Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
A
Загружено:
SaikumarVavilaАвторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
A
Загружено:
SaikumarVavilaАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
A hard disk drive (HDD), hard disk, hard drive or fixed disk[b] is a data storage device used for
storing and retrieving digitalinformation using one or more rigid ("hard") rapidly rotating disks
(platters) coated with magnetic material. The platters are paired with magnetic heads arranged
on a moving actuator arm, which read and write data to the platter surfaces.[2] Data is accessed in
arandom-access manner, meaning that individual blocks of data can be stored or retrieved in any
order and not only sequentially. HDDs are a type of non-volatile memory, retaining stored data
even when powered off.
Introduced by IBM in 1956,[3] HDDs became the dominant secondary storage device for generalpurpose computers by the early 1960s. Continuously improved, HDDs have maintained this
position into the modern era of servers and personal computers. More than 200 companies have
produced HDD units, though most current units are manufactured
by Seagate, Toshiba and Western Digital. As of 2015, HDD production (exabytes per year) and
areal density are growing, although unit shipments are declining.
The primary characteristics of an HDD are its capacity and performance. Capacity is specified
in unit prefixes corresponding to powers of 1000: a 1-terabyte (TB) drive has a capacity of
1,000 gigabytes (GB; where 1 gigabyte = 1 billion bytes). Typically, some of an HDD's capacity is
unavailable to the user because it is used by the file system and the computer operating system,
and possibly inbuilt redundancy for error correction and recovery. Performance is specified by the
time required to move the heads to a track or cylinder (average access time) plus the time it
takes for the desired sector to move under the head (average latency, which is a function of the
physical rotational speed in revolutions per minute), and finally the speed at which the data is
transmitted (data rate).
The two most common form factors for modern HDDs are 3.5-inch, for desktop computers, and
2.5-inch, primarily for laptops. HDDs are connected to systems by standard interface cables such
as PATA (Parallel ATA), SATA (Serial ATA), USB or SAS (Serial attached SCSI) cables.
As of 2016, the primary competing technology for secondary storage is flash memory in the form
of solid-state drives (SSDs), which have higher data transfer rates, better reliability,[4] and
significantly lower latency and access times, but HDDs remain the dominant medium for
secondary storage due to advantages in cost per unit of storage. [5][6] However, SSDs are replacing
HDDs where speed, power consumption and durability are more important considerations.[7]
[8]
Hybrid drive products, also known by the initialism SSHD, have been available since 2007,
[9]
made as a combination of HDD and SSD technology in a single device.
Вам также может понравиться
- Better Source NeededДокумент1 страницаBetter Source NeededSaikumarVavilaОценок пока нет
- Poiesis: Poetry (The Term Derives From A Variant of TheДокумент1 страницаPoiesis: Poetry (The Term Derives From A Variant of TheSaikumarVavilaОценок пока нет
- A. CCM OperationДокумент6 страницA. CCM OperationSaikumarVavilaОценок пока нет
- Tech 1Документ4 страницыTech 1SaikumarVavilaОценок пока нет
- Sujai TCS RESumeДокумент4 страницыSujai TCS RESumeSaikumarVavilaОценок пока нет
- Android (Operating System)Документ3 страницыAndroid (Operating System)SaikumarVavilaОценок пока нет
- 4K Resolution, Also Called 4K, Refers To A Display Device or Content Having HorizontalДокумент1 страница4K Resolution, Also Called 4K, Refers To A Display Device or Content Having HorizontalSaikumarVavilaОценок пока нет
- Understanding of Cathode Ray TubeДокумент3 страницыUnderstanding of Cathode Ray TubeSaikumarVavilaОценок пока нет
- The Japanese Launched 353 Aircraft During The Attack On Pearl HarborДокумент2 страницыThe Japanese Launched 353 Aircraft During The Attack On Pearl HarborSaikumarVavilaОценок пока нет
- World War 2 Facts Tell Us About A Bloody Conflict That Involved All The Nations of The WorldДокумент2 страницыWorld War 2 Facts Tell Us About A Bloody Conflict That Involved All The Nations of The WorldSaikumarVavilaОценок пока нет
- Eee Unit VДокумент34 страницыEee Unit VSaikumarVavilaОценок пока нет
- Advanced Computer ArchitectureДокумент4 страницыAdvanced Computer ArchitectureSaikumarVavilaОценок пока нет
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (895)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5794)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (266)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (400)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (345)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2259)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (121)
- Chapter 2 - Input Output DevicesДокумент52 страницыChapter 2 - Input Output Devicesfarahreazy1Оценок пока нет
- Philips 246V5LДокумент96 страницPhilips 246V5Ldead dmitryОценок пока нет
- Ibm Thinkpad A31 Venice-1 Rev 2.04a SCH PDFДокумент76 страницIbm Thinkpad A31 Venice-1 Rev 2.04a SCH PDFempeeno1Оценок пока нет
- Asus Strix 1070 Cg411p 8gb Gddr5x Rev1.0Документ39 страницAsus Strix 1070 Cg411p 8gb Gddr5x Rev1.0Julio Bello100% (1)
- DP Bluetooth Wnt5 x86!32!910 XPДокумент26 страницDP Bluetooth Wnt5 x86!32!910 XPblindangleОценок пока нет
- LENOVOДокумент1 страницаLENOVOkartika elisabethОценок пока нет
- SCX-6555NX: Copier Based Multi-Function Laser Printer (Print, Copy, FAX, Scan)Документ99 страницSCX-6555NX: Copier Based Multi-Function Laser Printer (Print, Copy, FAX, Scan)Andres Lopez ArandaОценок пока нет
- 5 Axis CNC Breakout BoardДокумент13 страниц5 Axis CNC Breakout Boardzeca2zecaОценок пока нет
- List DevicesДокумент53 страницыList Devicesgrant tapia floresОценок пока нет
- Cost To Cost: Cost To Cost Whatsapp No: 9811616164 7303906164 Amd Ryzen-1400 (R-5) 6990Документ7 страницCost To Cost: Cost To Cost Whatsapp No: 9811616164 7303906164 Amd Ryzen-1400 (R-5) 6990NavpreetSinghDhunnaОценок пока нет
- A 320 MДокумент1 страницаA 320 MghulОценок пока нет
- It8718f S PDFДокумент191 страницаIt8718f S PDFJohnnyKerissonОценок пока нет
- Tabela Ilhatech DistribДокумент10 страницTabela Ilhatech DistribyuricasteloОценок пока нет
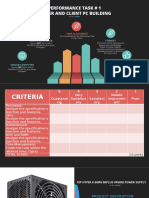
- Performance Task # 1 Server and Client PC BuildingДокумент21 страницаPerformance Task # 1 Server and Client PC BuildingJay CobbОценок пока нет
- KatalogДокумент35 страницKatalogNainОценок пока нет
- List DevicesДокумент78 страницList DevicesMharc KennethОценок пока нет
- Sony Vaio VPC-M Series PCG-21313M (Foxconn M9F1) PDFДокумент46 страницSony Vaio VPC-M Series PCG-21313M (Foxconn M9F1) PDFDanny CelyОценок пока нет
- 190CW7Документ85 страниц190CW7ferreralimaОценок пока нет
- Radio Comparision ChartДокумент1 страницаRadio Comparision ChartDanielMarínHernández100% (1)
- 8 Datasheet 46-Inch 3.5mm LCD Display Unit DS-D2046LU-Y1Документ4 страницы8 Datasheet 46-Inch 3.5mm LCD Display Unit DS-D2046LU-Y1ChristianОценок пока нет
- Cit 15 Computer Building ListДокумент12 страницCit 15 Computer Building Listapi-467328293Оценок пока нет
- A20 Bananapi SchematicДокумент13 страницA20 Bananapi SchematicingestevesОценок пока нет
- Contoh Hasil Stock Opname Produk A1Документ1 страницаContoh Hasil Stock Opname Produk A1Franky AugustОценок пока нет
- Delta - Offer - All Laptop Are With BagДокумент16 страницDelta - Offer - All Laptop Are With BagSantosh LakkavatriОценок пока нет
- Lista Integrados 20-8Документ99 страницLista Integrados 20-8Sergio GonzalesОценок пока нет
- 922651-Da-01-Ml-Isdn Adapter Rj45 Tae N Rj11 de enДокумент1 страница922651-Da-01-Ml-Isdn Adapter Rj45 Tae N Rj11 de enMax MaximОценок пока нет
- Carduri Memorie: Office@gimex - Ro WWW - GimexДокумент3 страницыCarduri Memorie: Office@gimex - Ro WWW - GimexofficeintrocarteОценок пока нет
- Certified Hard Disk DrivesДокумент2 страницыCertified Hard Disk DrivesnisarahmedgfecОценок пока нет
- c6525 0040Документ2 страницыc6525 0040joshi_ragsОценок пока нет
- M300 U400Документ38 страницM300 U400Sebastian FrancisОценок пока нет