Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Pedia Drug Study
Загружено:
ryanИсходное описание:
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Pedia Drug Study
Загружено:
ryanАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
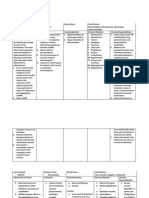
52
Generic/
Brand Name
&
Classification
(10%)
Dose,
Strength &
Fornulation
(10%)
Generic:
Paracetamol
Ordered:
(250
MG/5mL)
2.5 mL
Brand:
Tylenol
Classification:
Analgesics
(nonopoid)
Antypyretic
Timing:
q6
8am
1pm
7pm
Duration:
4-6 hours
Other forms:
-Caplets
Indication/Mechanis
m of Drug Action
(15%)
Indication:
-Temporary reduction
of fever.
-Temporary relief of
minor aches, and pain
cause by common cold
or influenza.
Mechanism of Action:
Reduces fever by
acting directly on the
hypothalamic heatregulating center to
cause vasodilation and
sweating , which help
dissipate heat.
Adverse/Side
Effects Drug
Interaction
(15%)
Nursing
Responsibilities
(20%)
Rationale
(10%)
Client
Teaching
(20%)
*CNS: headache
Before:
*Assess
patients pain or
temperature
before therapy
and regulatory.
*To indicate
baseline data
and monitor
drugs
effectiveness.
(Nursing Drug
Handbook
2010: p.71-72)
-Tell patient
not to use
drug for fever
thats higher
than 39.5C
lasts longer
than 3 days
or recurs.
*Avoid using
multiple
preparations
containing
paracetamol.
*To avoid
over dosage or
multiple
administration
of medication.
(Nursing Drug
Handbook
2010: p.71-72)
-Warn patient
that high
doses or
unsupervised
long-term use
can cause
liver damage.
*CV: chest pain,
dyspnea
*GI: Hepatic
toxicity and failure,
jaundice.
*GU: Acute renal
failure, renal tubular
necrosis.
*Hematologic:
Methemoglobinemi
a cyanosis;
hemolytic anemia,
hematuria, anuria,
During:
-Tell patient
to keep track
53
-Suppositories
-Chewable
tablets
Disintegrating
tablets
-Capsules
-Solution
neutropenia
(Nursing Drug
Handbook 2010: p.7172)
*Hypersensitivity:
Rash, fever
*Do not exceed
the
recommended
dosage.
*To minimize
complication.
(Nursing Drug
Handbook
2010: p.71-72)
*Give Drug
with food.
*To prevent
GI upset.
(Nursing Drug
Handbook
2010: p.71-72)
After:
*Monitor serum
level regularly
-Advice the
*Treatment of patient that
overdose.
drug only for
(Nursing Drug short term
Handbook
use and to
2010: p.71-72) consult the
physician if
*Lead to
giving to
complication
children
or
longer than 5
anaphylactic
days.
reaction.
*Discontinue
drug if
hypersensitivity
occurs.
(Nursing Drug
(Nursing Drug
Handbook 2010: Handbook
of daily drug
intake,
including
OTC and
prescription
to maintain
the
effectiveness
of the
therapy.
54
p.71-72)
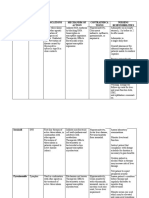
Generic/
Brand Name
&
Classification
(10%)
Generic:
Ibuprofen
Brand:
Advil
Dose,
Strength &
Fornulation
(10%)
Indication/Mechanis
m of Drug Action
(15%)
Adverse/Side
Effects Drug
Interaction
(15%)
Ordered:
(200
MG/2mL)
Indication:
-Relief mild to
moderate pain.
Timing:
q8
-Fever reduction
*CNS:
Headache,
dizziness,
somnolence,
fatigue,
tiredness,
tinnitus,
ophthalmologic
effects.
Duration:
4-6 hours
Classification:
Analgesics
(nonopoid)
NSAID
Other forms:
-Prevention and
treatment of migraine
headache.
*CV:
Hypertension,
palpitations,
arrhythmia,
Nursing
Responsibilities
(20%)
2010: p.71-72)
Rationale
(10%)
Before:
*Check 10
rights of
medication
administration.
*To avoid any
error of the
therapy.
(Nursing Drug
Handbook 2010:
p.609)
*Assess patient
condition before
giving the
medication.
*To gain
cooperation and
success of
therapy.
(Nursing Drug
Handbook 2010:
p. 609)
Client
Teaching
(20%)
- Instruct to
use drug only
as prescribed.
-Tell to eat
first before
taking the
medication to
avoid GI
upset.
-Avoid OTC
drugs. Many
of these drugs
55
Propionic acid
Derivative
-Tablets
-Chewable
tablets
-Suspension
-Oral drops
Mechanism of Action:
Inhibits prostaglandins
synthesis by decreasing
enzyme needed for
biosynthesis.
heart failure.
*Dermatologic:
Rash, pruritus,
sweating, dry
mucous
membranes,
stomatitis.
(Nursing Drug
*GI: Nausea,
Handbook 2010: p.609) dyspepsia, GI
pain, diarrhea,
vomiting,
constipation,
flatulence, GI
bleeding.
*GU: Dysuria,
renal
impairment,
menorrhagia.
*Hematologic:
Bleeding,
platelet
inhibition with
higher doses,
During:
*Maintain
Aseptic
Technique
during
administration.
*To minimize
transmission of
microorganisms.
(Nursing Drug
Handbook 2010:
p. 609)
*Give Drug with *To prevent GI
food.
upset.
(Nursing Drug
Handbook 2010:
p. 609)
*Stay with the
*To make an
patient
observation and
throughout the
assist.
therapy.
(Nursing Drug
Handbook 2010:
p. 609)
After:
*Arrange for
periodic
ophthalmologic
examination.
*To assess
effectiveness.
(Nursing Drug
Handbook 2010:
p.609)
contain similar
medication,
serious
overdose.
-Informed that
he may
experience
side effects
such nausea,
GI upset ,
dyspepsia,
diarrhea or
constipation.
56
neutropenia,
leukemia, bone
marrow
depression.
*Respiratory:
Dyspnea,
hemoptysis,
pharyngitis,
bronchospasm,
rhinitis.
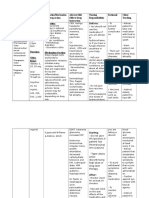
Generic/
Brand Name
&
Classification
(10%)
Dose,
Strength &
Fornulation
(10%)
Generic:
Penecillin G
Benzathine
Ordered:
575 MG, 100
units
Timing:
q6
Indication/Mechanis
m of Drug Action
(15%)
Indication:
-Severe infections
caused by sensitive
organisms
( Streptococci)
Adverse/Side
Effects Drug
Interaction
(15%)
*CNS: Lethargy,
hallucinations,
seizures.
*GI: Glossitis,
stomatitis,
gastritis, sore
*Observe the
patient
frequently.
*To observe any
adverse effect.
(Nursing Drug
Handbook 2010:
p.609)
(Nursing Drug
Handbook 2010:
p.609)
Nursing
Responsibilities
(20%)
Before:
*Check 10
rights of
medication
administration.
Rationale
(10%)
Client
Teaching
(20%)
*To avoid any
error of the
therapy.
(Nursing Drug
Handbook 2010:
p.923)
- Instruct to
report
difficulty
breathing,
rashes, severe
pain, mouth
57
Brand:
Permapen
Classification:
Antibiotic
-URTI caused by
sensitive streptococci
Duration:
2.4 million
units IM
weekly for 3
weeks.
-Prophylaxis of
rheumatic fever and
chorea.
mouth, furry
tongue, nausea,
vomiting,
diarrhea,
abdominal pain,
bloody diarrhea.
*Educate about
side effects of
drug.
*For the patient
to be
knowledgeable.
(Nursing Drug
Handbook 2010:
p. 923)
*GU: Nephrittis
Other forms:
-Powder for
injection
-Vial
Mechanism of Action:
Inhibits synthesis of
cell wall of sensitive
organisms, causing cell
death.
(Nursing Drug
Handbook 2010: p.
923)
*Hematologic:
Anemia,
leucopenia,
prolonged
bleeding time.
*Assess for
hypersensitivity
of drug.
*Hypersensitivity: *Reduce dosage
Rash, fever,
with hepatic or
wheezing,
renal failure.
anaphylaxis
*Local: Pain,
phlebitis,
thrombosis at
injection site
During:
*Do not mix
drug with IV
solutions.
*Prevent
anaphylactic
reaction.
(Nursing Drug
Handbook 2010:
p. 923)
*To minimize
complications..
(Nursing Drug
Handbook 2010:
p. 923)
*drug is not for
IV use.
(Nursing Drug
Handbook 2010:
p. 923)
sore, unusual
bleeding or
bruising.
-Instruct
patient to take
medication as
directed for
the full
course of
therapy, even
if feeling
better.
-Informed
that he may
experience
side effects
such nausea,
mouth sores,
diarrhea,
vomiting and
pain.
58
*Avoid contact
with the
instruments.
* To minimize
transmission of
microorganisms..
(Nursing Drug
Handbook 2010:
p. 923)
*Stay with the
patient
throughout the
whole duration
of
administration..
*To observe any
reaction.
(Nursing Drug
Handbook 2010:
p.923)
After:
*Monitor client.
*Arrange for
regular follow
up tests
*To manage any
adverse reaction.
(Nursing Drug
Handbook 2010:
p.923)
*To evaluate
effects.
. (Nursing Drug
Handbook 2010:
p.923)
59
*Do proper
documentation
*For future use
and legal basis.
(Nursing Drug
Handbook 2010:
p.923)
(Nursing Drug
Handbook 2010:
p.923)
Generic/
Brand Name
Dose,
Strength &
Indication/Mechanis
Adverse/Side
Effects Drug
Nursing
Responsibilities
Rationale
(10%)
Client
Teaching
60
&
Classification
(10%)
Fornulation
(10%)
m of Drug Action
(15%)
Generic:
Amoxicillin
Trihydrate
Ordered:
250 MG/ 5Ml
Syrup P.O.
Indication:
-To treat ear, nose,
throat, GU tract, skin
and soft tissue
infections caused by
susceptible gram
positive and negative
organisms.
Timing:
T.I.D.
Brand:
Amoxil
Duration:
6-8 Hours
Classification:
Antibiotic
Other forms:
-Chewable
tablets
- Oral
Suspension
-Capsules
-ER tablets
-Tablets
Mechanism of Action:
Inhibits synthesis of
cell wall of sensitive
organisms, causing cell
death.
(Nursing Drug
Handbook 2010: p.
124)
Interaction
(15%)
*CNS: Lethargy,
hallucinations,
seizures.
*GI: Glossitis,
stomatitis,
gastritis, sore
mouth, furry
tongue, nausea,
vomiting,
diarrhea,
abdominal pain,
bloody diarrhea.
(20%)
(20%)
Before:
*Check 10
rights of
medication
administration.
*To avoid any
error of the
therapy.
(Nursing Drug
Handbook 2010:
p.125)
*Know that
patient with
mononucleosis
shouldnt
receive
amoxicillin.
*This class of
drug may cause
erythematous
rash.
(Nursing Drug
Handbook 2010:
p. 125)
*Culture
infected area.
*prior to
treatment;
reculture area if
response is not
expected.
(Nursing Drug
Handbook 2010:
p. 125)
-Instruct
patient to take
medication as
directed for
the full
course of
therapy, even
if feeling
better.
-Tell to take
medication
round the
clock.
*GU: Nephrittis
*Hematologic:
Anemia,
leucopenia,
prolonged
bleeding time.
*Hypersensitivity
- Instruct to
report
difficulty
breathing,
rashes, severe
pain, mouth
sore, unusual
bleeding or
61
:
Rash, fever,
wheezing,
anaphylaxis
*Local: Pain,
phlebitis,
thrombosis at
injection site.
During:
*Maintain
Aseptic
Technique
during
administration.
*Give in oral
preparations
only.
After:
*Assess for any
unpleasant side
effects .
*Use
corticosteroid or
antihistamine.
bruising.
* To minimize
transmission of
microorganisms.
(Nursing Drug
Handbook 2010:
p. 125)
-Informed
that this
antibiotic is
specific for
this problem
and should
*Amoxicillin is not be used to
not affected with self-treat any
food.
infections.
(Nursing Drug
Handbook 2010:
p. 125)
* To prepare
intervention that
lessen
complications.
(Nursing Drug
Handbook 2010:
p. 125)
*For any skin
reactions
(Nursing Drug
62
Handbook 2010:
p.125)
(Nursing Drug
Handbook 2010:
p.125)
Вам также может понравиться
- MetoclopramideДокумент3 страницыMetoclopramideKrizzia CarlosОценок пока нет
- Drug StudyДокумент13 страницDrug StudyAbdullah Mascardo BarabagОценок пока нет
- Drug Study DengueДокумент3 страницыDrug Study DengueiamELHIZAОценок пока нет
- Drug StudyДокумент6 страницDrug Studyuntoned100% (1)
- PiperacillinДокумент3 страницыPiperacillinmyer pasandalanОценок пока нет
- Jam (Drug Study)Документ11 страницJam (Drug Study)Vincent QuitorianoОценок пока нет
- Discharge Plan With Other ReferncesДокумент3 страницыDischarge Plan With Other ReferncesApril Joy PrestoОценок пока нет
- Hydrocortisone Ointment-Drug StudyДокумент1 страницаHydrocortisone Ointment-Drug StudyTrisha CayabyabОценок пока нет
- Drug Name Indication Action Adverse EffectsДокумент4 страницыDrug Name Indication Action Adverse EffectsMaryjoy Gabriellee De La CruzОценок пока нет
- Brand Name: Bactrim Generic Name: Sulfamethoxazole, Trimethoprim, Co-Trimoxazole Drug ClassificationДокумент2 страницыBrand Name: Bactrim Generic Name: Sulfamethoxazole, Trimethoprim, Co-Trimoxazole Drug Classificationianecunar100% (2)
- Drug Study (Rocephin)Документ2 страницыDrug Study (Rocephin)YakumaОценок пока нет
- Drug StudyДокумент4 страницыDrug StudyCheriz LukbanОценок пока нет
- Salbutamol Drug StudyДокумент2 страницыSalbutamol Drug StudyVinz Khyl G. CastillonОценок пока нет
- Duavent Drug StudyДокумент2 страницыDuavent Drug StudyNicole cuencosОценок пока нет
- TergecefДокумент2 страницыTergecefianecunar100% (3)
- DrugДокумент4 страницыDrugAugene ToribioОценок пока нет
- CEFRADINEДокумент2 страницыCEFRADINEAngelica Cassandra VillenaОценок пока нет
- Drug Ana Rifampicin Isoniazid Pyrazinamide Ethambutol StreptomycinДокумент4 страницыDrug Ana Rifampicin Isoniazid Pyrazinamide Ethambutol StreptomycinDeinielle Magdangal Romero100% (1)
- DRUG STUDY Ceftriaxone ForgramДокумент1 страницаDRUG STUDY Ceftriaxone ForgramJ-lie GonzalesОценок пока нет
- Salbutamol (ASMALIN)Документ2 страницыSalbutamol (ASMALIN)Kristine YoungОценок пока нет
- Drug StudyДокумент2 страницыDrug StudyemmanuelmyagokayeОценок пока нет
- Cefotaxime: Antibiotic ClassДокумент2 страницыCefotaxime: Antibiotic ClassMentari AmirОценок пока нет
- NAPREXДокумент2 страницыNAPREXKarl EdemОценок пока нет
- Azithromycin Drug StudyДокумент2 страницыAzithromycin Drug StudyMelissa Marie Custodio100% (1)
- AmikacinДокумент1 страницаAmikacinMuhammad ArsalanОценок пока нет
- Problem List Cues Problems Priority JustificationДокумент3 страницыProblem List Cues Problems Priority JustificationgrazheОценок пока нет
- Drug Study: MontelukastДокумент3 страницыDrug Study: Montelukastunkown userОценок пока нет
- ClonidineДокумент1 страницаClonidineKhryss Paula BaldonadoОценок пока нет
- Pneumonia Case Study FinalllДокумент56 страницPneumonia Case Study Finalllbethrice melegritoОценок пока нет
- Arixtra & Plavix Drug StudyДокумент3 страницыArixtra & Plavix Drug StudyShayneAngelMarieMatubangОценок пока нет
- Aerovent, Apovent Atronase, Ipraxa, Ipvent Rhinovent, Rinatec Rinovagos, Atrovent, Atrovent HFAДокумент3 страницыAerovent, Apovent Atronase, Ipraxa, Ipvent Rhinovent, Rinatec Rinovagos, Atrovent, Atrovent HFAGwyn RosalesОценок пока нет
- MetronidazoleДокумент2 страницыMetronidazoleJm RomancapОценок пока нет
- AMIKACINДокумент2 страницыAMIKACINJesrel DelotaОценок пока нет
- Clindamycin Drug Study WWW RNpedia ComДокумент4 страницыClindamycin Drug Study WWW RNpedia ComChristian LlerinОценок пока нет
- Burn - Concept MapДокумент1 страницаBurn - Concept MapAaron RafaelОценок пока нет
- Drug Study For AsthmaДокумент3 страницыDrug Study For AsthmaDianne MaeОценок пока нет
- AcetazolamideДокумент2 страницыAcetazolamideAlexandra Antondy0% (1)
- Health Teaching PlanДокумент4 страницыHealth Teaching Plani & vОценок пока нет
- KetorolacДокумент1 страницаKetorolacChaotic Insignia LaquianОценок пока нет
- Azithromycin Drug StudyДокумент2 страницыAzithromycin Drug Studycuakialyanna50% (2)
- Drug Study AzithromycinДокумент2 страницыDrug Study Azithromycinkuro hanabusaОценок пока нет
- Drug StudyДокумент6 страницDrug StudyJorge RabajaОценок пока нет
- Drug StudyДокумент10 страницDrug StudybaniniycsebОценок пока нет
- Drug Study 04-21-09Документ2 страницыDrug Study 04-21-09obietobiОценок пока нет
- Drug Study - CefuroximeДокумент2 страницыDrug Study - CefuroximeSiergs Smith GervacioОценок пока нет
- DRUG-STUDY PediaДокумент5 страницDRUG-STUDY PediaRhea Jane Bongcato50% (2)
- Drug Study EntecavirДокумент4 страницыDrug Study EntecavirClarimae AwingОценок пока нет
- Drug Study: AmoxicillinДокумент3 страницыDrug Study: AmoxicillinKrzia TehОценок пока нет
- Drug StudyДокумент19 страницDrug StudyCalimlim KimОценок пока нет
- Cetirizine 2Документ2 страницыCetirizine 2ianОценок пока нет
- Sine CodДокумент2 страницыSine CodshayneОценок пока нет
- Paracetamol DrugstudyДокумент2 страницыParacetamol DrugstudyEninaj Ozacip100% (1)
- Drug Study FДокумент3 страницыDrug Study FFatima Love Ariate-ArcasetasОценок пока нет
- OmeprazoleДокумент1 страницаOmeprazoleFritz JanobasОценок пока нет
- BFC NCPДокумент2 страницыBFC NCPMonica Melo HernandezОценок пока нет
- NalbuphineДокумент5 страницNalbuphineGab PagalilauanОценок пока нет
- Drug Study FORTДокумент3 страницыDrug Study FORTLysa Mae EleazarОценок пока нет
- Cefpodoxime Proxetil - Print VersionДокумент5 страницCefpodoxime Proxetil - Print Versionchristina_1990Оценок пока нет
- Drug Study OR AreaДокумент7 страницDrug Study OR AreaVal FielОценок пока нет
- CefuroximeДокумент6 страницCefuroximetrinkets0914Оценок пока нет
- The Problem and Its Design Rationale of The StudyДокумент29 страницThe Problem and Its Design Rationale of The StudyryanОценок пока нет
- Chapter 5 NotesДокумент13 страницChapter 5 NotesryanОценок пока нет
- RU - Trauma and Emergency CareДокумент32 страницыRU - Trauma and Emergency CareryanОценок пока нет
- Virginia HendersonДокумент15 страницVirginia HendersonryanОценок пока нет
- Chapter 5 For StudesДокумент8 страницChapter 5 For StudesryanОценок пока нет
- Pedia Care Study - Appendix B - Drug StudyДокумент8 страницPedia Care Study - Appendix B - Drug Studyryan100% (1)
- Drug StudyДокумент5 страницDrug StudyryanОценок пока нет
- Drug Study - CiprofloxacinДокумент2 страницыDrug Study - CiprofloxacinryanОценок пока нет
- Drug Study - FurosemideДокумент2 страницыDrug Study - FurosemideryanОценок пока нет
- Neurons Modulate The Growth of Blood VesselsДокумент2 страницыNeurons Modulate The Growth of Blood VesselsryanОценок пока нет
- Drug Study - HydrocortisoneДокумент4 страницыDrug Study - Hydrocortisoneryan89% (9)
- AdrenalДокумент7 страницAdrenalryanОценок пока нет
- Drug Study - ClopidogrelДокумент2 страницыDrug Study - Clopidogrelryan100% (1)
- Iii. Health Assessment A. Health History A.1 History of Present IllnessДокумент2 страницыIii. Health Assessment A. Health History A.1 History of Present IllnessryanОценок пока нет
- Drug Study - FluconazoleДокумент2 страницыDrug Study - Fluconazoleryan100% (1)
- Ivf Study d5lrДокумент2 страницыIvf Study d5lrryan0% (1)
- NCP - Excessive Fluid VolumeДокумент4 страницыNCP - Excessive Fluid VolumeryanОценок пока нет
- Drug Study - SalbutamolДокумент2 страницыDrug Study - SalbutamolryanОценок пока нет
- Discharge PlanДокумент4 страницыDischarge PlanryanОценок пока нет
- Drug Study - AzithromycinДокумент3 страницыDrug Study - Azithromycinryan100% (1)
- Drug Study - HydrocortisoneДокумент5 страницDrug Study - HydrocortisoneryanОценок пока нет
- NCP - Acute PainДокумент5 страницNCP - Acute Painryan50% (2)
- Discharge Plan FinalДокумент4 страницыDischarge Plan FinalryanОценок пока нет
- Discharge PlanДокумент3 страницыDischarge Planryan100% (2)
- Lola Lolo Lola Lolo: Maternal Side Paternal SideДокумент2 страницыLola Lolo Lola Lolo: Maternal Side Paternal SideryanОценок пока нет
- PRC Forms - 2017 Expiration - UC BaniladДокумент4 страницыPRC Forms - 2017 Expiration - UC BaniladryanОценок пока нет
- The Effect of 3.2% and 3.8% Sodium CitrateДокумент6 страницThe Effect of 3.2% and 3.8% Sodium CitrateBambang KurniawanОценок пока нет
- Dilatation and Curettage ProcedureДокумент3 страницыDilatation and Curettage Proceduresagi muОценок пока нет
- Daily Inspiration: Powered by Crystallive™Документ8 страницDaily Inspiration: Powered by Crystallive™douglaszimbaОценок пока нет
- Pham Ngoc Thach University of Medicine DUOC2019Документ109 страницPham Ngoc Thach University of Medicine DUOC2019Nhung PhamОценок пока нет
- Cardo & Barceló (2005) PDFДокумент5 страницCardo & Barceló (2005) PDFAna Catarina InácioОценок пока нет
- Moxibustion OutputДокумент2 страницыMoxibustion OutputJhon Carlo TegioОценок пока нет
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Explanation Planning Nursing Intervention RationaleДокумент2 страницыAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Explanation Planning Nursing Intervention Rationalekimglaidyl bontuyanОценок пока нет
- White Blood Cells TugasДокумент6 страницWhite Blood Cells TugasanisaОценок пока нет
- Seminar On MumpsДокумент40 страницSeminar On Mumpssushmitabiswas052Оценок пока нет
- Nursing Infomatics Hospital/Critical Care ApplicationsДокумент42 страницыNursing Infomatics Hospital/Critical Care ApplicationsKyla CarbonelОценок пока нет
- Tarife AnalizeДокумент1 страницаTarife AnalizeVincze Alina ClaudiaОценок пока нет
- Dosis Obat Untuk Anak: No. Nama Obat Frekuensi Dosis Dosis Maksimal Sediaan SumberДокумент1 страницаDosis Obat Untuk Anak: No. Nama Obat Frekuensi Dosis Dosis Maksimal Sediaan SumberAbikbaeОценок пока нет
- Nursing Care Plan For Patient With Musculoskeletal InjuryДокумент2 страницыNursing Care Plan For Patient With Musculoskeletal Injuryoliviapalmer100% (1)
- A Patient of Poisoning in ICU (Ankit Jain)Документ48 страницA Patient of Poisoning in ICU (Ankit Jain)SharryОценок пока нет
- Pediatric Assessment TriangleДокумент2 страницыPediatric Assessment TriangleVanessa BergollaОценок пока нет
- Microscopic Potassium Hydroxide Preparation: Top 10 Forgotten Diagnostic ProceduresДокумент1 страницаMicroscopic Potassium Hydroxide Preparation: Top 10 Forgotten Diagnostic ProceduresasfwegereОценок пока нет
- Guidelines On Blood Cultures: Journal of Microbiology, Immunology and InfectionДокумент3 страницыGuidelines On Blood Cultures: Journal of Microbiology, Immunology and InfectionSumesh Shreekhanda ShresthaОценок пока нет
- Sahi ExportДокумент8 страницSahi ExportHeena ChoudharyОценок пока нет
- FCP Rheumatoid ArthitisДокумент2 страницыFCP Rheumatoid ArthitisMiguela CincoОценок пока нет
- Moor Field UpdatedДокумент754 страницыMoor Field UpdatedIrini ChatziralliОценок пока нет
- Blood Cells LabДокумент7 страницBlood Cells LabKameron WardОценок пока нет
- MATUCOL 3 Meses Seguridad Efectividad de Metodos de InduccionДокумент11 страницMATUCOL 3 Meses Seguridad Efectividad de Metodos de InduccionMitsury Jacqueline Flores C.Оценок пока нет
- Assessment of Pregnant Woman 2023Документ2 страницыAssessment of Pregnant Woman 2023ysohidalgo13Оценок пока нет
- CP 4Документ79 страницCP 4Kalichandren ArumugamОценок пока нет
- Lifetree Gut Relax, An Ayurvedic Health SupplementДокумент13 страницLifetree Gut Relax, An Ayurvedic Health SupplementLifetree WorldОценок пока нет
- Aloe VeraДокумент39 страницAloe VeraAyush TiwariОценок пока нет
- Miami Harrington ProgramДокумент1 страницаMiami Harrington ProgramZaniru Raúl Marín MartínezОценок пока нет
- Concepts of Diet Therapy and The Role of The NurseДокумент18 страницConcepts of Diet Therapy and The Role of The NurseHartiem FarrellОценок пока нет
- Literature Review: The Relationship Between Sleep Patterns and The Incidence of Hypertension in The ElderlyДокумент22 страницыLiterature Review: The Relationship Between Sleep Patterns and The Incidence of Hypertension in The ElderlyCalvin permana pinemОценок пока нет
- Module 4 Assignment PosterДокумент1 страницаModule 4 Assignment PosterChelsie Rachelle BrownОценок пока нет