Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
ECE Questionnaire Mix
Загружено:
Cris Diane G. Datingginoo0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
180 просмотров3 страницыECE
Авторское право
© © All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документECE
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
180 просмотров3 страницыECE Questionnaire Mix
Загружено:
Cris Diane G. DatingginooECE
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 3
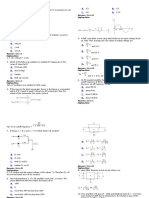
1.
How many international commercial AM
broadcast channels (assume BW=10 kHz) can fit
into the bandwidth occupied by a commercial
FM broadcast channel (assume BW=200 kHz)?
A. 20
B. 200
C. 10
D. 5
2. _______ is an arrangement of conductors
designed
to
radiate
(transmit)
an
electromagnetic field in response to an applied
alternating voltage and the associated
alternating electric current.
A. transmission lines
B. antenna
C. counterpoise
D. stub
3. Distortion is caused by:
A. creation of harmonics of baseband
frequencies
B. baseband frequencies mixing with
each other
C. shift in phase relationships between
baseband frequencies
D. all of the above
4. A sound wave that moves back and forth in the
direction of propagation is an example of which
of the following types of wave motion?
A. Longitudinal B. Composite
D. Concentric
D. Transverse
5. Radio-frequency waves cannot be seen for which
of the following reasons:
A. Because the human eye detects only
magnetic energy
B. Because radio-frequency waves are
below the sensitivity range of the
human eye
C. Because radio-frequency waves are
above the sensitivity range of the human
eye
D. Because radio-frequency energy is low
powered
6. A unique band of frequencies within the
wideband frequency spectrum of the medium is
allotted to each communication channel on a
continuous time basis.
A. Time Division Duplexing (TDD)
B. Frequency Division Duplexing (FDD)
C. Frequency Division Multiplexing (FDM)
D. Time Division Multiplexing (TDM)
7. The process of modifying a high-frequency
carrier with the information to be transmitted is
called
A. Multiplexing B. Telemetry
C. Modulation D. Detection
8. A signal is measured at two different points. The
power is P1 at the first point and P2 at the
second point. The dB is 0. This means
_________.
A. P2 is zero
B. P2 equals P1
C. P2 is much larger than P1
D. P2 is much smaller than P1
9. A carrier is modulated by three audio tones. If
the modulation indexes for the tones are 0.3,
0.4, and 0.5, then what is the total modulation
index?
A. 0.636
B. 1.2
C. 0.707
D. 0.9
10. Calculate the power in one sideband of an AM
signal whose carrier power is 50 watts. The
unmodulated current is 2 A while the modulated
current is 2.4 A.
A. 22.1 W
B. 31.4 W
C. 50 W
D. 25 W *11W
11. What is the carrier power in one sideband of an
AM signal whose carrier power is 300 W, with
80% modulation?
A. 300 W B. 96 W
C. 150 W D. 48 W
12. An AM transmitter is modulated by two sine
waves at 1.5 kHz and 2.5 kHz, with modulation of
20% and 80% respectively. Calculate the
effective modulation index.
A. 82%
B. 85%
C. 80%
D. 78%
13. At 80% modulation J3E, what is the percentage
power saving?
A. 16.67%
B. 66.67%
C. 75.75%
D. 87.87%
14. What will be the deviation caused by a 3-kHz
tone if the modulation index is 3?
A. 4.5 kHz
B. 9 kHz
C. 0 kHz
D. 6 kHz
15. Using Carsons rule, what is the approximate
bandwidth of an FM signal with a modulation
index of 2 being modulated by a 5-kHz signal?
A. 15 kHz
B. 10 kHz
C. 30 kHz
D. 45 kHz
16. Determine the modulation index of a standard
FM broadcast having a hypothetical maximum
carrier frequency deviation of 12 kHz and a
maximum modulating frequency of 4 kHz.
A. 6
B. 5
C. 3/2
D. 3
17. What is the modulation index of an FM
transmitter whose frequency deviation is 50 kHz,
while its actual frequency is 10 kHz?
A. 100
B. 5
C. 0.5
D. 3
22. A diode generator is required to produce 12 V
of noise in a receiver with an input impedance of
75 and a noise power bandwidth of 200 kHz.
Determine the current through the diode in
milliamperes.
A. 39.8 mA
B. 0.398 mA
C. 3.98 mA
D. 398 mA
23. A 20,000 resistor is at room temperature
(290K). Calculate the threshold noise voltage for
a bandwidth of 100 kHz.
A. 56.58 V
B. 5658 V
C. 565.8 V
D. 5.658 V
24. An amplifier with an overall gain of 20 dB is
impressed with a signal whose power lvel is 1
watt. Calculate the power output in dBm.
A. 50 dBm
B. 62.61 dBm
C. 31.45 dBm
D. 45.67 dBm
18. The local FM stereo rock station is at 96.5 MHz
Calculate the local oscillator frequency and the
image frequency for a 10.7 MHz IF receiver.
A. LO= 105.7 MHz, IMAGE= 127.9 MHz
B. LO= 107.2 MHz, IMAGE= 117.9 MHz
C. LO= 105.2 MHz, IMAGE= 117.9 MHz
D. LO= 107.2 MHz, IMAGE= 127.9 MHz
25. In a microwave communication system,
determine the noise power in dBm for an
equivalent noise bandwidth of 10 MHz.
A. -121.4 dBm
B. -169.28 dBm
C. 117.89 dBm D. -103.98 dBm
19. Which oscillators preferred for carrier
generators because of their good frequency
stability?
A. LC
B. RC
C. LR
D. Crystal
26. The signal power in the input to an amplifier is
100 W and the noise power is 1 W. At the
output the signal power is 1W and the noise
power is 40 mW. What is the amplifier noise
figure?
A. 87.5 dB
B. 31.67 dB
C. 6.02 dB
D. 16.13 dB
20. The resistor R1 and R2 are connected in series at
300K and 400K temperatures respectively. If R1
is 200 and R2 is 300, find the power produced
at the load (R1 = 500) over bandwidth of 100
kHz.
A. 0.496 fW
B. 5.78 pW
C. 0.15 fW
D. 52.48 pW
1. For a BPSK modulation with a carrier frequency
of 80 MHz and an input bit rate of 10 Mbps,
determine the minimum Nyquist BW.
A. 1 MHz
B. 5 MHz
C. 10 MHz
D. 2.5 MHz
21. What is the effect on the signa-to-noise ration in
a system (in dB) if the bandwidth is doubled,
considering all other parameters to remain
unchanged expect the normal thermal noise
only. The S/N will be ______.
A. S/N ratio is decreased by 1/16
B. S/N ratio is decreased by 1/4
C. S/N ratio is decreased by 1/8
D. S/N ratio is decreased by
2. What is the channel capacity for a signal power
of 200 W, noise power of 10 W and a bandwidth
of 2 kHz of a digital system?
A. 8.779 kbps
B. 9.128 kbps
C. 4.751 kbps
D. 6.143 kbps
3. Baseband transmission of a digital signal is
possible only if we have a ______ channel.
A. low-pass
B. low rate
C. bandpass
D. high rate
4. QAM stands for:
A. Quadrature Amplitude Modulation
B. Quadrature Amplitude Masking
C. Quadrature Amplitude Marking
D. Quadrature Alternate Modulation
5. Which layer of the OSI model is responsible for
reliable network communication between end
nodes and provides mechanisms for the
establishment, maintenance, and termination of
virtual circuits, transport fault detection and
recovery, and information flow control?
A. Network Layer B. Transport Layer
C. Data Link Layer D. Physical Layer
6. What is the principal difference between the
asynchronous and synchronous transmission?
A. The clocking is derived from the data in
synchronous transmission
B. The clocking is mixed with the data in
synchronous transmission
C. The bandwidth required is difficult
D. The pulse are difficult
12. Which is true of asynchronous bit system?
A. They use continuous signals to transmit
bits
B. They use intermittent signals to transmit
bits
C. They are commonly used for
maintenance-to
mainframe
communication
D. They require an external clocking device
13. A method that relies upon transmitting and
receiving devices to maintain their own internal
clock is ______.
A. synchronous B. bisynchronous
C. isochronous
D. synchronous
14. A network that spans the earth is called _______.
A. An enterprise network
B. A wide area network
C. A metropolitan area network
D. A global network
15. A modem is _____.
7. In a peer to peer network, which of the following
may acts as both client and a server?
A. A dedicated server
B. A peer computer
C. A dedicated station
D. A standalone computer
A. Device that converts computer digital signal
to an analog signals to use with telephone lines
B. Device that can receive and transmit
electromagnetic signals across the transmission
media
C. Device that converts analog signals into
digital signals
D. Connectivity device between computers
8. A _____ is a set of rules that governs data
communication.
A. forum
B. protocol
C. standard
D. timing
16. Which IEEE standard was created to satisfy the
LAN needs of industrial automation?
A. IEEE 802.4
B. IEEE 802.5
C. IEEE 802.6
D. IEEE 802.7
9. In ______ transmission, the channel capacity is
shared by both communicating devices at all
times.
A. Simplex
B. Half-simplex
C. Half-duplex
D. Dull-duplex
17. What does the acronym TCP/IP stand for?
A. top core protocol / international
protocol
B. telephone communications policy /
internet procedure
C. traffic communications protocol /
information protocol
D. transport control protocol / internet
protocol
10. Which topology
connection?
A. Ring
C. Star
requires
multipoint
B. Bus
D. Mesh
11. The _______ layer is responsible for moving
frames from one hop (node) to the next.
A. physical
B. data link
C. network
D. transport
18. URL address identify all except the following
A. e-mail server
B. physical location user
C. users network
D. ISP server
Вам также может понравиться
- Communication ReviewerДокумент3 страницыCommunication ReviewerAchilles Aldave100% (1)
- Ece Board Exam AwarenessДокумент3 страницыEce Board Exam AwarenessDarwin TacubanzaОценок пока нет
- Pre Board Comms 2 (Nov 2006) AnsДокумент6 страницPre Board Comms 2 (Nov 2006) AnsKurarin Jan MaikeruОценок пока нет
- Cebu - FB 7 - ESTДокумент4 страницыCebu - FB 7 - ESTKei DeeОценок пока нет
- Esat MCQS: Section 1: Basic Communications/ Noise/ AM/ FM/ PMДокумент27 страницEsat MCQS: Section 1: Basic Communications/ Noise/ AM/ FM/ PMRayanОценок пока нет
- Est Questions - ECEДокумент35 страницEst Questions - ECERJ BedañoОценок пока нет
- Pinoybix WAДокумент28 страницPinoybix WAKenОценок пока нет
- (EDGE) MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS in COMMUNICATIONS ENGINEERING by Yu and CamachoДокумент88 страниц(EDGE) MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS in COMMUNICATIONS ENGINEERING by Yu and CamachocathyОценок пока нет
- PINOYBIX NoiseДокумент50 страницPINOYBIX NoiseNida Bagoyboy NatichoОценок пока нет
- MCQ in Communications Engineering by Lomboy & VillanuevaДокумент114 страницMCQ in Communications Engineering by Lomboy & VillanuevaSheehan Kayne De CardoОценок пока нет
- Chapter 1: Introduction To Communication Systems Chapter 2: Radio-Frequency CircuitsДокумент17 страницChapter 1: Introduction To Communication Systems Chapter 2: Radio-Frequency CircuitsAriel Paulo G. TabangayОценок пока нет
- ELEX Book ReviewДокумент67 страницELEX Book ReviewRaine LopezОценок пока нет
- Microwave Pinoy BixДокумент48 страницMicrowave Pinoy BixKenОценок пока нет
- ECE Formulae BookДокумент39 страницECE Formulae BookThashil Nagaraju Tnr TnrОценок пока нет
- GEAS ExamДокумент2 страницыGEAS ExamJonas Parreño100% (1)
- PERC Comms 2Документ7 страницPERC Comms 2sadke213Оценок пока нет
- Elecs 2008Документ4 страницыElecs 2008Denaiya Watton LeehОценок пока нет
- EST Chapter 3 Pages 40-48Документ14 страницEST Chapter 3 Pages 40-48Nico RobinОценок пока нет
- Transmission MediasДокумент3 страницыTransmission MediasCrissa Vin BabaanОценок пока нет
- Excel Review Center Refresher Course EST: Give Your Best Shot !Документ4 страницыExcel Review Center Refresher Course EST: Give Your Best Shot !Nida Bagoyboy NatichoОценок пока нет
- INDIABIXДокумент7 страницINDIABIXJanicz BalderamaОценок пока нет
- Ece ReviewДокумент77 страницEce ReviewLeonard Jobet Villaflor PantonОценок пока нет
- Sand NotesДокумент226 страницSand NotesHGFLJJ0% (1)
- Unit 1 2 3 - MCQ StudentsДокумент17 страницUnit 1 2 3 - MCQ StudentsLiu Li100% (1)
- Transmission Line 101Документ6 страницTransmission Line 101George Ezar N. QuiriadoОценок пока нет
- Group Study - Antennas - QuestionnaireДокумент7 страницGroup Study - Antennas - QuestionnaireSheehan Kayne De CardoОценок пока нет
- Transmi Finals Set BДокумент10 страницTransmi Finals Set BKerwin TejucoОценок пока нет
- Indiabix With ExplanationsДокумент46 страницIndiabix With ExplanationsJustin ConsonОценок пока нет
- MCQ in Modulation Part 1 ECE Board ExamДокумент13 страницMCQ in Modulation Part 1 ECE Board ExamXyОценок пока нет
- MCQ in ESTДокумент30 страницMCQ in ESTaldruinoОценок пока нет
- Periodic Exam 6Документ5 страницPeriodic Exam 6Inah RamosОценок пока нет
- ObjectiveДокумент20 страницObjectiveAnonymous sBvtnZQОценок пока нет
- Pinoybix CommsДокумент62 страницыPinoybix CommsRalph Jayson SilangОценок пока нет
- Instrumentation AptitudeДокумент77 страницInstrumentation AptitudePrasath KumarОценок пока нет
- Frenzel Exam Sheet (Key To Correction)Документ22 страницыFrenzel Exam Sheet (Key To Correction)Patrick James De LeonОценок пока нет
- ECE Board Performance Review 2019Документ20 страницECE Board Performance Review 2019Elaine R RiveraОценок пока нет
- Analog Television Systems QUIZДокумент12 страницAnalog Television Systems QUIZArpee PalomoОценок пока нет
- Microwave Communications - Mcqs (1-300)Документ43 страницыMicrowave Communications - Mcqs (1-300)Abdul Hameed100% (1)
- Power Elex Sec.1Документ26 страницPower Elex Sec.1Kuya KimОценок пока нет
- Est Reviewer Final and OriginalДокумент437 страницEst Reviewer Final and Originalvon kervy onrade0% (1)
- Transmission MCQ Pinoy Bix 400Документ23 страницыTransmission MCQ Pinoy Bix 400kathrineОценок пока нет
- Iecep EsatДокумент29 страницIecep EsatIvy Cee100% (1)
- BlakeДокумент47 страницBlakeReanne Rose Ello HoreОценок пока нет
- MCQ's NoiseДокумент19 страницMCQ's NoiseRomeo Ganelo100% (1)
- 1AT3 Microwave Communications and Satellite CommunicationsДокумент1 страница1AT3 Microwave Communications and Satellite CommunicationsNicholson ZapantaОценок пока нет
- Communications QBДокумент38 страницCommunications QBDenaiya Watton LeehОценок пока нет
- BE Electronics and Telecommunication Engineering PDFДокумент670 страницBE Electronics and Telecommunication Engineering PDFRahul TadeОценок пока нет
- Quiz Question and Answers For ElectricalДокумент119 страницQuiz Question and Answers For ElectricalShrikant MaliОценок пока нет
- A. B. C. D.: Answer: Option B ExplanationДокумент10 страницA. B. C. D.: Answer: Option B ExplanationKuya KimОценок пока нет
- CN BitsДокумент41 страницаCN BitsVenkata PrasadОценок пока нет
- Transmi Finals Set BДокумент10 страницTransmi Finals Set BKerwin TejucoОценок пока нет
- Modulation QuestionaireДокумент28 страницModulation QuestionaireGepel OntanillasОценок пока нет
- Refresher ModulationДокумент28 страницRefresher Modulationvon kervy onrade100% (1)
- Comms 1 - Modulation AnswersДокумент4 страницыComms 1 - Modulation AnswersRovina LacunaОценок пока нет
- Modulation: TransmitterДокумент11 страницModulation: TransmitterMarghel Rañigo BuenaventuraОценок пока нет
- Communications EngineeringДокумент5 страницCommunications EngineeringMiko GorospeОценок пока нет
- Refresher ModulationДокумент28 страницRefresher ModulationMairiz MontealtoОценок пока нет
- ELEMENT V - Signals, Frequencies and EmissionДокумент7 страницELEMENT V - Signals, Frequencies and EmissionAlarm Guardians50% (2)
- Chapter 1. Introductory TopicsДокумент14 страницChapter 1. Introductory Topicsaoi_blue89Оценок пока нет
- MillerДокумент17 страницMillerAllen LariosОценок пока нет
- Manufacturing Process DiagramДокумент3 страницыManufacturing Process DiagramCris Diane G. DatingginooОценок пока нет
- Digital CommunicationsДокумент62 страницыDigital CommunicationsCris Diane G. DatingginooОценок пока нет
- Logic - 1st LabДокумент2 страницыLogic - 1st LabCris Diane G. DatingginooОценок пока нет
- Baguio Reaction PaperДокумент39 страницBaguio Reaction PaperCris Diane G. Datingginoo100% (1)
- Gardenia PaperДокумент45 страницGardenia PaperCris Diane G. Datingginoo100% (3)
- GardeniaДокумент57 страницGardeniaCris Diane G. Datingginoo50% (2)
- Grp1 Case StudyДокумент8 страницGrp1 Case StudyCris Diane G. DatingginooОценок пока нет
- Ece Laws ReportДокумент19 страницEce Laws ReportCris Diane G. DatingginooОценок пока нет
- Diode Clipper and Clampers Lecture 8-18-11Документ17 страницDiode Clipper and Clampers Lecture 8-18-11Joshua DuffyОценок пока нет
- Ch12 - Are Accidents Man-MadeДокумент18 страницCh12 - Are Accidents Man-MadeCris Diane G. DatingginooОценок пока нет
- AdvComms - Presentation (REVISED)Документ160 страницAdvComms - Presentation (REVISED)Cris Diane G. DatingginooОценок пока нет
- Junction TemperatureДокумент16 страницJunction TemperatureCris Diane G. DatingginooОценок пока нет
- Ece Laws ReportДокумент19 страницEce Laws ReportCris Diane G. DatingginooОценок пока нет
- Junction TemperatureДокумент16 страницJunction TemperatureCris Diane G. DatingginooОценок пока нет
- DCGENand DYNAMOДокумент87 страницDCGENand DYNAMOCris Diane G. DatingginooОценок пока нет
- Experiment #3 A. Logic Diagram ObjectivesДокумент9 страницExperiment #3 A. Logic Diagram ObjectivesCris Diane G. DatingginooОценок пока нет
- Basic Elex ReviewerДокумент3 страницыBasic Elex ReviewerCris Diane G. Datingginoo0% (1)
- Math Coaching1 1stbooklet (FINAL)Документ15 страницMath Coaching1 1stbooklet (FINAL)Yael FabayosОценок пока нет
- Rotated Axes DiscriminantДокумент8 страницRotated Axes DiscriminantCris Diane G. DatingginooОценок пока нет
- Diodes and Applications FinalДокумент117 страницDiodes and Applications FinalCris Diane G. DatingginooОценок пока нет
- PRC List of RequirementsДокумент24 страницыPRC List of RequirementscharmainegoОценок пока нет
- Stat and Proba PDFДокумент8 страницStat and Proba PDFCris Diane G. DatingginooОценок пока нет
- Transistors and AmplifiersДокумент285 страницTransistors and AmplifiersCris Diane G. DatingginooОценок пока нет
- Alternating Current CircuitsДокумент4 страницыAlternating Current CircuitsCris Diane G. DatingginooОценок пока нет
- Eco Industrial DevelopmentДокумент47 страницEco Industrial DevelopmentCris Diane G. Datingginoo100% (1)
- Assign Sa C++Документ1 страницаAssign Sa C++Cris Diane G. DatingginooОценок пока нет
- Header File "Conio.h" - Old C HeaderДокумент5 страницHeader File "Conio.h" - Old C HeadercdianegdОценок пока нет
- Specifications: Fastener Tightening Specifications Application Specification Metric EnglishДокумент23 страницыSpecifications: Fastener Tightening Specifications Application Specification Metric EnglishmarceloОценок пока нет
- 1N4007SMDДокумент2 страницы1N4007SMDDAHLI-EFFECTОценок пока нет
- Artis ZeeДокумент318 страницArtis Zeeihsan ul haq100% (5)
- Electromagnetic Braking System: A Seminar Report Submitted byДокумент46 страницElectromagnetic Braking System: A Seminar Report Submitted byJain Karan100% (1)
- Syllabus of LPVДокумент2 страницыSyllabus of LPVkalaiyarasiОценок пока нет
- Lightning Arrester Modeling Using Atp-Emtp: Trin Saengsuwan and Wichet ThipprasertДокумент4 страницыLightning Arrester Modeling Using Atp-Emtp: Trin Saengsuwan and Wichet ThipprasertgumilarОценок пока нет
- Chapter 7 Optical AmplifiersДокумент23 страницыChapter 7 Optical AmplifiersNur AmalinaОценок пока нет
- 01v 96 PDFДокумент227 страниц01v 96 PDFsmftecОценок пока нет
- Major PPT Batch 6Документ19 страницMajor PPT Batch 6starboyОценок пока нет
- Micom P125/P126 & P127: Directional/Non-directional RelayДокумент596 страницMicom P125/P126 & P127: Directional/Non-directional Relayjigyesh29Оценок пока нет
- OS-5020 NewДокумент2 страницыOS-5020 Newadak avijitОценок пока нет
- SinoTimer TM610 ManualДокумент2 страницыSinoTimer TM610 ManualpettherburnОценок пока нет
- How To Use A Multimeter The Quick Guide To Accurately Measure Electrical Quantities and Make The Most of Your MultimeterДокумент23 страницыHow To Use A Multimeter The Quick Guide To Accurately Measure Electrical Quantities and Make The Most of Your MultimeterMohamad Hakimi Bin MakhtarОценок пока нет
- INST+ +Measurement+of+FrequencyДокумент2 страницыINST+ +Measurement+of+Frequencyhammad100Оценок пока нет
- The Hourmeter Range - 3ppДокумент3 страницыThe Hourmeter Range - 3ppN.I.C.E spares & serviceОценок пока нет
- OPAMP by COEP ProfДокумент171 страницаOPAMP by COEP Profonkarsinare1Оценок пока нет
- Easy Speed Control: SeriesДокумент28 страницEasy Speed Control: SeriesRbhatОценок пока нет
- Miller XR Control Wire Fedder Owner ManualДокумент72 страницыMiller XR Control Wire Fedder Owner Manualalberto lealОценок пока нет
- MFJ 949e PDFДокумент10 страницMFJ 949e PDFWeerut SrhidharaОценок пока нет
- Murata MA40 SERIESДокумент2 страницыMurata MA40 SERIESMiltonAlvaradoPonceОценок пока нет
- Manual EATONДокумент20 страницManual EATONJohan Maroto ValverdeОценок пока нет
- Wharfadale SVP-X Users ManualДокумент12 страницWharfadale SVP-X Users ManualrdbassesОценок пока нет
- Ec8701 Ame Unit-2 NotesДокумент174 страницыEc8701 Ame Unit-2 Notesajaykarthicsp.ece2020Оценок пока нет
- Electrochemistry Study GuideДокумент2 страницыElectrochemistry Study GuideAbhi DevathiОценок пока нет
- Choosing The Right Electronics Manufacturing Testing EquipmentДокумент6 страницChoosing The Right Electronics Manufacturing Testing EquipmentjackОценок пока нет
- Spec Silage Making MachineДокумент2 страницыSpec Silage Making MachineSandeepNairОценок пока нет
- Himel Residential PDFДокумент12 страницHimel Residential PDFAlbertОценок пока нет
- Elexia FP2 RELAY Axicom D3016Документ4 страницыElexia FP2 RELAY Axicom D3016Коресендович ЮрийОценок пока нет
- DTC P0017 Codigo AvengerДокумент6 страницDTC P0017 Codigo Avengerflash_24014910Оценок пока нет
- ME Series 1000M Ethernet Slip RingsДокумент28 страницME Series 1000M Ethernet Slip RingsPhiBa-ChannelОценок пока нет