Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Google Search, Commonly Referred To As Google Web Search or Just Google, Is A
Загружено:
wan2shareИсходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Google Search, Commonly Referred To As Google Web Search or Just Google, Is A
Загружено:
wan2shareАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Google Search, commonly referred to as Google Web Search or just Google, is a web
search engine owned by Google Inc. It is the most-used search engine on the World
Wide Web,[4] handling more than three billion searches each day.[5][6] As of February
2015 it is the most used search engine in the US with 64.5% market share.[7]
The order of search on Google's search-results pages is based, in part, on a priority rank
called a "PageRank". Google Search provides many different options for customized
search, using Boolean operators such as: exclusion ("-xx"), alternatives ("xx OR yy OR
zz"), and wildcards ("Winston * Churchill" returns "Winston Churchill", "Winston Spencer
Churchill", etc.)[8] The same and other options can be specified in a different way on an
Advanced Search page.
The main purpose of Google Search is to hunt for text in publicly accessible documents
offered by web servers, as opposed to other data, such as images or data contained in
databases. It was originally developed by Larry Page and Sergey Brin in 1997.[9] Google
Search provides several features beyond searching for words.[10] These include
synonyms, weather forecasts, time zones, stock quotes, maps, earthquake data, movie
showtimes, airports, home listings, and sports scores. There are special features for
numbers, dates, and some specific forms, including ranges, [11] prices, temperatures,
money and measurement unit conversions, calculations, package tracking, patents, area
codes,[10] and language translation. In June 2011 Google introduced "Google Voice
Search" to search for spoken, rather than typed, words.[12] In May 2012 Google introduced
a Knowledge Graph semantic searchfeature in the U.S.
Analysis of the frequency of search terms may indicate economic, social and health
trends.[13] Data about the frequency of use of search terms on Google have been shown
to correlate with flu outbreaks and unemployment levels, and provide the information
faster than traditional reporting methods and surveys.
Competitors of Google include Baidu and Soso.com in China; Naver.com and Daum
Communications in South Korea; Yandex in Russia; Seznam.cz in the Czech
Republic;Yahoo! in Japan, Taiwan and the US, as well as Bing and DuckDuckGo.[14] Some
smaller search engines offer facilities not available with Google, e.g. not storing any
private or tracking information; one such search engine is Ixquick.
Contents
[hide]
1 Search
o
1.1 PageRank
1.2 Search products
1.3 Non-indexable data
1.4 Google optimization
1.5 Universal search
2 Functionality
o
2.1 Search syntax
2.2 Query expansion
2.3 "I'm Feeling Lucky"
2.4 Rich snippets
2.5 Special features
2.6 Search options
2.7 Error messages
2.7.1 January 2009 malware bug
2.8 Google Doodles
2.9 Google Caffeine
2.10 Conversational search (OK Google)
2.11 Hummingbird update
3 Privacy
o
3.1 Encrypted search
3.2 FTC Fines
4 Instant Search
5 Redesign
6 Mobile app
7 International
8 Search products
9 Energy consumption
10 Possible misuse of search results
11 See also
12 References
13 Further reading
14 External links
Search[edit]
PageRank[edit]
Main article: PageRank
Google's rise to success was in large part due to a
patented algorithm called PageRank that helps rank web pages that match a given
search string.[15] When Google was a Stanford research project, it was nicknamed
BackRub because the technology checks backlinks to determine a site's importance.
Previous keyword-based methods of ranking search results, used by many search
engines that were once more popular than Google, would rank pages by how often the
search terms occurred in the page, or how strongly associated the search terms were
within each resulting page. The PageRank algorithm instead analyzes humangenerated links assuming that web pages linked from many important pages are
themselves likely to be important. The algorithm computes a recursive score for pages,
based on the weighted sum of the PageRanks of the pages linking to them. PageRank is
thought to correlate well with human concepts of importance. In addition to PageRank,
Google, over the years, has added many other secret criteria for determining the ranking
of pages on result lists, reported to be over 250 different indicators,[16][17] the specifics of
which are kept secret to keep spammers at bay and help Google maintain an edge over
its competitors globally.
In a potential hint of Google's future direction for their Search algorithm, Eric Schmidt,
Google's then chief executive, said in a 2007 interview with the Financial Times: "The
goal is to enable Google users to be able to ask the question such as 'What shall I do
tomorrow?' and 'What job shall I take?'".[18] Schmidt reaffirmed this during a 2010
interview with the Wall Street Journal: "I actually think most people don't want Google to
answer their questions, they want Google to tell them what they should be doing next." [19]
In 2013 the European Commission found that Google Search favored Google's own
products, instead of offering consumers the best result for their needs.[20] In February
2015 Google announced a major change to its mobile search algorithm which would
favor mobile friendly over other websites. Nearly 60% of Google's online search
traffic comes from mobile phones. Google wants its users to have access to premium
quality websites. Those websites which lack a mobile friendly interface would
be demoted and it is expected that this update will cause a massive shake-up of ranks.
Business who fail to update their websites accordingly could see a massive dip in their
regular websites traffic.[21]
Вам также может понравиться
- Google SearchДокумент4 страницыGoogle Searchwan2shareОценок пока нет
- Google Search, Commonly Referred To As Google Web Search or Just Google, Is AДокумент4 страницыGoogle Search, Commonly Referred To As Google Web Search or Just Google, Is Awan2shareОценок пока нет
- Google Search, Commonly Referred To As Google Web Search or Just Google, Is AДокумент8 страницGoogle Search, Commonly Referred To As Google Web Search or Just Google, Is Awan2shareОценок пока нет
- Google Search, Commonly Referred To As Google Web Search or Just Google, Is AДокумент7 страницGoogle Search, Commonly Referred To As Google Web Search or Just Google, Is Awan2shareОценок пока нет
- Google SearchДокумент5 страницGoogle Searchwan2shareОценок пока нет
- Google Search, Commonly Referred To As Google Web Search or Just Google, Is AДокумент8 страницGoogle Search, Commonly Referred To As Google Web Search or Just Google, Is Awan2shareОценок пока нет
- Google Search, Also Referred To As Google Web Search or Simply Google, Is AДокумент1 страницаGoogle Search, Also Referred To As Google Web Search or Simply Google, Is Aezhilarasi pОценок пока нет
- Research Paper EДокумент26 страницResearch Paper EfelОценок пока нет
- Case 7-1 PDFДокумент3 страницыCase 7-1 PDFasdfОценок пока нет
- Chapter I - Introduction: The Future of Management London Business School Professor, Gary HamelДокумент30 страницChapter I - Introduction: The Future of Management London Business School Professor, Gary HamelJermaine WeissОценок пока нет
- Binjal (The Success Story of Google.)Документ73 страницыBinjal (The Success Story of Google.)TanviChokseyОценок пока нет
- Google Case StudyДокумент10 страницGoogle Case Studyharish chanderОценок пока нет
- Success Story of GoogleДокумент44 страницыSuccess Story of GoogleNeel KeshariaОценок пока нет
- Research DocumentДокумент24 страницыResearch DocumentZiaBilalОценок пока нет
- Is Google Enough?Документ11 страницIs Google Enough?Joe PОценок пока нет
- Assignment 2: Google Inc.: From Follower To Leader Innovation and Technology ManagementДокумент7 страницAssignment 2: Google Inc.: From Follower To Leader Innovation and Technology ManagementHuda RazakОценок пока нет
- Google Inc. Human Resource Management ReportДокумент21 страницаGoogle Inc. Human Resource Management ReportMegat Azwan0% (1)
- Concept Paper GoogleДокумент7 страницConcept Paper GoogleMsAzeal MoranteОценок пока нет
- Google Case Study and AnalysisДокумент12 страницGoogle Case Study and AnalysisSaad AliОценок пока нет
- Google Search, Also Referred To As Google Web Search or Simply Google, Is AДокумент1 страницаGoogle Search, Also Referred To As Google Web Search or Simply Google, Is AasklkaslaksОценок пока нет
- A Research Report OnДокумент43 страницыA Research Report Onarijitguha07Оценок пока нет
- HHAHAHAHAHAAHAHДокумент3 страницыHHAHAHAHAHAAHAHDaniel MosoretiОценок пока нет
- Google orДокумент8 страницGoogle orChuna JunaОценок пока нет
- History: Earch Engine Optimization (SEO) Is The Process of Affecting The Visibility of AДокумент7 страницHistory: Earch Engine Optimization (SEO) Is The Process of Affecting The Visibility of ASujata KumarОценок пока нет
- Google's EFEДокумент10 страницGoogle's EFEBhanu TyagiОценок пока нет
- Escholarship UC Item 0nj460xnДокумент11 страницEscholarship UC Item 0nj460xnHakuNama TataОценок пока нет
- Google Inc.: Type: Traded AsДокумент9 страницGoogle Inc.: Type: Traded AsNaimul Haque NayeemОценок пока нет
- Sucess Story of GoogleДокумент4 страницыSucess Story of GoogleRalsha DinoopОценок пока нет
- Company Overview: To Organize The World's Information and Make It Universally Accessible andДокумент11 страницCompany Overview: To Organize The World's Information and Make It Universally Accessible andAtul MalhotraОценок пока нет
- Google in China ReportДокумент2 страницыGoogle in China Reportmpique07Оценок пока нет
- How Google Works: Case HistoryДокумент6 страницHow Google Works: Case HistoryRahul KumarОценок пока нет
- GoogleДокумент18 страницGoogleMony MstОценок пока нет
- Enterprenour MindsetДокумент29 страницEnterprenour MindsetgitanshОценок пока нет
- Holistic SEO: SEO Copywriting Training - Lesson 1.1Документ15 страницHolistic SEO: SEO Copywriting Training - Lesson 1.1jijijijОценок пока нет
- ROLL NO: 320-33014 Subject: Introduction To IctДокумент7 страницROLL NO: 320-33014 Subject: Introduction To IctAdil Javed CHОценок пока нет
- SEO (Disambiguation) : Internet MarketingДокумент8 страницSEO (Disambiguation) : Internet Marketingmrchavan143Оценок пока нет
- Google: Contents (Документ4 страницыGoogle: Contents (Jeelian LeongОценок пока нет
- Search EngineДокумент4 страницыSearch EngineMoieenОценок пока нет
- 1 1 Search Engines SEO For BeginnersДокумент11 страниц1 1 Search Engines SEO For BeginnersVuyisile khupisoОценок пока нет
- Google Case Study Final ExamДокумент23 страницыGoogle Case Study Final ExamAudley R Grimes100% (5)
- Etech Mainstream Search EnginesДокумент11 страницEtech Mainstream Search EnginesfuritsuuОценок пока нет
- Quarter 1 Module 3Документ2 страницыQuarter 1 Module 3lbel9351Оценок пока нет
- Online Advertising Is A Form ofДокумент5 страницOnline Advertising Is A Form ofR Straw Hatz RОценок пока нет
- Google LLC: Google Search Google (Disambiguation) GoogolДокумент12 страницGoogle LLC: Google Search Google (Disambiguation) GoogolVedansh MalviyaОценок пока нет
- Google's HRM Strategies Presentation-Ambesh Govind, MBA-4B - 078Документ34 страницыGoogle's HRM Strategies Presentation-Ambesh Govind, MBA-4B - 078purple0123100% (1)
- Research Paper On Google 1: Organizational Analysis PapeДокумент9 страницResearch Paper On Google 1: Organizational Analysis PapeRikky AbdulОценок пока нет
- Google Competitve StrategyДокумент2 страницыGoogle Competitve StrategyKrisli KutrolliОценок пока нет
- Google Turns 20: How One Search Engine Changed The WorldДокумент6 страницGoogle Turns 20: How One Search Engine Changed The WorldSandWich TutorialsОценок пока нет
- Case Study GoogleДокумент6 страницCase Study GoogleDevyana Indah Fajriani100% (1)
- GoogleДокумент26 страницGoogleseety2Оценок пока нет
- Business Model of Google IncorporationДокумент82 страницыBusiness Model of Google IncorporationRishabh AroraОценок пока нет
- Marketing Management Case Study 2Документ3 страницыMarketing Management Case Study 2phuc phanОценок пока нет
- Case Analysis - Google - Document TranscriptДокумент4 страницыCase Analysis - Google - Document TranscriptscrpmtlОценок пока нет
- Google GlassДокумент21 страницаGoogle GlassFathima RashmiОценок пока нет
- SEO For Beginners Module 1 1 Google PDFДокумент13 страницSEO For Beginners Module 1 1 Google PDFPayal MehtaОценок пока нет
- Partner I TechДокумент4 страницыPartner I Techvignesh krishnanОценок пока нет
- Project On Internet MarketingДокумент18 страницProject On Internet MarketingSameer JadhavОценок пока нет
- Sales: 1st QTR 2nd QTR 3rd QTR 4th QTRДокумент1 страницаSales: 1st QTR 2nd QTR 3rd QTR 4th QTRwan2shareОценок пока нет
- Sales: 1st QTR 2nd QTR 3rd QTR 4th QTRДокумент1 страницаSales: 1st QTR 2nd QTR 3rd QTR 4th QTRwan2shareОценок пока нет
- JadualДокумент1 страницаJadualwan2shareОценок пока нет
- How Do I Insert A Landscape Page Into MyДокумент1 страницаHow Do I Insert A Landscape Page Into Mywan2shareОценок пока нет
- Google Search, Commonly Referred To As Google Web Search or Just Google, Is AДокумент8 страницGoogle Search, Commonly Referred To As Google Web Search or Just Google, Is Awan2shareОценок пока нет
- AutoPIPE Tutorial PDFДокумент156 страницAutoPIPE Tutorial PDFdhaktodesatyajitОценок пока нет
- Case Digest 2 S.C. MEGAWORLD CONSTRUCTIONДокумент3 страницыCase Digest 2 S.C. MEGAWORLD CONSTRUCTIONRomualdo CabanesasОценок пока нет
- Natural Gas DistributionДокумент46 страницNatural Gas DistributionscribdmisraОценок пока нет
- E9d30c8 4837smartДокумент1 страницаE9d30c8 4837smartSantoshОценок пока нет
- Mamalawo? The Controversy Over Women Practicing Ifa DivinationДокумент20 страницMamalawo? The Controversy Over Women Practicing Ifa DivinationE_SherwoodОценок пока нет
- Hitachi Zx330 3 Series Hydraulic ExcavatorДокумент15 страницHitachi Zx330 3 Series Hydraulic ExcavatorAgung ArdhanaОценок пока нет
- New Rich Text DocumentДокумент12 страницNew Rich Text Documentsonam dorjiОценок пока нет
- Internship Proposal FormДокумент3 страницыInternship Proposal FormMuhammad FidaОценок пока нет
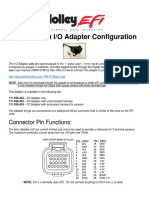
- Digital Dash I/O Adapter Configuration: Connector Pin FunctionsДокумент8 страницDigital Dash I/O Adapter Configuration: Connector Pin FunctionsAfeef Ibn AlbraОценок пока нет
- Tutorial 2 - Financial EnvironmentДокумент5 страницTutorial 2 - Financial EnvironmentShi ManОценок пока нет
- UNIX Introduction 1Документ18 страницUNIX Introduction 1Akash SavaliyaОценок пока нет
- Detailed Lesson Plan in HousekeepingДокумент6 страницDetailed Lesson Plan in HousekeepingreyОценок пока нет
- B2 UNIT 4 Test StandardДокумент6 страницB2 UNIT 4 Test StandardВладимир РанцовОценок пока нет
- Motivation MBAДокумент31 страницаMotivation MBAAkshitaОценок пока нет
- 20 Heirs of Alfredo Bautista VS LindoДокумент3 страницы20 Heirs of Alfredo Bautista VS LindoJerome LeañoОценок пока нет
- RagragsakanДокумент6 страницRagragsakanRazel Hijastro86% (7)
- Intro To Semiology Reading NotesДокумент6 страницIntro To Semiology Reading NotesRyan DrakeОценок пока нет
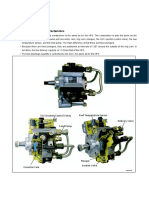
- Denso HP4Документ87 страницDenso HP4Abraham Janco Janco100% (2)
- Sistem Informasi Pencatatan Data Pelanggan Pada Telkomsel Grapari Banda AcehДокумент6 страницSistem Informasi Pencatatan Data Pelanggan Pada Telkomsel Grapari Banda AcehJurnal JTIK (Jurnal Teknologi Informasi dan Komunikasi)Оценок пока нет
- Bang Thong Ke Phep NamДокумент16 страницBang Thong Ke Phep NamTiến Tươi TỉnhОценок пока нет
- Job Board Week WhituДокумент5 страницJob Board Week WhituAnonymous MZh1KUUXОценок пока нет
- Buyer Behavior ModelДокумент1 страницаBuyer Behavior ModelraihanulhasanОценок пока нет
- Lesson Plan 4Документ6 страницLesson Plan 4Lilay Barambangan100% (3)
- Title Toolbox 1 AДокумент2 страницыTitle Toolbox 1 AGet LiveHelpОценок пока нет
- Emcee Script For CompetitionДокумент2 страницыEmcee Script For CompetitionArdini Izzati100% (3)
- The Camera Obscura Was Increasingly Used by ArtistsДокумент4 страницыThe Camera Obscura Was Increasingly Used by Artistsapi-284704512Оценок пока нет
- R Don Steele - How To Date Young Women For Men Over 35Документ232 страницыR Don Steele - How To Date Young Women For Men Over 35gonzalo_barandiarán83% (6)
- The Spokesman Weekly Vol. 32 No. 39 May 30, 1983Документ12 страницThe Spokesman Weekly Vol. 32 No. 39 May 30, 1983SikhDigitalLibraryОценок пока нет
- How To Use KEATДокумент5 страницHow To Use KEATAamir KhanОценок пока нет
- This I BeleiveДокумент3 страницыThis I Beleiveapi-708902979Оценок пока нет