Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Catabolic Pathways
Загружено:
Study SmarterИсходное описание:
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Catabolic Pathways
Загружено:
Study SmarterАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
UNIT 03-09.
01
CATABOLIC PATHWAYS
BOOKNOTES
LIFE IS WORK
Where does the energy stored in
organic molecules ultimately come
from?
What form does energy exit the
ecosystem?
The energy stored in the organic molecules of
food ultimately comes from the sun.
Energy flows into an ecosystem as sunlight and
exits as heat.
Chemical elements essential to life are recycled
What products does
photosynthesis generate?
What process breaks down fuel
and generates ATP?
Photosynthesis generates oxygen and
organic molecules that are used by the
mitochondria of eukaryotes (plants &
algae) as fuel or cellular respiration.
o Respiration breaks this fuel down,
generating ATP.
Waste products of this type
of respiration, carbon dioxide
and water are the raw
materials for photosynthesis.
CATABOLIC PATHWAYS YIELD ENERGY BY
OXIDIZING ORGANIC FUELS:
GENERAL BIOLOGY - CELLULAR RESPIRATION & FERMENTATION
UNIT 03-09.01
CATABOLIC PATHWAYS
BOOKNOTES
Define catabolic pathways.
CATABOLIC PATHWAYS:
Metabolic pathways that release stored
energy by breaking down complex
molecules.
CATABOLIC PATHWAYS & PRODUCTION OF
ATP
Compounds that participate in
what type of reaction can act as
fuel?
Define fermentation.
Define aerobic respiration.
Compounds that can participate in exergonic
reactions can act as fuels.
FERMENTATION:
A partial degradation of sugars or other
organic fuel that occurs without the use of
oxygen
AEROBIC RESPIRATION:
Oxygen is consumed as a reagent along
with the organic fuel- glucose.
- Food provides the fuel for respiration &
the exhaust is carbon dioxide and water.
Define anaerobic respiration.
Define cellular respiration.
What is the major source of
carbohydrates and what can it be
broken down into?
Why type of reaction is the
breakdown of glucose?
ANAEROBIC RESPIRATION:
Respiration w/o oxygen to harvest chemical
energy.
CELLULAR RESPIRATION:
Includes both aerobic and anaerobic
processes.
- Often used to refer to the aerobic
process.
Major source of carbohydrates is starch
storage polysaccharide that can be broken down
into glucose (C6H12O6) subunits.
The breakdown of glucose is exergonic
o G = -686 kcal/mol
GENERAL BIOLOGY - CELLULAR RESPIRATION & FERMENTATION
UNIT 03-09.01
CATABOLIC PATHWAYS
BOOKNOTES
How do the catabolic pathways
that decompose glucose and other
organic fuels yield energy?
Define Redox reaction.
Negative G indicates that
the products of the chemical
process store less energy
than the reactants and that
the reaction can happen
spontaneously (no input of E)
REDOX REACTIONS: OXIDATION AND
REDUCTION
How do the catabolic pathways that decompose
glucose and other organic fuels yield energy?
The relocation of e-s release energy stored
in organic molecules, and this energy
ultimately is used to synthesize ATP.
THE PRINCIPLE OF REDOX
Define oxidation.
Define reduction.
REDOX REACTIONS:
(oxidation-reduction reactions)
A chemical reaction in which there is a
transfer of one or more e-s from one
reactant to another.
OXIDATION:
The loss of electrons from one
substance
REDUCTION:
The addition of electrons to a
substance
(adding negatively charged e-s to an
atom reduces the amount of positive
charge on that atom)
Define reducing agent.
GENERAL BIOLOGY - CELLULAR RESPIRATION & FERMENTATION
UNIT 03-09.01
CATABOLIC PATHWAYS
BOOKNOTES
Define oxidizing agent.
What does an electron transfer
require?
REDUCING AGENT:
The electron donor
OXIDIZING AGENT:
The electron acceptor
An electron transfer requires both an electron
donor and acceptor oxidation and reduction
always go hand in hand.
What must be added to pull an
electron away from an atom?
When it comes to pulling electrons
away from an atom, what happens
when an atom is more
electronegative?
Energy must be added to pull an electron away
from an atom.
-
What is the greatest energy-
The more electronegative the atom (the
stronger its pull on electrons), the more
energy is required to take an electron
always from it.
o An electron loses potential energy
when it shifts from a less
electronegative atom toward a
more electronegative one.
GENERAL BIOLOGY - CELLULAR RESPIRATION & FERMENTATION
UNIT 03-09.01
CATABOLIC PATHWAYS
BOOKNOTES
yielding redox process that affect
A redox reaction that moves electrons closer to
all of us?
oxygen, such as the burning (oxidation) of
methane, therefore releases chemical energy that
can be put to work.
Define respiration.
OXIDATION OF ORGANIC FUEL MOLECULES
DURING CELLULAR RESPIRATION
The greatest energy-yielding redox process that
affect all of us is respiration.
Organic molecules have an
abundance of what type of fuel
source?
RESPIRATION:
The oxidation of glucose and other
molecules in food.
What type of barrier holds back the
flood of electrons to a lower energy
state?
The fuel (glucose) is oxidized
Oxygen is reduced.
The electrons lose potential energy along
the way as energy is released.
Organic molecules that have an abundance of
hydrogen are excellent fuels b/c their bonds are a
source of hilltop electrons, whose energy may
be released as these electrons fall down an
energy gradient when they are transferred to
oxygen.
-
Cellular respiration rxn. Indicates that H
is transferred from glucose to oxygen.
The oxidation of glucose transfers e-s to
a lower energy state
o Liberates energy that becomes
available for ATP synthesis.
The barrier of activation energy holds back the
flood of electrons to a lower energy state.
-
W/o this barrier: a food substance like
GENERAL BIOLOGY - CELLULAR RESPIRATION & FERMENTATION
UNIT 03-09.01
CATABOLIC PATHWAYS
BOOKNOTES
glucose will combine almost
Glucose is broken down in a series
instantaneously with oxygen.
of steps, each catalyzed by what?
- Body T is not enough to initiate burning,
instead if you swallow some glucose,
enzymes in your cells will lower the
Electrons travel with what in the
barrier of activation energy, allowing the
ETC?
sugar to be oxidized in a series of steps.
STEPWISE ENERGY HARVEST VIA NAD+ &
THE ELECTRON TRANSPORT CHAIN
Glucose is broken down in a series of steps,
each one catalyzed by an enzyme.
@ key steps e-s are stripped from glucose.
How does NAD+ trap electrons
from glucose & other molecules in
food?
Each electron travels with a proton (H
atom).
o H atoms are not transferred
directly to oxygen, usually passed
to an electron carrier, a coenzyme
called NAD+ (nicotinamide
adenine dinucleotide)
Well suited as an e- carrier
b/c it can cycle easily
between oxidized (NAD+)
and reduced (NADH) states.
How does NAD+ trap electrons from glucose &
other organic molecules in food?
Enzymes called dehydrogenases remove a
pair of hydrogen atoms (2 e-s and 2
protons) from the substrate, thereby
oxidizing it.
The NAD+ to NADH shows what?
What molecule is the most
versatile electron acceptor in
The enzyme delivers the 2 electrons along
with 1 proton to its coenzyme NAD+
The other proton is released as a hydrogen
ion (H+) into the surrounding solution.
GENERAL BIOLOGY - CELLULAR RESPIRATION & FERMENTATION
UNIT 03-09.01
CATABOLIC PATHWAYS
BOOKNOTES
cellular respiration?
What does each NADH molecule
formed during respiration
represent?
By receiving 2 negatively charged e-s but
only 1 positive charged proton, NAD+ has
its charge neutralized and is reduced to
NADH.
The name NADH shows the hydrogen that
has been received in the reduction.
How do electrons that are
extracted from glucose and stored
as potential energy in NADH finally
reach oxygen?
NAD+ is the most versatile electron acceptor in
cellular respiration and functions in several of the
redox steps during the breakdown of glucose.
Each NADH molecule formed during respiration
represents stored energy.
-
How does cellular respiration bring
hydrogen and oxygen together to
form water?
Energy can be tapped to make ATP when
the electrons complete their fall in a
series of steps down an energy gradient
from NADH to oxygen.
How do electrons that are extracted from
glucose and stored as potential energy in NADH
finally reach oxygen?
Comparing the redox chemistry of cellular
respiration to a much simpler reaction:
The reaction between H gas and O
gas to form water.
Provides a spark for activation
energy, & the gases combine
explosively.
Explosion represents a
release of energy as the
electrons of H fall closer
to the electronegative
oxygen atoms.
Cellular respiration also brings hydrogen
and oxygen together to form water, but
there are 2 important differences:
o The hydrogen that reacts with the
GENERAL BIOLOGY - CELLULAR RESPIRATION & FERMENTATION
UNIT 03-09.01
CATABOLIC PATHWAYS
BOOKNOTES
oxygen is derived from organic
molecules rather than H2
o Instead of occurring in one
explosive reaction, respiration uses
an electron transport chain to
break the fall of electrons to
oxygen into several energyreleasing steps.
Explain why NAD+ is an electron
shuttle?
Define electron transport chain.
The reduced form has an extra H, along with 2 es, bound to the carbon. There are different
numbers and positions of double bonds in the two
forms:
- The oxidized form has 2 double bonds in
the ring, while the reduced form has only
2.
- In the oxidized form there is a + charged
on the N, whereas in the reduced form it
is only sharing 3 electron pairs.
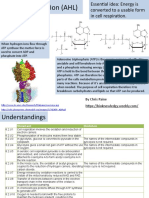
ELECTRON TRANSPORT CHAIN:
Consists of a number of molecules, mostly
proteins, built into the inner membrane of
GENERAL BIOLOGY - CELLULAR RESPIRATION & FERMENTATION
UNIT 03-09.01
CATABOLIC PATHWAYS
BOOKNOTES
the mitochondria of eukaryotic cells. (&
plasma membrane of respiring prokaryotes)
Electrons removed from glucose are
shuttled by NADH to the top, higherenergy end, Oxygen captures these
electrons along with the hydrogen nuclei
(H+), forming water.
(prokaryotes have an electron acceptor at
the end of the chain that is different from
O2)
Is the reaction of electron transfer
from NADH to Oxygen exergonic or
endergonic?
Explain how energy is being
produced / processed in the
electron transport chain?
What is the final electron acceptor
in the electron transport chain?
Electron transfer from NADH to oxygen is an
exergonic reaction with G = -53 kcal/mol (222kj/mol)
Instead of this energy being released and
wasted in a single explosive step, electron
cascade down the chain from one carrier
molecule to the next in a series of redox
reactions, losing a small amount of energy with
each step until they finally reach oxygen, the
GENERAL BIOLOGY - CELLULAR RESPIRATION & FERMENTATION
UNIT 03-09.01
CATABOLIC PATHWAYS
BOOKNOTES
terminal electron acceptor, which has a very
great affinity for electrons.
-
What are the stages in cellular
respiration?
Each downhill carrier is more
electronegative (capable of oxidizing)
than its uphill neighbor, with oxygen at
the bottom of the chain.
o e-s transferred from glucose to
NAD+ (reduced to NADH) fall down
an energy gradient in the electron
transport chain to a far more
stable location in the
electronegative oxygen atom.
Define glycolysis.
Define the citric acid cycle.
Oxygen pulls electrons down
the chain in an energyyielding tumble analogous to
gravity pulling objects
downhill.
SUMMARY:
During cellular respiration, most e-s travel
the following downhill route:
Glucose NADH electron transport chain
oxygen.
THE STAGES OF CELLULAR RESPIRATION: A
PREVIEW
Define oxidative phosphorylation.
GLYCOLYSIS:
Occurs in the cytosol, begins the
degradation process by breaking glucose
into 2 pyruvates
-
In eukaryotes pyruvate enters the
mitochondria and is oxidized into acetyl
CoA, which enters the citric acid cycle
CITRIC ACID CYCLE:
GENERAL BIOLOGY - CELLULAR RESPIRATION & FERMENTATION
10
UNIT 03-09.01
CATABOLIC PATHWAYS
BOOKNOTES
The breakdown of glucose to carbon dioxide
is completed (prokaryotes occurs in
cytosol)
-
Define substrate-level
phosphorylation.
Involves 8 steps that completes the
metabolic breakdown of glucose
molecules begun in glycolysis by
oxidizing acetyl CoA (derived from
pyruvate) to carbon dioxide.
Occurs w/in the mitochondria in
eukaryotic cells.
The energy released at each step of the ETC is
stored in a form the mitochondrion can use to
make ATP from ADP.
OXIDATIVE PHOSPHORYLATION:
The production of ATP using energy derived
from the redox reactions of an electron
transport chain; the 3rd major stage of
cellular respiration.
(ETC & chemiosmosis)
- Accounts for almost 90% of the ATP
generated by respiration.
Define substrate molecule.
Do you think the energy in this is
higher for the reactants or product
in the reaction?
SUBSTRATE-LEVEL PHOSPHORYLATION:
The enzyme-catalyzed formation of ATP by
direct transfer of a phosphate group to ADP
from an intermediate substrate in
GENERAL BIOLOGY - CELLULAR RESPIRATION & FERMENTATION
11
UNIT 03-09.01
CATABOLIC PATHWAYS
BOOKNOTES
catabolism.
For each molecule of glucose
degraded to carbon dioxide and
water, how many molecules of ATP
are made?
-
This mode of ATP synthesis occurs when
an enzyme transfers a phosphate group
from a substrate molecule to ADP, rather
than adding an inorganic phosphate to
ADP as in oxidative phosphorylation.
Substrate molecule:
Refers to an organic molecule
generated as an intermediate during
catabolism of glucose.
Concept Check 9.1:
1. Compare and contrast
aerobic and anaerobic
respiration.
2. WHAT IF? If the following
redox reaction occurred,
which compound would be
oxidized? Reduced?
Making connections:
Because there is no external source of energy for
the reaction, it must be exergonic, and the
reactants must be at a higher energy level than
the products.
+
+ C 4 H 4 O5 + NADH + H
C 4 H 6 O5 + NAD
For each molecule of glucose degraded to
carbon dioxide and water by respiration, the cell
makes up to about 32 molecules of ATP (each w/
7.3 kcal/mol of free energy)
GENERAL BIOLOGY - CELLULAR RESPIRATION & FERMENTATION
12
UNIT 03-09.01
CATABOLIC PATHWAYS
BOOKNOTES
1. Both processes include glycolysis, the citric
acid cycle and oxidative phosphorylation. In
aerobic respiration, the final electron
acceptor is molecular oxygen (O2); in
anaerobic respiration, the final electron
acceptor is a different substance.
2. C4H6O5 would be oxidized
NAD+ would be reduced.
GENERAL BIOLOGY - CELLULAR RESPIRATION & FERMENTATION
13
Вам также может понравиться
- CH 1 Answers For Chemical BiologyДокумент2 страницыCH 1 Answers For Chemical BiologyStudy Smarter33% (6)
- Ebook Campbell Biology Concepts and Connections 9Th Edition Taylor Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFДокумент32 страницыEbook Campbell Biology Concepts and Connections 9Th Edition Taylor Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFtristandoyledtnpkozbgj100% (13)
- Bioenergetics of Exercise and TrainingДокумент62 страницыBioenergetics of Exercise and Trainingswordplay716Оценок пока нет
- Jack Westin MCAT Content BiochemistryДокумент52 страницыJack Westin MCAT Content BiochemistryLora100% (2)
- Bio AP CHP 9 NotesДокумент13 страницBio AP CHP 9 Noteslauren roОценок пока нет
- AP Bio Notes Chapter 9Документ12 страницAP Bio Notes Chapter 9Michael LinОценок пока нет
- Chapter 9Документ32 страницыChapter 9DivineGloryMalbuyoОценок пока нет
- Chapter 9 Cellular Respiration NotesДокумент31 страницаChapter 9 Cellular Respiration NotesLisandrea BrownОценок пока нет
- Cellular Respiration & Respiratory CarriersДокумент12 страницCellular Respiration & Respiratory CarriersAsim AliОценок пока нет
- BCH 202 GENERAL BIOCHEMISTRY Biological OxidationДокумент11 страницBCH 202 GENERAL BIOCHEMISTRY Biological OxidationAyomiposi OloyedeОценок пока нет
- 1esc590. CH 1.biol OxДокумент28 страниц1esc590. CH 1.biol OxAndrae GenusОценок пока нет
- The Biological Processes in CellДокумент123 страницыThe Biological Processes in Cellanon_183990983Оценок пока нет
- Cellular RespirationДокумент16 страницCellular RespirationizabelaОценок пока нет
- Bio Exam 2Документ7 страницBio Exam 2юрий локтионовОценок пока нет
- Class 99999Документ14 страницClass 99999Areeba AamirОценок пока нет
- Cell Resp1 PaxsonДокумент9 страницCell Resp1 Paxsonrashmi_harryОценок пока нет
- Integrated ScienceДокумент12 страницIntegrated ScienceMalinda GreeneОценок пока нет
- Plants and Other Autotrophs Are The Producers of The BiosphereДокумент12 страницPlants and Other Autotrophs Are The Producers of The Biosphereюрий локтионовОценок пока нет
- What Is Respiration?Документ10 страницWhat Is Respiration?Yana LouisseОценок пока нет
- 7B InggrisДокумент2 страницы7B InggrisAlestya PutriОценок пока нет
- Bio HWДокумент9 страницBio HWedgar batotoОценок пока нет
- Oxidation and Reduction (Redox) Reactions: Electron DonorsДокумент11 страницOxidation and Reduction (Redox) Reactions: Electron DonorsMilica RančićОценок пока нет
- Oxidation and Reduction in Organic Chemistry AssignmentДокумент9 страницOxidation and Reduction in Organic Chemistry AssignmentAmanuel TarekegnОценок пока нет
- Lecture 4 Carbohydrate-GlycolysisДокумент20 страницLecture 4 Carbohydrate-GlycolysisBiology BảoОценок пока нет
- Photosynthesis and Cellular RespirationДокумент53 страницыPhotosynthesis and Cellular Respirationpia nodanaОценок пока нет
- Introduction To Metabolism Glycolysis and T.C.A. CycleДокумент23 страницыIntroduction To Metabolism Glycolysis and T.C.A. Cycleمحمد جانОценок пока нет
- Exam 2 - Chapter 9 Possible Test QuestionsДокумент4 страницыExam 2 - Chapter 9 Possible Test QuestionsChristinaFAUОценок пока нет
- Photosynthesis Respiration Corrosion: Reduction Is The Loss of Oxygen Atom From A Molecule or The Gaining of One orДокумент4 страницыPhotosynthesis Respiration Corrosion: Reduction Is The Loss of Oxygen Atom From A Molecule or The Gaining of One orEd GestonОценок пока нет
- ReportДокумент10 страницReportSems AlcozbaryОценок пока нет
- Agricultural University of Georgia Durmishidze Institute of Biochemistry and BiotechnologyДокумент63 страницыAgricultural University of Georgia Durmishidze Institute of Biochemistry and BiotechnologyZainab Jamal SiddiquiОценок пока нет
- BCH 202 - Oxidative Phosphorylation Metabolism and EnzymesДокумент10 страницBCH 202 - Oxidative Phosphorylation Metabolism and EnzymesOloruntomi AdesinaОценок пока нет
- Oxidation and Reduction (Redox) ReactionsДокумент11 страницOxidation and Reduction (Redox) ReactionsAbie BadhurahmanОценок пока нет
- Chapter 15.4 Lecture NotesДокумент23 страницыChapter 15.4 Lecture NotesZach MaxwellОценок пока нет
- Chapter 10 PhotosynthesisДокумент12 страницChapter 10 PhotosynthesisstarcandypricessОценок пока нет
- Cellular RespirationДокумент5 страницCellular RespirationjasmineОценок пока нет
- Group 4 PhotosynthesisДокумент11 страницGroup 4 PhotosynthesisJv Dela CruzОценок пока нет
- Reviewer in BiochemДокумент11 страницReviewer in BiochemLile RajabaОценок пока нет
- Biochemical PathwaysДокумент46 страницBiochemical PathwaysHameed FarisiОценок пока нет
- Chapter 18 - Photosynthesis: LightДокумент11 страницChapter 18 - Photosynthesis: LightCvitaCvitićОценок пока нет
- Paula B. Matheus CarnevaliДокумент24 страницыPaula B. Matheus CarnevalisankarОценок пока нет
- Green PhotocatalystДокумент22 страницыGreen Photocatalystniraj nairОценок пока нет
- Bio EnergeticsДокумент9 страницBio EnergeticssagarОценок пока нет
- PhotosynthesisДокумент7 страницPhotosynthesisjeankayzelrodelasОценок пока нет
- Thermodynamics of Energy Conversions in Living SystemsДокумент48 страницThermodynamics of Energy Conversions in Living SystemsraassfasfsaОценок пока нет
- 15 PhotosynthesisДокумент10 страниц15 PhotosynthesisEarl Adam LambacoОценок пока нет
- Photosynthesis Cell Biology FileДокумент16 страницPhotosynthesis Cell Biology FileRei KaplanОценок пока нет
- Photosynthesis Cell Biology FileДокумент16 страницPhotosynthesis Cell Biology FileRei KaplanОценок пока нет
- Electron Transport ChainДокумент19 страницElectron Transport Chaingaurav saxenaОценок пока нет
- CHAPter 9 STDGDДокумент9 страницCHAPter 9 STDGDGrigori ChulakiОценок пока нет
- Biochem Lecture Lesson 10.1 Biological Oxidation 1Документ16 страницBiochem Lecture Lesson 10.1 Biological Oxidation 1Ryan Carlo IbayanОценок пока нет
- Mid-Term Review Sheet John FarmerДокумент2 страницыMid-Term Review Sheet John FarmerJohn FarmerОценок пока нет
- Biological OxidationДокумент11 страницBiological OxidationendangtrisniatiОценок пока нет
- Photosynthesis: Leaves and Leaf StructureДокумент11 страницPhotosynthesis: Leaves and Leaf StructureMatthew BetinolОценок пока нет
- Photosynthesis Study GuideДокумент9 страницPhotosynthesis Study GuideJunhee KimОценок пока нет
- Gen Bio W3-5Документ9 страницGen Bio W3-5Alyson EscuderoОценок пока нет
- Section A: The Principles of Energy Harvest: Cellular Respiration: Harvesting Chemical EnergyДокумент14 страницSection A: The Principles of Energy Harvest: Cellular Respiration: Harvesting Chemical EnergyAhmedAbdelZaherОценок пока нет
- Photosynthesis (Light and Dark Reaction) :: Concept Notes With Formative ActivitiesДокумент12 страницPhotosynthesis (Light and Dark Reaction) :: Concept Notes With Formative ActivitiesMonica SolomonОценок пока нет
- C 3 RedoxДокумент28 страницC 3 RedoxRina P ShresthaОценок пока нет
- Reviewer For General Biology Chemistry 1Документ6 страницReviewer For General Biology Chemistry 1Bianca SuarezОценок пока нет
- La Ode Muhammad Zuhdi Mulkiyan F1C116075 Faculty of Math and Science Haluoleo UniversityДокумент20 страницLa Ode Muhammad Zuhdi Mulkiyan F1C116075 Faculty of Math and Science Haluoleo UniversityMuh Zuhdi MulkianОценок пока нет
- Chemistry and Electricity:: ElectrochemistryДокумент5 страницChemistry and Electricity:: ElectrochemistrySuleman TariqОценок пока нет
- 3 4 Group 6 Written Report With CommentsДокумент7 страниц3 4 Group 6 Written Report With CommentsJanine Abiegale PeraltaОценок пока нет
- Organic Chemistry Study Guide: Key Concepts, Problems, and SolutionsОт EverandOrganic Chemistry Study Guide: Key Concepts, Problems, and SolutionsРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (10)
- MCAT Krack Study GuideДокумент29 страницMCAT Krack Study GuideStudy SmarterОценок пока нет
- Purpose Summit Workbook: C L A S S 0 F 2 0 2 1Документ44 страницыPurpose Summit Workbook: C L A S S 0 F 2 0 2 1Study SmarterОценок пока нет
- 9 Tips To Integrate Into Health Center Care TeamsДокумент2 страницы9 Tips To Integrate Into Health Center Care TeamsStudy SmarterОценок пока нет
- 11 STUDY GUIDE Nitrogen Fixation, Amino Acid Biosynthesis, Nucleotide SynthesisДокумент18 страниц11 STUDY GUIDE Nitrogen Fixation, Amino Acid Biosynthesis, Nucleotide SynthesisStudy SmarterОценок пока нет
- Lab 01 NOTES On Scientific Data and GraphsДокумент9 страницLab 01 NOTES On Scientific Data and GraphsStudy SmarterОценок пока нет
- Palliative Care/Hospice and The Withdrawal of DialysisДокумент11 страницPalliative Care/Hospice and The Withdrawal of DialysisStudy SmarterОценок пока нет
- 16 General PharmacologyДокумент19 страниц16 General PharmacologyStudy SmarterОценок пока нет
- Set A Suggested Answer Mosys SB025 - 230430 - 191516Документ4 страницыSet A Suggested Answer Mosys SB025 - 230430 - 191516nursyakiramailanОценок пока нет
- Chapter 2 - BiomechanicsДокумент11 страницChapter 2 - Biomechanicstjewert23Оценок пока нет
- Biology - Module 5Документ11 страницBiology - Module 5ASHLEY MONICA PLATAОценок пока нет
- Organic Acid Metabolism and The Impact of Fermentation Practices On Wine AdicityДокумент16 страницOrganic Acid Metabolism and The Impact of Fermentation Practices On Wine AdicityOz HdzОценок пока нет
- BIO 101 Fundamentals of Biology ModuleДокумент66 страницBIO 101 Fundamentals of Biology ModuleCathleen AndalОценок пока нет
- Physiology of SportsДокумент460 страницPhysiology of SportsOnwaree Ing100% (3)
- GlycolysisДокумент7 страницGlycolysisTahirat NasiruОценок пока нет
- Microbiology With Diseases by Taxonomy 4th Edition Bauman Test Bank 1Документ538 страницMicrobiology With Diseases by Taxonomy 4th Edition Bauman Test Bank 1ricardo100% (46)
- BIOCHEM-Carbohydrate Metabolism 3-Alternative PathwayДокумент6 страницBIOCHEM-Carbohydrate Metabolism 3-Alternative PathwayStd DlshsiОценок пока нет
- Diagnostic Test. BiologyДокумент23 страницыDiagnostic Test. BiologyXia SanfordОценок пока нет
- Defining The Essence of The DiseaseДокумент26 страницDefining The Essence of The DiseaseAh MagdyОценок пока нет
- Chapter 9 - Cardio and ESD PDFДокумент28 страницChapter 9 - Cardio and ESD PDFDDVОценок пока нет
- UNSW BIOC2101: Review of PracticalsДокумент6 страницUNSW BIOC2101: Review of Practicalsrhea_supergirl7859Оценок пока нет
- Lecture 11 On Regulation of MetabolismДокумент23 страницыLecture 11 On Regulation of MetabolismSaad KazmiОценок пока нет
- Lesson 2 EnergyДокумент11 страницLesson 2 EnergyMichael John SongcuanОценок пока нет
- Chapter 15 Cellular Respiration 1Документ6 страницChapter 15 Cellular Respiration 1zeemboyzОценок пока нет
- Crop Production MCQДокумент31 страницаCrop Production MCQNsengimanaОценок пока нет
- Holiday Assignment - EssayДокумент13 страницHoliday Assignment - EssayElaine ChoiОценок пока нет
- High-Intensity Interval Training, Solutions To The Programming PuzzleДокумент30 страницHigh-Intensity Interval Training, Solutions To The Programming PuzzleArnav VoОценок пока нет
- The Science Behind Peak Metabolic Health DR Inigo San Millan The Proof Podcast - YouTubeДокумент50 страницThe Science Behind Peak Metabolic Health DR Inigo San Millan The Proof Podcast - YouTubeDavid RodriguezОценок пока нет
- Human Anatomy and Physiology II: Biology 1414 Unit 8 Metabolism and NutritionДокумент103 страницыHuman Anatomy and Physiology II: Biology 1414 Unit 8 Metabolism and Nutritionciroj25Оценок пока нет
- BioK 8.2 Cell Respiration AHLДокумент71 страницаBioK 8.2 Cell Respiration AHLSoham JaybhayОценок пока нет
- General BIology 1 Q2 M5 SCДокумент10 страницGeneral BIology 1 Q2 M5 SCAldrin James DafunОценок пока нет
- ATP Production From Carbs Protein FatsДокумент16 страницATP Production From Carbs Protein Fatshuraira bhattiОценок пока нет
- A2 Biology Syllabus 9700: Unit 1: Energy, Respiration and PhotosynthesisДокумент18 страницA2 Biology Syllabus 9700: Unit 1: Energy, Respiration and PhotosynthesisaduhaikОценок пока нет
- Glycolysis and TCA CycleДокумент38 страницGlycolysis and TCA CycleAboubakar Moalim Mahad moh'dОценок пока нет
- Season 2018Документ257 страницSeason 2018Gifton WrightОценок пока нет