhaka');
Press GO button to insert data.
As you can see, to insert multiple data at a time you have to put each rows data inside brackets and
have to separate those using commas.
Now, to see all your inserted data click student from the left side bar.
Figure 21: Opening Student table.
Deleting Database:
To delete a database go to SQL and write
DROP DATABASE `database name`;
But by default the DROP DATABASE function is disabled in Xampp. So if you want to drop your database
then you have to follow the process below:
1. First go to http://localhost/phpmyadmin/ or click 127.0.0.1 from top.
13 | P a g e
MIS 310 Tutorial (RZZ)
Figure 22: Opening phpMyadmin Home page.
2. Click Database.
Figure 23: Opening database list.
3. Select your database name from the list and click drop button.
14 | P a g e
MIS 310 Tutorial (RZZ)
Figure 24: Select and Drop Database.
Deleting Tables:
To delete a table from your database first go to the SQL page and write
DROP TABLE `table name`;
The table will be deleted.
Queries:
Query is the most important part of sql. Till now we learnt how to create database, table using CREATE
DATABASE and CREATE TABLE statement, learnt how to insert data into table using INSERT INTO
statement and how to delete database and table using DROP DATABASE and DROP TABLE statement.
Now we will learn the use of SELECT statement.
Lets go back to our student table. Go to the SQL page. Lets say you want see all the data from your
student table. Write the query below:
SELECT*FROM `student`;
15 | P a g e
MIS 310 Tutorial (RZZ)
Youll get all the data you have in your student table.
Figure 25: Query Result.
In short, SELECT* means all. So, here in this query we wanted to see all from the table student.
Now if you want to see particular column/columns from the database then all you have to do is to write
the column name/names after SELECT. In case of multiple columns you have to put commas to separate
them. Lets see an example,
See all first names from the table. Go to SQL and type:
SELECT `first_name` FROM `student`;
Figure 26: Query Result.
Image above shows how the result is going to look. Lets see multiple columns. Go to SQL and write the
query below:
SELECT `first_name`, `last_name`, `dept` FROM `student`;
16 | P a g e
MIS 310 Tutorial (RZZ)
Figure 27: Query Result.
Click the GO button to see the result.
SQL WHERE
Most of the time we want to find a particular record from our database. For example, you may want to
find details of a particular student name. To run this query you have to write
SELECT `first_name`, `last_name`, `dept`, `address` FROM `student` WHERE `first_name` = Faisal;
Image below shows the result we are going to get.
Figure 28: Query Result.
SQL Operators
In the last query we used an operator (=) to find our required value. There is also some other operators
avileable for constracting a query. A list of operators are given below.
Operators
Definition
Equal to the specified value.
!=
Not equal to the specified value.
<>
Also a Not equal operator.
17 | P a g e
MIS 310 Tutorial (RZZ)
>
Greater than.
<
Less than.
>=
Greater than or equal
<=
Less than or equal
Lets see an example,
Lets say, from our five students of database we only know name and department of Faisal. But we dont
know other four students name and department. So if we want to see students name and department
other than Faisal then we have to use != operator. Now, we can use either <> or != to write our
SELECT statement. Go to the SQL page and write:
SELECT `first_name`, `last_name`, `dept` FROM `student` WHERE `first_name` != Faisal;
Click the Go button to run the query. In the result (Figure 30) we will get what we were looking for.
Practice other operators using different columns and data yourself.
Figure 29: Result of NOT EQUAL Query.
LOGICAL OPERATORS
There are three Logical Operators AND, OR, and NOT. These operators compare two conditions at a time
to determine whether a row can be selected for the output. It allows you to combine more than one
condition.
AND:
Returns result if all conditions are TRUE.
OR:
Returns result if any of the conditions is TRUE.
NOT:
Returns result if specified condition is NOT TRUE.
Lets see examples of each of the logical operators,
AND
18 | P a g e
MIS 310 Tutorial (RZZ)
Lets find a students details whose last name is Islam and department is BBA. Write down the query in
SQL page,
SELECT * FROM `student` WHERE `last_name` = Islam AND `dept` = BBA;
Click GO to see the result.
Figure 30: Logical Operator AND
We can see the result from Figure 31. We got the result because both of our conditions were satisfied.
OR
Again find details of student/students whose last name is either Islam or student of BBA. Open SQL and
write,
SELECT * FROM `student` WHERE `last_name` = 'Islam'OR `dept` = 'BBA';
Click GO and see the result.
Figure 31: Logical Operator OR
Or operator returns rows if any of the conditions is true. But if both the conditions are true, returns all
the rows that fulfills conditions.
NOT
Write the query in SQL page
19 | P a g e
MIS 310 Tutorial (RZZ)
SELECT * FROM `student` WHERE NOT `last_name` = Islam;
Click GO button.
Figure 32: Logical operator NOT.
As you can see, query returned all the rows without the row that contains Islam as lastname.
You can also construct complex queries combining multiple logical operators. Practice complex queries
yourself.
ORDER BY
The ORDER BY clause is used in a SELECT statement to sort results either in ascending or descending
order. Mysql sorts query results in ascending order by default.
Write the query in your SQL page,
SELECT `first_name`, `last_name`, `dept` FROM `student` ORDER BY `first_name`;
Now, click GO button to execute the query.
Figure 33: ORDER BY
20 | P a g e
MIS 310 Tutorial (RZZ)
So, first_name is in ascending order and rest of the columns is being ordered accordingly. You can also
try multiple columns to order your result. You can write ORDER BY `first_name`, last_name if you
want your result to be ordered by both first name and last name.
Comparison Keyword
LIKE, BETWEEN.AND, IN, IS NULL are called comparison keywords in sql.These operators help to
enhance the search capabilities of sql.
LIKE
The LIKE operator is used to return all rows in a table whose column values match the specified pattern.
LIKE is very useful when do not know the entire value. We have to use wildcard character '%' to get our
desired result.
Now, Go to SQL page and write,
SELECT * FROM `student` where `first_name` LIKE Sh%;
Click GO button.
This query will show all the rows whose first name starts with Sh and % means rest of the letters in
the name can be any character. As you can see we have only one first name that starts with Sh, thats
why the query returned the row of Shajib.
Figure 34: LIKE operator.
There is another wildcard character which also used with LIKE. _ Underscore is used to signify a single
character with LIKE.
BETWEENAND
BETWEENAND operator is used to compare data for a specified range of values.
For example, we want to see student details whose ids are between 2 to 4. Lets write the query in SQL
page
SELECT * FROM `student` WHERE `id` BETWEEN 2 AND 4;
Click GO to see the result.
21 | P a g e
MIS 310 Tutorial (RZZ)
Figure 35: BETWEENAND.
IN
The IN operator is used when we want to compare a column with more than one value. It is similar to
OR condition.
Lets say we want to see the students who is studying eitherBBA or CSE. Write the query in SQL,
SELECT `first_name`, `last_name`, `dept` FROM `student` WHERE `dept` IN(BBA, CSE);
Click GO button.
Result shows the list of students who studies BBA or CSE (Figure 47).
Figure 36: IN Operator.
IS NULL
IS NULL shows the rows for columns that dont have any values. For example, if we want to find student
who dont have a last name then the query will be
SELECT `id`, `first_name`, `dept`FROM `student` WHERE `last_name` IS NULL;
Click GO button.
Our query returned an empty set, because we do not have any empty rows or columns. You can try this
query after inserting some new rows with empty values.
22 | P a g e
MIS 310 Tutorial (RZZ)
Lets say 3 of the students of student table gets a certain amount of financial aid from University each
month. Lets create a new table named aid to show the amounts. Write the query below to create
aid table
CREATE TABLE `aid` (
`id` INT NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`first_name` VARCHAR(100),
`last_name` VARCHAR(100),
`amount` INT,
PRIMARY KEY(`id`)
);
Now, click GO to create new table.
Figure 37: Creating table `aid`.
Click `aid ` to open the table.
As you can see our `aid` table is empty. So, first we have to inset data into it. Go to SQL page and write,
23 | P a g e
MIS 310 Tutorial (RZZ)
INSERT INTO `aid` VALUES (, 'Tanveer', 'Khan', 9000),
('', 'Anik', 'Hasan',6000),
('', 'Nazmul', 'Islam', 8000),
('', 'Faisal', 'Jahan', 5600),
Click GO to insert data. Now go to the aid table.
Figure 38: `aid` Table.
Figure 39 shows all the information of aid table we just inserted. But we were suppose to insert 3
students in our aid table, we mistakenly added Faisal in this list. So, we have to delete this entry.
DELETE
DELETE statement deletes specified information from a specified table. Lets delete Faisals information
from aid table. Go to SQL and write,
DELETE FROM `aid` WHERE `first_name` = `Faisal`;
Click GO button to delete the row.
Figure 39: Deleting data from `aid`.
We deleted the data we inserted mistakenly. Now if you go to aid table youll find only three names
listed.
ALTER TABLE
24 | P a g e
MIS 310 Tutorial (RZZ)
The SQL ALTER TABLE command is used to modify the definition (structure) of a table by modifying the
definition of its columns. Simply,its main functions are Add, drop, modify table columns, adding and
dropping primary key. Though we are not going to use ALTER TABLE statement in our database, we will see
how to write ALTER TABLE statements.
Adding a new column:ALTER
TABLE `tablename` ADD `columnname` datatype;
Here datatype means the type of data we are going to insert in this column (INT, VARCHAR etc.). If your
data type is VARCHAR then you have to set the character length inside brackets, which we have learnt
before.
Dropping column from table:ALTER TABLE
`tablename` DROP `columnname`;
This statement above will drop the specified column from you specified table.
Changing Datatype of column:ALTER TABLE `table name` ALTER COLUMN `column name` DATATYPE;
This statement is used to change the datatype of a column.
Default:
In short, DEFAULT statement shows a default value if on data is inserted under a particular column. Lets go
back to our student table to get a better understanding about it. In student table our 4th column is dept,
which shows the departments of each student. Now, you want that dept column will show BBA for each
student if students department is not specified while inserting data into the dept column. DEFAULT can be
specified when you are creating a new table or you can use the ALTER TABLE statement to spacify the
default value for a column.
You could either write:
CREATE TABLE `student` (
`id` INT NOT NULL PRIMARY KEY,
`first_name` VARCHAR(100),
`last_name` VARCHAR(100),
`dept` varchar (3) DEFAULT BBA,
`address` VARCHAR(255)
);
or we can write:
ALTER TABLE `student`
ALTER `dept` SET DEFAULT 'BBA';
UPDATE
25 | P a g e
MIS 310 Tutorial (RZZ)
UPDATE statement is used to update, edit or modify data from table. For example, in our `aid` table we
inserted a wrong amount in the 3rd row. We inserted 8000, while our actual amount is 11000.
Figure 40: `aid` table before updating data.
So, to correct this we have to write the query below:
UPDATE `aid` SET `amount` = 11000 where `id` = 3;
Click GO to run. Click `aid` to open the table.
Figure 41:`aid` tableafter correcting data.
SQL JOINS
SQL Joins are used to relate information in different tables.A brief explanation of different types of joins
are given below:
JOIN: Return rows when there is at least one match in both tables
INNER JOIN:Returns rows when there is at least one match in both tables.
LEFT JOIN: Return all rows from the left table, even if there are no matches in the right table
RIGHT JOIN: Return all rows from the right table, even if there are no matches in the left table
FULL JOIN: Return rows when there is a match in one of the tables
26 | P a g e
MIS 310 Tutorial (RZZ)
We will use our student and aid tables to see examples of Join.
JOIN, INNER JOIN
As you can see join and inner join produce same result, thats why we are going to see example of
joinand inner join together. Type the query below:
SELECT * FROM `student` JOIN `aid`;
or
SELECT * FROM `student` INNER JOIN `aid`;
Click GO to run the query.
As you can see in Figure 43, our query returned 15 rows. This result do not express any meaningful
information. We got this result because we havent specified a common column between these two
tables (It can be either first_name or last_name, because these columns are same in both the tables).
Figure 42: JOIN and INNER JOIN Query (Common field is not specified).
But if we write the query correctly then the query becomes
SELECT * FROM `student` JOIN `aid` ON (`student`.`first_name` = `aid`.`first_name`);
or
SELECT * FROM `student` INNER JOIN `aid` ON (`student`.`first_name` = `aid`.`first_name`);
Click GO.
27 | P a g e
MIS 310 Tutorial (RZZ)
Figure 43: Result of JOIN, INNER JOIN Query.
This time query returns 3 rows, which fulfills the condition (`student`.`first_name` = `aid`.`first_name`).
You must be wondering, what is this `student`.`first_name`? After ON we have to set the column
names from both the tables which contain identical values. But if the column names are same then
database shows error message. Thats why we have to put the table name before the column names
joined by a dot .. So, `student`.`first_name` means first_name is a column of student table. But you
can write only the column names if your column names are not same.
LEFT JOIN
Left join returnsall the values from the left table, even if there is no match found in the right table.
Write the query below:
SELECT * FROM `student` LEFT JOIN `aid` ON ( `student`.`first_name` = `aid`.`first_name` );
Click GO to see the result.
Figure 44: LEFT JOIN
RIGHT JOIN
Right join returnsall the values from the right table, again, even if there is no match found in the left
table.
Write down the query:
SELECT * FROM `student` RIGHT JOIN `aid` ON ( `student`.`first_name` = `aid`.`first_name` );
Click GO.
28 | P a g e
MIS 310 Tutorial (RZZ)
Figure 45: RIGHT JOIN
We got this result because all the data of right table is available in the left table too.
SQL FUNCTIONS
SQL functions are built-in SQL functions that work on groups of rows and return one value for the entire
group. These functions are: COUNT, MAX, MIN, AVG, SUM, DISTINCT
COUNT()
COUNT()function returns the number of rows in the table that satisfies the condition specified in the
WHERE condition. If the WHERE condition is not specified, then the query returns the total number of
rows in the table.
Write the query below in you sql page:
SELECT COUNT(`last_name`) FROM `student`;
Click GO for see result.
Figure 46: No. of rows in last_name column
MAX()
This function returns the maximum value from specified column. Write the query below.
SELECT MAX(`amount`) FROM `aid`;
Click GO.
29 | P a g e
MIS 310 Tutorial (RZZ)
Figure 47: Maximum value of column amount.
MIN()
MIN() function returns the minimum value from specified column. Write this query
SELECT MIN(`amount`) FROM `aid`;
Click GO.
Figure 48: Minimum value of column amount.
AVG()
This function calculates the average value from specified column. Type this query in sql,
SELECT AVG(`amount`) FROM `aid`;
Click GO to run the query.
Figure 49: Average value of column amount.
SUM()
Im sure you already understood what this function does. It returns the sum of a numeric column. Type
the query below,
SELECT SUM(`amount`) FROM `aid`;
Cilck GO
30 | P a g e
MIS 310 Tutorial (RZZ)
DISTICNT
In our student table dept column contains value BBA in multiple rows. Likewise columns may contain
duplicate values. Sometimes you will want to list only the different (distinct) values in a table. The
DISTINCT keyword can be used to return only distinct (different) values.
Lets see the distinct values of dept column:
SELECT DISTINCT `dept` FROM `student`;
Figure 50: Query Result.
31 | P a g e
Вам также может понравиться
- Kumpulan Soal Dan Jawaban SQLДокумент17 страницKumpulan Soal Dan Jawaban SQLReds MichaОценок пока нет
- Relational Schema ExercisesДокумент3 страницыRelational Schema ExercisesSa SyОценок пока нет
- Lab 6Документ12 страницLab 6Dinesh BhawnaniОценок пока нет
- DBMS 2012 1Документ129 страницDBMS 2012 1Wil-Ly de la CernaОценок пока нет
- DSSharing - Datastage Admin CommandsДокумент3 страницыDSSharing - Datastage Admin CommandsKaren MaciasОценок пока нет
- Extra QueriesДокумент17 страницExtra QueriesAkhileshОценок пока нет
- Employee SQL ExerciseДокумент3 страницыEmployee SQL ExerciseTimothyОценок пока нет
- Statements in SQLДокумент19 страницStatements in SQLSachin100% (1)
- PL - SQL AssignmentДокумент4 страницыPL - SQL Assignmentamit kumarspОценок пока нет
- Working With Triggers in A MySQL Database PDFДокумент10 страницWorking With Triggers in A MySQL Database PDFI Made Dwijaya MalehОценок пока нет
- SQL QueriesДокумент32 страницыSQL QueriesAmarnath ReddyОценок пока нет
- Asme 2 EjДокумент4 страницыAsme 2 EjMichael AjayiОценок пока нет
- RDBMS Lab GuideДокумент33 страницыRDBMS Lab GuideRamasamy GoОценок пока нет
- COSC2429 - Intro To Programming Assessment 2 - Sem A 2021: RMIT Classification: TrustedДокумент3 страницыCOSC2429 - Intro To Programming Assessment 2 - Sem A 2021: RMIT Classification: Trustedroll_wititОценок пока нет
- SQL CommandsДокумент48 страницSQL CommandsPremendra YadawОценок пока нет
- Ms SQL NotesДокумент14 страницMs SQL Notesvitu3075Оценок пока нет
- Practice Ques: Select As FromДокумент3 страницыPractice Ques: Select As Fromilakkiya RОценок пока нет
- Java Program To Add Two NumbersДокумент5 страницJava Program To Add Two NumbersIrfaan Khan QasmiОценок пока нет
- Hands-On Exercise: SQLДокумент15 страницHands-On Exercise: SQLRishabh ChoudharyОценок пока нет
- CH 2 Word Assignment Sheet-2Документ2 страницыCH 2 Word Assignment Sheet-2Deedra RossiОценок пока нет
- PLSQLДокумент10 страницPLSQLAshi SrivastavaОценок пока нет
- Lab1 - Vlsi EceДокумент19 страницLab1 - Vlsi EceMichelleCYLОценок пока нет
- Generate A Report Using Crystal Reports in Visual Studio 2010Документ30 страницGenerate A Report Using Crystal Reports in Visual Studio 2010chintan_mca23Оценок пока нет
- A00-211 SasДокумент30 страницA00-211 SasArindam BasuОценок пока нет
- Cursor-Based Linked ListsДокумент4 страницыCursor-Based Linked Listslakshmipriya_brОценок пока нет
- Lomba Kompetensi Siswa Sekolah Menengah Kejuruan: Tingkat Kabupaten Karawang TAHUN 2021Документ43 страницыLomba Kompetensi Siswa Sekolah Menengah Kejuruan: Tingkat Kabupaten Karawang TAHUN 2021Citra SintiarahmaОценок пока нет
- ABAP SQL Injection - How To Protect Your Code Right?Документ8 страницABAP SQL Injection - How To Protect Your Code Right?Vivek V NairОценок пока нет
- Dbms Lab Assignments-6Документ3 страницыDbms Lab Assignments-6parveenОценок пока нет
- LABS 1-12 & Bonus TaskДокумент75 страницLABS 1-12 & Bonus TaskFahad AqeelОценок пока нет
- SQL CommandsДокумент25 страницSQL CommandsAkanksha JainОценок пока нет
- 55 Final Paper PDFДокумент8 страниц55 Final Paper PDFDatta KumarОценок пока нет
- Murugappan Sir Notes - GTДокумент35 страницMurugappan Sir Notes - GTsyed ziauddinОценок пока нет
- SQL Project 1Документ40 страницSQL Project 1Rajjo 07100% (1)
- Learn MVC Project in 7 Days Day 1 PDFДокумент118 страницLearn MVC Project in 7 Days Day 1 PDFYogesh RoyОценок пока нет
- Basic Lab For MySQLДокумент6 страницBasic Lab For MySQLleulОценок пока нет
- Project On Mainframe Training byДокумент30 страницProject On Mainframe Training byShubham Ajinath JadhavОценок пока нет
- Employees Sample DatabaseДокумент30 страницEmployees Sample DatabaseShey AustinОценок пока нет
- First Script: Job - ContactДокумент5 страницFirst Script: Job - ContactPunith M PОценок пока нет
- Worksheet BFH - SolutionДокумент7 страницWorksheet BFH - SolutionAmogh D GОценок пока нет
- Program No - 1: Write A Program To Create A Dfa That Accepts The String Ending With "Abb"Документ40 страницProgram No - 1: Write A Program To Create A Dfa That Accepts The String Ending With "Abb"surajrtkОценок пока нет
- Taller 4-KATHERN ROJAS PDFДокумент5 страницTaller 4-KATHERN ROJAS PDFbriggyd rojasОценок пока нет
- Rdbms LC LabguideДокумент0 страницRdbms LC LabguideAlberto HernandezОценок пока нет
- PASCAL TutorialДокумент46 страницPASCAL Tutorialmickaylia greenОценок пока нет
- Intertest Setup: To Prepare A Program For Using IntertestДокумент13 страницIntertest Setup: To Prepare A Program For Using IntertestKumar Abhishek100% (1)
- SQLДокумент3 страницыSQLKrishnaReddyОценок пока нет
- Crystal Report 8.5 For Visual - 89028Документ8 страницCrystal Report 8.5 For Visual - 89028dsadsadОценок пока нет
- LAB Activity 5 - Create Project Plan (Part 1)Документ2 страницыLAB Activity 5 - Create Project Plan (Part 1)Shivani VaruОценок пока нет
- SQL QueriesДокумент8 страницSQL Queriesapi-3732352Оценок пока нет
- Tutorial 2Документ2 страницыTutorial 2SOMEONEОценок пока нет
- Interview Questions: AmazonДокумент2 страницыInterview Questions: AmazonSrishti KumariОценок пока нет
- Database Lab 5Документ14 страницDatabase Lab 5Mydah NasirОценок пока нет
- Digital Assignment - 4Документ16 страницDigital Assignment - 4shubh kapil100% (1)
- BCA 2ND Semester LAB AssignmentДокумент1 страницаBCA 2ND Semester LAB AssignmentAshis PradhanОценок пока нет
- Declare (@local - Variable Data - Type ( Value) ) : @testvariable 100 @testvariableДокумент26 страницDeclare (@local - Variable Data - Type ( Value) ) : @testvariable 100 @testvariableSrinivas Gorantla100% (1)
- Coding The PIC Microcontroller With PIC CДокумент10 страницCoding The PIC Microcontroller With PIC CmatsoppiОценок пока нет
- Project 3 MS SQLДокумент1 страницаProject 3 MS SQLSHIVAM Singh0% (1)
- Autocad® Architecture and Autocad® Mep: About The SpeakerДокумент31 страницаAutocad® Architecture and Autocad® Mep: About The SpeakerKevin Villota100% (1)
- Delphi For PHPДокумент6 страницDelphi For PHPVladica SavićОценок пока нет
- MySQL Database and Java Desktop GUI Part 1Документ59 страницMySQL Database and Java Desktop GUI Part 1rednriОценок пока нет
- Lenovo's Culture & Students RecommendationДокумент2 страницыLenovo's Culture & Students RecommendationShàhríàrõ Dã RàkínskìОценок пока нет
- Ethical Issue Analysis GuidelineДокумент2 страницыEthical Issue Analysis GuidelineShàhríàrõ Dã RàkínskìОценок пока нет
- Report On Bank AsiaДокумент18 страницReport On Bank AsiaShàhríàrõ Dã RàkínskìОценок пока нет
- Advising Policy:: Offered Course List Will Be Posted Online When All Academic Departments Are Complete With TheirДокумент1 страницаAdvising Policy:: Offered Course List Will Be Posted Online When All Academic Departments Are Complete With TheirShàhríàrõ Dã RàkínskìОценок пока нет
- NSU Advising System Part 3 PDFДокумент5 страницNSU Advising System Part 3 PDFShàhríàrõ Dã RàkínskìОценок пока нет
- MKT202 MBT NSU Chapter 01Документ22 страницыMKT202 MBT NSU Chapter 01Shàhríàrõ Dã RàkínskìОценок пока нет
- Letter of RecommendationДокумент1 страницаLetter of RecommendationShàhríàrõ Dã Ràkínskì100% (1)
- Running Head: Farmers Restaurant Case Analysis 1Документ9 страницRunning Head: Farmers Restaurant Case Analysis 1Shàhríàrõ Dã RàkínskìОценок пока нет
- An American Tragedy: How A Good Company DiedДокумент5 страницAn American Tragedy: How A Good Company DiedShàhríàrõ Dã Ràkínskì100% (3)
- Report GuidelineДокумент2 страницыReport GuidelineShàhríàrõ Dã RàkínskìОценок пока нет
- Basic German Language Lesson Chapter 1 From Moment Mal 1st PartДокумент8 страницBasic German Language Lesson Chapter 1 From Moment Mal 1st PartShàhríàrõ Dã RàkínskìОценок пока нет
- MIS205 MMB NSU Lecture 1Документ33 страницыMIS205 MMB NSU Lecture 1Shàhríàrõ Dã RàkínskìОценок пока нет
- Human Resource Management - RahimafroozДокумент20 страницHuman Resource Management - RahimafroozShàhríàrõ Dã RàkínskìОценок пока нет
- Fin433 ReportДокумент30 страницFin433 ReportShàhríàrõ Dã Ràkínskì100% (1)
- Simple Strategies To Boost Your IELTS Skills PDFДокумент8 страницSimple Strategies To Boost Your IELTS Skills PDFShàhríàrõ Dã RàkínskìОценок пока нет
- Revised - Chinese Phonetics and Tone RulesДокумент13 страницRevised - Chinese Phonetics and Tone RulesShàhríàrõ Dã RàkínskìОценок пока нет
- Mis205 Course Outline Summer2015Документ4 страницыMis205 Course Outline Summer2015Shàhríàrõ Dã RàkínskìОценок пока нет
- Fuwangfood 2013-2014 AnnualДокумент68 страницFuwangfood 2013-2014 AnnualShàhríàrõ Dã RàkínskìОценок пока нет
- Presentation On The 13th & 14th Amendents To The Onstitution of BangladeshДокумент15 страницPresentation On The 13th & 14th Amendents To The Onstitution of BangladeshShàhríàrõ Dã Ràkínskì100% (3)
- Bagerhat Group of MonumentsДокумент24 страницыBagerhat Group of MonumentsShàhríàrõ Dã RàkínskìОценок пока нет
- Evaluation Test Grade: 8 (L1) Textbook: Cambridge English For Schools 4, Cambridge University Press Authors: AndrewДокумент4 страницыEvaluation Test Grade: 8 (L1) Textbook: Cambridge English For Schools 4, Cambridge University Press Authors: AndrewAnonymous Wfl201YbYoОценок пока нет
- 21 Century Literature From The World and The PhilippinesДокумент13 страниц21 Century Literature From The World and The PhilippinesRutchelОценок пока нет
- Adverbs of FrequencyДокумент2 страницыAdverbs of FrequencyisabelОценок пока нет
- Features of Academic WritingДокумент2 страницыFeatures of Academic WritingAlex QuackityОценок пока нет
- Ingles Brenda Jazmin Zaleta PereaДокумент3 страницыIngles Brenda Jazmin Zaleta PereaBrenn PereaОценок пока нет
- Exercises Prepositions of TimeДокумент2 страницыExercises Prepositions of TimeJohanna Paola Casallas LeonОценок пока нет
- Write The Past Participle Forms of The Irregular VerbsДокумент2 страницыWrite The Past Participle Forms of The Irregular VerbsYessi Gi100% (2)
- Cecilia Proceedings TranssformedSpace FinalДокумент7 страницCecilia Proceedings TranssformedSpace FinalTamamaОценок пока нет
- No Tenses Active Voice Passive VoiceДокумент5 страницNo Tenses Active Voice Passive VoiceIstikharohОценок пока нет
- Relative Clauses PDFДокумент2 страницыRelative Clauses PDFcasОценок пока нет
- Middle School Debate TopicsДокумент7 страницMiddle School Debate TopicsAtanda Babatunde Mutiu100% (3)
- L4 FinalДокумент2 страницыL4 FinalGaby CastroОценок пока нет
- 5° Ingles Plan 14 17 NovДокумент5 страниц5° Ingles Plan 14 17 NovRaoul BarrettОценок пока нет
- English Jss3Документ5 страницEnglish Jss3Adenigbo Oluwole JoshuaОценок пока нет
- Curme: Syntax (1931)Документ634 страницыCurme: Syntax (1931)mhc032105636100% (4)
- Ielts Reading Test - Short VersionДокумент4 страницыIelts Reading Test - Short VersionBảo TrâmОценок пока нет
- Eiu2 Aio Ep 1-1Документ2 страницыEiu2 Aio Ep 1-1Nieves Fuertes IbañezОценок пока нет
- French Diction and Repertoire Notes and SuggestionsДокумент26 страницFrench Diction and Repertoire Notes and Suggestionsapi-258658569100% (1)
- Learning at Home Packet 5th Grade Week 5 Part 1Документ35 страницLearning at Home Packet 5th Grade Week 5 Part 1api-234451394Оценок пока нет
- Action Plan On Reading Intervention in EnglishДокумент3 страницыAction Plan On Reading Intervention in EnglishIhla Katrina TubiganОценок пока нет
- Object Oriented Programming (OOP) - CS304 Power Point Slides Lecture 27Документ29 страницObject Oriented Programming (OOP) - CS304 Power Point Slides Lecture 27Sameer HaneОценок пока нет
- Look at The Picture Then Fill in The Blanks With The Right Preposition!Документ2 страницыLook at The Picture Then Fill in The Blanks With The Right Preposition!malaikahariОценок пока нет
- Past Simple Vs Past ContinuousДокумент2 страницыPast Simple Vs Past ContinuousAndrea Magdolna MoldovanОценок пока нет
- Blooms TaxonomyДокумент4 страницыBlooms Taxonomygaliana.david8070Оценок пока нет
- New Inside Out Pre-Intermediate CMДокумент2 страницыNew Inside Out Pre-Intermediate CMRaquel Bernal100% (1)
- Table of Specifications For English 8 (Afro-Asian Literature)Документ2 страницыTable of Specifications For English 8 (Afro-Asian Literature)Lee MarquezОценок пока нет
- CS T (Summative)Документ5 страницCS T (Summative)Мартиненко Вероніка, ЯЕ-32Оценок пока нет
- Assistive Devices and Technology For Visually and Hearing ImpairementДокумент171 страницаAssistive Devices and Technology For Visually and Hearing Impairementmont21Оценок пока нет
- LNHS Goal ChartДокумент13 страницLNHS Goal ChartSirElwoodОценок пока нет
- Let The Imagination Fly: ScriptДокумент1 страницаLet The Imagination Fly: ScriptNElitreviewОценок пока нет