Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Chocolate Industry cp1
Загружено:
rajulramiАвторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Chocolate Industry cp1
Загружено:
rajulramiАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
S. K. PATEL Institute of Management & Computer Studies Gandhinagar.
A
Project Report
On
Chocolate Industry
Submitted in Partial Fulfillment of award of MBA Degree
Project Guide(s):Prof. Krupa Mehta
Submitted by:
Leuva Jignasha S. (40)
Parmar Khushbu M. (56)
Rohit Payal M. (81)
S. K. PATEL INSTITUTE OF MANAGEMENT & COMPUTER STUDIES
Gandhinagar, India
KADI SARVA VISHWAVIDYALAYA 2014 -2016
S. K. PATEL Institute of Management & Computer Studies Gandhinagar.
CERTIFICATE
This is to certify that Miss. Leuva Jignasha, Miss.Rohit Payal, Miss Parmar Khushbu
are the students of MBA 3rd SEMESTER of S. K. Patel Institute of Management and
Computer Studies, have completed their comprehensive project titled CHOCOLATE
INDUSTRY in the year 2015, in partial fulfillment of curriculum requirements for the
award of MBA degree under Kadi Sarva Vishwa Vidhyalaya University.
Dr.Bhavin Pandya
Director
Prof. Krupa Mehta
Faculty Guide
KADI SARVA VISHWAVIDYALAYA 2014 -2016
S. K. PATEL Institute of Management & Computer Studies Gandhinagar.
DECLARATION
we, here by, declare that the comprehensive project report titled, Brief study of the
chocolate industry with special focus on the Cadbury india is original to the best of our
knowledge and has not been published elsewhere. This is for the purpose of partial
fulfillment of Kadi Sarva Vishwa Vidhyalaya University requirements for the award of the
title of Master of Business Administration, only.
Student Names
Signature
Leuva Jignasha S. (40)
Parmar Khushbu M. (56)
Rohit Payal M. (81)
KADI SARVA VISHWAVIDYALAYA 2014 -2016
S. K. PATEL Institute of Management & Computer Studies Gandhinagar.
CHAPTER : 1
INTRODUCTION ABOUT THE INDUSTRY
KADI SARVA VISHWAVIDYALAYA 2014 -2016
S. K. PATEL Institute of Management & Computer Studies Gandhinagar.
From its origin in South America to the tables of Europe and America, chocolate has a long history.
As European countries colonize
d different areas of the world, they established cocoa plantations to ensure a constant supply of
chocolate.
Cocoa trees only grow in tropical climates and they require a labor-intensive process to harvest.
Consequently, plantation owners turned to the slave trade as a means of supplying cheap labor.
As the popularity of chocolate soared, new production processes developed. These innovations
helped turn chocolate into an inexpensive luxury people of all social classes could enjoy.
Today cocoa is still grown in many of the same regions as generations ago, and it is consumed by
people throughout the world.
ORIGINS
The ancient Maya are believed to be the first people to make chocolate, over 2,000 years ago. Cocoa
trees, native to Central and South America, provided the beans used to make a bitter, spicy chocolate
drink.
In the fourteenth century the Aztecs dominated Central Mexico and they developed a sophisticated
trade network of cocoa until the Spanish conquered the region in 1521. Conquistador Hernn Corts
is often credited with introducing cocoa to Spain in 1528, but no one truly knows when and how
cocoa traveled to Europe.
COCOA TRADE
Spain could not keep chocolate a secret for very long, and the rest of Europe quickly fell in love with
the drink. By the seventeenth century, as Britain, France, and the Netherlands colonized countries
around the world, they established cacao plantations in tropical locations such as Ceylon (Sri Lanka),
Venezuela, and the West Indies, respectively. These equatorial areas were critical to developing cacao
5
KADI SARVA VISHWAVIDYALAYA 2014 -2016
S. K. PATEL Institute of Management & Computer Studies Gandhinagar.
production because cacao trees thrive in tropical regions, which provide continual moisture and a
temperate climate.
Once a trade network was established to keep Europe well-supplied in chocolate, European landowners in the Caribbean looked to Africa for their workforce. For over two hundred years cacao
plantations relied on enslaved Africans for labor. Cocoa was one of many products in the triangular
trade network between Europe, West Africa, and the Caribbean.
CHOCOLATE CONSUMPTION
Originally chocolate was exclusively consumed as a drink. Because Europeans did not like the bitter
taste, they added sugar and cinnamon. Gradually chocolate was mixed with milk instead of water to
produce a much lighter and smoother drink, and in 1657 the first known chocolate house opened in
London. Like taverns, and later coffee houses, chocolate houses were comfortable places for
socializing.
Until the mid-eighteenth century chocolate was an expensive drink, a luxury reserved for the wealthy.
The main reason for the high cost was that cocoa was ground by hand. The use of powered
machinery began, not in Europe, but in the American colonies, after New England began trading
cacao from the West Indies in the 1750s.
The earliest known machine-powered chocolate producers were Obadiah Brown of Providence,
Rhode Island, in 1752 and John Hannon of Milton, Massachusetts, in 1765. Water-powered mills
were able to mass-produce chocolate at a much faster pace and in greater quantities. This early
industrialization dramatically reduced the cost of the final product and chocolate became affordable
to the general public.
The world continues to consume great quantities of chocolate. Statistics calculated in 2002 average
the worlds yearly chocolate intake at approximately 1.2 pounds per person. The average European
consumes just over four pounds per year. The Americas come in second at 2.6 pounds per person,
with Africa at a third of a pound, then Asia and the Pacific islands at just under a quarter pound per
year.
TODAY'S CACAO PRODUCING REGIONS
Today cocoa is grown in the Ivory Coast, Ghana, and Indonesia, with Nigeria and Brazil rounding
out the top five countries. Many of the cacao regions established centuries ago still grow the beans
today, along with dozens of new regions located along the equator. The Netherlands, the United
States, Ivory Coast, Brazil, and Germany are the top five importers of cacao beans.
KADI SARVA VISHWAVIDYALAYA 2014 -2016
S. K. PATEL Institute of Management & Computer Studies Gandhinagar.
CHAPTER :2
RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
KADI SARVA VISHWAVIDYALAYA 2014 -2016
S. K. PATEL Institute of Management & Computer Studies Gandhinagar.
OBJECTIVES OF THE STUDY OF PRODUCT MARKET ANALYSIS
To Study of chocolate industry
To do five forces model
Pestel Analysis
OT Analysis
RESEARCH DESIGN
Descriptive research design:
Descriptive research is a study designed to depict the participants in an accurate way. More simply
put, descriptive research is all about describing people who take part in the study.
DATA COLLECTION & SOURCES.
1. SECONDARY DATA
2. INTERNET, BOOK
KADI SARVA VISHWAVIDYALAYA 2014 -2016
S. K. PATEL Institute of Management & Computer Studies Gandhinagar.
CHAPTER :3
INDUSTRY STUDY
KADI SARVA VISHWAVIDYALAYA 2014 -2016
S. K. PATEL Institute of Management & Computer Studies Gandhinagar.
Chocolate industry
Produced from the seed of the tropical Theorem cacao tree, cocoa has been cultivated for at least
three millennia. This food originated in Mexico, Central and Northern South America and dates back
to around 1100 BC when the Aztecs made it into a beverage known as Nahunta or "bitter water" in
English.
The chocolate-making process remained unchanged for hundreds of years. It wasn't until the
Industrial Revolution, when mechanical mills were used to squeeze out cocoa butter which created
durable chocolate, which many changes occurred.
Even though cocoa beans were discovered in the Americas, about two-thirds of the world's cocoa is
produced in West Africa. In 2011, 32 percent of all chocolate sales were generated from Western
Europe. According to Euro monitor, the United Kingdom had the highest chocolate consumption per
person than any other country.
On average, every U.K. citizen consumed about eleven kilograms (24.25 lbs) of chocolate in 2011,
with the United States coming in at fifteenth position at 4.6 kilograms.
Milk chocolate also appears to be favored throughout the United States compared to any other
chocolate type. In 2012, just over 50 percent of consumers preferred to eat this type of chocolate.
Chocolate is a global industry that will continue to grow steadily and is prevalent on five out of the
seven continents.
Global scenario of industry
The global chocolate industry has been in a moderate growth trajectory since the last five years. This
growth is largely fueled by the increased global demand for premium chocolate.
The major developing countries such as China and India are expected to offer great opportunities to
the global chocolate industry; thanks to the use of chocolate as a functional fo
10
KADI SARVA VISHWAVIDYALAYA 2014 -2016
S. K. PATEL Institute of Management & Computer Studies Gandhinagar.
Organic and fair trade chocolate is a rapidly growing segment of the industry. With consumers
developing more awareness regarding environment-friendly products, this segment is expected to rise
rapidly in the next five years.
The global chocolate market is highly consumer driven and companies need to focus on their
development and marketing strategies towards capturing a larger consumer base, and acquiring new
markets.
Cocoa is the main raw material for chocolate production and has no other substitute. Moreover, it can
only be grown within 10 degrees (latitudes) of the equator. Due to this constraint, global production
of cocoa is highly concentrated in West African countries such as Ghana, Cote d'Ivoire, Cameroon,
and Nigeria.
Vanilla is the most preferred flavor in the chocolate industry. A number of other important flavors
such as mint, coffee, strawberry, and orange are being increasingly used these days as the consumer
is more open to experimenting; however, the traditional chocolate flavor is still the most sought-after.
Almost 90% of the total vanilla used as a flavor is synthetic.
The major demand for sugar is fueled by the manufacturing and food preparation sectors, including
the beverages market. Developing economies such as India, China, and Indonesia are expected to
account for more than 3.2 million tons (72%) of the overall sugar consumption by 2015.
These are the same countries expected to witness high CAGR in the global chocolate market. The
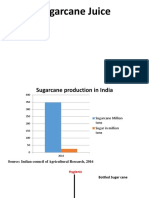
growth in the overall sugar market is attributed to India, a result of the expansion in the sugarcane
area, and generally favorable weather.
The report analyzes global chocolate market by product, sales category, geography and raw
materials; forecasting revenues and analyzing trends in each of the following submarkets:
By product types:
Dark chocolate
Milk chocolate
White chocolate
By sales category:
Everyday chocolate
Premium chocolate
Seasonal chocolate
By geography:
North America
11
KADI SARVA VISHWAVIDYALAYA 2014 -2016
S. K. PATEL Institute of Management & Computer Studies Gandhinagar.
Europe
Asia
ROW (Rest of the World)
characteristics of global industry
Who are the main manufacturers of chocolate in the world?
Candy Industry publishes an annual list of the top 100 global confectionery companies.
ranking them by net sales.
The table below is an extract from this list, giving the top ten global confectionery companies that
manufacture some form of chocolate, by net confectionery sales value in 2014:
Company
Net Sales 2014 (US$ millions)
Mars Inc (USA)
18,480
Mondelz International (USA)
14,350
Ferrero Group (Luxembourg / Italy)
10,911
Nestl SA (Switzerland)
10,466
Meiji Co Ltd (Japan)
9,818*
Hershey Foods Corp (USA)
7,485
SChocoladenfabriken Lindt & Sprngli AG (Switzerland)
4,022
Arcor (Argentina)
3,500*
Ezaki Glico Co Ltd (Japan)
3,049*
August Storck KG (Germany)
2,272
Fair Trade cocoa and chocolate
Fair Trade is a trading partnership, based on dialogue, transparency and respect, that seeks greater
equity in international trade. It contributes to sustainable development by offering better trading
conditions to, and securing their rights of, disadvantaged producers and workers - especially in the
South (FINE, 2001).
12
KADI SARVA VISHWAVIDYALAYA 2014 -2016
S. K. PATEL Institute of Management & Computer Studies Gandhinagar.
Fair Trade certified producer organizations must comply with a number of requirements, related to
social, economic and environmental developments. In addition, labour conditions in these
organizations must follow certain standards.
The essential characteristic of Fair Trade cocoa is that producer organizations receive a higher price
for their cocoa beans. The Fair Trade price represents the necessary condition for the producer
organizations to have the financial ability to fulfil the above requirements, and to cover the
certification fees.
It is calculated on the basis of world market prices, plus fair trade premiums. The Fair Trade
premium for standard quality cocoa is US$ 150 per tonne. The minimum price for Fair Trade
standard quality cocoa, including the premium, is US$ 1,750 per tonne. Other benefits for certified
producer organizations are better "capacity building" and "market access".
Presently, cocoa sold with the Fair Trade label still captures a very low share of the cocoa market
(0.5%).
Organic cocoa and chocolate
The organic cocoa market represents a very small share of the total cocoa market, estimated at less
than 0.5% of total production. ICCO estimates production of certified organic cocoa at 15,500
tonnes, sourced from the following countries: Madagascar, Tanzania, Uganda, Belize, Bolivia, Brazil,
Costa Rica, Dominican Republic, El Salvador, Mexico, Nicaragua, Panama, Peru, Venezuela, Fiji,
India, Sri Lanka and Vanuatu.
However, the demand for organic cocoa products is growing at a very strong pace, as consumers are
increasingly concerned about the safety of their food supply along with other environmental issues.
According to Euro monitor International, global organic chocolate sales were estimated to have
increased from a value of US$ 171 million in 2002 to US$ 304 million in 2005.
Certified organic cocoa producers must comply with all requirements associated with the legislation
of importing countries on production of organic products. The benefit for cocoa farmers is that
organic cocoa commands a higher price than conventional cocoa, usually ranging from US$ 100 to
US$ 300 per tonne. However, originating countries with smaller volumes can fetch much higher
premiums. This premium should cover both the cost of fulfilling organic cocoa production
requirements and certification fees paid to certification bodies.
PEST Analysis of Industry in world Market
PEST Analysis
Market trends of confectioneries are highly determined by the elements of the external environment.
Companies operating in the different sectors have little or no influence on these factors. The only
solution is to adapt to the current situation and try to find the best ways to operate in it, and gain the
most favorable positions. In the case of a new product it is especially important to be clear with the
political, economic, social and technological factors affecting the targeted market. These factors are
examined within a PEST analysis.
13
KADI SARVA VISHWAVIDYALAYA 2014 -2016
S. K. PATEL Institute of Management & Computer Studies Gandhinagar.
Political factors
The foreign and domestic politics, monetary processes have significant effects on the performance of
Hungarian companies. A long-term correction and restructuring program has been introduced by the
government in 2007 to meet the requirements of the EU Convergence Program and to create a stable
economic environment in Hungary.
It contains the introduction of new taxes, energy price and tax increases, and the reform of medical
and educational system as well. As it was expected it caused a significant setback in the economic
performance of the country in the first period. The high tax regime and the unstable business
environment have resulted in a remarkable fall of foreign and domestic investments and
reinvestments of profits.
Besides that, due to the high uncertainty level, peoples faith in the government has been shaken.
Thus, parallel to the growing economic problems an inner political crisis is about to evolve, which
can hinder the future success of the reform and development plans. In 2004 Hungary entered the
European Union and new principles were introduced, which has to be followed by the companies
operating in the confectionary industry.
Strict rules were implemented in the new member states regarding the food safety, like the ISO 9002
and HACCP (Hazard Analysis Critical Control Point) preventative food safety. These require meeting
the basic quality, safety and environmental requirements of the EU.The primary goal of these new
regulations is to protect the consumers and the market from low quality, unhealthy and harmful
product.
Economic factors
As a consequence of the long-term correction program introduced last year, the short-term
macroeconomic situation became quite problematic. Last year data show that among the 10 member
states entered into the EU in 2004, Hungary is one of the worst performing countries The country has
the lowest GDP growth within the European Union with 1.3%,the unemployment rate is around 8%,
prices increase faster than wages, and the consumer price index is higher then it was forecasted in the
previous year. These factors all contribute to the fall of purchasing power of households.
Service sector and those sectors which sales are directed to the domestic market suffer most from the
correction program, since they are limited by the declining domestic demand. The earlier flourishing
construction sector, which established significant capacities over the last few years, also has huge
losses. Furthermore, foreign direct investments show decreasing trend and investment willingness
shads significantly dropped. The success area of the Hungarian economy is manufacturing ,recording
a growth rate of 8% in 2007 (Kopint-Trki).
The EU accession had important effects on the confectionery market. First, the export-import trade
accelerated and many cheap and low quality products flooded the Hungarian market. Then
multinational companies arrived with modern equipments, lower production costs, therefore cheaper
products, and they became extremely important players.
14
KADI SARVA VISHWAVIDYALAYA 2014 -2016
S. K. PATEL Institute of Management & Computer Studies Gandhinagar.
New, earlier unknown companies and products were introduced, and the supply of chocolate grew
rapidly. They pushed out the old traditional Hungarian companies, or bought them and continued the
production of domestic brands along with their own well-known international products. Therefore,
the confectionary market is characterized by high level of concentration.
Just a few examples: Nestl bought the traditional Szerencsi chocolate factory in 1991; Kraft Foods
had a subsidiary in Hungary, but from 2004 production has been shifted to the neighboring countries,
where conditions are better; while Sweet Point - the largest Hungarian-owned confectionery
company -will be liquidated in 2008 (www.hunbisco.hu). The competition is still quite fierce; there
are many players on the market from the small specialty Hungarian firms, tothe big multinationals.
The only chance for smaller domestic companies to survive and be successful is in the innovation
and the continuous development of product.
Social Factors
According to the data of the Hungarian Central Statistical Office (KSH) the population of Hungary
has been decreasing in the last few decades. The number of children is less endless, while the society
is getting older, thus all though there are more companies offering wide variety of products the
number of potential consumers decreases every year.
Smaller households with one or maximum two children are quite typical in Hungary. Parents in small
families give everything to their children including many food and sweet products as well Companies
try to take advantage of this situation and they always come out with new and innovative products
which can attract children and stimulate their parents to buy them. Gfk Researcher Company
regularly analyzes the role of children within the households.
According to their 2007 data, this role is increasing considerably, since shopping often become a
family program, or children usually go with their mother to the shops. They are attracted by products
in colored packages, sweets packed with toys, and they are especially interested in those products
that they can recognize from advertisements. Besides that, a new young generation has grown up
since the change of regime in the 1990s.
They are now about 20-25 years old, often live alone, work in a good position and spend large part of
their income on themselves. They can afford to follow the newest trends, and they reactquickly to the
changing and fast developing environment. It is very important for the confectionery market, since
this and the following similar generations will constitute the largest part of consumers in the future.
Due to the changed consumer needs quick spread of hyper- and supermarkets can be observed in
Hungary. Consumers try to reduce the duration of shopping, and buy everything in one place at lower
prices. Hypermarkets, like Tesco, Auchan or Metro turn out in force not just in Budapest, but all
over the country in the bigger towns. The number of small grocery stores is continuously decreasing:
last year data shows a decrease from 21959 to 21340.
Contrarily, the number of hyper markets has increased from 109 to123 in 2007, which is a
considerable increase regarding the size of the country. The share of hypermarkets from the total
retail market of food products is about 30%; while this ratio is 18.3% in the case of supermarkets.
One-third of chocolate products are also bought in these large facilities. (AC Nielsen)
15
KADI SARVA VISHWAVIDYALAYA 2014 -2016
S. K. PATEL Institute of Management & Computer Studies Gandhinagar.
Technological factors
On the Hungarian market the consumers are becoming more health conscious, and spend more on
quality food, just like in the Western European area. Only those companies can survive who are able
to follow the trends and satisfy perfectly the consumer needs.
Companies on the confectionery market need to continuously come out with innovations, and to
provide more special and unique products than before; it is true for producers and traders as well.
FEDA has to choose carefully from the many producers, and to keep good relationship with them.
For an importer company it is necessary to make sure of the quality of the products that they buy
from foreign producers..
Chocolates as sensitive and perishable goods - need to be stored in a warehouse which keeps the
products in the same temperature during the winter and the summer periods as well. And finally,
customers should be informed thoroughly about the products characteristics, origins and quality
List of corporate & countries suppliers / customers.
Chocolate is a product of the cacao bean, which grows primarily in the tropical climates of Western
Africa, Asia, and Latin America.[1] The cacao bean is more commonly referred to as cocoa, so that is
the term that will be used throughout this article. Western African countries, mostly Ghana and the
Ivory Coast, supply more than 70% of the worlds cocoa. The cocoa they grow and harvest is sold to
a majority of chocolate companies, including the largest in the world.
In recent years, a handful of organizations and journalists have exposed the widespread use of child
labor, and in some cases slavery, on cocoa farms in Western Africa. Since then, the industry has
become increasingly secretive, making it difficult for reporters to not only access farms where human
rights violations still occur, but to then disseminate this information to the public. In 2004, the Ivorian
First Ladys entourage allegedly kidnapped and killed a journalist reporting on government
corruption in its profitable cocoa industry In 2010, Ivorian government authorities detained three
newspaper journalists after they published an article exposing government corruption in the cocoa
sector.
The farms of Western Africa supply cocoa to international giants such as Hersheys, Mars, and Nestl
revealing the industrys direct connection to the worst forms of child labor, human trafficking, and
slavery.
16
KADI SARVA VISHWAVIDYALAYA 2014 -2016
S. K. PATEL Institute of Management & Computer Studies Gandhinagar.
The Worst Forms of Child Labor
In Western Africa, cocoa is a commodity crop grown primarily for export; 60% of the Ivory Coast
export revenue comes from its cocoa. As the chocolate industry has grown over the years, so has the
demand for cheap cocoa. On average, cocoa farmers earn less than $2 per day, an income below the
poverty line. As a result, they often resort to the use of child labor to keep their prices competitive.
The children of Western Africa are surrounded by intense poverty, and most begin working at a
young age to help support their families. Some children end up on the cocoa farms because they need
work and traffickers tell them that the job pays well.
Other children are sold to traffickers or farm owners by their own relatives, who are unaware of the
dangerous work environment and the lack of any provisions for an education. Often, traffickers
abduct the young children from small villages in neighboring African countries, such as Burkina Faso
and Mali, two of the poorest countries in the world. Once they have been taken to the cocoa farms,
the children may not see their families for years, if ever.
Most of the children laboring on cocoa farms are between the ages of 12 and 16, but reporters have
found children as young as 5. In addition, 40% of these children are girls, and some stay for a few
months, while others end up working on the cocoa farms through adulthood.
A childs workday typically begins at six in the morning and ends in the evening. Some of the
children use chainsaws to clear the forests. Other children climb the cocoa trees to cut bean pods
using a machete. These large, heavy, dangerous knives are the standard tools for children on the
cocoa farms, which violates international labor laws and a UN convention on eliminating the worst
forms of child labor. Once they cut the bean pods from the trees, the children pack the pods into
sacks that weigh more than 100 pounds when full and drag them through the forest [17] Aly Diabate, a
former cocoa slave, said, Some of the bags were taller than me. It took two people to put the bag on
my head. And when you didnt hurry, you were beaten.
In addition to the hazards of using machetes, children are also exposed to agricultural chemicals on
cocoa farms in Western Africa. Tropical regions such as Ghana and the Ivory Coast consistently deal
with prolific insect populations and choose to spray the pods with large amounts of industrial
chemicals. In Ghana, children as young as 10 spray the pods with these toxins without wearing
protective clothing.
17
KADI SARVA VISHWAVIDYALAYA 2014 -2016
S. K. PATEL Institute of Management & Computer Studies Gandhinagar.
To date, relatively little progress has been made to reduce or eliminate child labor and slavery in the
cocoa industry of Western Africa. At the very least, the industry has agreed to work to eliminate what
the ILO calls the worst forms of child labor. These are defined as practices likely to harm the
health, safety, or morals of children and include the use of hazardous tools and any work that
interferes with schooling.[26] Approximately1.8 million children in the Ivory Coast and Ghana may
be exposed to the worst forms of child labor on cocoa farms.
Slavery
Recently, investigators have discovered children trafficked into Western African cocoa farms and
coerced to work without pay. Abby Mills, campaigns director of the International Labor Rights
Forum, adds, Every research study ever conducted in [Western Africa] shows that there is human
trafficking going on, particularly in the Ivory Coast. While the term slavery has a variety of
historical contexts, slavery in the cocoa industry involves the same core human rights violations as
other forms of slavery throughout the world.
Cases often involve acts of physical violence, such as being whipped for working slowly or trying to
escape. Reporters have also documented cases where children and adults were locked in at night to
prevent them from escaping. Former cocoa slave Aly Diabate told reporters, The beatings were a
part of my life. I had seen others who tried to escape. When they tried, they were severely beaten.
Drissa, a recently freed slave who had never even tasted chocolate, experienced similar
circumstances. When asked what he would tell people who eat chocolate made from slave labor, he
replied that they enjoyed something that he suffered to make, adding, When people eat chocolate,
they are eating my flesh.
Is Slave-free Chocolate Possible?
Despite their role in contributing to child labor, slavery, and human trafficking, the chocolate
industry has not taken significant steps to remedy the problem. Within their $60-billion industry,
chocolate companies have the power to end the use of child labor and slave labor by paying cocoa
farmers a living wage for their product.
The chocolate industry is also being called upon to develop and financially support programs to
rescue and rehabilitate children who have been sold to cocoa farms. To date, the industry has done
little to remove child labor, let alone aid survivors of child labor.
18
KADI SARVA VISHWAVIDYALAYA 2014 -2016
S. K. PATEL Institute of Management & Computer Studies Gandhinagar.
Hersheys, the largest chocolate manufacturer in North America, has not thoroughly addressed
accusations of child labor in its supply chain and refuses to release any information about where it
sources its cocoa.[31] This lack of transparency is characteristic of the chocolate industry, which has
the resources to address and eliminate child labor but consistently fails to take action.
Are the Labels on Chocolate Meaningful?
Aside from large-scale production in Western Africa, a significant amount of cocoa is also grown in
Latin America. This is where the majority of organic cocoa originates. At this time, neither slavery
nor child labor have been documented on these cocoa farms. While it remains possible that some
Latin American farms may employ these practices, it is not widely documented as it is in Western
Africa.
The truth is that consumers today have no sure way of knowing if the chocolate they are buying
involved the use of slavery or child labor. There are many different labels on chocolate bars today,
such as various fair trade certifications and the Rainforest Alliance Certification; however, no single
label can guarantee that the chocolate was made without the use of exploitive labor. In 2009, the
founders of the fair trade certification process had to suspend several of their Western African
suppliers due to evidence that they were using child labor.
Chocolate companies, however, continue to certify their products to tell consumers that they source
their cocoa ethically. But in 2011, a Danish journalist investigated farms in Western Africa where
major chocolate companies buy cocoa. He filmed illegal child labor on these farms, including those
certified by UTZ and Rainforest Alliance. Despite the industrys claims, child labor still plagues
cocoa farms in Western Africa.
Multiple government and NGO programs have been developed, attempting to address the root causes
of the worst forms of child labor and slavery in West Africa. However, the success of these efforts
will depend greatly on the genuine support or lack thereof from the chocolate industry over the
coming years.
19
KADI SARVA VISHWAVIDYALAYA 2014 -2016
S. K. PATEL Institute of Management & Computer Studies Gandhinagar.
Recommendations
Consumers play an essential role in diminishing the food industrys injustices. Child slavery on cocoa
farms is a difficult issue to fully address because the most serious abuses take place across the world;
however, that does not mean our responsibility is reduced, since chocolate is a luxury and not a
necessity like fruits and vegetables. Taking all of this into consideration and looking at the research
that is available at this time, F.E.P. has created a list with vegan chocolates that we do and do not
recommend based on the sourcing of the cocoa. Other than a few exceptions (which are explained),
we encourage people not to purchase chocolate that is sourced from Western Africa. The list is
available on our website along with free downloadable apps for the iPhone and Android.
Global Trends In production, consumption, product development & marketing.
Coffee is a truly global commodity and a major foreign exchange earner in many developing
countries. The global coffee chain has changed dramatically as a result of deregulation, new
consumption patterns, and evolving corporate strategies. From a balanced contest between producing
and consuming countries within the politics of international coffee agreements, power relations
shifted to the advantage of transnational corporations.
A relatively stable institutional environment where proportions of generated income were fairly
distributed between producing and consuming countries turned into one that is more informal,
unstable, and unequal. Through the lenses of global commodity chain analysis, this paper examines
how these transformations affect developing countries and what policy instruments are available to
address the emerging imbalances.
Keywords
coffee;
commodity chains;
development;
globalization;
regulation
20
KADI SARVA VISHWAVIDYALAYA 2014 -2016
S. K. PATEL Institute of Management & Computer Studies Gandhinagar.
21
KADI SARVA VISHWAVIDYALAYA 2014 -2016
S. K. PATEL Institute of Management & Computer Studies Gandhinagar.
CHAPTER : 4
STUDY OF INDIAN MARKET :
22
KADI SARVA VISHWAVIDYALAYA 2014 -2016
S. K. PATEL Institute of Management & Computer Studies Gandhinagar.
The stock market is witnessing heightened activities and is increasingly gaining importance. In the
current context of globalization and the subsequent integration of the global markets this paper
captures the trends, similarities and patterns in the activities and movements of the Indian Stock
Market in comparison to U.S Stock Market. New York Stock Exchange (NYSE) and Bombay stock
exchange (BSE) has been used in the study as a part of study. The time period used is from 20122013 to test the correlation between the Indian Stock Exchanges and U.S. Stock Exchanges.
Introduction
Stock markets refer to a market place where investors can buy and sell stocks. The price at which
each buying and selling transaction takes is determined by the market forces (i.e. demand and supply
for a particular stock). Let us take an example for a better understanding of how market forces
determine stock prices. ABC Co. Ltd. enjoys high investor confidence and there is an anticipation of
an upward movement in its stock price.
More and more people would want to buy this stock (i.e. high demand) and very few people will
want to sell this stock at current market price (i.e. less supply). Therefore, buyers will have to bid a
higher price for this stock to match the ask price from the seller which will increase the stock price of
ABC Co. Ltd. On the contrary, if there are more sellers than buyers (i.e. high supply and low
demand) for the stock of ABC Co. Ltd. in the market, its price will fall down.
STOCK MARKET OF INDIA
In earlier times, buyers and sellers used to assemble at stock exchanges to make a transaction but
now with the dawn of IT, most of the operations are done electronically and the stock markets have
become almost paperless. Now investorsdont have to gather at the Exchanges, and can trade freely
from their home or office over the phone or through Internet.
The Indian stock exchanges hold a place of prominence not only in Asia but also at the global stage.
The Bombay Stock Exchange (BSE) is one of the oldest exchanges across the world, while the
National Stock Exchange (NSE) is among the best in terms of sophistication and advancement of
technology. The Indian stock market scene really picked up after the opening up of the economy in
the early nineties. The whole of nineties were used to experiment and fine tune an efficient and
effective system. The corporate
23
KADI SARVA VISHWAVIDYALAYA 2014 -2016
S. K. PATEL Institute of Management & Computer Studies Gandhinagar.
History of Industry in India
History
The Indian Chocolate Industry has come a long way since
long years. Ever since 1947 the Cadbury is in India,
Cadbury chocolates have ruled the hearts of Indians with
their fabulous taste. Indian Chocolate Industry?s Cadbury
Company today employs nearly 2000 people across India.
The company is one of the oldest and strongest players in
the Indian confectionary industry with an estimated 68%
value share and 62% volume share of the total chocolate
market. It has exhibited continuously strong revenue
growth of 34% and net profit growth of 24% throughout
the 1990?s. The brand of Cadbury is known for its
exceptional capabilities in product innovation, distribution
and marketing. With brands like Dairy Milk, Gems, 5 Star,
Bournvita, Perk, Celebrations, Bytes, Chocki, Delite and
Temptations, there is a Cadbury offering to suit all
occasions and moods.
Today, the company reaches millions of loyal customers through a distribution network of 5.5 lakhs
outlets across the country and this number is increasing everyday. In 1946 the Cadbury?s
manufacturing operations started in Mumbai, which was subsequently transferred to Thane. In 1964,
Induri Farm at Talegaon, near Pune was set up with a view to promote modern methods as well as
improve milk yield. In 1981-82, a new chocolate manufacturing unit was set up in the same location
in Talegaon. The company, way back in 1964, pioneered cocoa farming in India to reduce
dependence on imported cocoa beans. The parent company provided cocoa seeds and clonal
materials free of cost for the first 8 years of operations. Cocoa farming is done in Karnataka, Kerala
and Tamil Nadu. In 1977, the company also took steps to promote higher production of milk by
setting up a subsidiary Induri Farms Ltd., near Pune.
In 1989, the company set up a new plant at Malanpur, MP, to derive benefits available to the
backward area. In 1995, Cadbury expanded Malanpur plant in a major way. The Malanpur plant has
modernized facilities for Gems, Eclairs, and Perk etc. Cadbury operates as the third party operations
at Phalton, Warana and Nashik in Maharashtra. These factories churn out close to 8,000 tonnes of
chocolate annually. In response to rising demand in the chocolate industry and reduce dependency
on imports, Indian cocoa producers have planned to increase domestic cocoa production by 60% in
the next four years. The Indian market is thought to be worth some 15bn rupee (?0.25bn) and has
been hailed as offering great potential for Western chocolate manufacturers as the market is still in its
early stages.
24
KADI SARVA VISHWAVIDYALAYA 2014 -2016
S. K. PATEL Institute of Management & Computer Studies Gandhinagar.
Chocolate consumption is gaining popularity in India due to increasing prosperity coupled with a
shift in food habits, pushing up the country's cocoa imports. Firms across the country have
announced plans to step-up domestic production from 10,000 tonnes to 16,000 tonnes, according to
Reuters. To secure good quality raw material in the long term, private players like Cadbury India are
encouraging cocoa cultivation, the news agency said. Cocoa requirement is growing around 15%
annually and will reach about 30,000 tonnes in the next 5 years.
Brief Introduction
Indian Chocolate Industry as today is dominated by two
companies, both multinationals. The market leader is Cadbury
with a lion's share of 70%. The company's brands like Five Star,
Gems, Eclairs, Perk, Dairy Milk are leaders in their segments.
Untill early 90's, Cadbury had a market share of over 80 %, but
its party was spoiled when Nestle appeared on the scene. The
other one has introduced its international brands in the country
(Kit Kat, Lions), and now commands approximately 15% market
share. The two companies operating in the segment are Gujarat
Co-operative Milk Marketing Federation (GCMMF) and Central
Arecanut and Cocoa Manufactures and Processors Co-operation
(CAMPCO). Competition in the segment will soonly get keener
as overseas chocolate giants Hershey's and Mars consolidate to
grab a bite of the Indian chocolate pie.
The UK based confectionery giant, Cadbury is a dominant player in the Indian chocolate market and
the company expects the energy glucose variant of its popular Perk brand to be singularly responsible
for adding five per cent annually to the size of the company?s market share.
Market capitalization
The Indian candy market is currently valued at
around $664 million, with about 70% share ($
461 million) in sugar confectionery and the
remaining 30% ($ 203 million) in chocolate
confectionery. Indian Chocolate Industry is
estimated at US$ 400 million and growing at 18%
per annum. Cadbury has over 70 % share in this
market, and recorded a turnover of over US$ 37m
in 2008.
25
KADI SARVA VISHWAVIDYALAYA 2014 -2016
S. K. PATEL Institute of Management & Computer Studies Gandhinagar.
Size of the industry
The size of the market for chocolates in India was estimated at 30,000 tonnes in 2008. Bars of
moulded chocolates like amul, milk chocolate, dairy milk, truffle, nestle premium, and nestle milky
bar comprise the largest segment, accounting for 37% of the total market in terms of volume. The
chocolate market in India has a production volume of 30,800 tonnes. The chocolate segment is
characterized by high volumes, huge expenses on advertising, low margins, and price sensitivity.The
count segment is the next biggest segment, accounting for 30% of the total chocolate market. The
count segment has been growing at a faster pace during the last three years driven by growth in perk
and kitkat volumes. Wafer chocolates such as kit kat and perk also belong to this segment. Panned
chocolates accounts for 10% of the total market. The chocolate market today is primarily dominated
by Cadbury and Nestle, together accounting for 90% of the market.
Major Players
Cadburys India Limited
Nestle India
Gujarat Co-operative Milk Marketing Federation
Cocoa Manufactures and Processors Co-operative (CAMPCO)
Bars Count Lines Wafer Panned Premium
Cadbury?s Dairy Milk & Variants
5-Star, Milk
Amul Milk Chocolate
Treat Perk Gems,
Tiffins Temptation & Celebrations
Nestle Milky Bar & Bar One.
Latest developments
Chocolate-lovers may soon find their chocolate dearer if the problems plaguing the industry
continue. Raw material costs have risen by more than 20 % in the last few years. Although retail
prices have not increased, a rise in input costs will force the manufacturers to consider a price hike.
The Bigger players in the country such as Cadbury, which leads the Rs 2,500 crore chocolate markets
in India with a share of 72%, will find it easier to absorb the surge in input costs as it has products at
various price points in the market, said industry experts. Cadbury may also opt for a price hike, albeit
marginal, if the current trend continues. Indian Chocolate Industry's Margin range between 10 and
20%, depending on the price point at which the product is placed. The input costs in India are under
check owing to the 24% decline in the prices of sugar.
The World?s Leading manufacturer of high quality cocoa and chocolate products Barry Callebaut,
has announced the opening of its first, state-of the art, Chocolate Academy in Mumbai, India in July
2007.
26
KADI SARVA VISHWAVIDYALAYA 2014 -2016
S. K. PATEL Institute of Management & Computer Studies Gandhinagar.
According to the analysis of the international market intelligence provider Euromonitor, the relatively
small Indian chocolate market with volumes of about 55,000 metric tonnes of chocolate and
compound per year is expected to grow on average per year by around 17.8% between 2008 and
2012.
Ferrero the Italian confectionery giant of $8 billion has planned up for a new production facility in
Maharashtra with an investment of over $125 million to whip up some of its popular brands that
include Rocher and Kinder.
Indian Scenario of Industry
Chocolates are not just meant for kids but for everyone. If you look at the consumption scenario in
India only, then you will get to know that from adolescents to young people to middle-aged people all
are consumers of chocolates And there have been studies proving this fact. This is the reason the
chocolate industry is day-by-day growing in India. Chocolates now grace the most auspicious
occasions in India, be it festivals like Diwali, a wedding, an engagement or birthday ceremonies.
Most of the chocolate brands in India produce chocolates in different sizes, shapes and designs that
are priced accordingly. Most popular chocolates like Diary Milk and Five Star can be bought for just
Rs. 5.
In India, chocolates are tardily but steadily replacing traditional Indian sweets, or we can say
Mithai. Owing to ascending social cognisance, on festivities and functions, people choose to gift
well-wrapped chocolates over traditional sweets. Capitalising this situation, top chocolate brands in
India are currently concentrating more on the packaging and introducing well-packaged designer
chocolates for specific occasions. Apart from that, increasing health consciousness among the urban
masses is also tempting them towards dark chocolates rather than calorie-stuffed sweets. Ad
campaigns like Meethe Pe Kuch Meetha Ho Jaye and Shubh Arambh are also luring consumers
towards making chocolates a part of their everyday life.
List of India's leading and popular chocolate brands:
Cadbury is a British multinational chocolate major. It is handled by Mondelez India. Cadbury was
established in Birmingham, U.K. by John Cadbury in 1824. Cadbury entered India in 1948 and
started its operations by importing chocolates. Today, Cadbury is the most loved and most widely
sold in India. According to Euromonitor International, Cadbury accounted for 55.5% of the total
chocolate sales in India during 2014. Dairy Milk is the flagship brand of Cadbury. Here are some of
the most famous Cadbury variants:
Dairy Milk
5 Star
27
KADI SARVA VISHWAVIDYALAYA 2014 -2016
S. K. PATEL Institute of Management & Computer Studies Gandhinagar.
Gems
Perk
Silk
Bournville
Celebrations
Founded in 1866, Nestle is a multinational beverage and consumer food items company based in
Switzerland. Henry Nestle founded the company in Vevey, Switzerland. Nestle came to India in the
late 1950s. Nestle was the second best-selling chocolate brand in India in 2014 with 17% share of the
total sales volume. Kit Kat, a bar of crisp wafer fingers covered with chocolate layer, is Nestle's
flagship variant in India. Some of the widely consumed Nestle brands are as follows:
Extra Smooth
Kit Kat Senses
Kit Kat Dark Senses
Alpino
Kit Kat
Bar-One
Munch
Ferrero India
Ferrero is an Italian food and beverage company founded in 1946 by Michele Ferrero. The company
started its business in India in 2004 and has gained a considerable ground in the Indian chocolate
industry within a decade. It is famous for its unique taste defined by its main ingredients creamy
filling, a crunchy wafer and a hazelnut centre. Ferrero India was the third biggest chocolate brand in
India as it held 5% market share in 2014. Ferrero Rocher is the flagship variant of Ferrero India. Here
are some of the Ferrero variants:
Ferrero Rocher
Nutella
28
KADI SARVA VISHWAVIDYALAYA 2014 -2016
S. K. PATEL Institute of Management & Computer Studies Gandhinagar.
Kinder
Raffaello
Mon Cheri
Amul
Amul is India's indigenous dairy cooperative primarily dealing in dairy products. It is also one of the
biggest players involved in chocolate manufacturing industry of India. Amul is owned by Gujarat Cooperative Milk Marketing Federation Ltd. (GCMMF) and was founded in 1946 by Dr. Verghese
Kurien. The credit of making India the largest producer of milk and dairy products by bringing about
the 'White Revolution' goes to Amul. Milk chocolate is Amul's most trusted brand amongst Indians.
Accounting for 1.1% of India's overall chocolate sales volume in 2014, Amul stands fourth. Some of
its variants are as follows:
Milk Chocolate
Dark Chocolate
Fruit & Nut Chocolate
Tropical Orange Chocolate
Almond Bar
Mars India International
Mars was established in 1911 by Franc C. Mars in Washington, U.S.A. The first recognised brand of
Mars was Milky Way that was launched in 1920s. Mars has been popular in India as well. Very
recently, Mars has started its manufacturing in India. Snickers and Galaxy are the most popular
chocolates in India that are made by Mars. The company was the fifth biggest seller of chocolates in
India in 2014 as it got 1.1% share of the total sales. Some of its products are as follows:
Snickers
Galaxy
Mars
Milky Way
Skittles
29
KADI SARVA VISHWAVIDYALAYA 2014 -2016
S. K. PATEL Institute of Management & Computer Studies Gandhinagar.
M&M's
Twix
Campco
Campco (Central Arecanut and Cocoa Marketing and Processing Cooperative Ltd.) is an Indian
cooperative that was founded in 1973 in Mangalore, Karnataka. Areca nut is the main ingredient of
the Campco chocolate products, which is mainly cultivated in Indian states of Kerala, Karnataka and
Assam. Campco processes, procures, markets and sells areca nut and cocoa. Some of its products are
as follows:
Bar
Krust
Fun Tan
Melto
Snack Bar
Treat
Turbo
Dairy Cream
ChocOn India
ChocOn started making chocolates in 1998, but it was founded in 1994 and started off with
manufacturing bottled mineral water. The company's operations were stretched to a whole new
manufacturing segment of sweet and the first brand was Milk N Nut, which was launched in 1998.
Since then, a series of exciting tasty chocolate brands have been launched. Some of ChocOns
products are as follows:
Chocolaty Bar
Milcreme Choco Bar
ChocOn Coconut
30
KADI SARVA VISHWAVIDYALAYA 2014 -2016
S. K. PATEL Institute of Management & Computer Studies Gandhinagar.
Parle
World's best-selling biscuit Parle-G is the flagship product of Parle, an Indian manufacturer of
consumer goods, confectioneries and beverages. Parle was founded in 1929 by Vile Parle's Chauhan
family. The company is the biggest biscuit manufacturer in India. It deals in confectionery items as
well. Parle products are a rare combination of fine taste, nutrition and quality. Chocolate variants of
Parle are as follows:
Kismi Bar
Kismi Toffee
2-in-1 Eclairs
2-in-1
Fruit Drops
Lotus
The Lotus chocolate company was founded in 1992 and is the maker of some of India's finest and
most exquisite chocolates, cocoa derivatives and cocoa products. Lotus supplies cocoa and chocolate
products to local bakeries as well as multinational chocolate manufacturers.
Chuckles
Milky Punch
Eclairs
Kajoos
Candyman
31
KADI SARVA VISHWAVIDYALAYA 2014 -2016
S. K. PATEL Institute of Management & Computer Studies Gandhinagar.
Candyman is owned by Indian conglomerate ITC founded in 1910 and based in Kolkata, West
Bengal. ITC launched its confectionery brands in 2002. Within a little more than a decade of its
existence, Candyman has launched a wide range of confectionery variants that have ruled over Indian
masses. Candyman is admired by the people of India for the innovative and unique taste it provides
through various products.
Choco Double Eclairs
Eclairs
Creme Lacto
Toffichoo
Cofitino
Growth and Evolution of Industry in India
Chocolate, the world's most illustrious food item has become a vital part of daily appetite among
Indians. Be it a birthday, job promotion, salary increment, examination success or religious and
traditional fiesta, every Indian is ready to nibble his / her share of chocolate to rejoice.
Today, the Indian confectionery industry is one of the fastest growing in the world with an estimated
market size of over Rs 2,000 crore per annum accounting for an annual growth of 18-20 per cent.
The global chocolate market is estimated to be around $85 billion. The Indian confectionery industry
is further categorized into sub-sectors such as sugar- based confectionery, chocolatebasedconfectionery and gums.
The Beginning Chocolate has a long history of almost 3,400 years. At the beginning, it was consumed
as beverage by the Central American people including Mayan and Aztecs. Ancient Mayans and
Aztecs linked chocolate with their gods and goddesses of fertility and so they called it Food of the
Gods. Dr J S Pai, executive director, Protein Foods and Nutrition Development Association of India
(PFNDAI), said, "Early chocolate products were beverages rather than solid sweets.
Even fermented alcoholic drinks prepared from it were consumed. After the Spanish conquest of
Aztecs, chocolate was brought to Europe and the rich started drinking chocolate beverage." After its
inception as a beverage drink, the chocolate-making process remained unchanged for hundreds of
years.
Cocoa drink
Later, when the Industrial Revolution arrived, many changes occurred that brought the hard, sweet
candy to life. "Famous British physician Hans Sloane in Jamaica came across a drink made of cocoa
enjoyed by locals. He made it more palatable by mixing it with milk, thus making the first milk
chocolate beverage. This recipe was eventually acquired by Cadbury Brothers who then started to
manufacture in the 19th century.
32
KADI SARVA VISHWAVIDYALAYA 2014 -2016
S. K. PATEL Institute of Management & Computer Studies Gandhinagar.
The Industrial Revolution enabled separation of cocoa butter and cocoa powder, so various different
products including the most popular chocolate candy were made from the various ingredients. As
cocoa plantation was possible in other parts of the world besides Central and South American places,
especially in Africa, and large manufacturing units started producing chocolate-based products, these
were then affordable by common people too," Dr Pai, noted in one of his article titled Chocolate Food of the God.
According to confectionery experts, one of the primary demand drivers for chocolate and other
sweets globally is consumer taste, and patrons continue to love chocolate. Matt Sena, research
analyst and trader, said in a published paper, "Long a beloved treat in the Western world, a recent
study in Great Britain showed that 91% of females and 87% of males consume chocolate products.
The taste for chocolate is now expanding into highly populated nations with a growing middle-class,
such as India and China. Rising disposable incomes and changing tastes will continue to drive
growth in the industry overseas, just as improving domestic economic conditions increase sales at
home."
After LPG - Liberalisation, Privatisation and Globalisation, India has witnessed tremendous growth
in F&B sector, particularly, in the confectionery segment. Many foreign players like Nestle and
Cadbury forayed into the Indian market to tap 100+ million customers. Growth drivers
Hussain Shaikh, proprietor, Heena Sales Corporation, suppliers of candies & premium chocolates in
Pune, said, "The growth we achieved in last years of 21st century is remarkable.
Today, the key growth drivers of chocolate industry in India are tradition of gifting sweets, shifting in
consumer preference from traditional mithai to chocolates, rising income levels and attractive pricing
which is suitable for every pocket.
The urban India and tier I, II cities have woken up to the fad of chocolate being considered as a gift
proposition. While even till few years back sweets were the only option in delicacy gifting, overt
media exposure and smart marketing techniques have positioned chocolates as an alternative."As per
research study done by Technopak Advisors, the two giants Cadbury with 70 per cent and Nestle
around 25 per cent have been instrumental in building up the chocolate market in India with huge
investments in product development, advertising and brand building. Here, the chocolate industry has
plethora of opportunities.
33
KADI SARVA VISHWAVIDYALAYA 2014 -2016
S. K. PATEL Institute of Management & Computer Studies Gandhinagar.
CHAPTER:5
PRODUCT PROFILE
34
KADI SARVA VISHWAVIDYALAYA 2014 -2016
S. K. PATEL Institute of Management & Computer Studies Gandhinagar.
Brands
Varieties
Wilbur chocolate with a bold American flavor
profile
Swiss-style Peters chocolate
Veliche Belgian chocolate
Milk
Dark
White
With a full line of chocolates including milk, dark and white, Wilbur
offers the right chocolate coatings to meet your needs. Using the
highest-quality cocoa beans to produce our chocolate coatings, we
roast beans and manufacture chocolate liquor in a way that ensures
quality throughout the entire chocolate-making process.
Product
Cashmere milk chocolate
Description
Our most popular milk chocolate with a well-balanced flavor
profile.
Sable milk chocolate
The same flavor profile of Cashmere in a thin viscosity.
Cupid milk chocolate
A medium viscosity chocolate coating with vanilla and whole
milk flavor. Ideal for hand dipping or enrobing.
Windsor milk chocolate
A silky smooth milk chocolate with a slightly caramelized note
made with vanilla.
H732 milk chocolate
An economical chocolate coating with a pleasant milk flavor
made with vanilla.
Bronze Medal semisweet chocolate Our most popular semisweet with a strong chocolate impact and
added milk fat to inhibit bloom. Made with vanilla.
Warwick semisweet chocolate
A dark, sweet, non-alkalized chocolate with a hint of bitterness.
A rich, fudgy semisweet chocolate with a hint of bitterness, that
Westbrook semisweet chocolate
is made with vanilla. Great for complementing a sweet center.
Our darkest semisweet chocolate with strong Dutched
Velvet semisweet chocolate
characteristics and added milk fat to inhibit bloom.
Platinum white chocolate
Premium white chocolate made with vanilla.
M540 milk chocolate drop
Robust chocolate impact made with vanilla.
B558 semisweet drop
Well-rounded, rich flavor for upscale cookies. Made with vanilla.
T110 classic semisweet drop
Nice dark flavor for economical applications. Made with vanilla.
R377 durable semisweet drop
Intense flavor with dextrose makes this drop excellent for
challenging baking applications.
T157 semisweet drop
A smooth and creamy release of fruit and cacao in drop form.
35
KADI SARVA VISHWAVIDYALAYA 2014 -2016
S. K. PATEL Institute of Management & Computer Studies Gandhinagar.
R900 semisweet drop
T559 semisweet drop
S192 semisweet drop
W742 semisweet drop
P1383 glazed semisweet drop
S843 white chocolate drop
Y252 white chocolate drop
A sweet economical drop with high impact chocolate notes.
Made with dextrose for a quick-setting chocolate chip cookie
application.
Robust chocolate drop with a hint of sweetness.
Blended liquor piece with a well-rounded chocolate flavor
profile and a hint of vanillin.
A mild semisweet chocolate drop with strong sweetness and
vanillin impact.
Highly polished panned drop with a robust roasted chocolate
flavor. Coated in a barrier that inhibits bloom and helps to
improve gloss stability.
A premium white cocoa butter drop offering a white chocolate
impact. Made with vanilla.
A white chocolate drop containing low sweetness with a milky,
cocoa butter flavor.
M540 milk chocolate chunk
Premium milk chocolate in a rectangular chunk.
(rectangular)
M540 milk chocolate chunk (square) Premium milk chocolate in a thin, square chunk.
T157 semisweet chunk
Premium chocolate flake with a smooth and creamy release of
fruit and cacao.
S390 semisweet chunk
Smooth semisweet chocolate in a thin chunk.
S836 semisweet chunk
Thick square chunk with a well-balanced flavor profile. Made
with vanilla.
T559 semisweet chunk
Robust chocolate chunk with a hint of sweetness.
V995 Brandywine bittersweet
Traditional Brandywine chocolate in chunk form.
chunk
S842 white chocolate chunk
Sweet and creamy white cocoa butter chunk.
S843 white cocoa butter chunk
Premium white cocoa butter chunk offering a strong white
chocolate impact.
S843 white cocoa butter drop
A premium white cocoa butter drop offering a white chocolate
impact your customers are expecting. Made with vanilla.
Peters milk chocolates have always exhibited the distinct flavor
characteristics of the original Swiss inventors, Daniel Peter and Henri
Nestl. Peters semisweet chocolates are formulated with special
flavor beans to provide the unique flavors not found in other
36
KADI SARVA VISHWAVIDYALAYA 2014 -2016
S. K. PATEL Institute of Management & Computer Studies Gandhinagar.
chocolates.
Product
Ultra milk chocolate
Description
Our lightest colored milk chocolate with a very distinct flavor
resulting from uniquely flavored beans.
Crema milk chocolate
A typical Swiss-styled milk chocolate with a medium strength
chocolate flavor, popularly used with peanut flavored centers.
Broc milk chocolate
Our most popular milk chocolate, this original Swiss formula
has a predominant milk flavor and is less sweet.
Madison milk chocolate
A fine flavor balance of milk chocolate makes this product a
natural for chocolate covered pretzels.
Maridel milk chocolate
Containing 33% cocoa solids and a subtle infusion of vanilla,
its balanced flavor profile makes this one of our most versatile
milk chocolates.
Glenmere milk chocolate
A sweet and somewhat darker milk chocolate designed for
enrobing; it especially complements nut confections.
Chatham milk chocolate
This product has the most intense chocolate flavor of all our
milk chocolate.
Vallen milk chocolate
Our original Swiss formula with a predominant milk flavor and
a subtle infusion of vanilla, perfect for enrobed confections.
Superfine milk chocolate
Newport semisweet chocolate
Viking semisweet chocolate
A golden colored milk chocolate with spicy overtones.
Specially roasted beans provide a strong chocolate flavor.
A full roast chocolate, used when a mild semisweet flavor is
desired. Preferred by bakers.
A robust, semisweet chocolate with fudgy and fruity flavor
notes. Made with vanilla.
A full dark roast chocolate with fruity and smoky overtones. An
excellent match with cordial cherries.
Lenoir semisweet chocolate
Monogram semisweet chocolate
37
KADI SARVA VISHWAVIDYALAYA 2014 -2016
S. K. PATEL Institute of Management & Computer Studies Gandhinagar.
Burgundy semisweet chocolate
Our most popular semisweet chocolate. Has a reddish cast and
a fruity, winey flavor note.
Cambra bittersweet chocolate
A bittersweet chocolate with 72% cocoa solids blended with
European-style low roast liquor and aged to produce a mellow,
balanced flavor. Made with vanilla.
Gibraltar bittersweet chocolate
A true bittersweet chocolate with 60% cocoa solids especially
adapted to blend with sweet centers. Excellent for chocolate
covered mints. Packed 5 blocks per case - net weight 50 lbs.
Peter's Original white chocolate A rich cream color and cocoa butter-based, whole milk coating.
It has delicate chocolate aroma and flavor.
Gourmet chocolate chips
A smooth, creamy chip with spicy overtones and a strong
semisweet chocolate flavor.
Flavored with vanilla and non-alkalized liquor, the Veliche brand is
chocolate in the Belgian tradition -- rich in character and complex in
flavor, yet remarkably workable in form.
Product
Chocolat Blanc 29%
White Chocolate
Chocolat Lait 40%
Milk Chocolate
Chocolat Noir
58% Bittersweet
Chocolate
Chocolat Noir 64%
Bittersweet Chocolate
Description
A clean, balanced milk flavor with a buttery mouth-feel, inviting aroma and
a subtle suggestion of vanilla.
Balanced and smooth milk character with harmonious undertones of
caramel, honey and butterscotch.
Dusky and intense cocoa flavor with bittersweet, lightly fudgy aftertaste.
Made with Tahitian vanilla.
Complex and dimensional bittersweet with mellow notes of roasted coffee
and tobacco, and a lingering chocolate richness that melts into the palate.
Made with Tahitian vanilla.
Chocolat Noir 72%
Subtle depths of flavor with surprisingly delicate bittersweet roasted notes
Bittersweet Chocolate that form gradually and dissipate slowly. Made with Tahitian vanilla.
38
KADI SARVA VISHWAVIDYALAYA 2014 -2016
S. K. PATEL Institute of Management & Computer Studies Gandhinagar.
CHAPTER :-6
Demand determination of the Industry
39
KADI SARVA VISHWAVIDYALAYA 2014 -2016
S. K. PATEL Institute of Management & Computer Studies Gandhinagar.
DETERMINANTS OF DEMAND AND SUPPLY OF CADBURY
Determinants of Demand
Income
Population and Age Group
Brand Image
Consumer Preference and Taste
Expected Future Price
Competition
Price of Complementary Goods
Cooling Weather and Recession
Determinants of Supply
number of supplier
expected price
price of input costs
Factors that Affect The Demand of Cadbury
Income of the consumer will also affect the demand of goods. For example, if the income of the
consumer increase, they have more money to spend, therefore they will buy more goods. At that
moment, the demand curve for the goods will shift to the right. However, not demand for the goods
will increase only, demand for normal good will increased.
There is a real life instance for this theory. When our salary increases, we will have extra money to
spend, so before increase of salary, we may only purchase 1 or 2 chocolate bars. However, after
increase of salary, maybe we will buy dozens of chocolate bars. This made us to purchase more of the
goods sold. Therefore the demand of the product will increased due to the raise of income. So, there
is a positive relationship between income and the product demand.
The determinant that affects the demand of Cadbury is population and age group. The product is
known for the children, adults and also for the old people so the age group are not much affected the
demand of the product. In this case, demand remains constant. If by increasing in the population,
there will be more buyers than there must be more of the market demand. Thus, the demand of the
Cadbury products will increase and the demand curve shifts leftward to rightward.
40
KADI SARVA VISHWAVIDYALAYA 2014 -2016
S. K. PATEL Institute of Management & Computer Studies Gandhinagar.
The brand image also determines the demand of the product as its brand of Cadbury plays an
important role in the demand of the Cadbury. This product has built such a brand image that it has
attracted the mind of the consumers so they will not like to go for any other product.
The demand of Cadbury product also depends on consumers preference and taste. If people
enjoy eating and develop a preference for the sweet and classic tasting Cadbury Chocolate, they
will want more of it. If consumer do not prefer by its sweetness tasting, they will want less of it
or change to other brand. Income changes and lower priced substitutions could affect their taste
and a cheaper priced alternative could become a new preference.
Expected price is also included. If consumer expects that the price of a certain commodity will
rise in future, the demand will increase as the product is under the current lower price before the
price rise. Inversely, consumers may believe that a price of a good will be reduced in future; they
will delay on purchasing the product until the price reduces to the lower rate. Many consumers
may purchase Cadbury products if they know that the price is going to be increasing in the near
future. On the other hand, consumers may wait to buy the products if they know the prices are
going to drop in the near future.
Competition is also other factors that affect the demand of Cadbury products. In this market,
consumers can find a lot variety of different brands of chocolate that are available such as Nestle
Kit-Kat, Ferrero Roche, Hershey ,Mars and so on. All chocolates are sold according to the market
price including Cadbury. So it is a tough competition for all confectionery companies. In order to
increase the demand for Cadbury products, the price of the competitors have to be increase. In
vice versa, if the price of the competitors decrease, the demand of Cadbury products not much
affected by it as it is considered as consumers brand loyal but the sales volume is not much as
the previous. In the results, the profits will not that high as before the changes of price of
competitors.
Furthermore, price of complementary goods is also another determinant. If the price of
complementary goods increases then there will be no change in the demand as Cadbury has
referred to normal goods. It becomes every people daily needs. But there is another consideration
that the demand will be affected if the price of complementary goods increases highly. For
example, in 2009 a shortage of cocoa was reported in UK. The cost of cocoa has increased
drastically to 2,055 a ton, the highest since 1985. The sale revenues dropped drastically as many
41
KADI SARVA VISHWAVIDYALAYA 2014 -2016
S. K. PATEL Institute of Management & Computer Studies Gandhinagar.
consumers may be unwilling to buy the product. They would rather to purchase sweet or candy
rather than buy chocolate.
Other factors for affect the change in demand could be related to the cooling weather and to the
recession. Cooler weather encourages the increase in sales of chocolate and the recession could
mean that people are staying at home rather than going out to eat. In 2009, Cadbury have that a
stay-at-home culture that have helped increase Cadburys UK sales by 12% in the first half year
(BBC News, 2009). Thus, the weather affects the demand curve shift from left to right as demand
increases.
Factors that Affect The Supply of Cadbury
The price of related goods will affect the supply that will shift the supply curve. For example, in
2009, UK had faced inflation in the price of cocoa that brought a huge impact to all confectionery
companies including Cadbury. (mail online, 2009).The increases in the price of the related good
(cocoa) will affect less supply on the confectionery products although the price of the product
remains constant. This shifts the supply curve to the left.
Besides, the number of suppliers also will affect supply. For example, as Cadbury expands their
business to more than 70 countries, there are a lot of supplies for Cadbury product. An increase in
number of suppliers shifts the supply curve rightward. The greater the number of suppliers in the
market, the greater the supply of Cadbury products in the market. There will be more Cadbury
products to go around for the consumers.
Expected price of the good also determines the supply of Cadbury products. Producers may delay the
production of Cadbury in the current period if they expect the price of the products to rise. They will
be more willing to sell the products at a higher price rather than selling and producing at the lower
price. The higher price will increase their net revenue.
price
42
KADI SARVA VISHWAVIDYALAYA 2014 -2016
S. K. PATEL Institute of Management & Computer Studies Gandhinagar.
Items in search results
Cadbury Glow 16 Luxurious Praline Wrapped in Delicious Chocolate 160 gms
Excellent Gift for DIWALI CHRISTMAS & NEW YEAR
Rs. 425.00
Buy It Now
+Rs. 70.00 shipping
Cadbury Caramel Nibbles Chocolate Imported From Uk
Free Shipping Bluedart / Fed Ex Same Day Shipping
Rs. 699.00
Buy It Now
Free shipping
4 watching
43
KADI SARVA VISHWAVIDYALAYA 2014 -2016
S. K. PATEL Institute of Management & Computer Studies Gandhinagar.
Cadbury Fingers Creamy White Chocolate Biscuits (Imported Chocolates)
Made in UK & fast shipping
Rs. 499.00
Buy It Now
Free shipping
Send Online Cadbury Celebrations 126 gms On Birthday as Chocolate Gift
Rs. 349.00
Buy It Now
Free shipping
Cadbury Twirl Bites Chocolate Imported From Uk Limited Edition
Free Shipping Bluedart / Fed Ex Same Day Shipping
Rs. 599.00
Buy It Now
Free shipping
3 watching
44
KADI SARVA VISHWAVIDYALAYA 2014 -2016
S. K. PATEL Institute of Management & Computer Studies Gandhinagar.
Cadbury Dairy Milk Bubbly Milk Chocolate Imported (Limited Quantity Available
Very Rare To Fine In India // Fast Shipping
Rs. 599.00
Buy It Now
Free shipping
15 watching
Imported Cadbury Flake Dipped Chocolate (32g x 3 bars) Total 96g
FAST & FREE SHIPPING (100% IMPORTED) Lowest Price
Rs. 299.00
Buy It Now
Free shipping
10 watching
45
KADI SARVA VISHWAVIDYALAYA 2014 -2016
S. K. PATEL Institute of Management & Computer Studies Gandhinagar.
CADBURY DAIRY MILK CHOCOLATES - 5 RS - 72 PCS IN 1 BOX
100% QUALITY PRODUCT AND FAST SHIPPING
Rs. 360.00
Buy It Now
+Rs. 69.00 shipping
CADBURY 5 STAR CHOCOLATE - 5 RS - 54 PCS IN 1 BOX
100% QUALITY PRODUCT AND FAST SHIPPING,TOP RATED SELLER
Rs. 270.00
Buy It Now
+Rs. 69.00 shipping
Imported Cadbury's Dairy Milk Chocolate Black Forest 165g 2016/11 Expiry
Ready to ShipMalayasian ProductBlack Forest
Rs. 349.00
Buy It Now
Free shipping
46
KADI SARVA VISHWAVIDYALAYA 2014 -2016
S. K. PATEL Institute of Management & Computer Studies Gandhinagar.
Imported Cadbury Flake Fine Chocolates
Quantity/Weight 4 pcs/ 25gm Each
Rs. 550.00
Buy It Now
Free shipping
10 watching
Cadbury DAIRY MILK Bubbly Chocolates 3 Pack X 87g (100% Imported)
Fast & Free Shipping (LOWEST PRICE)
Rs. 599.00
Buy It Now
Free shipping
47
KADI SARVA VISHWAVIDYALAYA 2014 -2016
S. K. PATEL Institute of Management & Computer Studies Gandhinagar.
Imported Cadbury's Dairy Milk Chocolate Mixed Nuts 165g 2016/12 Expiry
Ready to ShipMalayasian ProductMixed Nuts
Rs. 349.00
Buy It Now
Free shipping
CADBURY DAIRY MILK CHOCOLATES - 5 RS - 72 PCS IN 1 BOX BY
FAIRBASKET
Lowest Price + Delivery by fedex
Rs. 360.00
Buy It Now
+Rs. 60.00 shipping
48
KADI SARVA VISHWAVIDYALAYA 2014 -2016
S. K. PATEL Institute of Management & Computer Studies Gandhinagar.
Imported cadbury flake dipped chocolate (32gmx12 bars) total 384 gm
Free & fast shipping (LONG EXPIRY 100% ORIGINAL)
Rs. 1,449.00
Buy It Now
Free shipping
Cadbury chocolates Bags (Crispello / / Pebbles / Twirl Bites)
Fast Bluedart Shipping Made in UK
Rs. 550.00
Buy It Now
Free shipping
11 watching
Imported Cadbury Flake Treat Size 250g-Family Pack Milk Chocolate.
FAST SHIPPING/FREE SHIPPING/LOWEST PRICE
Rs. 899.00
Buy It Now
Free shipping
49
KADI SARVA VISHWAVIDYALAYA 2014 -2016
S. K. PATEL Institute of Management & Computer Studies Gandhinagar.
The biggest bar of Cadburys Dairy Milk Chocolate 850g Imported Chocolate
Limited Edition and Imported Chocolate
Rs. 3,800.00
Buy It Now
Free shipping
3 watching
Income of taegeted customers
On the last Marketing Communication we were talking about how advertisements can be persuasive
when it comes to chocolate brands. Chocolate industry is very nice example to work with because
almost everyone, including me, is crazy about chocolate ;)
I will speak about specific chocolate brands and market which they target.
Kinder
This in the example of one brand with different types of the products which have different targets.
Let me explain this using the example.
Kinder Surprise, also known as a Kinder Egg or, in the original Italian, Kinder Sorpresa, is
a confection manufactured by Italian company Ferrero. Originally intended for children, it has the
form of a chocolate egg containing a small toy.
Kinder Bueno (kinder is German for children, bueno is Spanish for good or tasty) is
a chocolate bar made by Italian confectionery maker Ferrero. Kinder Bueno is a hazelnut cream
filled wafer with a chocolate covering. Target of this product are basically all the the people who
likes chocolate bars, but using advertisements like the example below, suggest that is more for
adults than for children.
Lindt
50
KADI SARVA VISHWAVIDYALAYA 2014 -2016
S. K. PATEL Institute of Management & Computer Studies Gandhinagar.
Lindt is recognized as a leader in the market for premium quality chocolate, offering a
large selection of products in more than 100 countries around the world. When I was
wandering about target market of a company, I visited lindt website and I came across two
sentences which made me solve my problem.
A cosy fireplace, family and friends, sparkling children eyes To make those moments truly
unforgettable indulge your loved ones with our best pralines. Or treat your friends to a SWISS
LUXURY SELECTION box, an elegant chocolate gift, which everyone adores.
I realized that lindt target market are all the people who want to make a pleasure to themselves or to
people who they love, buying the best kind of chocolate
Milka
For me, Milka is family target brand. It`s all about advertisements which show naturally beautiful
and clean environment, where cows give the best milk, and happy families with children, enjoying
the taste of chocolate
.
Some of milka products are created to be a gifts (like in the picture below) which specialize their
target. But at the same time, since all the people, no matter to the age or gender like chocolate, milka
products are perfect for everyone.
Penetration level
51
KADI SARVA VISHWAVIDYALAYA 2014 -2016
S. K. PATEL Institute of Management & Computer Studies Gandhinagar.
Per capita consumption of chocolates and confectionery in India is minuscule at 20gms in India as
compared to around 5-8 kgs and 8-10 kgs respectively in most European countries. Penetration of
chocolate products averages at 4.2% at all India level. Consumption is concentrated in large metros
with population of over 1mn, where penetration is comparatively higher at 15.4%.
Penetration in small and medium size towns averages 9-10%.
In rural areas, the products are perceived as conspicuous consumption and poor value for money.
Penetration is understandably low at 1.9%. Confectionery products such as hard-boiled sweets,
toffees, mint, chewing/ bubble gums on the whole have penetrated in 14.2% of Indian households.
Urban penetration is 23% and rural penetration is 10.7%. The penetration of boiled sweets/ toffee/
mint is 10.3% in urban areas and 7% in rural areas, whereas the same for chewing/bubble gums is
8.7% in urban areas and 2.5% in rural areas. In relative terms, the penetration is higher in large and
medium size towns/cities. Confectionery products sold in rural areas are largely from unorganized
local players. Awareness about chocolates is very high in urban areas at over 95%.
In rural areas, awareness about confectionery products is significantly higher at 80-90% compared to
chocolate awareness at 30-40%. Due to the small size of rural market, most players have not extended
their distribution network to rural areas. A part of consumption therefore is represented by the
products brought from urban areas, by male members who work in cities and visit their village
periodically.
Advertisements
Availability of Finance
MCLEAN, VA/ZURICH, SWITZERLAND The unique and good-for-you cocoa flavanols the
natural compounds found in the cocoa fruit linked to important circulatory and other health benefits
will soon be easier to identify and obtain when making nutrition choices. Mars, Incorporated and
Barry Callebaut AG recently signed a cross-licensing and cooperation agreement that is expected to
increase the availability and uniformity of cocoa flavanol-rich chocolate products worldwide.
The agreement between these global chocolate leaders is seen as the beginning of a path leading to
consistent standards for beneficial cocoa flavanol products.
Decades of research suggest cocoa flavanols can have a positive impact on circulatory health and
related conditions, but manufacturers have struggled with consistency, reliable measurement methods
and communication of the flavanol benefits and content of foods. Mars, the world's largest retail
52
KADI SARVA VISHWAVIDYALAYA 2014 -2016
S. K. PATEL Institute of Management & Computer Studies Gandhinagar.
chocolate manufacturer, selling seven of the worlds 20 best selling chocolate snacks, with its
pioneering scientific know-how in flavanol analytics, preservation and health benefits, is partnering
with Barry Callebaut AG, the worlds leading manufacturer of high-quality cocoa and chocolate
products for the entire food industry, to progress towards creating a commonly used standard for
measuring useful flavanols in foods, broadening acceptance and availability of flavanol-containing
products with guaranteed flavanol content.
Cocoa flavanol containing products can be a part of a healthy diet. But simply having a higher
percent cacao, being a darker chocolate, or claiming antioxidants as the main benefit of cocoa,
misses the point and demonstrates the need for a means to measure and indicate adequate levels of
flavanols consistent with recent scientific studies.
Over the last five years we have also sold products like CocoaVia, and continue to sell Dove Rich
Dark Chocolate, both high in flavanol content. This agreement with Barry Callebaut will now
guarantee reliable flavanol levels in more chocolate products around the globe.
Beginning February 2010, Barry Callebaut AG began licensing Mars patents and will display the
Mars Cocoapro bean in hand logo on its Acticoa products in the US and other markets with an
assured consistently high level of cocoa flavanol content. Acticoa chocolate has been on the
European market for nearly five years and this new cooperation will allow us to even better serve our
customers worldwide, in particular also in the US.
This agreement is an important step in making chocolate alternatives with clear flavanol levels
available to a much broader audience, around the world. Were excited to embark on this journey
with Mars, Incorporated said Hans P. Vriens, Chief Innovation Officer at Barry Callebaut. Based on
years of our own clinical studies, we know cocoa flavanols offer a potentially substantial health
benefit, and we know consumers are increasingly seeking healthier products that offer added value.
We can all gain through a consistent method to assure consumers that were delivering these
important compounds in our products, and through an aligned way in which we communicate these
levels.
Both companies have agreed to cooperate in promoting flavanol rich chocolate products with a
guaranteed level of flavanols inside. Over the next few months, both companies will be updating their
science and marketing communications as well as their websites to reflect the implications of this
new cooperation.
53
KADI SARVA VISHWAVIDYALAYA 2014 -2016
S. K. PATEL Institute of Management & Computer Studies Gandhinagar.
About Mars, Incorporated Mars, Incorporated is a private, family-owned company founded in 1911
and employing more than 65,000 associates at over 230 sites, including 135 factories, in 68 countries
worldwide. Headquartered in McLean, Virginia, U.S.A., Mars, Incorporated is one of the worlds
largest food companies, generating global revenues of more than $28 billion annually and operating
in six business segments: Chocolate, Petcare, Wrigley Gum and Confections, Food, Drinks, and
Symbioscience. These segments produce some of the worlds leading brands:
Chocolate M&MS, SNICKERS, DOVE, GALAXY, MARS, MILKY WAY and
TWIX; Petcare PEDIGREE, WHISKAS, SHEBA, CESAR and ROYAL CANIN;
Wrigley ORBIT, EXTRA, STARBURST, DOUBLEMINT and SKITTLES; Food
UNCLE BENS, DOLMIO, EBLY, MASTERFOODS and SEEDS OF CHANGE; Drinks
KLIX and FLAVIA; Symbioscience WISDOM PANEL, SERAMIS, CIRKUHEALTH
and COCOAPRO.
About Barry Callebaut AG
With annual sales of about CHF 4.9 billion for fiscal year 2008/09, Zurich-based Barry Callebaut is
the worlds leading manufacturer of high-quality cocoa and chocolate from the cocoa bean to the
finished product on the store shelf. Barry Callebaut is present in 26 countries, operates about 40
production facilities and employs about 7,500 people.
The company serves the entire food industry, from food manufacturers to professional users of
chocolate (such as chocolatiers, pastry chefs or bakers), to global retailers. Barry Callebaut is the
global leader in cocoa and chocolate innovations and provides a comprehensive range of services in
the fields of product development, processing, training and marketing. The company is actively
engaged in initiatives and projects that contribute to a more sustainable cocoa supply chain.
54
KADI SARVA VISHWAVIDYALAYA 2014 -2016
S. K. PATEL Institute of Management & Computer Studies Gandhinagar.
CHAPTER : 7
Players in the Industry
55
KADI SARVA VISHWAVIDYALAYA 2014 -2016
S. K. PATEL Institute of Management & Computer Studies Gandhinagar.
Number of players
56
KADI SARVA VISHWAVIDYALAYA 2014 -2016
S. K. PATEL Institute of Management & Computer Studies Gandhinagar.
Market share of various brands/firms
57
KADI SARVA VISHWAVIDYALAYA 2014 -2016
S. K. PATEL Institute of Management & Computer Studies Gandhinagar.
58
KADI SARVA VISHWAVIDYALAYA 2014 -2016
S. K. PATEL Institute of Management & Computer Studies Gandhinagar.
CHAPTER : 8
Distribution channel in the Industry
chocolate industry in distribution channel
59
KADI SARVA VISHWAVIDYALAYA 2014 -2016
S. K. PATEL Institute of Management & Computer Studies Gandhinagar.
60
KADI SARVA VISHWAVIDYALAYA 2014 -2016
S. K. PATEL Institute of Management & Computer Studies Gandhinagar.
CHAPTER : 9
KEY ISSUES AND CURRENT TREND
61
KADI SARVA VISHWAVIDYALAYA 2014 -2016
S. K. PATEL Institute of Management & Computer Studies Gandhinagar.
Cargill reports first-quarter fiscal 2016 earnings
MINNEAPOLIS Cargill today reported financial results for the fiscal 2016 first quarter ended
Aug. 31, 2015. Key measures include.
Adjusted operating earnings in the first quarter were $611 million, compared with $619 million in the
same period a year ago.Net earnings were $512 million, a 20 percent increase from last years $425
million. Revenues were $27.5 billion, down 17 percent from $33.3 billion a year ago. Cargill posted
a productive start to the new fiscal year, led by solid performance globally in grain and oilseeds
processing and animal nutrition, said David MacLennan, Cargills chairman and chief executive
officer.
Our team ably navigated the quarters weather-driven agricultural commodity markets, as well as
the effects of more volatile emerging markets, currency fluctuations and other macroeconomic
uncertainty.
Across the company, we made good headway on operational improvements aimed at strengthening
business performance. The integration of ADMs chocolate business is proceeding on target, and we
are excited to welcome EWOS, a global leader in salmon nutrition, to our company.
Segment performance:
The Origination & Processing segment made the largest contribution to Cargills first quarter, with
adjusted operating earnings up slightly from a year ago. Within the platform, combined results for the
grain and oilseed supply chain businesses rose considerably, based on effective positioning in
agricultural commodity markets distinguished by persistent downward trends and occasional sharp
price reversals.
Adjusted operating earnings in Animal Nutrition & Protein decreased in the first quarter, with
increased results in animal nutrition offset by lower earnings in animal protein. Global animal
nutrition earnings exceeded last years solid start due to higher sales volumes of customer-aligned
products and services, and good cost management.
Areas of particular strength included the U.S. and Vietnam, and aquaculture nutrition in Latin
America. Unseasonable pressures in cattle and beef markets led to a weaker quarter in North
American beef. Cattle costs remained high, and continued high beef prices caused consumers to seek
less expensive alternatives such as pork and poultry.
Results in Food Ingredients & Applications were down slightly from last years first quarter, though
efforts to reduce costs and improve performance showed good progress across the segment.
Profitability in starches and sweeteners was pressured in Europe by historically low sugar prices and
in North America by the impact of low crude oil prices on markets for corn-based ethanol.
62
KADI SARVA VISHWAVIDYALAYA 2014 -2016
S. K. PATEL Institute of Management & Computer Studies Gandhinagar.
The energy businesses posted a solid first-quarter profit due to effective trading strategies in more
volatile, downward trending markets. Metals and ocean transportation also posted better results in
challenging markets.
Explanation of non-GAAP financial measure
Cargill reports financial results in accordance with U.S. generally accepted accounting principles
(GAAP). Effective in the fiscal 2016 first quarter, the company also reports adjusted operating
earnings, a non-GAAP financial measure that management believes provides additional insight into
the underlying financial performance of the companys ongoing operations.
In calculating adjusted operating earnings, Cargill excludes the following items: timing differences
related to inventory, derivatives and hedging; last-in-first-out (LIFO) inventory adjustments;
amortization of intangible assets; gains and losses on changes in investment structure; asset
impairment and restructuring charges; and gains and losses on sales of businesses and other longterm assets.
About Cargill
Cargill provides food, agriculture, financial and industrial products and services to the world.
Together with farmers, customers, governments and communities, we help people thrive by applying
our insights and 150 years of experience. We have 155,000 employees in 68 countries who are
committed to feeding the world in a responsible way, reducing environmental impact and improving
the communities where we live and work.
Zero calories, great tasting: Cargill introduces new EverSweet next-generation,
stevia sweetener
Cargill to unveil its next-generation sweetener, EverSweet, at SupplySide West, Oct. 7-8
MINNEAPOLIS Oct. 1, 2015 Food and beverage companies are looking for sweetener
options to satisfy consumer health without sacrificing great taste.
Cargills answer to this: EverSweet next-generation zero calorie sweetener. Ever Sweet
sweetener will debut at Supply Side West (Oct. 7-8), where attendees can be the first to sample it in a
variety of beverages (booth3659). At a time when many consumers want to reduce sugar
consumption and adopt healthier lifestyles, EverSweet sweetener offers a new, delicious choice for
reduced and zero calorie food and beverages, said David Henstrom, vice president for health
ingredients, Cargill.
EverSweet sweetener is made with the same sweetness found in the stevia leaf, Reb M and Reb D,
and provides consumers the great taste they crave with better sweetness intensity, faster sweetness
onset and improved sweetness quality without the bitterness or off-note aftertaste common with
other stevia sweeteners.
Because the stevia plant produces only trace amounts of these molecules, using Reb M and Reb D to
produce a sweetener hasnt been commercially or environmentally viable until now with
fermentation.
63
KADI SARVA VISHWAVIDYALAYA 2014 -2016
S. K. PATEL Institute of Management & Computer Studies Gandhinagar.
Product quality/technology
This technology is used by the majority of chocolate producers in Europe. A typical line consists of
mixer, 2-roll-refiner, 5-roll-refiner and conch.
In the mixer the largest part of the recipe is blended, although some fat is left out, as otherwise the
mix would be too fluid for the refiners. The 2-roll-refiner crushes sugar crystals to sizes below
100m. Alternatively, sugar can be ground separately by a sugar mill, which was common practice
some decades ago. Although sometimes this set-up can still be found, most companies nowadays
prefer the 2-roll-refiner due to the danger of dust explosions in sugar mills.
The following 5-roll-refiner is a sophisticated machine, not very easy to operate, but essential for
final product quality. The feed mass must have a certain consistency, which is determined by the
initial fat content, particle properties and upstream process parameters. Here the particles are ground
to their final size, usually below 30m in order to avoid a sandy texture in the mouth in the final
product..
The Swiss company Bhler is market leader in this technology and looks back to a long experience in
building and installing complete production lines 8. In order to also meet the needs of smaller
producers, recently the MicroFactory line was launched with a capacity of 300-600 kg/h, where the
2+5-roll-refiners are replaced by two three-rollers, see Figure 2.
Since the Dutch company Duyvis Wiener joined with F.B.Lehmann and Thouet, they are also in a position to
supply complete lines consisting of refiners and Thouet-conches. Interesting for smaller companies is the
F.B.Lehmann 5-roll-refiner with integrated micro-2-roller9. Nevertheless also here one refiner would need
several hours to fill a large 6-t-conch, which can only be solved by always having one machine idle or by
using at least two smaller conches. For very small scale or test production the company also builds a pilot
scale 5RR with 50cm rolls and 3-rollers.
Another solution for smaller companies or for niche products is offered by BSA-Schneider, an
established conch builder, who since recently also builds refiners. Their CHOCompact system
combines a small 5-roll-refiner with a conch10 (see Figure 3). Only one machine is operating at the
64
KADI SARVA VISHWAVIDYALAYA 2014 -2016
S. K. PATEL Institute of Management & Computer Studies Gandhinagar.
time, so the conch has to wait for the refiner and vice versa. There are several other companies
building refiners, e.g. Carle&Montanari-OPM11, HDM-Petzholdt-Heidenauer12 and conches such as
Thouet13 and Lipp Mischtechnik
Promotion
The mission statement for my company is "Bringing the Best to Everyone We Touch and Being the
Best in Everything We Do" The new Desert Plum lipstick is from the fall collection which offers a
rich lip color with a soft-matte finish.
It ties into Bobbie Brown Cosmetics target market because lipstick is a fast and easy way to change
not only your look but helps a woman feel pretty as well. Convince and quality are important to the
"on the go career woman" who is also fashion forward which is Bobbie's main target market. This
new lipstick color offers a trendy color that moisturizes and comforts lips. It was recently featured in
"In Style" Magazine addressing their target market Marketing Objectives.
SWOT Analysis
The size of the chocolate market in Mumbai is about 1.05 tones and is valued at Rupees 10.2 million khroma
chocolate has the biggest market share at 58 per cent while other brands has captured 20% of market
Confectionary unit 2004-05
Sugar Confectionary / candy (Volume) Tones .02 Sugar Confectionary / candy (Value) Rs lakh 12,412,25
Chocolates (Value) Rs lakh 25,446,21
Cadbury is one of the topmost fmcg brands in India and hence there is no doubt that the strengths and
opportunities of Cadbury are far more than its weaknesses and threats. Let us delve deeper in the SWOT of
Cadbury
Strength
World leader Cadbury is the worlds leader in chocolates. Known to have the best manufacturing and a
wide distribution channel, Cadbury has a presence in 200 or more countries.
Powerhouse brands and Products Cadbury has many strong brands in its product portfolio such as dairy
milk, Bournvita, oreo, five star and others. The product are high quality products and some of them are cash
cows for Cadbury.
65
KADI SARVA VISHWAVIDYALAYA 2014 -2016
S. K. PATEL Institute of Management & Computer Studies Gandhinagar.
Brand name, brand equity and Brand loyalty Cadbury products are blessed with a fantastic brand
loyalty. Due to its marketing and strong branding over the years, the brand equity of Cadbury is also high
and hence Cadbury is comfortable charging a premium for its product because of the high brand equity.
Finally some brand names within the Cadbury family are known world wide and are desired by many.
Positioning as gift The smartest tactic that Cadbury has done over the years with products like dairy milk
and celebrations is that these chocolates are positioned for gifting. In fact the recent bournville, has a
complete focus on the gifting position. Due to this smart strategy Cadbury has safely differentiated itself
from majority of its competitors.
Promotions With an amazing tag line of kuch meetha ho jaye along with fantastic ATL and
BTL activities, Cadbury has one of the strongest promotions in the fmcg industry. This further imparts
strength to Cadbury because it provides excellent brand recall.
Indian connect Cadbury is one of the few brands which connects so well with the Indian diaspora. For
Indians, family, friends and love are all important parts of their life. And Cadbury has always focused on
emotional marketing to connect with the Indian audience.
Placement and distribution Cadbury has a superb distribution strategy in place and like all FMCG
companies, it uses the strategy of breaking the bulk. Distributing to 200 countries with a variety of more than
40 variants is not a small feat. And cadbury has been achieving the same for the past many years. It is known
to have one of the best FMCG distribution channels in India.
Weakness
As mentioned previously, a brand like Cadbury is expected to have many strengths and few weaknesses, and
the same is the case. Cadburys weakness is its rural distribution considering India has such a wide rural
diaspora which can be covered.
At the same time, A few cases here and there have happened based on the quality of the product where cockroaches or
other rodents were found in the chocolate. It is inexcusable for a brand like Cadbury to show such ignorance because
such infected chocolates should not leave quality control at all. Thus quality control needs to be strengthened.
Opportunities
Rural markets What is a weakness can become an opportunity. Penetrating rural markets and distribution
in rural markets can be a large opportunity for Cadbury. It is present in foreign countries and a rural presence
is much needed for Cadbury which will boost the brands presence and turnover.
New Tastes Indian consumers have a sweet tooth and they frequently like to eat small chocolates as well
as chocolate bars. On top of it, there are various flavors which consumers like. Thus, new tastes and new
flavors are an opportunity which Cadbury can generate regularly.
Threats
66
KADI SARVA VISHWAVIDYALAYA 2014 -2016
S. K. PATEL Institute of Management & Computer Studies Gandhinagar.
Cost and price increase With an increase in fuel cost as well as cost of transportation, distribution cost
has gone up. At the same time, the cost of procurement and manufacturing is high as well. Thus, over the
years, the constant increase in costing and thereby pricing of the product is a threat to Cadbury as it creates a
gap for other companies to enter.
Health consciousness on the rise Health consciousness is on the rise amongst the Indian population.
Many people prefer drinking health juices as well as fruits rather than having chocolates. Every week you
will see articles on news papers as well as on blogs which advice against eating chocolate and propagate the
benefits of staying healthy. At the same time, many parents have stopped giving chocolates to their kids
looking at the adverse affects.
Decreasing importance of festivals Cadbury has spent years to get the position of a gift on festivals and
occasions. What happens when the importance of these festivals drops? The buying of chocolates also drops.
Rising demand of people, growing purchasing power Nowadays, if you gift a chocolate to children, they
are likely to demand a toy car, a bicycle or for a young adult, a computer. Thus, with a rise in purchasing
power, the demands of gifts also has gone up in value and just a chocolate will not suffice. This is also a
threat for Cadbury.
The Marketing objectives:
1. To increase potential sales through promotional programs planned through the year especially during the
holiday seasons.
2. Repackage Hershey's so that it's new look will appeal to the customers considering that will be tagged as
a low calorie snack.
3. Continue to expand globally and have a stronger presence in foreign markets and with a special focused in
their declining Asian market.
4. Promote their core brands such as Kisses through numerous tv and magazine ads.
5. To leverage existing products to new markets and consumers through the new collections such as the
Pieces Collection.
Company specific marketing strategies
Production of chocolate has seen a constant growth in the recent past. Chocolate manufacturing
industry has been stable since 19th century when solid pieces were introduced.
Chocolate is one product that has continued to be loved by many people all over the world. It falls
under the category of most craved food products. It's soothing nature has been proven scientifically.
Chocolate helps in raising serotonin in the brain.
This hormone helps people to have a feeling of relaxation and calmness (Beckett, 2000). As a result,
chocolate has found a constant place in most tables today. It is one of the favourite desserts and snack
67
KADI SARVA VISHWAVIDYALAYA 2014 -2016
S. K. PATEL Institute of Management & Computer Studies Gandhinagar.
in most homes. With the new technology in place, chocolate industry is set to grow. Its history so far
is enough proof to argue that it will endure turbulent economic tides.
Segmentation and Positioning
Suppose you have an idea for a great new offering you hope will become a hot seller. Before you quit
your day job, youll need to ask yourself, Does my idea satisfy consumers needs and add value to
existing products? Whos going to buy my product? and Will there be enough of these people to
make it worth my while?
Your goal is to figure out which people and organizations are interested in your product ideas. To do
this you will need to divide or segment the people and organizations into different groups of potential
buyers with similar characteristics. This process is called market segmentation and involves asking
the question, What groups of buyers are similar enough that the same product or service will appeal
to all of them?
Bruce R. Barringer and Duane Ireland, Entrepreneurship: Successfully Launching New Ventures, 3rd
ed. (Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice Hall, 2010). After all, your marketing budget is likely to be
limited. You need to get the biggest bang for your buck by focusing on those people you truly have a
shot at selling to and tailoring your offering toward them.
Total Market
SIZE OF INDIAN CHOCOLATE INDUSTRY Market Size (by value): Rs. 650 Crore a year.
Market penetration: 4% (majority in urban areas)
Top 5 Chocolate brands:
Dairy Milk Kit Kat 5 Star Bar One Munch Major Chocolate Manufacturing
Companies: Cadbury Nestle Amul Candico Campco
The size of the market for chocolates in India was estimated at 30,000 Tonnes in 2008. Bars of
molded chocolates like Amul, milk chocolate, dairy milk, truffle, nestle premium, and nestle milky
bar comprise the largest segment, accounting for 37% of the total market in terms of volume. The
chocolate market in India has a production volume of 30,800 Tonnes.
The chocolate segment is characterized by high volumes, huge expenses on advertising, low margins,
and price sensitivity. The count segment is the next biggest segment, accounting for 30% of the total
chocolate market.
The count segment has been growing at a faster pace during the last three years driven by growth in
perk and kitkat volumes. Wafer chocolates such as kitkat and perk also belong to this segment. (Refer
68
KADI SARVA VISHWAVIDYALAYA 2014 -2016
S. K. PATEL Institute of Management & Computer Studies Gandhinagar.
Figure 2) Panned chocolates accounts for 10% of the total market. The chocolate market today is
primarily dominated by Cadbury and Nestle, together accounting for 90% of the market.
Figure 2: Positioning of Dominant Chocolate brands in the Indian Market
69
KADI SARVA VISHWAVIDYALAYA 2014 -2016
S. K. PATEL Institute of Management & Computer Studies Gandhinagar.
CHAPTER : 10
PESTEL Analsis
70
KADI SARVA VISHWAVIDYALAYA 2014 -2016
S. K. PATEL Institute of Management & Computer Studies Gandhinagar.
Political
Conservative/Liberal Democrat is bound to influence Cadburys operations. By last estimates, the 8
Cadbury factories in the UK had employed 3,000 workers. However, the stringent restrictions on the
entry of skilled workers from rest of Europe can affect Cadburys hiring decisions in the future.
The imposition of taxes is yet another political factor that will determine how Cadbury manages its
investment and payment to shareholders. For example, Value-added Tax rose by 2.5% in 2010 and
increased chocolate prices and reduced sales. And even before that in 2007, In the context of the UK,
the change of government from the Labour party to the Cadbury Schweppes decided to outsource a
major portion of its accounting and HR to an Indian firm in the face of increasing operational
expenses and reducing margins. If other business units follow suit, this can result in a loss of
hundreds of jobs across the globe. But conversely, it will also create new employment opportunities
in countries like India.
Economic
Even though the global economic downturn did affect Cadburys expansion plans (owing to a
reduction in disposable income of customers and other stakeholders), sales actually remained quiet
steady.In fact, Cadbury was able to gain a 30% increase in its annual profits, predominantly from the
sales of Dairy Milk and Trident. But even then, recession did play its part as the company managed
only to hit the lower end of its 4%-6% revenue for 2009, the peak of the recession. And while Dairy
Milk chocolate and Trident Gum sold well, other brands like Halls also saw a rise in their annual
sales.
Social
In one respect, Cadbury was born as a result of social factors. Being run by a Quaker family, their
opposition to alcohol served as the basis of running a business that sold tea, coffee, cocoa, and liquid
chocolate. But while chocolate and other products sold by the company are socially acceptable
worldwide, Cadbury has been on the receiving end of controversies, the recent one involving
Cadbury products being Halal Certified to cater to Muslim markets around the world.
In addition, there are also concerns in the western world owing to rising cases of obesity, especially
among children. Many nutritionists recommend people to reduce their consumption of chocolate and
candy, which is likely to affect Cadbury sales in the future.
Technology
Finally, technology has changed Cadburys production and packing process over the years, starting
with the introduction of new brew machines to blend coffee and cocoa gains. Recent moves in this
regard include the use of pathogen testing systems and filing patents for heat-resistant chocolate.
Import duties on components and finished goods
71
KADI SARVA VISHWAVIDYALAYA 2014 -2016
S. K. PATEL Institute of Management & Computer Studies Gandhinagar.
Goods imported into Turkey are subject to various charges: customs taxes and levies (customs tariffs,
and the mass housing fund levy); and internal taxes (excise duties, i.e. special consumption tax, VAT,
and
the stamp duty).
As a result of the CUD, Turkey applies the EC common external tariff (CET) to all industrial
products and to the industrial component of processed agricultural products imported from third
countries (since 1 January 1996). Turkey's tariff is based on the 2007 Harmonized Commodity
Description and Coding System (HS), and comprises 18,253 lines (19,478 in 2003) at the HS twelvedigit level (Table AIII.1).1 The tariff has 214 bands (372 in 2003), including ad valorem equivalents.
Turkey does not have seasonal tariffs.
Law No. 474 on Customs Tariff Schedule enables the Government to increase applied MFN tariff
rates (adopted by the Council of Ministers for a given year) when they are deemed not high enough
to provide "adequate" protection to domestic industries.2 The Law has set the so-called statutory tariff
(different from the applied MFN tariff which is adopted annually by the Council of Ministers).
Under the Law, the Government can replace applied MFN tariff rates by 150% of the corresponding
rates of the statutory tariff, with a view to ensuring higher protection to local industries. In the case of
products subject to tariff bindings, when the new rate (i.e. 150% of the statutory tariff rate) is higher
than the corresponding bound tariff rate, then the latter applies)
Taxes and Levies
1.
Introduction
We are grateful to the mother nature that she provides to the mankind various things like vegetables,
fruits, cereals, pulses etc. She is very kind to the mankind. It is said that God helps those, who helps
themselves. Thus, for producing various things like cereals, pulses, vegetables, farmers toil very
hard on the land and for the hard work done by the farmers, mother nature showers her kindness and
gives production manifold compared to the quantum of inputs sow.
On the products produced by farmers, various processes are being done on them and the same is
being put in manufacture or production of various items. During this, many persons also provides
various services in this regard. Many dishes are also produced and are consumed. For all this
activities, processes, n attempt has been made to study the impact of Indirect taxes more particularly
central excise and service tax and the said impact has been explained in subsequent paragraphs.
1
2
72
KADI SARVA VISHWAVIDYALAYA 2014 -2016
S. K. PATEL Institute of Management & Computer Studies Gandhinagar.
2.
Tax on activity of Production of Agriculture Produce.
As per section 3 of Central Excise Act, 1944, There shall be levied and collected in such manner as
may be prescribed, a duty of excise to be called the Central Value Added Tax (CENVAT), on all
excisable goods (excluded goods produced or manufactured in special economic zones) which are
produced or manufactured
Thus, central excise duty is there on manufacture or production of goods.
The term manufacture is defined by section 2(f) of the Central Excise Act, 1944 which reads as
under: manufacture includes any process,
i. incidental or ancillary to the completion of a manufactured product;
ii. which is specified in relation to any goods in the Section or Chapter notes of the First Schedule to
the Central Excise Tariff Act, 1985 (5 of 1986) as amounting to manufacture; or iii. which, in relation
to the goods specified in Third Schedule involves packing or re-packing of such goods in a unit
container or labeling or re-labeling of containers including the declaration or alteration of retail sale
price on it or adoption of any other treatment on the goods to render the product marketable to the
consumer and the word manufacturer shall be construed accordingly and shall include not only a
person who employs hired labour in the production or manufacture of excisable goods, but also any
person who engages in their production or manufacture on his own account;
In CCE v. Kiran Spinning Mills, 1988 (34) E.L.T. 5 (S.C.) similar view has been expressed by the
Apex Court regarding the expression manufacture. It has been observed in that case, by the Court
as under It is true that etymological word manufacture properly construed would doubtless cover
the transformation, but the question is whether that transformation brings about fundamental change,
a new substance brought into existence or a new different article having distinct name, character or
use results from a particular process of particular activity.
In Hindustan Polymer v. CCE, 1989 (43) E.L.T. 165 the Apex Court has defined the expression
manufacture as under :- manufacture under the Excise Law is the process or activity which brings
into being articles which are known in the market as goods and to be goods these must be different,
identifiable and distinct articles known to the market as such. It is then and then only that
manufacture takes place attracting duty.
Thus, a process whereby farmer converts the seeds into vegetables, cereals, fruits, flowers, etc.,
which is very much raw material for food industry is manufacture as new different product comes
into existence which has its independent use, character, identity and satisfies the test of manufacture
as set by Hon Apex court in the case of UOI v. Delhi Cloth & General Mills (1963) AIR 791 (SC).
Every product is known by a HSN (Harmonized System Nomenclature). In order to know where a
product is classifiable, one has to refer to First Schedule of Central Excise Tariff Act, 1985. Whether
a particular product is chargeable to duty of excise or not will depend upon rate of duty specified in
the Central Excise Tariff Act, 1985 read with any exemption Notification, if any.
73
KADI SARVA VISHWAVIDYALAYA 2014 -2016
S. K. PATEL Institute of Management & Computer Studies Gandhinagar.
Chapter I contains the products of animal origin like meat, milk etc. Most of them either are nonexcisable or chargeable to NIL rate of duty. Even the products such as butter milk, cheese, ghee,
butter (except condensed milk having sweetener) are also chargeable to NIL rate of duty.
All vegetables like potato, tomato, cabbage, coconut, cashew, mango, dried fruits, rice, tea (with few
exceptions), maize, copra are chargeable to Nil rate of duty (with few exceptions) and are contained
in chapter 6 to 14 of the Central Excise Tariff Act, 1985.
Non Tariff Barriers
Non-Tariff Barriers to Exports:
IV.2.1 Non-tariff restrictions in the EC:
NTBs cover a wide range of measures. Some, such as quotas, voluntary export restraints,
variable levies, import deposit20, declaration with visa etc. are applied at the border and others, such
as discriminatory public purchasing, technical standards biased in favour of local producers arid
subsidy payments are applied internally.
Estimates reveal that the proportion of trade subject to various NTBs in the EC9 appears to be
similar to that in the US, although in the former NTBs have been growing at a slower rate (Table 8),Laird and Yeats (1988).Non-tariff measures in EC countries: Tables 9 & 9a record the incidence of
various NTMs in a particular member country in the EC during the period 1979-8621. The table
records 24 varieties of NTMs which the EC utilised, though some forms of NTMs may be
unrecorded in the UNCTAD Data Base due to lack of information22. Denmark (16) and France (8)
used wider varieties of NTMs as compared to the rest and Germany (3) and Belgium (6) is a fewer
variety. The most commonly applied NTMs in the EC are license for surveillance, quota, prohibition
of indirect imports and MFA in textiles. The diverse pattern of use of NTMs and insufficient
information about them in itself acts as an important NTB. In recent years the Community appears to
have utilised anti-dumping measures to blunt the competitive edge of Japanese and other Asian
producers (Hine 1991).
74
KADI SARVA VISHWAVIDYALAYA 2014 -2016
S. K. PATEL Institute of Management & Computer Studies Gandhinagar.
CHAPTER : 11
COMPANY STUDY
75
KADI SARVA VISHWAVIDYALAYA 2014 -2016
S. K. PATEL Institute of Management & Computer Studies Gandhinagar.
COMPANY INFORMATION
COMPANY NAME
Cadbury india ltd
ADDRESS
Cadbury House,
19, Bhulabhai Desai Road,
Mumbai
Maharashtra
400026
CHAIRMAN
C . Y PAL
CONTACT NUMBER
Tel: 022-40073100
Fax: 022-23521698
Email: parveen.vasaigara@csplc.com
WEBSITE
Website: http://www.cadburyindia.co
m
GROUP
MNC
About Cadbury India Ltd
76
KADI SARVA VISHWAVIDYALAYA 2014 -2016
S. K. PATEL Institute of Management & Computer Studies Gandhinagar.
Cadbury India Limited, a part of the famous London based company called Kraft Foods, was
established in the year 1948 on 19th July in this country. Initially the company just used to import
chocolates. With the passing of years, they started operating in the following five categories of food
items though:
Beverages
Biscuits
Candy
Chocolate confectionery
Gum
However, over these years of business, this company of India has successfully maintained an undisputed
leadership in the field of chocolate confectionery. With their aim of "make today delicious", they have
touched the heart of every Indian with their different products. Apart from their corporate office in the
city of Mumbai, this Indian company has got 6 manufacturing units, the location of which are given
below:
Baddi at Himachal Pradesh
Bangalore
Hyderabad
Induri at Pune
Malanpur at Gwalior
Thane
Following locations has got the sales offices of Cadbury India:
Chennai
Kolkata
Mumbai
New Delhi
Clients and Investors of Cadbury India Limited
This well known Indian company, being a subsidiary of the Kraft Foods, is associated with the following
global brands:
77
KADI SARVA VISHWAVIDYALAYA 2014 -2016
S. K. PATEL Institute of Management & Computer Studies Gandhinagar.
Jacobs
Biscuits
L. U.
Maxwell House
Milka
Eclairs
Nabisco
Eclairs Rich
Oreo
Halls
Oscar Mayer
Philadelphia
Bournville Almond
Tang
Bournville Hazelnut
Trident
Bournville Raisin and Nut
Bournville Rich Cocoa
Cadbury Celebrations
Following are the institutional investors of the
Kraft Foods:
Oreo
Candy
Chocolate
Berkshire Hathaway Inc.
Cadbury Celebrations Rich Dry Fruit
Black Rock Institutional Trust Company, N.
A.
Cadbury Dairy Milk (Plain)
Cadbury Dairy Milk Crackle
Capital Research Global Investors
Cadbury Dairy Milk Fruit and Nut
Capital World Investors
Cadbury Dairy Milk Roast Almond
Franklin Mutual Advisers L. L. C.
Cadbury Dairy Milk Shots
Invesco Advisers, Inc.
Cadbury Dairy Milk Silk (Plain)
Jennison Associates, L. L. C.
Cadbury Dairy Milk Silk Roast Almond
State Street Global Advisors (U. S.)
Cadbury Dairy Milk Silk Fruit and Nut
Vanguard Group, Inc.
Gems (Plain)
Wellington Management Company, L. L. P.
Gems Share Pack
To name another shareholder of Cadbury India is:
Ernst and Young
Gems Surprise
Products and Services of Cadbury India
Limited
Perk (With Glucose Energy)
5 Star (Plain)
5 Star Crunchy
5 Star Fruit and Nut
Operating in the main 5 categories mentioned
earlier, this company has got numerous products.
Some of them are categorised below:
Beverages
Gum
Bubbaloo Cool Mint
Bournvita
Bubbaloo Decision Gum
Bournvita Li'l Champs
Bubbaloo with added strawberry flavor
Tang
Achievements of Cadbury India Limited
78
KADI SARVA VISHWAVIDYALAYA 2014 -2016
S. K. PATEL Institute of Management & Computer Studies Gandhinagar.
Apart from pioneering the cultivation of cocoa in India in 1965, this company of India has earned
many respectable awards while their operation lasting for over 60 years in the country. Names of
some of the most recent awards won by this Indian chocolate company are mentioned in the table
below:
Sl.
No.
1
Year
2011
U. A. and P. (University of
Asia and Pacific) Tambuli 2011
Awards
Asian Marketing
Effectiveness Award
2011
Goa Fest Creative Abby
Awards
2011
5
6
7
Name of Award or
Recognition
A. P. P. I. E. S. Awards
(Gold Standard)
Make A - Wish Corporate
2011
Partner Award
Indias Most Respected
2011
Companies
Best Companies to Work
2011
For
Details of Award or Recognition
For the campaign of the "Shubh Aarambh" of Cadbury
Dairy Milk
Silver Trophy in the category of Best Insights and Strategic
Thinking and Bronze Trophy in Best Creative Ideas and
Execution for the campaign of Mithaas of Cadbury
Celebrations during Diwali
Gold Medal in Strategic Thinking and Insights Category
for the campaign of Shubh Aarambh
8 Awards between the campaigns for "Shubh Aarambh" as
well as "Diwali Celebrations" and Grand Prix for the 1st
one
This is an award from the U. S. based Make A - Wish
foundation
As per the survey of Business World Magazine, this
company occupied the 3rd rank in F. M. C. G. sector
Ranked 6th in the Business Today Magazines survey of
the durables sector
Office Address and Website of Cadbury India Limited
The contact details of the registered office of this Cadbury Company in India are given below:
Cadbury India Limited
Cadbury House,
19, B Desai Road,
Mumbai - 400 026,
Maharashtra, India.
Tel: + 91 - 022 40073100
Official Website:
Last Updated on 1/25/2012
FMCG Companies in India
Hindustan Unilever Ltd.
ITC (Indian Tobacco Company)
Nestl & India
Dabur India
Asian Paints (India)
79
KADI SARVA VISHWAVIDYALAYA 2014 -2016
S. K. PATEL Institute of Management & Computer Studies Gandhinagar.
Cadbury India
Britannia Industries
Procter & Gamble Hygiene and Health Care
Marico Industries
Colgate-Palmolive (India) Ltd.
Godrej Consumers Product Ltd.
Nirma Ltd.
Tata Tea Ltd.
Parle Agro
H. J. Heinz
LG Care
Gillette
Godfrey Phillips
Henkel Spic
ITC
Johnson & Johnson
Modi Revlon
Biopac India
Goodricke
Amrut International
Dalmia Consumer Care
Dharampal Satyapal
Indeutsch
JK Helene Curtis
Jyothy Laboratories
Perfetti
Cavin care
Himalaya Health Care
Godrej Sara Lee
Reynolds
Parker
Emami Ltd
GlaxoSmithKline Pharma Ltd
CCL Products India Ltd
GTC Industries Ltd
Hamdard (Wakf) Laboratories
KRBL Ltd
80
KADI SARVA VISHWAVIDYALAYA 2014 -2016
S. K. PATEL Institute of Management & Computer Studies Gandhinagar.
Lakshmi Energy & Foods Ltd
Lotus Herbals Ltd
Nippo Batteries Company Ltd
Nivea India Pvt Ltd
VST Industries Ltd
Wimco Ltd
Scotch Brite
Balsara Home Products
Introduction and company profile
From its origin in South America to the tables of Europe and America, chocolate has a long history.
As European countries colonized different areas of the world, they established cacao plantations to
ensure a constant supply of chocolate. Cacao trees only grow in tropical climates and they require a
labor-intensive process to harvest. Consequently, plantation owners turned to the slave trade as a
means of supplying cheap labor.
As the popularity of chocolate soared, new production processes developed. These innovations
helped turn chocolate into an inexpensive luxury people of all social classes could enjoy.
ORIGINS
The ancient Maya are believed to be the first people to make chocolate, over 2,000 years ago. Cacao
trees, native to Central and South America, provided the beans used to make a bitter, spicy chocolate
drink. In the fourteenth century the Aztecs dominated Central Mexico and they developed a
sophisticated trade network of cacao until the Spanish conquered the region in 1521.
Conquistador Hernn Corts is often credited with introducing cacao to Spain in 1528, but no one
truly knows when and how cacao traveled to Europe.
Growth of the company
81
KADI SARVA VISHWAVIDYALAYA 2014 -2016
S. K. PATEL Institute of Management & Computer Studies Gandhinagar.
Mumbai: The acquisition of its parent Cadbury Plc by Kraft Foods Inc. two years back has left a
sweet taste in the mouth of Cadbury India Ltd which recorded its highest growth at 30% in 2010 and
grew 40% in the first nine months of 2011.
The company clocked a turnover of Rs 2,503 crore in fiscal 2010, and Anand Kripalu, Cadbury India
president, India and South-East Asia, hopes to sustain the 20% growth.
The chocolate market in India is pegged at approximately Rs 2,000 crore and growing at 18-20% per
annum with Cadbury having a 70% share and Nestl India Ltd around 20%, according to a December
2011 report by Technopak Advisors Pvt. Ltd, a Delhi-based retail and consumer goods consultancy
firm
Arvind Singhal, chairman of Technopak, said Cadbury India has not been affected despite being in a
discretionary-spending category which is typically hit by high inflation. Among its peers in the
chocolate category, its the only one that has achieved growth, he said, attributing much of the
success to the local management team and quality of leadership.
India head Kripalu, a Unilever veteran of 22 years, used the experience he gained there to good
effect. Within six months of joining Cadbury, in April 2006, he spoke of doubling the companys
growth rate from the historical 10% to 20% per annum.
Cadbury India also got on board consulting firm AT Kearney to prepare and implement a three-year
road map for internal transformation. The firm also introduced small changes such as stopping the
practice of giving away 20% free chocolates every quarter and big ones such as implementing the
power brands strategy, which Kripalu adopted from his previous employer.
The power brands strategy (implemented at HUL in the late 1990s as the company looked for higher
growth in India) meant being ruthless and hard-nosed to push a few brands for growth as they get the
company growth, said Aniruddha Lahiri, president, The Chatterjee Group (TCG), and a former
Unilever employee who spent three decades at the consumer products company.
In keeping with this strategy Kripalu, for instance, discontinued weak brands such as powdered
beverage Delight, a lollipop Mr. Pops and Cadbury Dairy Milk 2-in-1. The strategy yielded results
82
KADI SARVA VISHWAVIDYALAYA 2014 -2016
S. K. PATEL Institute of Management & Computer Studies Gandhinagar.
and saw brands such as Cadbury Dairy Milk, a driver of the chocolate category in India, grow at a
compounded growth rate of 30% per annum.
Kripalu and his team simultaneously widened the brand portfolio to cater to consumers in rural areas
with products such as Cadbury Dairy Milk Shots that can even survive an ambient temperature of 35
degree Celsius (chocolates typically melt at 32 degree Celsius).
Kripalu also attributes Cadbury Indias success to Kraft empowering managers in the Indian
company, giving them the power to make independent decisions. Today, the firm has added new
categories and changed its management structure which now spans five categorieschocolates, gum,
candies, biscuits and powdered beveragewith the person who heads each also being responsible for
the profit and loss account of his unit.
NESTL
NESTL's relationship with India dates back to 1912, when it began trading as The NESTL AngloSwiss Condensed Milk Company (Export) Limited, importing and selling finished products in the
Indian market. After India's independence in 1947, the economic policies of the Indian Government
emphasised the need for local production. NESTL responded to India's aspirations by forming a
company in India and set up its first factory in 1961 at Moga, Punjab, where the Government wanted
NESTL to develop the milk economy.
Progress in Moga required the introduction of NESTL's Agricultural Services to educate, advise and
help the farmer in a variety of aspects. From increasing the milk yield of their cows through
improved dairy farming methods, to irrigation, scientific crop management practices and helping
with the procurement of bank loans.
NESTL set up milk collection centres that would not only ensure prompt collection and pay fair
prices, but also instil amongst the community, a confidence in the dairy business. Progress involved
the creation of prosperity on an on-going and sustainable basis that has resulted in not just the
transformation of Moga into a prosperous and vibrant milk district today, but a thriving hub of
industrial activity, as well.
83
KADI SARVA VISHWAVIDYALAYA 2014 -2016
S. K. PATEL Institute of Management & Computer Studies Gandhinagar.
NESTL has been a partner in India's growth for over nine decades now and has built a very special
relationship of trust and commitment with the people of India. The Company's activities in India
have facilitated direct and indirect employment and provides livelihood to about one million people
including farmers, suppliers of packaging materials, services and other goods.
The Company continuously focuses its efforts to better understand the changing lifestyles of India
and anticipate consumer needs in order to provide Taste, Nutrition, Health and Wellness through its
product offerings. The culture of innovation and renovation within the Company and access to the
NESTL Group's proprietary technology/Brands expertise and the extensive centralized Research
and Development facilities gives it a distinct advantage in these efforts.
It helps the Company to create value that can be sustained over the long term by offering consumers
a wide variety of high quality, safe food products at affordable prices.
NESTL India manufactures products of truly international quality under internationally famous
brand names such as NESCAF, MAGGI, MILKYBAR, KIT KAT, BAR-ONE, MILKMAID and
NESTEA and in recent years the Company has also introduced products of daily consumption and
use such as NESTL Milk, NESTL SLIM Milk, NESTL Dahi and NESTL Jeera Raita. NESTL
India is a responsible organization and facilitates initiatives that help to improve the quality of life in
the communities where it operates.
84
KADI SARVA VISHWAVIDYALAYA 2014 -2016
S. K. PATEL Institute of Management & Computer Studies Gandhinagar.
CHAPTER : 12
PRODUCT PROFILE
85
KADI SARVA VISHWAVIDYALAYA 2014 -2016
S. K. PATEL Institute of Management & Computer Studies Gandhinagar.
Cadbury Your Favourites, 509.6g
by Cadbury
400.00Fulfilled
Cash on Delivery eligible.
#1 Best Seller in Hampers & Gourmet Gifts
Show only Cadbury items
Cadbury Celebration, 75g
by Cadbury
50.00
Show only Cadbury items
86
KADI SARVA VISHWAVIDYALAYA 2014 -2016
S. K. PATEL Institute of Management & Computer Studies Gandhinagar.
See available choices
Ferrero Rocher, 24 Pieces
by Ferrero
Show only Ferrero items
4 out of 5 stars 51
Ferrero Rocher, 16 Pieces
by Ferrero
398.00
Show only Ferrero items
4.3 out of 5 stars 94
87
KADI SARVA VISHWAVIDYALAYA 2014 -2016
S. K. PATEL Institute of Management & Computer Studies Gandhinagar.
Cadbury Chocolate Spread Smooth Spread, 400g
by Cadbury
587.00Fulfilled
Cash on Delivery eligible.
Show only Cadbury items
3.1 out of 5 stars 7
Cadbury Dairy Milk Block Roast Almond Chocolate Bar 220 Grams
by Cadbury
Show only Cadbury items
88
KADI SARVA VISHWAVIDYALAYA 2014 -2016
S. K. PATEL Institute of Management & Computer Studies Gandhinagar.
See available choices
Cadbury Imported Original Drinking Chocolate, 250g
by Cadbury
390.00Fulfilled
Cash on Delivery eligible.
Show only Cadbury items
3.5 out of 5 stars 11
Cadbury Dairy Milk, Silk Orange Peel Pouch, 60g
by Cadbury
Show only Cadbury items
89
KADI SARVA VISHWAVIDYALAYA 2014 -2016
S. K. PATEL Institute of Management & Computer Studies Gandhinagar.
Britannia Good Day Chunkies, 100g (Pack of 2)
by Britannia
100.00Fulfilled
Cash on Delivery eligible.
Show only Britannia items
4.2 out of 5 stars 832
Cadbury Flake Chocolate - Pack of 4 - 102 Grams
by Cadbury
Show only Cadbury items
1 out of 5 stars 1
90
KADI SARVA VISHWAVIDYALAYA 2014 -2016
S. K. PATEL Institute of Management & Computer Studies Gandhinagar.
Cadbury Dairy Milk, Marvellous Creations Jelly Popping Candy, 38g (Pack of 12)
by Cadbury
1,450.00
Only 1 left in stock - order soon.
Cash on Delivery eligible.
Show only Cadbury items
Skylofts sweet Chocolate Coated Butterscotch Nutties 300gms Heart Box
by Skylofts
499.00
Cash on Delivery eligible.
Show only Skylofts items
5 out of 5 stars 2
91
KADI SARVA VISHWAVIDYALAYA 2014 -2016
S. K. PATEL Institute of Management & Computer Studies Gandhinagar.
Cornitos Nachos Crisps, Tikka Masala, 60g
by Cornitos
35.00Fulfilled
Cash on Delivery eligible.
#1 Best Seller in Chips
Show only Cornitos items
3.7 out of 5 stars 146
Britannia Pure Magic Chocolush, 75g (Pack of 3)
by Britannia
90.00Fulfilled
Cash on Delivery eligible.
Show only Britannia items
92
KADI SARVA VISHWAVIDYALAYA 2014 -2016
S. K. PATEL Institute of Management & Computer Studies Gandhinagar.
4.1 out of 5 stars 91
Cadbury Dailry Milk Silk - Orange Peel, 145 g Pouch
by Cadbury
Show only Cadbury items
Cadbury Flake 99 Crumbliest Milk Chocolate 16 Bars Box
by Cadbury
Show only Cadbury items
1 out of 5 stars 2
93
KADI SARVA VISHWAVIDYALAYA 2014 -2016
S. K. PATEL Institute of Management & Computer Studies Gandhinagar.
Biskotto Wafer Roll, Chocolate, 400g
by Biskotto
235.00Fulfilled
Cash on Delivery eligible.
Show only Biskotto items
3.2 out of 5 stars 18
Unibic Assorted Cookies (Pack of 6), 450g
by Unibic
125.00Fulfilled
Cash on Delivery eligible.
#1 Best Seller in Biscuits
Show only Unibic items
4.3 out of 5 stars 181
94
KADI SARVA VISHWAVIDYALAYA 2014 -2016
S. K. PATEL Institute of Management & Computer Studies Gandhinagar.
Cadbury Crunchie Chocolate Small Bar 3 + 1
by Cadbury
Show only Cadbury items
See available choices
Chocholik's Legend Heart Shape Nicely Wrapped Chocolates
by Chocholik
449.00 561.00
You Save: 112.00 (20%)
Cash on Delivery eligible. and 1 more promotion
Show only Chocholik items
4.1 out of 5 stars 33
Sapphire Magic Stix, Chocolate, 200g
by Sapphire
125.00Fulfilled
95
KADI SARVA VISHWAVIDYALAYA 2014 -2016
S. K. PATEL Institute of Management & Computer Studies Gandhinagar.
Cash on Delivery eligible.
Show only Sapphire items
3.5 out of 5 stars 33
Cadbury Cookies Shorties, 300g
by Cadbury
450.00Fulfilled
Cash on Delivery eligible.
Show only Cadbury items
See available choices
Chocholik's Perfect Combination of Almond and Fruit & Nut Chocolate Truffles
by Chocholik
1,099.00 1,419.00
You Save: 320.00 (23%)
Cash on Delivery eligible. and 1 more promotion
Show only Chocholik items
96
KADI SARVA VISHWAVIDYALAYA 2014 -2016
S. K. PATEL Institute of Management & Computer Studies Gandhinagar.
4.3 out of 5 stars 14
Sponsored
Nutty and Fiery Combo of Chocolate Bars - Chocholik Belgium Chocolates
by Chocholik
699.00
Cash on Delivery eligible.
5 out of 5 stars 1
Sponsored
Chocholik's Legend Heart Shape Nicely Wrapped Chocolates With Mug
by Chocholik
675.00 844.00
You Save: 169.00 (20%)
Cash on Delivery eligible.
4.1 out of 5 stars 33
97
KADI SARVA VISHWAVIDYALAYA 2014 -2016
S. K. PATEL Institute of Management & Computer Studies Gandhinagar.
Sponsored
Chocholik's Amazing and Perfect Combination of Chocolate Truffles
by Chocholik
730.00 913.00
You Save: 183.00 (20%)
Cash on Delivery eligible.
4.2 out of 5 stars 9
98
KADI SARVA VISHWAVIDYALAYA 2014 -2016
S. K. PATEL Institute of Management & Computer Studies Gandhinagar.
CHAPTER: 13
PRODUCT MARKET DESCRIPTION
99
KADI SARVA VISHWAVIDYALAYA 2014 -2016
S. K. PATEL Institute of Management & Computer Studies Gandhinagar.
Product information
Product name
German
Schooled, fest (Tafels chocolate)
English
Chocolate (Slab chocolate)
French
Chocolate (Chocolate en tablettes)
Spanish
Chocolate (Tablets de chocolate)
CN/HS number *
1806 ff.
(* EU Combined Nomenclature/Harmonized System)
Product description
Chocolate is a product of cocoa, made by mixing cocoa mass, cocoa butter and sugar (sucrose) using
special machinery, with so-called conching (kneading) having a considerable influence on the quality
of the chocolate. Conching reduces water content, improves texture and moderates the bitterness and
aroma of the chocolate. In conching, the rolled mixture is refined by uninterrupted shearing to yield a
homogeneous texture, with lecithin increasing the fluidity of the liquid chocolate.
100
KADI SARVA VISHWAVIDYALAYA 2014 -2016
S. K. PATEL Institute of Management & Computer Studies Gandhinagar.
Production of chocolate products:
Figure 1
The greater the cocoa content, the higher the quality of the chocolate. Thus, bitter chocolate, with a cocoa
mass content of 60%, is the highest grade of chocolate.
Chocolate type
Cocoa mass
Milk solids
Milk fat
Sugar
[%]
[%]
[%]
[%]
Full-cream milk chocolate
30
18
4.5
< 47.5
Sweetened dairy chocolate
25
Bittersweet chocolate
50
< 50
Bitter chocolate
60
< 40
White chocolate
20
14
14
60
3.5
< 55
101
KADI SARVA VISHWAVIDYALAYA 2014 -2016
S. K. PATEL Institute of Management & Computer Studies Gandhinagar.
DEFINE PRODUCT
DIFFERENTIATING
FINE CHOCOLATE
The definition of fine chocolate can be as elusive as the definition of fine coffee, fine wine or even
fine art.
At the heart of many creations that are considered fine is a purely aesthetic expression. The saying
Art for arts sake, for example, means that art which is not intended to be produced in any quantity
or widely sold but is to be shared by anyone who loves art. Of course, it doesnt make sense not to
make and sell chocolate because consuming chocolate is really a key purpose of making chocolate in
the first place!
Another problem in defining fine is the fact that personal subjectivity plays a major role. You may
enjoy a rich roast coffee without any cream or sweetener while your best friend prefers a mild roast
with sugar and frothed milk. The coffee used in both your drink and that of your friends may be
from the same bean but handled very differently in order to deliver two very distinct beverages. A
high quality coffee bean and roasting processes help ensure that both you and your friend have a very
pleasant coffee beverage experience.
Fine chocolate may be defined by both a selection of high quality ingredients and also by the unique
artistry that a Chocolatier uses to create chocolates, truffles and other chocolate confections. In
general, there are five areas that combine to define a fine chocolate product:
cacao origin and processing
chocolate production practices
non-chocolate ingredient quality
chocolates technical expertise
artistry and presentation
102
KADI SARVA VISHWAVIDYALAYA 2014 -2016
S. K. PATEL Institute of Management & Computer Studies Gandhinagar.
COCOA ORIGIN AND PROCESSING
Ask most people whats in their chocolate bar and they will probably answer chocolate, milk and
sugar. While this answer is true, it is an incomplete picture of the chocolate inside the wrapper.
Perhaps you have recently heard more about cacao percentages. Even mainstream chocolate bar
producers have gotten on the bandwagon to promote their Cacao reserve or seventy percent dark
chocolate. But what do all these terms really mean? Are all 70% cacao bars equal? What should the
consumer know and learn to taste to differentiate fine chocolate from the candy bar of our youth?
Like wine, chocolate is an agricultural product whose character and flavor are dependant on genetics,
climate, soil and processing practices to yield a finished product. The higher the quality and care
taken along the route from bean to bar, the better the finished product will taste. So first lets look at
these individual components and explore them a little more, to learn how they affect the taste and
quality of chocolate.
Climate- Cacao grows roughly within the latitudes of 20 degrees north or South of the equator. Cacao
thrives in countries like Venezuela, Columbia, Dominican Republic, Mexico, Belize, Costa Rica,
The Ivory Coast of Africa, Madagascar and even Hawaii. While the crop is naturally a rainforest
understory plant, requiring high humidity, fertile soils , rainfall and warm temperatures it has also
been grown successfully in drier, poorer conditions under irrigation. Sound Plantation management
practices including organic fertilization and pest management affect the quality of beans being
produced by the trees. Since soil conditions vary widely throughout the equator the terroir or
specific geography, soil and climatic conditions of a region can add distiniction to the character and
flavor of the cacao.
The flavor of Forastero however is considered flat or monotone, even acidic and lacks the rich
flavor notes of the Criollo bean. A third variety of Cacao, called Trinitario is a hybrid of the two,
hardier than Criollo and better tasting than the the Forastero., although still not considered as
flavorful as a pure Criollo. As cacao trees cross polinate readily, it becomes very hard to determine
exactly what the genetics of a particular orchard without the help of DNA testing. There are a number
of claims of criollo when in fact the genetics are in doubt. Without that testing chocolate
103
KADI SARVA VISHWAVIDYALAYA 2014 -2016
S. K. PATEL Institute of Management & Computer Studies Gandhinagar.
manufacturers have to rely on their own experience and contacts within each cacao growing region to
find the best beans.
Processing in the field - Chocolate processing starts at the plantation where skilled personnel select
the right time to remove ripe pods from the trees and carefully extract the seeds (or beans) from the
pods. When Cacao beans are harvested they must first be properly fermented and dried. The care
given to the fermenting process is one of the most important factors in the quality of the chocolate.
Different varieties require different fermentation process to create the complex chemical change that
will take place within the bean and allow the true flavor of the chocolate to develop properly. Also
proper drying of the beans ensures the correct fermentation process is not compromised on the beans
long trip to the manufacturer.
Fine chocolate relies upon those plantations that have established a reputation for high quality
cultivation, pods selection, and fermentation/drying prior to shipping the beans to chocolate
manufacturers. Newer plantations have sprung up that produce smaller cacao production volume, or
more rare or mixed cacao product hoping to be supported by the demand for fine flavor chocolate.
CHOCOLATE PRODUCTION PROCESSES
Upon arriving at the bulk chocolate manufacturer, the fermented and dried beans are cleaned and
blended the blending (or not) of bean types is what helps establish the final flavor of the chocolate.
The blended beans are then roasted to remove moisture and further establish the final characteristics,
including aroma and flavor.
The shells are separated from the roasted bean (nib), which contains about 50% cocoa butter. The
nibs are crushed and refined into a paste. That paste is conched along with any additional ingredients
such as sugar, vanilla and lecithin. After conching the chocolate is tempered and poured into molds to
create blocks of bulk chocolate used by the chocolatier to create chocolate products such as bonbons,
pralines and bars.
The total percentage of cacao solids and cocoa butter in the chocolate is referred to in the industry as
cocoa liquor. The product can be called a number of different terms on a product label such as
chocolate liquor, unsweetened chocolate, cacao mass, cocoa mass, chocolate fondant, cocoa beans,
cacao beans, chocolate beans, cacao seeds, cocoa seeds, chocolate seeds..
The higher the cacao content, the lower the sugar content. This is important information for the
discerning consumer: cocoa percentage simply refects the sweetness of the product. Although a cacao
percentage may be high, that does not indicate that the chocolate is a fine chocolate. Given what we
have just learned, the origin of the cacao plant, the conditions under which it was grown and
harvested and proper fermentation, drying and production practices go a long way in creating a
distinctive flavor profile.
NON CHOCOLATE INGREDIENT QUALITY
104
KADI SARVA VISHWAVIDYALAYA 2014 -2016
S. K. PATEL Institute of Management & Computer Studies Gandhinagar.
Non-chocolate ingredients are all those elements that a chocolaty uses to complement the core
chocolate, for example: butter, heavy cream, nuts, spices, natural flavoring and colorings in bonbons,
pralines and bars.
Only pure flavoring ingredients such as sugar, vanilla, and soy lecithin ( a stabilizer) are acceptable
in dark chocolate bars . If the bar is flavored, it should be done so with natural spices , herbs or fruit
extracts. In milk chocolate, milk solids will be added to the mix. Cocoa butter is the only acceptable
fat ingredient - fine chocolates contain no vegetable or animal fats, and no artificial flavoring
ingredients.
Fine bonbons/pralines should use only the finest and freshest non-chocolate ingredients and little to
no chemical preservatives. When made into bon-bons, choose chocolates that use in their ganaches
only pure cream, butter, herbs, spices, and glucose. As you become aware of the quality of the
ingredients and orgins of your chocolate, so your palette will become more discerning.
CHOCOLATE TECHNICAL EXPERTISE
Chocolates arrive at their art from a variety of origins. Some are born into a family business and
learn the trade from their predecessors. Others arrive from other artistic endeavors such as chef,
painter or sculptor. Still others make a step change in their career path as a nurse, attorney, or other
non-food profession. Each Chocolatier brings with her all of her past experiences, professional and
personal, which in some way color her choices as a Chocolatier. Regardless their starting points,
however, Chocolatiers all share a passion for the chocolate arts.
Training is vital to the Chocolatier and encompasses not only the basics of chocolate tempering,
recipe development and artistic design, but also of safe food handling, packaging and business
acumen. As with any vital area, new concepts are constantly emerging in the chocolate arts, and the
Chocolatier must stay abreast of these developments.
The constant companion to training is experience; it is not enough to have only book knowledge in
the chocolate arts. The Chocolatier must invest hours upon hours of practice, experimentation, trialand-error, and refinement in order to consistently produce fine chocolate confections.
This combination of passion, training and experience enable the Chocolatier to make the proper
technical and artistic decisions that produce fine chocolate. How well has the Chocolatier selected
her core chocolates and non-chocolate ingredients? How well has the Chocolatier blended his
chocolates and ingredients into a finished product? As you bring the chocolate to your nose do you
detect a pleasant aroma? When you close your eyes and savor the first bite does the chocolate meet
your expectations of what its description and presentation promised? That moment of exquisite
pleasure that chocolate lovers experience begins with the Chocolatier.
ARTISTRY AND PRESENTATION
Fine chocolate products such as bonbons, pralines and bars benefit from their presentation, from the
shape and finish of the chocolate, to the packaging that contains the chocolate. Molds may be used
with fine hand detail work to present pieces that are like small pieces of sculpture. Hand-crafted
chocolates with irregular surfaces and a more rustic look also meet the presentation requirement of
105
KADI SARVA VISHWAVIDYALAYA 2014 -2016
S. K. PATEL Institute of Management & Computer Studies Gandhinagar.
fine chocolate, especially if such products elicit childhood memories or reflect back to simpler time
and place.
DEFINE SUBSTITUTE PRODUCT AND CRITERIA OF SUBSTITUTION.
Chocolate Substitutes
Chocolate
Amount
Substitute
3 Tablespoons Unsweetened (or Dutch) Cocoa Powder + Plus 1
Unsweetened Chocolate
1 Ounce (or 1
Tablespoon of either butter, margarine, shortening OR
substitute
Square)
vegetable oil
*OR* 3 Tablespoons Carob Powder +plus 2 Tablespoons Water
Bittersweet Chocolate
1 Ounce (or 1
1 Ounce Semisweet Chocolate
substitute
Square)
Semisweet Chocolate
1 Ounce (or 1 1 Ounce (or 1 square) or Unsweetened Chocolate +plus 4
substitute
Square)
teaspoons Sugar
*OR* 1 Ounce Semisweet Chocolate Chips +plus 1 teaspoon
Shortening
Semisweet Chocolate Chip 6 Ounce
6 ounces sweet cooking chocolate
substitute
package
*OR* 6 Ounces Unsweetened Chocolate +plus 6 Tablespoons
of Sugar
*OR* 2 ounces (2 squares) Unsweetened Chocolate +plus 2
Tablespoons of Shortening and 1/2 Cup Sugar
German Chocolate
6 Ounce
3 Tablespoons Cocoa Powder +plus 4 teaspoons Sugar +plus 1
substitute
package
Tablespoon of Butter
White Chocolate substitute 1 Ounce
1 Ounce Milk Chocolate
*OR* 1 ounce sweet dark Chocolate
Natural Unsweetened
Cocoa Powder substitute
1/4 Cup
1 Ounce (1 square) Unsweetened Chocolate
*OR* 1/4 Cup Dutch processed Cocoa plus 1/8 teaspoon cream
or tartar or white vinegar
*OR* 1/4 Cup Carob powder
1/4 Cup natural unsweetened Cocoa powder plus 1/8 teaspoon
baking soda
Dutch Processed Cocoa
substitute
1/4 Cup
106
KADI SARVA VISHWAVIDYALAYA 2014 -2016
S. K. PATEL Institute of Management & Computer Studies Gandhinagar.
Chocolate Substitute Warnings:
There are a few don'ts when substituting for chocolate:
Don't substitute chocolate syrup (because it contains water) for melted chocolate.
Don't substitute instant cocoa mixes (because they contain powdered milk) for cocoa powder.
Chocolate Substitute Choices:
To better understand what to substitute for chocolate, here's an explanation of what makes up each form of
chocolate.
All chocolate begins the same - Cacao beans are roasted and shelled - but they are then processed into
different varieties. Varieties include:
Unsweetened chocolate - is pure & natural chocolate liquor (not alcohol, that's just what the chocolate
liquid is called when it is processed and separated from the fatty part of the bean). It's most often used in
brownies.
Bittersweet chocolate - is 35% chocolate liquor, some cocoa butter has been added back in along with a
very small amount of sugar.
Semisweet chocolate- this dark chocolate has some sugar and flavoring added. By U.S. standards it may
contain between 15-35% chocolate liquor which make some brands of semisweet the same as bittersweet,
depending on the manufacturer.
Semisweet Chocolate Chips - have a stabilizer added so they will hold their shape.
Baking chocolate - is either unsweetened or bittersweet chocolate (50-58% cocoa butter by US
standards).
Milk chocolate - is made of chocolate, milk solids, sugar and vanilla (and/or other flavors).
Cocoa Powder- this powder is what's left after all the fat (cocoa butter) has been pressed from the
chocolate.
White Chocolate - is only the cocoa butter portion of the bean which is then generally mixed with milk,
sugar and salt. This type of chocolate is the fattiest and contains NO antioxidents because it contains none of
the dark color solids from the bean.
Remember, when making substitutions be sure to measure accurately for best results. Some chocolate
substitutes or cocoa powder substitutes may alter slightly the taste, texture, weight, or moisture content of
the finished product. These recommendations are meant to save you a trip to the store during your cooking
process.
PRODUCT HISTORY
The first recorded evidence of chocolate as a food product goes back to Pre-Columbian Mexico. The
Mayans and Aztecs were known to make a drink called "Xocoatll from the beans of the cocoa tree.
In 1528, the conquering Spaniards returned to Spain with chocolate still consumed as a
107
KADI SARVA VISHWAVIDYALAYA 2014 -2016
S. K. PATEL Institute of Management & Computer Studies Gandhinagar.
beverage.
A similar chocolate drink was brought to a royal wedding in France in 1615, and England welcomed
chocolate in 1662. To this point "chocolate" as we spell it today, had been spelled variously as
"chocalatall, "jocolatte", "jacolatte", and "chockelet.11
In 1847, Fry & Sons in England introduced the first "eating chocolate," but did not attract much
attention due to its bitter taste. In 1874, Daniel Peter, a famed Swiss chocolateer, experimented with
various mixtures in an effort to balance chocolates rough flavor, and eventually stumbled upon that
abundant product -- milk. This changed everything and chocolate's acceptance after that was quick
and enthusiastic.
1
GROWING COCOA BEANS
1
Cocoa beans are usually
grown on small plantations in suitable land areas 20 degrees north or south of the Equator.
One mature cocoa tree can be expected to yield about five pounds of chocolate per year.
These are planted in the shade of larger trees such as bananas or mangos, about 1000 trees per
hectare (2,471 acres).
Cocoa trees take five to eight years to mature. After harvesting
from the trees, the pods (which contain the cocoa beans) are
split open, beans removed, and the beans are put on trays
covered with burlap for about a week until they brown. Then
they are sun dried until the moisture content is below 7%. This
normally takes another three days.
After cleaning, the beans are weighed, selected and blended before roasting at 250 degrees
Fahrenheit for two hours. Then shells are removed leaving the "nib." Nibs are crushed to create a
chocolate "mass." This is the base raw material from which all chocolate products are made.
KINDS OF CHOCOLATE
108
KADI SARVA VISHWAVIDYALAYA 2014 -2016
S. K. PATEL Institute of Management & Computer Studies Gandhinagar.
Milk Chocolate
This consists of at least 10% chocolate liquor ("raw" chocolate pressed from carob nibs) and 12%
milk solids combined with sugar, cocoa butter (fat from nibs), and vanilla. Sweet and Semi-Sweet Chocolate
Are made from 15-35% chocolate liquor, plus sugar, cocoa butter, and vanilla. Imprecision of the two terms
causes them to commonly be called "dark" or "plain" chocolate. Dark chocolate has a large following among
dessert makers, and for this reason is referred to as "baking" chocolate.
Bittersweet and Bitter Chocolate
Bittersweet usually contains 50% chocolate liguor and has a distinct "bite" to the taste. Bitter or
unsweetened chocolate liquor also is used in baking and is also referred to as "bakers" chocolate.
Creams and Variations
Bite sized and chocolate covered. They are filled with caramels, nuts, creams, jellies, and so forth.
White Chocolate
Is not really chocolate as it contains no chocolate liquor, Carob This is a brown powder made from the
pulverized fruit of a Mediterranean evergreen. It is used by some as a substitute for chocolate because it can
be combined with vegetable fat and sugar, and made to approximately the color and consistency of
chocolate.
HOW CHOCOLATES ARE MADE
There are four basic methods of coating chocolate onto something such as caramel or a nut.
109
KADI SARVA VISHWAVIDYALAYA 2014 -2016
S. K. PATEL Institute of Management & Computer Studies Gandhinagar.
They are:
Enrobing
Least expensive method. Centers are carried by conveyer through a machine that showers them with
chocolate.
Panning
Chocolate is sprayed on the centers as they rotate in revolving pans, then cool air is blown in pan to
harden the chocolates.
Dipping
Generally done by hand by small scale producers. Shell Moldinq Most sophisticated method. Used
for most sculptural chocolates. The process consists of many intricate steps, thus causing it to be
more expensive than other methods.
PRODUCT LIFE CYCLE
110
KADI SARVA VISHWAVIDYALAYA 2014 -2016
S. K. PATEL Institute of Management & Computer Studies Gandhinagar.
CHAPTER: 14
Industry Analysis
111
KADI SARVA VISHWAVIDYALAYA 2014 -2016
S. K. PATEL Institute of Management & Computer Studies Gandhinagar.
PORTERS FIVE FORCE MODEL FOR CADBURY
Five Forces model of Porter is a strategy tool that is used to make an analysis of the attractiveness of
an industry structure. The Competitive Forces analysis is made by the identification of 5 fundamental
competitive forces:
Entry of competitors
The entry of competitors will be difficult because there are already well established companies within
this market these include, mars, nestle, Ferrero, Kraft, Hersheys and Lindt. These companies
dominate the confectionary market with their own particular types of chocolates.
This makes the barrier for entry very hard for another new company to start Cadburys competitors
have the power to attract and influence the customers by more attractive substitute, prices and
marketing techniques.
Threat of substitutes
The main threat of substitutes which Cadburys and any other confectionary brand is the supermarket
own brands this is because they tend to copycat popular chocolates for example nestle Kit Kat and
provide their own brand on the shelves at a cheaper price.
Moreover, the only hindrance that might affect the production of Cadbury is to find a good location
and gather the requirements for the smooth entry and the foreign policy that might affect its
operation.
Bargaining power of buyers
112
KADI SARVA VISHWAVIDYALAYA 2014 -2016
S. K. PATEL Institute of Management & Computer Studies Gandhinagar.
For Cadburys they have a large buying power being one of the largest confectionary producers in the
world, but this may be threatened due to the June 2006 recall of chocolate bars which contained
salmonella this has been said to affect Cadburys and should lose some of their buying power.
However Cadburys buyers are scattered all around the world and they are in billions. The price
subjectivity of the products is not a question for the people but the increasing number of competitors
that offers the same type of products at a lower cost might be the cause of customer loyalty alteration.
Thus Cadbury has to be very precautious in deciding about prices and keep the customers satisfied.
Bargaining power of suppliers
Cadbury prides itself on creating and maintaining positive relationships with its suppliers all over the
world. It has a large purchasing power and the suppliers of agricultural commodities offer a product
that is far from unique and hence Cadbury has higher bargaining power than its suppliers as the
industry relies heavily on a complex agro business supply chain.
Although there is an existing competition, raw materials like nuts, milk, cocoa or special ingredients
are sufficient enough to satisfy Cadburys production. Cadburys have the main power over its
suppliers because they are so large companies supplying them need their business so Cadburys can
use economies of scale and buy there raw materials for cheaper and more in bulk than a medium
sized business could.
Rivalry among the existing players
Many businesses are competing against Cadbury and planning to take over the supremacy the
company has for several years. Several competitors are continuously developing their products and
innovating ideas to make competing even harder. Companies such as Nestle, Hersheys, Ferrero etc.
are Cadburys main rivals because they are also long established confectionary brands and like
Cadbury are developing new ranges of products new promotions.
Rivalry will always be strong among these companies because they sell from the same types of stores
and their products are similar in some respects.
113
KADI SARVA VISHWAVIDYALAYA 2014 -2016
S. K. PATEL Institute of Management & Computer Studies Gandhinagar.
CHAPTER: 15
BCG MATRIX
114
KADI SARVA VISHWAVIDYALAYA 2014 -2016
S. K. PATEL Institute of Management & Computer Studies Gandhinagar.
BCG MATRIX for Cadbury
Boston consulting group Matrix based on Product life cycle approach to use the charts analyst plot a
scattered graph to rank line product on the basis of relative market shares and growth rate. The BCG
Matrix is used in business to under where to invest, harvest, and divest. This Matrix also shows the
relationship between cash-generating products and cash caters.
1) StarProduct in rapidly growing Networks in which the company has high relative market share. Star
products generates the high earning potencials is likely to be needed is the company wants to retain
its market positions as competitiors will be trying to ambulate stars. Cadbury india has two star
products Cadbury dialy milk chocolates with 30% market share in chocolate market & Cadbury
bournvilla 16.2% share in method foods category.
2) Cash Cows: Products in slow growth, or even static, market in which they have relatively high market share are
called as Cash Cows. They require little promotion although under investment can turn them into
dogs . they should not be taken for granted. The company's objective is likely to be hold this position
in order to obtain maximum return on investment (ROI). Cadbury India has two cash cow products
Perk & Gums
3) Dogs: Dogs are in stagnant or slow-growing markets have relatively low market Share. One company's dog
can become another's cash cow or even a star if they are operating in different markets or market
segments. Cadbury India has three dogs 5 Star. GEMS & Eclairs.
4) Question mark: Products in this quadrant are in rapid growing market but hold a relatively low market share.
Cadbury India has two dogs Toblerone & Bournville
115
KADI SARVA VISHWAVIDYALAYA 2014 -2016
S. K. PATEL Institute of Management & Computer Studies Gandhinagar.
Swot Analysis:
Strength:
High brand equity and top of the mind chocolate brand.
Strong brand recall and customer loyalty.
An employee strength of around 71,000.
Strong parent brand of Kraft Foods.
Successful marketing and advertising campaigns.
A wide variety of products on offer.
116
KADI SARVA VISHWAVIDYALAYA 2014 -2016
S. K. PATEL Institute of Management & Computer Studies Gandhinagar.
Weakness:
A few controversies regarding advertising, worms etc made international news.
A few instances of product recall hampering brand image.
Opportunity:
Increase reach in rural markets.
Increase its reach and penetration in untapped markets
Acquire competition.
Diiversification of product range.
Threats:
Health consciousness amongst people .
Increase in cost of raw material.
Inflation can cause reduction in sales.
Nestle and BCG matrix strategy:
Nestle is a multinational food and beverage producer, based in Switzerland. The firm currently has the 69th
highest revenue in the world, generating $98,484m worth of sales in 2012. Nestle sell over 8,000 brands,
ranging from bottled water to pet food, of which 29 brands have sales of approximately $1 billion. However,
Nestles CEO, Paul Baulk, recently announced plans to divest (sell-off) under-performing brands due to poor
sales.
It is highly likely that the marketers at Nestle have used the Boston Consulting Group Matrix (BCG Matrix)
to identify which brands to sell off. This post will look at what Nestles BCG Matrix is likely to look like
and critique how useful the matrix is.
Based on recent news sources and Nestles 2012 Annual Report (PDF), here is Nestles current BCG Matrix
for a slection of their brands:
1)Question MarksThese strategic business units (SBUs) have a low market share of a high growth market. Magi 2-minute
Noodles currently require lots of investment in order to capitalize on the growing culinary segment, which
may not offer the highest return on investment in Nestles brand portfolio.
117
KADI SARVA VISHWAVIDYALAYA 2014 -2016
S. K. PATEL Institute of Management & Computer Studies Gandhinagar.
2)Stars
SBUs with a high share of a high growth market. Nestles wide range of mineral water has benefited from
the combination of healthier lifestyle trends and emerging markets. These products require large amounts of
investments in order to differentiate the bottled water brands from competitors in mature markets and grow
brand awareness in emerging markets.
3)Dogs
SBUs in this category have a low market share in a low growth market. Sales of Jenny Craig and Lean
Cuisine, weight loss management brands, have failed to expand outside of the USA these two brands are
tipped to be divested in the future. Sports performance and nutrition brand, PowerBar, is confirmed to be
divested. This is most likely because of poor sales in a saturated market. SBUs in this classification may
generate enough profit to be self-sufficient, be are considered to never be major sources of revenue.
4)Cash Cows
perhaps the most important SBU, Cash Cows have a high share of a low growth market. They require very
little investment to generate revenue, which allows funds generated from such SBUs to be reinvested into
Stars or Question Marks.
Although Nestle appear to have taken the recommendations from the BCG Matrix, there is no such thing as
a fool-proof strategic tool. As such, Nestle should be aware of the following drawbacks of using this
analysis:
118
KADI SARVA VISHWAVIDYALAYA 2014 -2016
S. K. PATEL Institute of Management & Computer Studies Gandhinagar.
Swot Analysis:
Strengths:
Globally recognized as one of the largest and powerful food producers, covering almost every country
(factories and plants). Employs approximately 280,000 people globally. Powerful brand positioning in the
consumers mind. It has a vastly diversified product portfolio containing approximately 6000 brands
(beverages, ice creams, frozen food items, chocolates and biscuits, pet care nutrition items, etc.).
Top 50 list of Fortunes Americas Most Admired Food Companies, and ranked on top on Consumer Food
Products. Strong internal growth and emphasis on innovation internally. Strong cultural environment, that
acts as a loyalty carrier for the employees.
Nestle has taken a visionary step as being one of the many companies that represent and encourage
globalization that has also become an identity for its logo. Quality is a vital element regarding nestle
products. Largest consumer products organization that operates globally Powerful marketer, and never seizes
any opportunity to embed the brand image in the mind of the consumer. It also has low operating costs.
Globally, biggest ice-cream producer, having a market share of approximately 17.5% (2006).
Weaknesses:
Hovering over the stats of 2008, the food industry grew 8.9% but Nestle lacked the potential to raise their
sales in the organic food division that lay flat.
Regulators like FDA and AMA (American Medical Association) are pressing on the firm for removing tags
that hold no ground such as low cholesterol or heart healthy. Parents have also reported diabetic epidemic
due to the consumption of such goods, in children especially. Promoting infant milk products comparing to
breastfeeding.
Coordination between country specific plants with the Center, due to which some plants are running
exceptionally smooth while operations in other countries lack effectiveness. Transportation as well as storage
(proper warehousing) problems.
Supply Chain having a complex stature (India plant transitional traceability). The immense diversification
portfolio of the firm makes it impossible to run every division smoothly.
Opportunities:
Due to the high intensity of the health conscious awareness in the society, more health based products are
required especially not compromise in quality. Can go into the anti-allergy products that are very common,
such as peanut free or gluten free products.
They can also invest in snacks that would further diversify its product portfolio. LC-1 having the opportunity
of having a greater impact in Germany (2 years had them go for 60% of the market share), and being the
established market leader, they can establish more brands in the market.
119
KADI SARVA VISHWAVIDYALAYA 2014 -2016
S. K. PATEL Institute of Management & Computer Studies Gandhinagar.
Middle class share in most of the economies are growing much larger. Nestle India may hold the position
of being the export hub due to the low cost of labour comparatively to developed countries.
Recession has created such an impact that the market is struggling and has almost got out of that
recession that will surely increase the cycle of cash flow which will be profitable for Nestle to cash in on
such a time.
Threats:
Contamination of products should be regarded strictly (Cookie Dough, March 2009). The company has a
not so pretty history with the FDA. Pet Food contamination 2007 (imported from China, the vegetables
contained rat poison).
Inflation rise is giving birth to high prices. Raw chocolate prices are jumping, along with the Dairy costs;
which leaves heavy cuts in the margin in order to make the customers brand loyal. They have also shrink the
packaging which is not really noticeable, so the customers are paying the same amount for a lesser product.
Competitors like Cadbury Schweppes, Hersheys, Quaker, Heinz, Del Monte, Kelloggs, and Kraft Foods
are also well established. Its a tough market with a tougher competition for gaining market share. Market is
quite mature and the competitors specialize in a certain product that can hit hard on Nestle. (Yogurt Market
US: General Mills).
In the Indian market, fresh food is preferred than ready-to-eat meals. In still developing countries as well as
underdeveloped countries, Nestle will
Strengths and Weaknesses
Strengths of the BCG Model:
The BCG Matrix allows for a visual presentation of the competitive position of all units in a business
portfolio.
The BCG model allows companies to develop a customized strategy for each product or business unit
instead of having a one-size-fits-all approach.
Simple and easy to understand.
It works well for companies with multiple divisions and products
Allows for quick and simple screening of business opportunities in order to determine investment
priorities in the portfolio of products/business units.
It is used to identify how corporate cash resources can be best allocated to maximize a companys
future growth and profitability.
Useful for the development of investment, marketing and operating decisions:
o a. Investment in the business unit in order to build its market share
o b. Sufficient investment to maintain the business unit's market share at the current level
120
KADI SARVA VISHWAVIDYALAYA 2014 -2016
S. K. PATEL Institute of Management & Computer Studies Gandhinagar.
o c. Determine which business unit/product will function as a cash cow to provide necessary
cash flow for the other business units/products
o d. Divest a business unit
Weaknesses of the BCG Model:
The BCG model assumes that high market share and market growth are the only success factors.
Based on numerous real life examples, we can conclude that high market share does not always lead
to profitability. Businesses with low market share can be highly profitable as well. Relative market
strength is also determined by the following factors which the BCG does not take into account:
o a. Technological competence
o b. Ability to maintain low manufacturing costs
o c. Financial strength of competition
o d. Distribution capabilities
o e. Human resources
The BCG model focuses on major competitors when analyzing the relative market share of a
company. However, it neglects some small competitors with fast growing market shares.
It is a rather short-term model that doesnt fully show how characteristics of business units change
over the long term.
The BCG model is more focused on business units than individual products
Assumes that high rates of profit are directly related to high market share
The BCG model looks at a business unit in isolation without taking into consideration the possible
cooperation among various business units within the organization
BCG is a primarily qualitative model
The Y axis represents the annual market growth which fails to see the full picture that goes beyond a
one year span
It does not take into consideration other important factors such as: market barriers/restrictions,
market density, profitability, politics
121
KADI SARVA VISHWAVIDYALAYA 2014 -2016
S. K. PATEL Institute of Management & Computer Studies Gandhinagar.
With this or any other such analytical tool, ranking business units has a subjective element involving
guesswork about the future, particularly with respect to growth rates.
Application to Competitive Intelligence: Automotive Industry
GE/MCKINSEY MATRIX
Background
The GE/McKinsey Matrix was developed jointly by McKinsey and General Electric in the early
1970s as a derivation of the BCG Matrix. GE, by that time, had approximately 150 different business
units and was disappointed with the profits derived from its investments. This raised internal
concerns about the approach the organization had to investment decision making. While exploring
new models to implement, GE started to be interested in visual strategic frameworks like the GrowthShare Matrix created by the Boston Consulting Group (BCG) a few years before. However, the BCG
Matrix showed to have some limitations. It was considered not flexible enough to include all the
broader issues that a company was facing while operating in a fast changing global environment. The
GE/McKinsey Matrix solves most of the issues of the BCG model and proposes a more sophisticated
and comprehensive approach to investment decision making.
How it Works
The GE/McKinsey Matrix is a nine-cell (3 by 3) matrix and it is primary used to perform business
portfolio analysis on the strategic business units (SBU) of a corporation. A business portfolio is the
collection of all the business units within a corporation and a large corporation has normally many
SBUs. Each SBU is a distinctive and unique unit that falls under the same strategic hat. A well
balanced portfolio is one of the top priorities of a large organization. The strategic business units are
the basic blocks that compose a business portfolio. A unit can be a divisions or even a whole
company owned by the parent organization.
The nine-box matrix provides decision makers with a systematic and effective framework for a
decentralized corporation to make better supported investment decisions and for developing
strategies for future product development or new market segment entries. Instead of looking solely at
each unit's future prospects, a corporation can adopt a multi-dimensional approach based on two
components that will indicate how well the unit will perform in the future. The two components used
to evaluate businesses, which also serve as the axes of the matrix, are the 'attractiveness' of the
relevant industry and the unit's 'competitive strength' within the same industry. Each axis is then
divided into Low, Medium and High.
122
KADI SARVA VISHWAVIDYALAYA 2014 -2016
S. K. PATEL Institute of Management & Computer Studies Gandhinagar.
Figure 2: Factors that influence the axes of the GE/McKinsey Matrix
Six steps are necessary to implement the GE/McKinsey analysis:
1. Determine which factors are relevant for the corporation in the industry where it operates
2. Assign a weight to each factor
3. Score each factor
4. Multiply the relative scores and weights
5. Sum all up and interpret the graph
6. Perform a review / sensitivity analysis
The plotted circles convey the information in the following way:
The size of the circle represents the market size of the SBU
The share owned by the SBU is expressed as a pie slice with its relative percentage inside
The expected future direction of the SBU is represented with an arrow
The circles representing SBUs are then placed within the matrix. As a result, the executives of the
corporation will have a clear and powerful analytic map for understanding and managing their entire multi123
KADI SARVA VISHWAVIDYALAYA 2014 -2016
S. K. PATEL Institute of Management & Computer Studies Gandhinagar.
unit business. The units that fall above the diagonal indicate the investment and growth to be pursued; the
units along the diagonal require a thorough analysis and individual selection for investment; finally the units
below the diagonal might indicate divestments are necessary or otherwise that businesses can be kept only
for cash reasons. The placement of the units within the matrix is a necessary first step before the analysis
phase that requires human judgement can begin. For example, a strong unit in a weak industry is in a very
different situation than a weak unit in a highly attractive industry.
Strengths and Weaknesses
The GE/McKinsey Matrix, as an extension of the BCG framework, shares the aforementioned
advantages of the BCG model. Though the GE/McKinsey Matrix is more sophisticated than the BCG
matrix and can provide higher value information for the executive management, it has several flaws
and limitations:
No proven relationship between market attractiveness and business position.
The relationships between different units are not taken into account.
The core-competencies that lead to value creation are not taken into consideration.
The approach requires extensive data gathering.
Scoring is personal and subjective (risk of bias)
There is no hard and fast rule on how to weight elements.
The GE/McKinsey Matrix offers a broad strategy and does not indicate how best to implement it.
For the above limitations and issues, the GE/McKinsey Matrix can serve more as a quick strategic
visual framework rather than as a resource allocation tool.
Application to Competitive Intelligence: Apple Inc.
124
KADI SARVA VISHWAVIDYALAYA 2014 -2016
S. K. PATEL Institute of Management & Computer Studies Gandhinagar.
Apple Inc. is a large technology company with several business units operating in different markets,
including desktop computers, laptops, tablet computers (iPads), portable music players (iPods),
smartphones (iPhones) and software to support these products. A competitor wishing to gain
competitive intelligence on the activities of Apple Inc. could do so by placing its business units into a
GE/McKinsey Matrix. By analyzing this matrix, it could determine which business units Apple is
likely to invest in heavily, develop selectively, or divest.
The market attractiveness axis would be relatively easy for the competitor to assess if it is currently
operating in that market, since this consists of factors external to Apple. This includes easily
obtainable information such as the current market size and market growth rate. However, some
factors would have to be assessed subjectively, such as barriers to entry and the state of technological
development.
In contrast, the business unit strength axis would be more difficult to assess since it consists of
factors internal to the company, such as customer loyalty, access to resources, and management
strength. However, a great deal of information could be obtained from secondary sources, such as the
Internet, the media, and shareholder reports.
Figure 4: Assessment of Apple business units in the GE/McKinsey Matrix
From an assessment of the above GE/McKinsey Matrix, it becomes clear that Apple is at least
moderately strong in each of its business units and it competes in a number of attractive and fastgrowing segments, such as tablet computers and smartphones. A competitor performing this analysis
would realize that Apple is unlikely to divest any of these business units and is likely using its
personal computer and music products as cash cows in order to fund R&D and growth in the fastergrowing markets. The barriers to entry in all of these markets are considerable, since entry would
require a large amount of funding for either R&D or the acquisition of the necessary technology and
expertise. If the company performing this analysis decides to compete with Apple, it should do so in
the newest, fastest-growing markets (tablets and smartphones), as these represent the areas of greatest
opportunity, despite Apples early dominance.
125
KADI SARVA VISHWAVIDYALAYA 2014 -2016
S. K. PATEL Institute of Management & Computer Studies Gandhinagar.
126
KADI SARVA VISHWAVIDYALAYA 2014 -2016
S. K. PATEL Institute of Management & Computer Studies Gandhinagar.
CHAPTER: 16
FINANCIAL ANALYSIS
127
KADI SARVA VISHWAVIDYALAYA 2014 -2016
S. K. PATEL Institute of Management & Computer Studies Gandhinagar.
FINANCIAL ANALYSIS
128
KADI SARVA VISHWAVIDYALAYA 2014 -2016
Dec '09 Dec '08 Dec '07 Dec '06
Dec '05
Dec '09
Dec '08
Dec '07
Dec '06
S. K. PATEL Institute of Management & Computer Studies Gandhinagar.
Investment Valuation Ratios
Face Value
10.00
10.00
10.00
10.00
Dividend Per Share
2.00
2.00
2.00
2.00
Operating Profit Per Share (Rs)
860.21
67.91
51.73
40.56
Net Operating Profit Per Share (Rs)
6,226.39 493.61
389.56
308.02
Free Reserves Per Share (Rs)
--111.56
99.75
Bonus in Equity Capital
84.02
81.11
78.61
75.97
Profitability Ratios
Operating Profit Margin(%)
13.81
13.75
13.27
13.16
Profit Before Interest And Tax
11.47
11.28
10.44
9.88
Margin(%)
Gross Profit Margin(%)
11.54
11.45
10.62
14.11
Cash Profit Margin(%)
11.93
12.53
11.18
9.53
Adjusted Cash Margin(%)
11.93
12.53
11.18
9.97
Net Profit Margin(%)
9.68
10.27
8.94
6.42
Adjusted Net Profit Margin(%)
9.68
10.27
8.94
6.85
Return On Capital Employed(%)
43.48
40.91
38.44
29.68
Return On Net Worth(%)
35.53
35.69
28.96
17.55
Adjusted Return on Net Worth(%)
35.53
35.69
27.77
19.42
Return on Assets Excluding
1,708.53 144.30
122.32
9.78
Revaluations
Return on Assets Including
1,708.53 144.30
122.32
9.78
Revaluations
Return on Long Term Funds(%)
43.48
43.68
38.56
29.92
Liquidity And Solvency Ratios
Current Ratio
1.04
1.12
0.61
0.61
Quick Ratio
0.68
0.79
0.22
0.20
Debt Equity Ratio
0.02
0.09
0.02
0.03
Long Term Debt Equity Ratio
0.02
0.02
0.02
0.02
Debt Coverage Ratios
Interest Cover
136.88
39.80
106.72
77.60
Total Debt to Owners Fund
0.02
0.09
0.02
0.03
Financial Charges Coverage Ratio
162.29
46.82
95.43
68.67
Financial Charges Coverage Ratio
135.78
39.88
75.82
46.95
Post Tax
Management Efficiency Ratios
Inventory Turnover Ratio
10.23
7.86
11.04
8.78
Debtors Turnover Ratio
76.20
96.83
105.54
95.97
Investments Turnover Ratio
10.23
7.86
11.04
10.41
Fixed Assets Turnover Ratio
2.67
2.71
2.40
4.90
Total Assets Turnover Ratio
3.56
3.14
3.16
2.67
Asset Turnover Ratio
2.67
2.71
2.40
2.49
Dec '05
Average Raw Material Holding
--42.87
Average Finished Goods Held
--28.10
Number of Days In Working Capital
3.68
28.99
-43.07
KADI
SARVA
VISHWAVIDYALAYA
2014
-2016
Profit & Loss Account Ratios
Material Cost Composition
43.02
46.11
43.53
Imported Composition of Raw
53.76
24.77
-38.19
--129
-13.79
41.72
27.98
10.00
2.00
27.73
246.37
-7.66
73.08
11.25
7.23
12.83
8.91
8.91
5.11
5.11
18.74
10.59
11.30
6.96
6.96
18.74
0.85
0.38
0.02
0.02
48.73
0.02
68.77
48.07
8.77
49.89
9.83
4.92
1.99
2.22
S. K. PATEL Institute of Management & Computer Studies Gandhinagar.
Key Financial Ratios of Cadbury India
CHAPTER: 17
OT Analysis
130
KADI SARVA VISHWAVIDYALAYA 2014 -2016
S. K. PATEL Institute of Management & Computer Studies Gandhinagar.
OT VIII is the highest current auditing level in Scientology. Collectively, the OT levels are referred
to as the Operating Thetan materials or "advanced technology." OT VIII is known as "The Truth
Revealed" and was first released to the public in 1988.
"This Solo-audited level addresses the primary cause of amnesia on the whole track and lets one see
the truth of his own existence. This is the first actual OT level and brings about a resurgence of
power and native abilities for the being himself. This may be done at the Flag Ship Service
Organization only."
Contents
1 Versions of OT VIII
1.1 "Original" (Fishman) version
1.2 "Revised" (Wikileaks) version
2 References
Versions of OT VIII
Various outlines purporting to describe New OT VIII have been provided by ex-members who have
completed the course, such as Ariane Jackson and Michael Pattinson. Jackson has described the
course as having two parts: a preparatory e-meter drill, followed by a review of Scientology: A
History of Man and an examination of previously identified past lives to find out which ones are
false. According to Pattinson, the course included an affirmation from L. Ron Hubbard that "now he
[Pattinson] knew who he wasn't, and was interested in finding out who he was."
"Original" (Fishman) version
In August 1995, Arnie Lerma posted the Fishman papers on the Internet. The posting contained
disputed portions of OT VIII, including an exercise for communicating with animals and plants, and
a passage depicting Jesus Christ as a "lover of young boys and men ... given to uncontrollable bursts
of temper and hatred."
In OT VIII, dated 1980, Hubbard explains the document is intended for circulation only after his
death. Its purpose is to explain the untold story of Hubbard's life's work. Hubbard explains that the
reader has "undoubtedly heard pieces of data over the years that hinted at the greater untold reality of
my mission here on Earth" but "the story was never written, nor spoken... It is only now that I feel it
safe to release the information".
131
KADI SARVA VISHWAVIDYALAYA 2014 -2016
S. K. PATEL Institute of Management & Computer Studies Gandhinagar.
Hubbard mentions the Book of Revelation and its prophecy of a time when "an arch-enemy of Christ,
referred to as the anti-Christ, will reign". According to Hubbard, the "anti-Christ represents the forces
of Lucifer". Hubbard writes "My mission could be said to fulfill the Biblical promise represented by
this brief anti-Christ period."
Church of Scientology lawyers have asserted that the OT VIII documents posted by Lerma are fake;
George White, a public scientologist who had received OTVIII in the summer of 1988, asserts the
document is authentic. Frank Oliver, a former operative with Scientology's Office of Special Affairs,
reports having discovered the document in the church's archives.Lawrence Wollersheim, a notable
defector, claims they are genuine: "Two sets of defectors, at different times in different parts of the
world, came out with those documents," he says. "I've been working with defectors for fifteen years.
I have never dealt with anyone as afraid of having their identity revealed as the people who came out
and verified those documents." Jesse Prince, former second-in-command of Scientology's Religious
Technology Center, reports that OTVIII was revised after early participants were "horribly upset" by
the content.
"Revised" (Wikileaks) version
On March 24, 2008, Wikileaks placed what it claimed was a complete set of OT levels on their site,
including a version of OT VIII not previously publicly available. The Church of Scientology
objected, arguing that posting this information on the Wikileaks website was clear violation of
copyright. Wikileaks did not remove the documents and said the legal action ironically verified that
the documents were authentic.
132
KADI SARVA VISHWAVIDYALAYA 2014 -2016
S. K. PATEL Institute of Management & Computer Studies Gandhinagar.
CHAPTER: 18
Problems identification,
problems analysis and remedial measures
133
KADI SARVA VISHWAVIDYALAYA 2014 -2016
S. K. PATEL Institute of Management & Computer Studies Gandhinagar.
Autism therapies are therapies that attempt to lessen the deficits and behaviours associated with
autism and other autism spectrum disorders (ASD), and to increase the quality of life and functional
independence of autistic individuals, especially children. Treatment is typically catered to the child's
needs. Treatments fall into two major categories: educational interventions and medical management.
Training and support are also given to families of those with ASD.
Studies of interventions have methodological problems that prevent definitive conclusions about
efficacy. Although many psychosocial interventions have some positive evidence, suggesting that
some form of treatment is preferable to no treatment, the methodological quality of systematic
reviews of these studies has generally been poor, their clinical results are mostly tentative, and there
is little evidence for the relative effectiveness of treatment options.
Intensive, sustained special education programs and behavior therapy early in life can help children
with ASD acquire self-care, social, and job skills, and often can improve functioning, and decrease
symptom severity and maladaptive behaviors; claims that intervention by around age three years is
crucial are not substantiated.
Available approaches include applied behavior analysis (ABA), developmental models, structured
teaching, speech and language therapy, social skills therapy, and occupational therapy. Educational
interventions have some effectiveness in children: intensive ABA treatment has demonstrated
effectiveness in enhancing global functioning in preschool children, and is well established for
improving intellectual performance of young children.
Neuropsychological reports are often poorly communicated to educators, resulting in a gap between
what a report recommends and what education is provided. The limited research on the effectiveness
of adult residential programs shows mixed results.
Many medications are used to treat problems associated with ASD. More than half of U.S. children
diagnosed with ASD are prescribed psychoactive drugs or anticonvulsants, with the most common
drug classes being antidepressants, stimulants, and antipsychotics.[
Aside from antipsychotics, there is scant reliable research about the effectiveness or safety of drug
treatments for adolescents and adults with ASD.A person with ASD may respond atypically to
medications, the medications can have adverse effects, and no known medication relieves autism's
core symptoms of social and communication impairments.
Many alternative therapies and interventions are available, ranging from elimination diets to
chelation therapy. Few are supported by scientific studies. Treatment approaches lack empirical
support in quality-of-life contexts, and many programs focus on success measures that lack
predictive validity and real-world relevance.
Scientific evidence appears to matter less to service providers than program marketing, training
availability, and parent requests. Even if they do not help, conservative treatments such as changes in
diet are expected to be harmless aside from their bother and cost. Dubious invasive treatments are a
much more serious matter: for example, in 2005, botched chelation therapy killed a five-year-old boy
with autism.
134
KADI SARVA VISHWAVIDYALAYA 2014 -2016
S. K. PATEL Institute of Management & Computer Studies Gandhinagar.
Treatment is expensive; indirect costs are more so. For someone born in 2000, a U.S. study estimated
an average discounted lifetime cost of $4.05 million (2015 dollars, inflation-adjusted from 2003
estimate), with about 10% medical care, 30% extra education and other care, and 60% lost economic
productivity. A UK study estimated discounted lifetime costs at 1.59 million and 1.03 million for
an autistic person with and without intellectual disability, respectively (2015 pounds, inflationadjusted from 2005/06 estimate). Legal rights to treatment are complex, vary with location and age,
and require advocacy by caregivers.
Publicly supported programs are often inadequate or inappropriate for a given child, and
unreimbursed out-of-pocket medical or therapy expenses are associated with likelihood of family
financial problems; one 2008 U.S. study found a 14% average loss of annual income in families of
children with ASD, and a related study found that ASD is associated with higher probability that
child care problems will greatly affect parental employment.
After childhood, key treatment issues include residential care, job training and placement, sexuality,
social skills, and estate planning.
135
KADI SARVA VISHWAVIDYALAYA 2014 -2016
S. K. PATEL Institute of Management & Computer Studies Gandhinagar.
CHAPTER: 19
Conclusion
136
KADI SARVA VISHWAVIDYALAYA 2014 -2016
S. K. PATEL Institute of Management & Computer Studies Gandhinagar.
Conclusion :
The per capita consumption of chocolate in India is 300 gram compared with 1.9 kilograms in
developed markets such as the United Kingdom.
The Cadbury's chocolates should start concentrating more and more on potential markets in India.
Measures should be taken to ensure brand loyalty as well as introduction of 'Saving Packs.'
Talking about rural and semi urban markets, the company can re-brand some of its products which
appear a little easy on the pocket.
A new brand ambassador who can appeal strongly to the youth of small towns and villages would
help the company in terms of exploring new markets.
More of outdoor promotion activities are suggested.
Increased use of Traditional media like Setting up Cadbury's stalls in small fairs.
A new concept of Cadbury's Jhoola (Swing) should be infroduced in all public parks in towns and
villages where anyone who takes more than 5 rides would get a small Cadbury's Perk free.
Cadbury's should set up small Tapris (Tea joint) where all the products of Cadbury's are available in
small packs (so that it doesn't feel too expensive).
Cadbury's should sponsor the Ramlila and Krishna Janmashtami in a large number of villages all
around the country and set up Cadbury's sales stalls in the venue.
All the products sold at such places should not exceed the price limit of Rs 5.
137
KADI SARVA VISHWAVIDYALAYA 2014 -2016
S. K. PATEL Institute of Management & Computer Studies Gandhinagar.
CHAPTER : 20
Bibliography:
138
KADI SARVA VISHWAVIDYALAYA 2014 -2016
S. K. PATEL Institute of Management & Computer Studies Gandhinagar.
www.buhlergroup.com/europe/en/industry-solutions/processed-food/chocolate/chocolate-mass.h
www.fblehmann.com/chocolate-processing/refining/5-roll-refiner
www.chocompact.com/
www.cm-opm.com/en/applications/cocoa-chocolate/a4_1
www.petzholdt-heidenauer.de/chocolate.h
www.thouet.com/chocolate-processing
www.lippmischtechnik.de/en/produkte/conchier-maschinen/
www.duyviswiener.com/chocolate-processing
www.buhlergroup.com/europe/en/about-buehler/events/interpack-2014/interpack-2014-exhibits-at-aglance.h
www.netzsch-grinding.com/en/confectionery-division/home.hl
http://lipstickaffair.blogspot.in
http://pestleanalysis.com
http://www.tis-gdv.de
Beckett ST (2009) Industrial chocolate manufacture and use. Wiley, Chichester
Bolenz S, Kutschke E, Lipp E (2008) Using extra dry milk ingredients for accelerated conching of
milk chocolate. Eur Food Res Technol 227: 16771685
Bolenz S, Manske A (2013) Impact of fat content during grinding on particle size distribution and
flow properties of milk chocolate. Eur Food Res Technol 236: 863872
Bolenz S, Kutschke E, Lipp E, Senkpiehl A (2007) Pre-dried Refiner Flakes Allow Very Short or
Even Continuous Conching of Milk Chocolate, Eur Food Res Technol 226:153160
Bolenz S, Kutschke E, Lipp E (2008) Using extra dry milk ingredients for accelerated conching of
milk chocolate. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 227: 1677-1685
139
KADI SARVA VISHWAVIDYALAYA 2014 -2016
Вам также может понравиться
- Unit 6 General Test: Listen To The Conversations. Then Choose The Word or Phrase That Correctly Completes Each SentenceДокумент7 страницUnit 6 General Test: Listen To The Conversations. Then Choose The Word or Phrase That Correctly Completes Each SentenceGokú Del Universo 780% (5)
- Innovative ProductsДокумент28 страницInnovative Productshamzakhan09Оценок пока нет
- Tampa City Council MeetingДокумент22 страницыTampa City Council MeetingABC Action NewsОценок пока нет
- Tecnia Institute of Advanced Studies: Business PlanДокумент21 страницаTecnia Institute of Advanced Studies: Business Plantajinder kaurОценок пока нет
- MC Donalds Final Report M-CommerceДокумент40 страницMC Donalds Final Report M-CommerceAli TahirОценок пока нет
- Summer internship report on menthol company and industrial visitsДокумент43 страницыSummer internship report on menthol company and industrial visitsAnkit Shahi0% (1)
- Executive Summary: Babasab PatilДокумент85 страницExecutive Summary: Babasab PatilRahil MapariОценок пока нет
- Business Plan Project Report On: "Fruit Juice Processing, Tetrapackaging & Supply in Delhi, Ghaziabad & Noida"Документ26 страницBusiness Plan Project Report On: "Fruit Juice Processing, Tetrapackaging & Supply in Delhi, Ghaziabad & Noida"Mohammad Shehata0% (1)
- Pharmacovigilance Programme of India The Journey Travelled and The Way ForwardДокумент8 страницPharmacovigilance Programme of India The Journey Travelled and The Way ForwardPreeti KharbОценок пока нет
- Internship Project Report - Shweta - FinalДокумент101 страницаInternship Project Report - Shweta - FinalshwetaОценок пока нет
- Impact of Social Media and Digital Marketing On Brand EngagementДокумент44 страницыImpact of Social Media and Digital Marketing On Brand EngagementDeepak RahejaОценок пока нет
- Chemistry Project 2Документ21 страницаChemistry Project 2hermoine grangerОценок пока нет
- LG Project ReportДокумент35 страницLG Project Reportdeeksha singhОценок пока нет
- Electronic Product Design Engineer Manager in Amarillo Austin TX Resume Randy KingДокумент2 страницыElectronic Product Design Engineer Manager in Amarillo Austin TX Resume Randy KingRandyKingОценок пока нет
- UP TourismДокумент24 страницыUP TourismpuranjayyОценок пока нет
- PARTIAL - A STUDY ON EFFECTIVENESS OF DIGITAL MARKETING SERVICES AT DOMAIN2HOST (With Table of Contents) (5 SPSS) 120 SamplesДокумент61 страницаPARTIAL - A STUDY ON EFFECTIVENESS OF DIGITAL MARKETING SERVICES AT DOMAIN2HOST (With Table of Contents) (5 SPSS) 120 SamplesKalaivani SubburajОценок пока нет
- PepsiCo 02Документ76 страницPepsiCo 02Priyesh MPОценок пока нет
- Project On Cadbury11Документ65 страницProject On Cadbury11Amit GautamОценок пока нет
- Final Project ReportДокумент102 страницыFinal Project Reportsri vinayaka studioОценок пока нет
- Economic Analysis of Cut Flower Production and MarketingДокумент104 страницыEconomic Analysis of Cut Flower Production and Marketingyogendra adhikariОценок пока нет
- C C CCCCCCCCCC C C CCC CC C CCC CДокумент46 страницC C CCCCCCCCCC C C CCC CC C CCC CSyed AhmadОценок пока нет
- Mukesh Yadav Kingfisher Project in JaipurДокумент89 страницMukesh Yadav Kingfisher Project in JaipurMUKESH YADAVОценок пока нет
- Consumer Satisfaction and Demand Pattern of Patanjali ProductsДокумент104 страницыConsumer Satisfaction and Demand Pattern of Patanjali ProductsRandheer RaiОценок пока нет
- Anas Marketing Research Report Dominoes 6th SemesterДокумент37 страницAnas Marketing Research Report Dominoes 6th SemesterMohammed AnasОценок пока нет
- Project Report For ReferenceДокумент45 страницProject Report For ReferencecarmightyОценок пока нет
- Innovation in India Project ReportДокумент23 страницыInnovation in India Project ReportAbdussalam KhanОценок пока нет
- Kingfisher Brand Building and Personal Selling Activities in JaipurДокумент56 страницKingfisher Brand Building and Personal Selling Activities in Jaipurnirmal_brar111Оценок пока нет
- Inventory ManagementДокумент65 страницInventory ManagementSagar KhursangeОценок пока нет
- Organisation Study at Tolins TyresДокумент82 страницыOrganisation Study at Tolins TyresVINEETH17% (6)
- Marketing Strategies of ViДокумент10 страницMarketing Strategies of ViAshmil AliarОценок пока нет
- Food Additives: The Need For The Use of Food AdditivesДокумент6 страницFood Additives: The Need For The Use of Food AdditivesATHIRA MОценок пока нет
- Consumer Perception Towards Agriculture Tractors (60 HP Class) "A Comparative Study of Mahindra & Mahindra and EscortДокумент59 страницConsumer Perception Towards Agriculture Tractors (60 HP Class) "A Comparative Study of Mahindra & Mahindra and EscortJag Jeet100% (4)
- A Study of New Dimension of Direct Marketing by FMCG CompaniesДокумент91 страницаA Study of New Dimension of Direct Marketing by FMCG CompaniesPrints BindingsОценок пока нет
- Food ProductionДокумент9 страницFood ProductionBharat dhusiyaОценок пока нет
- Shreya Keshari PDFДокумент75 страницShreya Keshari PDFANKIT SINGHОценок пока нет
- Integral Building Services PDFДокумент5 страницIntegral Building Services PDFKrish DoodnauthОценок пока нет
- Comparative Study Between Fruit Juice Brand With Special Context of Tropicana and Real in Dehradun City by Mohd Ashad Lovely Professional UniversityДокумент84 страницыComparative Study Between Fruit Juice Brand With Special Context of Tropicana and Real in Dehradun City by Mohd Ashad Lovely Professional UniversityAyaz RazaОценок пока нет
- FDI Boon or BaneДокумент6 страницFDI Boon or Banemuralib4u5Оценок пока нет
- Major ProjectДокумент44 страницыMajor Projectrahul kumar100% (1)
- Chemical Composition and Legal Standards of Dairy Products 0.2Документ23 страницыChemical Composition and Legal Standards of Dairy Products 0.2shraddha dubeyОценок пока нет
- Cafe Coffee Day Project by Mohammed Faizan-1Документ79 страницCafe Coffee Day Project by Mohammed Faizan-1SoundaryaОценок пока нет
- Entrepreneurship Project: Tanuja Water'S ReportДокумент16 страницEntrepreneurship Project: Tanuja Water'S ReportPrabir Kumar PatiОценок пока нет
- A Study On Effectiveness of Performance Apprasial System at PUMA Sports India Pvt. Ltd. BangaloreДокумент68 страницA Study On Effectiveness of Performance Apprasial System at PUMA Sports India Pvt. Ltd. BangaloreAKSHIT VERMAОценок пока нет
- Arunachal Pradesh Promotes Adventure, Spiritual TourismДокумент37 страницArunachal Pradesh Promotes Adventure, Spiritual TourismRita Sarda BinaniОценок пока нет
- General Awareness of Pathology With Special Reference To Typhoid DiseaseДокумент41 страницаGeneral Awareness of Pathology With Special Reference To Typhoid DiseaseNiveditaPandeyОценок пока нет
- Amul The Taste of IndiaДокумент44 страницыAmul The Taste of IndiaTeena SareenОценок пока нет
- Digital Marketing Effectiveness at Domain2HostДокумент109 страницDigital Marketing Effectiveness at Domain2HostNaga LakshmiОценок пока нет
- Sugar Cane ProductionДокумент12 страницSugar Cane ProductionMans SGОценок пока нет
- Final ProjetcДокумент38 страницFinal ProjetcMahes100% (2)
- Business PalnДокумент4 страницыBusiness PalnAmy-Leigh ArriesОценок пока нет
- Project of ShaliniДокумент15 страницProject of ShaliniLalit MittalОценок пока нет
- Internship Training ReportДокумент44 страницыInternship Training ReportAfi MuhammedОценок пока нет
- Organisation Study ReportДокумент66 страницOrganisation Study ReportAshik SureshОценок пока нет
- Smart DustbinДокумент24 страницыSmart Dustbinhamed raza100% (1)
- Market Share of Dabur Real JuiceДокумент66 страницMarket Share of Dabur Real Juicesushmit raj badolaОценок пока нет
- Patanjali SWOT AnalysisДокумент7 страницPatanjali SWOT AnalysisDivyajit MahakulОценок пока нет
- Minor Project On KFCДокумент44 страницыMinor Project On KFCAman GargОценок пока нет
- Summer Training Report On Sudha Ice-CreamsДокумент39 страницSummer Training Report On Sudha Ice-CreamsVivek Raj0% (3)
- JP Ffinal Project V SemДокумент157 страницJP Ffinal Project V SemVipin RajОценок пока нет
- Supplier Quality Management System Manual: A Corporate OverviewДокумент14 страницSupplier Quality Management System Manual: A Corporate OverviewwaynefwilliamsОценок пока нет
- School of CommerceДокумент14 страницSchool of CommerceAnshika SrivastavaОценок пока нет
- Buying Behavior of Consumers of Age Group 18-25 For Milk Chocolate Bars With Special ReferenceДокумент62 страницыBuying Behavior of Consumers of Age Group 18-25 For Milk Chocolate Bars With Special ReferenceVikash BhanwalaОценок пока нет
- IHRM Approaches to Staffing and International AssignmentsДокумент19 страницIHRM Approaches to Staffing and International AssignmentsrajulramiОценок пока нет
- An Investment Perspective of Human Resource ManagementДокумент23 страницыAn Investment Perspective of Human Resource ManagementrajulramiОценок пока нет
- Banking in IndiaДокумент57 страницBanking in IndiaPiyush PatelОценок пока нет
- Banking in IndiaДокумент57 страницBanking in IndiaPiyush PatelОценок пока нет
- Job Satisfaction SKPДокумент53 страницыJob Satisfaction SKPrajulramiОценок пока нет
- New MBA Detailed Syllabus Sem IIIДокумент121 страницаNew MBA Detailed Syllabus Sem IIIsweetlionОценок пока нет
- Introduction To Human Resource DevelopmentДокумент28 страницIntroduction To Human Resource DevelopmentrajulramiОценок пока нет
- SK Patel First PagesДокумент5 страницSK Patel First PagesrajulramiОценок пока нет
- Chap 011Документ24 страницыChap 011rajulramiОценок пока нет
- Chap 012 SM Mba Sem 3Документ27 страницChap 012 SM Mba Sem 3rajulramiОценок пока нет
- ReportДокумент6 страницReportimcool552Оценок пока нет
- Chap 001Документ28 страницChap 001Vishal Singh JaswalОценок пока нет
- Brief Study of Chocolate Industry With Special Focus On The Cadbury IndiaДокумент106 страницBrief Study of Chocolate Industry With Special Focus On The Cadbury IndiarajulramiОценок пока нет
- CultureДокумент9 страницCultureJayagokul SaravananОценок пока нет
- Example Chemical and Biological CompositionДокумент8 страницExample Chemical and Biological CompositioniskandarОценок пока нет
- FTT eДокумент2 страницыFTT eSyarifah Lubbna YahyaОценок пока нет
- The Ambitious TortoiseДокумент2 страницыThe Ambitious TortoiseTeo Pei WeiОценок пока нет
- Report Text The Duck Billed Platypus: (Ornithorhynchus Anatinus)Документ2 страницыReport Text The Duck Billed Platypus: (Ornithorhynchus Anatinus)Lilis IndriyaniОценок пока нет
- Refrigerator Cooling and Storage EssentialsДокумент20 страницRefrigerator Cooling and Storage EssentialsSanjay VermaОценок пока нет
- Camp Staff Application: Form FM 10NДокумент4 страницыCamp Staff Application: Form FM 10NCampGarrettОценок пока нет
- Allrecipes - June-July 2022 USДокумент100 страницAllrecipes - June-July 2022 USÉva TőkésОценок пока нет
- It Is in Your Hands To Live Without DiseasesДокумент33 страницыIt Is in Your Hands To Live Without DiseasesAnbalagan V100% (1)
- PIDA - Inception ReportДокумент270 страницPIDA - Inception ReportTrevor T ParazivaОценок пока нет
- To Compare The Rate of Fermentation of Apple and Carrot JuiceДокумент12 страницTo Compare The Rate of Fermentation of Apple and Carrot JuiceRitesh Singh80% (5)
- Practice Test: Responda Las Preguntas 1 A 5 de Acuerdo Con El EjemploДокумент8 страницPractice Test: Responda Las Preguntas 1 A 5 de Acuerdo Con El Ejemplocarlos puche ojedaОценок пока нет
- Banana Crisis WorksheetДокумент2 страницыBanana Crisis Worksheetapi-327823961Оценок пока нет
- Snails and Slugs Ipm 09Документ2 страницыSnails and Slugs Ipm 09DbaltОценок пока нет
- EO LA Cocktail MenuДокумент2 страницыEO LA Cocktail MenuMatthewKangОценок пока нет
- Elene Shermadini Unit 6Документ7 страницElene Shermadini Unit 6Elene ShermadiniОценок пока нет
- Coca-Cola Report Prepared by Manish SaranДокумент61 страницаCoca-Cola Report Prepared by Manish SaranManish Saran100% (14)
- Transitional Input VATДокумент21 страницаTransitional Input VATJoanne TolentinoОценок пока нет
- Scouts & Guides For Animals & Birds Agenda For Education About Animals and Birds - Mrs. Sukanya BerwalДокумент7 страницScouts & Guides For Animals & Birds Agenda For Education About Animals and Birds - Mrs. Sukanya BerwalNaresh KadyanОценок пока нет
- Purple Hibsicus QuestionsДокумент7 страницPurple Hibsicus Questionssehaj mОценок пока нет
- Introduction To BakingДокумент18 страницIntroduction To BakingJennalyn GomezОценок пока нет
- ScriptДокумент3 страницыScriptNidonama E. KabmatОценок пока нет
- 510k Guidance 1Документ23 страницы510k Guidance 1hemkenbpОценок пока нет
- Guidance Note 18 Determination of Product Shelf Life PDFДокумент56 страницGuidance Note 18 Determination of Product Shelf Life PDFHiếu LêОценок пока нет
- Rotary Club of Moraga, CA Newsletter For January 28th, 2014Документ3 страницыRotary Club of Moraga, CA Newsletter For January 28th, 2014Frank MayОценок пока нет
- French BreadДокумент10 страницFrench BreadtvmОценок пока нет
- BANYUWANGI PRICELIST (Periode 15-20 Mar 2021) SKU Code Nama Barang Harga JualДокумент6 страницBANYUWANGI PRICELIST (Periode 15-20 Mar 2021) SKU Code Nama Barang Harga JualMas FiОценок пока нет