Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Java Collection Matrix - Java Collection Matrix
Загружено:
Satish SarrafАвторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Java Collection Matrix - Java Collection Matrix
Загружено:
Satish SarrafАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
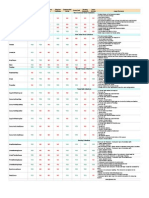
Ordering
Random
Access
Key-Value
Pairs
Allows
Duplicates
Allows Null
Values
Thread Safe
YES
YES
NO
YES
YES
NO
NO
NO
HashMap
NO
YES
YES
NO
YES
NO
NO
NO
Vector
YES
YES
NO
YES
YES
YES
NO
NO
Hashtable
NO
YES
YES
NO
NO
YES
NO
NO
ArrayList
Blocking
Upper
Operations
Bounds
Most Commonly Known Collections
Usage Scenarios
* Default choice of List implementation
* To store a bunch of things
* Repetitions matters
* Insertion order matters
* Best implementation in case of huge lists which are read intensive
(elements are accessed more frequently than inserted deleted)
* Default choice of Map implementation
* Majorly used for simple in-memory caching purpose.
* Historical implementation of List
* A good choice for thread-safe implementation
* Similar to HashMap
* Do not allow null values or keys
* Entire map is locked for thread safety
Most Talked About Collections
* To store bunch of things
* A very nice alternative for ArrayList if
** Do not want repetitions
** Ordering does not matter
HashSet
NO
YES
NO
NO
YES
NO
NO
NO
TreeSet
YES
YES
NO
NO
NO
NO
NO
NO
LinkedList
YES
NO
NO
YES
YES
NO
NO
NO
ArrayDeque
YES
YES
NO
YES
NO
NO
NO
NO
Stack
YES
NO
NO
YES
YES
YES
NO
NO
TreeMap
YES
YES
YES
NO
NO
NO
NO
NO
Special Purpose Collections
WeakHashMap
NO
YES
YES
NO
YES
NO
NO
NO
* The keys that are not referenced will automatically become eligible for
garbage collection
* Usually used for advanced caching techniques to store huge data and
want to conserve memory
Arrays
YES
YES
NO
YES
YES
NO
NO
YES
* A Utility class provided to manipulate arrays
** Searching
** Sorting
** Converting to other Collection types such as a List
Properties
NO
YES
YES
NO
NO
YES
NO
NO
* Properties are exactly same as the Hashtable
* Keys and Values are String
* Can be loaded from a input stream
* Usually used to store application properties and configurations
* To store bunch of things in sorted order
* A very nice alternative for ArrayList if
** Do not want repetitions
** Sorted order
* Sequential Access
* Faster adding and deleting of elements
* Slightly more memory than ArrayList
* Add/Remove elements from both ends of the queue
* Best alternative in case of huge lists which are more write intensive
(elements added / deleted are more frequent than reading elements)
* Random Access
* Faster searching and retrieval of elements
* Add/Remove elements from both ends of the queue
* Best alternative in case of huge lists which are more read intensive
* Similar to a Vector
* Last-In-First-Out implementation
* A very nice alternative for HashMap if sorted keys are important
Thread Safe Collections
CopyOnWriteArrayList
YES
YES
NO
YES
YES
YES
NO
NO
* A thread safe variant of ArrayList
* Best use for
** Small lists which are read intensive
** requires thread-safety
ConcurrentHashMap
NO
YES
YES
NO
NO
YES
NO
NO
* A thread safe variant of Hashtable
* Best use for
** requires thread-safety
** Better performance at high load due to a better locking mechanism
ConcurrentSkipListMap
YES
YES
YES
NO
NO
YES
NO
NO
* A thread safe variant of TreeMap
* Best use for
** requires thread-safety
ConcurrentSkipListSet
YES
NO
NO
NO
NO
YES
NO
NO
* A thread safe variant of TreeSet
* Best use for
** Do not want repetitions
** Sorted order
** Requires thread-safety
CopyOnWriteArraySet
YES
YES
NO
NO
YES
YES
NO
NO
* A thread-safe implementation of a Set
* Best use for
** Small lists which are read intensive
** requires thread-safety
** Do not want repetitions
ConcurrentLinkedQueue
YES
NO
NO
YES
NO
YES
NO
NO
* A thread-safe variant of PriorityQueue
* Best use for
** Small lists
** No random access
** requires thread-safety
ConcurrentLinkedDeque
YES
NO
NO
YES
NO
YES
NO
NO
"* A thread-safe variant of LinkedList
* Best use for
** Small lists
** No random access
** Insertions, retrieval on both sides of the queue
** requires thread-safety"
Blocking Collections
ArrayBlockingQueue
YES
NO
NO
YES
NO
YES
YES
YES
LinkedBlockingQueue
YES
NO
NO
YES
NO
YES
YES
YES
LinkedTransferQueue
YES
NO
NO
YES
NO
YES
YES
YES
PriorityBlockingQueue
YES
NO
NO
YES
NO
YES
LinkedBlockingDeque
YES
NO
NO
YES
NO
YES
SynchronousQueue
YES
NO
NO
YES
NO
YES
DelayQueue
YES
NO
NO
YES
NO
YES
Source:
* Best use for Producer - Consumer type of scenarios with
** Lower capacity bound
** Predictable capacity
* Has a bounded buffer. Space would be allocated during object creation
* Best use for Producer - Consumer type of scenarios with
** Large capacity bound
** Unpredictable capacity
* Upper bound is optional
* Can be used in situations where the producers should wait for consumer
to receive elements. e.g. Message Passing
"* Best use for Producer - Consumer type of scenarios with
** Large capacity bound
** Unpredictable capacity
** Consumer needs elements in sorted order
* A Deque implementation of LinkedBlockingQueue
YES
YES
** Can add elements at both head and tail
* Both producer and consumer threads will have to wait for a handoff to
occur.
YES
NO
* If there is no consumer waiting. The element is not added to the
collection.
* Similar to a normal LinkedBlockingQueue
* Elements are implementations of Delayed interface
YES
NO
* Consumer will be able to get the element only when it's delay has
expired
http://www.janeve.me/articles/which-java-collection-to-use
YES
NO
Вам также может понравиться
- Java Collection MatrixДокумент1 страницаJava Collection MatrixJessica HarveyОценок пока нет
- Java Collection TematrixДокумент1 страницаJava Collection Tematrixteste909Оценок пока нет
- Heaps: Analysis of AlgorithmsДокумент27 страницHeaps: Analysis of AlgorithmsAsma SajidОценок пока нет
- Downloadfile 2Документ279 страницDownloadfile 2Sabari NathanОценок пока нет
- Java Collection Framework GuideДокумент263 страницыJava Collection Framework GuideSabari NathanОценок пока нет
- RAID Level Comparison TableДокумент2 страницыRAID Level Comparison TableDilum MaddumageОценок пока нет
- 01Документ12 страниц01Shubham KumarОценок пока нет
- Basic Java collection types: Lists, Sets, Maps and QueuesДокумент5 страницBasic Java collection types: Lists, Sets, Maps and Queuesisaac_bОценок пока нет
- Introduction To NOSQL and Cassandra: @rantav @outbrainДокумент60 страницIntroduction To NOSQL and Cassandra: @rantav @outbrainchrisjaureОценок пока нет
- Java Performance Optimization Tips & Interview QuestionsДокумент12 страницJava Performance Optimization Tips & Interview QuestionsVijay KumarОценок пока нет
- Java Collection Types IntroductionДокумент3 страницыJava Collection Types IntroductionNourhane IbrahimОценок пока нет
- Data Structure&GenericsДокумент60 страницData Structure&GenericssanalОценок пока нет
- Java GenericsДокумент7 страницJava GenericsZachary KermanОценок пока нет
- DS NotesДокумент13 страницDS NotesOM UTTARKARОценок пока нет
- Dotnet Programming Concepts Difference FAQs-1Документ2 страницыDotnet Programming Concepts Difference FAQs-1Umar AliОценок пока нет
- System Verilog IIДокумент18 страницSystem Verilog IIAhmed ShafeekОценок пока нет
- QuickSort Java and AES EncryptionДокумент7 страницQuickSort Java and AES EncryptionPrabhakar PrabhuОценок пока нет
- MATLAB Introduction Chapter 1: Why Learn to Code and MATLAB's StrengthsДокумент40 страницMATLAB Introduction Chapter 1: Why Learn to Code and MATLAB's StrengthsMonicaОценок пока нет
- Java Collections Cheat Sheet EasyДокумент40 страницJava Collections Cheat Sheet EasyJashan Bansal0% (1)
- Data Structure 2Документ2 страницыData Structure 2p-jornОценок пока нет
- Chapter 09Документ24 страницыChapter 09ssMShahzadAhmedssОценок пока нет
- Data Structure&AlgorithmsДокумент52 страницыData Structure&AlgorithmspriyanjayОценок пока нет
- Symbol Tables and Compiler ImplementationДокумент26 страницSymbol Tables and Compiler ImplementationSrinadh ReddyОценок пока нет
- System Verilog Data TypeДокумент34 страницыSystem Verilog Data Typeshazarul bappiОценок пока нет
- Data Structure and Algo - Prelim To Finals! (Main)Документ54 страницыData Structure and Algo - Prelim To Finals! (Main)CedОценок пока нет
- Basic Part 1Документ46 страницBasic Part 1xo3ugyfwОценок пока нет
- Java Interview Questions: Why Doesn't Collection Extend Cloneable and Serializable?Документ62 страницыJava Interview Questions: Why Doesn't Collection Extend Cloneable and Serializable?Umamahesh MavuluriОценок пока нет
- 33 - Java - Documentation Comments - The Javadoc TagsДокумент4 страницы33 - Java - Documentation Comments - The Javadoc Tagsso_monika_cmvОценок пока нет
- Advanced Encryption Standard (AES)Документ40 страницAdvanced Encryption Standard (AES)SharukhОценок пока нет
- Dsmaterials VasuДокумент49 страницDsmaterials VasuKiran All Iz Well100% (1)
- Relational Databases and Postgresql: Charles SeveranceДокумент45 страницRelational Databases and Postgresql: Charles SeveranceJamie NuñezОценок пока нет
- Lec12 XMLCSДокумент60 страницLec12 XMLCSsankarilakshmiОценок пока нет
- Comp 258: Assignment 2Документ9 страницComp 258: Assignment 2Hamza SheikhОценок пока нет
- ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONIC ENGINEERING Cache CachingДокумент15 страницELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONIC ENGINEERING Cache CachingEnock OmariОценок пока нет
- Array List in JavaДокумент5 страницArray List in JavaPriyansh GuptaОценок пока нет
- SAX (Simple API For XML)Документ16 страницSAX (Simple API For XML)SheebaОценок пока нет
- Assignment Set - 2: Data Structures Including Queues, Binary Trees, Searching and HashingДокумент7 страницAssignment Set - 2: Data Structures Including Queues, Binary Trees, Searching and HashingSumitavo NagОценок пока нет
- Cyber SecurityДокумент6 страницCyber SecuritySugam GiriОценок пока нет
- Grep CommandДокумент10 страницGrep Commandsubha99RanjanОценок пока нет
- Cassandra: Wa'el Belkasim Arash Akhlaghi Badrinath JayakumarДокумент37 страницCassandra: Wa'el Belkasim Arash Akhlaghi Badrinath JayakumarrickitОценок пока нет
- HashingДокумент5 страницHashingjeneel1811Оценок пока нет
- Computer Notes - Data Structures - 5Документ24 страницыComputer Notes - Data Structures - 5ecomputernotesОценок пока нет
- 2.3 ArraysДокумент5 страниц2.3 ArraysdkandpalОценок пока нет
- Java Cheat SheetДокумент12 страницJava Cheat SheetMaria MihailaОценок пока нет
- Working With Master Pages Themes & Skins Collections & Lists Data Binding Working With XMLДокумент30 страницWorking With Master Pages Themes & Skins Collections & Lists Data Binding Working With XMLonline_narendraОценок пока нет
- A Data Structures and Algorithm Notes - FinalДокумент18 страницA Data Structures and Algorithm Notes - Finalnana fosuОценок пока нет
- Comparatie Tipuri de ColectiiДокумент4 страницыComparatie Tipuri de ColectiiSoltan GheorgheОценок пока нет
- Reading in Larger Datasets With Read - Table Reading in Larger Datasets With Read - TableДокумент4 страницыReading in Larger Datasets With Read - Table Reading in Larger Datasets With Read - TableRustEdОценок пока нет
- J2SE 5.0 New FeaturesДокумент68 страницJ2SE 5.0 New FeaturesUday KumarОценок пока нет
- Lecture Stack Processing With ISCE2Документ12 страницLecture Stack Processing With ISCE2gwisnuОценок пока нет
- Containers & Generics: Click To Edit Master Subtitle StyleДокумент33 страницыContainers & Generics: Click To Edit Master Subtitle StyleOmotayo FakinledeОценок пока нет
- Parallel Hashing: John Erol EvangelistaДокумент42 страницыParallel Hashing: John Erol EvangelistaJohn Erol EvangelistaОценок пока нет
- AI Lecture on Defglobal Construct and File I/OДокумент20 страницAI Lecture on Defglobal Construct and File I/OSarmad RehanОценок пока нет
- C Sharp Corner TwoДокумент36 страницC Sharp Corner TwoArfan MohammadОценок пока нет
- Stacks and QueuesДокумент21 страницаStacks and QueuesDhivya NОценок пока нет
- Lecture#02 ArraysДокумент16 страницLecture#02 ArraysSwaira RiazОценок пока нет
- XMLXpath Support in My SQLДокумент23 страницыXMLXpath Support in My SQLangelvilaboaОценок пока нет
- Mikrotik QueueДокумент7 страницMikrotik QueueBijay ShakyaОценок пока нет
- Collection in C#Документ14 страницCollection in C#Raj AkhaniОценок пока нет
- Database Connection With SAP BI - BW (DB Connect)Документ12 страницDatabase Connection With SAP BI - BW (DB Connect)Farrukh HanifОценок пока нет
- SQL Server NotesДокумент215 страницSQL Server NotesSHANTANU BHATTACHARYAОценок пока нет
- Scribal Pattern BookДокумент58 страницScribal Pattern BookavatarОценок пока нет
- Web Mining Techniques and ApplicationsДокумент13 страницWeb Mining Techniques and ApplicationsSunil Kr Pandey100% (2)
- Lectura 1 - PARSE (Transact-SQL) - SQL Server - Microsoft DocsДокумент6 страницLectura 1 - PARSE (Transact-SQL) - SQL Server - Microsoft Docsluis fernando mansilla musajaОценок пока нет
- Data Types and DMLДокумент2 страницыData Types and DMLvenuОценок пока нет
- As400 - JournalingДокумент5 страницAs400 - Journalingaminem_mpОценок пока нет
- PHP and MYSQL Introduction Course Outline: Page 1 of 3Документ3 страницыPHP and MYSQL Introduction Course Outline: Page 1 of 3babasherОценок пока нет
- Active Directory Interview Questions and AnswersДокумент4 страницыActive Directory Interview Questions and AnswersUlaga NathanОценок пока нет
- 1z0-820.exam.75q: Number: 1z0-820 Passing Score: 800 Time Limit: 120 MinДокумент68 страниц1z0-820.exam.75q: Number: 1z0-820 Passing Score: 800 Time Limit: 120 MinTchakalaFissaleОценок пока нет
- Database Systems & Applications ER-Data ModelДокумент30 страницDatabase Systems & Applications ER-Data ModelHaneesha MuddasaniОценок пока нет
- Semester 1 - Final PDFДокумент12 страницSemester 1 - Final PDFRaduľkoMiruľkinVandžuraОценок пока нет
- Web Data ManagementДокумент440 страницWeb Data ManagementAmalОценок пока нет
- Transaction Management and Con Currency ControlДокумент14 страницTransaction Management and Con Currency Controlshevadanze100% (1)
- Obia Install GuideДокумент150 страницObia Install GuidenareshreddyguntakaОценок пока нет
- HDHackerДокумент2 страницыHDHackerMisa MisaОценок пока нет
- Twenty-Five SQL Practice Exercises: These Questions and Example Solutions Will Keep Your Skills SharpДокумент39 страницTwenty-Five SQL Practice Exercises: These Questions and Example Solutions Will Keep Your Skills Sharpashokkumar gОценок пока нет
- GBAK Firebird Backup and Restore: General SyntaxДокумент4 страницыGBAK Firebird Backup and Restore: General SyntaxAlby MuktionoОценок пока нет
- EVBackupsДокумент12 страницEVBackupsshaluprakОценок пока нет
- Management Information Systems, 10/E: Raymond Mcleod Jr. and George P. SchellДокумент46 страницManagement Information Systems, 10/E: Raymond Mcleod Jr. and George P. SchellSyadep KhairunnisaОценок пока нет
- AIS Lec2Документ48 страницAIS Lec2Monique del RosarioОценок пока нет
- PSTable QueryДокумент27 страницPSTable QuerysivanblОценок пока нет
- Data Structures With Python: G V SivanarayanaДокумент40 страницData Structures With Python: G V SivanarayanaVijayKumar LokanadamОценок пока нет
- Practical's for Term-2 Exam on Python Stack Operations & MySQL QueriesДокумент6 страницPractical's for Term-2 Exam on Python Stack Operations & MySQL QueriesPrabhat singhОценок пока нет
- SacДокумент16 страницSacPradeep KVKОценок пока нет
- Configuring Oracle 10g ASM On LinuxДокумент27 страницConfiguring Oracle 10g ASM On LinuxMohd YasinОценок пока нет
- Rename Relocate Data Files and Resizing Log Files in DR Env PDFДокумент15 страницRename Relocate Data Files and Resizing Log Files in DR Env PDFG.R.THIYAGU ; Oracle DBA50% (4)
- MT6735M Android ScatterДокумент7 страницMT6735M Android ScatterBulls On Parade100% (1)
- Project 2 DetailsДокумент10 страницProject 2 DetailsEllie grayОценок пока нет
- Advanced Database Sample TestДокумент6 страницAdvanced Database Sample TestDobre DanielОценок пока нет