Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Transistor
Загружено:
Siti Arbaiyah AhmadИсходное описание:
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Transistor
Загружено:
Siti Arbaiyah AhmadАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
LESSON 3
Understanding transistors
Introduction
A transistor consists of a crystal of one type of doped
semiconductor sandwiched between two crystals of
the opposite type.
A transistor is a semiconductor device capable of
amplification in addition to rectification.
It is the basic unit radio, television and computer.
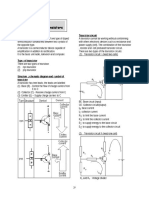
Transistor circuit
A transistor cannot be working without combinining
with others electronic devices such as resistance and
power supply (cell). The combination of thre transistor
, resistor and cell produced transistor circuit.
There are two types of the transistor circuits:
(1)
Transistor circuit I (need two cells)
Types of transistor
There are two types of transistor
(1)
npn transistor
(2)
pnp transistor
Structure ,schematic diagram and symbol of
transistor
A transistor has tree leads; the leads are labelled
(1) Base (B) - Control the flow of charge carriers from
E to C
(2) Collector (C) - Receive charge carriers from E
(3) Emitter (E) Supply charge carriers to C
BE: Base circuit (input)
CE: Collector circuitl(output)
Ib: base current
Ic: collector current
R1: to limit the base current
R2: to limit the collector current
E1: to supply energy to the base circuit
E2: to supply energy to the collector circuit
(2)
Transistor circuit II (need one cell)
Rx and RY : Voltage divider
Working principle of a transistor
VRx =
Rx
x V
( Rx + Ry)
VRY =
Ry
xV
( Rx + Ry)
Example 1
The figure shows a transistor circuit. Resistor P has a
resistance of 10 k. In order to light the bulb , the
potential difference across resistor P must be at least
2V.
(1)
it
The base current is very small (in A) when
compare with the collector current (in mA).
( Ib <<< Ic )
Current amplification = Ic
Ib
(2) A small change in base current, Ib will cause a
big change in the collector current, Ic
( Ib <<< Ic)
What is the maximum value of resistor Q when the
bulb lights?
Solution
(3)
Ie = Ib + Ic
From the working principles above , we
conclude that a transistor functions as a current
amplifier by allowing a small current to control a
larger current.
(4) When R1 = 0 , the base voltage VR1 = 0.
The base current does not flow and the
collector current als does not flow.
Ib = 0 and IC = 0
(5) When the resistance of R1 is increased, the
base voltage will increase until the base
voltage exceeds a certain minimum value,
the base current flows and cause a large
collector current flows.
From the working principles above , we
conclude that a transistor functions as an
automatic switch,so that the transistor turned
ON or OFF.
(2) The transistor as a light controlled switch
(6) When there is no Ic flowing in the collector
circuit , Ib still flows in the collector circuit.
(Ic = 0 hence Ib 0 )
(7) A transistor has not its own energy. The
energy in a transistor is supplied by the
power supply , such as cell.
Applications of transistors
(1)
The transistor as an amplifier
In bright light, the light-dependent resistor(LDR) has a
very low resistance. Therefore the potential diference
across LDR is low and hence the potential difference
across resistor R is high. The base current flows
and cause a large collector current flows. The bulb
lights up
In darkness , the light-dependent resistor(LDR) has a
very high resistance. Therefore the potential diference
across LDR is high and hence the potential difference
across resistor R is low. The base current does not
flow and cause the collector current does not flow.
The bulb not lights up.
If the positions of the LDR and R are interchanged,
the bulb is switched on in the dark and off in the bright
light.
(3) The transistor as a tempearture controlled
switch
When a person speaks into a microphone,
sound waves are converted into an alternating
current .
The small changes in the base circuits cause
the base current flows.
A small change in base current, will cause a big
change in the collector current.
The earphone thus receives a large alternating
current from the collector circuit and converts it
into a loud sound.
The capacitor blocks a steady current (direct
current) from flowing into the transistor and
microphone.
When the thermistor is cold, it has a larger resistance
than R. Therefore the potential diference across
thermistor is high and hence the potential difference
across resistor R is low. The base current does not
flow and cause the collector current does not flow.
The bulb not lights up.
When the temperature rises,the resistance of
thermistor falls and the bulb lights up.
Вам также может понравиться
- Lesson 3 - Understanding Transistors: Transistor CircuitДокумент9 страницLesson 3 - Understanding Transistors: Transistor CircuitSiti Arbaiyah AhmadОценок пока нет
- Lesson 9.4Документ14 страницLesson 9.4Siti Arbaiyah AhmadОценок пока нет
- Common Terminology of Logic GatesДокумент4 страницыCommon Terminology of Logic GatesSiti Arbaiyah Ahmad0% (2)
- (Bahagian C)Документ22 страницы(Bahagian C)Siti Arbaiyah AhmadОценок пока нет
- X A-Plus Module SBP Physics 2013 - 2Документ15 страницX A-Plus Module SBP Physics 2013 - 2Siti Arbaiyah AhmadОценок пока нет
- X A-Plus Module SBP Physics 2013 - 1Документ111 страницX A-Plus Module SBP Physics 2013 - 1Siti Arbaiyah Ahmad100% (1)
- 10.skima Jawapan Bahagian CДокумент9 страниц10.skima Jawapan Bahagian CSiti Arbaiyah AhmadОценок пока нет
- Lenses: Gejala Mereka Yang Mengalami Rabun Dekat: Kuman Di Over Sea' Nampak, Gajah Termenung' Tak NampakДокумент12 страницLenses: Gejala Mereka Yang Mengalami Rabun Dekat: Kuman Di Over Sea' Nampak, Gajah Termenung' Tak NampakSiti Arbaiyah AhmadОценок пока нет
- Chapter 4 PDFДокумент20 страницChapter 4 PDFSiti Arbaiyah AhmadОценок пока нет
- 53B LIGHT Refraction Total Internal ReflectionДокумент20 страниц53B LIGHT Refraction Total Internal ReflectionSiti Arbaiyah AhmadОценок пока нет
- 51 LIGHT RefractionДокумент13 страниц51 LIGHT RefractionSiti Arbaiyah AhmadОценок пока нет
- Understanding Total Internal Reflection of LightДокумент21 страницаUnderstanding Total Internal Reflection of LightSiti Arbaiyah AhmadОценок пока нет
- 53A LIGHT Refraction Real N Apparent DepthДокумент2 страницы53A LIGHT Refraction Real N Apparent DepthSiti Arbaiyah AhmadОценок пока нет
- Topik Ting 4 P2 Trial 2015 Fizik SPMДокумент72 страницыTopik Ting 4 P2 Trial 2015 Fizik SPMSiti Arbaiyah AhmadОценок пока нет
- Investigation of Expectation Gap in EgyptДокумент12 страницInvestigation of Expectation Gap in EgyptSiti Arbaiyah AhmadОценок пока нет
- Investigation of Expectation Gap in EgyptДокумент12 страницInvestigation of Expectation Gap in EgyptSiti Arbaiyah AhmadОценок пока нет
- AEG-evidence From SingaporeДокумент13 страницAEG-evidence From SingaporeSiti Arbaiyah AhmadОценок пока нет
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (400)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (895)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (266)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (345)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (121)
- Liquid Crystal Display Panels For Commercial Airplanes: Shirahata Haruo ITAGAKI Michihisa Kousaka Fusao ISHIDA TakashiДокумент4 страницыLiquid Crystal Display Panels For Commercial Airplanes: Shirahata Haruo ITAGAKI Michihisa Kousaka Fusao ISHIDA TakashiFatih Ismail SelcukОценок пока нет
- Offshore Wind Park Connection To An HVDC Platform, Without Using An AC Collector PlatformДокумент120 страницOffshore Wind Park Connection To An HVDC Platform, Without Using An AC Collector PlatformHaseeb Ahmad100% (1)
- TIP110, T IP115: Darlington TransistorsДокумент5 страницTIP110, T IP115: Darlington Transistorsمحمدعبدالخالق العلوانيОценок пока нет
- Power Systems-II Question Bank: Unit-IДокумент8 страницPower Systems-II Question Bank: Unit-ISoniya GJОценок пока нет
- HP LJ M425 Pro 400 Parts ListДокумент29 страницHP LJ M425 Pro 400 Parts ListgsubtilОценок пока нет
- Jetson TX2 NX Pin and Function Names Guide DA-10697-001 v1.0Документ20 страницJetson TX2 NX Pin and Function Names Guide DA-10697-001 v1.0rehmat ullahОценок пока нет
- User Manual WR BSM30kДокумент38 страницUser Manual WR BSM30kChingiz KhudaverdiyevОценок пока нет
- Communication System Block Diagram PDFДокумент2 страницыCommunication System Block Diagram PDFVanessaОценок пока нет
- Quick Quiz 28Документ29 страницQuick Quiz 28Hồng NhơnОценок пока нет
- GATE Electronics Communication Syllabus 2021: Useful LinksДокумент7 страницGATE Electronics Communication Syllabus 2021: Useful LinksvipulОценок пока нет
- Ap1176e-Mb-120-Hpb Seb2-12 12.0B I 18.06.2020Документ29 страницAp1176e-Mb-120-Hpb Seb2-12 12.0B I 18.06.2020Miriam JonesОценок пока нет
- Driving Stepper Motors Using NXP I C-Bus GPIO Expanders: Rev. 2 - 11 October 2011 Application NoteДокумент31 страницаDriving Stepper Motors Using NXP I C-Bus GPIO Expanders: Rev. 2 - 11 October 2011 Application NoteMike ThomsonОценок пока нет
- Quanta - ZRD - Emachines - E732.Rusefix - Com WWW - Laptopfix.vnДокумент46 страницQuanta - ZRD - Emachines - E732.Rusefix - Com WWW - Laptopfix.vnMihohohoОценок пока нет
- Detection and Measurement of Partial Discharge (Corona) Pulses in Evaluation of Insulation SystemsДокумент10 страницDetection and Measurement of Partial Discharge (Corona) Pulses in Evaluation of Insulation Systemskamran719Оценок пока нет
- ASIC Design FlowДокумент10 страницASIC Design FlowNguyen Hoang MinhОценок пока нет
- Lp140wh2 Tlt1 LGДокумент28 страницLp140wh2 Tlt1 LGyanuario zelayaОценок пока нет
- SpecificationДокумент1 страницаSpecificationNguyen Duc ThinhОценок пока нет
- CIRED 2 - MatheusДокумент4 страницыCIRED 2 - MatheusEstácio Tavares Wanderley NetoОценок пока нет
- Fault Code 426 SAE J1939 Data Link - Cannot TransmitДокумент6 страницFault Code 426 SAE J1939 Data Link - Cannot TransmitAhmedmah100% (1)
- Tac Codes F10Документ17 страницTac Codes F10Alexandr AzonОценок пока нет
- Circutor Energy Meter ManualДокумент12 страницCircutor Energy Meter Manualtayyab1965Оценок пока нет
- GW DNS Datasheet-ENДокумент1 страницаGW DNS Datasheet-ENyutyОценок пока нет
- Service Manual: Mds-Ja20EsДокумент84 страницыService Manual: Mds-Ja20Esfoxmulder6161695Оценок пока нет
- Aiwa ZL700 - ZL800-62424 PDFДокумент46 страницAiwa ZL700 - ZL800-62424 PDFtulios6262Оценок пока нет
- 54LS04/DM54LS04/DM74LS04 Hex Inverting Gates: General Description FeaturesДокумент8 страниц54LS04/DM54LS04/DM74LS04 Hex Inverting Gates: General Description FeatureslynaОценок пока нет
- Fabrication and Electrical Measurements of Mis Based Memory DevicesДокумент5 страницFabrication and Electrical Measurements of Mis Based Memory DevicesErick OpiyoОценок пока нет
- 1047 ErДокумент34 страницы1047 ErVO DUC ThaoОценок пока нет
- Design and Implementation of Synchronous Buck Converter For Space ApplicationsДокумент8 страницDesign and Implementation of Synchronous Buck Converter For Space ApplicationsIJRASETPublicationsОценок пока нет
- P220 PDFДокумент12 страницP220 PDFSatya VasuОценок пока нет
- PCC/MCC Feeder Operation Check ListДокумент2 страницыPCC/MCC Feeder Operation Check Listsuperthambi0% (1)