Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Biochemistry Lab Exam Reviewer (Carbohydrates and Lipids)
Загружено:
Kimberly EspaldonАвторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Biochemistry Lab Exam Reviewer (Carbohydrates and Lipids)
Загружено:
Kimberly EspaldonАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
MARY KIMBERLY L.
ESPALDON
CHEM LAB EXAM
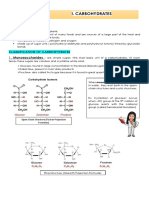
CARBOHYDRATES
saccharides
Most abundant organic molecule
First molecule in the energy cycle
MONOSACCHARIDES
Building blocks of carbohydrates
Two types:
1. Aldose polyhydroxy aldehyde
2. Ketose polyhydroxy ketone
Derivatives of monosaccharides
1. Sugar acids
2. Sugar alcohol
3. Deoxysugars
4. Amino sugars
5. Sugar phosphates
DISACCHARIDES
-d-glucose
Lactose
-d-galactose
-d-glucose
Sucrose
-d-fructose
-d-glucose
Cellobiose
-d-glucose
-d-glucose
Maltose
-d-glucose
POLYSACCHARIDES
Isomers molecules with the same
molecular formula but have a different
arrangement of atoms in space
Compounds do
CONSTITUTIONAL not have the same
connectivity
Different
FUNCTIONAL
functional groups
Mirror images;
ENANTIOMERS
nonsuperimposable
Not mirror images
DIASTREOMERS
of one another
Stereoisomers
ANOMERS
that differ in at the
anomeric carbon
Only different at
EPIMERS
one stereogenic
center
ALDOPENTOSES
Ribose
Xylose
Arabinose
Lyxose
ALDOHEXOSES
Glucose
Mannose
Galactose
Talose
Altrose
Idose
KETOPENTOSES
Ribulose
Xylulose
KETOHEXOSES
Fructose
Tagatose
Linear homoglycans
Branched
homoglycans
Heteroglycans
Glycuronans
Glycosaminoglycans
Glucans
amylose,
cellulose, chitin
Galactans
agar,
carrageenan
Glucans
glycogen,
amylopectin
Glucomannans,
galactomannans
Contains uronic acids
Mucopolysaccharides
Starch
Reserve carbohydrates for plants
Found in plant seeds and tubers
Form in which glucose is stored for
later use by plants
Composed of two polysaccharides:
1. Amylose water soluble
(20%)
2. Amylopectin water
insoluble (80%)
Hydrolysis of starch would give only
glucose
Amylose
Linear polymer
4000 monomers of glucose joined by
-1,4-glycoside bonds
Amylopectin
Highly branched polymer
24-30 units of glucose joined by 1,4-glycoside bonds and branch at
points -1,6-glycoside bonds
Glycogen
Reserve carbohydrate for animals
MARY KIMBERLY L. ESPALDON
Non-linear, branched polymer
Lower molecular weight; higher
branching than amylopectin
Branching every 12-18 units
Cellulose
Most abundant organic compound
on Earth
Linear polymer
3000 glucose monomers joined by
-1,4-glycoside bonds
ISOLATION OF CARBOHYDRATES
Glycogen from chicken liver
o Energy storage polysaccharide in
animals
o Branched chain
o Linear chain of glucose units
o Connected by -1,4-glycosidic
bonds and branched every 1-10
units linked by -1,6-glycosidic
bonds
o Isolation:
Homogenization disrupts
the membrane
0.1% acetic acid removes
protein via precipitation
Glycogen is insoluble in
ethanol
Method:
Protein denaturation
Solubility of glycogen
Starch from potatoes
o Energy storage of polysaccharide in
plants
o Mixture of amylose and amylopectin
o Isolation:
Starch is slightly soluble in
H2O
Method: selective dissolution
HYDROLYSIS OF CARBOHYDRATES
Acid hydrolysis
o 2N HCl
o Complete hydrolysis
o Efficient method to obtain
monosaccharides
o Starch/glycogen glucose
Enzymatic hydrolysis
o Salivary amylase -amylase
o Very specific
o Yield a mixture of glucose, maltose,
dextrin and other hydrolysates
THIN LAYER CHROMATOGRAPHY
Based on adsorption
Stationary phase: silica G-250
Mobile phase: butanol: acetic acid:
ether: H2O (9:6:3:1)
Visualizing agent: p-anisaldehyde
Appear as dark green spots
LIPIDS
Insoluble in water
Soluble in organic nonpolar solvents
Hydrophobic nature due to the
predominance of hydrocarbons chains
Functions:
o Storage and transport of metabolic
fuel
o Structural component of cell
membrane
o Carriers of lipid-soluble vitamins
Vitamins A, D, E, K
Hypervitaminosis excess
vitamins
o Provide supply of essential fatty
acids
o Body insulation
Saponification basic hydrolysis of lipids,
produces soap
FATTY ACIDS
Synthesis occurs in the liver
Naturally occurring fatty acids even
number of carbon atoms
Two types:
o Saturated no carbon-carbon
double bond present
o Unsaturated carbon-carbon double
bond present
Two essential fatty acids:
o Linoleic acid
o Linolenic acid
PROSTAGLANDINS (PGS)
Synthesized from linoleic acid forms
eicosanoids
Cyclopentane ring with 2 side chains
(carboxyl group in one chain)
Development of inflammatory responses
Pain chemicals
Wound-healing process
FATTY ACID ESTERS
Acylglycerols esters formed between a
fatty acid and glycerol
Triglycerides
o From plants oils liquid at room
temperature
o From animals fats solid at room
temperature
PHOSPHOLIPIDS
Zwitterionic compounds of an alcohol that is
attached by a phosphodiester bridge to
either:
o Diacylglycerol
o Sphingosine
MARY KIMBERLY L. ESPALDON
Phosphoglycerides, glycerophosphates or
phosphoglycerol phospholipids that
contain glycerol
Lecithin
o Alcohol-soluble
o Acetone-insoluble
o Emulsifier in the food industry
Cephalin
o Alcohol-insoluble
o Acetone-insoluble
o Abundant in the brain nervous tissue
o Mixture of phosphatidyl
ethanolamine and phosphatidyl
serine
STEROIDS
Derivative of
perhydrocyclopentanophenanthrene
True terpenes
Synthesized from isoprene via squalene
Fused ring system essentially planar
structure
o Cis-fused ring bent structures
o Trans-fused ring flat structures;
cholesterol and testosterone
Sterols
o Steroids containing one or more
hydroxyl groups
o Cholesterol secondary alcohol
o Very hydrophobic, non-saponifiable,
unsaturated
o Component of all cell membranes,
precursor of bile acids, steroid
hormones and vitamin D
Sex hormones
o Testosterone
o Estrogens
o Progesterone
Adrenocorticoid hormones
o Stress hormone
o Synthesize and secrete cortisol
o Functions:
Increased glucogenesis
Anti-inflammatory action
Protein breakdown
Aldosterone
o Secretion of aldosterone from the
adrenal cortex
o Functions stimulates renal
reabsorption of Na+ and excretion of
K+ in the kidney tubules
Vitamin D
o Lipid soluble vitamins
o Derived from isoprenoids or
terpenoids
o Vitamin D2 found in plants
o Vitamin D3 found in animals
o Stored in adipose and liver tissue
Bile acids
o Contains lechitin and bile salts
o Pka = 6 not fully ionized in
physiologic pH
o Hydroxyl groups are in alpha
(above) orientation
o Methyl groups are in beta (below)
orientation
o Cholic acid
TERPENOIDS OR ISOPRENOIDS
Multiples of isoprene units
Most of plants pleasant odors come from
terpenoids
Vitamin A
o Collective term for:
Retinol
Retinoic acid
Retinal
-carotene
o Functions:
essential for vision
Rhodopsin visual pigment
Vitamin E
o vegetables oils, eggs
o naturally occurring tocopherols
o natural antioxidant
o least toxic fat-souble vitamin
Vitamin K
o Found in cabbage, cauliflower,
spinach, egg yolk
o Required in the hepatic synthesis of
prothrombin and clotting factors
o Hemolytic anemia and jaundice
SPHINGOLIPIDS
Isolated from the brain
Backbone compound: ceramide contains
sphingosine or 4 sphingenine
Complete hydrolysis releases:
o 1 mole of fatty acid
o 1 mole of sphingosine
o 1 mole of phosphoric acid
o 1 mole of choline
Glycolipids
o Does not contain phosphorus
o Primary hydroxyl group is
glycosylated substituted with a
carbohydrate
EXTRACTION OF LIPID
Chicken egg yolk
o Rich in lipids such as phospholipids,
triglycerides, triacylglycerols an
cholesterol
Phospholipid: lecithin
Fatty acids in acylated form
in triglyceride
MARY KIMBERLY L. ESPALDON
Unsaturated
linoleic, palmitoleic,
linoleic
Saturated
o Yellow color Is due to: carotenoid
alcohol zeaxanthin
Extraction by percolation at room
temperature
o Sample is allowed to stand with the
extracting solvent for a certain
period of time
o Solvent fractionation depends on
the differential solubility of lipids in
organic solvents
o Extracting solvents are introduced in
increasing polarity step gradient
1. Hexane least polar
2. Acetone
3. Hot ethanol most polar
o Hexane solvent
Lipids interact by induced
dipole induced dipole
interaction with hexane
Hexane extract contains the
least polar dipole
o Acetone solvent
Lipids interact by dipole
induced dipole and induced
dipole induced dipole
Intermolecular H-bonding
Extract contains sterol
o Hot ethanol solvent
Lipids interact by ion-dipole
interaction, hydrogen
bonding and dipole-induced
dipole interactions
Contains the most polar
lipids
Zwitterionic lipids
Amphiphatic lipids
COLUMN CHROMATOGRAPHY
Normal phase
Preparative procedure
Descending
Adsorption
Stationary phase solid silica gel
Mobile phase solvent system
Lipids are eluted in order of increasing
polarity
o Hexane
1. Sterol ester
2. Fatty acid methyl ester
3. Triglyceride
4. Phosphoglyceride or
glycophosphatide
5. Lecithin
6. Cephalin
o Acetone
Sterol
o Hot ethanol: sphingolipids
1. Sphingoglycolipids
2. Sphingomyelin
Solvent system in the mobile phase are
interacting one by one in increasing polarity
step gradient
1. Petroleum ether: ethyl ether (9:1)
2. 5% methane in dichloromethane
3. Dichloromethane: methanol: water
(1:3:1)
THIN LAYER CHROMATOGRAPHY
Normal phase
Analytical and preparative procedure
Ascending
Adsorption
Stationary phase: solid silica gel
Mobile phase: solvent system
2-dimensional: 2 developments
Used two solvent systems:
1. Petroleum ether: methanol: water
more polar
2. Petroleum ether: methanol: NH4OH
less polar
Visualizing agents:
1. I2
Yellowish brown spot against
a blue background
Oxidized the lipid and is
reduced to I-1 (yellow)
Prolonged exposure makes
the spots turn violet
2. Ninhydrin reagent
Blue to violet spots for lipids
MARY KIMBERLY L. ESPALDON
QUALITATIVE TESTS
TEST
Molisch
Carbohydrates
Iodine
Starch and Glycogen
Anthrone
Carbohydrates
Benedicts
Reducing sugars
Barfoeds
Reducing monosaccharides and
disaccharides
Bials Orcinol
Pentoses
Seliwanoffs
Ketohexoses
Mucic Acid
Galactose
Osazone
Reducing factor
CARBOHYDRATES
REAGENTS
(+) RESULT
Conc. H2SO4
Violet ring at interphase
-napthol
Blue-black starch
Iodine solution
Red glycogen
REACTION
Redox, ANE, furfural
formation
Furfural formation
complexation
Redox, ANE, furfural
formation
Conc. H2SO4, anthrone
Blue-green sln
CuSO4, NaC6H5O2,
NaCO3
Brick red ppt
Oxidation in less basic
CuAc2, acetic acid
Brick red ppt
Oxidation in aciding
Orcinol, HCl, FeCl3
Blue-green sln
Furfural formation
Resorcinol, HCl
Cherry red sln
Furfural formation
Conc. HNO3,
Broken glass crystals
Oxidation
2-DNPhenylhydrazine
reagent
Orange crystals
Osazone formation
Вам также может понравиться
- Modulator: Dr. P.B.Desai HOD, Dept of Biochemistry. Presenter: DR Vijayetha S. KagwadДокумент68 страницModulator: Dr. P.B.Desai HOD, Dept of Biochemistry. Presenter: DR Vijayetha S. KagwadvijayethaОценок пока нет
- LipidsДокумент65 страницLipidsharisОценок пока нет
- General Protein MetabolismДокумент72 страницыGeneral Protein MetabolismHafizie SyahmanОценок пока нет
- Structure and Function of LipidsДокумент8 страницStructure and Function of Lipidsalphius_mendoza50% (2)
- Biochem Lipids NotesДокумент9 страницBiochem Lipids NotesPatricia AnneОценок пока нет
- Reviewer in BiochemistryДокумент19 страницReviewer in BiochemistryMicole Manahan100% (1)
- Biochemistry Answer Key-GREEN PACOPДокумент18 страницBiochemistry Answer Key-GREEN PACOPailene agustinОценок пока нет
- Psychology KMTCДокумент250 страницPsychology KMTCMercy AdeolaОценок пока нет
- Subject: Biochemistry Topic:Lipid Metabolism 2 Lecturer: Dr. Laygo DATE: NOV. 2010Документ11 страницSubject: Biochemistry Topic:Lipid Metabolism 2 Lecturer: Dr. Laygo DATE: NOV. 2010Std DlshsiОценок пока нет
- BiochemistryДокумент9 страницBiochemistryAdriane BasaОценок пока нет
- Qualitative and Quantitative Tests For Lipids.: Prof. Liwayway Memije-CruzДокумент11 страницQualitative and Quantitative Tests For Lipids.: Prof. Liwayway Memije-CruzAurian TormesОценок пока нет
- BiochemistryДокумент82 страницыBiochemistryAmritzz Paul83% (6)
- Biochem Practice Exam (Lipids)Документ4 страницыBiochem Practice Exam (Lipids)Spencer Thomas100% (2)
- ProteinsДокумент20 страницProteinsJin Chung Kuan100% (2)
- LipidsДокумент25 страницLipidsJeaniee Zosa Ebias50% (10)
- Carbohydrate - Lecture NotesДокумент7 страницCarbohydrate - Lecture NotesKate Taylor100% (1)
- Amino AcidsДокумент25 страницAmino AcidsAkash Marathakam60% (5)
- LIPIDS BiochemistryДокумент52 страницыLIPIDS BiochemistryMark BagamaspadОценок пока нет
- Biochemistry QuizДокумент6 страницBiochemistry QuizPatrick Ngo'nga Chifwema100% (1)
- Part I Lab Manual 2013Документ44 страницыPart I Lab Manual 2013Professor Rakesh Sharma Biochemistry Lectures100% (1)
- BIOCHEM-Lipid Metabolism 1Документ12 страницBIOCHEM-Lipid Metabolism 1Std Dlshsi100% (1)
- Colour Reaction of Amino AcidsДокумент27 страницColour Reaction of Amino AcidsJacqueline Ann71% (7)
- Post Lab Amino Acids and ProteinsДокумент85 страницPost Lab Amino Acids and ProteinsELAINE MARIEJOY MANGAOILОценок пока нет
- Carbohydrates: Organic Vs Inorganic CompoundsДокумент16 страницCarbohydrates: Organic Vs Inorganic CompoundsTsu Wei Chua100% (5)
- Protein NДокумент57 страницProtein NdevitaОценок пока нет
- CarbohydratesДокумент3 страницыCarbohydratesJam Aica0% (1)
- Biochemistry Study Notes PDFДокумент5 страницBiochemistry Study Notes PDFLofiSophicalОценок пока нет
- Biochemistry 1.1 Introduction To Water and BuffersДокумент7 страницBiochemistry 1.1 Introduction To Water and Bufferslovelots1234Оценок пока нет
- Khan Academy Carbohydrates QuestionsДокумент3 страницыKhan Academy Carbohydrates QuestionsLoraОценок пока нет
- Protein Notes PDFДокумент38 страницProtein Notes PDFLUi Anne Mateo LatogОценок пока нет
- UNIT - II: Lipid MetabolismДокумент27 страницUNIT - II: Lipid Metabolismgaurav saxena100% (1)
- Biochemistry: Biochemistry, Sometimes Called Biological Chemistry, Is TheДокумент7 страницBiochemistry: Biochemistry, Sometimes Called Biological Chemistry, Is TheNens Angelo Calizo SandovalОценок пока нет
- Qualitative Color Reactions of AlbuminДокумент6 страницQualitative Color Reactions of AlbuminJennifer HerediaОценок пока нет
- Biochemistry IntroductionДокумент72 страницыBiochemistry IntroductionNatasha Jean100% (1)
- Lipid MetabolismДокумент60 страницLipid MetabolismYatricia SinghОценок пока нет
- Carbs LehningerДокумент9 страницCarbs LehningerElla BangalanОценок пока нет
- Amino Acids and ProteinДокумент37 страницAmino Acids and Proteinmoogambigai smОценок пока нет
- Biochemistry Amino AcidsДокумент13 страницBiochemistry Amino AcidsApril Aram100% (1)
- Biochemistry PDFДокумент20 страницBiochemistry PDFCha GabrielОценок пока нет
- Mic180 - Chapter 5 - Carbohydrate - EditedДокумент75 страницMic180 - Chapter 5 - Carbohydrate - EditedfarОценок пока нет
- Fatty Acid OxidationДокумент28 страницFatty Acid OxidationEmm NomanОценок пока нет
- BiochemistryДокумент3 страницыBiochemistrysummer168Оценок пока нет
- Lipid Metabolism IДокумент35 страницLipid Metabolism IGeorgios PlethoОценок пока нет
- Biochemistry MIDTERMS LABДокумент1 страницаBiochemistry MIDTERMS LABcha cuteОценок пока нет
- 2.6 (BIOCHEMISTRY) Glycogen MetabolismДокумент10 страниц2.6 (BIOCHEMISTRY) Glycogen Metabolismlovelots1234Оценок пока нет
- Biochemistry Board Exam2020 QuestionsДокумент6 страницBiochemistry Board Exam2020 Questionschristinejoan100% (1)
- Biochemistry Answer Key-BLUE PACOPДокумент26 страницBiochemistry Answer Key-BLUE PACOPChengD100% (1)
- Electron Transport ChainДокумент5 страницElectron Transport ChainTanya Dilshad100% (1)
- Carbohydrate MetabolismДокумент7 страницCarbohydrate Metabolismcalista osdonОценок пока нет
- Biochemistry ExamДокумент4 страницыBiochemistry ExamKyle Broflovski100% (1)
- ProteinsДокумент43 страницыProteinsBilalОценок пока нет
- Lab Report 4 RepairedДокумент21 страницаLab Report 4 RepairedAnnrisa Layong AbainОценок пока нет
- ..Digestion of ProteinДокумент21 страница..Digestion of Proteinaneeda shabirОценок пока нет
- CARBOHYDRATESДокумент31 страницаCARBOHYDRATESCheelsy P. ButronОценок пока нет
- Qualitative Test For Amino Acids and ProteinДокумент7 страницQualitative Test For Amino Acids and ProteinShamarie Love MaribaoОценок пока нет
- Biochemistry Notes - Nucleotide MetabolismДокумент5 страницBiochemistry Notes - Nucleotide MetabolismneedthisforepiОценок пока нет
- Activity 08 LipidsДокумент36 страницActivity 08 LipidsMaria67% (3)
- Biochemistry of Hormones Note PDFДокумент36 страницBiochemistry of Hormones Note PDFNeyan100% (1)
- Biochem - Lipids ReviewerДокумент6 страницBiochem - Lipids ReviewerKarmina SantosОценок пока нет
- Formal Report Experiment 4Документ3 страницыFormal Report Experiment 4Kimberly EspaldonОценок пока нет
- Immunosero SeminarДокумент7 страницImmunosero SeminarKimberly EspaldonОценок пока нет
- Hematology Lecture - AnemiaДокумент10 страницHematology Lecture - AnemiaKimberly EspaldonОценок пока нет
- Serological TestsДокумент2 страницыSerological TestsKimberly EspaldonОценок пока нет
- Biochemistry Chapter 12 - Translation ReviewerДокумент3 страницыBiochemistry Chapter 12 - Translation ReviewerKimberly EspaldonОценок пока нет
- Biochemistry First Shifting PDFДокумент5 страницBiochemistry First Shifting PDFKimberly EspaldonОценок пока нет
- Biochemistry First Shifting PDFДокумент5 страницBiochemistry First Shifting PDFKimberly EspaldonОценок пока нет
- Separation and Identification of Amino Acids of Enzymatic Hyldrolysates by ThinДокумент4 страницыSeparation and Identification of Amino Acids of Enzymatic Hyldrolysates by ThinKimberly EspaldonОценок пока нет
- Classification Tests For Carboxlyic Acids and Their Derivatives Experiment 10 Formal ReportДокумент4 страницыClassification Tests For Carboxlyic Acids and Their Derivatives Experiment 10 Formal ReportKimberly Espaldon100% (1)
- Experiment 3 Sublimation and Melting PointДокумент3 страницыExperiment 3 Sublimation and Melting PointJuan CarlosОценок пока нет
- Kevlar Technical GuideДокумент24 страницыKevlar Technical GuideR GopalanОценок пока нет
- Cannizzaros ReactionДокумент8 страницCannizzaros Reactionabubakar siddiqueОценок пока нет
- Mrs. Melendez-Beltran Pre-AICE ChemДокумент98 страницMrs. Melendez-Beltran Pre-AICE ChemTravel UnlimitedОценок пока нет
- Lecture Planner - Chemistry - MANZIL For JEE 2024Документ1 страницаLecture Planner - Chemistry - MANZIL For JEE 2024Rishi NairОценок пока нет
- Icse Class 9 Hy Chemistry 2019Документ4 страницыIcse Class 9 Hy Chemistry 2019Naveen PrabhuОценок пока нет
- Paper 1 Chemistry SPM SBPДокумент19 страницPaper 1 Chemistry SPM SBPsizzledeedle100% (2)
- Chemical Properties of Carbon CompoundsДокумент7 страницChemical Properties of Carbon CompoundsAnonymous HLkNDToОценок пока нет
- 4.CPP S BlockДокумент6 страниц4.CPP S BlockRuchira SahaОценок пока нет
- Student Handout: Making A Crystal Garden - Chemistry and ArtДокумент2 страницыStudent Handout: Making A Crystal Garden - Chemistry and ArtYT ChongОценок пока нет
- Callyspongia SP Callyspongia SP: Identification of Antioxidant Compounds in The Sponge The SpongeДокумент7 страницCallyspongia SP Callyspongia SP: Identification of Antioxidant Compounds in The Sponge The SpongeZulfajriОценок пока нет
- Hydrocarbons: Module - 7Документ32 страницыHydrocarbons: Module - 7UmarОценок пока нет
- B.SC I Organo Sulphur CompoundsДокумент3 страницыB.SC I Organo Sulphur CompoundsNickOoPandeyОценок пока нет
- Biuret Test For ProteinДокумент1 страницаBiuret Test For ProteinKal BuenaflorОценок пока нет
- Project Report On Unsaturated Polyester Resin (20 MT Per Day Output)Документ7 страницProject Report On Unsaturated Polyester Resin (20 MT Per Day Output)EIRI Board of Consultants and PublishersОценок пока нет
- Class 12 Chemistry Ch-6.Haloalkanes and HaloarenesДокумент45 страницClass 12 Chemistry Ch-6.Haloalkanes and Haloareneskarnan karupiahОценок пока нет
- Rekap Obat January 2020Документ19 страницRekap Obat January 2020Liska PrahestikaОценок пока нет
- Chemistry An Introduction To General Organic and Biological Chemistry Timberlake 12th Edition Test BankДокумент23 страницыChemistry An Introduction To General Organic and Biological Chemistry Timberlake 12th Edition Test Bankmeghanjeffersondwfpeomczg100% (23)
- Easy Way To Score in Organic ChemistryДокумент2 страницыEasy Way To Score in Organic ChemistryRoopa KhenedОценок пока нет
- CLS Aipmt-18-19 XIII Che Study-Package-7 SET-1 Chapter-28 PDFДокумент20 страницCLS Aipmt-18-19 XIII Che Study-Package-7 SET-1 Chapter-28 PDFHimanshi GuptaОценок пока нет
- Astm e 200 97 Standard Practice For PDFДокумент15 страницAstm e 200 97 Standard Practice For PDFSergioFernandoMendozaMendozaОценок пока нет
- Mescaline HCL From Echinopsis PachanoiДокумент62 страницыMescaline HCL From Echinopsis Pachanoitramp339100% (8)
- Moles and Stoich-07 PDFДокумент16 страницMoles and Stoich-07 PDFNabila Hanim100% (1)
- FormulaДокумент7 страницFormulamariayosefinaОценок пока нет
- Inorganica Chimica ActaДокумент10 страницInorganica Chimica ActaNikhil BhoumikОценок пока нет
- Edible Substances and Their Tastes Substance Taste (Sour/Bitter/Any Other)Документ6 страницEdible Substances and Their Tastes Substance Taste (Sour/Bitter/Any Other)Dhruv DesaiОценок пока нет
- DiscussionWorksheet6 004Документ6 страницDiscussionWorksheet6 004unknownnОценок пока нет
- Cetrimonium Chloride - CTC-30 - DS-83R-1Документ3 страницыCetrimonium Chloride - CTC-30 - DS-83R-1Jheison VillalobosОценок пока нет
- Nomenclature and IsomerismДокумент3 страницыNomenclature and Isomerismapi-3710134100% (1)
- Glycerol Production and Its Applications As A Raw MaterialДокумент10 страницGlycerol Production and Its Applications As A Raw Materialemi_v11Оценок пока нет
- Chem A A2 Task 3 EVAL Task Jun12 PDFДокумент7 страницChem A A2 Task 3 EVAL Task Jun12 PDFSophie PriorОценок пока нет