Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Breathing Problems in A Newborn
Загружено:
Muhammad Danantyo Himawan0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
8 просмотров2 страницыThis video will show how to evaluate and treat the baby with a breathing problem. Rapid breathing and chest indrawing are signs of a serious, often life threatening condition. Check for any other danger signs such as poor feeding and convulsions.
Исходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Breathing Problss
Авторское право
© © All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
DOC, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документThis video will show how to evaluate and treat the baby with a breathing problem. Rapid breathing and chest indrawing are signs of a serious, often life threatening condition. Check for any other danger signs such as poor feeding and convulsions.
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате DOC, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
8 просмотров2 страницыBreathing Problems in A Newborn
Загружено:
Muhammad Danantyo HimawanThis video will show how to evaluate and treat the baby with a breathing problem. Rapid breathing and chest indrawing are signs of a serious, often life threatening condition. Check for any other danger signs such as poor feeding and convulsions.
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате DOC, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 2
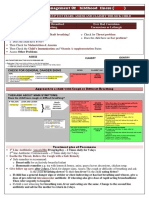
Newborn Care Series
Breathing problems in a newborn
Breathing problems in a young baby, especially rapid breathing and chest indrawing are signs of a serious, often life threatening condition.
This video will show how to evaluate and treat the baby with a breathing
problem.
Before checking the baby, wash your hands and the thermometer. As you
take the babys temperature, gather important background information;
especially evidence of danger signs:
When did the breathing problem start?
Was the labor or birth long and difficult?
Did the baby need any help to start breathing?
Check for any other danger signs such as poor feeding and convulsions.
The mother explains that the baby has been breathing fast since yesterday.
He is also not feeding well.
First observe: the baby looks listless. His chest shows indrawing: as he
draws a breath his chest draws in, and the belly appears to move out. Check
the lips and tongue for pinkness, look at the nose for nasal flaring, and listen
for grunting. Count how many breaths the baby takes in one minute. More
than 60 is too fast. Count again to be sure. This baby is taking 90 breaths in
one minute.
Now check the baby from head to toe for other signs of serious illness.
Here are examples of babies with signs of breathing difficulty. All of them
need urgent referral, especially for oxygen.
This baby has chest indrawing, fast breathing, and grunting, a sound
associated with breathing difficulty heard on the out breath. .
This baby is breathing too fast at 70 breaths per minute. She has chest
indrawing and nasal flaring.
This baby is breathing at a normal rate of 50 breaths per minute but he has
chest indrawing.
Here is another example of nasal flaring.
Global Health Media Project, 30 Common Road, Waitsfield, VT 05673 U.S. |
globalhealthmedia.org
Newborn Care Series
This baby has a very severe breathing problem. Hes taking 120 breaths per
minute and has severe chest indrawing, He urgently needs oxygen and
specialized care.
The health worker has determined that the baby is breathing too fast, has
chest indrawing, poor feeding and listlessness.
He has a serious breathing problem and needs to be referred for oxygen and
special care.
Discuss the babys urgent condition with the mother and advise her to take
the baby to a higher level facility.
Provide oxygen if possible on the way. Also give the baby the first doses of
intramuscular ampicillin and gentamicin.
Notify the hospital, arrange transportation, and write a referral note.
Make sure the baby has breast or cup fed and is warm with skin-to-skin
contact throughout the trip.
Breathing problems can be life-threatening. Every effort should be made to
refer the baby. If referral is not possible, do your best to care for the baby
in your clinic though realize that this care is not the same.
Provide oxygen if possible. Also give antibiotics. Effective treatment
options are intramuscular gentamicin plus either ampicillin, or procaine
penicillin. Procaine penicillin has the advantage of being given only once
daily
A secondline treatment can be intramuscular gentamicin plus oral
amoxicillin
Treat for 7 days.
Ensure that the baby is warm and fed every 2-3 hours.
Discharge when she has no further signs of breathing difficulty and is feeding
well. Be sure the baby completes the full 7 days of treatment.
Remember:
Rapid breathing and chest in drawing are signs of breathing difficulty.
Count the number of breaths for one minute, if more than 60, count
again.
Refer babies with breathing problems urgently for oxygen and special
care
Global Health Media Project, 30 Common Road, Waitsfield, VT 05673 U.S. |
globalhealthmedia.org
Вам также может понравиться
- Immediate Care of The NewbornДокумент12 страницImmediate Care of The NewbornLucilyn EbuengaОценок пока нет
- Neonatal ResuscitationДокумент16 страницNeonatal ResuscitationPrecilla C. Stephen100% (3)
- Care For The Child in Hospital: How To Identify and Treat Children Who Need Urgent CareДокумент22 страницыCare For The Child in Hospital: How To Identify and Treat Children Who Need Urgent CareDahrren Grace JalonОценок пока нет
- Newborn ResuscitationДокумент34 страницыNewborn ResuscitationNishaThakuri100% (2)
- Literature Review On Integrated Management of Childhood IllnessДокумент4 страницыLiterature Review On Integrated Management of Childhood Illnesstofonyduv1h2Оценок пока нет
- New Born Care: Slide 0: Learning ObjectivesДокумент10 страницNew Born Care: Slide 0: Learning ObjectivesAmelia ChristmasОценок пока нет
- CPR For Children and Infants: Cardiopulmonary ResuscitationДокумент2 страницыCPR For Children and Infants: Cardiopulmonary Resuscitationjanna mae patriarcaОценок пока нет
- Newborn Resuscitation (S.G)Документ21 страницаNewborn Resuscitation (S.G)GROOT GamingYTОценок пока нет
- Taking Care of Baby KiswahiliДокумент23 страницыTaking Care of Baby KiswahiliCOREGroupDCОценок пока нет
- Umbilical Infection in Newborns: Newborn Care SeriesДокумент3 страницыUmbilical Infection in Newborns: Newborn Care Serieszelvininaprilia990Оценок пока нет
- Immediate Care of The NewbornДокумент11 страницImmediate Care of The NewbornHannahKarizaОценок пока нет
- Choking Dangers: Partial BlockageДокумент4 страницыChoking Dangers: Partial BlockageNdatimana BruceОценок пока нет
- Blocked Nose in Babies: Snuffles: Children's Emergency DepartmentДокумент2 страницыBlocked Nose in Babies: Snuffles: Children's Emergency DepartmentElena ButunoiuОценок пока нет
- Asthma in ChildrenДокумент3 страницыAsthma in Childrenwaikit0822Оценок пока нет
- Case StudyДокумент7 страницCase StudyCaren MarquezОценок пока нет
- Teaching Plan Fo Cord Car1Документ15 страницTeaching Plan Fo Cord Car1jaden1233Оценок пока нет
- Unciano Colleges Inc. Sta. Mesa ManilaДокумент14 страницUnciano Colleges Inc. Sta. Mesa Manilanaman24Оценок пока нет
- Choking From A Foreign Body and Paediatric Basic Life SupportДокумент4 страницыChoking From A Foreign Body and Paediatric Basic Life SupportOber SánchezОценок пока нет
- Assess and Classify Cough or Difficulty in BreathingДокумент11 страницAssess and Classify Cough or Difficulty in BreathingGlizzle MacaraegОценок пока нет
- Immediate Newborn CareДокумент4 страницыImmediate Newborn CareDani MichaelaОценок пока нет
- Basic Cardiac Life SupportДокумент3 страницыBasic Cardiac Life SupportNozomi YukiОценок пока нет
- CPR Procedures: Can Result in Unconsciousness and Cardiopulmonary ArrestДокумент10 страницCPR Procedures: Can Result in Unconsciousness and Cardiopulmonary ArrestDayCee Ditz Gulane OrbetaОценок пока нет
- IMCI UpdatedДокумент5 страницIMCI UpdatedMalak RagehОценок пока нет
- CASE SIMUlation 112Документ6 страницCASE SIMUlation 112Princess Levie CenizaОценок пока нет
- Case Simulation in Pediatric Nursing Case Study 1Документ4 страницыCase Simulation in Pediatric Nursing Case Study 1Cheska PalomaОценок пока нет
- IMCIДокумент116 страницIMCIPAUL MICHAEL G. BAGUHIN0% (1)
- Case Study 116Документ4 страницыCase Study 116Jonah MaasinОценок пока нет
- Imci Cough or DobДокумент11 страницImci Cough or DobRenz Jian MacasiebОценок пока нет
- NCM 107 Postpartum Care Guide QuestionДокумент6 страницNCM 107 Postpartum Care Guide QuestionMiguel LigasОценок пока нет
- PatientДокумент6 страницPatientpasaronjustinОценок пока нет
- Newborn Discharge Instruction 2015Документ4 страницыNewborn Discharge Instruction 2015Carla AbalaОценок пока нет
- NRPДокумент24 страницыNRPrajvikram8750% (6)
- Birth AsphyxiaДокумент10 страницBirth Asphyxiasarita Singh MaharjanОценок пока нет
- CPR in A Baby (0 To 12 Months) - First AidДокумент4 страницыCPR in A Baby (0 To 12 Months) - First Aidمحمد خضير عليОценок пока нет
- Post Mature Newborn: Gervacio, Jonah Micah NДокумент20 страницPost Mature Newborn: Gervacio, Jonah Micah NJessa BorreОценок пока нет
- Neonatal ResuscitationДокумент15 страницNeonatal Resuscitationpriyanka88% (8)
- CPR-WPS OfficeДокумент5 страницCPR-WPS OfficeBellaОценок пока нет
- Demonstration On Newborn ResuscitationДокумент7 страницDemonstration On Newborn Resuscitationvineeta.ashoknagarОценок пока нет
- IMCI - ContentДокумент13 страницIMCI - ContentMarianne Daphne GuevarraОценок пока нет
- Pregnancy ConfirmationДокумент4 страницыPregnancy ConfirmationKath MaulionОценок пока нет
- Triase: Klasifikasikan 1. With Emergency Sign 2. With Prority Sign 3. Non-Urgent CaseДокумент12 страницTriase: Klasifikasikan 1. With Emergency Sign 2. With Prority Sign 3. Non-Urgent CaseLusi UtamiОценок пока нет
- New Born ResuscitationДокумент49 страницNew Born ResuscitationdivyamuthyalaОценок пока нет
- Mother's Class BFДокумент55 страницMother's Class BFriz04_fortitudessa5178Оценок пока нет
- Control of Acute Respiratory Infections 2Документ6 страницControl of Acute Respiratory Infections 2إحسان ماجد محمدОценок пока нет
- RPS 14Документ19 страницRPS 14Ridanna HartateanaОценок пока нет
- ResuscitationДокумент38 страницResuscitationsonics issacОценок пока нет
- Iwas Paputok LectureДокумент31 страницаIwas Paputok LectureShan Dave TupasОценок пока нет
- CUS Ethico-Moral ReasoningДокумент5 страницCUS Ethico-Moral ReasoningminjungОценок пока нет
- Case Study Baby HДокумент6 страницCase Study Baby HSharon Williams0% (1)
- Mother's Class BFДокумент55 страницMother's Class BFriz04_fortitudessa5178100% (1)
- Care of A NewbornДокумент54 страницыCare of A Newbornzachariah nkhukuzaliraОценок пока нет
- Pat ResiaДокумент8 страницPat ResiarendyjiwonoОценок пока нет
- Cough and Dyspnea Case StudyДокумент4 страницыCough and Dyspnea Case StudyAbigail Balbuena100% (1)
- Apnoea Bradycardia PremДокумент2 страницыApnoea Bradycardia PremmusafirlautОценок пока нет
- Pyloric StenosisДокумент8 страницPyloric StenosisRej PanganibanОценок пока нет
- Liquid Gold: Troubleshooting breastfeeding issues during baby's first monthОт EverandLiquid Gold: Troubleshooting breastfeeding issues during baby's first monthОценок пока нет
- Study Note Ga Eng 26 02 18 PDFДокумент15 страницStudy Note Ga Eng 26 02 18 PDFvikramОценок пока нет
- The Memories of Ana Calderon by Graciela LimonДокумент197 страницThe Memories of Ana Calderon by Graciela LimonArte Público Press100% (2)
- Avoiding Preanalysis Errors in Capillary TubesДокумент28 страницAvoiding Preanalysis Errors in Capillary TubesErika Movies100% (1)
- Lindo Wing Brochure Web VersionДокумент16 страницLindo Wing Brochure Web VersionNetwerk24Оценок пока нет
- Pediatric Nur Pediatric Nur Pediatric Nur Pediatric Nur Pediatric Nursing Sing Sing Sing SingДокумент10 страницPediatric Nur Pediatric Nur Pediatric Nur Pediatric Nur Pediatric Nursing Sing Sing Sing Singtheiam772Оценок пока нет
- Bioethics SalamanesДокумент2 страницыBioethics SalamanesShiella Mae SalamanesОценок пока нет
- Ongoing Nutrition Programmes and ProjectsДокумент10 страницOngoing Nutrition Programmes and ProjectsAB DivillierОценок пока нет
- Final Coaching - Infant Care and Feeding - Student Copy Part BДокумент10 страницFinal Coaching - Infant Care and Feeding - Student Copy Part BAshley Ann Flores100% (1)
- NCP OB Ward - Imbalanced NutritionДокумент2 страницыNCP OB Ward - Imbalanced NutritionCk JosueОценок пока нет
- Reflection in Teaching and Learning With Infants and ToddlersДокумент9 страницReflection in Teaching and Learning With Infants and Toddlersapi-401510206100% (1)
- Virag Suhajda: The Internal Neural Dynamics of Play, Learning and The Agency of The ChildДокумент9 страницVirag Suhajda: The Internal Neural Dynamics of Play, Learning and The Agency of The ChildVirág SuhajdaОценок пока нет
- Kangaroo Mother CareДокумент6 страницKangaroo Mother CareUday KumarОценок пока нет
- Newborn Thesis Neel Kamal 102802004Документ105 страницNewborn Thesis Neel Kamal 102802004Prabir Kumar ChatterjeeОценок пока нет
- For Safe & Quality Care of Birthing Mothers & Their NewbornsДокумент24 страницыFor Safe & Quality Care of Birthing Mothers & Their NewbornsCharmaine Rose Inandan Triviño100% (5)
- Design Guidlines For Regional Perinatal CenterДокумент14 страницDesign Guidlines For Regional Perinatal CenterwalayyoubОценок пока нет
- Illustrated Book of Pediatrics 2ndДокумент975 страницIllustrated Book of Pediatrics 2ndCarla Tapia Norambuena100% (2)
- Papalia SummarydocxДокумент38 страницPapalia Summarydocxec_ecОценок пока нет
- Cleft Lip and Palate: Critical Elements of CareДокумент51 страницаCleft Lip and Palate: Critical Elements of CareAnonymous Z9ypwrSОценок пока нет
- Dev Psych Chapter 7 13Документ71 страницаDev Psych Chapter 7 13hitoОценок пока нет
- Nurses' Role in Drug Administration To ChildrenДокумент7 страницNurses' Role in Drug Administration To Childrenanne_ochoa100% (1)
- The Obstructive ObjectДокумент13 страницThe Obstructive ObjectCarla Santos100% (1)
- Integrated Management of Childhood Illness (IMCI)Документ10 страницIntegrated Management of Childhood Illness (IMCI)Najia Sajjad KhanОценок пока нет
- Risk Case PresДокумент1 страницаRisk Case Presestavillok2367Оценок пока нет
- Food Group ChartДокумент16 страницFood Group ChartRajni Kothari100% (1)
- Urbanization and ImpactsДокумент52 страницыUrbanization and ImpactsDeepnath MajumderОценок пока нет
- Third Year Basic B.SC (N) Question Bank: QP 1769 Subject: Child Health Nursing SR. NOДокумент19 страницThird Year Basic B.SC (N) Question Bank: QP 1769 Subject: Child Health Nursing SR. NOSanal c SabuОценок пока нет
- Normal NewbornAssessmentДокумент53 страницыNormal NewbornAssessmentMidori SanОценок пока нет
- Birth Asphycia and Cerebral Palsy Clinics Perinatology 2005Документ16 страницBirth Asphycia and Cerebral Palsy Clinics Perinatology 2005Sebastián Silva SotoОценок пока нет
- Block 2.2 Safe Motherhood and NeonatesДокумент17 страницBlock 2.2 Safe Motherhood and Neonatesanon_55864979Оценок пока нет