Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Biomolecules MS
Загружено:
Abdullah HassanyАвторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Biomolecules MS
Загружено:
Abdullah HassanyАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
AS 2
BIOMOLECULES
ANSWERS & MARK SCHEMES
QUESTIONSHEET 1
(a)
C
C
C
OH
(b) condensation;
HO
; C
C
C
2
1
H2O;
(c) hydrolysis/digestion;
(d) liver/muscles;
(e) mix equal volumes of solution and dilute hydrochloric acid;
boil in a water bath (for 2 minutes) to hydrolyse sucrose (to glucose and fructose);
mix with equal volumes of Benedicts reagent;
boil in water bath (for 2 minutes);
if brick red precipitate appears then sucrose is present;
mix equal volumes of solution and (dilute/5 %) sodium hydroxide;
run dilute/1% copper sulphate solution into the solution;
a purple ring at the interface indicates protein is present;
Max 6
TOTAL 11
QUESTIONSHEET 2
(a) isomers;
(b) the position of -H and -OH groups on first carbon atom;
(c) leads to greater chemical variety/biochemical division of labour;
alpha glucose/starch is respiratory;
whereas beta glucose/cellulose is structural;
(d) glycosidic/condensation links;
max 2
1
TOTAL 5
Page 1
AS 2
BIOMOLECULES
ANSWERS & MARK SCHEMES
QUESTIONSHEET 3
(a) (i)
(ii)
saturated means that the molecule contains the maximum number of hydrogen atoms;
unsaturated means that the molecule contains fewer hydrogen atoms than it might/contains double bonds;
unsaturated fats have lower melting points than saturated fats;
unsaturated fats form oils but saturated fats are solid;
(b) Any four of:
dont dissolve in water/body fluids/
therefore dont affect osmotic balance of cells/tissues/
have higher calorific value than carbohydrates/
can yield more energy per gramme on oxidation/
reference to other useful properties/buoyancy/insulation;;;;
G
L
Y
C
E
R
O
L
(c) (i)
(ii)
4
1 mark for labelling the glycerol part of the molecule;
1 mark for labelling the fatty acids;
1 mark for labelling the bond;
fatty acid (side chain)
fatty acid (side chain)
fatty acid (side chain)
ester bond
one fatty acid molecule would be replaced by phosphoric acid/phosphate;
1
TOTAL 12
QUESTIONSHEET 4
(a) fatty acids joined to;
glycerol;
phosphate also attached;
reference to alcohol/choline attached to phosphate;
(credit points on a diagram)
max 3
(b) (i)
(fatty acid) side chain
polar head
Correct drawing;
Correct labels;
2
(ii)
polar heads mix with water, non polar tails do not;
thus heads face water on both sides with tails to middle;
(c) Any 2 of:
waterproofing/protection qualified/cell membrane structure/insulation/give buoyancy;;
(d) Either
or
emulsion test - take sample and add equal volume of ethanol and an equal volume of cold water;
mix and if positive a white emulsion forms;
Sudan III test - add a few drops of Sudan III to sample;
red fat droplets appear if positive;
2
TOTAL 11
Page 2
AS 2
BIOMOLECULES
ANSWERS & MARK SCHEMES
QUESTIONSHEET 5
(a)
R
N
(ii)
OH
R
N
(b) (i)
R
N
H2O;
+
C
H
C
OH
correct peptide bond;
O
C
O
C
OH
rest of the molecule/side chain;
hydrogen/methyl group/any correct group;
(iii) peptide;
(c) their molecules contain both acidic and basic groups;
1
TOTAL 7
QUESTIONSHEET 6
(a) secondary protein structure/beta-pleated sheet;
(b) many hydrogen bonds between polypeptide chains;
(c) polypeptide chain;
bends/folds extensively;
into a compact/globular structure;
(d) Any two of:
ionic/
hydrogen/
disulphide bridges;; (reject peptide since these hold the primary structure together)
(e) haemoglobin/myoglobin/antibodies;
(f) add equal volume of (dilute/5%) potassium hydroxide solution to test solution;
(down side of test tube) add a few drops of (1%) copper sulphate solution;
presence of a purple ring at interface;
which dissolves to form a purple solution on shaking, indicates protein;
max 3
TOTAL 11
Page 3
AS 2
BIOMOLECULES
ANSWERS & MARK SCHEMES
QUESTIONSHEET 7
(a) A - phosphate;
B - pentose/ribose/deoxyribose; (not. sugar).
C - nitrogenous base/pyrimidine/purine;
D- nucleotide;
(b) (i)
(ii)
bases that will join together;
by hydrogen bonds;
A to T and G to C;
max 2
RNA has uracil instead of thymine;
RNA has ribose sugar instead of deoxyribose;
RNA is single stranded instead of double stranded;
3
TOTAL 9
QUESTIONSHEET 8
(a)
monosaccharide
disaccharide
polysaccharide
ribose
glucose
maltose
starch
lactose
glycogen
cellulose
7
(b) starch contains -glucose, cellulose contains -glucose;
starch linked by - glycosidic links, cellulose by -glycosidic links;
starch may contain branched chains, cellulose is unbranched;
max 2
TOTAL 9
Page 4
AS 2
BIOMOLECULES
ANSWERS & MARK SCHEMES
QUESTIONSHEET 9
(a) (i)
(ii)
(b) (i)
S = deoxyribose; P = phosphate; G = guanine; C = cytosine; T = thymine; A = adenine;
G - C:
S - S:
hydrogen;
phosphate bridge/bond;
supply energy;
for all energy-requiring reactions/synthesis/anabolism;
(ii)
co-enzyme;
hydrogen acceptor in respiration;
(iii) responsible for transfer of acetyl units; from glycolysis to Krebs cycle;
6
TOTAL 14
QUESTIONSHEET 10
(a) disaccharide/maltose;
(b) 1,4-glycosidic/alpha link;
(c) condensation;
(d) respiration/energy substrate;
C
(e) (i)
C
O
C
C
O;
C
C
C
(ii) (1, 4 -)glycosidic beta link;
1
TOTAL 6
QUESTIONSHEET 11
(a) protein;
(b) Any three of:
mix together equal volumes of solution and Benedicts reagent/
boil in a waterbath for (2 minutes)/
presence of brick red precipitate indicates glucose;;;
(c) use same volumes of test and standard solutions;
add same volume of glucose oxidase solution to each;
incubate for a standard/stated time at a suitable/stated temperature;
add same volume of peroxide and indicator;
read intensity of colour in photometer;
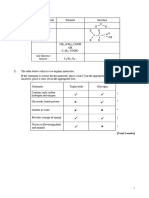
Reading of Test
calculate answer using formula Concentration of test
;
=
Concentration of standard Reading of Standard
max 4
TOTAL 8
Page 5
AS 2
BIOMOLECULES
ANSWERS & MARK SCHEMES
QUESTIONSHEET 12
(a) A - (beta)-glucose;
B - (1,4) glycosidic beta link;
(b) condensation/removal of water;
(c) main component plant cell walls;
d)
SUBSTANCE
Starch
Protein
DNA
Only contains C, H, and O
Contains nitrogen
Positive when boiled with Benedicts
reagent
Hydrolysed to smaller units
during digestion
Contains uracil
5
TOTAL 9
QUESTIONSHEET 13
(a) A & B;
(b) (hydrophobic) tails;
of phospholipid molecules;
(c) (i)
glycocalyx;
(ii)
polysaccharide/glycoprotein/carbohydrate;
(ii)
any two of: aids cell recognition/cell adherence/receptor sites for hormones/antibodies;;
2
TOTAL 7
Page 6
AS 2
BIOMOLECULES
ANSWERS & MARK SCHEMES
QUESTIONSHEET 14
(a) X - nucleic acid/DNA/RNA/ATP/nucleotide;
Y - protein/amino acid/polypeptide;
Z - cellulose/hemicellulose;
(b) amylose; amylopectin;
amylose is an unbranched chain but amylopectin is branched;
2
1
(c) (i)
(ii)
forms covalent/sulphur bonds;
holding adjacent polypeptides together/contributes to secondary/tertiary structure;
increases proteins stability to pH change;
increases proteins stability to temperature change;
(allow 1 mark if just refer to strong bonding)
2
TOTAL 10
QUESTIONSHEET 15
(a) X - phospholipid;
Y - extrinsic/external/surface protein;
Z - intrinsic/integral/internal protein;
(b) Y - cell recognition/support glycocalyx/has receptor groups;
Z - facilitated diffusion/active transport;
(c)
Phospholipid
Protein
Carbohydrate
Act as enzymes
Allows passage of
water soluble substances
Involved in cell recognition
TOTAL 8
Page 7
AS 2
BIOMOLECULES
ANSWERS & MARK SCHEMES
QUESTIONSHEET 16
(a) A: phosphate;
B: glycerol;
(b) circle round
C
(CH2)13
;
1
CH 3
(c) Precursors for prostaglandins/hormones/other fatty acids/essential for growth/provide energy/ATP synthesis;
(d) (i)
(ii)
vitamin A:
night blindness/hyperkeratosis/xerophthalmia;
failure to synthesise retinol/rhodopsin/drying/hardening/fracturing of epithelial tissues;
vitamin D:
rickets in children/osteomalacia in adults;
failure to regulate calcium/phosphate metabolism/absorption/mobilisation from bone/bent long bones/bow legs/
broken bones in adults;
TOTAL 8
QUESTIONSHEET 17
a) (i)
(ii)
(b) (i)
helix/secondary structure/fibrous structure;
Any three of:
hydrogen bonds/ionic bonds/sulphur bonds/peptide bonds;;;
max 3
tertiary structure/globular structure;
1
(ii)
quaternary structure;
1
(c) consists of 4 polypeptide chains/2 chains and 2 chains;
tightly folded globular structure/compact;
to fit in red blood cells;
each chain contains a haem group which contains iron;
each haem group can reversibly bind with an oxygen molecule;
max 4
TOTAL 10
QUESTIONSHEET 18
(a) alpha-;
glycosidic;
(b) liver/muscles;
(c) many ends/exposed/terminal glucose units;
allows rapid release of glucose/rapid digestion of molecule/rapid mobilisation in respiration;
make molecule compact so much can be stored in a small space;
(d) glucoses linked by beta-glycosidic links;
molecules are unbranched;
max 2
Page 8
TOTAL 7
AS 2
BIOMOLECULES
ANSWERS & MARK SCHEMES
QUESTIONSHEET 19
(a)
Macromolecule
Composition
RNA/DNA/nucleotides;
amino acids;
glycerol;
alpha-glucose;
beta-glucose;
5
(b) sequence of amino acids;
governs distribution of bonding regions;
which influence the position of hydrogen bonds/ionic bonds/disulphide bridges;
max 2
TOTAL 7
QUESTIONSHEET 20
deoxyribose/pentose; nitrogenous; hydrogen; cytosine; adenine; complementary; purine; thymine/cytosine; double helix; ten;
TOTAL 10
QUESTIONSHEET 21
(a) (i)
(ii)
on the single chromosome strand/in a plasmid;
in the nucleus/on every chromosome;
(iii) a nucleotide;
(iv) A - adenine; T = thymine;
1
C = cytosine; G = guanine; P = phosphate; D = deoxyribose;
(b) C pairs with G thus these must add up to 54% ;
thus A and T must form remaining 46% ;
in equimolecular proportions thus thymine = 23%;
3
TOTAL 12
Page 9
Вам также может понравиться
- Bio Molecules (C1) SA Mark SchemeДокумент11 страницBio Molecules (C1) SA Mark SchemeelatskiisОценок пока нет
- 2.2 Biological Molecules Ans PDFДокумент18 страниц2.2 Biological Molecules Ans PDFtess_15Оценок пока нет
- GCE Biology O-Level Paper 2 Mark SchemeДокумент8 страницGCE Biology O-Level Paper 2 Mark SchemeJonMortОценок пока нет
- Marking Schemes For Topic 1,2 Stafford PapersДокумент57 страницMarking Schemes For Topic 1,2 Stafford PapersSuha AbdullahОценок пока нет
- A Level Programme Mark SchemeMax7Max5Документ8 страницA Level Programme Mark SchemeMax7Max5Arvin DiNozzoОценок пока нет
- A-LEVEL BIOLOGY MARK SCHEMEДокумент4 страницыA-LEVEL BIOLOGY MARK SCHEMEAsmaa KhalidОценок пока нет
- 3.2 Cell Transport Ans PDFДокумент23 страницы3.2 Cell Transport Ans PDFtess_15Оценок пока нет
- If2 Letter Given, No Mark: CREDIT Answers From Clearly Drawn Diagrams With BondsДокумент4 страницыIf2 Letter Given, No Mark: CREDIT Answers From Clearly Drawn Diagrams With BondsEllie_Louise93Оценок пока нет
- 5090 w08 Ms 2Документ6 страниц5090 w08 Ms 2mstudy123456Оценок пока нет
- Paper 2 June 2001Документ5 страницPaper 2 June 2001MSHОценок пока нет
- GCE Biology Marking SchemeДокумент33 страницыGCE Biology Marking SchemeRabea2222sweetandsouОценок пока нет
- Cells AnswersДокумент9 страницCells AnswersLematha ParimalamОценок пока нет
- Unit 1 MsДокумент100 страницUnit 1 MselverineОценок пока нет
- Aqa Unit 1 June 2002 MsДокумент6 страницAqa Unit 1 June 2002 MsYanahan ParamalingamОценок пока нет
- EPAs Biology B A - Level Ch1Документ2 страницыEPAs Biology B A - Level Ch1Simon LecamionОценок пока нет
- MRN AS Biology B - 1Документ2 страницыMRN AS Biology B - 1Filsan HusseinОценок пока нет
- IB BIO Midterm PrepДокумент92 страницыIB BIO Midterm Prepptzpwpjk7gОценок пока нет
- Mark Scheme (Results) January 2007: GCE Biology (8040/9040)Документ12 страницMark Scheme (Results) January 2007: GCE Biology (8040/9040)Fathmath MohamedОценок пока нет
- Paper 1 Answers KeyДокумент7 страницPaper 1 Answers KeyAnshul BhangaleОценок пока нет
- Biology Unit 1 & 2 Questions 1996 To 2005 MS PDFДокумент97 страницBiology Unit 1 & 2 Questions 1996 To 2005 MS PDFLeen WaheedhОценок пока нет
- Mark Scheme (Results) January 2007: GCE Biology (8040/9040)Документ12 страницMark Scheme (Results) January 2007: GCE Biology (8040/9040)Fathmath MohamedОценок пока нет
- 2001 June Module 1 MSДокумент4 страницы2001 June Module 1 MSCharles ChunОценок пока нет
- Checked - Unit 5 Respiration, Internal Environment, Coordination and Gene Technology - Exam - MSДокумент20 страницChecked - Unit 5 Respiration, Internal Environment, Coordination and Gene Technology - Exam - MSEllane leeОценок пока нет
- Digestion and absorption of disaccharidesДокумент7 страницDigestion and absorption of disaccharidestess_15Оценок пока нет
- Nutrition AnswersДокумент9 страницNutrition Answersnoddy600% (1)
- Biology Photosynthesis AnswersДокумент9 страницBiology Photosynthesis AnswersalmahaОценок пока нет
- Benha University exam on metabolismДокумент2 страницыBenha University exam on metabolismnarita gaОценок пока нет
- ATP AnswersДокумент5 страницATP AnswersJavin SandhuОценок пока нет
- OCR A-Level Biology Module 2 Foundations in biology Mark schemeДокумент31 страницаOCR A-Level Biology Module 2 Foundations in biology Mark schemeDahamna KotuwelleОценок пока нет
- GCE Biology Marking Scheme HighlightsДокумент29 страницGCE Biology Marking Scheme Highlightsadam wilsonОценок пока нет
- 4BI0 1B MSC 20120121Документ16 страниц4BI0 1B MSC 20120121avishkabandaraОценок пока нет
- 9700 s07 Ms 2Документ7 страниц9700 s07 Ms 2NaeemMalikОценок пока нет
- AS Biology Unit F212 Molecules, Biodiversity, Food and HealthДокумент34 страницыAS Biology Unit F212 Molecules, Biodiversity, Food and HealthTravisJohn-JohnsonReadОценок пока нет
- Mark Scheme For Oct/Nov 2012 Biology (IGCSE)Документ11 страницMark Scheme For Oct/Nov 2012 Biology (IGCSE)Anonymous pVmgtFLyTОценок пока нет
- Paper 2 November 2001Документ5 страницPaper 2 November 2001MSHОценок пока нет
- Mark Scheme (Results) January 2013: International GCSE Biology (4BI0) Paper 1BДокумент20 страницMark Scheme (Results) January 2013: International GCSE Biology (4BI0) Paper 1BJohn HopkinsОценок пока нет
- Paper 2 June 2000Документ6 страницPaper 2 June 2000MSHОценок пока нет
- Biology Pp1 Marking Scheme Edited-1Документ5 страницBiology Pp1 Marking Scheme Edited-1Godwin OliechОценок пока нет
- 5096 s07 Ms 2Документ7 страниц5096 s07 Ms 2mstudy1234560% (1)
- Organisation of The Organism 3 MSДокумент6 страницOrganisation of The Organism 3 MSJ.Chang ChangОценок пока нет
- Marking Schemes For Topic 3 Stafford PapersДокумент30 страницMarking Schemes For Topic 3 Stafford Papersrifu91Оценок пока нет
- Metabolic Pathways MSДокумент8 страницMetabolic Pathways MSKajana Sivarasa ShenthanОценок пока нет
- Photosynthesis AnswersДокумент9 страницPhotosynthesis AnswersMusonda MwenyaОценок пока нет
- Biochem 3Документ20 страницBiochem 3eastereveОценок пока нет
- 5090 w01 Ms 2Документ4 страницы5090 w01 Ms 2Ahmed Kaleem Khan NiaziОценок пока нет
- As OCR Biology Notes Unit 2Документ34 страницыAs OCR Biology Notes Unit 2Jawwad Lnd KhanОценок пока нет
- 7040 01 Rms 20080306Документ14 страниц7040 01 Rms 20080306MERCY LAWОценок пока нет
- Respiration in Plants: Fact/Definition Type QuestionsДокумент12 страницRespiration in Plants: Fact/Definition Type QuestionsAditya DeshmukhОценок пока нет
- Aqa Byb4 W MS Jun08Документ9 страницAqa Byb4 W MS Jun08Jhon Key KeyОценок пока нет
- Carbohydrates: Monosaccharides, Polysaccharides and Glycosaminoglycans/TITLEДокумент10 страницCarbohydrates: Monosaccharides, Polysaccharides and Glycosaminoglycans/TITLELohith HanumОценок пока нет
- Biology Form 1 MsДокумент4 страницыBiology Form 1 Mspaqurette3Оценок пока нет
- 5090 w05 Ms 2Документ6 страниц5090 w05 Ms 2mstudy123456Оценок пока нет
- AS 2.1.2 Spec Notes AnswersДокумент6 страницAS 2.1.2 Spec Notes Answersmilksheikh2004Оценок пока нет
- Aqa Bya1 Sms Jun09Документ7 страницAqa Bya1 Sms Jun09atbtbtbОценок пока нет
- Association of Teachers in Biological Sciences: National Standard Examination in Biology 2012-2013Документ17 страницAssociation of Teachers in Biological Sciences: National Standard Examination in Biology 2012-2013Mrinal ChaudharyОценок пока нет
- AS2 Biomolecules QuestionsheetsДокумент9 страницAS2 Biomolecules Questionsheetsschan4bОценок пока нет
- 5090 BIOLOGY: MARK SCHEME For The October/November 2006 Question PaperДокумент6 страниц5090 BIOLOGY: MARK SCHEME For The October/November 2006 Question Papermstudy123456Оценок пока нет
- Homeostasis AnswersДокумент9 страницHomeostasis AnswersNur AmalinaОценок пока нет
- June 2015 DoneДокумент10 страницJune 2015 DoneAbdullah HassanyОценок пока нет
- January 2014 (IAL) QP - M1 Edexcel DONEДокумент28 страницJanuary 2014 (IAL) QP - M1 Edexcel DONEAbdullah HassanyОценок пока нет
- Module 1 - em Radiation and Quantum MsДокумент23 страницыModule 1 - em Radiation and Quantum MsAbdullah HassanyОценок пока нет
- Specimen MS - Paper 1 OCR Chemistry As-LevelДокумент17 страницSpecimen MS - Paper 1 OCR Chemistry As-LevelAbdullah HassanyОценок пока нет
- m1 Mock DoneДокумент5 страницm1 Mock DoneAbdullah HassanyОценок пока нет
- Chromatography NotesДокумент5 страницChromatography NotesAbdullah HassanyОценок пока нет
- Indian Calendar With HolidaysДокумент12 страницIndian Calendar With HolidayssmiledepakОценок пока нет
- Biological MoleculesДокумент53 страницыBiological MoleculesAbdullah HassanyОценок пока нет
- Biomolecules Chemistry AssignmentДокумент23 страницыBiomolecules Chemistry AssignmentArchita PanchalОценок пока нет
- Biomolecules: Organic Compounds of LifeДокумент43 страницыBiomolecules: Organic Compounds of LifeEunice AcunaОценок пока нет
- Biomolecules in Cell OrganellesДокумент16 страницBiomolecules in Cell OrganellesMary SutingcoОценок пока нет
- Test Lipids Sudan IVДокумент5 страницTest Lipids Sudan IVSHAFIKANOR3661Оценок пока нет
- Biochemical Education - April 1995 - Vella - Principles of Bioinorganic Chemistry by S J Lippard and J M Berg PP 411Документ1 страницаBiochemical Education - April 1995 - Vella - Principles of Bioinorganic Chemistry by S J Lippard and J M Berg PP 411Neeraj MundaОценок пока нет
- Lab Report 1 Safety Biological Molecules FillableДокумент6 страницLab Report 1 Safety Biological Molecules Fillableapi-433281064Оценок пока нет
- Course of First Year BPharmДокумент36 страницCourse of First Year BPharmpokhara144Оценок пока нет
- Teaching Guide Biology 1Документ18 страницTeaching Guide Biology 1AILEEN DULAYОценок пока нет
- Biomolecules: Dr. Vishwajeet S. GhorpadeДокумент49 страницBiomolecules: Dr. Vishwajeet S. GhorpadeVishwajeet GhorpadeОценок пока нет
- Protein Structure and FunctionДокумент35 страницProtein Structure and FunctionPRAJWAL SHYAM BHOSALEОценок пока нет
- Biochemistry 153A: Introduction To Structure, Enzymes and MetabolismДокумент21 страницаBiochemistry 153A: Introduction To Structure, Enzymes and MetabolismStephanie NobelОценок пока нет
- Test Bank Essential Biochemistry 3rd Edition Pratt CornelyДокумент36 страницTest Bank Essential Biochemistry 3rd Edition Pratt Cornelybeastlyfulberj6gkg100% (41)
- CBSE Quick Revision Notes (Class-11 Biology) Chapter-09 BiomoleculesДокумент5 страницCBSE Quick Revision Notes (Class-11 Biology) Chapter-09 BiomoleculesSIDHARTH SBОценок пока нет
- BIOLOGY CELL GUIDEДокумент20 страницBIOLOGY CELL GUIDELaivey Ligan Luig Lemeric0% (1)
- 1628172537BS-Curriculum-GEB 2019-2020 OnwordДокумент113 страниц1628172537BS-Curriculum-GEB 2019-2020 OnwordLuminous AudioBooksОценок пока нет
- Identifying biomolecules in samplesДокумент7 страницIdentifying biomolecules in samplesMa. Karyl Ashrivelle CarreonОценок пока нет
- Biology 9 PDFДокумент278 страницBiology 9 PDFZahid MehmoodОценок пока нет
- Benefits of Biomolecules in the Human BodyДокумент3 страницыBenefits of Biomolecules in the Human BodyRamona Grace SimeraОценок пока нет
- 1 Intro To BiochemДокумент60 страниц1 Intro To BiochemJOHAINA NORОценок пока нет
- Enzyme Models and BiomoleculesДокумент3 страницыEnzyme Models and BiomoleculesJeffrey DaclanОценок пока нет
- The Chemical Building Blocks of Life: Multiple Choice QuestionsДокумент115 страницThe Chemical Building Blocks of Life: Multiple Choice QuestionsJing LiОценок пока нет
- Biomolecule Test Review 2016 - KeyДокумент6 страницBiomolecule Test Review 2016 - KeyVannyОценок пока нет
- 1.2. All Four Biomolecules V2Документ112 страниц1.2. All Four Biomolecules V2Clàudia VicenteОценок пока нет
- Q4 Science 10 Module 2Документ26 страницQ4 Science 10 Module 2Francine Alburo75% (4)
- Biology Elements Atoms CompoundsДокумент36 страницBiology Elements Atoms Compoundsho laОценок пока нет
- Bio Biological Molecules AlevelsДокумент28 страницBio Biological Molecules AlevelsMunazzagulОценок пока нет
- BiomoleculesДокумент83 страницыBiomoleculesZairaJallorinaОценок пока нет
- Biological MoleculesДокумент6 страницBiological MoleculessanaullahОценок пока нет
- Biochem SyllabusДокумент14 страницBiochem SyllabusLymberth BenallaОценок пока нет
- BIO20 - The Biomolecules (Handouts) PDFДокумент13 страницBIO20 - The Biomolecules (Handouts) PDFKeith Ryan LapizarОценок пока нет