Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Lenses and Ray Diagrams Qs
Загружено:
keyur.galaАвторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Lenses and Ray Diagrams Qs
Загружено:
keyur.galaАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Lenses and Ray Diagrams Qs
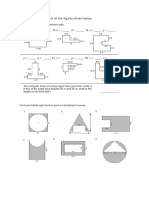
Q1.
(a)
(i)
The diagram shows two parallel rays of light, a lens and its axis.
Complete the diagram to show what happens to the rays.
(2)
(ii)
Name the point where the rays come together.
...........................................................................................................................
(1)
(iii)
What word can be used to describe this type of lens?
...........................................................................................................................
(1)
(b)
The diagram shows two parallel rays of light, a lens and its axis.
(i)
Which point A, B, C, D or E shows the focal point for this diagram?
Point ..................
(1)
(ii)
Explain your answer to part (b)(i).
...........................................................................................................................
Page 1
Lenses and Ray Diagrams Qs
...........................................................................................................................
(1)
(iii)
What word can be used to describe this type of lens?
...........................................................................................................................
(1)
(c)
Complete the following three sentences by crossing out the two lines in each box
which are wrong
film
In a camera a converging lens is used to produce an image on a
lens
screen
larger than
The image is
smaller than
the object.
the same size as
further away from
Compared to the distance of the image from the lens, the object is
nearer to
the same distance from
the lens.
(3)
(d)
Explain the difference between a real image and a virtual image.
.....................................................................................................................................
.....................................................................................................................................
.....................................................................................................................................
.....................................................................................................................................
.....................................................................................................................................
Page 2
Lenses and Ray Diagrams Qs
.....................................................................................................................................
(3)
(Total 13 marks)
Q2.
(a)
(i)
The diagram shows how parallel rays of light pass through a convex lens.
Mark the position of the focus.
(1)
(ii)
Is this a converging lens, a diverging lens, both or neither?
.........................................................................................................................
(1)
(b)
The diagram shows how parallel rays of light pass through a concave lens.
(i)
Mark the position of the focus.
(1)
(ii)
Is this a converging lens, a diverging lens, both or neither?
.........................................................................................................................
(1)
Page 3
Lenses and Ray Diagrams Qs
(c)
Complete these sentences by crossing out the two lines in each box that are wrong.
In a camera, a
lens is used to produce an image of an object on a
The image is
the object.
The image is
object from the lens.
the lens, compared to the distance of the
(4)
(d)
In a cinema projector, a convex lens is used to produce a magnified, real image.
(i)
What does magnified mean?
.........................................................................................................................
.........................................................................................................................
(1)
Page 4
Lenses and Ray Diagrams Qs
(ii)
What is a real image?
.........................................................................................................................
.........................................................................................................................
(1)
(e)
You are in a dark room. You have a box containing some lenses. Only one of them
is a
converging lens.
Describe how, by just feeling the lenses, you can pick out the converging lens.
...................................................................................................................................
...................................................................................................................................
...................................................................................................................................
...................................................................................................................................
(2)
(Total 12 marks)
Q3.
The diagram shows a lens being used as a magnifying glass.
(a)
(i)
What type of lens is shown in the diagram?
Draw a circle around your answer.
Page 5
Lenses and Ray Diagrams Qs
concave
converging
diverging
(1)
(ii)
Use the equation in the box to calculate the magnification produced by the
lens.
The object and image in the diagram have been drawn to full size.
Show clearly how you work out your answer.
...............................................................................................................
...............................................................................................................
Magnification = ........................................
(2)
(b)
The diagram shows how the image changes when the object has been moved
closer to the lens.
Complete the following sentence by drawing a ring around the correct line in the
box.
increases
Moving the object closer to the lens does not change the magnification produced
decreases
by the lens.
(1)
Page 6
Lenses and Ray Diagrams Qs
(Total 4 marks)
Q4.
The ray diagram shows a converging lens being used as a magnifying glass.
The diagram has been drawn to scale.
(a)
What name is given to the type of lens used as a magnifying glass?
........................................................................................................................
(1)
(b)
Calculate the magnification produced by the lens.
Write down the equation you use, and then show clearly how you work out your
answer.
........................................................................................................................
........................................................................................................................
........................................................................................................................
........................................................................................................................
Page 7
Lenses and Ray Diagrams Qs
........................................................................................................................
........................................................................................................................
Magnification = .....................................
(2)
(c)
Describe the image produced by a magnifying glass.
........................................................................................................................
........................................................................................................................
........................................................................................................................
(3)
(Total 6 marks)
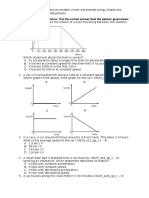
Q5.
A student investigates how the magnification of an object changes at different
distances from a converging lens.
The diagram shows an object at distance d from a converging lens.
(a)
(i)
The height of the object and the height of its image are drawn to scale.
Use the equation in the box to calculate the magnification produced by the
lens shown in the diagram.
Page 8
Lenses and Ray Diagrams Qs
Show clearly how you work out your answer.
...............................................................................................................
...............................................................................................................
...............................................................................................................
Magnification = ............................................................
(2)
(ii)
The points F are at equal distances on either side of the centre of the lens.
State the name of these points.
...............................................................................................................
(1)
(iii)
Explain how you can tell, from the diagram, that the image is virtual.
...............................................................................................................
...............................................................................................................
(1)
(b)
The student now uses a different converging lens. He places the object between the
lens and point F on the left.
The table shows the set of results that he gets for the distance d and for the
magnification produced.
Distance d
measured in cm
Magnification
1.2
10
1.5
15
2.0
20
3.0
25
6.0
His friend looks at the table and observes that when the distance doubles from 10
cm to 20 cm, the magnification doubles from 1.5 to 3.0.
Page 9
Lenses and Ray Diagrams Qs
His friends conclusion is that:
The magnification is directly proportional to the distance of the object from the lens.
His friends observation is correct but his friends conclusion is not correct.
(i)
Explain, with an example, why his friends conclusion is not correct.
...............................................................................................................
...............................................................................................................
...............................................................................................................
...............................................................................................................
(2)
(ii)
Write a correct conclusion.
...............................................................................................................
...............................................................................................................
(1)
(iii)
The maximum range of measurements for d is from the centre of the lens to F
on the left.
The student cannot make a correct conclusion outside this range.
Explain why.
...............................................................................................................
...............................................................................................................
(1)
(Total 8 marks)
Q6.
(a)
(i)
Page 10
The diagram shows a converging lens being used as a magnifying glass.
On the diagram, use a ruler to draw two rays from the top of the object which
show how and where the image is formed. Represent the image by an arrow
drawn at the correct position.
Lenses and Ray Diagrams Qs
(3)
(ii)
Use the equation in the box to calculate the magnification produced by the
lens.
Show clearly how you work out your answer.
...............................................................................................................
...............................................................................................................
Magnification = ........................................
(2)
(b)
A camera also uses a converging lens to form an image.
Describe how the image formed by the lens in a camera is different from the image
formed by a lens used as a magnifying glass.
........................................................................................................................
........................................................................................................................
Page 11
Lenses and Ray Diagrams Qs
........................................................................................................................
........................................................................................................................
(2)
(Total 7 marks)
Q7.
A student investigated how the nature of the image depends on the position of the
object in front of a large converging lens.
The diagram shows one position for the object.
(a)
Use a ruler to complete a ray diagram to show how the image of the object is
formed.
(4)
Page 12
Lenses and Ray Diagrams Qs
(b)
Describe the nature of this image relative to the object.
........................................................................................................................
........................................................................................................................
........................................................................................................................
(2)
(Total 6 marks)
Q8.
The diagram shows a lens, the position of an object and the position of the image of
the object.
(a)
What type of lens is shown?
........................................................................................................................
(1)
(b)
What is the name of the points, F, shown each side of the lens?
........................................................................................................................
(1)
(c)
(i)
The image is real and can be put on a screen.
How can you tell from the diagram that the image is real?
...............................................................................................................
Page 13
Lenses and Ray Diagrams Qs
...............................................................................................................
(1)
(ii)
inverted
Draw a ring around a word in the box which describes the image produced by
the lens.
larger
upright
(1)
(d)
A student investigates the relationship between the distance from the object to the
lens and the magnification produced by the lens.The students results are given in
the table.The student did not repeat any measurements.
Distance
in millimetres
Height of object
in millimetres
Height of image
in millimetres
Magnification
produced
40
20
58
2.9
50
20
30
1.5
60
20
20
1.0
70
20
14
0.7
80
20
12
0.6
90
20
10
0.5
The student plots the points for a graph of magnification produced against distance.
Page 14
Lenses and Ray Diagrams Qs
(i)
Draw a line of best fit for these points.
(1)
(ii)
Complete the following sentence by drawing a ring around the correct word in
the box.
A line graph has been drawn because both variables are
categoric.
described as being
continuous
.
discrete.
(1)
(iii)
Describe the relationship between magnification produced and distance.
...............................................................................................................
...............................................................................................................
...............................................................................................................
(2)
(Total 8 marks)
Page 15
Lenses and Ray Diagrams Qs
Q9.
The diagram shows an object located vertically on the principal axis of a diverging
lens. A student looks through the lens and can see an image of the object.
(a)
Using a pencil and ruler to draw construction lines on the diagram, show how light
from the object enters the students eye and the size and position of the image.
(3)
(b)
Describe the nature of the image by comparing it to the object.
.....................................................................................................................................
.....................................................................................................................................
.....................................................................................................................................
.....................................................................................................................................
(2)
(Total 5 marks)
Page 16
Lenses and Ray Diagrams Qs
Q10.
Malik uses a camera to photograph the Moon.
(a)
Complete each sentence by choosing the correct words from the box.
You may use each word once, more than once or not at all.
converging
diverging
image
longer
object
real
shorter
virtual
In a camera a ........................................ lens is used to produce
an ............................
of an ........................................ on a film. The ........................................ is smaller
than
the ........................................ and it is a ........................................ distance from the
lens.
(6)
(b)
The Moon moves in a nearly circular path around the Earth.
(i)
What is the name of the force which causes the Moon to move around the
Earth?
...........................................................................................................................
(1)
Page 17
Lenses and Ray Diagrams Qs
(ii)
In which direction does this force act?
...........................................................................................................................
(1)
(c)
A force is needed to make a car change direction when it goes round a bend.
(i)
What is the name of this force and where does it act?
...........................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................
(2)
(ii)
Complete the two spaces in the sentence.
The force needed is greater if the ........................................ of the car is
greater and
the ........................................ of the bend is smaller.
(2)
(d)
What word is used to describe any force which causes an object to move in a
circular path?
....................................................................................................................................
(1)
(Total 13 marks)
Page 18
Lenses and Ray Diagrams Qs
##
(a)
(i)
rays continued to meet on the right hand side of the lens and beyond
must be straight lines from the right hand side of the lens
ignore details through the lens
allow if no arrows
1
meet exactly on the axis
negate mark if contradictory arrow(s) added
do not need to go beyond the focus for this mark
1
(ii)
(principal) focus
or focal (point)
1
(iii)
converging
or convex
1
(b)
(i)
A
1
(ii)
rays seem to come from this point
or words to this effect
or shows this on the diagram
1
(iii)
diverging
or concave
1
(c)
film
accept any unambiguous method of showing the correct
response
1
smaller than
1
further away from
1
Page 19
Lenses and Ray Diagrams Qs
(d)
any three from:
real image can be put on a screen
allow film
virtual image cannot be put on a screen / film
virtual image is imaginary
real image is formed where (real) rays cross / converge
allow real image has light travelling through it
virtual image is where virtual / imaginary rays (seem to) come from
or virtual image is where rays seem to come from
virtual image formed where virtual rays intersect / cross
3
[13]
M2.
(a)
(i)
point where the rays cross
do not credit if ambiguous
1
(ii)
converging (lens)
do not accept convex
1
(b)
(i)
point where the rays appear to diverge from
this should appear to be within 10mm in front of the back of
the arrows on the approximate centre line
need not be accurately constructed using a ruler
1
(ii)
diverging (lens)
do not accept concave
1
Page 20
Lenses and Ray Diagrams Qs
(c)
converging
1
film
1
smaller than
nearer to
accept any clear indication of the response e.g. ticking,
ringing, writing in after a mistake
1
(d)
(i)
(image) bigger than object enlarge
accept just 'made bigger'
1
(ii)
it / real image can be put on a screen or real image on the opposite side
of the lens to the object
accept 'not an imaginary or virtual image'
assume 'it' refers to a real image
do not credit 'it can be seen'
1
(e)
either (the converging lens is) thick in the middle thin(ner) at the edge
1
thickest in the middle gains 2 marks
1
or (both) sides bend outwards (1) in the middle (1)
convex gains 2 marks
suitable diagrams gains 2 marks
or one side bends in the middle (1) more than the other side bends inwards
(in the middle) (1)
1
[12]
M3.
(a)
(i)
converging
1
Page 21
Lenses and Ray Diagrams Qs
(ii)
(x) 2
allow 1 mark for correct substitution
ie 10/5 or 20/10 or 2/1
ignore any units
2
(b)
decreases
1
[4]
M4.
(a)
converging
accept convex
1
(b)
3
allow 1 mark for substitution into the correct equation
ie
2
(c)
bigger
accept magnified
1
upright
1
virtual
1
[6]
Page 22
Lenses and Ray Diagrams Qs
M5.
(a)
(i)
answer in the range 3.0 3.1 inclusive
accept for 1
3.6 1.2 or 3.7 1.2
or 36 12 or 37 12
or 18 6 or 18.5 6
or 10.2 3.4 or 102 34
or answer in the range but with a unit eg 3 cm
2
(ii)
(principal) focus / focal (point(s)) / foci / focus
accept focusses
accept focals
do not accept focal length
1
(iii)
at the intersection of virtual / imaginary rays
or where virtual / imaginary rays cross
or the rays of (real) light do not cross
or the image on the same side (of the lens) as the object
or the image is drawn as a dotted line
or the image is upright
do not accept cannot be put on a screen
do not accept any response which refers to reflected rays
1
(b)
(i)
another correct observation about relationship between values of d (1)
(but) not the same relationship between corresponding
values for magnification (1)
example
15 is three times bigger than 5 but
2.0 is not three times bigger than 1.2
2
(ii)
when the distance / d increases the magnification increases
or the converse
accept there is a (strong) positive correlation
do not accept any response in terms of proportion / inverse
proportion
1
Page 23
Lenses and Ray Diagrams Qs
(iii)
(student has) no evidence (outside this range)
accept data / results / facts for evidence
1
[8]
M6.
(a)
(i)
two correct rays drawn
1 mark for each correct ray
ray parallel to axis from top of object and refracted through focus
traced back beyond object
and
ray through centre of lens and traced back beyond object
ray joining top of object to focus on left of lens taken to the lens
parallel to axis and traced back parallel to axis beyond object
refracted
an arrow showing the position and correct orientation of the image for their
rays
to gain this mark, the arrow must go from the intersection of
the traced-back rays to the axis and the image must be on
the same side of the lens as the object and above the axis
1
(ii)
(x) 3.0
accept 3.0 to 3.5 inclusive
or
correctly calculated
Page 24
Lenses and Ray Diagrams Qs
allow 1 mark for correct substitution into equation using their
figures
ignore any units
2
(b)
any two from:
in a camera the image is:
real not virtual
inverted and not upright
accept upside down for inverted
diminished and not magnified
accept smaller and bigger
accept converse answers but it must be clear the direction of
the comparison
both parts of each marking point are required
2
[7]
M7.
(a)
any two for 1 mark each
deduct (1) from the first two marks if a ruler has not been
used but the intention is clear
ray from the object's arrowhead
through centre of lens
parallel to the axis then, when it reaches the lens, through F on the right
through F on the left then, when it reaches the lens parallel to the axis
example of a 4 mark response
if more than two construction lines have been drawn all must
be correct to gain 2 marks
construction lines drawn as dashed lines do not score credit
2
image shown as vertical line from axis to where their rays intersect
image need not be marked with an arrowhead but, if it is, it
must be correct
1
Page 25
Lenses and Ray Diagrams Qs
ray direction shown
only one correct direction
arrow needed but there must not be any contradiction
1
(b)
any two from:
inverted
accept upside down
magnified
accept bigger
real
accept not virtual / not imaginary
one correct feature gains 1 mark
ignore any reference to position
an incorrect feature negates a correct response
2
[6]
M8.
(a)
converging (lens)
accept convex (lens)
accept biconvex
1
(b)
(principal) foci
accept focus / focuses / focis
focal point(s)
1
(c)
Page 26
(i)
formed where (real) rays (of light) intersect / meet / cross
accept rays (of light) pass through the image
accept image is on the opposite side (of the lens to the
object)
accept (construction) lines cross over
a response relating to a screen or similar is neutral
Lenses and Ray Diagrams Qs
lines are solid and not dotted is neutral
1
(ii)
inverted
accept any unambiguous correct indication
1
(d)
(i)
smooth curve which matches the points
judge by eye but do not accept point to point by ruler or
otherwise
1
(ii)
continuous
1
(iii)
as distance increases, magnification decreases
accept negative correlation
a statement inversely proportional is incorrect and limits
maximum mark for this part question to 1
1
further detail eg magnification falls steeply between 40 and 50 cm
or
magnification begins to level out after / at 70 cm
1
[8]
M9.
(a)
straight line from the tip of the object
straight through the centre of the lens (1)
parallel to the axis, then diverges from the lens as if from F (1)
image drawn from where these lines intersect, vertically to the axis (1)
example
Page 27
Lenses and Ray Diagrams Qs
(b)
any two from:
smaller (than the object)
(both) upright
image is virtual / imaginary (whereas object is real)
no errors carried forward from the candidates diagram
mark first two points given
2
[5]
M10.
(a)
converging
1
image
1
object
1
image
1
object
1
shorter
1
(b)
Page 28
(i)
(Earths) gravity
accept centripetal
accept minor misspellings, however,
do not credit any response which could be centrifugal
Lenses and Ray Diagrams Qs
1
(ii)
to(wards) (the centre of the) Earth
allow inwards do not accept downwards
1
(c)
(i)
either
friction (force) or centripetal force
allow grip
1
between the tyres / wheels and (the surface of) the road
allow on the tyres / wheels
or towards the centre of the bend / arc / circle
1
(ii)
mass or speed or momentum
allow weight allow velocity
1
radius / diameter
do not credit curvature or circumference
1
(d)
centripetal
accept minor misspellings (see above)
1
[13]
Page 29
Вам также может понравиться
- Q Names1 PDFДокумент4 страницыQ Names1 PDFClement Charles100% (1)
- Area and Trianle For KidsДокумент1 страницаArea and Trianle For Kidskeyur.galaОценок пока нет
- Modulus FunctionДокумент2 страницыModulus Functionkeyur.galaОценок пока нет
- PolynomialsДокумент4 страницыPolynomialskeyur.galaОценок пока нет
- Surface Area and Volume Word ProblemsДокумент2 страницыSurface Area and Volume Word Problemskeyur.galaОценок пока нет
- 12 Farmers Harvest The Crops in The Field in 20 HoursДокумент1 страница12 Farmers Harvest The Crops in The Field in 20 HoursJyoti ManwaniОценок пока нет
- 10 Advanced Trigonometry Part 1Документ4 страницы10 Advanced Trigonometry Part 1keyur.galaОценок пока нет
- Organic NomenclatureДокумент12 страницOrganic Nomenclatureitbwng100% (1)
- Matrices IGCSE QuestionsДокумент4 страницыMatrices IGCSE Questionskeyur.gala100% (2)
- Profit and Loss - AnswersДокумент3 страницыProfit and Loss - Answerskeyur.gala100% (1)
- Class Worksheet Date - Name: - Grade: 6th Unit: Ratio Subject: MathsДокумент4 страницыClass Worksheet Date - Name: - Grade: 6th Unit: Ratio Subject: Mathskeyur.galaОценок пока нет
- 12 Farmers Harvest The Crops in The Field in 20 HoursДокумент1 страница12 Farmers Harvest The Crops in The Field in 20 HoursJyoti ManwaniОценок пока нет
- Algebraic Expression (6th STD)Документ6 страницAlgebraic Expression (6th STD)keyur.galaОценок пока нет
- Percentages (6 TH STD)Документ2 страницыPercentages (6 TH STD)keyur.galaОценок пока нет
- Profit and Loss - AnswersДокумент3 страницыProfit and Loss - Answerskeyur.gala100% (1)
- Simple Interest - For KidsДокумент2 страницыSimple Interest - For Kidskeyur.galaОценок пока нет
- Speed, Velocity and Acceleration: Graphs, Equations and Falling BodiesДокумент4 страницыSpeed, Velocity and Acceleration: Graphs, Equations and Falling Bodieskeyur.galaОценок пока нет
- Simple Interest - For KidsДокумент2 страницыSimple Interest - For Kidskeyur.galaОценок пока нет
- 21 - Kinetic and Potential Energy (Answer)Документ4 страницы21 - Kinetic and Potential Energy (Answer)keyur.gala100% (2)
- 21 - Kinetic and Potential Energy (Answer)Документ4 страницы21 - Kinetic and Potential Energy (Answer)keyur.gala100% (2)
- MEP Y9 Practice Book B Sequences FormulaeДокумент28 страницMEP Y9 Practice Book B Sequences FormulaeRahique ShuaibОценок пока нет
- Quadratics ProblemsДокумент2 страницыQuadratics Problemskeyur.galaОценок пока нет
- Venn Diagram Word Problems and Set Theory QuestionsДокумент2 страницыVenn Diagram Word Problems and Set Theory Questionskeyur.galaОценок пока нет
- Q.I) Multiple Choice Questions. Tick The Correct Answer From The Options Given BelowДокумент4 страницыQ.I) Multiple Choice Questions. Tick The Correct Answer From The Options Given Belowkeyur.galaОценок пока нет
- 19 - Speed, Velocity and AccelerationДокумент4 страницы19 - Speed, Velocity and Accelerationkeyur.galaОценок пока нет
- 20 - Graphs and Equations (Answer)Документ5 страниц20 - Graphs and Equations (Answer)keyur.gala0% (1)
- 19 - Speed, Velocity and Acceleration (Answers)Документ4 страницы19 - Speed, Velocity and Acceleration (Answers)keyur.gala100% (1)
- Motion and EnergyДокумент43 страницыMotion and Energykeyur.galaОценок пока нет
- Motion and Energy (Notes)Документ32 страницыMotion and Energy (Notes)keyur.galaОценок пока нет
- 13 - Moment and Levers (Answers)Документ7 страниц13 - Moment and Levers (Answers)keyur.gala100% (1)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (894)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (399)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5794)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2219)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (344)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (265)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (119)
- First Quarter - Curriculum Map - Science 8Документ7 страницFirst Quarter - Curriculum Map - Science 8Mich Hora100% (7)
- Uncontrolled: Direct Shear Test of Soils Under Consolidated Drained ConditionsДокумент9 страницUncontrolled: Direct Shear Test of Soils Under Consolidated Drained ConditionsMohannad QutubОценок пока нет
- Friction Clutches 2020 CompressedДокумент14 страницFriction Clutches 2020 Compressedfikadu435Оценок пока нет
- Astm D2899Документ6 страницAstm D2899btwilliОценок пока нет
- Physico-Chemical Properties of DrugsДокумент64 страницыPhysico-Chemical Properties of DrugsYap Jacky33% (6)
- CO2 Dosing and Generation SystemДокумент344 страницыCO2 Dosing and Generation SystemABAID ULLAHОценок пока нет
- John Deere 772d 6wd GraderДокумент6 страницJohn Deere 772d 6wd GraderyaserattiaОценок пока нет
- Laura Hasley Statistics-Chi-Squared Goodness of Fit Test Lesson PlanДокумент11 страницLaura Hasley Statistics-Chi-Squared Goodness of Fit Test Lesson Planapi-242213383Оценок пока нет
- RPGS Complete Lecture Note1 Inpdf Compressed1Документ203 страницыRPGS Complete Lecture Note1 Inpdf Compressed1Purusottam PandeyОценок пока нет
- Manual LDM5 U enДокумент3 страницыManual LDM5 U enLuizAugustoMedeirosОценок пока нет
- VT2009B Eng 02 953680Документ2 страницыVT2009B Eng 02 953680gabrieltracto100% (1)
- Phase Shift of 180 Degrees On Reflection From Optically Denser MediumДокумент1 страницаPhase Shift of 180 Degrees On Reflection From Optically Denser MediumGreato HibernatoОценок пока нет
- Lsi/Csi: 24-Bit Dual-Axis Quadrature CounterДокумент12 страницLsi/Csi: 24-Bit Dual-Axis Quadrature CounterWilliam Méndez PérezОценок пока нет
- CS2204 Analog & Digital Communication Question BankДокумент16 страницCS2204 Analog & Digital Communication Question BankJesse VincentОценок пока нет
- Survey Whole Circle BearingДокумент19 страницSurvey Whole Circle BearingVin GaragiОценок пока нет
- I. 8-Bit Microprocessors Architecture, Instruction Set and Their ProgrammingДокумент4 страницыI. 8-Bit Microprocessors Architecture, Instruction Set and Their ProgrammingSaorabh KumarОценок пока нет
- Product Guide (English 140702)Документ11 страницProduct Guide (English 140702)Dineshkumar MahedranОценок пока нет
- Fire ZoneДокумент8 страницFire ZoneKannan NОценок пока нет
- Analysis of Excessive Hydrogen Generation in TransformersДокумент8 страницAnalysis of Excessive Hydrogen Generation in TransformersandikaubhОценок пока нет
- AerialSolution - 280 - Brochure - LT - New Design - Final - LRДокумент20 страницAerialSolution - 280 - Brochure - LT - New Design - Final - LRRover DmsОценок пока нет
- Laminar Flow Reactor ProblemДокумент6 страницLaminar Flow Reactor ProblemAileen Banua Añonuevo100% (1)
- FETs DatabookДокумент189 страницFETs DatabookTito Titon0% (1)
- Basic Probability and Reliability Concepts: Roy Billinton Power System Research Group University of Saskatchewan CanadaДокумент248 страницBasic Probability and Reliability Concepts: Roy Billinton Power System Research Group University of Saskatchewan CanadaSimon van BentenОценок пока нет
- Mech Vi Non Traditional Machining (10me665) NotesДокумент45 страницMech Vi Non Traditional Machining (10me665) Notesnikhil0% (1)
- Operating Instruction Precision Balance: Kern EwДокумент15 страницOperating Instruction Precision Balance: Kern EwjohnОценок пока нет
- Structural Design of Penstock - Criteria: Indian StandardДокумент21 страницаStructural Design of Penstock - Criteria: Indian StandardAlok KumarОценок пока нет
- Two Sigma - LeetCodeДокумент2 страницыTwo Sigma - LeetCodePeeyushОценок пока нет
- LEMBARAN KERJA BI TAHUN 4 (m7-10) PDPRДокумент9 страницLEMBARAN KERJA BI TAHUN 4 (m7-10) PDPRnurulwaznahОценок пока нет
- TG SkripsiДокумент138 страницTG SkripsiYudanto SetyoОценок пока нет
- Symmetric GroupДокумент13 страницSymmetric GroupPriyanka PatelОценок пока нет