Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Hembafan Two
Загружено:
Origbo Robert Jinga0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
14 просмотров3 страницыStatistics is defined as the science comprising rules and procedure for collecting, organizing, summarizing, describing analyzing, presenting and interpreting numerical data. It plays a significant role in modern day business and educational decision making and forecasting. As a student you need to study statistics because of its usefulness in making prediction and taking decision on educational matters.
Исходное описание:
Оригинальное название
hembafan two.docx
Авторское право
© © All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документStatistics is defined as the science comprising rules and procedure for collecting, organizing, summarizing, describing analyzing, presenting and interpreting numerical data. It plays a significant role in modern day business and educational decision making and forecasting. As a student you need to study statistics because of its usefulness in making prediction and taking decision on educational matters.
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
14 просмотров3 страницыHembafan Two
Загружено:
Origbo Robert JingaStatistics is defined as the science comprising rules and procedure for collecting, organizing, summarizing, describing analyzing, presenting and interpreting numerical data. It plays a significant role in modern day business and educational decision making and forecasting. As a student you need to study statistics because of its usefulness in making prediction and taking decision on educational matters.
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 3
What is statistics?
Statistics is defines as the science comprising rules and
procedure for collecting, organizing, summarizing, describing analyzing,
presenting and interpreting numerical data which are used in making decisions,
valid estimates, predictions and generalizations.
Apart from using statistics to inform people, it plays a significant role in
modern day business and educational decision making and forecasting. Statistical
methods offer us the opportunity to evaluate an uncertain future using limited
information to access the likelihood of future events occurring.
As a student you need to study statistics because of its usefulness in making
prediction and taking decision on educational matters. downier and Health (1970)
indicated the following as reasons for studying statistics:
Daily use: statistics is of immediate and practical utility they help one get
work done quickly and efficiently.
Problem solving: when action reaches are conducted to solve immediate
problems, statistical methods are applied to the data.
Theoretical research: Theories predict what we expect to observe in specific
circumstances, most researches in the behavioral sciences are now very
sophisticated and are therefore more quantitative.
Comprehensive and use of research: The competent educator and researcher
must be able to read, with understanding reports of applied and theoretical
research. Learning in any field comes largely through reading
Employment: statistical logic, statistical thinking and statistical operations
are necessary components.
Purpose of statistics
As earlier mentioned, statistics is used in a variety of forms by different
people. However, the primary purposes of statistics are to:
Reduce large array of data to manageable and comprehensible form.
Aid in the study of populations and samples.
Aid in making reliable inferences about events beases on observational data.
And
a)
Wwwwh
b) The following are the methods of data collection procedures in Nigeria.
Census: a census is a study that obtains data from every member of a
population. In most studies and /or time required.
Sample survey: a sample survey is a study that obtains data from a subset of
a population in order to estimate population attributes.
Experiment, an experiment is alcohol study in which the research attempt
to understand causes and effect relationship . The study controlled in the
sense that research control (i) how subject are assigned to group and (ii)
which treatment each group receives.
In the analysis phase, the researcher compares group scores some dependent
variables. Based on the analyses, the researcher draws a conclusion about
whether the treatment. (Independent variable) had a causal effect on the
dependent variables.
Observational study: Like experiments, observational studies attempt to
understand causes and effect relationships. However, unlike experiments, the
researcher is not able to control (i) hoe subjects are assigned to groups
and/or (ii) which treatment each group receives.
Interviewing: It is a methods where an interviewer contacts the member of
the sample or population personally to ask questions in the questionnaire (a
list of questions used in a survey) this is mostly used for such survey as
human population census. Rural and urban house hold inquires market
prices survey, family expenditure survey and other statistical inquiries where
personal content of interviewer with respondent is necessary.
Mail questionnaire: In this method a list of questions to be used in the survey
(the questionnaire) is prepared and it is used to collect the required
information. These question are sent out to various people, organizations
departments e.t.c to be answered and returned.
Abstraction from publish statistics: In this method data are taken from other
peoples figures or published statistics.
Reference
Best, J.W and Kahn, J.u (1986): Research in Education Practice Hall Inter.
Boyinbode I R (1984) Fundamental Statistics Methods In Education and
Research, Ile-Ife, Dc S. S Books.
Gullford, J. P and Fruchter, b (1973) Fundamental Statistics in Statistics
Psychology and Education
Business statistics I by P. O Ugbem (Ben Poly)
Вам также может понравиться
- Robert OrzaniyolДокумент7 страницRobert OrzaniyolOrigbo Robert JingaОценок пока нет
- Charity SlidesДокумент46 страницCharity SlidesOrigbo Robert JingaОценок пока нет
- N T I Kaduna AdmissionДокумент9 страницN T I Kaduna AdmissionOrigbo Robert JingaОценок пока нет
- Price List Sept., 2014Документ74 страницыPrice List Sept., 2014Origbo Robert JingaОценок пока нет
- Robert OrfankwaghДокумент5 страницRobert OrfankwaghOrigbo Robert JingaОценок пока нет
- Three Domains of LearningДокумент7 страницThree Domains of LearningOrigbo Robert JingaОценок пока нет
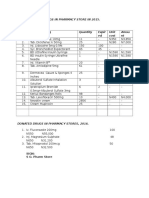
- Donated Drugs in Pharmacy StoreДокумент1 страницаDonated Drugs in Pharmacy StoreOrigbo Robert JingaОценок пока нет
- Charity's ClaimДокумент2 страницыCharity's ClaimOrigbo Robert JingaОценок пока нет
- Pain ManagementДокумент8 страницPain ManagementOrigbo Robert JingaОценок пока нет
- Partial WithdrawalДокумент1 страницаPartial WithdrawalOrigbo Robert JingaОценок пока нет
- Ass OneДокумент3 страницыAss OneOrigbo Robert JingaОценок пока нет
- Ass TwoДокумент3 страницыAss TwoOrigbo Robert JingaОценок пока нет
- Origbo Robert AssignmentДокумент3 страницыOrigbo Robert AssignmentOrigbo Robert JingaОценок пока нет
- Expired Drugs, 2016Документ4 страницыExpired Drugs, 2016Origbo Robert JingaОценок пока нет
- Curriculum VitaeДокумент1 страницаCurriculum VitaeOrigbo Robert JingaОценок пока нет
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5794)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (895)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (344)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (399)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (266)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (121)
- Electric Arc Furnace Voltage Flicker Analysis and PredictionДокумент9 страницElectric Arc Furnace Voltage Flicker Analysis and PredictionWilver SánchezОценок пока нет
- Sample Paper2Документ18 страницSample Paper2bcingenieria6435Оценок пока нет
- Vol.2 Issue 6Документ1 089 страницVol.2 Issue 6Pragyan Bhattarai100% (1)
- Tour de France Technical WhitepaperДокумент14 страницTour de France Technical WhitepaperBrúnó Róbert SalomonОценок пока нет
- Group 1-FMS - Week - 11Документ23 страницыGroup 1-FMS - Week - 11RameshОценок пока нет
- Prevention of Corrosion by PaintДокумент37 страницPrevention of Corrosion by PaintSanjib DekaОценок пока нет
- Assignment 5 - BUS 336Документ3 страницыAssignment 5 - BUS 336Omar Al-lheebiОценок пока нет
- Science You Cant See Amp-BookДокумент28 страницScience You Cant See Amp-BookMОценок пока нет
- Rock Characterisation Using PercussiveДокумент15 страницRock Characterisation Using Percussiveparpejo100% (1)
- 1995 Impc Usim Pac Mineral Processing Simulator Supervisor PDFДокумент6 страниц1995 Impc Usim Pac Mineral Processing Simulator Supervisor PDFLuis Steiler Cespedes CastilloОценок пока нет
- The Delphi Technique A Case StudyДокумент3 страницыThe Delphi Technique A Case StudyFeisal Ramadhan MaulanaОценок пока нет
- Revolutionizing The Prediction of Reservoir PerformanceДокумент1 страницаRevolutionizing The Prediction of Reservoir PerformanceSundus TahirОценок пока нет
- 365 Day Astrological Prediction - Jane DallasДокумент810 страниц365 Day Astrological Prediction - Jane Dallas蔡舒Оценок пока нет
- Analysis of Transport Choice of Employees - A Project On Machine LearningДокумент24 страницыAnalysis of Transport Choice of Employees - A Project On Machine LearningShyam Kishore Tripathi100% (10)
- History Matching Helps Validate Reservoir Simulation ModelsДокумент9 страницHistory Matching Helps Validate Reservoir Simulation ModelsMarielis SifontesОценок пока нет
- ML Assignment PresentationДокумент37 страницML Assignment PresentationpitchappanОценок пока нет
- Transportation Engineering: Approaches To Pavement DesignДокумент15 страницTransportation Engineering: Approaches To Pavement DesignSaddaqatОценок пока нет
- BDM Unit I Slides Part 1Документ27 страницBDM Unit I Slides Part 1Janarthanan Siva KumarОценок пока нет
- 8-Simple Regression AnalysisДокумент9 страниц8-Simple Regression AnalysisSharlize Veyen RuizОценок пока нет
- Me 6 Demand Forecastingfgfgdfgdfgdfgdfgmf,,gdgdf - GDF.GD..GMDF - GF.DGDF.G.DFMG - DF.GD - FGMF.,GD..GDF..GDGDG - Dmg.,dmg.,d.,mg,.df.g.d.Документ24 страницыMe 6 Demand Forecastingfgfgdfgdfgdfgdfgmf,,gdgdf - GDF.GD..GMDF - GF.DGDF.G.DFMG - DF.GD - FGMF.,GD..GDF..GDGDG - Dmg.,dmg.,d.,mg,.df.g.d.ctpie05Оценок пока нет
- Senate Hearing, 110TH Congress - Examining Threats and Protections For The Polar BearДокумент475 страницSenate Hearing, 110TH Congress - Examining Threats and Protections For The Polar BearScribd Government DocsОценок пока нет
- Journal of Manufacturing Processes: SciencedirectДокумент11 страницJournal of Manufacturing Processes: SciencedirectJeferson MarcelinoОценок пока нет
- Mauboussin - The Importance of Diverse ThinkingДокумент13 страницMauboussin - The Importance of Diverse Thinkingkdoherty7503100% (1)
- Orlove 2002 - Ethnoclimatology en The AndesДокумент8 страницOrlove 2002 - Ethnoclimatology en The AndesreempeОценок пока нет
- Comparing Numerial Methods To Estimate Vertical Jump Height PDFДокумент9 страницComparing Numerial Methods To Estimate Vertical Jump Height PDFLuis MuñozОценок пока нет
- Week 1-2 Scientific SkillsДокумент7 страницWeek 1-2 Scientific Skillsjessica ignacioОценок пока нет
- Software Testing Defect Prediction Model - A Practical ApproachДокумент5 страницSoftware Testing Defect Prediction Model - A Practical ApproachesatjournalsОценок пока нет
- Maintenance Book Ch22 On CBMДокумент648 страницMaintenance Book Ch22 On CBMBridge Iit At Ranchi100% (4)
- Predictive Analytics White Paper PDFДокумент5 страницPredictive Analytics White Paper PDFdh212312Оценок пока нет